All the changes that a woman goes through during the thorny road of pregnancy cannot pass without leaving a trace on the body. Metamorphoses affect both external and internal organs of a pregnant woman. The uterus enlarges twenty times, which affects the hip bones, which diverge under its pressure, the ribs can also be modified.
When pregnancy occurs, the ovaries, together with the appendages, are primarily subject to restructuring. Promoting the maturation of eggs and the production of sex hormones, the ovaries can be called the dominant organ of the female reproductive system.
Corpus luteum in the ovary during pregnancy
During pregnancy, the corpus luteum, located in the ovaries, begins to produce progesterone, a hormone responsible for the physiological course of pregnancy and the development of the laid embryo. After the fundamental child's place, namely the placenta, is finally formed after the twelfth week of pregnancy, the corpus luteum dies.
During pregnancy, the functional work of the ovaries is suspended, since the main mission they perform to mature eggs is completed, and there is no need for new ovulation. Under the influence of circulating blood, increased in volume, the ovaries change location and slightly increase in size.
Intestinal pain
If the expectant mother has an incorrect diet, if her diet is not enriched with fresh vegetables, fruits and essential fiber, and the menu consists of canned food, sweets, a large number of baked goods and sausages, then she is guaranteed to have problems with the intestines. Hormones produced during pregnancy slow down the gastrointestinal tract. Intestinal pain at this time is very similar to the sensations when the ovaries hurt during pregnancy, because they radiate to the lower abdomen.
If a pregnant woman suffers from irregular bowel movements and constipation, she needs to change her diet. Perhaps after changing your diet, the pain will go away. But if the pain is too frequent or constant, you should consult a doctor.
Ovarian diseases during pregnancy
Due to the fact that the ovaries go into “sleep”, as their functional features are unnecessary, a woman may experience discomfort in the place where they are located, but there is no need to worry. Such pain disturbs the female body due to stretching of the muscle tissue, which ensures the support of the growing uterus and displaced internal organs under the pressure of the fetus gaining weight and growth every day.
But it is worth distinguishing between false pain and real inflammation in the ovaries. The inflammatory process that occurs in the area of the ovaries and uterine lips is usually called adnexitis or oophoritis. If the inflammatory process begins before pregnancy, then as pregnancy progresses it will only gain momentum, increasing discomfort and pain. It is easier to solve any problem at the initial stage, without allowing it to develop, which indicates the need for a visit to the treating doctor.
Therefore, it is necessary to learn to distinguish between imaginary pain symptoms and those associated with an illness that has arisen in the body. If you are haunted by acute or aching pain, which goes away with a little rest associated with limiting physical activity and changing body position from vertical to horizontal, then most likely this is pain from an enlarged fetus lying in the uterus.
Diseases of the genitourinary system
Painful, aching sensations in the lower abdomen can be caused by an exacerbation of cystitis. Inflammation of the mucous membrane of the bladder is diagnosed in many women in the early stages of pregnancy.
The development of pathologies of the genitourinary system of a pregnant woman is facilitated by a high concentration of the hormone progesterone in the blood. It causes deterioration of ureteral peristalsis. As a result of hormonal changes, the movement of urine through the urinary tract slows down. Stagnation of urine creates an ideal environment for the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms.
With cystitis, there is a pulling in the lower abdomen. Aching pain is accompanied by a frequent urge to urinate. When emptying the bladder, sharp pain and burning sensation occur in the urethra. The amount of urine excreted is insignificant. With cystitis, body temperature often rises. A pregnant woman may experience nausea and vomiting.
If left untreated, pathogenic microorganisms that cause inflammation of the mucous membrane of the bladder rise up the urinary tract. They create new foci of inflammation in the tissues of neighboring organs.
When the kidney tissue becomes inflamed, pyelonephritis develops. Most often, pyelonephritis is diagnosed in pregnant women who suffered from cystitis or pyelonephritis before conception.
With pyelonephritis, pain occurs in the ovarian region, as well as in the lumbar region. With bilateral pathology, pain can be observed on the right and left. When changing body position, the intensity of pain does not change. A pregnant woman's appetite decreases, nausea develops, turning into vomiting. The disease causes fever, chills and headache.
Pyelonephritis can cause intrauterine infection of the fetus. The disease often provokes early termination of pregnancy, the development of renal failure and complications of pregnancy.
https://youtu.be/XCB_oRbUiJE
Survey
You should not forget to undergo a mandatory full gynecological examination every six months; this applies to any woman, even if there is no special reason for this. Medical observation will allow you to find out in time about the presence of a problem in the body and eliminate it in a timely manner, without waiting for subsequent complications. A woman may not even be aware that she is pregnant, so any inflammatory process jeopardizes the normal development of the fetus and can lead to an unwanted termination of pregnancy, called a miscarriage.
