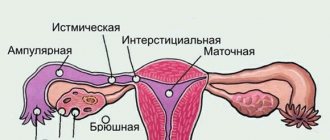
What is delay in girls, its norms
Delayed menstruation is a failure of menstrual function, which is manifested by the absence of regular monthly bleeding for more than 35 days.
The delay can be caused by both physiological reasons and various functional and organic disorders. Irregular menstruation can accompany various periods of a woman’s life.
So, at puberty and during menopause, a delay in menstrual periods is the norm.
Let's consider the basic delay standards:
- if the delay does not exceed 5-7 days, it should not be considered a pathology. Such a short absence of critical days is typical for the period of puberty and premenopause, as well as for some disorders of the menstrual cycle (oligomenorrhea, opsomenorrhea, amenorrhea);
- if there are infections and diseases in the body, menstruation may be delayed for 10 or more days, in this case it is necessary to consult a doctor;
- During pregnancy, menstruation does not occur throughout the entire period of gestation until the cessation of breastfeeding. In this case, menstruation is delayed by 1-3 years. If a woman is not pregnant, and her period does not occur for more than a year, this may indicate the arrival of menopause.
To know exactly why menstruation has not occurred, you should definitely visit a gynecologist.
https://youtu.be/92RoFZ3Y1zA
What is considered a delay?
When a woman is not sexually active and knows for sure that she is “not in danger” of pregnancy, then she calmly accepts a delay in menstruation. In a similar situation, girls who take precautions at random begin to panic. The latter consider the delay to be up to a week. In fact, this concept requires clarification.
The norm is a cycle whose duration varies from 21 to 35 days. The calculation is carried out from the first day of allocations. Those women who keep a calendar know that problems may not occur during pregnancy. But these are isolated cases and such cases may not happen more than twice a year.
But if menstruation is absent 10 days after the period during which it should begin, then this is called a delay. If this happens often in your life and the test does not show pregnancy, then this is a reason to visit the doctor.
A regular delay in menstruation within a week is most often caused by the following factors:
- emotional experiences, stress;
- heavy loads – moral and physical.
Possible reasons are also related to moving, poor diet, colds and chronic diseases. Well, of course, you need to remember that after 40 years, every woman may experience a period of irregular periods. The so-called harbingers of menopause.
When the absence of critical days is the norm
First, let's look at what can cause a delay in menstruation in women in good physical health. It is considered normal that if menstruation is delayed, their absence can only occur during certain periods of the life of the fair sex:
- during puberty;
- during pregnancy;
- after childbirth;
- with the decline of reproductive function.
Now let's look at why periods don't come, and this is the norm, in more detail.
Why is there a delay of 5 or 7 days in menstruation?
What to do if your period is late and the test is negative? First of all, all women and girls assume pregnancy and do a test. If the result is negative, many panic and imagine serious, serious illnesses.
In fact, in reproductive age, a delay in the monthly cycle of up to 7 days is not a pathology. The norm can be periodically violated under the influence of many physiological reasons.
A slight delay in menstruation, in addition to pregnancy, of course, can occur:
- due to heredity, if there were similar disorders in the family;
- in the postpartum period;
- after discontinuation of contraceptives;
- when using hormones for emergency contraception;
- during the premenopausal period;
- with physical or mental fatigue;
- during vacation when climatic conditions or time zones change.
Cycle instability is normal during a girl’s puberty. During adolescence, there is no hormonal stability, so after the first menstruation, a delay should not cause concern if there are no alarming symptoms and pregnancy is ruled out.
Various non-hormonal diseases and associated drug treatment are also common reasons for the absence of “red calendar days” on schedule. A one-time shift for a few days is not dangerous.
Why no periods - puberty
Starting from 8-10 years of age, girls begin puberty, during which the reproductive system of a young lady is formed. Usually, by the age of 12-13 years, the first menstruation or so-called menarche appears.
Due to the fact that the reproductive system and hormonal background have not yet fully formed, during this period it is quite natural to have disruptions in the menstrual cycle.
During puberty, delays may appear for 1-2 years after the first menstruation, but if two years have passed and the cycle has not become regular, you should definitely consult a doctor and be examined for diseases.
