A lump in the throat is not a disease that requires specific treatment. Rather, this is a sign of the development of the disease, but a specific diagnosis can be made after assessing the accompanying symptoms. This condition causes discomfort and anxiety, so it is better to get rid of it and not torment yourself with doubts about what triggered it.
Discomfort in the throat can be observed constantly or visit a person periodically, but in any case, this phenomenon needs to be paid attention to. The sensation of a foreign body can be the cause of minor inflammation, or it can indicate serious diseases that, without the attention of doctors, will lead to serious complications. Also, the degree of discomfort can be very different, sometimes it’s enough to drink water and the discomfort goes away, and sometimes there’s such pressure in the throat that it’s simply difficult to breathe.
general information
A lump in the throat is a symptom that is manifested by the sensation of a foreign body or mass at the level of the pharynx or larynx . This disorder can make swallowing difficult or even painful.
A lump in the throat is a relatively common symptom that can occur as a result of various pathological conditions. Causes include certain emotional conditions, gastroesophageal reflux, muscle diseases, and nodular lesions in the neck or mediastinum that cause compression of the esophagus.
In some cases, the sensation is perceived as a local irritation and can be explained by rather trivial reasons (for example, anxiety, excitement or nervousness); in other cases, a lump in the throat is similar to choking and indicates the need for medical evaluation.
When you need a doctor
If you are often bothered by a burning sensation in your throat after eating and pain in the epigastric region, you should visit a gastroenterologist.
Attention! A serious symptom is the sensation of a lump or foreign body in the throat. This sign indicates a developing tumor. But it is not always malignant. In the initial stage, the disease occurs with hoarseness, which in most cases forces you to consult an ENT doctor.
Whatever the causes of the pathology, you cannot delay a visit to the doctor. Only a qualified specialist can suspect the disease at an early stage. But the diagnosis is confirmed by instrumental examination methods:
- fibrogastroduodenoscopy;
- computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging;
- X-ray examination;
- laryngoscopy.
Diagnosis is carried out by doctors of various profiles. But if you complain about discomfort in the larynx, you should first consult an ENT doctor.
Causes
A lump in the throat can result from a variety of reasons, including:
- gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD);
- state of anxiety or depression;
- pharynx tumors;
- esophageal tumors;
- muscle diseases.
These pathologies affect swallowing and/or cause other symptoms in addition to the sensation of a lump in the throat. In general, high cricopharyngeal pressure (due to muscles in the throat) or abnormal mobility of the hypopharyngeal system (pharynx) may contribute to these manifestations.
Gastroesophageal reflux
Often, a lump in the throat is associated with gastroesophageal reflux , a disorder characterized by an increase acidic stomach contents in the esophagus. Within certain limits, this is a physiological phenomenon and therefore normal; however, when reflux becomes too intense and frequent, it causes a number of problems in the patient, including a lump in the throat that encroaches on the pathology. In these cases, it is more correct to talk about gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) .
The cause of this pathology is often a malfunction of the cardiac nodes, a valve whose task is to deliver food coming from the esophagus to the stomach, preventing its return.
The sensation of a lump in the throat may be accompanied by a persistent cough, chest burning, regurgitation, chest pain and excessive salivation.
Hysterical lump (or pharyngeal ball)
A lump in the throat may feel like a mass in the larynx or a feeling of choking due to strong emotions . In this case we are talking about hysterical coma , an unpleasant manifestation that occurs in the absence of real pathological situations .
Treatment by an otolaryngologist, therapist, pulmonologist
The most common cause of a feeling of a lump in the Adam's apple is a viral or bacterial infection that affects the respiratory tract. The penetration of pathogenic pathogens into the lower and upper respiratory tract provokes the development of an inflammatory process in the larynx, pharynx, trachea or bronchi. Patients with diagnosed tonsillitis, bronchiolitis, and oropharyngeal candidiasis complain about the pathological symptom.
