Doctor Komarovsky: what to do if a child is vomiting
All mothers and fathers know very well that vomiting in children is not such a rare occurrence. However, in practice, when faced with an attack, many are simply lost and do not know how to provide first aid to the baby, what to do and where to call. Authoritative children's doctor Evgeny Komarovsky, author of numerous articles and books on children's health, explains why vomiting happens and what adults should do about it.
Should I worry?
Vomiting, which is not accompanied by fever and diarrhea in children, occurs quite often. This is due both to physiological age-related characteristics and to the presence of various pathologies that require medical supervision. For parents who are attentive to the health of their baby, this condition causes great concern, because they do not understand what is happening to their child.
If vomiting occurs without diarrhea and the baby has a fever, you should definitely show it to your pediatrician. Even in the absence of other warning signs, mom and dad should understand the seriousness of the situation. This is due to the fact that vomiting often acts as a symptom of serious diseases. In this case, you should pay attention to other manifestations in the child.
Vomiting is not an independent disease. It occurs as a protective reaction of the body in various pathologies.
About vomiting
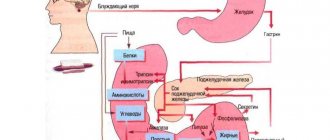
Vomiting is a protective mechanism, a reflexive eruption of stomach contents through the mouth (or nose). During an attack, the abdominal press contracts, the esophagus expands, the stomach itself relaxes and pushes everything that is in it up the esophagus. This rather complex process regulates the vomiting center, which in all people is located in the medulla oblongata. Most often, vomit is a mixture of undigested food debris and gastric juice. Sometimes they may contain impurities of pus or blood, bile.
The most common cause of childhood vomiting is food poisoning. Vomiting can be observed with various infectious diseases: rotavirus infection, scarlet fever, typhus.
Less commonly, this problem is caused by accumulated toxins; this condition can occur with serious kidney disease.
Other causes of vomiting include diseases of the stomach and intestines, neurological diagnoses, and head injuries.
In children, vomiting can often be provoked by severe emotional shocks.
Doctors distinguish several types of infant vomiting:
- Cyclic vomiting (acetonemic).
- Renal.
- Hepatogenic.
- Diabetic.
- Cardiac.
- Psychogenic.
- Cerebral.
- Bloody.
In most cases, vomiting in children begins at night. The baby wakes up from severe nausea. In this situation, it is important not to be scared or confused. Parents' actions should be calm and confident.
The younger the child, the more dangerous vomiting is for him, since dehydration can occur, which can be fatal for children.
A single vomiting (without any additional symptoms) in a child should not cause much concern for parents, says Evgeny Komarovsky. The fact is that this is how the body “cleanses” itself of accumulated toxins and food elements that the child could not digest. However, parental inaction can be fraught with tragic consequences in cases where vomiting is repeated, as well as if there are other symptoms indicating disorders in the body.
The most common cause of vomiting in children is food poisoning. Poison can enter a baby’s body through various foods: dairy, meat, seafood, vegetables and fruits.
In the vast majority of cases, the gag reflex is caused by nitrates and pesticides used on fruits and vegetables. Even very high-quality meat products can cause severe poisoning if they are prepared incorrectly.
Evgeny Komarovsky emphasizes that the first symptoms of food poisoning usually begin to appear between 4 and 48 hours after eating. Quite often, you can stop vomiting caused by food on your own, at home.
However, Evgeny Komarovsky reminds that there are situations in which mothers and fathers should not engage in independent healing. Medical attention is required:
- Children from 0 to 3 years old.
- Children who vomit due to elevated body temperature.
- Children who have vomiting, diarrhea and abdominal pain (all or just some of the symptoms) have lasted for more than two days.
- Children who are not “alone” in their illness (if other household members have similar symptoms
There are situations in which a child needs emergency medical attention as soon as possible. You should call an ambulance in one or more of the following conditions:
- Vomiting occurred after eating mushrooms.
- The vomiting is so intense that the baby cannot drink water.
- Vomiting is accompanied by clouding of consciousness, incoherent speech, poor coordination of movements, yellowing of the skin, dry mucous membranes, and the appearance of a rash.
- Vomiting is accompanied by visual enlargement (swelling) of the joints.
- Against the background of repeated vomiting, there is no urination for more than 6 hours, the urine has a dark tint.
- Vomit and (or) feces contain impurities of blood and pus.
While waiting for the doctor to arrive, the child should be placed on his side so that during the next vomiting attack the child does not choke on the vomit. The baby should be held in your arms, on its side. There is no need to give any medications.
In order for the doctor to quickly understand the true cause of the child’s condition, parents must remember in as much detail as possible what the baby ate over the last 24 hours, what he drank, where he was and what he did. In addition, mom and dad will have to carefully examine the vomit in order to then tell the doctor about its color, consistency, whether there is an unusual smell, whether there are any impurities of blood or pus in it.
Analyzing color
Dark vomit (the color of coffee grounds) may indicate serious stomach problems, including peptic ulcers.
If there is an admixture of bile in the masses and there is a bitter-sweet smell, one may suspect a problem with the gallbladder and biliary tract.
The green color of the vomit may indicate the neurological nature of the reflex; vomiting also occurs in a severe stressful situation, when the child cannot cope with anxiety and emotions in any other way.
It is recommended to leave samples of vomit and feces of a sick child until the doctor arrives in order to show them to a specialist. This will facilitate the fastest and most accurate diagnosis of the true cause of the condition.
Vomiting in an infant may be a completely natural process of developing digestive functions, but it is better if it is diagnosed by a doctor. Komarovsky emphasizes that vomiting in infants is often a completely expected cause of banal overeating if parents are too zealous in their desire to feed their child more and more calories.
Vomiting can also be of another nature - allergic, traumatic, and also inflammatory. In other words, this reflex accompanies a great variety of different diseases, some of which require prompt hospitalization followed by surgical care, and therefore vomiting attacks should not be underestimated.
So, parents should make every effort not to stop vomiting at any cost and try to treat something with folk remedies, but to carefully observe. It will be just great if they can provide the following information to the doctor who comes to the call:
- Frequency and periodicity of attacks (at what intervals does vomiting occur, how long does it last).
