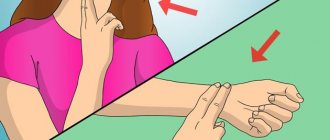
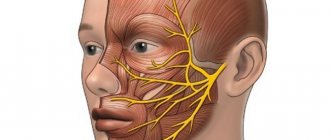
Numbness of the tip of the tongue and lips
Numbness of the tip of the tongue begins with a slight tingling sensation that does not cause much trouble while eating or talking.
This is why most people do not seek help from a doctor immediately, but after some time, when numbness in certain areas of the tongue is already observed. From about the middle of pregnancy, women may experience numbness in the tip of their tongue. This is explained by the fact that with the development and intensive growth of the fetus, the expectant mother begins to experience a deficiency of many microelements and vitamins, especially B12, which is responsible for the speed of nervous reactions. In such a situation, such a patient is shown medications containing all the necessary vitamins and minerals, in doses corresponding to the duration of pregnancy.
Often, numbness of the tongue or certain parts of it can be associated with dental procedures and the use of anesthesia. Such numbness, if it goes away within a few hours, is usually considered normal, but a similar symptom does not disappear for more than a day, you should consult your doctor.
Paresthesia of the tongue or its tip can be observed after the removal of some teeth, and most often this can be associated with “wisdom teeth”. The tip of the tongue is most likely to become numb in older patients after visiting the dentist, as well as in people who suffer from teeth that are close to the base of the tongue.
After complex dental procedures, numbness of the tongue or its individual parts can last from one to several days, and sometimes up to a month.
Very often, patients complain that the tip of the tongue goes numb. What does it mean? To find out the reasons, it is necessary to undergo an examination.
The main complaints about numbness of the tip of the tongue are:
- Heavy smokers often complain of numbness in the tip of the tongue.
- People receiving chemotherapy.
- If the body lacks vitamin B12.
- Damage to the glossopharyngeal nerve.
- Side effects of medications.
- Heavy metal poisoning.
- Alcohol abuse.
- Glossalgia.
- Hypoglycemia.
- Depression.
- Excess or deficiency of minerals in the body.
Quite often the tongue and lips go numb at the same time. Numbness of the lips occurs as a consequence of sensory impairment. But this is not the main problem, but becomes only a consequence of the underlying disease. You can only guess on your own which specialist you need to go to, and in no case can you make an accurate diagnosis yourself and prescribe treatment for yourself.
Numbness often affects the tip of the tongue and lips, causing discomfort; the reasons for this are:
- A side effect from certain medications, in particular antibiotics. By damaging nerve endings, they can cause numbness of the entire tongue, as well as its tip and lips.
- Some diseases of the oral cavity and speech. Often such a disease is glossalgia. It often occurs in women after 40 years of age, causing problems with the digestive system, endocrine disorders, etc.
- Age characteristics. For the most part, this applies to women during menopause. This period in the fairer sex is associated with various disruptions and changes in the body, the mucous membrane is disrupted and this often affects the sensitivity of the tip of the tongue, and sometimes the lips.
- Various allergic reactions. It is known that allergies are characterized by swelling, impaired sensitivity, difficulty breathing, and numbness of the lips and tongue is often observed.
- Often, numbness of the lips is associated with various mental disorders. At the same time, rapid heartbeat, shortness of breath, redness of the face, and a feeling of anxiety develop.
- High blood pressure can also lead to severe numbness of the lips, and loss of sensation in the lower extremities can also occur. In this case, you need to take medications that lower blood pressure or, in more complex cases, call a medical team.
- Side effects during pregnancy associated with increased blood pressure and swelling.
- Poisoning, alcohol and tobacco abuse, radiation.
In addition, numbness of the tip of the tongue and lips can also be observed in certain diseases:
- Stroke
- Diabetes
- Hyperthyroidism
- Neuritis
- Syphilis
- Multiple sclerosis
- Brain tumors
- Malignant tumors of the spinal cord
- Bell's palsy
- Certain types of migraine.
In addition to the listed diseases, this phenomenon is diagnosed with tumors of the nasopharynx, multiple sclerosis, herpes zoster on the face, with some viral infections, etc.
Particular attention should be paid to vascular problems, since they are becoming the leading cause of death in the world. In addition to impaired coordination and speech, a patient with a stroke attack is almost always diagnosed with numbness of the lips and tongue, and sometimes paralysis of one part of the face. If the listed signs are observed, you should immediately call an ambulance. Before her arrival, place the patient on a high pillow, provide access to air, and do not use any medications yourself.
What causes the tongue tingling sensation?
A feeling like tingling in the tongue area can be a consequence of various factors, which include low calcium levels, glossalgia, low levels of parathyroid hormones in the body, stroke, etc.
Numbness of the tongue, or in other words, tingling of the tongue, according to experts, is the result of the presence of trauma to the human nervous system. Paresthesia in this area often affects the tongue itself, although in some situations it spreads to other nearby parts, such as the lips. At the same time, glossalgia is considered to be one of the most popular causes of this phenomenon. This disease is characterized by the following symptoms: dry mouth, metallic taste, burning sensation in the tongue. The disease has a number of specific causes, which include hormonal changes in the body, diseases such as diabetes, the presence of all kinds of fungal infections, allergies, and, of course, the appearance of such feelings as anxiety.
In some situations, a sensation such as tingling on the tip of the tongue may occur. Moreover, one of the equally common causes of this phenomenon is considered to be hypocalcemia. In other words, most often numbness of the tongue is observed at a time when the level of calcium in the human body sharply decreases. All this can happen as a result of some disease that is not dangerous for a person, for example, vitamin deficiency, or, accordingly, turn out to be the result of cirrhosis of the liver.
In addition, it is worth noting that hypoparathyroidism most often occurs when the human parathyroid glands perform the function of generating hormones in insufficient quantities. Thus, answering the question of why your tongue tingles, it is worth noting that this sensation may be one of the most serious signals that you urgently need to check your hormone levels. Experts believe that another equally important reason for such a feeling as tingling in the tongue is a deficiency of vitamins, or rather vitamin B12. It allows the nervous system to correctly perform its assigned functions. That is why if its level in the body is too low, then this excess can result in a disorder of the nervous system. Here it is necessary to take into account the fact that the tongue is considered the focus of a huge number of nerve endings, which is why it is often the first to respond to vitamin deficiency.
In this case, nerve damage in the face can, in principle, be a side effect of various dental procedures. It is also quite possible for the lingual nerve to be damaged even, for example, during the period of cleaning a tooth canal. In addition, the tongue pricks like needles even as a result of the removal of the well-known wisdom tooth. Moreover, prolonged exposure to novocaine or the presence of an allergic reaction to it are two more reasons for this phenomenon.
The cause of constant or periodic tingling of the tongue in our time may also be the presence of a stroke or a disease such as multiple sclerosis. In this case, the human nervous system begins to function incorrectly, constantly sending various warning signals to other areas of the body, which leads to the appearance of all kinds of tongue diseases. In principle, these types of ailments are accompanied by other additional symptoms, for example, blurred vision, as well as dizziness. Severe headaches and deterioration in speech are established signs of a stroke.
It turns out based on what has been said that such a phenomenon as numbness or tingling of the tongue is, unfortunately, not uncommon. Although it is quite possible that at first glance, for the majority of people without medical education, this phenomenon causes great concern. Moreover, this symptom can manifest itself in various ways under the guise of loss of sensitivity, the appearance of a tingling sensation in the area of the tip of the tongue, or a sensation of goosebumps. In some situations this happens in a rather weak form, and sometimes even very strongly, causing significant discomfort to everyone. Although there is actually no clear answer to the question regarding the main cause of tingling in the tongue area. This may include the side effects of using a variety of medications, for example, antihistamines.
Thus, although there are plenty of reasons for a tingling tongue, one of the main ones today is considered to be an insufficient amount of calcium, vitamin B12 in the body, or the presence of certain diseases.
www.medcent.ru
General information
Decreased sensitivity or numbness of the tongue and lips indicate problems that are developing in the body. A person immediately notices if their lips lose sensitivity or their tongue becomes numb.
What this means, and what specific diseases may be manifested by a decrease in taste and tactile sensitivity, is best to find out from a doctor. But there are still certain features of this symptom. Thus, the tongue or lips may become numb gradually or almost instantly. Almost always, this symptom is accompanied by other signs of the disease, which makes it possible to facilitate diagnosis.
Sensitivity decreases due to impaired innervation of the lips and tongue. Speaking about whether numbness of the tongue is a sign of what and what diseases it may indicate, a number of factors should be noted: infectious, vascular, mechanical, etc. However, it is important to find out exactly what disease is causing the tongue and lips to numb. The features of this symptom and the diseases in which it manifests itself will be discussed below.
