What kind of coating on the tongue should raise suspicions and prompt a person to undergo examination?
The following conditions require consultation with a doctor:
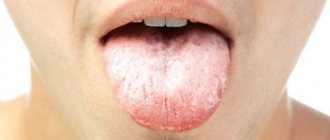
- if the coating on the tongue is quite dense, grayish or yellowish (a sign of a serious chronic illness);
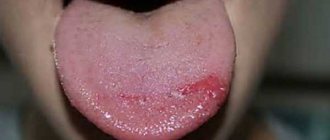
- a dark gray coating on the lower third of the tongue is a symptom of lung or heart disease;
- the sides of the tongue covered with a dense gray coating indicate liver or gall bladder disease;
- if a yellowish film covers the upper third of the tongue (root), this means the person has gastrointestinal diseases.
There is a kind of test for the presence of diseases during plaque:
- you need to brush your teeth and tongue, removing all possible plaque from them;
- measure the time until a new film appears;
- if the plaque appeared in less than 3 hours, during this time there were no meals, and the person did not smoke - this is not a good sign.
If your tongue hurts or burns
In many cases, painful sensations in the tongue appear as a result of not following a balanced diet. In particular, pain can occur due to a lack of iron, vitamins B6, B3 (PP) and B12.
A burning sensation on the surface of the muscle may indicate that the stomach is producing too few digestive juices, so this symptom usually indicates a malfunction of the gastrointestinal tract.
Sometimes, if the tongue looks no different, but there is a burning sensation, this may indicate a hormonal imbalance. By the way, women experience this symptom almost 7 times more often than men. In addition, the burning sensation may be the result of an allergy to the wrong toothpaste.
Morning raid
In most absolutely healthy people in the morning, immediately after waking up, you can notice a light, loose grayish coating on the tongue. This film can be easily removed with an ordinary toothbrush. If the brush does not cope, then it is necessary to add rinsing the mouth with specialized compositions, including herbal decoctions and antibacterial components, to your daily morning procedures.
You can buy such rinses at the pharmacy or prepare yourself (chamomile decoction is an excellent assistant in the fight for a clean mouth). Balms have an excellent antiseptic effect and kill pathogenic bacteria on the tongue and gums.
Therapeutic measures
If scrotal tongue is an independent disease, then no special therapy is required. There is usually no discomfort, no pain occurs, so a person with a mottled tongue does not even notice his problem. In case of concomitant diseases, complex therapy is required, which is selected individually.
When the inflammatory process develops, drug therapy is usually prescribed. The treatment regimen includes:
- taking anti-inflammatory drugs and antibiotics as needed;
- the use of corticosteroids to relieve acute inflammation;
- in case of a fungal infection, antifungal drugs are indicated;
- To intensively cleanse the oral cavity and relieve inflammation, rinses with the use of herbal remedies are prescribed;
- use of cooling gels and analgesics in case of increased pain;
- carrying out immunostimulating therapy.
To eliminate inflammation, applications with chlorhexidine are prescribed. It is also recommended to treat the tongue with drugs with keratoplastic properties. This group of products includes glycerin and retinol solution.
Furrows can be removed mechanically using a laser. The procedure involves smoothing the grooves, as a result of which the tongue acquires an anatomically correct shape and becomes smooth. Surgical intervention is advisable in case of intensive increase in the size of the tongue. The procedure involves suturing the grooves. During the recovery stage, it is necessary to observe “speech rest” and adhere to a gentle diet.
Reasons for the raid
There are several quite serious reasons for the appearance of an unpleasant grayish coating on the tongue. The darker the film, the more serious the disease. In chronic diseases, the dark gray plaque turns into a dense film of almost earthy color. What are the main reasons for the appearance of plaque? 1. Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract can cause the appearance of a dark grayish-yellow dense coating on the entire surface of the tongue. This film is difficult to clean off with a toothbrush and returns after a few hours. If, apart from plaque, there are no symptoms of gastrointestinal disease, it is recommended to adhere to the following nutritional recommendations:
- eat less salty and sweet foods;
- completely remove fried, smoked and spicy foods;
- eat more fresh plant foods.
If after a few weeks of such a “diet” the plaque has not disappeared, the person is recommended to see a gastroenterologist. 2. A course of taking antibacterial agents is a common cause of the appearance of a dense gray film on the patient’s tongue. As a rule, after finishing taking antibiotics, the plaque disappears on its own (subject to hygiene rules). During this period, it is recommended to brush not only the gums and teeth, but also the surface of the tongue. If after two weeks the plaque has not disappeared, it is worth looking for the true reason for its appearance. 3. Presence of HIV infection in the body. Gray tongue is a common side symptom of the human immunodeficiency virus, since the disease most often affects the stomach and other organs involved in the digestive process. 4. Gray plaque and bad breath with a sore throat are normal. The disease should be treated while carefully observing oral and tongue hygiene. Brushing your teeth should be more thorough and be accompanied by mandatory rinsing with antiseptic solutions to remove bacteria. 5. Dehydration can cause a gray, dry film on the tongue. The tongue swells and becomes covered with a dry crust with a gray tint, and the body temperature is usually slightly elevated.
