Trichomoniasis is considered the most common sexually transmitted disease (STD). The cause is a single-celled microorganism called Trichomonas vaginalis. The pathogen belongs to the class of anaerobic bacteria, that is, it cannot live in the air, but is perfectly adapted to exist in human organs. There are three types of Trichomonas, the main danger is parasitic in the genitourinary system.
Trichomoniasis is diagnosed more often in women. But this is not due to a special predisposition of the weaker sex to the disease, but is due to the fact that women are more willing to consult with doctors and undergo timely diagnosis.
With insufficient treatment, the disease easily takes on a chronic form. Untreated trichomoniasis is dangerous for a woman’s body and can cause complications.
- Inflammation of the vagina (vaginitis);
- Cervical infection;
- Narrowing, poor patency of the fallopian tubes;
- Pathologies of the bladder, kidneys.
What is Trichomonas
The causative agent of trichomoniasis is a single-celled anaerobic organism that belongs to the protozoa. It moves with the help of flagella. Penetrating into the vagina, Trichomonas spreads upward and settles in the cervix and cervical canal, where in almost 90% of cases a pathological process develops; in other cases, asymptomatic carriage develops.
To date, there are more than 50 species of identified Trichomonas. Among them, only the following varieties can be parasitic in the human body:
- intestinal Trichomonas (Trichomonas hominis) - vaginal Trichomonas (Trichomonas vagimalis) - oral Trichomonas (Trichomonas tenax).
As for vaginal Trichomonas, it is worth noting its increased adaptability to development and progression directly in the female genital tract, urethra, and it was also diagnosed in the rectum. However, in the external environment, Trichomonas vaginalis is quite unstable and dies quickly, since it does not form cysts.
Trichomonas are parasites, they exist due to nutrients found directly in the infected female body. By absorbing mucosal cells and vaginal secretions, as well as other microorganisms, Trichomonas can remain in the genital tract for quite a long period of time. Trichomonas vaginalis damages the mucous membrane and promotes the penetration of other sexually transmitted infections (including HIV). Without appropriate treatment, Trichomonas will not leave its “home” on its own.
The highest intensity of Trichomonas reproduction is observed directly during menstruation and after its completion. This is due to the fact that during this period a change in the acidity of the vaginal contents occurs in the female body. In addition, this pathogen strengthens its resistance to the protective factors of the human body by enriching it with iron from menstrual blood.
General information about the pathogen
Trichomoniasis (sometimes called trichomoniasis) urogenital is a multifocal infectious inflammatory disease in men and women caused by the simplest single-celled organism - Trichomonas vaginalis (Trichomonas vaginalis).
Trichomoniasis is a predominantly sexually transmitted infection (STI), and occupies a leading place among them (approximately 170 million cases of this disease are registered every year; in Russia, the number of cases of infection fluctuates around 200 people per 100,000 population).
Trichomonas vaginalis (Trichomonas vaginalis) is a protozoan microorganism of the genus Trihomadidae, adapted to parasitize the organs of the human urogenital tract. Can live in a nutrient medium with a pH in the range of 4.9-7.5 and at an ambient temperature of 35-37 ° C.
Figure 1 - Structure of Trichomonas vaginalis
It should be noted that trichomanas vaginalis quickly dies at temperatures above 45-50 °C, dies instantly at temperatures above 60 °C, and remains viable for 45 minutes at an ambient temperature of -10 °C.
In freshwater bodies of water, their death occurs within 30-45 minutes. They do not completely tolerate drying out, but the moist environment of cotton fabrics and sponges is favorable for it, but even in such conditions it dies within 2 hours. Does not tolerate alkaline solutions (laundry soap) and antiseptics.
Three types of trichomonas can live in the human body: Trichomonas tenax (oral), Trichomonas hominis (intestinal), Trichomonas vaginalis (vaginal), but the main infectious agent today is considered exclusively T. vaginalis. A person can only become infected with this disease from a person; such diseases are called anthroponotic.
Signs of trichomoniasis in women
Symptoms of trichomoniasis in women are not specific; they are similar to many other sexually transmitted infectious diseases. In women, acute trichomoniasis can manifest as cervicitis, vulvovaginitis, bartholinitis or urethritis.
In most cases, the manifestation of discomfort begins immediately after unprotected sexual intercourse. The duration of the incubation period is often no more than a day, but in medical practice there have been cases when it lasted up to a month.
How does trichomoniasis manifest in women?
The most common symptoms of this pathological process:
- Copious vaginal discharge, foamy in texture and with an unpleasant odor. They are yellow in color with a grayish tint.
— The presence of discomfort in the vagina or vulva area, manifested in the form of itching and burning.
— Skin irritation in the perineal area caused by pathological discharge.
- Pain during sexual intercourse, often quite intense.
— The occurrence of erosions on the mucous membrane of the genital organs.
- In case of damage to the urethra, a feeling of pain, itching and burning at the time of urination.
Impact of the disease on pregnancy
Like many infectious diseases, trichomoniasis negatively affects the course of pregnancy. Pathogenic microorganisms contribute to the development of inflammatory processes that increase the risk of premature birth, miscarriages, and the appearance of weakened children.
Antibacterial therapy is carried out after the end of the first trimester. If there are no acute symptoms of the disease, treatment with medications may not be carried out. Self-medicating an infection during pregnancy is extremely dangerous. If there is a high risk of infection of the fetus, therapy is carried out using tinidazole, ornidazole, atrican, metronidazole. Women also undergo vaginal irrigation with antiseptic solutions.
Infection with vaginal trichomoniasis in most cases occurs through unprotected sexual intercourse. The use of condoms and regular examinations with a gynecologist help prevent infection and the development of complications.
Classification and features of the course of urogenital trichomoniasis
Depending on the time of onset of symptoms, the affected areas and the characteristics of the symptoms, there are several types of course of the disease:
— Fresh trichomoniasis of any form: acute, subacute, asymptomatic.
- Chronic trichomoniasis.
— Trichomonas carriage.
Acute trichomoniasis
The course of the acute form of the disease is accompanied by a bright clinical picture, which manifests itself in the form of copious discharge with an unpleasant odor, burning and itching. The presence of discomfort should be a reason to immediately visit a gynecologist.
Chronic trichomoniasis
In case of untimely and poor-quality medical care or in the absence of treatment, after an average of 2-3 months, trichomoniasis becomes chronic. It is characterized by minimal manifestations of milky vaginal discharge, or even its complete absence. But the pathological process continues to develop on the mucous membrane.
Sometimes, when the immune system is weakened, periodic exacerbations are observed. They can be caused by vitamin deficiency, menstruation, and even alcohol abuse.
Asymptomatic carriage of trichomoniasis
The greatest danger to female reproductive health is trichomoniasis. The insidiousness of this type of disease is the absence of any clinical signs. Therefore, many infected people do not even suspect that they are carriers of this pathogen. And during sexual contact they infect all their partners.
To date, the exact number of carriers of vaginal Trichomonas has not been established. According to statistical data, this form of the pathogen occurs in 50% of cases in women diagnosed with urogenital trichomoniasis.