Why does the side of my tongue hurt? What causes tongue tingling?
There are a lot of diseases, the symptom of which can be tingling or numbness of the tongue. Here are some of them: glossalgia, stroke, lack of calcium and vitamins in the body. Sometimes it's damage.
Tingling of the tongue or loss of sensitivity may be symptoms of the disease. The main factors causing these symptoms are:
- the appearance of glossalgia;
- decreased levels of calcium and parathyroid hormones;
- vitamin deficiency;
- injury to the facial nerve;
- development of sclerosis or stroke.
Numbness, itching and a tingling sensation in the tongue indicate injury to the nervous system. Sensory loss can spread to the jaw or lip area.
Glossalgia
This disease is caused by a functional sensory disorder, which causes burning, itching, tingling in the tongue, soreness of the tongue or lips, and sometimes the palate and oral mucosa. The main symptom is a sore tongue when eating, talking or touching. The color of the tongue changes, it becomes less moisturized and swells, erosions and ulcers appear, which causes increased pain. There may be a loss of taste, the reasons for this are burning and numbness, and increased salivation.
With deep glossitis, inflammation occurs deep in the tongue. It manifests itself as phlegmon or an abscess. It often spreads to the floor of the mouth, neck and chin. The development of this disease often occurs in women after 40 years of age.
The causes of glossitis lie in trauma to the tongue from the edges of crumbled teeth, dentures, thermal and chemical burns. Excessive consumption of alcohol or cigarettes, as well as poor oral hygiene, can lead to the development of the disease. Often the development of glossitis occurs in conjunction with diseases of the stomach and blood. It can also appear with hypovitaminosis, diphtheria, scarlet fever and measles.
If treatment for this disease is not started, serious consequences can occur. One of them is a swollen tongue, which causes difficulty breathing.
Treatment should be aimed at eliminating the underlying disease that caused glossitis or eliminating the damage. The diet should not contain irritating foods. It is also necessary to rinse the mouth with furatsilin, a weak solution of iodine, potassium permanganate or chlorhexidine. The use of physical therapy and acupuncture may be prescribed by a doctor.
If there are ulcers or erosions, it is necessary to remove the plaque that appears systematically. This is done with a cotton swab, then the tongue needs to be covered with an antiseptic solution. Ointment and jelly containing applications with solcoseryl can speed up healing. Sometimes the removal of keratinized areas is performed during surgery.
Decreased calcium
A drop in calcium levels in the blood can cause numbness or a tingling sensation in the tongue. This is a symptom of many diseases, the less dangerous of which is vitamin deficiency, and the more dangerous of which is cirrhosis of the liver.
The causes of this disease are insufficient generation of hormones by the parathyroid glands. These hormones help control calcium levels. Numbness or a tingling sensation indicates the need to visit a doctor to check your thyroid hormone levels.
Vitamin deficiency
The body needs vitamin B12 for the functioning of the nervous system. A decrease in its level contributes to the fact that the nervous system may fail.
The appearance of dry mouth is a symptom that the body lacks vitamin A. The epithelium becomes keratinized, cracks take a long time to heal, and there is pain.
Sclerosis and stroke
These diseases can cause a tingling sensation in the i
heame.ru
Numbness of the tip of the tongue in late pregnancy
| Headache | Sensory disorders | Features of the blood test | Additional examinations | |
| Migraine | Appears an hour after numbness | My hands are going numb | No changes | Taking triptans, monitoring results |
| Bell's palsy | Doesn't appear | Half of the face loses sensitivity | In rare cases, markers of inflammation are present | Perform MRI, CT |
| Stroke | Long-lasting, intense, appears before numbness | Most often, sensitivity is impaired in one half of the body | The parameters of the coagulation system change. Possible increase in platelet count | Perform MRI, CT |
| Hypoglycemia | Doesn't appear | Diabetic polyneuropathy | Blood glucose levels drop to 3 mmol/l or less | MRI, CT to rule out insulinoma |
| Anemia (B12 deficiency) | Doesn't appear | Peripheral polyneuropathy | The content of hemoglobin and red blood cells decreases, in some cases leukopenia and thrombopenia | A bone marrow puncture is performed |
| Anxiety disorders | Does not manifest itself, dizziness bothers me | Possible short-term disturbances in the sensitivity of parts of the body associated with the stress experienced | No changes | Schedule a consultation with a psychotherapist and conduct tests to determine anxiety and depression |
| Angioedema | Does not appear if the swelling is extensive, discomfort in the head area is possible | Loss of sensitivity in the area of edema | Inflammatory markers may appear | If allergic edema develops, tests are performed with allergens; if it is hereditary, an examination for defects in the complement system is performed. |
| Formations benign and malignant | Pain at the site of the tumor or diffuse pain if the meningeal membrane is involved in the process. It is poorly controlled with analgesics. | Not with all formations, sometimes | If the process is malignant, all blood counts decrease; if it is benign, there are no changes. | CT, MRI of neck, head, brain |
Why your tongue tingles, why your lips go numb - the reasons for this can be determined by a doctor after a comprehensive examination. A blood test, MRI, and CT Dopplerography of blood vessels will help to specifically determine why the lower lip is numb and the reasons for the numbness of the tongue. The treatment regimen depends on the underlying disease.
All diseases in which the tongue goes numb, numbness of the lower lip and chin manifests itself, are divided into several groups.
- Reaction to medications. For some medications this is a side effect, and some cause nerve damage.
- Menopause. Very often, women during menopause experience damage to the mucous membranes. The mucous membrane becomes thin and sensitive. Plus, functional changes in the thyroid gland also occur.
- Anemia. As a result of a lack of vitamin B12 and iron. Blood tests show decreased red blood cells, hemoglobin, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia. Bone marrow puncture is recommended.
- Glossalgia. A fairly common disease of the oral mucosa associated with sensory neuroses. Manifested by tingling and numbness.
- An allergic reaction to toothpaste, chewing gum, mouthwash, air freshener, and anything that has any contact with the tongue.
- Reflux esophagitis. Reverse reflux of gastric contents, which can also lead to numbness.
- Various types of injuries in the facial area, dental procedures (especially when removing “wisdom teeth”, after anesthesia, which is required for this procedure, numbness can torment the patient for up to six months), maxillofacial operations, jaw fractures. The result is damage to nerve endings.
- After drinking very cold or hot liquid. Or in case of accidental use of acid or alkali.
- Nervous, depressed state. Sleep disturbance, increased irritability, dizziness. There will be no changes in the blood. Consultation with a psychotherapist is required.
- Functional disorders in pregnant women. More often observed in the third trimester. This occurs against a background of high blood pressure and swelling.
- Features in the structure of the skull that cause compression of the glossopharyngeal nerve.
- diabetes mellitus (dry mucous membranes, development of neuropathy - cause of numbness);
- stroke (the brain is affected; speech impairment, long-term headache with accompanying numbness of half the body, drooping corner of the mouth; lack of coordination; consciousness is depressed; tests show a violation of the coagulation system; CT, MRI are recommended);
— hypothyroidism (lack of thyroid hormones, consultation with an endocrinologist);
- Lyme disease (as a result of a tick bite);
— multiple sclerosis (all parts of the body go numb, the tongue is no exception);
- cerebral aneurysm;
- syphilis;
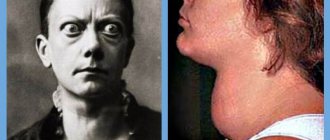
- Bell's palsy (the whole face goes numb);
- migraine;
- sarcoidosis;
- preeclampsia;
- spinal cord cancer (local pain, decrease in all blood counts);
- brain tumor (compression of various parts of the brain - the cause of numbness).
1. Lips go numb for the following reasons: Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine. As a result of compression of the spinal cord, blood circulation is disrupted and thereby the nutrition of the organs is disrupted. Numbness of the lips appears.
2. Neuritis of the facial nerve. Inflammation of the facial nerve leads to disruption of impulse transmission to the facial muscles and can be complicated by facial paralysis. You urgently need to consult a doctor to prevent such a dangerous picture.
3. Lack of B vitamin. Lack of this vitamin leads to disorders of the nervous system. A large amount of this vitamin is found in: bread, nuts, bran, liver, meat, potatoes.
4. High or very low blood pressure. Then not only the lips go numb, but also the upper and lower limbs. Life threatening. You urgently need to call an ambulance.
5. Diabetes mellitus. One of its symptoms is numbness of the lips, clammy sweat, weakness, and trembling hands. By adjusting your blood glucose levels, the numbness will go away. You can eat honey, sugar, candy. If attacks recur frequently, insulin dosage should be discussed with your doctor.