Medical assistance is also needed in cases where the girl is already 15 years old, but menarche has not occurred.
You should definitely find out why there are no periods if, in addition to a delay, the girl has problems with excess weight, excess hair growth on the face and body, and a change in voice. All this may be a sign of hormonal disorders that require medical correction.
In adolescents, by the age of 15, the menstrual cycle is usually normalized, and then a cyclical change in the level of hormones in the body occurs every month, which causes new regulations.
Delay of menstruation
Pregnancy is the most common cause of missed periods in women of childbearing age. In addition to a delay in menstruation, the probable occurrence of pregnancy is indicated by changes in taste and olfactory sensations, appetite, the appearance of nausea and vomiting in the morning, drowsiness, and painful sensations in the mammary glands. The possibility of pregnancy cannot be rejected even in cases where there has been interrupted sexual intercourse, sexual contact during menstruation, on “safe” days or using a condom, in the presence of an intrauterine device, taking oral contraceptives, etc., since neither One method of contraception does not provide 100% contraceptive effect.
If there is a delay in menstruation, and in the previous month the woman had sexual intercourse, then pregnancy can be determined using special tests. The principle of operation of all pregnancy tests (test strips, tablet or inkjet) is the same: they determine the presence of human chorionic gonadotropin hormone (hCG or hCG) in the urine, the production of which begins in the body 7 days after fertilization of the egg. The concentration of hCG in the urine increases gradually, and modern, even the most sensitive tests, are able to detect it only after a delay in menstruation and no earlier than 12-14 days after conception has occurred. It is necessary to “read” the test result in the first 5-10 minutes. The appearance of even a barely noticeable second stripe during this period of time indicates a positive result and the presence of pregnancy. If the second stripe appears later, then this result is not reliable. If your period is late, to obtain a reliable result, it is recommended to repeat the pregnancy test twice with an interval of 2-3 days.
It should be remembered that while being sexually active, a woman can always become pregnant, so it is necessary to closely monitor the menstrual cycle and pay attention to delays in menstruation. However, a delay in menstruation can be caused not only by pregnancy, but also by a number of very other, sometimes very serious and dangerous to health reasons.
Why no periods - pregnancy
To understand why critical days are delayed during pregnancy, we will describe the main processes that take place in a woman’s body during the menstrual cycle.
In the first half of the cycle, the ovaries begin to intensively produce estrogens, which promote the maturation of a new egg, which until it is fully ready is located in a special vesicle, a follicle. When the reproductive cell has matured, the follicle bursts and it exits into the uterine cavity.
Thus, ovulation occurs, accompanied by slight mucous discharge from the genital tract and mild pain on the right or left side of the abdomen.
At the site of the ruptured follicle, the corpus luteum begins to rapidly develop, which synthesizes progesterone. Under the influence of this hormone, the inner mucous layer of the uterus begins to grow, increasing in size, and thus prepares to receive a fertilized egg in the event of conception.
If fertilization does not occur, less progesterone is produced, and the endometrium, as unnecessary, begins to exfoliate and be removed from the uterus. This is how menstruation begins.
If the egg is fertilized, then the production of progesterone by the corpus luteum does not stop, but increases. Under the influence of this hormone, the zygote is implanted into the endometrium, the placenta begins to form and pregnancy develops.
In this case, degradation and rejection of the endometrium does not occur, and progesterone suppresses the maturation of new eggs and the onset of subsequent ovulations. As a result, new periods do not occur.
Thus, pregnancy is the main cause of delay for women who are sexually active and have no health problems.
Start of menstruation
The first period, or menarche, begins during adolescence (twelve to fourteen years). At this time, the hormonal background is not yet fully formed, so delays may occur. But after a certain period (one or two years), a healthy girl’s cycle must be established. If this does not happen, you should consult your doctor.
Menstrual cycle
The menstrual cycle is the period between two menstruation (more precisely, between their first days). In a healthy woman, this period does not change and can range from twenty-one to thirty-five days. For most, it is within twenty-eight to thirty days. A delay is considered to be an increase in the menstrual cycle.