- Does the child feel better after the next attack, does the abdominal pain decrease?
- What is the approximate volume of vomit, its color and whether there are any impurities.
- What has the baby been sick with over the past year, over the past two weeks?
- What did the baby eat, and do the parents suspect food poisoning?
- Has the child's weight changed over the past 2 weeks?
Features of diagnosis and treatment
Treatment of vomiting without fever in a child is effective if the cause of this symptom is precisely established. And this can be difficult to do, since vomiting is a “companion” of diseases of various natures.
How is diagnostics carried out?
There are several effective examination methods for profuse vomiting.
- Visually. The quantity, presence of impurities (pus, bile, blood, mucus), color, smell, consistency of vomit - all these parameters will help the doctor determine the type of vomiting characteristic of a particular disease.
- Laboratory examination of vomit. Confirms or refutes the preliminary diagnosis.
- Instrumental examination of the digestive organs. Ultrasound, gastrofibroscopy (examination using a probe), x-ray.
How is the treatment carried out?
If the diagnosis is established, then the disease is treated by specialized specialists.
- Pediatrician. The first doctor to contact if a child has repeated bouts of vomiting. He will refer you to specialists for examination.
- Gastroenterologist. Specializes in the treatment of gastrointestinal diseases. Therapy can be carried out in a hospital or at home. The disease is treated with medication, and a strict diet is also important.
- Neurologist. All attacks of cerebral vomiting are associated with neurology. Treatment is medicinal, physiotherapy and massage are also prescribed.
- Surgeon. Acute appendicitis, pyloric stenosis, intestinal obstruction, cardiospasm, foreign body in the esophagus - all these situations are considered by a pediatric surgeon.
What should parents do?
- Control the situation. Don't leave the child alone. The baby should be held in your arms, slightly tilted forward, so that vomit does not enter the respiratory tract.
- After each bout of vomiting, clean your mouth. An older child can rinse his mouth independently after vomiting.
- When lying down, place the child on his side. You can lie on your back with your head turned to the side; you can place a high pillow under your head.
- Do not feed while vomiting. The exception is infants.
- Seal with rehydration solutions. This is a must. You need to drink frequently, every 5-10 minutes, in fractional portions. Read more about the principles of providing help at home for vomiting in our other article.
Adviсe
If a child has some of the above symptoms, but is not vomiting, Komarovsky advises inducing the reflex on his own. To do this, you need to give the baby 2-3 glasses of warm water or milk to drink, and then gently insert your fingers into the oropharynx and move them slightly. You can lightly press the root of your tongue with your fingers or a spoon.
There is no need to feed the child anything. However, drinking is a must. At the same time, you should know that drinking water from a child who is vomiting is a whole science; it must be carried out strictly according to the rules. Firstly, says Evgeny Komarovsky, drinks should be small, but very frequent. A single dose is a few sips. Secondly, the temperature of the water should be similar to body temperature, so the liquid will be absorbed more quickly, which will protect the child from dehydration. When asked what to drink, the doctor answers that the best option is oral rehydration solutions or homemade saline solutions. If desired, you can give your child still mineral water, tea, compote.
No self-medication!
There is no need to try to rinse the child’s stomach at home using potassium permanganate. This can burn your baby's esophagus. It is also better not to offer medications of your own choice.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytpressru
If a child vomits once at night (undigested food), does not have diarrhea, and is quite active, then there is no need to worry too much. But if the urge to vomit occurs quite often and diarrhea begins in tandem with fever, then this is a reason to quickly seek help from a doctor.
Types of vomiting in a child
Vomiting can occur under various circumstances, for example, with traumatic brain injury, poisoning, motion sickness, accompanied by dizziness, fainting and loss of consciousness, be repeated, accompanied by abdominal pain and diarrhea.
If vomiting is not accompanied by fever, then the most likely cause of its occurrence may be disorders of the gastrointestinal tract, food poisoning (expired or low-quality food, chemicals), intoxication after taking medication, dysbacteriosis.
Vomiting as a reaction to a new product
In a baby under one year old, new foods in the diet may cause vomiting. A different milk formula, a new tea or the first complementary food - all this can cause nausea, as well as provoke the development of other digestive tract disorders.
Vomiting in a newborn after formula feeding is a fairly common reaction of the body that does not accept the new food. That is why, if you need to change the manufacturer of baby food, you should consult your pediatrician. And if there is no urgent need to buy another type of milk formula, then there is no point in experimenting.
As for the introduction of complementary foods, a whole scheme has been developed for expanding the infant's diet . Following all the recommendations will help you avoid the unpleasant consequences of food intolerance. It is also important to monitor the quality and timing of juices and purees offered to your child. Expired jars of baby food may well cause vomiting and diarrhea in a one-year-old child. So storing them after opening is not allowed.
Causes of vomiting in a child
Most often, vomiting without fever in a child is associated with diseases or various conditions of the gastrointestinal system. Let's look at some of them:
Pylorospasm or pyloric spasm is a stomach spasm that most often occurs in newborns due to underdevelopment of the nervous system. Vomiting may be profuse. Such a child is usually restless and does not gain weight well. Pylorospasm should not be confused with regurgitation, which is most often observed when the stomach is full of food.
Intestinal obstruction is accompanied by severe pain, bloating, cramps, and blood in the stool. Intestinal obstruction in children is most often associated with worms or intussusception, which is the penetration of a section of the intestine into a segment of an adjacent section of the intestine. Vomit may contain bile.
Foreign body in the esophagus . Since children can put anything in their mouth, the entry of a foreign body into the esophagus can trigger an attack of vomiting. If a foreign body damages the mucous membrane of the esophagus or stomach, blood may be found in the vomit. Food poisoning. Vomiting often occurs with food poisoning (for example, expired or poor-quality foods, eating unwashed vegetables and fruits), and may be accompanied by diarrhea. In some cases, the temperature rises.