6. Allergy to the use of a new medicine. Quincke's edema causes swelling of parts of the body, including the lips. The cause often remains unclear. Edema is a terrible swelling of the larynx; difficulty breathing can lead to asphyxia. If an attack has occurred in your life, then you should always carry antihistamines and glucocorticosteroids with you to relieve this condition.
7. Migraine. As a consequence of nervous breakdowns and constant worries, it leads to disruption of the nervous system. The headache occurs half an hour after numbness, then the limbs go numb. Numbness is a kind of aura before a headache. There are no significant changes in the analyses. Increased levels of potassium and magnesium, reduced stress and good sleep will help. Avoid foods that trigger migraines: wine, cheese, sweets.
8. Disease of teeth and gums. If before the numbness of the lips there was pain in the teeth or gums, then, most likely, this is due to problems in the teeth. You need to see a dentist.
9. Multiple sclerosis. It is with numbness that this disease begins. Nervous tissue cells in the body begin to be affected. Only a neurologist can help in this case.
10. Shingles. Its typical onset is itching, redness and numbness. If there is still a burning sensation in the cheek area, then this is one hundred percent shingles.
11. Bell's palsy. It affects the entire face, but the lips and eyebrows are affected first. The disease is preceded by some viral diseases (ARVI, simple herpes virus). Tingling and numbness are characteristic of this disease. May go away on its own. If treated, a course of antibiotics and antiviral drugs is prescribed.
12. Infectious disease of various etiologies, which affects the nerves. Very often, complications after meningitis or herpes are nerve damage with the leading syndrome being numbness.
As we found out, there are quite a few reasons for numbness of the tongue and lips. After this article, you can already decide which specialist you need to contact. If you cannot associate your numbness, which torments you periodically, with any of these diseases, then you need to contact a neurologist. And you shouldn’t delay this.
Do not worry if numbness occurs as a result of prolonged exposure to very cold, after anesthesia, or lying on the lip for a long time. And at the same time there are no more complaints, and there never were.
What is the cause of unpleasant sensations in the tongue? What causes tongue tingling?
The causes of tongue pain can be very diverse, ranging from mechanical damage to the presence of cancer. Most often, pain occurs for the following reasons:
The most common cause of pain on the tip or sides of the tongue is mechanical damage. Most often, the patient receives such injuries during eating, and they include biting, burns, scratches and cuts. The tongue can also be injured by chipped tooth enamel, an uncomfortable denture, or an unscrupulously installed filling with sharp edges. Constant, even minor injury can lead to long-term pain.
Inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity are dangerous and painful. If a patient has a sore tongue, throat, palate, and it hurts to swallow, the doctor has every reason to suspect the presence of inflammatory processes in the oral cavity. They can be caused by viral diseases of the nasopharynx, as a result of which the patient's sublingual lymph nodes become enlarged. In this case, the patient complains of pain when swallowing at the base of the tongue. With such symptoms, you should consult an otolaryngologist, since the cause of pain in the tongue may be acute purulent tonsillitis, which requires immediate medical treatment.
Another cause of pain is viral stomatitis. It affects both the surface of the tongue and the entire mucous membrane of the oral cavity. The disease is painful, causes difficulty in eating, and causes discomfort to the patient.
Often the causes of pain in the tongue lie in the presence of an allergic reaction in the patient. This could be an allergy to food or medications. Typically, the patient complains of tongue pain after eating, especially after kiwi, pineapple, seeds, drinking alcohol, and also after smoking a pipe and cigarettes.
Most often, an allergic reaction is expressed in the form of stomatitis or fungal diseases. Consumption of spicy food and alcohol only aggravates the painful condition. Discontinuation of those drugs and products that cause an allergic reaction leads to the disappearance of allergy symptoms.
Neuralgic diseases usually significantly complicate correct diagnosis; in this case, it is difficult to determine why the patient’s tongue hurts. The most common neuralgic disease is glossalgia. It occurs as a result of malfunctions of the endocrine system, as a result of neurogenic disorders, and also as a reaction to mental trauma or severe stress. With glossalgia, partial or complete numbness of the tongue, tingling, burning, and rapid fatigue of the tongue when speaking are observed. Often with glossalgia, the lips also hurt; the patient complains that he has a headache and a numb tongue.
Another reason for the appearance of pain in the tongue is the presence of hidden diseases of other organs and systems in the patient. The tongue reacts sharply to any changes in the state of the body, and the result of infectious diseases is
heame.ru
Migraine with aura
People who suffer from migraines often experience changes in their sense of smell, vision, and hearing before an attack. Sometimes these are only short flashes - the appearance of lines before the eyes, numbness, tingling of the face. The aura appears one hour before the attack and disappears completely after the condition has returned to normal.
Triptans are used to treat migraines, but the form of the drug and its dosage must be selected by a doctor. Those who often have migraines should reconsider their diet and avoid those foods that can trigger headache attacks. This includes cheese, chocolate, wine, canned food, etc. It is also important to prevent stressful situations as much as possible.
Classification of pain
Based on localization, the following types of pain are distinguished.
- On the tip of the tongue
.
What to do if your tongue starts to hurt, what caused it?
Pain at the tip occurs for a number of reasons:
- mechanical damage
- biting while chewing food, burns from food that is too hot. As a result, the papillae or the tongue itself are injured. The patient feels severe pain at the site of injury. In some cases, problems arise when eating. Such mini-injuries heal on their own; - glossalgia
. This is a complex disease that is difficult to treat. It manifests itself as soreness at the tip, and in some cases, at the sides of the organ. The nature of the pain is a burning sensation, like after a thermal burn. As the disease develops, painful manifestations can spread to other organs. Patients report pain in the tongue, gums, lips, and cheeks. If any symptom occurs, it is recommended to consult a doctor; - glossitis.
This disease is infectious in nature. In this case, it is the tip that is affected, which is associated with an increased likelihood of injury. It manifests itself as an inflammatory process at the site of damage and infection; - stomatitis
. This disease is manifested by the spread of painful ulcers over the surface of the tongue. Any touch to them results in pronounced pain; - allergic reaction
.
- Under the tongue at the base
.
Another type is the presence of pain at the base of the tongue. Painful sensations do not allow you to talk or eat normally, which affects the general emotional state of a person.
Why does the root, base of the tongue hurt when swallowing? The reasons can be very different - from allergies to serious inflammatory processes.
The following are distinguished:
- glossalgia.
Depending on the constitutional characteristics of the tongue, the pain syndrome in this disease can be localized not only at the tip of the tongue, but also at its base. More detailed symptoms are described above; - allergic reactions
; - diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Prolonged pain in the area of the base of the tongue can result from various types of diseases of this organ;
- vitamin deficiency
. It manifests itself as a painful tingling at the root of the tongue; - phlegmon, abscess.
These are purulent diseases of inflammatory nature. They manifest as acute pain in the base of the tongue, putrid breath, and increased salivation. It is also difficult for the patient to close his mouth. Subsequently, the tongue swells, speech becomes slurred, and breathing becomes difficult. Both diseases are dangerous, so if you have at least one sign, you need to consult a doctor.
- On the sides of the tongue
.
Complaints of pain on the sides of the tongue are provoked by all of the above reasons - injury, glossalgia, rashes and stomatitis.
What to do if your tongue hurts
However, there are several less common factors that can provoke the appearance of painful sensations:
- poorly adjusted dentures
, the sharp edges of which rub and injure the mucous membrane; - regular smoking
; - neuralgia.
Differential diagnosis of glossalgia
In order to accurately establish the cause of numbness in the tip of the tongue, it is necessary to undergo a certain study.
First of all, the patient should contact a general practitioner, who will collect a detailed history and prescribe the first studies, including a general blood test. After this, as a rule, a comprehensive examination of the cardiovascular system is prescribed.
In addition, magnetic resonance imaging and ultrasound examinations can be used to diagnose pathological conditions associated with tongue numbness.
In order to get a complete picture of the patient’s health status, the specialist must assess the patient’s blood sugar level, as well as the performance of the thyroid gland.
So, what to do: does the tip of your tongue go numb?
The diagnosis is made based on the patient's history and complaints. Glossalgia must be differentiated from other organic diseases of the tongue. The main difference between glossalgia and other diseases is the absence of visible changes and the discrepancy between pain sensations and the degree of impact.
It is necessary to differentiate glossalgia from pathological bite syndrome and from incipient osteochondrosis of the cervical spine. Differentiation is carried out through an in-depth medical examination.
The difference between neuralgia is that the pain in this case is localized at the site of innervation of a particular nerve. With glossalgia, the pain is vague; this is due to inorganic damage to the vagus nerve.
Pain in the presence of neuritis is most often one-sided, the sensitivity of the tongue in the affected area is significantly reduced or completely absent. With neuritis, the pain intensifies while eating; with glossitis, the opposite happens.