Changes during the cycle
During the cycle, many changes occur in the body. At the beginning of this period, the production of the hormone estrogen increases. The endometrium (internal tissue) begins to actively grow in the uterus, ready to receive a fertilized egg (embryo). Eggs are formed in the ovary. By the middle of the menstrual cycle (the twelfth to fourteenth day), the mature egg is released into the tube and a period of ovulation favorable for conception begins. In the place where the egg was, the corpus luteum begins to function, which is the source of the hormone progesterone. This hormone plays an important role in the first stage of pregnancy. With its deficiency, miscarriages often occur or the threat of miscarriage is diagnosed. If the egg has been fertilized, it descends into the uterus and implants there. Thus, pregnancy occurs, and menstruation stops for a while. If pregnancy does not occur, progesterone and estrogen levels drop and the next menstruation begins. As we can see from what is described above, the cause of delays in most cases lies in changes in hormonal levels.
Pregnancy and postpartum period
Pregnancy is the most common cause of delay. During the entire nine months and for some time after childbirth, a healthy woman should not have periods. When breastfeeding, depending on the individual characteristics of the body, menstruation can begin either one and a half to two months after birth, or only after the end of the lactation period (sometimes this period extends to two to three years). This is facilitated by the presence of the hormone prolactin in the body, which suppresses other female hormones. In the absence of breastfeeding, periods usually begin six to eight weeks after the baby is born.
Ovarian dysfunction
If menstruation is delayed by five days or more (unless, of course, there is no pregnancy), doctors make an initial diagnosis of “ovarian dysfunction.” It denotes a general condition in which cycle failures and delays occur. The cause of “dysfunction” can be various diseases (for example, thyroid or endocrine) and problems in the body. Therefore, you must definitely visit an endocrinologist, do an ultrasound of the uterus, ovaries, thyroid, adrenal glands, laboratory tests and brain tomography.
Why no periods - childbirth
Childbirth affects a woman’s body differently, so the restoration of menstrual function occurs individually for each mother. The type of feeding of the newborn most influences the duration of the recovery period.
If a child immediately begins to eat artificial formula after birth, then the maximum delay in menstruation should not exceed 1 month.
With combined feeding, critical days may be absent for 3-4 months. Regulae are delayed the longest for nursing mothers, since milk is produced under the influence of prolactin, which simultaneously inhibits the synthesis of progesterone and the onset of ovulation.
Thus, prolactin prevents the maturation of the egg and the development of the endometrium, which means there is no germ cell for fertilization and a place for implantation of the zygote.
Against the background of breastfeeding with the gradual introduction of complementary foods (usually supplementing the baby’s diet with foods begins at six months of age), restoration of menstrual function occurs after 8-12 months.
At the same time, for 2-3 months the cycle may be irregular, and it is quite possible that delays may occur; if critical days do not appear after this period, a pregnancy test should be taken.
Delays in women with irregular menstrual cycles
If you have an irregular cycle, meaning you can't tell when your next period will start or the difference between your longest cycle and your shortest is more than a week, then unprotected sex or contact with sperm is not advisable for you at any time during your cycle if you don't want to get pregnant.
You can take a pregnancy test two weeks after you have had unprotected sex. If the result is negative, and you haven’t had your period for another week, then it makes sense to try taking a home pregnancy test from another manufacturer, donating blood for hCG—laboratory tests more accurately measure the amount of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), which determines the presence of pregnancy, or contact doctor.
Why no periods - menopause
The number of eggs that mature in a woman’s body throughout her life is strictly limited, therefore, starting from the age of 40-45, reproductive function gradually fades away and menstruation becomes irregular.
Their duration and nature also change. At this time, ovulation periodically occurs, so pregnancy should not be ruled out as a possible cause of delay. During menopause with an irregular cycle, it is better to use contraceptives to prevent pregnancy.
Hormonal medications will help alleviate the symptoms of menopause and additionally protect against unwanted conception.
Why don't I get my period?
Most often, when menstruation is delayed, women who are sexually active suspect conception, but if there is no pregnancy and the test is negative, you should know what other reasons there are for the absence of menstruation besides the “interesting” position.
When a woman experiences a delay in menstruation, but is not pregnant, the lack of regulation can be caused by other physiological reasons besides pregnancy. First, you should rule them out, and only then suspect the presence of pathology and immediately seek help from a specialist.