One of the properties of Trichomonas is the absorption of different types of microorganisms located directly inside it. Due to this, they become inaccessible not only for diagnosis, but also for many medications.
Trichomoniasis: associated diseases
In most cases, trichomoniasis is accompanied by the following infections:
— Gonorrhea — Bacterial vaginosis — Chlamydia — Mycoplasmosis — Fungal infections (thrush in women).
This information should be taken into account when prescribing the appropriate course of therapy. Timely treatment will save any woman from this type of infection and prevent the development of a chronic form of the disease.
Pathological manifestations of the lesion
As microorganisms multiply, they release a huge amount of metabolic products that destroy epithelial cells and cause inflammation, accompanied by the formation of erosions and ulcers.
The acute stage of trichomoniasis is observed during the first two months from the moment of infection and indicates a high level of activity of the pathogen. This stage is characterized by the development of urethritis.
If the exact time period of infection is unknown or more than two months have passed, the disease is considered chronic. In men at this stage, the development of prostatitis is observed.
When living conditions change for the worse, Trichomonas sheds its flagella and turns into a dormant cyst-like form. In this case, microorganisms secrete a gelatinous or horny substance, with the help of which a protective shell is formed around the Trichomonas colony - a cartilage-like tumor or cyst.
Drug action on Trichomonas at this stage forces microorganisms to flee. They leave the tumor through the bloodstream and affect those areas of the mucosa whose tissues contain fewer drugs.
Additional factors may also contribute to the active development of trichomonas:
- Ionizing irradiation accelerates the biological functions of pathogenic cells and stimulates their growth.
- Smoking and alcohol are irritants of this microorganism, provoking the transition of cells into an aggressive form, followed by active reproduction.
How is trichomoniasis transmitted?
In order to understand how you can become infected with trichomoniasis, you need to consider all possible ways of transmitting this infection.
Sexual transmission of infection is the most common, which is why trichomoniasis is classified as a sexually transmitted infection. The pathogen is transmitted from an infected person through sexual contact. There is a high probability of infection from an asymptomatic carrier of the infection who has been sick for a long time.
There is also theoretically a possibility of transmission of the pathogen through contact and household contact when using common hygiene items. But it is worth noting that transmission of infection in this way is unlikely due to the fact that this parasite is weakly resistant to environmental conditions.
Another possible route of infection is transmission of the pathogen to the child from an infected mother during childbirth. Due to the specific structure of the mucous tissues of the urogenital tract of newborns, trichomoniasis does not take root well in infants. This creates conditions that do not allow this infection to develop, and in many cases a process of voluntary self-healing occurs.
Promiscuous sex life and neglect to use various methods of contraception create an increased likelihood of Trichomonas entering the female body.
Trichomoniasis during pregnancy
Trichomoniasis, entering the female body during pregnancy, can affect the development of many diseases:
- Proctitis.
- Cervicitis.
- Erosion of the cervix.
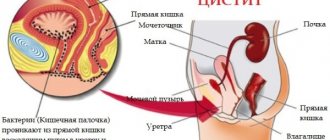
- Cystitis and other diseases.
Therefore, if a woman is diagnosed with trichomoniasis during pregnancy, the doctor should pay maximum attention to her.
The disease caused by these parasites during pregnancy can affect premature birth, the birth of children with very low body weight, as well as fetal death at different stages of pregnancy.
During pregnancy, inflammatory processes are active, and the chronic form easily transforms into acute. As a rule, in pregnant women the infection affects several organs, sometimes the entire genitourinary system.
In expectant mothers, the immune response to infection is activated, aimed at protecting the embryo.
So after 4 months, special protective membranes are formed that prevent Trichomonas from entering the uterus. But infection of a woman’s body before 16 weeks of pregnancy in most cases leads to miscarriage. Later infections are easier to treat and have a positive tendency to recover.
A woman may not be aware of her illness. The disease trichomoniasis during pregnancy occurs in both acute and chronic forms. The acute form of trichomoniasis during pregnancy is characterized by rapid manifestation of signs of the disease.
Within 2-14 days the following may begin:
- Diarrhea.
- Fever.
- Heat with heaviness in the lower abdomen.
- Severe weakness and fatigue.
- There is a discharge that is sharp-smelling, foamy, yellow with a greenish tint.
- Pregnant women experience severe itching with pain in the genitourinary system.
The chronic form of trichomoniasis is characterized by the fact that the patient may not be aware of her disease for six months. It appears as follows:
- Metabolism is disrupted, often attributed to pregnancy.
- Pregnant women feel occasional pain in the lower abdomen and itching.
- More difficult to diagnose.
- Sometimes purulent mucous discharge appears.
Trichomoniasis itself cannot in any way affect the fetus during the mother's pregnancy, since the parasites are not able to penetrate the placenta.
But Trichomonas takes pathogens without destroying them. Inside it, they become inaccessible to antibiotics. As a result, microbes have free access to the uterine cavity and influence the fetus.
If trichomoniasis is diagnosed on time, it is better to treat it before pregnancy. Naturally, the disease will have an effect on subsequent pregnancies, since traces of inflammatory changes will remain on the uterine mucosa.
Because of this, the fertilized egg may be positioned in such a way that a caesarean section will have to be performed during childbirth. However, this is the only complication that pregnant women can fear after completely cured trichomoniasis.
Diagnosis of trichomoniasis in women
In modern medical practice, there are various methods by which it is possible to determine the exact presence of Trichomonas infection in a woman’s body. Without treatment, the disease becomes chronic and hardly manifests itself outwardly, but upon examination pathological changes can be detected.
Inspection
At a gynecological consultation, a visual examination and colposcopy are performed, with the help of which the doctor can identify pathological changes in the woman’s genitourinary system. The following signs are characteristic of infection with vaginal Trichomonas:
— Inflammatory process of the mucous membranes of the vagina and cervix, accompanied by pronounced redness, the presence of erosions and pinpoint hemorrhages.
— Concentration in the posterior vaginal vault of mucus and secretions of a yellow color with a gray tint, which are easily separated and foam at the same time.
— There are cases of changes in the color and structure of the cervical mucosa. It becomes loose and rich red in color.
Trichomonas tests
If there are visual signs of trichomoniasis, the gynecologist prescribes additional laboratory examination to clarify the diagnosis. To confirm the presence of urogenital trichomoniasis, the following clinical tests are performed:
— Microscopic examination of a smear from the cervical canal, vagina and urethra.
— Sowing the resulting material on various nutrient media.
— Serological diagnostics of blood: immunofluorescence reaction, indirect hemagglutination reaction, enzyme immunoassay.
— Carrying out a polymerase chain reaction to isolate Trichomonas DNA.
Each of these surveys contains both advantages and disadvantages. If the results of one of the tests give a negative answer, this does not mean a complete absence of trichomoniasis infection in the body. Therefore, they must be taken comprehensively and look at all the results, which depend on the characteristics of the disease. With the help of laboratory monitoring, it is possible to observe the dynamics of successful therapy for trichomoniasis or the lack of result, which is a reason for changing the drug.