Inflammatory diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, acute gastritis, gastroduodenitis, pancreatitis, cholecystitis . These diseases can occur due to poor diet, abuse of fried, smoked, and fatty foods. In these cases, vomiting is often accompanied by diarrhea, abdominal pain, loss of appetite, and bloating. An increase in temperature is usually not observed, but in some cases it can reach 37 ° C. In some forms of gastritis, blood may be present in the vomit. With gastroduodenitis, the nature of the stool is changeable, prolonged constipation can be replaced by diarrhea. In acute pancreatitis, the nature of vomiting attracts attention - it is repeated and profuse. In this case, the contents of the stomach are released first, followed by bile and the contents of the duodenum. Such vomiting threatens to dehydrate the child’s body. Vomiting in acute cholecystitis is usually not accompanied by diarrhea. The child is usually bothered by pain in the right hypochondrium and bitterness in the mouth.
Dysbacteriosis is a disorder of the intestinal microflora due to long-term use of antibiotics, often accompanied by vomiting and diarrhea. It is important to be careful when taking antibiotics, since they are harmful not only to pathogenic microbes, but also to normal microflora.
Types of baby vomiting
Medical terminology identifies several types of infant vomiting:
- cyclic - characterized by episodes of frequent attacks of vomiting for no apparent reason (lasting from several hours to days), which alternate with asymptomatic periods;
- renal, hepatogenic – occurs with renal failure;
- diabetic – one of the common symptoms of diabetes;
- cardiac form of vomiting - can occur in children under 2 years of age, when the tone of the cardiac part of the stomach is reduced, which disrupts the physiologically correct movement of food;
- psychogenic – associated with acute psycho-emotional disorders, overwork;
- vomiting with blood – may be a symptom of a serious disease in the body;
- visceral – occurs when internal organs are damaged.
Infants and young children vomit more often at night. The child may wake up feeling nauseous. It is important that parents are not afraid and are able to provide first aid to the child.
Important! The younger the child is, the greater the danger vomiting poses to him. It can cause severe dehydration, which can be fatal for the baby.
Vomiting without fever in children
Infant vomiting is very common. The reasons for it are varied. To determine them, you need to take into account age, accompanying symptoms: the presence or absence of fever, diarrhea, vomit, etc. Vomiting in a child without fever does not mean the absence of a disease; sometimes in such cases the help of a doctor is necessary. The center of the nervous system responsible for its occurrence is located in the medulla oblongata. Impulses can come from completely different internal organs, the vestibular apparatus and cortical centers of perception. Sometimes vomiting occurs due to the effects of various toxins and drugs on the medulla oblongata.
Complications
Severe consequences can occur when vomiting with fever. But the presence of such in asymptomatic eruptions of stomach contents is extremely rarely diagnosed.
Regurgitation observed in babies does not cause health complications. Psychogenic types in a child also do not cause consequences. Complications may arise if the association related to this type becomes established and there is repeated vomiting.
Frequent, severe vomiting does not go away without consequences. Dehydration is a sign of complications. Occasional vomiting rarely causes the mass to enter the lung system, causing aspiration pneumonia.
Periodic urges with accompanying intense sweating lead to hyperkalemia.
Providing first aid to a child who is vomiting
If a child’s vomiting appears suddenly and without fever, what should be done before the doctor arrives? First aid should be provided during and immediately after gastric emptying.
Necessary:
- make sure that the child does not choke - do not let his head fall back, do not lay him on his back, you need to turn his head to the side, preferably raising it by 30°;
- After vomiting, rinse the child’s mouth with warm water or wipe the mouth, corners of the mouth and lips with a wet cotton swab. Instead of water, you can use a weak disinfectant solution, for example, potassium permanganate or boric acid;
- Give the child small amounts of water often; the water should be cool; for older children, cold. To eliminate the urge to vomit, you can add a few mint drops and use Regidron. For children up to one year old, give 2 teaspoons every 5 minutes, from one year to 3 years - 3, from 3 years - 4.
If the attack of vomiting is one-time and is not accompanied by fever, diarrhea, or deterioration in the child’s general condition, you can wait to call a doctor.
All you need to do is carefully monitor the baby and if it worsens or additional symptoms appear, seek medical help.
Parental behavior
Children's crying, changes in condition, and the onset of vomiting make parents think. It is necessary to conduct a thorough inspection and measure the temperature. You can't leave the situation to chance. The sitting child is held upright. The reason for this is to prevent vomited food from entering the lungs. When the child is lying down, he is turned over on his side. The reason is similar. In other positions, it is allowed to lie exclusively under the supervision of an adult with the head turned to one side.
The mouth and face should be washed regularly with water to prevent skin irritation. Applies to infants; older children are able to do this on their own. Infants have stomach pain along with vomiting, but in the intervals between urges they feed as prescribed by the doctor. A prerequisite is to take special solutions that restore electrolytes in the body. Every 2-3 minutes the child should take sips of the solution. Due to the dehydration of the baby’s weak body, he needs to be given water after each emptying of the stomach.
Vomiting is not a common occurrence, but a possible symptom that provokes a serious illness. Repeated vomiting serves as a wake-up call for parents. A small child is not able to fully combat most causes of vomiting. When the situation does not improve, the disease progresses, call a doctor.
Reasons for calling an ambulance
Vomiting in a child without fever can be a sign of some serious illnesses, including those requiring immediate surgical intervention. Therefore, you should not delay seeking medical help and self-medicate.
You need to call an ambulance immediately if:
- vomiting occurs frequently and does not stop;
- it is not possible to give the child something to drink due to the frequent eruption of vomit;
- there are additional symptoms - high fever, diarrhea, abdominal pain;
- fainting, semi-fainting or, conversely, excessive excitability (crying, screaming, physical activity);
- severe abdominal pain combined with bloating and constipation;
- vomiting occurred after consuming products of dubious quality, chemical additives, medications;
- vomiting occurred after a head injury, fall, blow - an urgent examination by a neurologist is needed;
- lethargy, drowsiness, convulsions, and fever are observed.
If vomiting occurs once or twice, the stool is loose or normal, and the child drinks water normally, plays, and sleeps well, then it is not necessary to call an ambulance, but you should contact your local pediatrician.
Dangerous causes of vomiting: when to sound the alarm
If the occurrence of vomiting has nothing to do with feeding, this should alert parents . In this case, it is recommended to take a closer look at the vomit. If mucus, blood particles or bile are found in them, you should urgently consult a pediatrician. If vomiting occurs repeatedly, call an ambulance.