Physiological reasons
During the menstrual cycle, normally all processes occur in a certain sequence, the main purpose of which is to prepare the woman’s body for conception and bearing offspring.
Even a physically healthy woman sometimes experiences a delay in her period; this disruption is provoked by various external factors. Common causes of delay can be:
- emotional overstrain. Even excessive anticipation of menstruation can provoke a delay; this happens when a woman has had unprotected sex and is under stress due to a possible unwanted pregnancy. A similar reaction of the body can be caused by a stressful situation at work or personal experiences;
- excessive physical and mental stress, intense sports training and exercises associated with lifting heavy weights;
- change of place of residence, change of climate zone, also a delay in regulation may be associated with a change in daily routine and type of activity;
- unbalanced diet, large amounts of unhealthy foods in the diet, strict diets, insufficient amounts of vitamins and nutrients, problems with excess weight;
- colds, diseases of the digestive system and kidneys, diabetes;
- taking antibacterial drugs and some other medications;
- hormonal contraception, starting to take contraceptives, abrupt change in oral contraception or its cancellation;
- poisoning of the body with excessive doses of alcohol, drugs and nicotine;
- work in hazardous industries and on night shifts.
Physiological reasons for the absence of menstruation also include the factors discussed above: puberty, menopause and lactation. If after childbirth menstruation does not appear after a year, you should undergo a gynecological examination to rule out the presence of diseases due to birth injuries.
If you have ruled out all physiological causes, then your period is delayed due to pathology in the body. To identify it and prescribe adequate treatment, you should definitely seek help from a gynecologist.
No menstruation – pathology
The older a woman is, the more reasons can be found in her body that cause a delay in menstruation. If critical days do not occur, you first need to exclude pregnancy, and then suspect the presence of pathological conditions.
Diseases of the genital area and endocrine system can cause periodic delays in menstruation. Let's consider the most common pathologies of each direction.
Disease affecting hormonal levels
Diseases of the thyroid gland, adrenal glands, ovaries and pituitary gland can lead to hormonal imbalances and, as a result, to systematic and long-term delays of critical days:
- hypothyroidism A condition in which the thyroid gland produces insufficient amounts of thyroxine and triiodothyronine. These substances are directly involved in the synthesis of estrogens, progesterone and follicle-stimulating hormone in the ovaries. Without a sufficient amount of these hormones, the egg cannot mature, which means ovulation does not occur and menstruation does not begin. At the initial stage of the disease, a delay in the onset of menstruation is one of the symptoms of thyroid problems;
- hyperprolactinemia - with this disease, the functions of the pituitary gland are affected. Intensive production of prolactin begins, which suppresses the secretion of estrogen, which prevents the timely maturation of the egg, ovulation does not occur, which explains the absence of menstruation;
- oncological tumors in the brain or congenital hypoplasia of the pituitary gland;
- benign neoplasm (adenoma) in the pituitary gland or adrenal glands. This tumor causes obesity, increased hair growth on the face and body, and menstrual irregularities;
- improper functioning of the ovaries caused by hormonal imbalance, past inflammation;
- If a girl’s period does not come on time, this may be caused by the installation of an IUD and the use of hormonal-based drugs.
Anorexia can cause a delay in menstrual periods. This is a mental illness that is associated with a disorder of digestive behavior.
Most often it affects young girls who strive to conform to the “glossy” canons. The desire to lose weight develops into an obsession, which is why food is not absorbed by the body, and it is completely depleted.
Stopping menstrual function in this case is a protective reaction of the female body, so when normal weight is restored, menstruation resumes. For this disease, you may need to consult a psychotherapist and gastroenterologist.
If your periods are delayed due to the presence of endocrine pathologies, then in addition to visiting a gynecologist, you may need to consult an endocrinologist, but most often the delays are due to gynecological diseases.
Gynecological pathologies
Gynecological causes of delayed menstruation are inflammatory diseases of the uterus and ovaries, which lead to hormonal disorders. At the same time, the concentration of hormones responsible for the maturation of the germ cell and the mucous layer of the uterus changes.