Pathologies affecting sensitivity
When the tongue or other organ becomes numb, doctors say that the patient has paresthesia. Simple causes of deterioration in sensitivity include mechanical damage. As a result, the ability to transmit impulses deteriorates for a short time, and wicking appears. In case of problems with the nervous system, paresthesia manifests itself without characteristic visual disturbances; this form of the disease is chronic.
Problems with the conduction of nerve impulses occur after the following diseases:
- Stroke.
- Infectious disorders.
- Neurodegenerative defects.
- Neoplasms.
- Autoimmune disorders.
- Results of drinking alcohol.
- Diabetes.
- Metabolic problems.
- Chickenpox.
- There are few useful microelements in the body.
- Osteochondrosis.
In this condition, deterioration in the sensitivity of the tongue may not be the only symptom. When the nervous system is damaged, numbness and tingling occur along the peripheral nerves in various organs.
Deterioration of sensitivity is not an independent disease. Numbness of the tip of the tongue is a symptom that occurs as a result of decreased conductivity of nerve fibers due to pathological factors. This process can increase gradually or occur immediately. Sensitivity worsens only at the tip of the tongue, near the frenulum or on the sides.
Idiopathic facial neuropathy (Bell's palsy)
In rare cases (approximately 1-2%), after a medical examination it is not possible to determine the causes of numbness of the lips. Often in this case, people complain of complete paralysis of the face or that half of the face is numb. The doctor will tell you what to do in this case. Idiopathic neuropathy often develops as a consequence of colds, flu, and sometimes the herpes simplex virus.
In most cases, patients with Bell's palsy recover without additional treatment, and there are no consequences for the nerves of the face.
If necessary, treatment with corticosteroid hormones is carried out in a hospital setting, which are combined with antiviral therapy for 1-2 weeks.
It is also advisable to practice gymnastic exercises for the facial muscles. Recovery can take a long time, up to one year.
Relapses of the disease are rare. But if they occur, it is necessary to additionally examine the brain in order to identify or exclude formations.
Treatment methods for tongue pain
If you have pain in your tongue, you should see a specialist. Try to describe the symptoms in as much detail as possible in order to establish the true cause of the disease. The doctor will then determine the appropriate treatment.
If it is determined that the cause of the pain is an injury, the wound will need time to heal. Sometimes pain appears after piercing, i.e. piercing In this case, it is recommended to carry out care measures and maintain oral hygiene.
A sore throat and a white tongue can be symptoms of a sore throat. Inflamed tonsils and lymph nodes also cause pain. In this case, you need to go to a therapist who will determine the appropriate treatment. As inflammation and redness decrease, the pain in the tongue will subside.
Painful sensations and the presence of a cheesy coating indicate candidal stomatitis. Treatment must be determined by a doctor.
When anesthetic drugs are administered during tooth extraction, swelling of the gums and pain in the tongue may occur. This is especially true for the posterior molars. However, the pain goes away on its own a few days after the procedure.
How to find out what caused the pain in the tongue? My tongue started to hurt - what are the causes of pain? Why does my tongue hurt - what is the treatment method? What to do if your tongue starts to hurt What to do if your tongue starts to hurt, what caused it?
Despite the fact that the tongue is a very important organ in the human body, people usually think about it only when it starts to hurt. Most often, pain appears on the side of the tongue, and if this happens, then you cannot ignore the problem. With such pain you need to contact a dentist, otolaryngologist or therapist.
There are many reasons for pain in the tongue, they are very diverse and range from ordinary mechanical damage to the tissue of the tongue to cancer.
Hidden diseases of the body can also cause pain, because this organ reacts acutely and sensitively to any changes in health. Only a specialist can determine the true cause of the problem.
Mechanical damage
Injury to the tongue is the most common cause of pain in the tongue.
For example, banal biting of the tongue while eating or falling, and the person does not always notice it. But over time, this damage responds with sharp pain.
People with epilepsy often experience tongue pain because they bite it during seizures.
The tongue can also be damaged by a piece of tooth enamel, a poorly ground filling, or an incorrect denture. The tongue may also hurt if it is burned by hot drink or food.
Inflammation
Pain in the tongue may indicate inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity, which are very dangerous for humans. As a rule, not only the patient’s tongue hurts, but also the palate and throat, and it hurts to swallow.
The tissues of the tongue can also become inflamed - this disease is called glossitis and is caused by viruses or bacteria. Inflammation of the tissues of the tongue can be caused by mechanical damage or a chemical or thermal burn.
Glossitis is divided into the following types:
- ulcerative
- not only the tongue hurts, but also the entire oral cavity, which is covered with small bleeding ulcers, and the gums swell; - catarrhal
- the tongue hurts on the side, the sense of taste of food disappears, salivation increases. such glossitis is caused by oral candidiasis, stomatitis, burns and injuries; - purulent-phlegmous
- the most severe type of glossitis with unbearable pain, high body temperature and vomiting.
Nasopharyngeal disease
Viral and bacterial diseases of the nasopharynx are another reason why the tongue hurts at the base.
The doctor can determine that the infection is coming into the oral cavity from the nasopharynx by the enlarged sublingual lymph nodes.
Pharyngitis (inflammation of the pharynx) and laryngitis (inflammation of the larynx) are often accompanied by pain at the base of the tongue.
Stomatitis
A disease in which the tongue not only hurts, but also stings, is stomatitis.
Sometimes it affects not only the surface of the tongue, but also the entire mucous membrane of the oral cavity.
Stomatitis is an unpleasant medical problem, accompanied by severe pain, causing serious discomfort to the patient and interfering with normal food intake.
Photo: Stomatitis - herpetic (left) and aphthous (right)
Stomatitis can be bacterial, viral and candidal; in the latter case, the oral cavity is covered with a white cheesy coating.
Inflammation of the salivary gland
The salivary gland located next to the tongue can become clogged and inflamed, leading to pain in and under the tongue. Inflammation of the salivary gland is accompanied by general soreness of the entire oral cavity and a constant feeling of discomfort.
Neuralgia
Neuralgic problems make diagnosis very difficult because the causes are difficult to detect.
With neuralgia, pain can be both severe and insignificant, both constant and occurring periodically, which further complicates the determination of the reasons for its occurrence.
The most common neuralgic problem that causes pain in the tongue is glossalgia. This disease occurs as a result of endocrine system failures, neurogenic disorders, mental trauma or severe stress.
Glossalgia is characterized by:
- complete or partial numbness of the tongue,
- burning,
- tingling,
- rapid fatigue of the tongue when speaking.
Sometimes not only the tongue hurts, but also the lips, and there is a headache.
Glossalgia mainly occurs in women between 25 and 30 years of age. You need to start fighting the disease as early and quickly as possible, because it is difficult to treat.
But sometimes pain in the tongue is caused by simple irritation of the nerves in it. This can occur due to damage to the nervous system, nerve damage during surgical interventions in the larynx and organs of the neck and mouth.
Irritation of the nerves can also be associated with pathologies of organs adjacent to the tongue, most often the teeth, i.e. due to dental problems. Neuralgia of the lower branch of the trigeminal nerve also causes severe pain in the tongue.
Video: what a neuropathologist says about this
Allergy
A common cause of pain is allergic reactions to foods or medications (mainly antibiotics).
Eliminating allergenic foods, the most common of which are pineapple, kiwi, seeds, and alcohol solve the problem of tongue pain. It's the same with medications.
Hot spices and smoking only aggravate the allergic reaction, so you should avoid them too. Allergies in the mouth can manifest themselves in the form of fungal infections or stomatitis.
Video: what is important to know about allergies?
Oncology
The most serious problem that can cause tongue pain is cancer.
In this case, complaints are received that the tongue hurts from the inside.
Unfortunately, in the early stages of oncology there are no unpleasant sensations. Pain indicates that the tumor is already at an advanced stage.
Oncological diseases of the tongue are treated by an oncologist, to whom the patient is immediately sent from the office of a dentist, therapist or otolaryngologist.
Video: Oral cancer
Treatment of glossalgia
If numbness of the lips and tongue is observed with cervical osteochondrosis, it is treated with medications, and also includes massage and physical therapy. Regarding this condition with neuritis, the therapeutic course includes: glucocorticoids, vasodilators, vitamins. When such a phenomenon is observed in viral diseases, treatment of the underlying pathology is mandatory.
Multiple sclerosis, which causes numbness of the lips and tongue, is treated with hormone therapy, immunomodulators, and some other drugs. This therapy allows you to cope with this disease and remove numbness.
Allergies can also cause the above condition. In this case, the allergen is determined; for the most part, food products and some medications can cause an allergic reaction. In parallel with this, antihistamines are prescribed.