Differential diagnosis of trichomoniasis with vaginal candidiasis, bacterial vaginosis and ureaplasmosis
| Signs | Vaginal candidiasis or thrush | Trichomoniasis | Bacterial vaginosis | Ureaplasmosis |
| The smell of discharge | Sourish-sweet smell | Strong foul odor of fish | Unpleasant fishy smell | May have a natural or ammonia odor |
| Nature of the discharge | Abundant, thick, homogeneous, milky, cheesy consistency | Abundant, foamy, purulent, yellow-green in color | Abundant, liquid, gray-white, may be foamy | Abundant, cloudy, sometimes whitish in color; between cycles there may be brown spotting |
| Feel | Burning and itching in the vagina, discomfort and pain during urination and during sexual intercourse, the burning intensifies when a woman sits cross-legged | Severe external and internal itching in the vagina and external genitalia, hyperemia of the vaginal mucosa, disturbances in the urination process | Vaginal itching, discomfort during intercourse | Pain in the lower abdomen, discomfort during intercourse, itching and burning in the genital area |
Diagnostics
Testing for trichomoniasis is recommended annually or urgently in the following cases:
- when planning pregnancy for both partners;
- during gestation for women;
- when symptoms of an STD appear;
- before operations on the pelvic organs;
- to identify the cause of infertility;
- after risky sexual intercourse.
To carry out the analysis, a smear from the vagina or urethra and blood are taken, depending on the study chosen. The infection is diagnosed in the following ways:
- Microscopic examination. A laboratory technician examines a smear under a microscope. The method is ineffective; the parasite successfully disguises itself as other cells and hides in the intercellular space.
- Microbiological research. The biomaterial is placed on a nutrient medium and in conditions favorable to the microorganism, where it actively multiplies.
- PCR analysis. Polymerase chain reaction is the most accurate method and helps detect traces of pathogen DNA.
- Serological methods, such as ELISA. Helps identify antibodies to the pathogen in the body. The disadvantage is that false positive reactions are common.
Diagnostic results can be obtained within 1-7 days, depending on the chosen study. Microscopy is carried out on the same day, but for microbiological analysis you will have to wait several days. PCR and ELISA results are issued within 24 hours.
Trichomoniasis in pregnant women
Conceiving a child must be approached with great responsibility. Therefore, it is very important to plan your pregnancy early. For normal development of the fetus in the womb, the presence of sexually transmitted diseases should be excluded in advance, and if they are diagnosed, get rid of them immediately.
In this case, trichomoniasis is one of the varieties of these pathologies. This disease provokes inflammatory changes that can prevent pregnancy. The altered composition of the vaginal flora contributes to the death of sperm, and they lose the ability to penetrate the lumen of the fallopian tube, where fertilization of the egg occurs.
Complications during pregnancy with trichomoniasis
— In the early stages of pregnancy, there is a high probability of miscarriage.
- Frozen pregnancy.
— Birth of a child before the established deadline.
— Inconsistency between the child’s weight and developmental dates.
— Penetration of trichomoniasis into the fetal membranes.
— Increased likelihood of infection through the mother’s birth canal.
In addition, the negative impact of medications on fetal development is monitored. Therefore, treatment of Trichomoniasis in pregnant women is prescribed no earlier than the second trimester of pregnancy.
The selection of pharmacological drugs is carried out strictly individually, depending on the physiological state of the woman’s health and the duration of pregnancy. Complex therapy for urogenital trichomoniasis during pregnancy is prescribed exclusively by leading specialists: a gynecologist and a venereologist.
Drug therapy
At the moment, a large number of treatment regimens for trichomoniasis in women have been proposed, many of them are currently outdated. Therefore, only modern and effective methods of treating this disease will be discussed below.
The following rules exist for the treatment of trichomoniasis:
- 1Treatment of sexual partners is carried out simultaneously!
- 2During treatment, it is not recommended to drink alcoholic beverages; sexual contact should be avoided.
- 3For greater effectiveness of treatment, concomitant diseases (hypovitaminosis, chronic diseases) should be treated.
- 4 Absolutely all forms of the disease are treated (acute, chronic, Trichomonas carriage and sexual partners of persons who have been diagnosed with the disease without positive results for the presence of Trichomonas, but with clinical signs of the inflammatory process).
- 5Curability control is carried out twice.
Currently, the Protocol approved by the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation on January 14, 2005 is used for the treatment of trichomoniasis . In accordance with this protocol, the leading group of drugs are antimicrobial drugs active against T. vaginalis. All these drugs belong to antiprotozoal and antimicrobial drugs, derivatives of 5-nitroimidazole.
Treatment regimens for chronic trichomoniasis in women and uncomplicated forms according to the Protocol are given in the table below (you must select one of the proposed regimens for one drug) *
Treatment regimens for trichomoniasis in women, pregnant women and children. * the dose and treatment regimen are chosen by your attending physician.
Prescribing intravaginal forms of drugs in women (vaginal suppositories) for the treatment of trichomoniasis is ineffective, this is due to the fact that the causative agent of the disease can parasitize not only in the vagina, but also in other organs of the genitourinary system.
Due to the lack of alternative drugs for the treatment of trichomoniasis, if an allergy to drugs derived from 5-nitroimidazole is detected, before starting treatment for T. vaginalis, hyposensitizing therapy is prescribed, which is carried out by an allergist-immunologist.
Treatment of trichomoniasis in women: drugs and treatment regimens
If there are suspicious symptoms, especially after unprotected sexual intercourse with unfamiliar partners, the woman should immediately undergo a gynecological examination to detect infection. If it is detected, it is strongly recommended to immediately begin its treatment in order to prevent the development of a chronic form.
A carrier of trichomoniasis infection has a negative impact not only on his own body, but is also a significant threat to the health of his sexual partners. Therefore, you should not put off visiting an antenatal clinic, despite the sensitivity of the problem itself and possible financial difficulties.
Trichomonas is a single-celled organism and is neither a bacterium nor a virus. Therefore, in its treatment, antibacterial and antiviral drugs are not used, which are powerless in the treatment of this pathology.
To combat Trichomonas, pharmacological medications belonging to the group of 5-nitroimidazoles are used. The most common of these is metronidazole.
Treatment of trichomoniasis with metronidazole (Dosage regimens)
The drug is taken during or after meals.
— Single oral administration of 2 g tablets.
— Taken twice a day with a dosage of 250 mg per dose for 10 days.
— Taken twice a day, 400 mg for 6-8 days.
Women are additionally prescribed intravaginal metronidazole, a single dose of 2 g or 500 mg 2 times a day, morning and evening, for a course of 10 days. During treatment, sexual intercourse should be avoided.
If necessary, the course can be repeated after 3-4 weeks with a control laboratory test.
Also, in the treatment of urogenital trichomoniasis, more modern antimicrobial medications from the same series as metronidazole are prescribed. These include the drugs ornidazole and secnidazole. Unlike metronidazole, they cause fewer side effects and are considered more effective. They are often prescribed for the treatment of chronic trichomoniasis or trichomoniasis carriage.