Pain in the ovaries during pregnancy
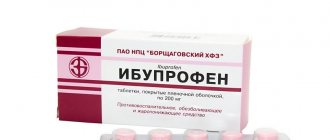
For any pain located in the abdominal area, you should not resort to painkillers. Since the pain can be of a different nature, from an inflamed appendix to the pancreas, it is necessary to tell the doctor about the existing problems so as not to bring the body to a clinical state.
Video: What is an ovarian corpus luteum cyst during pregnancy.
Many will agree with me if I say that with the onset of pregnancy, the entire female body is forced to endure a lot. And first of all, these are, of course, all sorts of changes, for which he is not always ready, but to which he is definitely subjected during this difficult period.
It is simply difficult to believe that this is even possible, isn’t it nonsense, for example, that a woman’s weight can increase on average twenty times over the entire period of pregnancy. Women's ribs can become deformed during pregnancy, and the pelvic bones almost always diverge to the sides... and this is considered quite normal. Sometimes it seems that women have practically nothing left unchanged, but first and foremost, and probably mainly, this process of change affects the female genital organs and, of course, the appendages of a pregnant woman. A woman’s ovaries also undergo dramatic changes during pregnancy.
What to do if pain occurs?
When the right, left, or both appendages hurt, you should not guess what caused the discomfort. The only reasonable solution would be to visit a medical facility. The gynecologist will determine the root cause that caused the pain and, if necessary, refer you for examination to exclude possible pathologies. Only after receiving test results can something be done to eliminate unpleasant symptoms. It is worth remembering that ignoring pain during pregnancy poses a threat not only to the pregnant woman, but also to her child.
If a woman did not have problems with the gonads and genitourinary system before conception, the likelihood of them appearing during pregnancy is low. Pregnant women need to protect themselves as much as possible from physical and mental fatigue; they should not lift heavy objects.
If discomfort appears, the first thing the expectant mother needs to do is lie down and relax. However, as soon as you feel a little better, you should consult a gynecologist. In case of increasing pain or bleeding, you cannot hesitate; you must immediately call emergency help. These symptoms may indicate the onset of spontaneous abortion.
In the later stages
If you experience minor pain in the pelvic area at the end of the third trimester, the main thing is not to panic. In the later stages of pregnancy, the body is actively preparing for the upcoming birth; under the influence of the hormone relaxin, the cervix, ligaments and cartilage become softer, and the pelvic bones gradually move apart.
- to eliminate discomfort due to stretching of the uterine ligaments, you can apply a slightly warm compress;
- to maintain the tone of the whole body, physical exercises for pregnant women are recommended;
- maintain sexual rest until the pain stops;
- adhere to the principles of healthy eating - exclude fried, canned, unhealthy foods and carbonated drinks from your menu;
- get as much rest as possible;
- Taking painkillers is allowed only after approval from a doctor.
If a slight dull pain develops into a tingling sensation, it is better to immediately contact a medical facility. You should not hesitate to visit a specialist in the following cases:
- the pain intensifies and does not go away for a long time;
- the temperature has risen;
- spotting with ichor appeared;
- the stomach seemed to be “petrified”;
- bleeding began;
- The discharge has a foul, unpleasant odor.
What happens to a woman's ovaries during pregnancy?
Let us immediately note that the ovaries in the female body are assigned by nature an extremely important and probably the most significant role: they are capable of producing sex hormones that are so necessary for a woman and, in addition, they also serve as a kind of cradle for the normal full maturation of eggs. But with the onset of pregnancy, the so-called corpus luteum usually forms directly in one of the ovaries, which is capable of intensively producing progesterone - so necessary for the preservation and normal development of an already fertilized egg. The corpus luteum itself usually lives in a woman’s body for up to twelve weeks and then, having completely transferred all its “powers” to the already fully formed body, it gradually dies off.
It is worth noting that during pregnancy, women's ovaries temporarily suspend their usual activity, because there is no urgent need for the maturation of new eggs: the main goal has already been achieved - and fertilization has taken place. And in order to prevent another new ovulation from occurring, the ovaries seem to “go into hibernation.” Although at the same time they still slightly increase in size, primarily due to increased general blood circulation. And besides, at this time, the ovaries somewhat change their usual location: somewhat displaced by the actively growing uterus, the ovaries simply emerge from the pelvic area, completely leaving their previous place. And now they are trying to rush a little upward and also a little forward.
Possible ovarian diseases that occur during pregnancy
So, as we see, the need for the ovaries to work during pregnancy completely disappears, of course, for a while, if one could even put it that way. The ovaries simply shut down and temporarily stop functioning normally. Consequently, the unpleasant feeling that many women often have that their ovaries hurt during pregnancy often turns out to be completely false. After all, the woman herself quite often does not even realize that in the previous place where her appendages were usually located, they are no longer there.