Numbness of the tongue and lips at first glance seems like a minor problem. But, having found out why this can happen, and if it concerns certain diseases, you should seek medical help, where they will help make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe the correct treatment.
Loss of tongue sensitivity is not an independent disease, but a symptom accompanying the underlying pathology. Only after identifying the reason why the tongue is numb will the specialist prescribe treatment, which will be aimed at eliminating the underlying disease or irritating factor.
In cases where paresthesia is caused by osteochondrosis, the following are indicated:
- physiotherapy;
- massage manipulations;
- physiotherapy;
- taking painkillers and drugs that enhance bone tissue regeneration.
Injuries that cause the feeling that the tip of the tongue is numb are treated with antiseptic rinses and dental gels. Allergic reactions that reduce the sensitivity of the organ are eliminated with antihistamines.
Oncological diseases require surgical intervention coupled with drug therapy; at the initial stage of the disease, endoscopy can be done. In case of laryngeal cancer, the affected tissue is removed; in case of pharyngeal cancer, partial removal is performed, followed by restoration using plastic surgery.
Trigeminal neuralgia can be treated surgically, but destruction of the nerve is often required. Radiosurgery, a minimally invasive (bloodless) operation, is sometimes used.
Numbness caused by diabetes mellitus is eliminated after a course of treatment of the underlying disease. Injections or tablets are prescribed to normalize insulin levels, which eliminates dry mouth, thirst and loss of sensitivity.
Depending on the cause of numbness in the tip, root, or sides of the tongue, treatment may include alternative medicine methods. Rinses and compresses can significantly improve the condition and speed up the restoration of sensitivity.
Common traditional medicine recipes used for diseases of the oral cavity:
- A spoonful of soda and 4 drops of iodine are dissolved in a glass of warm water. Rinsing is done daily, morning and evening.
- If the cause of numbness in the mouth is a disorder of the nervous system, the use of chamomile and sage in therapy is effective. In addition to pronounced anti-inflammatory properties, plants have a calming effect. Two tablespoons of dry herb are brewed with a glass of boiling water, the decoction is infused for 15 minutes. The resulting infusion is used for daily rinsing of the mouth and for oral administration: take 1 tablespoon.
- A tablespoon of St. John's wort and the same amount of celandine are poured into a glass of boiling water and infused for about 30 minutes. The resulting infusion should be used to rinse your mouth morning and evening.
- You can fight lost sensitivity of the tongue with the help of garlic. To do this, take a garlic clove and roll it in your mouth. The procedure should be done as often as possible. After using garlic, apply a compress with sea buckthorn oil to the tongue, which will prevent possible irritation of the mucous membrane.
- Dried femoral grass is poured with a glass of water, brought to a boil, and then boiled for about 5 minutes. The broth must be filtered and cooled. Rinsing is done twice a day, after which 1 tablespoon of infusion is taken orally.
Numbness of the tongue is a sign of a serious pathology, and not a separate disease. It is important to determine the root cause that caused the loss of organ sensitivity, and only a doctor can do this. Therefore, it is necessary to contact a therapist as soon as possible, who, after carrying out the necessary diagnostic measures, will redirect the patient to the right specialist. Timely identification of the cause of numbness and timely treatment will help prevent the development of the underlying disease and possible complications.
Treatment of tongue paresthesia is not aimed at eliminating the symptoms, but at the very reason due to which they arose. Therefore, the treatment of numbness in the tip of the tongue directly depends on the diagnosis that was made by a specialist when studying the causes of this condition.
For example, with vegetative-vascular dystonia, treatment is aimed at improving the patient’s cerebral circulation. In addition, he may be prescribed vitamin complexes that will strengthen the walls of blood vessels and help normalize the functioning of nerve endings.
When the tip of the tongue stings and goes numb due to osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, the patient is usually prescribed massage and certain physical procedures.
Laryngeal cancer is another cause of tongue paresthesia. This disease is most common among heavy smokers. The treatment of this disease is determined by the oncologist, and most often it consists of surgery.
When the nerves in the jaw and face of a patient suffering from paresthesia of the tongue are affected, both medication treatment and surgical and physiotherapeutic methods (pulse currents, acupuncture, etc.) are used.
It is important to find out in advance what diseases cause the tip of the tongue to go numb.
Diabetes mellitus leads to electrolyte imbalance, so the oral cavity often dries out, which provokes numbness. In advanced stages, small nerve fibers in the mouth can become damaged (this is called diabetic neuropathy). It is imperative to change your diet and monitor your blood glucose levels. Folk remedies will also be effective: linden tea, walnut infusion, burdock root juice, bay leaf infusion.
In the treatment of paresthesia of the tongue, traditional medicine is actively used, for example, you can chew a small clove of garlic several times a day. Medicinal herbs, infusions and decoctions of which are used to rinse the mouth, are very helpful in relieving the symptoms of tongue numbness. Such herbs include sage, celandine, chamomile, oak bark, etc.
In addition, many people with this disorder engage in exercise to help relax the muscles in the cervical spine.
Homeopathic medicines that help get rid of the symptoms of numbness of the tip of the tongue include Nervohel, Stonziana Carbonica, Gelarium Hypericum and others.
Despite the wide range of medications, a patient suffering from such an illness should first consult a doctor and not self-medicate.
Here's what to do when the tip of your tongue goes numb. We examined the causes and methods of treatment in detail.
How to treat glossalgia? Treatment begins with identifying the causes that led to the onset of the disease. If possible, the causes are eliminated or reduced.
Symptomatic treatment begins with sanitation of the oral cavity. If necessary, dentures and orthodontic structures are replaced, dental treatment is performed and other traumatic factors that stimulate the appearance and intensification of glossalgia symptoms are eliminated. Treatment continues with examination of the patient by multidisciplinary specialists: neurologist, gastroenterologist, endocrinologist, etc. Observation by a psychologist or psychotherapist is also indicated.
To normalize homeostasis and have a beneficial effect on the central and peripheral nervous system, bromine preparations, valerian in various forms, and mild tranquilizers are prescribed. A trimecaine blockade of the lingual nerve and a cycle of injections of B vitamins are carried out. A trimecaine blockade can completely restore the impaired functioning of the nerve, in which case glossitis will be cured.
To relieve pain and other unpleasant sensations, applications and baths with local anesthetic solutions (trimecaine solution, citral solution, etc.) are used. Physiotherapeutic and reflexology procedures are prescribed.
Sialadenitis - inflammation of the salivary glands Sialadenitis is a disease in which the salivary glands, most often the submandibular ones, become inflamed. There are two forms of sialadenitis: acute and chronic
What causes tongue tingling? — Cardiology news — Serdechno.ru
A tongue tingling sensation, or paresthesia, can be caused by a variety of factors, including glossalgia, low blood calcium, low parathyroid hormone levels, vitamin deficiency, facial nerve damage from dental procedures, multiple sclerosis, or stroke. Numbness of the tongue or tingling sensation is the result of injury to the body's nervous system. Tongue paresthesia usually affects the tongue, but can spread to the rest of the mouth, lips and jaw.
One of the most common causes of tongue tingling is glossalgia . Glossalgia is accompanied by dry mouth, discomfort, and the presence of a metallic taste in the mouth, in addition to a "burning tongue" sensation. The disease has a number of causes, including hormonal changes, diabetes, fungal infections, reflux disease, allergies, and anxiety.
Hypocalcemia, or low blood calcium, often leads to parasthesia.
When calcium levels in the blood drop significantly, it often results in a numb or tingling tongue. This condition can be the result of a benign disease, such as a vitamin deficiency, or a serious disease, such as cirrhosis of the liver.
Hypoparathyroidism occurs when the parathyroid glands stop producing enough hormones. These hormones control calcium levels and their deficiency leads to hypocalcemia. A numb or tingling tongue may be a sign that you should have your thyroid hormone levels checked.
Another cause of a tingling tongue may be a deficiency of vitamin B12.
Vitamin B12 helps the nervous system function, and if vitamin levels are low, it can throw the nervous system out of balance. Considering the fact that the tongue is a hotbed of nerve endings, therefore, most often the tongue first experiences symptoms of B12 deficiency.
Facial nerve damage can be an unwanted side effect of various dental procedures. The lingual nerve can become damaged during a root canal or wisdom tooth extraction. Prolonged effects of novocaine or an allergy to novocaine can also cause a tingling sensation in the tongue.
The cause of a tingling tongue may be multiple sclerosis or a stroke. The nervous system stops functioning properly and sends warning signals to the rest of the body, and the person may experience symptoms of these diseases on the tongue. In general, however, multiple sclerosis and stroke are accompanied by other additional symptoms, such as weakness in the limbs, vision problems, tremors and dizziness. Headache, speech problems, vision problems, and weakness in the arms and legs are additional symptoms of a stroke.