As a result, there is a delay, the intensity and composition of monthly discharge changes, pain appears in the lower abdomen or lower back, and other pathological symptoms appear.
In such a condition of the reproductive system, without proper treatment, tumors of both the genital organs and mammary glands can occur. Also, lack of proper therapy can lead to infertility.
The cause of inflammatory processes can be an infection that has entered the genitals due to poor hygiene, unprotected sex, trauma to the uterus after childbirth, abortion and medical curettage.
If you don’t have your period, this may be due to gynecological pathologies that lead to delays:
- salpingoophoritis is a disease in which the uterus and appendages become inflamed; it can lead to ovarian dysfunction;
- endometritis - the inflammatory process affects the inner mucous layer of the uterus, and hypomenstrual syndrome is observed when there is no discharge for 2-3 months;
- cervicitis – inflammation of the uterine cervix, which without proper treatment can spread to the uterus and its appendages;
- endometrial hyperplasia is characterized by severe thickening of the inner mucous layer of the uterus, and after a long delay in the critical days, severe bleeding occurs. The development of this disease is caused by hormonal imbalances due to endocrine pathologies;
- Uterine fibroids are a benign neoplasm. It looks like a single node or a cluster of several tumors. It can be localized both inside and outside the uterus. The presence of a tumor is indicated by an irregular cycle;
- Polycystic ovary syndrome is characterized by the formation of cysts inside and outside the ovary. The symptoms of the disease are not expressed; often only a very long delay can cause the detection of this disease;
- polyps are focal growths of the endometrium in the form of nodes, which under certain conditions can spread to the cervix. A polyp can cause delay, which is followed by heavy bleeding. Polyps are characterized by malignant tissue degeneration;
- endometriosis is a pathological growth of the mucous layer of the uterus beyond its limits (into the tubes, ovaries and other organs). Usually, with endometriosis, the patency of the fallopian tubes is disrupted, which causes delays;
- ectopic pregnancy. When a fertilized egg is implanted not in the uterine cavity, but in the tube, an ectopic pregnancy occurs. Untreated endometriosis may be to blame for this. If it is not surgically removed in time, the tube ruptures, which can lead to severe bleeding and death. A sign of ectopic implantation of the fetus may be spotting instead of the expected regular discharge. If such a daub is accompanied by nagging pain in the lower abdomen, nausea and vomiting, you should definitely consult a gynecologist. An ectopic pregnancy can occur not only after endometriosis, but also after salpingoophoritis, which causes adhesions in the tubes and ovaries;
- endometrial hypoplasia. A disease in which insufficient development of the endometrium occurs. With this disease, the inner uterine layer is so thin that it is unable to hold the zygote. This causes miscarriage in the early stages, when the woman does not even know she is pregnant. The next critical days come late and begin with a brown daub. Hypoplasia is caused by inflammatory processes in the organs of the reproductive and urinary systems, surgical interventions on the uterus and ovaries, as well as hormonal imbalance.
Not pregnant, but still no period: 8 reasons for delayed menstruation
You put a spiral
Some of their varieties can cause periods to become scanty or disappear altogether. If this happens, you should also periodically make your contribution to the treasury of pregnancy test manufacturers, since a small risk still remains, and the most striking (excuse the pun) indicator that conception has not occurred has disappeared.
You have problems with the thyroid gland
This gland regulates metabolism, produces hormones, controls temperature and does other things important for the body. If it works too hard or, conversely, not enough, it can stop ovulation and cause an irregular menstrual cycle.
If you also get tired quickly, your hair has become thin, your weight has jumped in either direction - your doctor may suspect that this is the reason. Then he will order a blood test and possibly prescribe medications. With the right treatment, the cycle should normalize within a few months.
You overdid it with sports training or dieting
If the gym is your home, you're overworked, you don't eat enough, you've lost weight quickly, or you suffer from eating disorders, this can also cause amenorrhea (lack of periods). Especially if your BMI is below 18−19.
If this is the case, it is usually enough to gain a couple of kilograms or reduce your training schedule for the cycle to improve. Of course, the temptation to get rid of the annoying “red days of the calendar” is great. But it is very dangerous and destructive to your body! If you put up with amenorrhea for a whole year, this is fraught with bone loss and osteoporosis.
You just stopped taking birth control pills
They clearly regulate your cycle, and when you stop taking them, your lazy body may not immediately remember how to do it yourself. He may need time to collect his thoughts. Sometimes it takes several months before menstruation returns.
Remember that after you stop taking the pill, your body's ability to conceive a baby may improve. (And that the absence of periods is not an indicator of safety: ovulation will occur before they do.) So be sure to use condoms if you are not planning a pregnancy yet.
You're stressed
If you have incredible work pressures or other life problems, your body may decide that now is not the time to give birth. And it will stop the cycle. If against this background you miss some periods or they are delayed, it’s not scary. But if you're missing cycle after cycle, it's time to see a doctor.
You have developed polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
His symptoms: menstruation did not come, acne came instead. Even if you try very hard to maintain a healthy lifestyle, your body weight still increases. On the face and chest, treacherous hairs grow out of nowhere. Such a diagnosis means a hormonal imbalance, because of this ovulation stops or becomes irregular - and menstruation too.
You have problems with your pituitary gland
I don’t want to scare anyone, but amenorrhea, headaches, milky-white discharge from the nipples - this set of symptoms may indicate the presence of a benign tumor of the pituitary gland called prolactinoma.
You've gained weight
Overweight girls are at risk just as much as those who are too thin. Australian researchers have calculated that obese women have irregular cycles twice as often as those whose weight is normal. The fact is that excess weight can be associated with hormonal imbalances and PCOS (see point 7). Proper nutrition and weight loss will help improve everything.
Popular
- Give birth and it will pass: how and why women are refused treatment
Did you like the article? Subscribe to the news and stay up to date with the most interesting and useful news.
Thank you.
We have sent a confirmation email to your email.
Delay examination
If there is no period for a long time, and a woman wants to find out why there was a delay in a negative pregnancy test, she must undergo a gynecological examination. In case of absence of menstruation for a very long period, the doctor may additionally prescribe the following tests and examinations:
- measuring and charting fluctuations in basal temperature, such a study will determine the presence or absence of ovulation;
- blood test for hCG levels, as well as tests for hormones of the ovaries, pituitary gland and other glands;
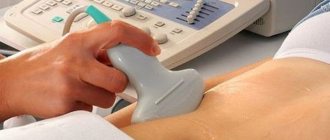
- Ultrasound examination of the organs of the reproductive and excretory system. This diagnostic method allows you to determine intrauterine and ectopic pregnancy, the presence of benign and malignant formations in the uterus, ovaries and signs of other diseases;
- To exclude neoplasms in the ovaries or pituitary gland, CT and MRI of the brain may be prescribed.
If menstruation does not occur due to non-gynecological diseases, an additional visit to an endocrinologist, psychotherapist, nutritionist and other specialized specialists may be required.
Delayed menstruation, but the test is negative: reasons not related to pregnancy
In addition to pregnancy, a delay in menstruation can be caused by many reasons, both serious diseases and other factors associated with sexual dysfunction. If your period does not come and the pregnancy test is negative, consult your doctor to find out the cause of this phenomenon.
Failure of the menstrual cycle occurs when:
- Polycystic ovary syndrome is a disease that is accompanied by excessive body hair and increased oiliness of the skin and scalp.
- Gynecological diseases - such as inflammation of the ovaries, appendages or uterus, cancer of the reproductive organs, endometriosis, adenomyosis.
- Endocrine diseases that are accompanied by ovarian dysfunction.
- Hormonal imbalances.
- Early menopause in women 35–45 years old - the problem arises as a result of a combination of disorders of the endocrine system and hormonal levels.
To identify the exact cause of the delay, you will need to consult a gynecologist. If necessary, an examination is carried out: tests, ultrasound of internal organs and the thyroid gland, brain tomography.
If the examination did not show any pathologies or diseases, then most likely the delay in menstruation was caused by one of the reasons:
- violation of the diet: fasting or overeating;
- change in climatic conditions;
- stress;
- injury;
- chronic or prolonged illness;
- taking medications or oral contraceptives;
- strong physical exertion, fatigue.