These diseases occur against the background of extensive swelling of the mucous membrane of the throat, which leads to a narrowing of its lumen. A dry or wet cough occurs, mucus, white lumps, and blood clots come out with sputum. The following medications are used to relieve symptoms of colds, ARVI, and flu:
- antibacterial drugs – Amoxiclav, Sumamed, Amoxicillin, Cephalexin;
- immunostimulants – Cycloferon, Cytovir, echinacea tincture;
- antiallergic drugs – Claritin, Zyrtec, Loratadine, Suprastin;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs - Nimesulide, Ibuprofen, Nise;
- antipyretics – Paracetamol, Panadol.
UHF therapy and ultraviolet light therapy help reduce the severity of symptoms of respiratory diseases and speed up recovery. The procedures help reduce inflammation and swelling of the pharynx and get rid of discomfort. At home, you can moisturize the airways, facilitate inhalation and exhalation, and restore the integrity of the epithelium using inhalations, compresses, and rubbing. In the treatment of viral and bacterial infections, infusions and decoctions of medicinal plants are actively used: sage, elecampane, marigold, St. John's wort, wild rosemary, lemon balm and chamomile. They are used for oral administration or gargling.
Only by curing cervical osteochondrosis can you get rid of the feeling of a lump in the throat
Symptoms and complications
Depending on the underlying cause, a lump in the throat may appear as a sporadic phenomenon (associated with a single episode), continuous, or recurrent (lasting until the underlying pathology is eliminated). Usually the sensation of a lump in the throat is not dangerous and does not cause complications, but it can also be caused by serious pathologies affecting the esophagus, pharynx and larynx, which should be carefully examined by a doctor.
Basic treatment
Most often, the uncomfortable feeling of a lump in the throat goes away on its own, but if the symptoms persist, it is necessary to look for the causes of their occurrence. After an examination and all the necessary research, the doctor will be able to prescribe the most appropriate and effective treatment.
If the problem is bacterial or infectious, then antibiotics may be prescribed. Particular attention is paid to streptococcal infection if it was found in the throat area. This infection is very resistant to various antibiotics, so especially strong ones are prescribed, taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient. If the discomfort is associated with inflammatory processes, drugs and topical agents can be prescribed, and homeopathy is also effective.
If the problem is related to psychological factors, the patient may be prescribed sedatives, antidepressants, and long rest and bed rest are recommended.
Diagnostics
A particularly irritating but occasional lump in the throat can be observed for some time without any disturbance; Rarely does this sensation require immediate medical attention.
However, if the disorder is persistent and progressive, careful clinical evaluation is necessary. Depending on the severity and nature of the lump in the throat, the doctor may suggest waiting for symptoms to appear or ordering diagnostic tests for the patient.
Useful investigations to determine the cause are "exclusion" tests: if the ENT doctor observes irritation of the mucous membrane of the larynx or pharynx caused by gastroesophageal reflux, he will refer the patient to a gastroenterologist; if the lump in the throat is caused by a hysterical coma, then psychiatric counseling is prescribed, and so on.
History and physical examination
To investigate the causes of a lump in the throat, the doctor asks the patient questions about symptoms and personal medical history (history), then performs a physical examination.
- History : The purpose of collecting a patient's history is to differentiate between a lump in the throat and dysphagia (difficulty swallowing). Therefore, this information suggests the presence of a structural disorder or motility (movement) of the throat or esophagus. During the history, the doctor asks the patient to clearly describe the symptoms, in particular their relationship to emotional states and swallowing disorders (for example, a feeling of stagnation of food). He also checks for any other associated manifestations.
- Physical examination : An otolaryngological examination focuses on the mouth and neck. The doctor will examine and palpate the mouth and neck to check for masses that may be responsible for the lump in the throat. An objective examination of the pharynx is then carried out using a flexible and thin research probe to examine the retropharyngeal area and vocal cords. During the visit, the doctor may ask the patient to swallow water or solid food, such as cookies or crackers.
