Definition
What is this condition, and in what cases can it be said that there is thinning? Normally, during the menstrual cycle, the thickness of the endometrium ranges from 0.5 to 1.5 cm, depending on the phase of the cycle. But if the indicator is less than 0.5 in the phase of maximum thinning, then the condition is considered pathological. If the endometrium is less than 1.5 cm in the phase of greatest thickening, then medical supervision is required.
Therapy methods
Treatment of thin endometrium can be carried out in several ways - therapeutic, medicinal and traditional medicine. One type or another is prescribed depending on the reasons that provoked it.
As for traditional medicine, in this case phytoestrogens are used - herbal preparations that contain large amounts of female hormones - estrogens.
They, in turn, have a beneficial effect on the thickness of the inner layer of the uterus. Seeds and grains of cereals and legumes, as well as herbs – chamomile, chaga and others – help.
But the action of traditional medicine cannot completely restore the balance of female hormones.
Traditional medicine only serves as prevention and additional assistance in the treatment of thin endometrium. Before using traditional methods, you should consult your doctor.
But the methods of therapeutic treatment are very effective. These include:
- Taking hormones (with low levels of estrogen and progesterone).
- Therapeutic massage.
- Gymnastics.
- Physiotherapeutic procedures.
- Magnetic therapy.
- Mud baths.
- Water therapy.
These methods can effectively cure pathology with poor blood flow or in the presence of inflammatory infectious processes in the uterus.
If the endometrium does not grow, then surgical operations are used. In this case, the upper small layer is surgically removed, stimulating the growth of new healthy endometrium.
All therapeutic procedures are recommended to be used in combination with proper nutrition and a healthy lifestyle, as well as frequent walks in the fresh air. You need to give up bad habits, soda, fast food and eat more foods that contain phytoestrogens.
Coagulation
Coagulation is a procedure for burning the uterine tissue with subsequent removal of the top layer of epithelium. In this case, the uterus is damaged, and then it begins to heal with the growth of new healthy epithelium.
Nowadays, this is a safe procedure that allows you to restore the former elasticity of the uterus; it is absolutely harmless for nulliparous girls.
There are 4 methods of coagulation: electrocoagulation, chemical, radio wave and argon plasma.
Each method has its own contraindications, so it is prescribed by the treating gynecologist. Also, each method has its own advantages and disadvantages.
Scraping
Scraping is also called “cleaning”. This procedure can only be prescribed by a gynecologist.
When curettage, the top layer of the uterine epithelium is removed, leaving the germinal layer. It is from this that a new layer of the required thickness grows.
Curettage is carried out both for diagnostic purposes and for treatment. For diagnostic purposes, a sample is taken and the pathology and root cause are determined. In case of treatment, the entire mucous membrane (top layer) is scraped out.
This procedure effectively treats pathology and is one of the most comfortable gynecological interventions.
Drug treatment
To grow the required layer - from 7 millimeters - a balance of female hormones is necessary.
In this case, medications containing estrogen and progesterone, prescribed by a doctor, are very helpful. The most commonly used oral medications are tablets.
Drug treatment is used when thin endometrium is associated with hormonal imbalance. A specific type of medication and course of treatment are prescribed.
Causes
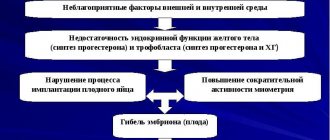
There are several reasons why a thin layer of endometrium may form, but all of them, one way or another, are related to the patient’s hormonal level. With a long-term decrease in estrogen or high levels of progesterone, which reduces estrogen activity, the endometrium gradually thins. It is renewed during menstruation and becomes thin, but due to a malfunction it is not renewed intensively enough, and does not gain sufficient thickness before the onset of the next period. In this case, the mucous membrane is usually slightly thinned.
Thin endometrium after curettage is a much more serious deviation. During this procedure, the entire endometrium is removed. If there is a hormonal imbalance, its recovery is extremely slow or does not occur at all. In this case, deviations from the norm are usually more significant than in the previous case.