Source: wisegeek.com
Read further:
www.serdechno.ru
Hypoglycemia
People suffering from diabetes mellitus often feel that their upper lip is numb due to poor insulin use. This symptom develops as a result of a decrease in blood glucose levels to 3 mmol/l or less. Symptoms of hypoglycemia may include the following:
- the appearance of cold and sticky sweat;
- numbness of parts of the face and body;
- trembling in hands;
- sharp feeling of hunger.
When glucose levels drop, a person feels unwell, but it is not difficult to stop this phenomenon. If signs of hypoglycemia appear, you should measure your glucose level by immediately eating about 20 g of sugar, honey, caramel or other foods that increase glucose levels. Foods with slow-release carbohydrates are not suitable.
Treatment
The diagnosis will allow us to find out the cause, and only after that the doctor will decide how to treat the disease.
Conventionally, treatment methods can be divided into official, prescribed by a doctor, and traditional, not recognized by medicine.
Medication
Medicines are mainly prescribed if the cause is stomatitis.
In this case, the patient is prescribed a course of antibiotics, and the oral cavity is additionally treated with antiseptics, for example, Chlorhexidine or Miramistin.
Other problems can be solved either by eliminating the source of the problem or by treating a specific disease. Only a doctor can prescribe antibiotics and antiseptics.
Folk remedies
In folk medicine, measures to reduce pain in the tongue include, first of all, remedies for stomatitis, which is a common cause of pain in the tongue.
So, for treatment, unofficial medicine advises rinsing your mouth with diluted alcohol tincture of propolis, soda solution or decoctions of medicinal herbs.
Decoctions of chamomile, common thyme (thyme), oak bark, and sage are effective.
Medications
Medicines that can help treat numbness in the tip of the tongue include:
- Vitamin complexes that contain vitamin B12, if this disorder occurs as a result of hypovitaminosis.
- Carbamazepine is a drug used in the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia.
- "Ambene" is a complex therapy for osteochondrosis, which includes substances such as phenylbutazone and cyanocobalamin.
- "Cavinton" is a medicine that is prescribed for the complex treatment of various vegetative-vascular disorders. This drug dilates the blood vessels of the brain, which promotes increased nutrition of the cells of this organ and normalizes the functioning of the central nervous system.
Non-hazardous causes of tongue numbness
The tongue is an extremely sensitive organ, and this applies not only to taste zones, but also to a pronounced reaction to tactile sensations. Numbness of the organ is immediately noted by the person. In most cases, if the phenomenon is temporary and does not recur with a certain frequency, its cause is not dangerous . Possible non-pathological sources of numbness include:
- use of medications with anesthetics in the oral cavity (Kameton throat spray, TeraFlu with lidocaine, Hexoral lozenges with benzocan, etc.). Drugs of this kind block the transmission of pain impulses to the brain, which provides an analgesic effect, and are often used for inflammatory diseases of the throat. During processing, the components also enter the tongue, temporarily depriving it of sensitivity and causing numbness;
- carrying out dental procedures. When an anesthetic is administered or during the process of tooth extraction, the nerves innervating (supplying nerve fibers) the mucous membrane of the tongue may be affected;
When using anesthesia during dental procedures, the nerves innervating the tongue may be affected, which will lead to temporary loss of sensitivity of the organ.
- increased blood pressure, swelling during pregnancy (most often in the 4th month). This is a temporary condition, most often localized at the tip of the tongue, associated with the body’s adaptation to changed working conditions;
- reaction to taking antibiotics or other medications. In this case, the sensation occurs on a temporary basis (lasts on average up to 2-3 days) and is usually not very pronounced, but you should consult a doctor about adjusting the course of treatment and selecting another drug;
- the effect of high or low temperature on the mucous membrane of the organ. Burns or cold exposure cause short-term loss of sensation.
Mental disorders
Why the tip of the tongue goes numb, and the causes of numbness in the lips may be associated with mental disorders. This symptom is combined with increased heartbeat, a feeling of lack of air, which makes the person feel anxious. If the tip of the tongue goes numb, what does this mean, doctors usually diagnose it by determining organic pathology.
If no such cause of numbness of the tip of the tongue and other symptoms are found, then the patient is diagnosed with “vegetative-vascular dystonia”. However, in fact, this condition is not a disease, but only a set of symptoms that are associated with psychological problems. Very often, vegetative-vascular dystonia is a sign of a depressive state or a state of increased anxiety. That is why a psychotherapist should treat such a symptom.
If we are talking about autonomic disorders of a psychogenic nature, the following symptoms may appear:
- tremor;
- rapid heartbeat;
- the face, tip of the tongue, palate in the mouth, limbs go numb;
- increased sweating;
- causeless discomfort in various organs;
- strong concern for health on the part of the patient.
In this case, the doctor can determine why the tip of a person’s tongue is numb and make the correct diagnosis by first ruling out all possible diseases with similar symptoms. For the purpose of treatment, psychotherapy sessions and antidepressants are prescribed.
Consequences of dental treatment
Often people have to have their wisdom teeth removed. The complexity of the removal procedure always depends on the location of the figure eights; it is difficult to perform and requires anesthesia.
Causes of numbness may be related to painkillers. Sensitivity is eliminated for some time. Numbness of the palate is also a consequence of dental procedures. This manifestation is not dangerous and is observed for six months, so patients feel discomfort for a long time.
Therapy is not required in such situations. But people need to accurately understand the reasons why the tongue goes numb and that this condition is caused by dental procedures, so as not to miss the appearance of complex pathologies.
Allergic manifestations
Many people suffer from hives. But sometimes this allergic manifestation is accompanied by damage to the deep layers of the skin. Then the patient may not only turn red in different areas of the skin, but also experience swelling and tingling. Sensitivity is lost. Sometimes a person suffering from allergies notices that his cheek becomes numb, his tongue becomes swollen, his limbs, genitals, and lips swell.
Angioedema is autoimmune in nature; this process is triggered when the body is exposed to an allergen. It is often difficult to determine which substance caused such a reaction. Therefore, a study is conducted of the patient’s body’s response to five different components:
- food and medicines;
- plant pollen, dust;
- insect bites and parenterally administered drugs;
- chronic diseases;
- infections.
If Quincke's edema has been confirmed. what to do is determined by the doctor. He prescribes hormonal, antihistamine, anti-inflammatory, and diuretics.
If the disease is not treated, its symptoms last for several days, after which they disappear along with discomfort. Every person who has been diagnosed with angioedema at least once should always have antihistamines, corticosteroids and Epinephrine readily available to stop the spread of edema to the larynx if necessary.
If a person's nose becomes numb, it may be due to an allergy to cold. True, the reasons why the tip of the nose goes numb may be associated with more serious problems. If the nose goes numb at the same time as the back of the head, this may indicate a stroke.
why does it start to hurt as if it was burned, how to treat it
The tongue is considered the strongest muscle in the body, and it is quite difficult to damage its muscle structures, but it is quite easy to injure the sensitive papillae. Hot liquids and spicy foods irritate the mucous membranes and cause a burning sensation, the tongue begins to hurt.
But it happens that burning pain at the tip of the organ, without any physical influence, indicates hidden health problems. Dentists refer to painful symptoms in the form of burning or numbness of the tongue as glossalgia.
The disease most often occurs in women over forty years of age and in people suffering from metabolic disorders. Only after finding out the true causes of the disease can treatment begin. The feeling of discomfort often goes away on its own. However, after a short period, the soreness again reminds itself, and, quite possibly, its appearance in another part of the tongue. In this case, consultation with a therapist and dentist is important, and a conversation with a psychologist would also be useful, since in some episodes glossalgia is provoked by nervous tension and depression.
Local factors causing burning pain on the tip of the tongue
There are many reasons that make a person experience a burning sensation in the main speaking organ. Familiarization with the patient’s medical history and a general blood test helps to diagnose the root cause of the tongue lesion; in the case of a complex disease, puncture.
The main causes of disturbance associated with the action of local irritants:
- Microtrauma of the speech organ
- Failure to comply with oral hygiene standards
- Allergy
- Infection of the mucous membrane with fungi and other pathogenic microorganisms
- Inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity
Mechanical injury to the tongue is often overlooked by people. While in a sleepy state, he may unnoticed bite his tongue due to malocclusion. In everyday life, microtraumas caused by various food elements are common - seeds, sucking candies, fish bones. The cause of a burning sensation on the tip of the tongue may be an incorrectly installed denture or if the dentist did not sharpen the filling well. As practice shows, this kind of injury does not lead to swelling and redness, but only exacerbates the sensitivity of damaged epithelial cells.