Complications of the disease
If, according to you, glossitis of this form does not pose a particular danger to humans, then this does not exclude the development of complications. The grooved tongue makes the oral cavity vulnerable to infections. Most often, fungi from the genus Candida settle in folds. In this case, the symptoms expand significantly. Candidiasis leads to the appearance of ulcers that are painful. Erosion of the oral cavity interferes with the normal absorption of food and negatively affects the general well-being of the patient.
Staphylococci and streptococci also thrive in the oral cavity when fimbriated furrows appear. Bacteria actively multiply, causing general intoxication of the body and the formation of abscesses. An intense inflammatory process leads to a deterioration in the patient’s condition: increased body temperature, weakness, loss of appetite.
Any weakening of the immune defense leads to the development of inflammatory reactions. Folded glossitis does not require drug therapy, but its complications force the use of aggressive medications.
A mottled tongue in itself does not cause discomfort. You need to consult a specialist if your tongue has acquired a bright red color, and the process of chewing food is associated with pain. Plaque, unpleasant odor and burning sensation in the mouth indicate the addition of a secondary infection. If the necessary therapy is not carried out at this stage, then the organs of the digestive system may be involved in the pathological process.
There are other complications of the disease that are more of an aesthetic nature. If the organ increases in size, the bite may change. This is especially noticeable in young children. If a folded tongue has recently begun to interfere with conversation, then you need to consult a specialist. Incorrect bite, impaired diction, psychological complexes - this is only part of what progressive pathology can lead to.
The category of aesthetic problems includes excessive salivation, distortion of the oval of the face, cracked lips and dry mucous membranes. An enlarged tongue is more likely to be injured. Regular damage to the mucosa can cause the development of tumor processes.
Diagnosis for language changes
Diagnostics in this case will include the following steps:
- Analysis of complaints and anamnesis . Takes into account the nature of the changes, the time of their appearance, the disorders that accompany them and the presence of symptoms to which the patient can associate the changes that have appeared;
- Life history analysis . Chronic diseases, if any, are taken into account, hereditary diseases, bad habits, taking certain medications, contact with toxic substances;
- Physical examination . In the process, the shape of the tongue and its size, shade, presence of plaque, and surface are determined. The general condition of the patient is also taken into account;
- Scraping from the surface of the tongue and examining it . Performed when there is a risk of infectious diseases;
- Consultations with specialized medical specialists. This could be a dentist, neurologist, gastroenterologist, dermatovenerologist.
Additional research methods. They are performed in accordance with individual indicators in order to clarify the diagnosis.
These can be laboratory methods, such as urine and blood tests, as well as instrumental methods: ultrasound and fibroesophagogastroduodenoscopy.
Causes in adults and children
The photo shows what the color of the tongue can indicate:
A change in tongue color may indicate problems:
- of cardio-vascular system;
- scurvy disease;
- poisoning with salts of heavy metals (mercury);
- oxygen deficiency;
- renal pathology;
- problems with the adrenal glands (blue-black plaque);
- tendency to bleed;
- cerebrovascular accidents;
- development of ischemic processes in the heart muscle;
- glossitis (in men who smoke).
Localization of the cyanosis of the tongue can indicate the source of the problem. The cause of a blue tongue can be determined by the location of the plaque:
- tip of the tongue – cardiopulmonary failure;
- root – kidney problems;
- upper surface – development of problems with the cardiovascular system in the initial period.
Contacting medical centers for examination will prevent the development of an acute or exacerbation of a chronic disease.
A blue tongue in a child under one year old serves as a signal of the progression of diseases in the internal organs. Pathologies include:
- anemia (with vitamin deficiency of folic acid, cyanocobalamin, iron);
- diseases of the abdominal cavity are accompanied by corresponding symptoms;
- cyanosis of the skin and mucous membranes (lack of oxygen).
The child, depending on his age, cannot adequately describe the problems and what worries him. The need for medical consultation and additional diagnostic procedures is beyond doubt.
Treatment
A specialist can prescribe treatment only after identifying the cause of plaque formation. Therapy is aimed at the source of the problem, and is usually carried out in combination with diet. If plaque is caused by bad habits or food dyes, then folk remedies will help get rid of it. You can rinse your mouth with a decoction of chamomile or calendula. The course lasts no more than 5 days. If during this time the color of the tongue has returned to normal, then there is no need to worry. But if rinsing does not help, you need to urgently go to the doctor.