Sometimes there are other reasons. This:
- Poor circulation in the uterus, as a result of which the mucous membrane does not receive the necessary nutrients and oxygen, and therefore cannot grow;
- Traumatic injuries during surgical interventions, at the site of which the layer does not grow;
- Inflammatory and infectious processes in the uterine cavity, preventing the growth of the mucous membrane, since all resources are spent on fighting the infection;
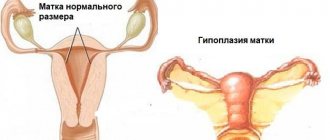
- Congenital underdevelopment of the reproductive system or its pathology, as a result of which the endometrium never returns to its normal state (it is in this case that it is most difficult to select therapy, and most often it fails).
Why is the endometrium thin in a particular case? Your doctor will help you answer this question. It is he who is able to make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment based on the results of tests and laboratory tests.
Thin endometrium: causes, treatment, pregnancy
[content]
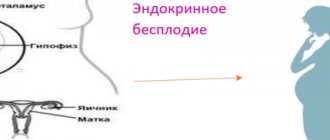
The endometrium is the upper mucous layer lining the uterus. A characteristic feature of the endometrium is the abundance of blood vessels. The endometrium is extremely sensitive to the amount of female hormones in the body, the lack of which leads to its thinning.
The main function of the endometrium is to create favorable conditions for the engraftment of the blastocyst in the uterus. In addition, the thickness of the endometrium is also extremely important for women’s health.
It is considered normal to gradually increase the size of the endometrium from 0.5 centimeters on the first day of the cycle, and to 1-1.3 centimeters by the 27th day of the cycle.
Naturally, for a woman’s normal healthy sex life, the size of the endometrium is not significant, but for women planning a pregnancy, these values are extremely important, since the possibility of pregnancy itself directly depends on them.
In a physically healthy woman who is in the last phase of the menstrual cycle, the size of the endometrium increases, which leads to its enrichment with iron and greater blood flow, and increases the chances of rapid implantation of the embryo.
Women whose endometrium is not thick enough cannot become pregnant for a long time and are forced to undergo a long course of treatment.
Cause of thin endometrium
The main and most common cause of thin endometrium in modern living conditions is prolonged hormonal imbalance. Being interested in why the endometrium is thin in a particular woman, the doctor will definitely send her to check the level of hormones in the body.
The second most common cause of thin endometrium is considered to be a violation of the uterine mucosa, which occurred as a result of curettage after an abortion and other operations on the uterus.
In addition, some women have a congenital circulatory disorder in the uterus, which also affects the thickness of the endometrium.
The first symptoms of possible problems with the endometrium
The thickness of the endometrial layer can be determined with reliable accuracy solely by ultrasound of the uterus, but each woman can make a preliminary diagnosis for herself, guided by the following signs and symptoms:
- Menstrual irregularities. Irregular, painful periods almost always indicate a problem with the endometrium;
- Discharge during menstruation in a healthy woman is quite abundant. The lack of a sufficient amount of blood during menstruation should make you think and lead you to the gynecological office for examination.
Consequences of thin endometrium
For a non-pregnant woman, it does not matter significantly how thick her endometrial layer is, but for a pregnant woman this circumstance is extremely important, since the main and most unpleasant consequence of a thin endometrium is spontaneous miscarriage in the early stages of pregnancy.
In addition, thin endometrium can cause severe uterine bleeding during a medical or conventional abortion.
How to prevent the risk of thin endometrium
Thin endometrium in women almost always poses a threat to future pregnancy, which is why gynecologists advise, before thinking about children, to undergo a small examination to determine the thickness of the endometrium. Statistics show that thin endometrium is observed today in every 3rd woman. This problem has long acquired global proportions, so all the means of modern medicine are being used to solve it. Thin endometrium and pregnancy are inextricably linked.
Treatment of thin endometrium
Let's take a closer look at what to do with thin endometrium:
- First of all, undergo an examination and determine the reason why the endometrium is thin;
- Determine together with your doctor how to treat thin endometrium;
- To identify the possible impact of thin endometrium on pregnancy.