Vomiting as a symptom of the development of pathology can signal a variety of diseases:
- viral and bacterial infections;
- brain concussion;
- diseases of the nervous system;
- complete or partial intestinal obstruction;
- abdominal organ injuries;
- increased intracranial pressure;
- appendicitis (rarely found in infants);
- drug intolerance (allergic reaction to drugs and their components).
In this situation, in addition to vomiting, other symptoms of these diseases will be present (fever, diarrhea, lethargy and drowsiness) . And based on the totality of all the signs, an accurate diagnosis will be made.
Diseases accompanied by vomiting without fever
Some serious illnesses in a child may be accompanied by diarrhea, nausea and vomiting without fever. This is most often observed in the following diseases.
Intestinal infections : typhoid fever, enterovirus, etc. These diseases may be accompanied by high temperature, but sometimes it remains normal. Vomiting occurs without connection with food and may occur one or more times. Read more about intestinal infections →
The vomit is always the same. Often the diarrhea is more pronounced, the stool is liquid, sometimes with foam, mucus, and has a pungent odor. The child is capricious and restless, exhausted, becomes drowsy and lethargic. Refuses to eat and drink and rarely or not urinates at all. Dehydration sets in.
Treatment is carried out only inpatiently in children under one year of age, in older children at home or in the hospital. Absorbent drugs, antibiotic, antiviral and rehydrating agents, and probiotics are prescribed. If necessary, painkillers and antipyretic medications can be used.
Food poisoning. Often occurs after consuming canned food, dairy products, meat and fruit purees. Nausea and vomiting occur after eating and are repeated several times. The stool is liquid and streaked with blood. Characterized by severe paroxysmal abdominal pain. Read about food poisoning →
General health becomes worse, the child is capricious, cries, gets tired quickly and becomes lethargic. Refuses to eat and drink. If a child is 3 years old or younger and vomiting without fever is due to food poisoning, then he needs to be hospitalized.
Treatment for older children can be organized at home. Gastric lavage is performed, absorbent agents, rehydrating drugs, prebiotics, and drugs that relieve spasms and inflammation are prescribed.
Allergy to food or medicine. Attacks of vomiting and diarrhea occur after the child has eaten. The masses contain undigested product. In addition, skin rashes, swelling of the mucous membranes, and difficulty breathing may appear. Treatment can be organized at home or in a hospital. More about food allergies →
The basis of therapy is antiallergic drugs. Absorbents and hormonal agents may be prescribed.
Dysbacteriosis. In this condition, vomiting does not appear often, stools are foamy, and sometimes give way to constipation. Flatulence and whitish plaque in the oral cavity are detected. Article about dysbiosis in children →
Possible skin itching, peeling, rash. Treatment is carried out at home and boils down to adjusting the diet and restoring the balance of microflora with the help of probiotics.
Intussusception . Without an increase in temperature, the child vomits bile. Cramping pain in the epigastrium is accompanied by screaming and crying. The stool is jelly-like and streaked with blood. Treatment is only possible with surgery.
Acute form of gastritis, duodenitis. First, nausea appears, then profuse repeated vomiting with bile. There is bloating, pain, and loss of appetite. Treatments are carried out at home. The main techniques are diet correction, frequent drinking, and taking pribiotics. Gastritis in children →
Diseases of the pancreas, liver and gall bladder. Vomiting occurs after eating, one or more times. Vomit with bile and food particles. Associated symptoms: severe epigastric pain, belching of air and gas, loss of appetite. Inpatient treatment using hepatoprotectors or drugs with enzymes, taking painkillers, following a therapeutic diet.
Diseases of the central nervous system (ischemia, hydrocephalus, tumors, intracranial pressure). Vomiting is frequent. The child's behavior changes from anxiety to lethargy. Infants also experience bulging of the fontanelle.
Depending on the disease, treatment is carried out at home or in the hospital. It involves taking medications that restore cell nutrition. For hydrocephalus and tumors - surgical methods.
Ingestion of a foreign object. Vomiting food particles with mucus, sometimes with blood. Breathing is impaired, the child is restless. Two options for help: observation and waiting for natural passage along with stool or surgical intervention.
Treatment methods
Treatment of vomiting in a patient is carried out depending on the pathogenesis of the disease. To find out the true reason for the development of this protective reaction of the body, it is necessary to seek qualified medical help.
What to do for gallbladder diseases
Therapy for biliary dyskinesia is carried out using a diet, excluding from the diet foods containing large amounts of oxalic acid, as well as spicy, fatty, smoked, fried, pickled, and too salty foods. The baby’s diet must be saturated with fermented milk products, cereals, vegetables, fruits, and herbs.
Medicines:
- Holenzyme;
- Allohol;
- Flamin;
- Galstena.
Sedatives may also be prescribed, including Persen, Fitosed, Edas. In severe cases of the disease, physiotherapy methods have proven themselves well - electrophoresis, galvanization and others.
Infectious cholecystitis is treated with antibacterial drugs. The fight against parasitic infections is carried out with the use of Mebendazole, Pyrantel, Levamisole and others.
Treatment of pancreatic pathologies
Acute pancreatitis must be treated in an inpatient setting. In this case, bed rest and refusal to eat for 12 hours are prescribed. To maintain the body, injections of glucose solution are given, alkaline mineral water is allowed.
Drug therapy includes painkillers, enzymes, and antispasmodics. Metoclopramide is administered to stop vomiting. The dosage of the medicine is calculated by the doctor depending on the age and weight of the baby. After normalization of the child’s condition, a strict diet is indicated.
Treatment of acute appendicitis
In case of acute appendicitis, treatment is carried out exclusively in a hospital setting by surgery. The recovery period after surgery lasts 7-14 days. The patient is advised to diet and avoid physical activity.
Treatment of acetone crisis
Therapy for this condition is carried out exclusively in a hospital setting. The child is prescribed a strict diet with complete abstinence from fatty foods and plenty of fluid intake. In case of repeated vomiting, injections with antiemetics, antispasmodics and sedatives are given.
Children with acetone syndrome must be registered with a medical institution and undergo regular examinations.
Treatment of diseases of the central nervous system
Therapy of central nervous system diseases is a complex task. A neurologist is involved in the treatment. Depending on the severity of the course and the factors that provoked the disease, therapy for the disease is carried out at home or in a hospital setting.