It must be said that usually, pain that occurs in the ovarian area during pregnancy can only be associated with tension in the muscles that are designed to support the actively growing uterus, on both sides of the abdomen. And as you understand, with every centimeter or every gram that increases the size of the uterus, certain changes occur in the entire body. And because of this, almost all nearby internal organs feel somewhat embarrassed and even experience some discomfort - and, of course, the woman in this case may well feel some unpleasant sensations, including even pain.
And, nevertheless, acute inflammation of the ovaries during pregnancy and some other complications are also quite possible, especially if this pregnancy has already taken place against the background of such problems. A woman may well be bothered by a variety of diseases that are closely related to ovarian function.
So it could be:
- Oophoritis (or rather adnexitis) is an acute or chronic disease, particularly of the ovaries, which can often be combined with inflammation occurring in the fallopian tubes (or rather with salpingitis). This disease usually occurs as a result of damage to the female genital organs by some kind of infection (possibly, or, and perhaps even);
- Such unpleasant conditions as a cyst or tumor are a kind of formation of protrusions directly on the body of the ovary, which can put pressure on all nearby tissues, thereby causing unpleasant and even painful sensations;
- A condition such as apoplexy is a rupture of the ovary, sometimes with extensive hemorrhages into the woman’s abdominal cavity.
Anxious pain sensations for the expectant mother
If a woman develops ovarian colitis early in pregnancy, in some cases immediate medical attention is required. The following symptoms should cause alarm:
- severe ovarian pain of a sharp, acute nature;
- the unpleasant sensation does not stop, intensifies or is regularly repeated;
- bloody issues;
- the entire abdomen or its lower part tenses, hardens, turns to stone;
- pain is accompanied by a sharp increase in temperature;
- yellow/green discharge with an unpleasant odor appears;
- in parallel, acute pain occurs in the lower back, tailbone, and rectum;
- general malaise: nausea, weakness.
We also recommend reading the article why the navel hurts in the first trimester. From it you will learn about the main reasons for the appearance of unpleasant sensations, why it itches, as well as the prevention of pain.
When is a woman usually bothered by her ovaries during pregnancy?
Let us immediately note that in the case where inflammation of the ovaries initially occurred, even before the onset of pregnancy, then with its onset such inflammation will certainly worsen. Almost always, diseases associated with the ovaries are accompanied by quite strong and sharp pain, which, by the way, may well not only persist, and for quite a long time, but, unfortunately, also intensify and even grow noticeably. In this case, urgent drug treatment will be simply vital - immediately contact your doctor without waiting for more serious consequences.
However, if you just from time to time feel some kind of aching or sometimes even sharp pain, which then quickly disappears, then, most likely, the main reason for this does not lie in the ovaries at all, but may be associated with an ever-growing uterus, which always happens during pregnancy time. To relieve such pain, if it bothers you greatly, simply taking a calm but rather deep breath and then exhaling, or calmly changing the position of your body, will help. Try sometimes to just lie down to rest - and, quite possibly, the pain will go away on its own. Be sure to also make sure that you empty your bowels every day, since frequent bowel movements that occur during pregnancy can also cause sharp pain felt in the abdomen, very similar to “ovarian pain.”
And yet, not entirely healthy ovaries during pregnancy may well become the real reason for not carrying a pregnancy or even its termination. In addition, sooner or later you will still have to treat the existing inflammation, and this certainly cannot benefit your future baby. This is actually why almost all gynecologists strongly recommend planning a pregnancy and undergoing the most complete medical (including gynecological) examination before pregnancy.
And of course, if for some reason you doubt anything, about your health, etc., then immediately visit your doctor for an unscheduled consultation: and may your soul be absolutely at peace!
With the onset of pregnancy, the female body is forced to endure a lot. First of all, these are all kinds of changes that he undergoes during this period. It’s just hard to believe that this is possible, but, for example, weight increases on average 20 times over the entire period, ribs can become deformed, pelvic bones diverge to the sides... It seems that practically nothing remains unchanged, but first of all First and foremost, this process affects the woman’s genitals and appendages. The ovaries also undergo changes during pregnancy.
Prevention of pain
To reduce pain, you must follow the recommendations of specialists. If they are followed, the intensity of the sensations decreases, and their attacks occur less frequently.
In the first 20-25 weeks of gestation, if pain occurs, it is necessary to undergo examination by specialists. In the absence of pathologies, you are allowed to use methods to alleviate your own condition:
- organization of daily proper rest - pregnant women need more rest, daytime sleep is useful - in a horizontal position and in a comfortable position the pain recedes;
- using a bandage - this is relevant from the 20th week of pregnancy to ease the load on the back, prevent stretch marks and give the stomach the correct position;
- light physical activity – regular attendance at fitness and yoga courses for pregnant women is optimal;
- a varied and balanced diet - if the rules of nutrition are followed, the well-being of the expectant mother will noticeably improve;
- prohibition on lifting weights and physical activity that strains the abdominal muscles.