The course of treatment for thin endometrium is very complex and lengthy, as it involves restoring the normal functioning of the entire reproductive system of a woman by taking various hormonal medications, as well as homeopathic remedies. In the fight to increase the size of the endometrium, the following treatment methods are used:
— physiotherapeutic;
- medicinal;
- surgical.
Traditional medicine in combination with special physiotherapeutic procedures aimed at increasing blood flow to the pelvis and, accordingly, increasing the size of the endometrium are very effective in the fight against thin endometrium. The use of sage is considered especially useful for thin endometrium.
Naturally, the use of any medications, including herbal ones, should be strictly under the supervision of a doctor and on his recommendation. There is no hope for a complete cure after using infusions and decoctions of medicinal herbs, but they are still good to use as a supplement to basic medical procedures.
In the most difficult cases, the doctor may recommend surgery, which involves complete removal and subsequent procedures such as thin endometrial augmentation.
It should be noted that treatment of thin endometrium is not possible in all cases; for example, if congenital or acquired uterine hypoplasia is detected, a woman is physically unable to become pregnant naturally. For such women, the only solution is artificial insemination, which involves implanting an already formed and fertilized egg into the uterus. Thus, thin endometrium and IVF are directly related.
So, the endometrium is an extremely important component of the lining of the uterus, without the proper thickness of which a woman will not be able to get pregnant normally and bear a healthy child. When planning a pregnancy, you should definitely check the thickness of the endometrium; it should not be less than 7 millimeters. Any deviations from this figure indicate the need to begin immediate treatment.
Symptoms
A scanty endometrium may not manifest itself in any way. But sometimes several symptoms still form:
- Menstrual irregularities;
- Decreased menstrual flow;
- The appearance of slight spotting acyclic discharge;
- Infertility;
- Frequent miscarriages;
- Anorgasmia;
- Late onset of menstruation;
- Indirect phenotypic signs - narrow pelvis, weak expression of secondary sexual characteristics, etc.;
- Periodic uterine bleeding.
It should be remembered that pregnancy with a thin mucous layer is difficult. This means that this condition cannot be ignored, especially in cases where you plan to have children in the future.
Why does the endometrium shrink?
The reasons for thin endometrium are various; among the main factors why the endometrium does not have the proper thickness are the following:
- hormonal imbalance;
- diseases of the endocrine system;
- chronic inflammatory diseases;
- disturbances in the blood supply to the uterus;
- congenital anomalies of the uterus;
- polycystic ovary syndrome;
- frequent use of Postinor (emergency contraception).
The condition of the endometrium is affected by reasons such as surgical interventions on the uterus, including abortion. Often a similar problem is diagnosed in women with insufficient physical development of the body, short stature, and narrow pelvis. This does not mean that insufficiency of the endometrial layer will be determined in all these cases, but the inability to become pregnant for a long time against the background of these factors should be the reason for visiting a doctor.
Consequences
The main consequence of this diagnosis is that getting pregnant with a thin endometrium is quite difficult, if not impossible. But besides this, there may be other possible consequences:
- Ectopic pregnancy;
- Spontaneous abortion (miscarriage);
- Severe toxicosis;
- Weakening of the birth process and its significant complication;
- Heavy bleeding during and after the birth process.
There is an opinion that this condition of the uterine mucosa leads to an increased likelihood of developing infections and inflammatory processes in it.
Diagnostics
If signs of pathology are detected, you should contact a gynecologist. He will prescribe an examination and further treatment.
According to statistics, every third woman in the world has a thin endometrium. There are modern examination technologies to identify the disease.
To determine the thickness of the endometrium of the uterus, the following examinations are prescribed:
- Ultrasound of the uterus - thin endometrium in the uterus is determined at any stage of the menstrual cycle, and it must be performed several times to accurately detect hypoplasia.
- Blood test to determine hormonal levels.
- Biopsy of the uterus.
- Histological analysis of uterine tissue.
- Analysis of urine.