You may be interested in: Constipation in infants: solving the problem at home quickly and effectively
Typically, the patient is prescribed drugs whose action is aimed at stimulating cerebral circulation. Severe hydrocephalus and brain oncology can only be treated surgically.
What to do if psychogenic vomiting develops
Vomiting without fever and diarrhea, which occurs against the background of severe emotional shock, fear or fright, is treated by seeking help from a psychotherapist. A specialist helps to find out the causes of stress and suggests methods for correcting the situation.
When introducing complementary foods
What to do if vomiting occurs after your child takes a new product? In this situation, it is better to refrain from eating this food for now. Perhaps the baby’s body is not yet ready to digest it. You should try again in a few months. By this time the body will be ready.
Treatment of gastroesophageal reflux
If a newborn regurgitates frequently, this should not be attributed to age-related characteristics. The child should be shown to a pediatrician or gastroenterologist. At an early age, it is possible to get rid of gastroesophageal reflux by switching to thicker foods and reducing portions.
If there are more serious problems, treatment is carried out with the use of drugs that suppress the production of hydrochloric acid. The doctor also prescribes antacids and medications that suppress the production of gastric secretions. Normalization of gastrointestinal motility is carried out with the help of prokinetics.
What to do for gastritis
Acute and chronic gastritis often occurs with the appearance of vomiting after eating. Treatment of the disease is carried out at home or in a clinic by a gastroenterologist. In acute cases of the disease, the patient must refuse to eat for at least 12 hours. The liquid should be taken in small sips.
Medicines:
- No-Shpa;
- Papaverine;
- Maalox.
After the end of the acute period, meatless food is allowed. The menu includes vegetable broths, jelly, and well-cooked porridge. It is forbidden to eat fatty, fried, spicy, salty, smoked, and sweet foods. In the future, the child must be registered in the hospital.
With timely and competent treatment, the prognosis for the patient is often favorable. Following a diet allows you to lead a fulfilling lifestyle.
Pyloric spasm
Treatment of the pathology is carried out by prescribing the patient a special diet and alkaline drinking. Antispasmodics are used as medications. It is important to follow the dosage of food in accordance with the age of the baby. You cannot overfeed your child.
Physiotherapeutic treatment, such as electrophoresis and paraffin baths, has proven itself well in the treatment of pyloric spasm.
Therapy for gastroduodenitis
Acute gastroduodenitis in children is treated mainly by following proper nutrition. Food should be taken in small portions. The frequency of doses is 5-6 times a day. In acute cases of pathology, bed rest must be observed.
Medicines are prescribed to reduce stomach acidity. Drugs such as Almagel, Omeprazole, Ranitidine are used. If the inflammation is caused by the bacterium Helicobacter pylori, treatment is carried out using antibacterial drugs. Among them, Metronidazole and De-Nol are often prescribed. In case of chronic duodenitis, the patient is indicated for sanatorium treatment.
What to do if a foreign body enters the gastrointestinal tract
If such a situation arises, the parents' reaction should be immediate. If the baby swallows a small smooth object, wait-and-see tactics are allowed. Most likely, the item will come out naturally. If a foreign body provokes suffocation, severe vomiting, or blood in the vomit, such a child requires urgent surgical treatment.
Even if a small object is swallowed, consulting a doctor is necessary.
Treatment of food poisoning
Food poisoning is accompanied by vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea or no diarrhea. Sometimes there is no temperature, but the character of the stool is not disturbed. Regardless of the accompanying symptoms, therapy should be carried out urgently. Among the medications, sorbents are used (Smecta, Enterosgel, Activated carbon). Antispasmodics are used to relieve pain.
In case of repeated vomiting, a gentle diet is necessary with the exception of spicy, salty, fatty, sweet, and smoked foods. You need to drink enough fluids per day to prevent dehydration. To normalize the functioning of the digestive system, the doctor may prescribe enzymes (Pancreatin, Creon, Mezim). Bacterial poisoning is treated with antibacterial drugs.
Diseases accompanied by vomiting without fever in children under one year of age
Gastroesophageal reflux. The erupting masses are few and have a sour odor. Gastric emptying occurs immediately after feeding. The child often hiccups, cries, and worries. Hypersalvation is noted.
Treatment is possible at home. Drugs that block the release of hydrochloric acid and antacids are prescribed. It is also necessary to adjust the frequency and volume of feedings.
Pyloric stenosis. The vomit is copious, homogeneous, and is expelled under pressure half an hour after feeding. The symptom appears 2–3 days after birth. The child loses weight, dehydration and convulsions occur. Treatment is surgical and urgent. Pyloric stenosis →.
Pylorospasm. The newborn has mild vomiting. Conservative treatment can be organized at home. It is recommended to feed in small portions and warm compresses on the stomach. If these methods fail, surgery is necessary.
Congenital esophageal diverticulum. There is slight vomiting of digested milk or formula. The disease leads to some weight loss and is treated surgically.
When not to panic
To be objective, there is never any need to panic. After all, a mother’s cool head in a difficult situation will be much more useful than a warm heart. But that’s not about that now...
There are conditions in which excessive regurgitation, similar to vomiting, can be observed. This does not indicate the occurrence of pathological processes, and is rather of a reflex nature. So if these are isolated episodes, and no impurities are observed in the vomit, it is quite possible that the vomiting was provoked by the following reasons:
- swallowing air during breastfeeding or bottle feeding;
- imperfection of the vestibular apparatus;
- excessive amounts of breast milk or formula (overeating);
- insufficiently crushed complementary feeding products;
- the baby being in an excited state immediately after feeding (for example, active games);
- process of teething.
Such vomiting in a baby after breastfeeding should not cause concern if it occurs occasionally . To save your baby from the unpleasant consequences of excessive regurgitation, you need to rinse your baby’s mouth using a syringe without a needle and give him clean water.
Causes of vomiting that do not require treatment
In some cases, vomiting without fever in a child does not require treatment. All you need to do is eliminate the causes of gastrointestinal dysfunction.