Regimen for taking ornidazole for urogenital trichomoniasis
Oral administration of the drug in a dosage of 500 mg in the morning and evening, with strict adherence to a 12-hour time interval. The course of therapy is at least 10 days.
Intravaginally, 1–2 g per day. within 5-10 days. Treatment of trichomoniasis in men is carried out similarly.
Secnidazole dosage regimen for urogenital trichomoniasis
Trichomoniasis is treated in one day; for this purpose, 2 g of the drug is taken once.
Treatment of trichomoniasis during pregnancy
Treatment of trichomoniasis in pregnant women is difficult, since all 5-nitroimidazole derivatives penetrate the placenta and have a toxic effect on the fetus. Therefore, treatment is carried out only in the second or third week of pregnancy, and only local drugs are used. As a rule, this is ornidazole, which, after hygienic treatment of the external genitalia, is administered intravaginally at a dose of 1–2 g/day for 5–10 days.
In parallel with taking drugs from the 5-nitroimidazoles group, medications are prescribed that enhance the etiotropic therapy of trichomoniasis. These include the following medications:
— Antifungal
— Antiviral
— Hepatoprotectors
— Antioxidants
— Immunostimulating drugs
— Vitamin and mineral complexes.
Main routes of transmission
How and where can you become infected with trichomoniasis? There are the following ways of spreading (transmitting) this infection:
- 1The most common route of infection is sexual (the infection is transmitted through any type of sexual contact: genital, oral, anal, you can even become infected through finger contact with your partner’s genitals, while the main route of infection remains genital contact). The probability of becoming infected with a single unprotected sexual intercourse varies from 4 to 80%.
- 2Trichomoniasis is transmitted from a sick mother to the fetus (when the fetus passes through the infected tissue of the mother’s birth canal).
- 3Contact-household transmission route (towel, robe, toilet seat), but because in the external environment the organism is extremely unstable; this route of transmission is very rare, although it is not completely excluded.
Figure 2 - Life cycle of Trichomonas
Vaccine SolkoTrichovak against trichomoniasis
Scientists have found that with urogenital trichomoniasis, the chemical composition of vaginal secretions deteriorates, the level of lactobacilli (Doderlein bacilli) decreases, and acidity changes. Such conditions reduce local protective reactions and create a favorable environment for the development of this pathology and associated infections.
In order to increase immunity and treat trichomoniasis, the SolcoTrichovac vaccine is used in medical practice. This drug consists of acidophilic lactobacilli (H2O2-negative strains) formed during urogenital trichomoniasis and bacterial vaginosis.
Its main effect is to stimulate the formation of antibodies (Ig A, Ig G) in vaginal secretions. These are proteins that eliminate various infectious pathogens and pathological forms of lactobacilli. This helps to increase the number of normal lactobacilli and restore the acidity and microflora of the vaginal secretion. The vaccine is prescribed in combination with antimicrobial medications.
Vaccination with SolkoTrichovak includes 3 injections of 0.5 ml intramuscularly, which are performed at intervals of 2 weeks. A year later, a second revaccination is carried out; 0.5 ml of the drug is administered intramuscularly once.
Treatment methods
Currently, specialists in the treatment of vaginal trichomoniasis use two drug therapy regimens:
- The patient is prescribed a single loading dose of Metronidazole tablets, not exceeding 2 g of the active substance. Provided that the pathogenic microflora is sensitive to this drug, such a dose will be sufficient to relieve the patient of the disease. But, otherwise, even increasing the dosage and prolonging therapy will not bring the expected results. The pathogenic microflora will survive, but the patient will develop serious complications.
- Metronidazole tablets are prescribed in a dose of 250 mg twice a day. The duration of drug therapy is 5 days.
Complications and consequences of trichomoniasis in women
Trichomoniasis, like any other infection, can lead to complications if left untreated. It can lead to such negative consequences as:
- female infertility;
- the likelihood of premature birth and spontaneous abortion;
- frozen pregnancy;
- pathological development of pregnancy;
- additional risk of infection with other sexually transmitted infections;
- cervical erosion;
- the likelihood of developing cervical cancer increases.
In the early stages, trichomoniasis responds well to treatment and can significantly reduce recovery time, as well as avoid the development of serious consequences.
How does infection occur?
The single-celled microorganism has a pear-shaped shape and dimensions of 8-24 mm; thanks to flagella and a unique membrane, it is able to actively move and parasitize on the topography of the epithelial layer.
Once in the urethra and cervical canal, Trichomonas colonize the mucous membrane and are found in connective tissues, which leads to inflammation of the gonads.
The following routes of infection with urogenital trichomoniasis have been established:
- Sexual contact of any kind (genital, oral, anal), infection is possible even if the hymen is preserved.
- Infection through household items contaminated with Trichomonas (towels, shower handles, toilet lid, etc.).
- Transmission of the pathogen to the fetus from an infected mother during labor (infected tissue of the birth canal).
By following normal hygiene rules, it is impossible to become infected in public places, since Trichomonas vaginalis dies outside the body of an infected person.
The active process of reproduction of the causative agent of urogenital trichomoniasis poisons the carrier of the infection with toxins, reducing his immune defense.
Important! In addition to the genitourinary system, the parasite is capable of colonizing other organs; it is found in the rectum, even on the tonsils and conjunctiva of the eyes, and in the lung tissue of newborns.
The ability of vaginal Trichomonas to absorb other microorganisms results in epithelial dysplasia, the development of extensive inflammation with hemorrhages and damage to smooth muscles.
Basically, infection with trichomoniasis occurs through sexual contact! Use condoms to protect yourself from unwanted diseases!
Classification of pathology by type of manifestation:
- A fresh form of the disease can be acute, develop as an asymptomatic or subacute type, if 1-2 months have passed since the onset of infection.
- Urogenital pathology of the chronic type develops 2 months after infection and occurs with scanty symptoms, but with exacerbations.
- In the complete absence of symptoms, but traces of the parasite are detected in discharge (vagina) or smears (urethra), trichomoniasis is classified as latent type (carriage).
Treatment of symptoms of urogenital pathology is prescribed depending on the form of its development, as well as the characteristics of its manifestation. An important condition for the effectiveness of the treatment process is simultaneous therapy of all sexual partners.
Prevention of trichomoniasis in women
The modern rhythm of a woman’s life and promiscuous sex life increases the risk of contracting this infection. First of all, Trichomonas affects a woman’s reproductive system, which can lead to problems with conception and gestation. Therefore, it is very important to take your health seriously: 1. be demanding of your sexual partner; 2. use protective contraception; 3. observe the work and rest regime; 4. eat a balanced diet; 5. undergo regular examination by a gynecologist (2-3 times a year). If any changes or discomfort appear in the genitourinary system, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Ways of infection with trichomoniasis
The most common route of transmission of the disease is sexual. Trichomonas lives in semen, vaginal secretions and urine. During sex without a condom, the partners' biological fluids mix and infection occurs.
The household route of transmission of trichomoniasis is unlikely, because the parasite is sensitive to the environment and dies quickly. If the room has a comfortable temperature and humidity, and there is no sunlight, the parasite can live for about an hour. This happens in the bathroom if you use one towel to wipe your genitals.