The above procedures help not only to detect pathology, but also to understand the reason for the thin thickness of the endometrium. And only after identifying these factors can you understand what to do and prescribe further treatment.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy with a thin endometrium is possible, but it can be significantly complicated. Conception occurs quite rarely due to the fact that the embryo cannot attach to the thinned mucous layer. For the same reason, miscarriage is possible in very early stages, which often goes unnoticed by the patient. For the same reason, spontaneous abortion can occur a little later - the endometrium rejects an embryo that does not receive sufficient nutrition.
Since the endometrium and pregnancy are directly related, there is also a complication of the birth process.
Diagnosis and treatment
After studying the general symptoms, the patient is prescribed:
- Ultrasound of the uterus, which is performed several times at different phases of the cycle;
- general urine and blood tests;
- analysis to determine the level of hormones responsible for the onset and successful course of pregnancy;
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs;
- taking samples of uterine tissue for histological examination;
- biopsy of the uterine body.
These studies make it possible not only to establish the fact of endometrial thinning, but also to determine the causes of the pathology.
Treatment for thin endometrium depends on the reasons that caused it. In most cases, this is an imbalance of the hormonal system. Therefore, pregnant women with this pathology need hormonal therapy with drugs containing progesterone. Treatment regimens, dosage, and duration of therapy are carried out exclusively by the attending physician on an individual basis.
If hypoplasia is caused by chronic inflammatory diseases of the genital organs, drug therapy should be aimed at eliminating the source of inflammation. In some cases, there may be indications for surgical treatment. It consists of removing the inner layer and further hormone therapy. These methods help to renew the mucous layer of the uterus and normalize its thickness.
For circulatory disorders, treatment is indicated using conservative methods, including: massage, physiotherapy, hirudotherapy, acupuncture, and therapeutic exercises.
Drug therapy
To ensure a normal pregnancy, it is necessary to increase the thin endometrium. The patient may be prescribed combined oral contraceptives that normalize hormone levels, a course of treatment with estradiol, and drugs containing progesterone (Utrozhestan, Duphaston).
- Duphaston
Although this drug is an artificially synthesized hormone, it successfully performs all the tasks that are inherent in progesterone. The product effectively prepares the uterus for the upcoming pregnancy, relieves its muscle tone, and prevents epithelial detachment. The usual regimen for taking the drug is from the 11th to the 25th day of the cycle, but you cannot make a decision about taking it yourself. Admission is carried out only on the recommendation of a doctor.
- Melsmon
The placental drug Melsmon contains placenta taken from women whose births occurred without complications. It is widely used in cosmetology, but is also used to normalize the menstrual cycle, relieve chronic fatigue syndrome, and eliminate symptoms of inflammation.
The drug is not used during pregnancy, in case of disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine system, renal or liver failure, or high blood pressure.
- Actovegin
Actovegin is intended to maximize blood circulation in the genital area. Increasing blood circulation is the key to successfully overcoming hypoplasia. The standard dosage regimen involves taking 1-2 tablets three times a day. Typically, the course of treatment lasts 4-6 weeks, determined by the doctor individually. The drug can also be taken during pregnancy, starting from the 16th week, when the formation of the placenta ends.
- Gormel
This remedy belongs to homeopathic medicines. It activates the synthesis of estrogen. It contains natural ingredients and alcohol tincture. The regimen for taking the drug is as follows: 10 drops are mixed with half a glass of water and the mixture is drunk half an hour to an hour before meals three times a day. The duration of treatment can vary from one to three times a month, depending on the results obtained.
Since the drug contains alcohol, it should not be taken during pregnancy. Contraindications also include brain injuries and diseases, renal failure. The drug should be completed before the stage of active pregnancy planning.
Stimulation of ovulation with thin endometrium should be carried out only as prescribed by a doctor and under his strict supervision. The use of the drug Clostilbegit can lead to even greater thinning, so it is usually taken simultaneously with the estrogen-containing drug Proginova.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy procedures indicated for thin endometrium have a number of advantages. They have a gentle therapeutic effect, do not cause side effects, and reduce drug dependence. They are usually prescribed as part of complex therapy.
Treatment uses magnetic therapy, ultrasound, ultraviolet light, massage, and mud baths. The most favorable period for treatment is the first days after the end of menstruation. You can enhance the effect of physiotherapy by following the rules of nutrition, taking walks in the fresh air, and regularly doing therapeutic exercises.
Treatment with folk remedies
In addition to the use of medications, you can increase the endometrium using folk remedies.
- Sage tea. A teaspoon of crushed plant is poured into 200 ml of boiling water and left to infuse for several hours. The resulting infusion is taken for four months in the first half of the menstrual cycle.
- Infusion of boron uterus. 2-3 teaspoons of the plant or ready-made sachets purchased at the pharmacy are poured with a glass of boiling water. After infusion for a quarter of an hour, you can take it daily.
- Pineapples and pumpkin, which are allowed to be eaten in unlimited quantities, provided that you are not allergic to these products. You can drink pineapple and pumpkin juices.
- Raspberry leaf tea. The prepared leaves are poured with boiling water and the tea is drunk in small quantities several times a day.
- A combined decoction prepared from elderberry inflorescences, yarrow herbs, mint, chamomile, nettle, and medicinal cap. A mixture of components taken in equal proportions is poured into 1 liter of boiling water, infused for an hour and taken half an hour before meals 3-4 times a day.
Regular treatment with folk remedies gives positive results within a few months. However, the use of any traditional medicine must be supported by drug therapy and carried out in consultation with the attending physician. It should be noted that some herbs have contraindications for use if the patient has other diseases.
Diet
The basis of successful treatment is proper nutrition. It must include foods rich in vitamins A and E, as well as foods with high levels of salicylates. The diet should include fatty fish, vegetables (tomatoes, bell peppers, spinach, cucumbers, beans, cabbage), fruits and berries (grapes, apples, currants, raspberries), dried fruits, honey, red wine.
A variety of spices are useful, such as paprika, thyme, cinnamon, curry. At the same time, a woman needs to limit her intake of fatty and sweet foods, as well as fast food, strong coffee and tea.
An active lifestyle plays an important role in growing the endometrium. It is useful to play sports and dance, visit the pool. This stimulates active blood circulation, which has a positive effect on his condition.
Hypoplasia and pregnancy
Thin endometrium during pregnancy increases the risk of miscarriage or fetal underdevelopment. And getting pregnant with it is very difficult, almost impossible.
To get pregnant if the inner layer is small, in vitro fertilization (IVF) is often prescribed.
This method allows you to introduce an already fertilized egg into the uterus, which is more likely to implant immediately. In this case, the probability of giving birth to a healthy baby is greater, but it is not high - no more than 1%.
Therefore, doctors recommend before IVF to conduct an examination and undergo therapeutic and drug treatment to restore the normal layer.
Women with this disease are often kept in storage for constant supervision and examination.
There are preparations in the form of gels and patches that help restore the balance of hormones and thus increase the thickness of the epithelium.
Endometrioid ovarian cyst
Treatment of endometrioid ovarian cysts can be conservative (hormonal, nonspecific anti-inflammatory and analgesic therapy, taking immunomodulators, vitamins, enzymes), surgical (organ-preserving removal of endometrioid lesions using laparoscopic or laparotomic access) or combined. Comprehensive treatment of endometriosis is aimed at eliminating symptoms, preventing the progression of the disease and treating infertility. Treatment tactics for endometrioid ovarian cysts depend on the stage, symptoms and duration of endometriosis, the patient’s age and the presence of problems with conception, concomitant genital and extragenital pathology.
Conservative treatment
If the size of the endometrioid ovarian cyst is small, it is possible to carry out long-term hormonal therapy using low-dose monophasic COCs, norsteroid derivatives (levonorgestrel), prolonged MPA, androgen derivatives, synthetic GnRH agonists. Pain syndrome associated with the growth of endometrioid ovarian cysts is relieved by taking NSAIDs, antispasmodics and sedatives.
Surgery
If conservative therapy is ineffective for endometrioid ovarian cysts larger than 5 cm, a combination of endometriosis and infertility, the risk of complications and oncological alertness, only surgical treatment is indicated.