Regurgitation of leftover food in infants is normal, occurring 2-3 times a day. The volume of the coming out masses is about 1–1.5 teaspoons. The reasons may be excessive food volume, horizontal position of the baby, insufficient development of gastrointestinal tract functions. In order to eliminate the symptom, you need to feed the baby with his head elevated, make a “soldier” (hold it upright) after each feeding, and do not overfeed. Regurgitation in infants →
Eruption of baby teeth. Vomiting is not profuse and does not affect body weight or appetite. The cause may be swallowing air or feeding during severe pain. To eliminate the symptom, you need to use special gels for the gums and teethers, and massage the gums. Teething →.
Introduction of complementary foods. Single vomiting due to insufficient amounts of enzymes, non-acceptance of the product by the child’s body. Help consists of temporarily eliminating the product.
Psychogenic vomiting in children after 3 years. It can develop against the background of stress, anxiety, or as a reaction to food refusal. It is necessary to eliminate the stressful situation; if this does not help, consult a psychologist.
Indigestion. Attacks of vomiting and loose stools with particles of undigested food. It is necessary to review the diet and give the child more liquid.
Climate change. Vomiting and diarrhea may occur once or twice, and disappear as the child adapts to new conditions.
Causes
Factors causing vomiting are divided into those requiring medical or surgical treatment and those that can go away on their own. These include a functional reaction to the product, climate change, excessive consumption of fatty and sweet foods, teething, rejection of complementary foods at an early age, and psychogenic causes. In infants, regurgitation is observed, in which spasm of the muscular wall of the stomach does not occur, so it does not require treatment and is considered normal. Among the diseases and conditions that cause nausea and vomiting are:
- traumatic brain injury, concussion;
- taking medications;
- pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract (gastrointestinal tract);
- pylorospasm (congenital pathology) or gastroesophageal reflux;
- neurological abnormalities;
- pyloric stenosis;
- diverticulosis;
- entry of a foreign body into the esophagus;
- intestinal obstruction;
- acetonemic syndrome;
- acute gastritis (the child has a stomach ache);
- surgical pathologies;
- inflammatory process in digestion;
- acute appendicitis.
No fever or diarrhea
There are 3 categories of causes of vomiting when the temperature does not rise: psychogenic factors, functional (caused by physiology) and disease-related. A psychogenic gag reflex often occurs in children over 6 years of age. The release of food occurs due to nervousness in adolescents, often as they grow older. Vomiting in children without fever and diarrhea can occur for the following reasons:
- gastroesophageal reflux;
- pyloric spasm;
- pyloric stenosis;
- intussusception;
- acute gastroduodenitis;
- nutritional gastritis;
- pancreatic diseases;
- gallbladder diseases;
- damage to the central nervous system.
Vomiting and diarrhea in a child without fever
Loose stools and vomiting without hyperthermia indicate the body's attempts to remove toxins. This condition develops with an intestinal infection, food poisoning, allergic reactions to food (new complementary foods) or a drug. Intestinal dysbiosis - the lack of bacteria necessary for the normal functioning of the intestines, can also cause indigestion. Vomiting and diarrhea in babies under one year old can be signs of appendicitis.
Vomiting in an infant without fever
In infancy, the release of food is typical for children in the first month of life and disappears after six months. In premature babies, the organs of the gastrointestinal tract may not be fully formed, which is also a reason, but in healthy and developed children, regurgitation is observed several times a day. Parents should be alerted to the situation if there is excessive regurgitation at each feeding and masses of green or yellow color. Other causes of regurgitation in children include:
- taking liquid food;
- short esophagus;
- sensitivity of gag reflex receptors in the stomach, esophagus and throat;
- poor development of the circular muscles.
Child vomits water
After the child vomits, it is necessary to give him something to drink in small portions, since a large amount of liquid provokes the release of water from the stomach contents. In this case, vomiting attacks are repeated. If the baby vomits with particles of eaten or undigested food, and the vomit is watery, then this is a consequence of taking medications that are not suitable for the child’s body. The components of medications negatively affect the gastric mucosa, irritating it. Rotavirus infection provokes vomiting with a fountain of water and diarrhea.
Activities prohibited when vomiting
If a child starts vomiting, under no circumstances should you:
- Perform gastric lavage if the child is unconscious.
- Give your child antispasmodics and antiemetics without a doctor’s recommendation.
- Perform gastric lavage using antiseptic solutions.
- Choose your own antibiotics.
- Do not come for a second examination if your health has returned to normal and your symptoms have disappeared.
Author: Olga Khanova, doctor, especially for Mama66.ru
What to do when your baby is healthy but vomits after every feeding
One of the main reasons for vomiting in a completely healthy baby is swallowing air during feeding. Such vomiting in an infant after milk is more reminiscent of excessive regurgitation; it does not cause any concern to the baby. Its occurrence can be prevented by ensuring proper attachment to the breast. Then, during eating, air will not enter the stomach along with mother's milk. In addition, do not rock or lay the baby down immediately after feeding, but hold it in an upright position for a little while to allow any trapped air to escape.
Another possible reason is improper daily routine . Yes, active games with the baby contribute to his development and at this stage are one of the main ways of communication. But you need to include them into your general daily routine wisely. Otherwise, what can you expect when you feed milk to a still dozing baby and immediately play a roller coaster with him. Even the strongest stomach and trained vestibular apparatus will not withstand such tough descents and ascents.
All active games, water treatments and transport trips should be carried out 1-1.5 hours after the last feeding!
Why does a child vomit: possible disorders and symptoms
The causes of this unpleasant phenomenon can be various disorders in the child’s body, including when the brain is exposed to toxic substances and certain medications.
Common prerequisites include:
- Congenital defect of the stomach muscles , in which a phenomenon such as pyloric stenosis is activated. In this dangerous condition, vomiting occurs immediately after feeding, mainly in female infants. If you look closely, you can see that the child has a sunken fontanelle, and besides, the child is clearly not gaining weight.
- A similar effect occurs when located at the outlet spasm Pylorospasm can occur with vitamin B deficiency, disorders and insufficient development of the nervous system and brain damage as a result of oxygen starvation.