Second half
Tips for pain in the ovaries for women who are late in pregnancy differ little from previous recommendations:
- regular rest and avoidance of physical or emotional stress - stress or active sports can provoke pain in the ovaries and even premature birth;
- using warm, non-hot compresses applied to the aching area;
- daily light exercise;
- refusal of heavy foods, gas-forming products, salt;
- wearing a bandage will reduce the load on the spine and lift the stomach, relieving tension from the internal organs.
Prevention is carried out in the absence of pathologies of the genital organs and the physiological nature of the pain. It consists of following the recommendations:
- regular observation by a gynecologist, testing;
- avoiding nervous tension and stress;
- moderate physical activity;
- daily rest;
- refusal of any diets, salt and heavy foods;
- eating large amounts of vegetables and fruits;
- drinking plenty of fluids.
Typically, pain in the ovaries during pregnancy is not considered dangerous and is caused by physiological changes in the body. To alleviate them, you should lead a healthy lifestyle, rest and avoid excessive physical activity. If the pain is intense or worsens, you should consult a doctor.
What happens to the ovaries during pregnancy?
The ovaries play an important role in the female body: they produce the necessary sex hormones and serve as a cradle for the maturation of eggs. With the onset of pregnancy, an ovary is formed in one of the ovaries, which is intensively produced - to preserve and develop the fertilized egg. The corpus luteum lives up to 12 weeks and then, having transferred its “powers” to the formed one, gradually dies.
During pregnancy, the ovaries suspend their activity, because there is no need for the maturation of eggs: the goal is achieved - fertilization has taken place. To prevent new ovulation from occurring, the ovaries “go into hibernation.” At the same time, they increase slightly in size due to increased blood circulation and change their location: the ovaries, displaced by the growing uterus, emerge from the pelvic area, leaving their original place. Now they rush a little upward and forward.
Ovarian diseases during pregnancy
As we can see, the need for ovaries during pregnancy temporarily disappears, so to speak. They simply turn off and stop functioning. Consequently, the feeling that many women have that their ovaries hurt during pregnancy often turns out to be false. After all, a woman most often does not even realize that at the previous location of the appendages they are no longer there. Typically, pain in the ovarian area during pregnancy is associated with tension in the muscles that support the uterus on both sides of the abdomen, and directly with an increase in the size of the uterus, which causes discomfort and discomfort in almost all internal organs - and you may also feel pain .
However, inflammation of the ovaries during pregnancy and other complications are quite possible if pregnancy has already occurred against their background. A woman may be worried about various diseases associated with the ovaries:
- oophoritis (adnexitis) - in particular of the ovaries, which is often combined with inflammation of the fallopian tubes (salpingitis); occurs due to damage to the genital organs by infection (candidiasis,);
- cyst or tumor - the formation of protrusions on the body of the ovary that put pressure on nearby tissues, thereby causing pain;
- apoplexy - rupture of the ovary with hemorrhage into the abdominal cavity.
What to do if a pregnant woman has ovarian pain?
Only specialists can accurately determine the reason why the lower abdomen feels tight or hurts after a delay or in the early stages. Therefore, visiting a gynecologist is mandatory at the slightest discomfort. If you do not seek help for a long time, the risk for the expectant mother and fetus increases. There are symptoms, the appearance of which indicates the need to immediately visit the hospital. So, you need to contact a specialist if:
- the pain has become sharp, increasing or acute;
- the stomach hurts regularly or there is aching in the lower abdomen throughout the day;
- unpleasant sensations appeared in the lumbar region, sacrum or coccyx;
- the temperature constantly rises;
- discharge with blood appeared;
- you feel tired and slightly nauseous.
Special attention should be paid to severe attacks of nausea, tone or hardening of the abdomen, and discharge with a green or yellow tint from the vagina.
Important! If, after a missed period, your stomach feels tight or your ovaries hurt, you should list all the accompanying symptoms during a consultation with a doctor. This will allow you to determine why these pains appeared and how to eliminate them.
If your ovary hurts and feels tight during pregnancy, you can try to calm down and stop thinking about the unpleasant sensations. Often this method helps. The use of a bandage can help calm pain in the ovaries, however, its use should be discussed with the gynecologist who is managing the pregnancy.
Important! The appearance of sharp, strong, intense and regular pain in the ovaries cannot be ignored. This is dangerous for the pregnant woman and the fetus. If your ovaries continue to hurt, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible.