In the structure of gynecological diseases, the diagnosis of uterine polyp occupies one of the leading places (on average about 25%). This disease is “out of age”, a neoplasm can be found in both a young girl and a postmenopausal woman. Removal of a polyp in the uterus is the main and most effective method of treatment, which guarantees a complete recovery. Drug therapy is usually used to prevent relapses or when preoperative preparation of the patient is necessary (if it is necessary to cure an infection or relieve symptoms of acute inflammation).
In the early stages, the disease can be asymptomatic, which makes diagnosis difficult: a polyp is often discovered during a routine visit to the gynecologist. Although the tumor is initially benign, it can degenerate into precancerous, cause infertility or provoke cancer. Therefore, it is important to solve the problem in the early stages (preferably surgically). Patients will benefit from information about the characteristics of this disease, which is where we will begin.
Understanding Polyp
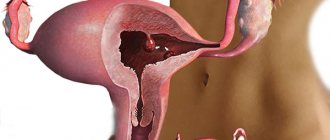
Uterine polyps are a consequence of pathological growth of the endometrium (hyperplasia), which can be caused by various provoking factors. As a result of the pathological process, a tumor is formed, which can be different:
- in shape: mushroom-shaped with a wide base on a thick stalk or round on a thin stalk;
- by color (from light pink and pale to dark burgundy and purple);
- by structure: depending on the cells predominant in the tumor, fibrous, glandular, fibroglandular polyps and adenomatous types are distinguished (the latter option is considered a precancerous neoplasm);
- by number: single or multiple (polyposis).
Dimensions are determined in millimeters and can be small, barely noticeable from a few mm or large up to 25 mm. Size is one of the main criteria when prescribing surgery. The choice of tactics is also influenced by the results of histology (determining the structure) and the characteristics of the course (asymptomatic, with bleeding, etc.).
The reasons for the formation of polyps are different. The main one is considered to be hormonal disorders (a shift in the balance of normal hormonal levels, in which estrogen is in excess and progesterone is in short supply). The cause of disruption of hormonal stability may be physiological changes (puberty, pregnancy, menopause). Or pathological (diabetes mellitus, obesity, diseases of the thyroid gland, pituitary gland, adrenal glands). Or taking hormonal medications, including for contraception.
Additional factors that provoke a pathological process in the uterine cavity are:
- gynecological diseases (endometriosis, cyst, fibroids, ovarian pathologies, etc.);
- injuries and microtraumas (received during examination, childbirth, termination of pregnancy, use of intrauterine contraceptives, sexual intercourse);
- pathological processes of various etiologies: infectious and venereal diseases, inflammation, disturbances in the composition of microflora.
Factors that provoke the development of a neoplasm can be constant stress, depression, overwork, and there are also cases when the specific etiology of the development of an endometrial polyp cannot be identified (unexplained etiology). For women with a history of at least one of the risk factors, it is especially important to undergo regular medical examinations. According to statistics, 70% of all identified cases of polyposis (multiple neoplasms) develop against the background of one of the above diseases. In such cases, treatment is complex: they are removed and therapy is prescribed to eliminate risk factors and concomitant diseases. This is necessary to eliminate the risk of relapse, since removal only solves the current problem, and eliminating its cause solves the main one.
There may be no symptoms in the early stages of polyp development, so women should visit their gynecologist regularly. With further development of pathology, the following may appear:
- bleeding (outside of menstruation) and significant changes in the cycle;
- any discharge (bloody, brown, whitish, etc.);
- nagging pain, including during sexual intercourse;
- problems with conception or threat of miscarriage.
If one of the symptoms appears, you must immediately consult a doctor to make a diagnosis and prescribe adequate treatment (most often removal). A specialized specialist conducts an examination and prescribes additional tests (a histological examination of the pathological focus is required). Based on the results obtained, a removal tactic is selected.
Postoperative period in case of endometrial polyp removal
After the polyps are eliminated, a histological diagnosis of the removed endometrial tissue should be performed.
After the operation, you need to visit a gynecologist within a week for an examination. This will eliminate the possibility of re-development of polyps. Such examinations in the future must be carried out systematically, despite the state of health and well-being.
After curettage of the endometrial polyp from the uterine cavity, the recovery period lasts about six months and during this time some complications may arise after the operation. During the first few months, a woman needs to take hormonal medications, vitamin and iron complexes.
Six months after the endometrial polyp has been removed, you can begin to plan a pregnancy. It is during this period that the female body is completely restored. The first menstruation occurs 30-40 days after surgery, but in some cases it may be later.
The period of sexual and physical rest is prescribed by the doctor individually, according to the complexity of the operation to remove the endometrial polyp, age and characteristics of the body. As a rule, this period lasts up to a month.
Video: Removal of endometrial polyp (hysteroresectoscopy).
Attention!
This article is posted for informational purposes only and under no circumstances constitutes scientific material or medical advice and should not serve as a substitute for an in-person consultation with a professional physician.
For diagnostics, diagnosis and treatment, contact qualified doctors! Number of reads: 1249 Date of publication: 10/03/2017
Gynecologists - search service and appointment with gynecologists in Moscow
Should I delete it?
Is it necessary to remove tumors? In some cases, surgery is mandatory; sometimes doctors recommend deferment. In the early stages, patients are given the opportunity to choose.
To make the right decision, it is worth analyzing the features of the pathology:
- At first, the polyp may be asymptomatic for a long time: but if the provoking factor is not eliminated, the tumor will increase in size. Then various threatening symptoms may appear (for example, anemia may develop against the background of constant bleeding). And in the future a more traumatic operation will be required. Therefore, even if it does not bother you, the pathological focus should be removed completely.
- If symptoms increase: the progressive disease will become a problem for the woman, and the tumor itself does not resolve and cannot be cured only by conservative methods. Without surgery, the polyp will provoke a further deterioration in general health, jeopardize reproductive function, and can lead to the development of polyposis, and in the worst case, to oncology.
- When using hormone therapy and symptomatic treatment: if you do not remove it, but try drug therapy, it will not lead to a complete recovery. For example, hormone therapy will help balance hormonal levels, but if it is discontinued, tumor growth usually resumes. That is, it is necessary to eliminate not only the cause (hormonal imbalance), but also the consequences - the tumor itself.
- Risk of degeneration: a polyp can degenerate into an adenomatous form (precancer) and provoke endometrial cancer of the uterus. Therefore, whether to have surgery or not is not a question; the risk of developing oncology is a sufficient basis for surgical intervention.
- Age of the patient: in postmenopausal patients, the risk of developing an adenomatous polyp and transition to oncology increases. Therefore, older women definitely need to remove the tumor.
Having considered what consequences may occur if surgical treatment is refused, each patient will be able to decide for herself whether to remove the growth or not. Or try other options (therapy, folk remedies). The only thing that is definitely unacceptable is the lack of treatment as such. Since most of the factors that provoke tumor development are themselves pathological, experienced gynecologists draw up a general plan for the management of such patients. It is aimed at eliminating concomitant diseases and surgical intervention to remove the tumor.
Surgery dimensions in millimeters
The size of the tumor is of great importance when choosing patient management tactics. A polyp is considered:
- small, if not reached 5 mm;
- medium if the size is from 5 to 15 millimeters;
- large if exceeds 15 mm.
A small polyp may not be removed immediately if it does not threaten health (no bleeding, does not provoke the threat of miscarriage, etc.). In any case, the clinical picture is assessed comprehensively, and an individual treatment plan for the provoking factors is selected. A woman with an identified tumor is at risk; she must undergo regular examination, and if it develops rapidly, the tumor is immediately removed.
Medium size is the standard indication for surgery. The indication for urgent surgery will be both a calm course and an increase in symptoms, growth of the tumor itself, and histological changes. Large tumors are removed as quickly as possible.
Indications and contraindications
Surgery to remove a polyp is most often a joint decision between the patient and the doctor. The doctor determines the degree of risk and explains all the consequences of refusal. In some cases, immediate surgery is the only option.
Indications for immediate surgery:
- medium to large tumor;
- the pathological process is actively progressing: symptoms increase, size increases, histology changes;
- ineffectiveness of drug treatment: bleeding does not stop, the tumor does not decrease in size, the woman cannot become pregnant;
- neoplasm of adenomatous type (precancer) or detection of cancer cells in the endometrium;
- risk of miscarriage;
- the patient’s age is over 40: hormonal changes will provoke the growth of the polyp, increasing the risk of developing cancer.
You can delay treatment and use drug therapy:
- during pregnancy, if there are no threatening symptoms;
- if the tumor is small in size, its size decreases under the influence of therapeutic treatment, the course of the disease is sluggish and asymptomatic;
Contraindications for immediate surgery will be:
- diseases of the external genital tract of any etiology (infectious, venereal, fungal);
- cervical pathology for which it is impossible to perform surgery (stenosis, cancer, etc.);
- acute infectious diseases;
- chronic diseases in the acute stage (high sugar levels in diabetes, high blood pressure in hypertension, exacerbation of stomach ulcers, thrombophlebitis, etc.);
- severe bleeding caused by other gynecological diseases until it stops.
In such cases, the cause of the delay is first eliminated, and then surgery is performed.
Conservative treatment
Treatment of polyps is carried out not only surgically, but also conservatively. Drug treatment can be suggested by a doctor in the absence of painful symptoms and large size of the formation. But this method does not exclude constant gynecological monitoring and regular additional diagnostic measures.
Treatment of uterine polyp without surgery also includes undergoing a number of physiotherapeutic procedures:
- Magnetotherapy;
- Ultrasound treatment;
- Electrophoresis with the use of medications;
- Electrical stimulation technique;
- Laser therapy.
Indications for one or another type of conservative complex therapy depend on many reasons, among which are:
- No complications;
- Mild symptomatic picture;
- Slight and slow growth of benign growth in the uterine cavity;
- The presence of contraindications for a woman to undergo surgical removal of a polyp.
Drug treatment
The main stage of treatment for polypous growths of the endometrium is the use of hormonal drugs (COCs and gestagens).
The formation of a pathological process in the uterine cavity in 70% of cases is associated with a hormonal imbalance in a woman’s body, which leads to excessive production of estrogen. Hormonal contraceptives eliminate pain in the lower abdomen and quickly stop uterine bleeding. Antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs are used in the treatment of endometrial polyps if the formation of a benign process occurred against the background of the presence of a sexually transmitted disease, chronic inflammation (adnexitis, cervicitis, oophoritis). The combination of these two classes of medications gives the most effective and high-quality results.
Vaginal suppositories for polyps in the uterus are also one of the methods of drug therapy for this disease. Suppositories have a number of advantages over other types of therapy. The active substance exerts its therapeutic effect directly on the pathological focus, quickly penetrating through the mucous membrane of the vaginal wall, bypassing the liver and kidneys.
Treatment of uterine polyps also includes the use of a vitamin complex and drugs with a high iron content to prevent anemia.
Preparatory stage
Before removing a polyp, some preparation is usually required. It is simple and takes place in several stages:
- tests are ordered first;
- if they are normal, the day of surgery is selected taking into account the menstrual schedule;
- it is necessary to carry out preoperative preparation;
- On the day of the operation, it is forbidden to eat and drink (if we are talking about surgery under anesthesia).
If the tests are normal and there are no other contraindications, a day for surgery is scheduled. Before hysteroscopy and other methods of removing a uterine polyp using anesthesia, you must refrain from drinking alcohol. Women who smoke are advised to abstain from smoking or reduce the number of cigarettes. The day before, it is recommended to adjust your diet and switch to easily digestible foods; at the last meal in the evening, it is better to drink a glass of kefir.
Now let's look at how to prepare for the operation in more detail. The examination is carried out on the eve of the operation; what tests need to be taken are determined by the doctor. Usually prescribed:
- blood and urine tests;
- smear (the degree of purity is determined);
- ECG;
- If you have chronic diseases, consultation with a specialized specialist is recommended.
As part of preoperative preparation, the doctor may prescribe hormonal drugs or antibiotics (as indicated, to reduce the risk of complications). It is advisable to abstain from sex for a week or use a condom. It is better not to use douching, medicated tampons, ointments, suppositories and creams (they can distort the results of a smear for purity).
The day before and on the day of the operation, a cleansing enema is performed and hair is removed from the external genitalia. It is advisable to empty your bladder immediately before the procedure. This is the standard preoperative period. The attending physician will tell you in more detail about the preparation procedure.
On what day of the cycle is the polyp removed?
In most cases, this is a planned operation. The doctor has the opportunity to choose which day to do it and adjust the date taking into account menstruation. This is important, since in the period after the end of bleeding, restoration processes occur in the endometrium. An exception will be older women, with an unstable cycle or absence of menstruation (at the onset of postmenopause). In this case, it does not matter on what day the surgery is performed.
It is better to remove polyps on the third day after the end of menstruation, when the menstrual rejection of the endometrium is completely over, and the process of its restoration is not yet completed. This helps to avoid possible complications, such as bleeding, which sometimes accompany hysteroscopy. The best day of the cycle, when removal occurs with minimal trauma to the female body, is considered to be 6-9 from the beginning of menstruation. It is during this period that the tumor is clearly visible and most accessible.
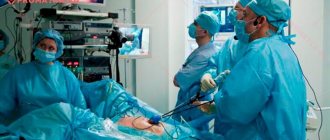
How to remove
In modern medicine, different methods are used to remove polyps inside the uterus. The choice of technique depends on the clinical picture, the extent of the pathology, the type of tumor, its shape and size. Currently used:
- diagnostic curettage;
- hysteroscopy (there are several subtypes of this operation);
- laser burning;
- instrumental removal (including using modern tools, for example, an electric loop);
- radio wave removal.
The need for pain relief (anesthesia)
Does it hurt to remove? This depends on the method in which the endometrial polyp will be removed. The peculiarity of the course of pathological processes in each specific case, the type of polyp, and individual pain threshold are also important. Even within the same method, anesthesia may be different or not used at all. For example, there is the concept of “office hysteroscopy”; anesthesia is not required for it (all methods will be discussed in detail in the “Common methods” section).
Local anesthesia is practically not used, preference is given to general. When using laser and radio waves, there is no anesthesia at all. These tumor removal techniques are painless. When using a laser, removal occurs in a hospital, but after 3 hours, if there are no complications, the woman can go home.
In some clinics, a diagnostic curettage may be performed under local anesthesia. During hysteroscopy, general anesthesia is used, and in 95% intravenous anesthesia is recommended, and only in 5% of patients, with individual intolerance or other contraindications, epidural anesthesia is used.
Common methods
The choice of method depends both on the volume and characteristics of the identified pathology, and on the technical capabilities and equipment of the clinic. In modern medicine, some methods are practically not used, as they are ineffective and are considered outdated. Next, we will consider in detail all the removal methods.
DIAGNOSTIC CURRETING. Today, diagnostic curettage is more often used not as an independent method of treatment, but as an auxiliary one after hysteroscopy. It helps to assess the condition of tissues and obtain material for histology. This is due to its unreliability. The risk of relapse after the procedure is quite high (about 30%). Most often used in medical institutions with insufficient modern equipment, where there are the simplest instruments (curette, uterine dilator).
The method is quite traumatic; the surgeon cannot fully control the removal process (this explains the high percentage of relapse). But it is recommended for emergency surgery, when it is necessary to stop bleeding and prevent significant blood loss.
HYSTEROSCOPY. The most common and frequently used method. It is considered the main method of surgical treatment of this pathology. Since there are different techniques for performing the operation, we will consider it separately and in more detail (see the chapter Hysteroscopy).
REMOVAL OF POLYP IN THE UTERUS WITH LASER. At the moment this is the most effective method. Its advantages can be considered:
- the ability to regulate the intensity of the beam, which eliminates damage to healthy tissue;
- absence of scars, which minimizes the risks of complications such as infertility;
- the method is non-contact, which virtually eliminates bleeding after surgery;
- does not require anesthesia, which allows you to leave the clinic within a few hours after surgery.
An additional advantage will be the use of a hysteroscope, which allows you to visualize the surgical field and accurately examine all pathological changes.
RADIO WAVE REMOVAL. In terms of effectiveness, safety and methodology, it is similar to the laser method. Only the impact on the tumor occurs with the help of directed radio waves. They, like a laser, destroy tumor tissue layer by layer without affecting surrounding tissues or injuring the mucous membrane.
INSTRUMENTAL METHOD. Removal occurs using scissors or forceps; a more modern option is an electric loop, which allows you to cauterize the base of the tumor and prevent blood loss. This option is often offered when it comes to a single pedunculated polyp; you can simply “unscrew” it.
Duration of surgery
How long does the operation take? With conventional surgery, removal usually takes no more than 1 hour. Laser and radio wave procedures take no more than 10-30 minutes. Hysteroscopy, even with a large volume of pathology, takes no more than 45 minutes, the standard time is 15 – 30 minutes. Elimination of polyposis will take the longest, when multiple tumors require more time to be destroyed. The shortest operations are those for unscrewing a single pedunculated polyp; they take about 10 minutes.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy after removal of a polyp in the uterus
Pregnancy after removal of an endometrial polyp in the uterus can occur quite quickly. After all, infertility, which had been developing for months, which so worried the married couple, was eliminated with the help of polypectomy by influencing its cause. Pregnancy can occur both in the first month, or rather, the cycle after curettage, and in subsequent months. In the first cycle, however, pregnancy occurs less frequently than in the second and subsequent months. This is due to the fact that the endometrium in the uterus is completely scraped out during curettage of the uterine cavity, and is not restored immediately. A defective endometrium cannot allow even a fertilized egg to implant into the uterine wall. Also, pregnancy is excluded during the last months in women who are prescribed hormonal therapy in the form of combined oral contraceptives. Curettage is considered a less favorable method in terms of restoring reproductive function than hysteroscopic removal of polyps. Since during its implementation, the polyp is removed under visual control, in a targeted manner, which allows minimizing trauma to the mucous layer of the female reproductive organ.
Hysteroscopy
Hysteroscopy of the uterus - removal of a polyp using a special hysteroscope device. This is the most common technique that allows you to get a visual picture of the pathological process. At the end of the inserted tube there is a video camera that transmits an image from the uterine cavity to the monitor. The diameter is small, the tube is hollow inside, and access to the uterus is provided through it (instruments are inserted).
In fact, any modern surgical intervention when identifying a tumor in the uterus can be considered hysteroscopy. Only the tool with which it is eliminated changes. A hysteroscope is used with laser and radio wave methods, and when using other instruments.
With the help of a hysteroscope, not only surgical intervention is performed, but also the so-called “office hysteroscopy”. This is rather a diagnostic method in which the doctor has the opportunity to examine the pathological focus in detail, determine its volume, quantity and shape of the tumor. And then, in accordance with the information received, the surgical tactics are chosen. That is, it is determined exactly how the operation will take place. Although the diagnosis is called hysteroscopy, it is just an instrumental examination method that is carried out using a hysteroscope and without anesthesia.
How the operation works:
- the patient is given anesthesia;
- the external genitalia are treated with a special aseptic solution;
- the cervical canal is “stretched” using dilators for free insertion of the hysteroscope tube;
- so that the walls of the uterus are straightened, its cavity is filled with liquid or gas;
- the instrument that was selected for polypectomy is inserted through the hysteroscope channel;
- the place where the tumor was located is “cleaned out”. A curette can be used for this (curettage of the endometrium located under the removed tumor is performed). Or they are treated with special means (a preventive measure to eliminate the risk of relapse). For this, a cryogenic method can be used, and electrocoagulation can be used to stop bleeding.
The resulting material (removed tumor and scraped tissue) is sent for histological examination. The doctor usually decides which method to perform hysteroscopy based on diagnostic data. After the operation is completed, the patient is taken to the ward, where she recovers from anesthesia (if one was used).
How it happens
How to remove an endometrial polyp in the uterus
The diagnosis of endometrial polyp or cervical canal polyp is a pathology that requires mandatory surgical treatment in almost 90% of cases of established diagnoses of hyperplastic processes of the uterus.
Many women who are diagnosed with uterine polyps are interested in how these tumors are removed? After all, a person always has a fear of surgical intervention and this is normal.
Methods for removing polyps in the uterus. Among the methods for removing hyperplastic polyps of the uterus are:
- polypectomy using curettage of the uterine cavity with a gynecological curette;
- hysteroresectoscopy, which involves the removal of polyps using optical instruments that are inserted into the uterine cavity and targeted removal of the endometrial polyp is carried out under video control
- laser polypectomy using a laser.
How is a polyp removed in the uterus under anesthesia?
Of course, removal of such a process as a uterine polyp must be carried out under the strict supervision of an anesthesiologist-resuscitator.
Indeed, to perform his work efficiently, it is important for the obstetrician-gynecologist to completely relax the woman, which can only be achieved under general anesthesia.
Under what anesthesia are polyps removed from the uterus?
He prepares the woman for the procedure and performs intravenous anesthesia. The procedure lasts 15-20 minutes, so the dose of drugs used by the anesthesiologist is minimal.
How to do hysteroscopy of the uterus for a polyp
Regardless of the method of removing this tumor, the preparatory stage is no different. The woman undergoes the entire scope of diagnostic tests, on the basis of which she is allowed to undergo this manipulation. The next step is choosing the date of surgery. The optimal time for surgical intervention, the indication for which is an endometrial polyp, is days 4-8 of the ovarian-menstrual cycle. These days were not chosen in vain, since the endometrium on these days has minimal thickness values and the polyp is perfectly visualized against this background.
On the day before surgery, a woman is advised not to eat in the evening and not to drink liquids 6 hours before. In the evening she is also examined by an anesthesiologist. On the morning of the surgery, the woman is transferred to the operating room, where the anesthesiologist provides her with anesthesia. And then the obstetrician-gynecologist begins to perform the chosen method of removing uterine polyps. Below we will look in more detail at how polyps are removed from the uterus (the operation, how it goes).
Methods for removing polyps in the uterus: curettage technique
A technique for curettage of the uterine cavity to remove an endometrial polyp. When the woman is seated in the gynecological chair and the anesthesiologist gives intravenous anesthesia, the obstetrician-gynecologist begins to perform his manipulations. First, the surgical field is treated with an antiseptic 3 times, and the cervix is exposed in the gynecological speculum. Having also treated the cervix with an antiseptic, iodine-containing drugs in the form of betadine are mainly chosen. Then the anterior lip of the cervix is grabbed with bullet clamps, and the cervical canal is expanded with special instruments - Hegar dilators. This is done so that the gynecological curette, which is used to perform the manipulation itself, passes freely into the uterine cavity.
After dilation of the cervical canal, a probe is inserted into the uterine cavity to measure its length. Then a curette is inserted and the walls of the uterus are scraped out one by one with careful movements.
Although this manipulation seems simple at first glance, it is, however, fraught with many complications, ranging from infectious and inflammatory processes, ending with perforation of the reproductive organ, which can entail surgical intervention, including removal of the uterus. Having completed the manipulation, the extracted specimen from the uterus is necessarily sent for histological examination.
How to remove polyps in the uterus: hysteroscopy
This procedure is carried out as follows: the cervix is exposed in gynecological speculums and grasped with bullet forceps. After treatment with betadine, if necessary, the cervical canal is dilated with Hegar dilators and an optical instrument - a hysteroscope - is inserted into the uterine cavity. At the end of the hysteroscope there is a video camera that transmits the image to the monitor screen, with the help of which the doctor exercises visual control over the manipulations being performed. The polyp is removed using a special loop, and all neoplasms are removed under visual control without unnecessary tissue trauma. This is precisely the significant difference between blind uterine curettage and hysteroresectoscopy. After the polyp is removed, the material is also sent for histological examination. The instruments are carefully removed from the uterine cavity, the cervix and vagina are treated with betadine, and the operation is considered complete. How a polyp in the uterus is removed with a laser. This manipulation is practically no different from hysteroresectoscopy, however, instead of mechanical removal of the polyp, it is removed with a laser.
These manipulations carry not only a therapeutic purpose, but also an important diagnostic one. After all, the histological response of the obtained material provides an answer to the question of tactics for further management of the patient. If the response is benign, the doctor will prescribe hormone therapy. When identifying an adenomatous polyp, the doctor should be quite alert in terms of oncological pathology.
Timely diagnosis and treatment help preserve reproductive function, the health of the female reproductive system, as well as the body as a whole, preventing the development of the oncological process.
Possible consequences and methods for eliminating them
Complications after removal are not common; they are usually caused by certain reasons. It is important for women to learn in advance about the possible consequences of hysteroscopy. They can be normal, that is, a natural reaction to surgery, or abnormal. Understanding this will help you promptly seek medical help in case of complications in the postoperative period.
Normal reactions include:
- light spotting for 2 – 3 days;
- discomfort or pain in the lower abdomen, including during sexual intercourse.
Possible complications, their causes and methods of elimination:
- Heavy bleeding after polyp removal: may indicate perforation. This complication most often occurs with “blind” curettage. Recommendations: consult a doctor; if a specialist determines that there is no danger, Oxytocin is prescribed;
- Temperature: typical for women who had a history of infectious diseases of the genitourinary system before the intervention. Usually the temperature does not rise above 380. Recommendations: check the condition of the endometrium for infection, prescribe anti-inflammatory drugs;
- Long delays in the next menstruation: you must consult a doctor if the delay is more than 3 months;
- Adhesions, scarring, infertility: usually the result of curettage. Recommendations: select a different technique for the operation in advance;
- Hematometer: accumulation of blood in the uterine cavity. This is a dangerous complication, so if there is any delay, you should immediately contact a gynecologist. Otherwise, there is a risk of severe complications, including death as a result of sepsis;
- Degeneration of endometrial cells: this risk exists initially, especially in older patients. Recommendations: regular monitoring by a gynecologist.
- Another risk is relapse. It does not depend on the type of surgery. Recommendations: elimination of provoking factors and preventive measures.
What are polyps, their symptoms and causes
Polyps in the uterus are endometrial hyperplasia, when the mucous membrane grows in some areas of the endometrium. Polyps come in various shapes - round, mushroom-shaped, on a stalk or a thick base, as well as in various colors from pale pink to dark burgundy, and can be numerous or solitary.
It is believed that the main reason for their appearance is a hormonal imbalance in a woman, usually an excess of estrogen and a lack of progesterone. Also, in combination with hormonal disorders, various inflammatory processes in the genital organs, mechanical damage, injuries during childbirth, frequent abortions (consequences), and diagnostic curettages have an impact.
There are several types of polyps: glandular, fibrous, fibroglandular and the most dangerous adenomatous. When polyps are detected, it is very important to conduct a histological examination to determine the state of the cells of the polypous tissue; if there are signs of proliferation, that is, the onset of oncological processes, such polyps should be removed along with the uterus. This is considered the early stage of uterine cancer and delaying surgery can be very dangerous.
Therefore, women who want to become pregnant must have polyps removed. After radical treatment and a course of postoperative hormonal therapy, the mucous membrane gradually recovers and the woman’s health returns to normal. You can learn more about polyps in the uterus, treatment, symptoms, and causes from our article.
Under the influence of inflammatory processes, hormonal disorders and many other reasons, a woman may develop endometrial hyperplasia in the uterus. Overgrowth of the mucous membranes leads to the formation of polyps. These formations are safe for life, but can provoke:
- chronic disruptions of the menstrual cycle;
- infertility;
- complicated pregnancy;
- miscarriage;
- development of malignant neoplasm.
A polyp in the uterine cavity has its own characteristics. The formation is found solitary or in the form of numerous processes. The shape is round or mushroom-shaped, has a thick base or a thin stalk, with a color from light pink to burgundy. Based on histological characteristics, types of endometrial tumors are distinguished, which are formed from:
- connective tissues – fibrous;
- glandular cells - glandular;
- combinations of two varieties - fibroglandular;
- tissues with atypical cells - adenomatous, developing into cancer;
- the remains of the placenta after childbirth are placental.
A small polyp in the uterus has no symptoms. Pronounced signs of pathology appear with large sizes or polyposis - multiple formations. Surgery is necessary if women experience:
- uterine bleeding;
- brown vaginal discharge in the middle of the menstrual cycle;
- pain in the lower abdomen and lumbar region;
- discomfort and bleeding during sexual intercourse;
- heavy and painful periods;
- problems of conception;
- the occurrence of iron deficiency anemia;
- discharge of mucous leucorrhoea from the vagina;
- miscarriages.
This is an endovideosurgical intervention using high-tech equipment. It is a minimally invasive operation and is performed in the operating room under anesthesia and after proper preparation of the woman.
The main instrument is a hysteroscope. It is a long tube with an optical system located inside. In addition, various additional devices necessary for removing tumors can be placed in it.
Hysteroscopy is performed in the operating room. The woman lies down on a special table (Rakhmanov chair) with her legs raised and spread apart. An anesthesiologist administers anesthesia, usually using intravenous drugs with hypnotic and analgesic effects. It is extremely rare (if a more serious and lengthy intervention is planned, for example, removal of a myomatous node) that spinal anesthesia is performed.
After the woman “falls asleep,” the gynecologist proceeds directly to hysteroscopy. The sequence of actions is as follows:
- the mucous membrane of the vagina and cervix is treated with antiseptic solutions;
- using a set of tools, the cervical canal is expanded so that the hysteroscope can freely pass into the cavity;
- the instrument is inserted into the uterus, first the doctor examines in detail all the structures (endometrium, uterine angles), and, if necessary, performs some manipulations, for example, removing a polyp or curettage.
After the doctor completes all his actions, the anesthesiologist finishes the anesthesia, and within a minute or two the woman wakes up. She is transferred to a ward, where she remains under observation for another two hours.
The entire procedure usually takes about 20–30 minutes.
A polyp is a small wart-like growth up to 3 cm in length. Under the influence of a number of provoking factors, it begins to grow from the endometrial mucosa in the uterine cavity and initially has a benign course. Gradually creating favorable conditions does not prevent the degeneration into cancer.
Localization of the polyp is possible both inside and on the surface of the cervical cavity.
The neoplasm is removed through surgery, although at the initial stage and according to the diagnostic results, it is possible to eradicate the polyp using medications and folk methods.
Recovery
The postoperative period after hysteroscopy (or another method), with a normal course, is calm. After 2–3 days, normally all unpleasant sensations disappear. The length of hospitalization depends on individual reactions to anesthesia; women are usually discharged on the second or third day. With the laser method - on the same day, and after using this method there are no most negative reactions. This is explained by the low-traumatic nature of the method and the absence of anesthesia.
The postoperative regimen in women depends on the individual characteristics of the body, the extent of the pathology and the presence of various diseases in the anamnesis. Since the main method at the moment is hysteroscopy, all recommendations on behavior can be considered general.
Recommendations:
- during the first weeks, avoid overheating (visiting the steam room, sauna, solarium, hot baths is prohibited during this period);
- You should not swim in open water, use tampons, vaginal suppositories, or douche;
- use any medications and folk remedies without first consulting a doctor;
- you need to give up sexual contact for a while (this is required to restore the endometrium);
- you need to limit physical activity and stress.
A month is a standard rehabilitation period; all recommendations must be followed especially strictly in the first week. This will help avoid any complications and infection of tissues that have not yet healed. Recovery after polyp hysteroscopy occurs quite quickly if there are no complications and doctors’ recommendations are followed. If the use of any drugs is required, then a drug that restores normal body functions must be prescribed by the attending physician.
Treatment after
Treatment after polyp removal is prescribed in accordance with the results of surgery. The patient’s health status is also important; the presence of chronic diseases requires additional treatment. Usually after 10-14 days the patient is examined again. At the same time, the results of a histological examination of the removed tumor and tissues are ready.
If there are no complications, and histology does not reveal malignant cells, then the recommendations in the postoperative period are standard. If complications begin, curettage may be prescribed, and if oncology is detected, a repeat operation to remove the pathological focus.
Treatment mainly begins with the diseases that provoked the development of the tumor.
- Antibiotics: can be prescribed both to treat identified infections and to prevent infection in the postoperative period;
- Antispasmodics: usually prescribed in the first days after surgery for the purpose of prevention;
- Hormone therapy: most often used in the postoperative period. This is due to the hormone-dependent etiology of tumor development. Hormonal therapy is prescribed to prevent relapses and also as a contraceptive (pregnancy in the first three months is undesirable). After this period, if all processes went well, women are advised to use the “withdrawal syndrome” - the chance of becoming pregnant increases. Or put an intrauterine device with gestagens. It will help avoid unwanted pregnancy and restore the endometrium faster.
- Herbal medicine: used according to indications; in the postoperative period, folk remedies and herbal treatment show good results.
It will be mandatory to visit a gynecologist every 2 months, treatment of chronic diseases, a gentle regime (it is advisable to exclude physical and psycho-emotional stress).
How to remove a polyp of the uterine cavity - methods, methods
The modern method that most effectively removes endometrial polyps is hysteroscopy followed by curettage of the cervix and uterine cavity (polypectomy and curettage), as well as subsequent histological examination of the removed material. It is also possible to use separate diagnostic curettage or laser removal of polyps.
Factors such as the size of the polyp, its structure, the age of the patient, the nature of the endometrium, the reasons for the development of the polyp, as well as the presence of metabolic and endocrine diseases in the woman determine the tactics of patient management.
- If a woman has fibrous polyps, they must be removed.
- If a woman has a glandular fibrous polyp, this 100% indicates a hormonal imbalance and hormonal therapy is indicated after surgery.
- For polyps that threaten cancer - adenomatous, in women before menopause (see the first signs of menopause) or during menopause, removal of the uterus is indicated - hysterectomy or supravaginal amputation with revision of the ovaries or even removal of the appendages.
Can it bleed and how much?
Bleeding is considered normal if it is not profuse and lasts no more than 3 days. It may not exist at all if one of the modern methods of surgical intervention (laser, radio waves) was used.
Why is it bleeding? This process is associated with recovery from endometrial injury. As normal healing progresses, this process ends quickly. Even small spotting of blood serves as a reason to contact a gynecologist and find out the cause of the bleeding.
What to do if the bleeding does not stop depends on the cause of the phenomenon. The main cause is trauma during surgery – uterine perforation. An examination will show which tactics will be effective. Small punctures will heal on their own; large ones will need to be sutured.
If there is bleeding, you should definitely consult a doctor. Its sudden stop against the background of increasing spastic pain can be especially dangerous. This phenomenon can be a sign of a hematometer (its danger was described earlier, see the section Possible consequences and methods for eliminating them).
Consequences, complications of the operation
If after surgery, both curettage and hysteroscopy, the following symptoms occur, you should immediately consult a doctor:
- Heavy bleeding
- Dark, unpleasant-smelling discharge
- Increased body temperature
- Pain lasting more than 2 days or acute, severe abdominal pain
What complications and consequences may arise after curettage removal surgery?
- Inflammation of the uterus
a very rare phenomenon, which is possible if the operation occurred against the background of an untreated infection, inflammatory process, and also if the rules of antiseptics and septics were violated during the operation. In this case, antibacterial therapy is prescribed.
- Perforation of the uterus
the formation of a puncture in the wall of the uterus, which can occur with loose walls or poor dilation. Large perforations have to be sutured, while small ones heal on their own.
- Hematometer
If there is a sudden cessation of bleeding after surgery, severe pain occurs - this may be a spasm of the cervix and the formation of a hematometer. In this case, infection and pain are possible, which are relieved by anti-inflammatory therapy and taking antispasmodics.
How long to stay in the hospital after the intervention
How many days do they stay in the hospital - usually the period of hospitalization does not exceed 3 days; if complications arise, the patient is left in the hospital for their elimination and observation in the postoperative period.
There is no hospital stay at all if the operation is performed using laser hysteroscopy. Then the procedure takes place in a semi-hospital setting, without anesthesia, and after a few hours the patient can go home. How long to stay in the hospital is usually determined by the attending physician, based on the actual clinical picture in the postoperative period.
When can you sleep with your husband?
Despite the apparent ease and relatively quick recovery after surgery, surgery is a rather serious burden on a woman’s body. After it, it is necessary to give the endometrium time to recover, so serious restrictions are introduced in the first month.
For the first month, sexual contact is strictly prohibited. If no complications arise, then unprotected contact should be avoided to eliminate the risk of infection of young tissue and to avoid pregnancy in the first six months. It’s best to check with your doctor when you can have sex.
Possibility of natural pregnancy and IVF
Natural pregnancy is possible both before surgery (the presence of a tumor does not always lead to infertility) and immediately after it. Most often, during the postoperative period, women are prescribed hormonal drugs, including contraceptives. When they are canceled, hormonal activity increases, so women are even recommended to conceive at this moment.
If you have difficulty conceiving after surgery, you can try IVF. Artificial insemination is usually successful, and subsequent pregnancy proceeds normally, especially if there are no relapses.
How to avoid polyps
Prevention includes the following activities:
- Timely treatment of inflammation and infections.
- Having a permanent sexual partner.
- Detection of hormonal disorders.
- Correct use of hormonal drugs.
- Avoiding trauma to the uterine cavity.
- Active lifestyle.
- Regular examination by a gynecologist.
https://youtu.be/UWYPULc9Y7s
There are many factors that cause mucosal proliferation. Timely detection and correct treatment tactics will help cope with the problem.
Histology of distant formation
Histology results after removal are usually ready within 10 days. Both the tumor itself and the tissue obtained as a result of curettage are sent for analysis. This is an important point that can determine the further management of the patient.
The results of a histological examination show not only the structure of the removed tumor (benign or malignant), but also help to assess the risk of future degeneration. In older women, risk factors include precancer – adenomatous tumor. Based on the results of histology of adjacent tissues at the site of polyp removal, a decision is made on further actions. Identification of atypical cells requires immediate treatment of an already oncological disease. Most often we are talking about surgical intervention.
Reviews
Maria, 25 years old
I am one of those who survived surgical removal. Before the operation, I tried to get pregnant for 2 years, but it didn’t work. Thanks to my doctor, he performed the operation and then described in detail all the procedures in the postoperative period. Immediately after stopping the contraceptive hormones, the long-awaited pregnancy occurred. We are already 4 months old, I gave birth on my own and without complications.
Svetlana, 28 years old
I read reviews from those who survived the operation. Girls, if your health is important to you, choose laser. 6 years have passed since the operation. I don't have any negative consequences. The procedure itself was painless, I was home in the evening. After that I gave birth. My doctor says that I no longer need to visit him so often, there are no relapses, everything is fine. I recommend this method.
Tamara, 47 years old
It will be useful for everyone who has not yet removed a formation to learn about my experience. The first time I was on the operating table was 12 years ago, after curettage I could not recover for a long time, I was in severe pain. The result is a repeat operation after 11 months. Less than a year later, I had surgery again. Three months ago, during a routine examination, another polyp was found. I was terrified. But now I can say that there is progress in gynecology. Everything went fine, no pain or bleeding. After the hysteroscopy, I woke up in the ward and was discharged home two days later. All my fears were in vain, medicine became humane and safe. I hope I don't experience a relapse again.
Julia, 28 years old.
The polyp was discovered during my second pregnancy. I was very scared, afraid of everything: losing the child, complications during childbirth, the operation itself. Thanks to my doctor, he insisted on a hysteroscopy. I spent exactly 15 minutes in the operating room (I was lucky, the polyp was on a stalk, they just unscrewed it). The tone of the uterus returned to normal, when the time came, she gave birth on her own.
Herbal medicine after polyp removal
Is it possible to resort to herbal medicine? Before making such a decision, you should definitely ask your doctor for advice. Self-medication can lead to allergic reactions and complications.
In the treatment of female diseases, an infusion of herbs such as celandine, boron uterus, and a vitamin complex is often used. The golden mustache is known for its healing properties. When treating polyps, its alcohol tincture is used.
Some recommend douching with celandine infusion. However, this plant is known not only for its healing, but also for its poisonous properties. Therefore, such use must be approached with extreme caution. And douching as such is not approved by all doctors. Some of them believe that such procedures wash out beneficial microflora from the vagina, upsetting the necessary balance.
An infusion of chaste vitex can improve progesterone production. It begins to be used only in the second phase of the monthly cycle. The course lasts 3-4 months.
It must be remembered that traditional methods used independently are not suitable for the treatment of this pathology, only in combination with medical treatment.
Price
Patients undergoing surgery are usually interested in the price. In this case, it is important to understand that the cost will be influenced by several factors simultaneously. The easiest way to find out how much removal will cost is from your doctor. He knows exactly the scope of pathology and the capabilities of his clinic in choosing the method of surgery.
You can check the pricing policy in advance on the Internet. It is enough to go to several sites to compare standard prices for the desired method.
Here are some prices. The following prices are set for different methods in private clinics:
- diagnostics using a hysteroscope – from 5 to 15 thousand rubles.
- abdominal surgery for removal - from 9 to 25 thousand rubles;
- scraping - from 5 to 7 thousand rubles;
- laser removal – from 11 to 36 thousand rubles.
The price of operations in private clinics and medical centers depends on the status, qualifications of the operating surgeon, and the level of equipment. And also on the complexity of the operation and the cost of hospital stay. The cost of the same services may differ in regions; even within the same city you can find hospitals with different price levels. Surgery is free in public medical institutions. But there may be a long waiting list for surgery. If the course of the disease is not threatening and the tumor does not progress, then removal can be postponed until the specified date. But it is necessary to be observed by a gynecologist. In case of threatening development, surgery can be performed for emergency reasons. Or offer the patient treatment in a private clinic.
Removal of polyps in the uterus with laser
Today, this method is used only in Moscow, but in the near future it will have to be used in every city - this is targeted removal of polyps in the uterus with a laser, which is melodramatic, does not leave scars, while maintaining reproductive function, which is especially important for women planning to have children. Since pregnancy is more likely after laser removal. In centers where modern technologies are used, a complete examination and laser removal of a polyp can be carried out in 3 hours, without a hospital stay, without disability, and without injuring the uterine cavity.
Also, for a more thorough diagnosis, it is possible to use mini-hysteroscopy or so-called office hysteroscopy, which occurs without trauma to the cervix and without anesthesia. In this case, the woman makes the choice of treatment method and assesses the condition of the uterine cavity together with the attending physician. With the help of such equipment, it is possible to determine any pathology of the uterus - uterine fibroids (symptoms of uterine fibroids), endometrial hyperplasia, intrauterine synechiae.
This is the most effective and gentle method of treatment, since the doctor controls the depth of laser penetration layer by layer, preventing injury, shortening the recovery period, blood loss is reduced, since the laser seals the vessels, the procedure does not leave scars, which is beneficial for future pregnancy, the recovery period after surgery is 6-8 months.
Discharge after polyp removal
What is considered normal after removal of uterine polyps?
- After hysteroscopy, a woman may experience minor spasmodic pain when the uterus contracts, as during menstruation
- There should be slight discharge for 14-20 days after the procedure
After the operation to remove polyps, a week later the patient should definitely undergo a routine gynecological examination, which will prescribe restorative therapy according to the nature of the polyp, the woman’s age and based on the main reason for the development of the tumor in the woman.