- Reflux disease , when there is an unnatural return of stomach contents to the lower part of the esophagus. Characteristic symptoms are attacks after each meal, but vomit is not profuse. However, the baby is losing weight, does not reach normal weight, and in the morning he has a cough and increased salivation. These signs include sour belching, breathing may be difficult, and the baby snores and grinds his teeth at night. Sometimes this can be explained by the fact that the child’s esophagus has not yet formed, and in the future this phenomenon may go away on its own. At the same time, this disorder can develop and cause other pathologies of the digestive system.
- Gastritis is an inflammation of the stomach walls, potentially also causing the release of vomit. In children, this is associated with dry mouth, hiccups, and also intense pain in the epigastric zone. Most often, the cause of the disease is an inappropriate diet for a child, which is more likely to correspond to the diet of an adult. Vomiting with alimentary gastritis comes with blood and is a real threat to the health and life of the baby.
- Pancreatitis and other diseases of the pancreas. The clinical picture is loss of appetite, abdominal pain, increased gas formation, and slightly elevated temperature. Vomiting is also not accompanied by diarrhea and chills, but it is very strong and subsequently, in addition to the gastric mixture, also contains duodenal bile. Such pathologies threaten significant dehydration. The reasons are an unbalanced diet, frankly unhealthy food, the predisposition of the child’s body to allergic reactions, and the use of potent medications.
- Sudden vomiting can occur with intestinal obstruction . Mostly it happens in infants when they are six months old. The causes of the phenomenon are infectious lesions with rotavirus and adenovirus, inflammation of the colon, allergies, improper feeding and complementary feeding of the baby. Symptoms: an attack that suddenly begins, accompanied by abdominal pain. Vomiting can last five minutes and subside just as suddenly, while there is no diarrhea, but the stool contains blood impurities.
- Often, the gag reflex can occur due to exacerbation of appendicitis . But usually this is only the first sign of an anomaly; a little later the child’s heartbeat quickens, and then the body temperature rises.
- Diseases of the nervous system almost always provoke nausea and vomiting, so this can also be the cause of attacks. Vomiting is a consequence of high pressure inside the skull; at the same time, children’s vision suffers, orientation is disturbed, and dizziness occurs. A tendency to seizures and epilepsy can aggravate unpleasant symptoms.
- The manifestation of vomiting in infants and older children may be associated with pathologies in the functioning of the gallbladder and bile ducts . With cholecystitis and stones in the organ, the child vomits without diarrhea, but if an exacerbation stage occurs, the temperature will steadily rise.
Along with these causes of childhood vomiting, there are other conditions that are important for moms and dads to know about. This is gastroduodenitis in acute form (inflammation of one of the parts of the stomach), enzymatic dysfunction of the liver, any concussions and head injuries, improper functioning of the stomach, which causes indigestion, and household food poisoning. In some cases, vomiting is psychogenic in nature - it is provoked by any stress, emotional overexcitation, or severe fear.
Medical practice shows that with a variety of disorders in the body, vomiting occurs in a child without fever or diarrhea. What to do in such cases? Adults do not need to take any steps in treating the baby - he requires qualified medical care.
What complications can occur with repeated and severe vomiting?
- Dehydration. A sudden loss of fluid disrupts the water-salt balance in the body, and this leads to serious consequences - disruptions in the functioning of all vital organs. With extremely severe degrees of dehydration, convulsions and loss of consciousness are observed. This condition is especially dangerous for infants.
- Weight loss. Dangerous for infants, premature and low birth weight babies. In such babies, critical weight loss can occur within 24 hours.
- Bleeding. With persistent vomiting, the mucous membrane of the stomach and esophagus is injured, blood vessels burst, and as a result, blood may appear in the vomit.
- Danger of suffocation from vomit entering the respiratory tract. The greatest risk is in infants and unconscious children.
- Aspiration pneumonia. Occurs when vomit enters the lungs. Gastric juice is dangerous for lung tissue. Inpatient treatment is required: suction of mucus from the trachea, antibacterial therapy, and, if necessary, artificial ventilation.
You cannot hesitate and self-medicate in such situations.
Vomiting in a child without fever can be a one-time reflex reaction to some irritant: the baby choked, coughed heavily, or ate something tasteless. This is due to the increased gag reflex in children. However, repeated, profuse vomiting, not associated with intestinal infections, can signal a number of serious diseases. In this case, you should definitely consult a doctor.
If a child feels sick or vomits, but there is no body temperature or diarrhea, this cannot be called a disease. But this symptom is an alarming sign for the parent, indicating a disruption in the functioning of the baby’s body or the first sign of illness.
Vomiting is an unpleasant symptom, provoked by a person’s unconditioned reflex, which helps to get rid of what prevents him from functioning normally, the cause of which is a variety of diseases. The process occurs with undigested food, through contraction of the pylorus.
Vomiting without diarrhea and without fever may be accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Morning and general lethargy, impotence.
- Frequent salivation and involuntary swallowing.
- Strong heartbeat and shortness of breath.
- Prolonged nausea.
- Sweating.
- Pale skin.
Fever and diarrhea are absent when the baby regurgitates. It occurs both in a month-old baby and in one year, two years and up to three years. More often, regurgitation stops at 7 months.
- Repeated sudden, one-time fountain, no nausea.
- Pale facial skin.
- Tense, hard abdomen.
If the child feels well and has the listed symptoms, there is no need to worry. Regurgitation after eating is a natural phenomenon of the development of the digestive system. Signs of regurgitation independent of food consumption are dangerous: when the skin turns blue, the baby’s temperature drops, and repeated vomiting occurs.
The process of eruption through the mouth without diarrhea, temperature, depending on the influencing factor, is divided into types:
- Psychogenic vomiting, the cause of which is problems with the central nervous system in children. The psychogenic form is diagnosed in a teenager, a child of 6-7 years old, and rarely in a small child. This type includes kinetosis - the process of motion sickness in transport: land, water, which results in vomiting.
- The urge to vomit is caused by the presence of gastrointestinal diseases.
- Eruption of stomach contents without fever, caused by poisoning.
Vomiting without fever or diarrhea indicates the absence of pathological health problems. An exception to the rule may be a traumatic brain injury or problems with the cardiovascular system. Eruption of stomach contents without additional symptoms.
Vomiting is a consequence of a number of diseases, the causes of which are many. The causes of the psychogenic type are mental disorders, rumination, severe anxiety, and stress. Associative (appearance and smell) eruption also occurs through a psychogenic type.