The likelihood of infection is low, because the development of the inflammatory process requires a large number of pathogens. Single parasites migrating from a damp towel will simply die under the influence of local immunity.
The vertical route of infection from mother to child is possible during the passage of the baby through the birth canal, and occurs in 5% of children born to sick women. The girl’s genitals are affected and an inflammatory process occurs. Boys suffer from trichomoniasis extremely rarely, due to the specific structure of the genitourinary system, the long urethra.
Childhood trichomoniasis should be treated with attention. If a child or teenager gets sick, and there are no people around him with infection, then violent actions can be suspected, which led to infection.
Transmission of Trichomonas through saliva is rare; the parasite can live in the oral cavity for 1-2 days, then dies. Only the oral type of microbe inhabits the oral mucosa, but it does not cause urogenital pathologies.
Cause and development of the disease
The infectious agent is a single-celled parasite Trichomonas vaginalis, transmitted mainly through sexual contact. Infection can also occur when the hymen is preserved.
Another route of transmission of the microorganism is also possible, but is observed extremely rarely: only in cases where healthy people use shower arms for a bidet toilet that are heavily infested with the parasite, shared toilet seats, shared towels, etc.
Infection in bathhouses, swimming pools, and open reservoirs, subject to normal hygiene rules, is impossible due to the low concentration of the pathogen in the aquatic environment. Outside the human body, Trichomonas vaginalis is unstable, although it can persist in urine, semen and water for up to 1 day.
It dies within a few seconds when dried, in direct sunlight, at a temperature of about 40°C, under the influence of antiseptic solutions, as a result of slow freezing. Even low concentration soap solutions can lead to its rapid destruction. On contaminated underwear, washcloths or body wash sponges, the parasite persists only as long as these items retain moisture.
Mostly people of active puberty are infected, and most of them are unmarried or divorced (80%). Thus, trichomoniasis in men is most common in the age group from 15 to 30, and in women - from 18 to 30 years.
The incubation period, that is, the time from the moment of infection to the appearance of the first symptoms of the disease, ranges from 1 day to 1 month, on average - from 5 to 15 days. During this time, the parasite, through contact with epithelial cells through the spaces between them and the cracks of the lymphatic network, penetrates into the connective tissue located under the layers of the epithelium. In the mucous membranes of the genitourinary tract, it is fixed on epithelial cells, penetrates the glands and the cracks between their cells.
During its life, the pathogen secretes the complex protein CRF (cellular disconnecting factor), which leads to significant tissue loosening. As a result of this, he himself, as well as accompanying microorganisms and toxic products of their metabolism, freely penetrate into the intercellular space.
CRF is active in an environment with a certain acidity and estrogen concentration, and for the life of Trichomonas, fatty acids and iron are needed, which are abundant in menstrual blood. Therefore, trichomoniasis in women manifests itself with severe symptoms during menstruation, especially immediately after their end.
All this can lead to the development of acute inflammatory processes in the mucous membranes, cause a weak reaction, or remain without obvious consequences. The severity of clinical manifestations depends on:
- virulence (activity) of vaginal Trichomonas and the intensity of its impact;
- condition of the epithelial layer of the mucous membrane of the genital and urinary tract;
- acidity of the genitourinary system;
- association of Trichomonas with concomitant pathogenic or conditionally pathogenic flora, its nature, degree of activity and the number of bacterial agents causing inflammation;
- the degree of the body's response; if it is higher than the degree of aggressiveness of the microorganism, the acute inflammatory process does not develop or is expressed rather weakly.
In addition, Trichomonas secretes substances that neutralize T-lymphocytes in the blood and antibodies formed in the body of the infected, and is also capable of absorbing and concentrating plasma proteins on its surface. The latter does not allow the body's immune system to recognize the pathogen as a foreign substance. Therefore, stable immunity is not developed. Although antibodies are found in the blood of those who have had the disease, the latter are unable to provide the body with adequate protection during re-infection.
Another property of vaginal Trichomonas is its ability to capture and reserve other opportunistic and pathogenic microorganisms, which leads to a pronounced tissue reaction, damage and destruction of the epithelium, and the formation of dysplasia of the epithelial layer. With reduced immunity of the body and significant inflammation, hemorrhages and damage to the smooth muscle layers adjacent to the inflamed mucous membrane occur.
Etiology of the disease
Trichomonas was first discovered and described in 1836 by anatomist Alfred Donnet. Since it was detected in a woman’s vagina, it received the name Trichomonas vaginalis, Trichomonas vaginalis. Its true role in the body could not be revealed until 1950 of the last century. Then scientists found that a dangerous microorganism parasitizes not only in the body of a woman, but also in the body of a man. For both women and men, this representative of the protozoa poses a significant danger, namely the development of chronic diseases of the genitourinary system and infertility.
The causative agent of trichomoniasis is Trichomonas vaginalis, a single-celled protozoan microorganism belonging to the class of flagellates. It is microscopic in size (from 10 to 40 microns), so it can only be detected using special laboratory optical instruments. The characteristics of these protozoan parasites are:
- All their vital activity takes place in the human genitourinary tract. This is a historically established anthropogenic parasite, and it cannot exist in other organisms;
- The ideal conditions for normal life of Trichomonas vaginalis is the vagina (pH 5-6, t - 37°C, certain humidity). At the same time, the microorganism does not need oxygen at all, since it is one of the anaerobic protozoa;
- They actively move in the intercellular space with the help of flagella and penetrate the organs of the genitourinary system, populating and destroying the mucous membrane of not only the vagina, but also the urethra and bladder and penetrating the cervix;
- They die quickly outside the body's conditions, as they are sensitive to heat and sunlight and the lack of moisture and certain acidity.
Penetrating into the human body, Trichomonas vaginalis moves its flagella to all parts of the vagina and urethra. At the same time, it multiplies quickly by normal cell division. Having reached a significant population, the protozoa begin to penetrate the epithelium, causing its massive destruction. At the site of the negative impact of parasites, inflammatory foci arise and infections such as vulvitis, colpitis, cervicitis, and cystitis develop.
Features of the development of trichomoniasis in women
It is known that in women Trichomonas vaginalis changes the intensity of development in accordance with the menstrual cycle. This phenomenon is explained by the presence of menstrual blood in the vagina during the menstrual phase. For Trichomonas vaginalis, organic iron is among the prerequisites for normal life. It ensures its virulence (the degree of ability to infect another organism) and cause vaginal trichomoniasis. It is the presence of this microelement that ensures Trichomonas’ survival and a high degree of penetration into other biosystems.
Red blood cells in menstrual blood quickly lose their structure and become an ideal source of nutrition and reproduction of single-celled parasites. More favorable conditions for them during menstruation are that the hormonal levels during this period are lower, which protects them from attacks by the immune system.
Protozoa can transform into atypical forms, masquerading as amoebas and squamous epithelium of the host. This gives them the ability to evade attacks from the immune system. In addition, Trichomonas vaginalis includes other pathological microorganisms, also protecting them from the immune system and antibiotics. In this form, chlamydia, gonococci and mycoplasma can move along with Trichomonas along the genitourinary tract, spreading infection there.