Delayed periods are normal for women after childbirth, as well as during breastfeeding. At this time, the young mother’s body produces the hormone prolactin, which inhibits reproductive function.
If your period is delayed by more than 3-4 days, first rule out pregnancy. After this, contact your gynecologist for examination and further treatment.
Ways to provoke regulation
If your period is delayed, you can speed up its onset in several ways:
- in order to restore menstruation, the delay of which is caused by stress, a strict diet, vitamin deficiency, excess stress and other non-pathological factors, it is enough to eliminate the external irritant. The menstrual cycle will quickly return to normal if you rest well, eat well and do not subject the body to physical and emotional overload;
- You can use emergency contraception such as Pastinor. This is a progesterone-acting drug, which after ovulation increases the level of progesterone in the body and can stimulate the rapid growth and detachment of the endometrium, thereby promoting the speedy onset of regulation. Other hormonal drugs, such as Duphaston, Utrozhestan, Norkolut, have a similar effect. But each of these drugs has a number of contraindications, so they can only be taken as prescribed by a doctor;
- if your period comes late, your doctor may also prescribe injections that stimulate the muscle activity of the uterus. Increased uterine tone can cause menstruation;
- at home, you can provoke regulation with the help of herbal decoctions and infusions of chamomile, bay leaf, tansy, parsley, blue cornflower, etc. Hot baths with iodine show good effectiveness for short delays.
Despite the fact that there are a huge number of methods for dealing with delayed menstruation, each of them should be prescribed exclusively by a specialized specialist, since the reasons for the delay can be very different, which means that the method of dealing with the problem should be selected individually based on the results of tests and examinations.
Preventive measures
Preventing a disease is always easier than treating it later. To prevent the delay of critical days, it is better to maintain your health in normal condition in advance; for this, it is enough to follow several recommendations:
- get rid of bad habits and lead a healthy lifestyle;
- play sports, but do not allow severe overload of the body;
- create a balanced diet, exclude all harmful foods and drinks;
- do not exhaust yourself with hunger and strict diets;
- use medications only as prescribed by a doctor;
- Go for preventive examinations to a gynecologist at least 2 times a year.
Every woman sometimes experiences delays, but if you follow the tips above, the likelihood of them occurring will be minimal.
What are the dangers of constant delays?
The absence of menstruation is not a dangerous condition for a woman; the reasons for the delay may be much more serious, especially when it occurs monthly. The most positive reason that the regulations are late is pregnancy.
Constant delays in menstruation not only cause discomfort to a woman, confusing her plans, but may also indicate the presence of serious pathologies in the body.
If there is a delay, it is necessary to visit a doctor every month as quickly as possible, since early diagnosis allows timely treatment of diseases and neoplasms, prevention of early menopause, prevention of infertility or elimination of ectopic pregnancy, which is dangerous not only for a woman’s health, but also for her life.
Hormonal disbalance
The causes of delayed menstruation can be divided into two groups: those originating in the endocrine (hormonal) system and gynecological. At the same time, we must not forget that all body systems are interconnected, and problems with one of them can lead to a cascade of unpleasant consequences for another system and health in general. That is why it is so important to be examined by a specialist in a timely manner and monitor your health.1
In the first case, the problem concerns the hormonal status of a woman, disorders associated with the functioning of organs that produce hormones. Even properly developed and healthy ovaries and the uterus will not be able to perform their functions if the functioning of this system that regulates the menstrual cycle is disrupted.
It is important to understand that hormone imbalance can be triggered by a number of negative factors that are known to cause delayed periods:2
- starvation;
- stress;
- poisoning with toxic substances;
- smoking;
- viral infections;
- abortions;
- operations;
- injuries.
Impaired hormone production, in turn, leads to irregular menstruation, and in the future can lead to their absence (more than 6 months). Among the target organs will be not only the ovaries and uterus, but also glands that produce hormones and suffer from unfavorable conditions, infections or bad habits. Quitting smoking, proper protection from unwanted pregnancy and taking care of your health are already preventive measures for missed periods. However, if your period is late, you should not engage in self-diagnosis, because only a qualified specialist can conduct a correct analysis of the condition, identify the true causes of the problem, study the results and develop a treatment plan.3