Lump in throat: what is it really?
The feeling of a lump in the throat is not such a rare symptom. Surely almost every person can remember a situation in which it seemed to him that a foreign body was stuck in his throat. This condition in itself is not dangerous, but if it appears often enough and reduces the quality of life, you should be wary and consult a specialist. Sometimes this is the first sign of serious illness.
What is a “lump in the throat” and where does it come from?
Naturally, there is actually no lump in the throat. What is perceived as a foreign body is either a reflex spasm of the pharyngeal muscles due to nervous strain, or a manifestation of some pathological process occurring in the throat (prolonged inflammation, irritation by a pathological formation located inside or outside the pharynx). In the first case, they talk about functional causes of the “lump in the throat”, and in the second – about organic ones.
Functional reasons
The most common causes of a lump in the throat are just functional; in this case, there are no structural changes. The symptom develops solely due to a reflex spasm of the pharyngeal muscles in response to emotional stress. In this case, a vicious circle often occurs. The more worried a person is, the stronger the spasm and the “lump in the throat,” which increases the excitement even more. Functional reasons include:
- stress;
- emotional stress;
- neurotic conditions;
- depression.
Confirmation of the functional nature of the symptom is possible only after a thorough examination and exclusion of more serious organic causes, which can be suspected by accompanying symptoms.
Main organic causes
It also happens that the “lump” in the throat is objectively present. Most often this is:
1. Long-term inflammation in the pharynx, larynx
(laryngitis, pharyngitis, tonsillitis). The sensation of “coma” develops due to swelling of the mucous membrane and increased mucus production, which is observed during inflammation. In addition to the feeling of a foreign body, these diseases may cause a sore throat, periodic exacerbations in the cold season with an increase in temperature to febrile levels and a sore throat.
Diagnostics:
Therapists and otorhinolaryngologists diagnose and treat this group of diseases. The diagnosis is confirmed by examining the organs of the pharynx and larynx.
2.
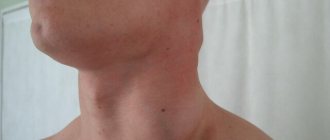
Diseases of the thyroid gland, accompanied by an increase in its size (for example, Graves' disease, or Graves' disease). The enlarged gland compresses the larynx, leading to the appearance of a “lump in the throat.” As a rule, with such diseases the level of thyroid hormones increases, which is manifested by an increase in appetite, an increase in heart rate, irritability, and exophthalmos (protrusion of the eyeballs).
Diagnostics:
If such symptoms are detected, consultation with an endocrinologist is necessary. The diagnosis is confirmed by determining hormone levels and ultrasound examination of the thyroid gland.
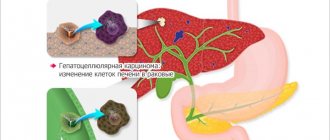
3. Neoplasms
located in the pharynx, larynx, trachea, mechanically complicate the processes of breathing and swallowing, leading to the appearance of a foreign body sensation. In the initial stages, a feeling of a lump in the throat may be the only symptom of a developing serious illness. Hoarseness, dry cough, and pronounced disturbances in swallowing and breathing may gradually develop. People who smoke need to be especially careful about this disease.
Diagnostics:
These diseases are dealt with by otorhinolaryngologists and oncologists. Diagnosis includes examination of ENT organs, X-ray examination, and biopsy.
4. Pathology of the cervical spine
spinal column (for example, cervical osteochondrosis) - the feeling of a lump in the throat is caused by compression of the nerves going to the pharynx and larynx. Pain in the spine, headaches, sometimes high blood pressure, nausea, and dizziness are also noted.
Diagnostics:
A neurologist can help with pathology of the cervical spine. The disease is diagnosed using an X-ray examination of the cervical spine.