Diseases of the central nervous system: epilepsy, hypoxia, meningitis, migraine, increased cranial pressure are accompanied by the eruption of gastric contents. Foreign body in the stomach, reflux disease, impaired motility and congenital diseases, which result in gastric emptying.
An infectious spectrum disease is always accompanied by fever. Parasites, bacteria and viruses are provocateurs of fever, stomach upset, and diarrhea. The only exceptions are diseases of the urinary system, bronchi and lungs. The disease develops into a chronic form without symptoms.
Vomiting without other symptoms is a consequence of pathologies: lactic acidosis, cyclic gastric eruption syndrome, which occurs periodically with severe migraines, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases.
Vomiting in a child without fever and diarrhea: what to do at home
Regarding vomiting, we can say that this is a serious indicator of pathological processes, so a doctor should find out what’s wrong with the child. However, parents can alleviate the baby’s condition at a difficult moment for him.
In such a situation you will need:
- put the child in bed, but not on his back, but on his side;
- its head should be slightly raised so that vomit cannot enter the respiratory tract;
- feeding during vomiting is excluded, but after an attack it is necessary to let the baby rinse his mouth with ordinary drinking water at room temperature or weak potassium permanganate;
- in the future, frequent drinking in small portions is allowed, and after two hours the child is allowed to feed thin porridge or unsaturated broth;
- if the baby is an infant and the baby vomits while eating, he needs to be held in his arms for 10-15 minutes in a vertical position;
- Since vomiting implies a loss of fluid in the body, it is important to offer the baby Regidron, which prevents dehydration.
If your baby’s vomiting is accompanied by diarrhea and fever, you should not give him antipyretic or antiemetic tablets or syrups until the doctor arrives. Especially those that are used for adults, albeit in a minimal dose. Calling a doctor is mandatory, since pathology can develop against the background of serious diseases of the internal organs and brain. It is better to be safe than to leave your child without the necessary help.
Single manifestations of vomiting occur in all small children - parents must be vigilant and monitor the well-being of their children every minute. Any additional symptoms already indicate the presence of a problem and this must be remembered.
What to do?
First of all, when vomiting occurs, parents need to closely monitor the child’s condition. It is important to prevent vomit from entering the respiratory tract, therefore:
- the child is placed on his side or held upright;
- After an attack, the oral cavity is cleared of masses; an older child is asked to rinse his mouth with water.
Also, do not force your child to eat. As your condition improves, your appetite will be restored. The main thing is to give enough liquid to avoid dehydration. However, this rule does not apply to newborns and infants, who are recommended to offer breast or formula every 2-3 hours.
To improve the condition, you should give the child rehydration solutions, which you can buy at the pharmacy or prepare yourself. To improve the removal of harmful and toxic compounds from the body, sorbents should be given. On the recommendation of a doctor, antiemetic medications may be taken.
How to help your baby with vomiting
In what cases does a child need immediate help?
When vomiting, self-medication is unacceptable, especially using folk methods. There are cases when the baby’s life depends on the speed of the parents’ reaction, for example, in case of acute appendicitis, when the baby needs urgent surgical intervention.
In this regard, adults need to know in what situations a doctor should be called immediately:
- if there is intense, virtually non-stop vomiting;
- the pathological condition is accompanied by a jump in temperature, severe abdominal pain, and intestinal upset;
- if you suspect food poisoning or household chemicals;
- when vomiting follows mechanical damage to the child’s head, after a fall or bruise;
- crying, hysterics, loud cries of a baby ambiguously indicate health problems;
- if the baby has trouble sleeping and refuses to eat;
- the child experiences semi-fainting, convulsive seizures, along with bouts of vomiting;
- flatulence, heaviness in the tummy, constipation and, at the same time, vomiting are an unnatural phenomenon that requires medical attention.
If a child repeatedly vomits without fever or diarrhea, common sense and love for their baby will tell them what to do for adults. This is a dangerous and abnormal condition that can negatively affect children's health, so the only right decision is to see a doctor and have a comprehensive examination.
Useful video on how to help a child with intestinal upset
https://youtu.be/3JzsPLixWZg
List of sources:
- A. V. Gorelov, D. V. Usenko. Rotavirus infection in children / Issues of modern pediatrics. – 2008. – vol. 7 – No. 6.
- P. L. Shcherbakov, V. A. Petukhov. Comparative effectiveness of enterosorbents for diarrhea in children / Issues of modern pediatrics. – 2005. – vol. 4 – No. 4.
- T. A. Ruzhentsova, A. V. Gorelov. Selection of an adequate treatment regimen for acute intestinal infections in children: results of a randomized trial / Chief Physician of the South of Russia. – 2020. – No. 1 (53).
- I. N. Zakharova, E. N. Andryukhina. Regurgitation and vomiting syndrome in young children / Pediatric pharmacology. – 2010. – vol. 7. – No. 4.
- L. I. Ilyenko, I. N. Kholodova. Intestinal dysbiosis in children / Medical practice. – 2008. – No. 2.
When to call an ambulance
If, in addition to nausea and profuse vomiting, any other symptoms are observed, you should urgently call an ambulance. Self-medication in this situation can seriously harm the baby:
- Diarrhea and vomiting in an infant without fever may indicate food poisoning from low-quality baby food or expired products . If the baby is only 1 month old, you should not give any medications until the doctor arrives. If the child is already 6 months old, you can try giving the sorbent in accordance with the age dosage. And be sure to provide the child with a sufficient amount of water, drinking 1 tsp every 15-20 minutes. If the urge to vomit persists without vomiting, for children over 7 months you can increase the amount of water to 1 tbsp. in one go.
- Fever and vomiting in an infant are clear signs of an intestinal infection. Until the type of pathogenic microflora that caused the infection is determined, treatment is not prescribed. Before the ambulance arrives, the child is advised to drink plenty of fluids.
- Vomiting after a fall is a symptom of a concussion . If, after hitting the head or falling even from a small height, the baby looks lethargic, cries a lot and vomits, urgently take the child for examination. At the age of up to 10 months, the bones of the skull are not yet strong enough, and a head injury at such a young age can have serious consequences.