Blood during mensis is a source of iron and favorable conditions for the proliferation of microorganisms.
Trichomonas vaginalis fixes on the epithelial cells of the mucous walls of the genitourinary system and causes an inflammatory process. At the same time, the hyaluronidase they produce loosens the tissues of the walls of the genitourinary system, and Trichomonas vaginalis releases toxic products of its vital activity into the loose intercellular space. This leads to a weakening of local immunity and a change in the pH of the vaginal environment, which creates conditions for the activation of opportunistic flora - fungi and other microorganisms.
Prevention
Trichomoniasis occurs due to the penetration of protozoan microorganisms into the body. The situation is aggravated in case of weakened immunity and concomitant colds. Prevention measures are simple:
- no casual sex (if you really want to, you should use a condom);
- Do not use other people's towels and underwear;
- you need to follow the rules of personal hygiene;
- you should be regularly examined by a gynecologist and venereologist;
- It is recommended to diversify your diet with vegetables and fruits to strengthen your immune system.
In addition, treatment of previously identified trichomoniasis should not be abandoned. Otherwise, relapse is almost inevitable.
Trichomoniasis is very common among women. After identifying the disease, you should undergo a course of therapy, which includes not only getting rid of the causative agent of the disease, but also strengthening the immune system, as well as relieving symptoms. During pregnancy, special care must be taken - some medications can harm the unborn baby. You can watch this video that explains in detail about trichomoniasis, its causes, and treatment options.
Features of the pathogen and form of the disease
The causative agent of the infectious disease - Trichomonas vaginalis (trichomonas vaginalis) has special flagella. With their help, the microorganism is able to move. Trichomonas reproduces by longitudinal division. The size is 12 - 18 microns. Can live without oxygen.
The causative agent of trichomoniasis, which parasitizes the human body, is divided into three types:
- Trcihomonas elongata, living on the oral mucosa;
- Trichomonas hominis, living in the intestinal area;
- Trichomonas vaginalis, located in the genitourinary system.
The first two varieties do not pose a threat to humans. The third variety is the most pathogenic. The microorganism is more active, it locally causes discomfort. Provokes inflammation.
Vaginal trichomoniasis, taking into account the duration of the disease and symptoms, is divided into three forms:
- spicy;
- chronic - the duration of the disease is from 60 days;
- carriage - symptoms are not observed when the pathogen is present in the vaginal secretion.
The incubation period (time from infection to the onset of manifestations) is approximately 5-15 days.
Modern diagnostic methods
Trichomoniasis in women is often discovered completely by accident during a gynecological examination. Using colposcopic methods, the gynecologist can notice small hemorrhages on the cervix - this symptom is called “strawberry cervix”. Unfortunately, such signs do not occur in all patients.
Laboratory tests are the most accurate. Today, several main methods are used:
- Microscopic examination of samples taken during a smear allows you to see living cells of the pathogen. In this case, laboratory technicians can examine both colored and unstained preparations. This is the simplest and most accessible method, but its accuracy is no more than 60%.
- Sowing the samples taken on an artificial nutrient medium is a more accurate method. It allows not only to determine the presence and nature of pathogenic pathogens, but also to find out which group of drugs they are sensitive to.
- Today, immunological research methods are quite accurate, in which the presence of specific antibodies in a woman’s body is determined.
- On the other hand, recently in modern medicine PCR methods are increasingly used, which help detect the genetic material of Trichomonas.
What complications are possible?
Most experts believe that trichomoniasis is the most harmless and safe sexually transmitted disease that is easily treatable. At the same time, some researchers put forward the theory that this infection is extremely dangerous and in some cases can lead to malignant tissue degeneration. In any case, the lack of treatment often provokes a wide variety of complications.
What are the consequences of trichomoniasis in women? As already mentioned, the infection rarely affects the internal genital organs, since the cervix is a kind of barrier. However, if its structure is damaged or disrupted (this is observed during menstruation, after childbirth or abortion), Trichomonas can spread further, causing various complications. In particular, the penetration of microorganisms into the uterine cavity can lead to an inflammatory process and endometritis. Trichomonas also penetrates the fallopian tubes and ovaries, causing inflammation, and subsequently the formation of cysts, adhesions, etc.
Thus, such a disease, if untreated, entails quite serious complications, including infertility. Therefore, under no circumstances should you ignore its symptoms and refuse therapy.
Cost of services
| Name of service | price, rub. |
| Primary, outpatient appointment with an obstetrician-gynecologist (complaints, history taking, examination, drawing up an examination plan) | 2100 |
| Repeated appointment with an obstetrician-gynecologist, outpatient | 2100 |
| Consultation with an obstetrician-gynecologist, candidate of medical sciences | 2400 |
| Consultation with an obstetrician-gynecologist, head of department | 2600 |
| Consultation with an obstetrician-gynecologist, candidate of medical sciences, head of department | 2800 |
| Consultation with an obstetrician-gynecologist, doctor of medical sciences, professor | 3000 |
| Consultation with an obstetrician-gynecologist, chief physician of the clinic | 3300 |
| Appointment with an obstetrician-gynecologist to interpret the results of an examination conducted in another medical institution | 3300 |
| Consultation with an obstetrician-gynecologist based on the results of the examination with the prescription of a treatment regimen | 4200 |
| Appointment with an obstetrician-gynecologist, candidate of medical sciences, head of department | 6300 |
| Drawing up an individual treatment program | 3500 |
| Anti-Trichomonas vaginalis IgG /antibodies to Trichomonas IgG/ | 700 |
| STD PCR complex (10 positions) (Chlamydia trachomatis, Mycoplasma hominis, Mycoplasma genitalium, Ureaplasma urealyticum, Herpes simplex virus type 1+2, Cytomegalovirus, Gardnerella, Trichomonas, Gonococcus, Fungi) | 2950 |
Dear patients!
You can view the full list of services and price list at the reception or ask a question by phone.
The administration tries to promptly update the price list posted on the website, but in order to avoid possible misunderstandings, we advise you to clarify the cost of services on the day of contact at the reception or call center by calling 8(495)223-22-22
. The posted price list does not constitute an offer.
What is trichomoniasis
Urogenital trichomoniasis (or trichomoniasis) is a disease exclusively of the human genitourinary system. The causative agent of trichomoniasis is Trichomonas vaginalis, which is sexually transmitted.
The target organs of trichomoniasis in men are the urethra, prostate, testicles and their appendages, seminal vesicles, and in women - the vagina, the vaginal part of the cervical canal, and the urethra. Trichomonas vaginalis is detected more often in women due to more pronounced manifestations of trichomoniasis and more frequent visits to the doctor for preventive purposes.
Trichomoniasis in women. Mostly, trichomoniasis affects women of reproductive age from 16 to 35 years. During childbirth, infection of a newborn with trichomoniasis from a sick mother occurs in approximately 5% of cases. In newborns, trichomoniasis occurs in a mild form due to the structural features of the epithelium and is capable of self-healing.