5. GERD (gastroesophageal reflux disease)
- “lump in the throat” occurs due to irritation of the mucous membrane of the pharynx and larynx with the contents of the stomach. GERD can be suspected by the connection between the appearance of a “coma” and food intake, the presence of heartburn, belching of sour contents, hoarseness, and epigastric pain.
Diagnostics:
If you have problems with the gastrointestinal tract, you should contact a gastroenterologist. FGDS and daily intraesophageal pH monitoring will help in diagnosing this group of diseases.
Less commonly, the development of symptoms can be caused by obesity (due to fat deposits in the neck, which can sometimes mechanically compress the throat), parasitic diseases of the body (some parasites, such as echinococci, sometimes lay eggs in the throat, causing mechanical irritation of the receptors), injuries ( When an injury occurs, the mucous membrane swells and becomes inflamed, which leads to a feeling of “coma”), etc.
There are many reasons for the appearance of a “lump in the throat,” and some of them are quite serious, so you should not delay going to the hospital or clinic. First, you should contact a therapist, who, after examination, will, if necessary, refer you to a specialist. Depending on the combination of symptoms, the specialist will prescribe an examination and treatment to eliminate the underlying disease that caused the “lump.”
Olga Starodubtseva
Photo istockphoto.com
Treatment
When it comes to treatment, options vary depending on the cause of a given symptom.
- The feeling of a hysterical lump does not require any treatment other than an approach of reassurance and empathic understanding . However, in case of depression, anxiety or behavioral disorders, supportive therapy with psychological/psychiatric counseling . Sometimes it can be helpful to explain to the patient the connection between a lump in the throat and a mood state.
- If a lump in the throat is caused by reflux, therapy is based on taking medications that protect against the secretion of stomach acid. Typically, gastroprotectors (such as proton pump inhibitors) as well as antacids (such as alginates) are prescribed.
- More complex situations responsible for a lump in the throat—for example, tumor masses and nodular lesions of the neck or mediastinum—can be resolved with endoscopic surgery (i.e., surgery performed through the mouth, without any external incision). Interventions with access from the outside (i.e. directly to the outside of the neck) are limited to a few specific cases.
What tests can be prescribed?
Initially, you should go to a therapist or ENT doctor; specialists will examine the throat area and may refer you to more specialized professionals and prescribe additional tests in order to establish the true causes of the problem. If we talk about analyzes and studies, the following are most often prescribed:
- urine and blood tests;
- detailed blood test;
- Ultrasound of the thyroid gland;
- CT and MRI;
- X-ray of the cervical spine.
All tests are prescribed at the discretion of the doctor and in the presence of certain symptoms strictly on an individual basis.
Endocrinological reasons
The next common cause of discomfort in the throat is a variety of pathologies of the thyroid gland. Endocrine diseases develop due to hormonal imbalance, autoimmune pathology, and iodine deficiency.
A hypertrophied thyroid gland is often accompanied by a feeling of a constant lump in the larynx.
Pathology of the endocrine system:
- Hyperthyroidism is a disease characterized by an enlarged thyroid gland with increased secretion of thyroid hormone. Signs: a feeling of squeezing in the throat, difficulty breathing, nausea. As hyperthyroidism progresses, the menstrual cycle is disrupted. In men, potency decreases.
- Diffuse toxic goiter or Perry's disease is an autoimmune pathology. The disease develops due to excess production of thyroid hormones. It manifests itself as a puffy face, enlarged neck, bulging eyes, and difficulty swallowing.
- Thyroiditis is an inflammation of glandular tissue. It manifests itself as enlarged lymph nodes and pain in the throat.
- Endemic goiter develops in people living in areas where there is a lack of iodine in the soil and water. The thyroid gland hypertrophies, signs of difficulty swallowing appear.
The treatment is carried out by an endocrinologist. Replacement therapy for gland pathology is long-term and requires constant medical supervision.