In women of reproductive age who want to have children, they try to avoid radical operations (oophorectomy, adnexectomy). The preferred methods of surgery for endometrioid cysts are enucleation of heterotopic formations or resection of the ovary. It is advisable to remove foci of endometriosis and endometrioid ovarian cysts with pre- and postoperative hormone therapy.
Postoperative management
Preoperative hormone therapy can reduce foci of endometriosis, their blood supply and functional activity, and the inflammatory reaction of surrounding tissues. After surgical removal of an endometrioid ovarian cyst, appropriate hormonal treatment promotes regression of remaining endometriotic lesions and prevents relapse of the pathology.
In the postoperative period, it is advisable to prescribe physical therapy for the purpose of correcting endocrine imbalance, preventing infiltrative and adhesive processes, relapses of endometrioid ovarian cysts (electrophoresis, ultrasound, phonophoresis, endonasal galvanization, SMT therapy, magnetic therapy, laser therapy, acupuncture, radon baths, etc.).
Treatment of follicular cysts
Treatment of follicular ovarian cysts is not difficult; usually, even without treatment, spontaneous regression is observed after 1-3 cycles. A good therapeutic effect can be achieved by prescribing hormonal contraceptives for therapeutic purposes. If it is impossible to prescribe contraceptives, for example in the second half of the cycle, progestin-type drugs may be prescribed. The purpose of their use is to correct the luteal phase defect that occurs in the absence of the influence of corpus luteum progesterone on the endometrium. Since it is known that a defect in the luteal phase can lead to a delay in menstruation, and it is one of the most important factors in triggering cyst regression.
Corpus luteum cyst
The mechanism of formation of a corpus luteum cyst is more complex and little studied. It is necessary to clearly distinguish between two concepts - the corpus luteum of a cystic structure (corpus luteum cyst in the classical sense) and the persistent corpus luteum, which in essence may not be a cyst, but can significantly disrupt reproductive function.
The corpus luteum itself is a burst follicle that secretes progesterone and forms the secretory transformation of the endometrium. The corpus luteum can be either cystic or solid in structure and, by and large, is not a pathology.
The importance of the corpus luteum of a cystic structure is given due to possible complications when it ruptures or twists around the uterine appendages. There are separate studies reflecting the fact that with a cystic variant of the structure of the corpus luteum, the level of serum progesterone is slightly lower. Thus, a corpus luteum with a cystic structure is not a pathology, and if such a cyst is present, one can become pregnant; moreover, the presence of a corpus luteum is a necessary component of pregnancy (regardless of its cystic or solid structure).
It is necessary to consider the persistence of the corpus luteum (cystic or solid structure) from a completely different perspective. Detection of the corpus luteum in the early follicular phase, or detection of an increased level of progesterone in the serum during this period, can lead to significant impairment of reproductive function. Progesterone released during the follicular phase of the cycle causes desynchronization of the development of the uterine mucosa, disrupts the formation of endometrial receptivity, which has an extremely negative impact on the possibility of implantation and pregnancy.
Treatment of corpus luteum cyst
Treatment of corpus luteum cysts in the second phase of the cycle is not required; it is only necessary, if possible, to minimize the risk of possible complications. If persistence of the corpus luteum is detected, observational tactics or the prescription of hormonal contraceptives for therapeutic purposes are acceptable.
Treatment with drugs
Drug treatment of thin endometrium involves taking the following medications:
- Duphaston (a synthesized drug similar to progesterone, reduces the tone of the uterus, prevents exfoliation of the epithelium, taken on days 11-25 of the cycle, prescribed only by a doctor);
- Melsmon (contains placenta, is used to eliminate symptoms of inflammatory processes, normalize the cycle, has a number of contraindications);
- Actovegin (normalizes blood circulation in the genital organs, accelerates the growth of the endometrium, the general course lasts 4-6 weeks, the exact regimen is calculated only by the supervising doctor);
- Hormel (a homeopathic remedy, the duration of treatment may vary, the dosage regimen is calculated only by a doctor).
Taking any medications, especially hormonal ones, can be prescribed by a doctor after an examination. It is not recommended to start taking it on your own, as this can cause a serious deterioration in the condition.