In men, usually, the presence of trichomonas does not cause obvious symptoms of trichomoniasis; they are often carriers of trichomonas and, without experiencing obvious illness, transmit the infection to their sexual partners. Trichomoniasis can be one of the causes of non-gonococcal urethritis, chronic prostatitis and epididymitis (inflammation of the epididymis), and contribute to the development of male infertility due to decreased sperm motility and viability.
Infection with trichomoniasis mainly occurs through sexual contact. Trichomoniasis is extremely rarely transmitted through household means - through linen, towels, and swimsuits contaminated by patients.
The number of diseases associated with trichomoniasis is large. Trichomoniasis is often detected with other STI pathogens (gonoccoccus, chlamydia, ureplasma, Candida fungi, herpes viruses). Currently, it is believed that Trichomonas contribute to the development of diabetes, mastopathy, allergies and even cancer.
Trichomonas is an extremely unstable organism. It does not tolerate drying out; it can last only 2–3 hours on wet laundry, and even tap water kills it in just a few minutes. That is, it is almost impossible to become infected with trichomoniasis through household means. This requires sexual contact.
Trichomoniasis: description of the disease
The disease in the fairer sex is provoked by a type of protozoan microorganism – trichomonas vaginalis. When the disease occurs, the mucous membrane of the vagina, urethra, and bladder is first affected. The excretory ducts of the vaginal glands are less likely to be affected.
Trichomonas is more often observed in patients of the reproductive age group (18 – 45 years). The fact is that this category of ladies actively leads an intimate life.
The causative agent of trichomoniasis can exist not only in the reproductive system. Microorganisms are able to penetrate into the blood through the lymph nodes.
Trichomonas is more often detected in women, since representatives of the fair sex undergo preventive medical examinations more often than men.
Diagnostic measures
The infection causing trichomoniasis is diagnosed starting with an examination of the patient. However, it is not possible to make a diagnosis based only on clinical signs.
The fact is that manifestations of infection with Trichomonas may be symptoms of another urogenital pathological process.
Small pinpoint hemorrhages on the mucous membrane of the uterine cervix are considered a sign pathognomonic of Trichomonas infection in women. But they can be detected only in 2% of cases.
Foamy discharge with trichomoniasis is also not always present. They are found in 12% of patients.
At the same time, the patient’s complaints and clinical picture may allow the doctor to suspect the presence of this infection.
The basis for diagnosing the disease are laboratory tests:
- Examination under a microscope of a smear from the vagina and urethra of the fair sex. They are carried out within half an hour after collecting the sample. The reliability of the method is 40 - 60%.
- Immunological technique.
- Microbiological examination (tank culture for pathogenic microflora).
- PCR. The advantage of this method is that it gives a 100% accurate result. Any biological fluid of the patient is suitable for conducting the study. The analysis results are ready the next day.
Treatment monitoring and prevention
How do you know that a person has been cured of Trichomonas vaginalis? Of course, for monitoring it is necessary to use modern methods - PCR or ELISA. Such studies can be carried out after a course of treatment for 3-6 months - once a month.
There is an opinion in medical circles that without appropriate therapy, the period of infection lasts about 5 years. After this period, trichomoniasis may disappear on its own. This opinion has not yet been fully confirmed. And if self-healing is still possible, then within five years the body will experience the negative effects of the pathogen and acquire many complications. Therefore, there is no point in refusing timely treatment for this disease.
Untreated trichomoniasis can cause diseases such as: prostatitis, epididymitis, orchitis, cervicitis, endometritis, salpingitis, cystitis, pyelonephritis, infertility (female and male).
The basis for preventing trichomoniasis is avoiding promiscuity. It is also necessary to observe basic rules of intimate hygiene during sexual intercourse.
If for some reason you had unprotected sexual intercourse with a doubtful partner, then in the first two hours after sexual intercourse you must use Miramistin solution. This drug has a detrimental effect on Trichomonas vaginalis and other sexually transmitted infections. Its nozzle is inserted into the vagina, and it is treated with a stream of solution. Before the procedure, the patient must urinate. In the same way, Miramistin solution is injected into the urethra of the male penis. The medicine should remain inside the genitals for 5 minutes. If Miramistin is not available, then you can use a low concentration solution of potassium permanganate, which can be injected into the genitals using a syringe without a needle.
It should be understood that only protected sex and periodic preventive examinations with a gynecologist or urologist will help both women and men avoid health problems.
Trichomoniasis during pregnancy
Unfortunately, trichomoniasis in pregnant women is diagnosed quite often. Moreover, the disease can occur both latently and with the manifestation of the main symptoms. In any case, it is worth understanding that this infection is extremely dangerous for the growing fetus. To begin with, it is worth noting that a child can easily become infected from the mother during intrauterine development or already during childbirth.
The presence of Trichomonas in the mother's body significantly increases the likelihood of pregnancy failure or miscarriage. In addition, most women with trichomoniasis experience premature breaking of their waters, resulting in the baby being born prematurely. In addition, do not forget that these protozoan microorganisms can contribute to the spread of bacterial infection by protecting pathogens from the effects of the immune system.
How to cure trichomoniasis in women during pregnancy? Therapy in this case is carried out under the constant supervision of a doctor. During the first trimester, vaginal suppositories or creams are usually used. In the future, short-term courses of treatment with small doses of drugs containing imidazole are allowed. Naturally, the partner should also undergo therapy, as this helps to avoid re-infection.
Women with trichomoniasis give birth in specialized clinics. It is essential to immediately evaluate the newborn for infection and initiate appropriate therapy if necessary.
Video with doctors
Nasonova N.V. Gynecology services at ON CLINIC.
Watch all videos with doctors here.
Patient reviews
"Hello! I can’t help but thank the wonderful doctors from On Clinic! My gynecologist cured me of trichomoniasis, and now I’m planning a pregnancy. Wonderful people work at this clinic! Always smiling and in a good mood! Thank you!!"
Best regards, Veronica, Moscow
“My husband and I were looking for a place to get treatment for trichomoniasis. We were looking for the best clinics in Moscow and got confused by the reviews. I found out about On Clinic, a friend was treated by you. We visited a gynecologist and urologist. We were very pleased, the doctors were competent and explained every medication prescription - what and why. Not like others who prescribe a bunch of pills and then you can’t figure out how to take them and for what. Doctors' offices have a lot of letters and certificates, which I consider a plus. They were treated with metronidazole. Now everything is fine - according to tests, neither I nor my husband have Trichomonas.”
Sincerely, Natalia Z., Sergiev Posad
See more reviews
Symptoms
Once Trichomonas vaginalis enters the human body, it must find optimal conditions for its life activity. The first condition is the presence of a moist mucous environment with a pH of 5.2 to 6.2 and a temperature of no more than 37 °C. The incubation period for the development of vaginal trichomoniasis lasts from 10 to 30 days.
More than half of men and women infected with trichomonas infection may not experience all of its symptoms. The other half of patients develop the following symptoms:
- Purulent or foamy, dirty gray in color, copious discharge from the genitals with a strong foul odor;
- Uncontrollable itching of the external genitalia;
- Swelling and inflammation of the labia, walls of the vagina and cervix, urethra;
- Difficulty urinating (in men with prostate damage);
- Pain and constant discomfort in the lower abdomen;
- Pain during sexual intercourse;
- Pain, burning and stinging during urination;
- Increased body temperature.