Esophageal diverticulum
Esophageal diverticulum is a protrusion of the layers of the esophageal wall caused by deformation of the esophagus. Pharyngeal-esophageal diverticula occur against the background of inflammatory reactions in the gastrointestinal tract or decreased tone of the muscular layer of the esophagus. As a rule, a pathology in which a lump may “stand” in the throat area is preceded by gastroesophageal reflux, tuberculosis of the lymph nodes and esophageal candidomycosis.
Symptoms of esophageal diverticula are determined by their location. Pharyngeal-esophageal diverticula are most often accompanied by:
- dysphagia;
- sensation of a lump in the throat;
- painful swallowing;
- burning in the oropharynx;
- hypersalivation (salivation);
- putrid odor from the mouth.
The disease is treated with medications in a hospital setting under the supervision of a gastroenterologist. During therapy, patients should refrain from eating solid foods in favor of liquid cereals, cream soups, etc. Surgical treatment of pathology is carried out only in the presence of extensive defects, which are accompanied by perforation of the walls of the esophagus, dysphagia and internal bleeding.
Infections
Infectious causes of discomfort in the throat are much more common. With such a problem, it is with these factors that the diagnosis begins:
1. Pharyngitis. This disease is qualified by the presence of inflammation of the pharyngeal wall. This happens due to exposure to fungi (Candida) or other bacteria.
Symptoms:
- sore throat;
- sore throat when swallowing with fever;
- cough with sputum production;
- voice disturbance or irritation.
Treatment is carried out using antifungal, antiviral or antimicrobial agents.
2. Tonsillitis. Or as it is also called - sore throat, it manifests itself as an inflammatory process of the upper respiratory tract and palatine tonsils. This occurs due to streptococci or other microorganisms. Very rarely of viral origin.
Symptoms of this disease will be:
- sharp pain in the throat;
- itching;
- possible difficulty breathing;
- burning;
- a feeling that something is blocking your throat;
- discharge of pus;
- unpleasant smell.
Specialists prescribe antiviral or antibacterial treatment. In rare cases, antimycotic drugs may be prescribed.
3. Laryngitis. This kind of disease involves inflammation of the tissues of the larynx. Caused by the presence of viruses, infections or fungi in the oropharynx.
The symptoms are similar to the disease tonsillitis, the only thing that distinguishes them is the less intense discharge of pus.
Dysphagia
Dysphagia is a swallowing disorder that interferes with the normal passage of food and liquid through the esophagus. Pathology can appear as a result of septic inflammation of the trachea, esophagus, larynx and oropharyngeal mucosa. Most often, dysphagia develops against the background of diffuse spasm of the esophagus or the formation of benign and malignant tumors.
Dysphagia is accompanied by specific manifestations, which include:
- periodic cough;
- difficulty swallowing saliva;
- pain when food passes through the esophagus;
- penetration of food particles into the trachea or larynx.
In most cases, patients have difficulty eating only solid foods. Therefore, at the time of undergoing therapy, they adhere to a diet that consists of eating only liquid food.
Oncological causes
Discomfort in the throat is often caused by tumors of malignant or benign origin. Diseases accompanied by this symptom:
- Laryngeal papilloma manifests itself as hoarseness, difficulty speaking and breathing.
- Carcinoma is a malignant tumor of the larynx. Patients suffer from difficulty speaking. The pain intensifies as the cancer process progresses. Subsequently, hemoptysis appears.
At the first sign of a lump in the larynx, as well as hoarseness, you need to rush to an ENT doctor. Instrumental and laboratory examination will be required. Early diagnosis will allow treatment to begin and prevent progression of the disease.
Unilateral pain
Sore throat on one side occurs very often. This symptom can be caused by many reasons.
Angina
With angina, the inflammatory process very often covers one tonsil. This is expressed in the fact that the throat begins to hurt on one side. Pain in one side of the throat with a sore throat can be burning or pulling. The pain intensifies when swallowing. A sore throat on one side with a sore throat often radiates to the jaw, neck and roots of the teeth. An additional symptom of the disease is swelling and tenderness of the lymph nodes on the right or left side.