A minor reaction in the form of an exacerbation of allergies may occur due to components of toothpaste, certain types of medications or foods. Similar sensations are observed after eating sour fruits, such as pineapple and kiwi, as well as after smoking a cigarette or drinking alcohol.
If the tongue is irritated for several days, continues to hurt , and small ulcers and a strong coating are found on it, then there is a possibility of the onset of a severe inflammatory process. One of these diseases is stomatitis, which develops due to a weakening of local and general immune functions of the body, followed by the addition of a virus. Poor oral hygiene and prolonged use of antibacterial and hormonal drugs can lead to infection of the mucous membrane of the tongue.
Diseases that can cause tongue pain
Why does the tip of the tongue begin to hurt , as if it were burned? Why is the pain not accompanied by other visible symptoms? The answer to these questions may well be the existing pathologies of internal organs and body systems:
- Xerostomia. A disease in which the secretion of salivary fluid is impaired. Because of this, the mucous tissues are not sufficiently moisturized. A similar disorder in the oral cavity appears against the background of diabetes mellitus or severe dehydration.
- Tartar. Hard limescale deposits on the inside of the enamel, saturated with pathogenic bacteria, can be one of the causes of burning and redness of the tissues.
- Candidiasis. The trigger for this fungal disease is reduced immunity and lack of vitamins. The entire oral cavity begins to ache.
- Herpes. An infectious disease that most often affects the gums, palate and inner cheeks. Unfortunately, the tongue is also not immune from the insidious symptoms of herpes; the tip and root will hurt.
- Bruxism. Included in the list of possible factors for the appearance of tingling and pain on the tip of the tongue. Uncontrolled clenching of the upper and lower jaw, intense grinding of teeth, mainly during night sleep or under severe stress. The attacks are uncontrollable, so a person may accidentally bite his tongue, which will make itself felt by a burning sensation.
- Leukoplakia. Pathological changes in the epithelial tissues of the mucosa can provoke discomfort and make the tongue hurt for a long time.
- Neurosis. Chronic stress and trauma of a psychological nature are accompanied by dry mouth, and the consistency of saliva is disrupted. The tongue becomes more sensitive. Patients complain of burning and tingling on the tip of the tongue when talking or eating. The symptoms disappear on their own and become disturbing again with increased nervous tension.
- Cervical neuralgia. With structural and morphological disorders of the cervical nerves, the pain syndrome can radiate to the muscle fibers of the tongue. It is very difficult to diagnose a direct relationship, especially if damage to the vagus and glossopharyngeal nerves and osteochondrosis have not previously been detected.
- Hormonal imbalances. It is more often observed in women over forty years of age. During menopause, women experience hormonal changes and endocrine changes, which can cause glossalgia.
- Hypovitaminosis. A lack of vital vitamins and microelements, especially B vitamins and iron, causes pain along the entire perimeter of the tongue.
- Diabetes. A burning sensation on the tip of the tongue is caused by dry mucous membranes in the mouth.
- Liver dysfunction
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract
The main symptoms of glossalgia as a cause of pain in the tongue
Glossalgia is mainly manifested by a burning sensation on the tip of the tongue. Other variations of painful sensations are also possible, such as tingling or pain, as if the tongue is burned. With all this, the mucous membrane retains its integrity.
In the absence of injuries to the soft tissues of the oral cavity, the pathology has absolutely no external signs.
If this is indeed glossalgia, then its appearance will not be sudden , so many patients are not able to determine the moment of onset of the first symptoms, which makes it difficult to make a correct diagnosis. Symptoms appear suddenly and then disappear imperceptibly. The disease can accompany a person for many years without causing him any inconvenience due to mild symptoms. External irritating factors can provoke an exacerbation.
Along with pain on the tip of the tongue, the patient may complain of dry mouth. Dryness increases when a person is worried or overtired. The yellow-white color of the root of the tongue is characteristic of some gastrointestinal problems and liver problems. Some people experience excessive saliva secretion.
Impaired diction, difficulty pronouncing words and difficulty chewing food, although rare symptoms, significantly limit normal life activities.
The pain syndrome is varied. Aching pain, raw pain , pinching or sharp burning. Painful sensations tend to be localized in different parts of the tongue, and not just at the tip. Manifestations largely depend on the current state of the central nervous system and emotional situation. The pain often worsens after prolonged communication. Allergens can cause irritation of the tongue mucosa and cause swelling.
By and large, glossalgia is not recognized as a separate disease , and its symptoms are nothing more than a consequence of the underlying disease. Knowing the main signs of vascular, endocrine and diseases of other systems, it becomes easier to determine the exact reason why the tongue began to hurt.
First aid at home
For minor pain in the tongue that does not cause health concerns, you can treat it at home:
- If the patient has experienced stress and severe nervous tension, the tongue is sore and numb, then the patient can take motherwort tincture, drops of valerian or peony
- If the patient knows that he has infectious diseases of the oral cavity or tissue damage, then rinsing with any antiseptics will come to the rescue: furatsilin, sage and chamomile solution.
- When severe pain does not subside for a long time, you can get painkillers and tranquilizers (analgin, paracetamol, phenazepam, ketonal) from the medicine cabinet.
- The condition is alleviated by local anesthetics - trimecaine solution, anesthesin.
- In case of vitamin deficiency and anemia, only multivitamin complexes can relieve pain in the tongue.
What to do if your tongue goes numb due to anemia?
The tongue goes numb with anemia.
With anemia, the body lacks iron and vitamin B12 . In addition to numbness of the tongue, the following signs of anemia are characteristic :
- Numbness of fingers and toes
- Tongue and lips become less sensitive
- Pale skin of the face and body
- Reduced body temperature
- Loss of coordination
It is important to consult a doctor as soon as possible and cure vitamin deficiency.
Prevention
For prevention it is advisable to:
- stop smoking
- give up spicy, sour and salty foods, alcohol;
- start taking vitamins, especially vitamin A.
In order to prevent pain, it is better not to pierce this area. After all, during the piercing procedure, an infection can be introduced into the tongue and oral cavity.
Piercing damages nerve endings, of which there are a large number in the tongue, and the pain can become chronic.
It is necessary to pay attention to oral hygiene and brush your tongue along with your teeth. Diseases of the upper respiratory tract should not be neglected; you should contact a therapist or otolaryngologist for their treatment, since self-medication is fraught with the appearance of chronic diseases.
Diagnosis of pinching the tip of the tongue
To find out the cause of tongue tingling, a thorough examination of the oral cavity is necessary. If there are rashes on the organ of taste or gums, it is necessary to take a smear for genital infections. If the patient has dentures, an allergy test should be performed. If oral diseases are excluded, the patient should be referred to a general practitioner for further examination.
What can you feel?
How do patients usually characterize this condition? By the way, they describe “numbness” quite individually. Some people only notice a loss of sensitivity in the area of the tip of the tongue. For some, mild discomfort accompanied by a feeling of “freezing” of the organ.
Depending on the cause of the condition, the patient may completely lose sensation of the tongue. Added to this alarming sensation is a feeling of tingling, burning in the organ itself. The unpleasant sensation can spread to other areas of the oral mucosa.
Since the symptom is incomprehensible and frightening, a person may additionally suffer from anxiety, fear, and be nervously excited. A phobia may appear that he has an incurable disease.
How to treat burning in the mouth
If the cause is not stomatitis or gastrointestinal diseases, doctors have to deal with the symptoms themselves. Some experts are inclined to believe that we are still talking about neuropsychic problems. They are eliminated with antipsychotics and tricyclic antidepressants. Some types of analgesics and topical medications may also be prescribed. However, no one can give the patient a guarantee that the problem will be eliminated once and for all. Any symptomatic treatment is only a temporary solution.
If you read online reviews of people who have treated similar problems, you may be very disappointed in modern medicine. If we are talking about a problem such as glossalgia, the forecasts are 50/50. Sometimes doctors are able to “guess” the cause of a burning sensation in the mouth and successfully eliminate it. But often attempts are unsuccessful and people have to learn to live with this symptom.
Why palate paresthesia occurs and quickly passes
This condition is associated with:
- Reflux esophagitis. The condition is accompanied by the reflux of gastric juice back into the oral cavity. This causes irritation of the mucous membrane, manifested in tingling and a feeling of numbness.
- Drinking large amounts of alcoholic beverages.
- Diseases of the gums or teeth.
- Taking certain medications. Short-term paresthesias are a side effect. Before taking it, it is important to study the instructions for the drug in order to be prepared for this. The described clinical picture is caused by the cough medicine Libexin and the painkiller Bellasthesin.
You need to pay attention to the nature of the numbness: if they appear systematically, then this is a reason to urgently consult a doctor.