Trichomoniasis tends to be combined with other sexually transmitted diseases - chlamydia or gonorrhea. Only in 10% of cases is trichomoniasis monoinfection observed. This combination of severe sexually transmitted diseases leads to chronic pathologies of the pelvic organs and then to infertility.
Symptoms of the chronic form
A chronic disease is considered if it occurs for more than two months from the moment of infection. The course of the chronic form of the disease is characterized by periods of exacerbation and remission. Alcohol and frequent sexual intercourse provoke exacerbations.
Symptoms of Trichomonas in the chronic period are manifested by dry vaginal walls, a change in the microflora towards opportunistic pathogens, which under favorable conditions becomes pathogenic.
At the same time, there is a weakening of the immune system, susceptibility to respiratory and infectious diseases, and signs of general fatigue of the body appear.
Trichomonas carriage
Half of those infected with T. vaginalis do not have any symptoms of the presence of the pathogen. Moreover, they are its carriers. Trichomonas carriage is a condition without clinical manifestations. It is diagnosed only when a series of tests are performed and the diagnosis is confirmed by the results.
Trichomonas carriers are potentially dangerous partners during unprotected sexual intercourse. This condition can develop into a chronic form with all the corresponding clinical manifestations.
Fighting the chronic form
Chronic trichomoniasis is characterized by a long course and periodic exacerbations. This form of the disease develops in the following cases:
- if the disease is ignored and there is no treatment;
- as a result of failure to comply with all recommendations of the attending physician;
- due to an incomplete course of antibiotic therapy.
The treatment regimen for a chronic form of pathology is as follows:
| Option #1 | 2 g of metronidazole once every 24 hours or 500 mg three times a day for a 7-10-day course, 2 g of tinidazole daily for 3 days. |
| Option No. 2 | 0.5 g of ornidazole twice a day. Course duration is 10 days. |
| Option No. 3 | Drip administration of a metronidazole solution into a vein, 500 mg 3 times a day for 1 week. |
In addition to basic medications, the therapeutic course involves the use of local antiseptics and vaginal suppositories. Nonspecific therapy is often used - autohemotherapy, lactotherapy, apitherapy, UHF. Honey or potassium orotate, used for local applications and vaginal electrophoresis, have a pronounced therapeutic effect. The course of such therapy takes from 25 to 30 days.
For patients with a chronic form of the disease and constant relapses, intravenous administration of a special vaccine (solcotrichovac) may be recommended.
This drug is prescribed intramuscularly in a dosage of 0.5 ml. It is planned to perform 3 injections, between which it is necessary to maintain a 2-week interval. After 1 year, another injection is given.
Morphology
Unlike other parasitic protozoa (Giardia lamblia, Entamoeba histolytica, etc.), Trichomonas vaginalis exists in only one morphological stage. It is slightly larger than a white blood cell, measuring 9 × 7 µm. Five flagella near the cytostome.
The functionality of the fifth flagellum is unknown. In addition, a noticeable spiny axostyle protrudes opposite the bundle of four flagella. The axostyle can be used to attach to surfaces.
Morphology
Treatment of trichomoniasis
The only class of drugs recommended for the treatment of urogenital trichomoniasis are 5-nitroimidazoles, to which most strains of T. vaginalis are sensitive.
Randomized controlled trials have shown that the recommended regimens for taking metronidazole can achieve clinical recovery and eradication of the pathogen in 90%–95% of patients, while taking tinidazole in 86%–100% of patients.
To avoid the development of severe adverse reactions (disulfiram-like reaction), patients should be warned to avoid alcohol and alcohol-containing products both during therapy with metronidazole and tinidazole and for 24 hours after its termination.
If oral metronidazole is intolerant, its intravaginal administration is also contraindicated.
The doctor should recommend that the patient, during the period of treatment and follow-up, abstain from sexual intercourse or use barrier methods of contraception until cure is established.
Indications for inpatient treatment:
Recommended treatment regimens:
- metronidazole 500 mg
- ornidazole 500 mg
- tinidazole 500 mg
Metronidazole
Alternative treatment regimens:
- metronidazole 2.0 g
- ornidazole 1.5 g
- tinidazole 2.0 g
Treatment of complicated and recurrent trichomoniasis:
- metronidazole 500 mg
- ornidazole 500 mg
- tinidazole 2.0 g
Tinidazole
When treating complicated forms of trichomoniasis, simultaneous use of local and systemic drugs is possible:
- Metronidazole, vaginal tablet 500 mg
- metronidazole, gel 0.75% 5 g intravaginally
Treatment of pregnant women with urogenital trichomoniasis is carried out no earlier than the second trimester of pregnancy according to the following scheme:
- metronidazole 2.0 g
- metronidazole 10 mg per kg body weight
- ornidazole 25 mg per kg body weight
Requirements for treatment results:
- eradication of T. vaginalis;
- absence of complaints and manifestations of the disease.
Cure is established by microscopy of the native drug, or by the culture method, no earlier than 14 days after treatment. PCR testing is carried out no earlier than 1 month after therapy. If the causative agent of trichomoniasis is not identified, then there is no need for further observation.
Tactics in the absence of treatment effect:
- avoiding re-infection;
- prescribing a different drug and according to a different regimen.
Where does Trichomonas live in the body?
Drits Irina Alexandrovna. Parasitologist Helminth infections can lead to numerous health problems, shortening life by 15-25 years. Many parasites are extremely difficult to detect. They can be anywhere - in the blood, intestines, lungs, heart, brain. Symptoms of helminthic infestation can be confused with ARVI, gastrointestinal diseases and others. The main mistake in such cases is delay! If you suspect the presence of parasites, you need to contact a specialist. If we talk about medications and self-treatment, then this antiparasitic complex .
From the urethra, the causative agent of the disease can penetrate the epididymis and prostate gland. Some researchers reported in the results of their observations the detection of trichomonas in human blood and organs.
They noted that microorganisms can be interstitial parasites. However, this idea has not received universal confirmation and requires re-examination.
The clinical picture of trichomoniasis lesions is nonspecific. Manifestations of urethritis are the same for different types of pathogens (gonococci, chlamydia, trichomonas).
Immunity to trichomoniasis does not develop.
Danger for pregnant women
The occurrence of the disease during this period may be a sign of primary infection or an exacerbation of an existing chronic form. Most often, the inflammation is widespread: the urethra, bladder, vagina, and rectum are affected.
The changes that occur in the body of a pregnant woman are aimed at preserving the developing fetus. When Trichomonas invades, the immune system initiates a phagocytic response.
Protective mechanisms begin to work from the moment of conception and become more advanced as the unborn child grows.
The likelihood of infection depends on the length of pregnancy. In the early stages, cervical mucus thickens, which creates an obstacle to the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms. In later stages, infection of the fetus is prevented by amniotic membranes. Infection in the first weeks of pregnancy contributes to inflammation of the endometrium and spontaneous abortion.