The cause of sore throat is infection with streptococcal infection. Treatment is carried out with antibacterial agents. The disease is contagious, so you should disinfect all objects used by the sick person and limit contact with other people.
Pharyngitis
With pharyngitis, inflammation of the mucous membrane of the oropharynx is observed. Quite rarely, a unilateral inflammatory process is observed, which indicates the localization of harmful microorganisms in one place. To prevent serious consequences, the cause of this should be identified by contacting an otolaryngologist.
Laryngitis
Unilateral sore throat can occur with laryngitis. Additional symptoms include hoarseness, the urge to cough, and a constant sore throat. With this disease, the temperature rises slightly. Painful sensations are characterized by the fact that they can move from one side to the other, but the pain does not increase when swallowing. Pain on one side of the throat with this pathology intensifies with vocal strain.
Focal ulcers
The most dangerous pathology that requires urgent response for unilateral sore throat is the occurrence of focal abscesses, or abscesses. In this case, there is difficulty swallowing. In severe cases, it becomes simply impossible to swallow anything, and a huge amount of saliva is released, which fills the oral cavity and flows out.
Tumors
Tumors that arise in the larynx also cause pain on the right or left side. In this case, a benign formation is usually less painful, and the discomfort is more associated with impaired swallowing. Malignant tumors are constantly progressing, so the pain is characterized by intensification. If such a phenomenon is observed, it is necessary to urgently undergo diagnostics, which consists of taking tests and performing a biopsy.
The progression of malignant tumors leads to changes in voice function, and in severe cases to aphonia (disappearance of the voice). Over time, the tumor grows and manifests itself as a mass formation in the neck. In severe cases, the lumen of the larynx narrows, which causes respiratory failure.
Benign formations are less dangerous. They progress very slowly and, with proper treatment, do not pose a threat to human health. Most often these are wen, fibroids and papillomas.
Injuries
Throat trauma very often causes pain on one side. Injury can occur when a foreign body enters the throat. Classic causes include ingestion of fish bones. It usually gets stuck on one side and can scratch the mucous membrane, causing constant pain.
As a rule, with pharyngeal injuries, the person’s general condition remains stable. No additional symptoms appear, therefore, during diagnosis, the cause of the pain is easily detected in accordance with the patient’s complaints. The risk of worsening the condition occurs if there is no adequate therapy. This can lead to the development of inflammation, which causes a rise in temperature.
For throat injuries, it is important to follow a gentle diet. The diet should be free of solid foods, as well as too hot or cold foods and drinks. The duration of recovery depends on the characteristics of the injury.
Traditional methods of treatment
After examination using instrumental and laboratory methods, the doctor conducts special therapy. Even the most simple disease requires treatment under the supervision of a doctor.
If the patient believes in traditional medicine, he can consult his doctor. Medicinal herbs are not indifferent to the body. Many of them cause allergies. In addition, they are not always combined with medications prescribed by a doctor.
Finally, you should know that traditional methods do not cure the disease, but mask the symptoms, temporarily improving the patient’s condition. During the time spent on herbs, the disease takes an advanced form, and sometimes turns into a malignant tumor.
But this does not mean that herbs are useless. On the recommendation of a doctor, you can gargle with anti-inflammatory herbs - chamomile, calendula, sage.
If bacteria have settled in the respiratory tract, when heated they multiply and spread to neighboring organs - ears, paranasal sinuses, lungs. This leads to complications.
Warming up the throat is especially dangerous in case of cancer. Heat accelerates tumor growth. No traditional methods should be used until a diagnosis is made and without a doctor’s recommendation.
Any discomfort in the throat occurs for some reason. The sooner you see a doctor, the sooner you can start treatment. In some diseases, this measure prevents complications. In another case, it saves a life.