Decreased calcium
A drop in calcium levels in the blood can cause numbness or a tingling sensation in the tongue. This is a symptom of many diseases, the less dangerous of which is vitamin deficiency, and the more dangerous of which is cirrhosis of the liver.
The causes of this disease are insufficient generation of hormones by the parathyroid glands. These hormones help control calcium levels. Numbness or a tingling sensation indicates the need to visit a doctor to check your thyroid hormone levels.
FAQ
After the holidays, my tongue is coated and hurts on one side, what is the reason for this?
Most likely, this was due to an allergy to increased alcohol consumption.
Why does my tongue hurt after tooth extraction?
Tooth extraction is inevitably accompanied by temporary swelling of the gums, which can also affect the tongue. In addition, the dentist may accidentally injure the tongue on the side during his manipulations.
What to do if a child’s tongue hurts?
Children may complain of a sore mouth or refuse to eat without giving a reason. Parents should realize that this indicates a pain in the tongue and take the child to the doctor.
The causes of pain in children are the same as in adults, but the problem itself is more common in children. This happens because children constantly put something dirty in their mouths and are prone to biting their tongues. Stomatitis also often occurs in children.
The doctor must prescribe treatment for the child, as well as determine the true cause of the problem. But before visiting his office, it would not be superfluous to disinfect the child’s oral cavity by rinsing it with a soda solution.
It is impossible to ignore the pain, if only because it may be caused by an inflammatory process. Failure to treat any kind of inflammation in the body can lead to serious complications in the future. You can start visiting doctors with this problem from a therapist, who will redirect the patient to the necessary specialist.
There are a lot of diseases, the symptom of which can be tingling or numbness of the tongue. Here are some of them: glossalgia, stroke, lack of calcium and vitamins in the body. Sometimes it's damage.
Tingling of the tongue or loss of sensitivity may be symptoms of the disease. The main factors causing these symptoms are:
- the appearance of glossalgia;
- decreased levels of calcium and parathyroid hormones;
- vitamin deficiency;
- injury to the facial nerve;
- development of sclerosis or stroke.
Numbness, itching and a tingling sensation in the tongue indicate injury to the nervous system. Sensory loss can spread to the jaw or lip area.
The main causes of discomfort
Why does the tip of my tongue sting? If your tongue stings, the reasons may lie in various diseases of the oral cavity or in pathologies of internal organs and systems. If the tip of the tongue stings, the reasons may lie in the following conditions or factors:
The causes and treatment of this condition are closely interrelated, since it is possible to get rid of such a symptom only after finding out the cause of its occurrence. If the production of salivary fluid decreases, additional examination is required. Since this condition can be provoked by diabetes mellitus, Sjögren's disease.
Red dots on the surface of the tongue and the entire oral cavity may indicate the development of allergic reactions to certain foods or personal hygiene products (toothpastes, mouthwashes), tobacco. In this case, the nose may also sting and be dry. The materials from which dentures, implants, and crowns are made can also cause an allergic reaction. Most often, this reaction occurs to low-quality acrylic.
If the tongue hurts at the tip and is cracked, the cause may be the presence of tartar on the inner surface of the dentition. If an organ is constantly in contact with deposits, its tip is constantly irritated, begins to burn or hurt. Why else could such a symptom appear? The feeling that the organ is burned can often occur with the development of oral candidiasis; in addition, a white coating of a cheesy consistency and itching appears. Candidiasis can also irritate the nose. Other common causes of this condition may be stomatitis and herpes. In this case, pain and itching appears. Sores spread to the inner surfaces of the mouth, sometimes herpes can spread to the nose, lips and above the lips.
Bruxism can also cause a burning and stinging sensation. Unconscious grinding of teeth or intense clenching of the jaw may accidentally injure the tip of the tongue. More often this occurs during sleep or in a stressful situation. Sometimes pathologies of the mucosal epithelium also cause similar symptoms. Another common cause may be lichen planus. It develops when the immune system is weakened
If pinching and other characteristic signs appear, it is important to promptly contact a specialist and treat the disease.
Tobacco is a common cause of stinging and burning. Tobacco contains tars that irritate the surface of the organ. Another cause may be glossitis or glossalgia.
What to do if such signs appear? It is important to consult a doctor in time, who will identify the main cause of pinching and help eliminate it.
Special Recommendations
If the tip of your tongue often goes numb, you should undergo an additional examination from a dentist or ENT doctor. Often it is the diseases associated with their profile that are the cause of the unpleasant symptom. You can get rid of a single numbness yourself at home using the following methods:
- adjust your diet by eliminating sugar and alcohol;
- rinse with a decoction of St. John's wort or rose hips;
- make applications with sea buckthorn oil;
- Rinse your mouth with a solution of sea salt.
Such procedures will relieve inflammation if it exists in mucous tissues, improve tissue trophism, and eliminate accumulations of bacteria. You should not delay consultation, since numbness in the mouth area may be the first sign of a stroke, stomach ulcer, or hernia of the cervical vertebrae.
First of all, you need to lay the person down, unfasten constricting clothing, open a window to let air in, and measure the pressure if you have a tonometer. If numbness is accompanied by high fever, vomiting, or paralysis, then urgent hospitalization is required.
If possible, without clarifying the diagnosis, you should stop taking any medications. Many people start taking Aspirin, No-shpu or other pills that they found in the medicine cabinet. This is dangerous and may cause the condition to worsen.
In any case, numbness of the tongue is a dangerous symptom if it occurs frequently. You cannot self-medicate. This will only make the situation worse. Careful diagnosis and consultation with specialists is required.
Folk remedies
Treatment is prescribed by a specialist in accordance with the cause of the unpleasant symptom. Non-traditional treatment options are not recommended and lead to complications. If the patient is sure that the numbness is caused by overload of taste buds or other irritants, you can relieve the discomfort yourself at home.
When paresthesia is not a symptom of a more complex disease, then traditional methods will help eliminate the unwanted symptom:
- 3 drops of iodine are mixed with 1 teaspoon of baking soda. The mixture is stirred in 250 ml of warmed clean water. Rinse your mouth 2-3 times a day.
- 1 tablespoon dried chamomile, 1 tbsp. A spoonful of oak bark is mixed and poured with boiled water. Cool the liquid, filter and rinse your mouth 2 times a day.
- 1 teaspoon of St. John's wort herb is mixed with 1 teaspoon of celandine. The mixture is poured with boiling water in a volume of 250 ml and left for half an hour. Rinse your mouth 2-3 times a day.
- Apply sea buckthorn, peach or rosehip oil to a cotton pad. Apply to tongue 3-4 times a day.
It is recommended to rinse your mouth with a solution of soda and salt in a 1:1 ratio. The described methods help relieve inflammation and paresthesia. But these remedies are not aimed at treating the underlying disease, the symptom of which is numbness.
To restore sensitivity and relieve swelling, cold compresses are used - an ice pack that is applied to the tongue for 15-20 minutes. If there is no swelling, you can apply a warm compress to improve blood circulation.
To normalize blood flow, you can massage and knead the numb area. Before such a massage, you should wash your hands. If paresthesia is caused by an allergic reaction, antihistamines are taken.
Sensitivity disorder is a disruption of the nervous system, so sedatives are effective: massage courses, baths with aroma oils, relaxation exercises.
If an unpleasant symptom occurs more than 2 times a month or does not go away within 2 days, it is important to immediately consult a doctor.
We must not forget that even traditional methods can be harmful if their use is not approved by a doctor. Before carrying out self-treatment procedures, it is important to consult with a specialist, undergo diagnostics and identify the causes of the disorder.
Organ structure
The tongue has 3 parts - the root, the body, and the apex. Each part is covered with epithelium and mucous membrane, the surface of which is equipped with various types of papillae (mushroom-shaped, filiform, groove-shaped, leaf-shaped).
- The entire surface of the organ is covered with filament papillae. Their structure resembles the shape of thin threads, which is why they got their name. The filament papillae do not have taste buds.
- Leaf-shaped papillae are located on the sides and back of the organ. They look like little folds. The leaf-shaped papillae have taste buds.
- The fungiform papillae are located in the center and at the top of the tongue. They are small red dots; taste buds are present in the epithelium of the fungiform papillae.
- The circumvallate papillae are located in the posterior part and in the body of the organ. Among all the others, the circumvallate papillae are the largest, but they also contain taste buds.
There are blood vessels throughout the muscle tissue of the tongue.
Drug treatment
The plan of therapeutic measures is drawn up individually, taking into account the characteristics of the body and the etiological factor.
- The infectious attack is stopped with specific medications: antibacterial - Metrogyl Dent;
- antifungal - Miconazole;
- antiviral - Zovirax.