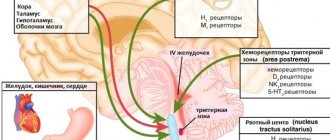
Digestive disorders happen to every person, but if an adult experiences vomiting and diarrhea, then this is a sure sign of a serious disorder in the body, which requires immediate intervention from specialists and medications. There is a fairly large list of diseases with this symptomatology, so it is almost impossible to independently determine the cause and choose the right therapy.
Vomiting and diarrhea in an adult often cause a large number of auxiliary symptoms that can lead to serious disorders in the body. It is worth remembering that it is better to provide the right help at the first stage of the development of the disease in order to prevent the development of serious complications. In addition, everyone should know how to act when such disorders appear, and what features of the condition may indicate the presence of a specific disease.
In what cases are diarrhea and vomiting not an indicator of pathology?
A reaction from the digestive system can occur as a result of many factors. In any case, it cannot be ignored, but it is worth understanding that not in all cases this is a signal of a serious disorder. At times, nausea and diarrhea can be a fairly harmless symptom.
In order to understand that there is no need to sound the alarm, you need to think about whether the following situations were observed in anticipation of the onset of diarrhea and nausea:
- Serious overeating, when the digestive system simply could not cope with large amounts of food.
- Eating large amounts of fatty foods, which also slows down the digestion process.
- Excessive alcohol consumption, which slows down the production of digestive enzymes and can also cause these symptoms.
- Following a strict diet, which causes a failure in the production of digestive enzymes.
- Severe stress.
In all these cases, nausea and loose stools are a functional disorder. These symptoms should gradually subside within the first 24 hours after the first signal. Immediately after eliminating the cause of diarrhea and nausea, a person should feel relief. Also, for these reasons, diarrhea may appear without vomiting, which indicates that the intestines have been overloaded. This condition should also resolve within 24 hours without drug treatment.
Important! If vomiting and diarrhea do not go away within three days, you need to sound the alarm and seek qualified help, since not only the cause of the symptoms is dangerous, but also the symptoms themselves. Frequent loose stools and vomiting can lead to dehydration, which is very dangerous for the entire body. This condition cannot be neglected.
What can you eat
For the first day, it would be good for the patient not to eat anything, but to drink only water. If the vomiting has passed, then you can start giving the patient food. It could be black tea with crackers. If after eating the vomiting does not recur, then the patient can gradually begin to eat. You can give crackers, rice water, rice porridge, well boiled, low-fat kefir. On the third day, you can have a weak chicken broth or light vegetable soup.
The room where the patient is located should be well ventilated, the air should be clean and cool. After vomiting, rinsing with chamomile decoction is recommended. You can use mint.
Intestinal infection
Diarrhea and nausea in many cases are the result of intestinal damage from infectious diseases. In this case, the microflora may be affected by viral, bacterial or parasitic pathogens that inhibit the favorable environment. This affects the digestive processes, and without the correct response, the infection can spread in the body.
If in the early stages diarrhea and nausea can be eliminated quite easily with the competent intervention of a specialist, then in advanced stages it is quite difficult to identify the pathogen, since many complications are observed.
With intestinal infections, diarrhea, nausea and vomiting occur suddenly and the patient's condition quickly deteriorates. Also, this disease is often accompanied by acute abdominal pain and fever as the inflammatory process begins.
In this case, you need to consult a doctor, and in order to prevent the development of infection until you see a doctor, it is better not to get rid of vomiting and diarrhea by taking medications, as this can significantly complicate diagnosis.
First aid for diarrhea
The first thing to do to bind and eliminate possible poisons is to take sorbents. For example, activated carbon or Enterosgel. If the diarrhea is very severe, use Loperamide. You should also take care to prevent dehydration. To do this, you need to take glucose-saline solutions to maintain sugar and electrolyte levels.
Take Regidron or Gastrolit according to the instructions for diarrhea to satisfy this point.
If you can’t buy the product, prepare it yourself in 1 liter of water: take half a spoon of soda, a spoon of salt, ¼ spoon of potassium chloride and 4 spoons of granulated sugar. You need to take the medicine 0.5-1 glass throughout the day. If potassium chloride is not available, you can make a decoction of dried apricots or add fresh orange juice.
If you have severe diarrhea, you should not eat as usual. In the first day or two, it is better to completely remove vegetables, fruits, and meat from your diet. Replace them with porridges - rice or buckwheat. Drink strong tea without sugar and eat crackers. And if by 3-4 days you feel noticeably better, then you can forget about the problem. But if you feel worse, be sure to consult a doctor.
Food poisoning
Missing or poorly processed foods can also cause diarrhea and vomiting. In this case, the symptoms begin to be very similar to an intestinal infection. There is also sudden onset of nausea, vomiting and diarrhea.
In this case, there are several more auxiliary symptoms:
- Headache.
- General weakness.
- Feeling of body aches.
- Sudden temperature rises to critical levels.
This is how the body reacts to an excess of toxins that have entered it. In this case, you will not be able to get rid of these disorders on your own; you need to call an ambulance. Until her arrival, you won’t be able to get rid of diarrhea and vomiting; you just need to drink as much fluid as possible to help remove toxic substances from the body. But how to treat this disease in each case is decided by the doctor after assessing the general condition of the patient.
Treatment
If the causes of diarrhea with vomiting are much more serious, then the patient is prescribed drug therapy in accordance with the cause of the pathology.
- First, sorbent preparations such as activated carbon, Sorbex, Enterosgel or Smecta are prescribed. If vomiting does not stop and prevents you from taking the drug orally, you can do an enema with a sorbent.
- Self-administration of drugs whose action is aimed at suppressing peristalsis, for example, Loperamide or Imodium, is unacceptable. Diarrhea and vomiting are natural organic reactions aimed at cleansing toxic substances. If these reactions are stopped, toxins will enter the bloodstream, leading to dangerous consequences.
- If diarrhea and vomiting are indomitable, it is recommended to prevent dehydration. To do this, you need to take solutions like Regidron or simply drink more water.
- If the ailment is of bacterial origin, antibiotic therapy or antimicrobial drugs such as Enterofuril or Nifuroxazide are prescribed. They are prescribed only by a doctor; self-medication can be dangerous.
- If there is a deficiency of enzyme substances or overeating, patients are recommended to take pancreatin, for example, Festal or Mezim.
- If vomiting is too frequent and does not go away for too long, then in addition to drinking plenty of fluids, medications like Metoclopramide or Diazepam can help calm the stomach.
Drinking plenty of fluids is necessary. You can use medications if the readings exceed 38 degrees. If the temperature continues to rise, then you need to call an ambulance.
Diseases that provoke this condition
Unfortunately, diarrhea and vomiting in an adult do not always go away after fairly simple treatment. In some cases, these unpleasant conditions serve as a signal for the development of serious diseases.
Such ailments include:
- Gastritis and peptic ulcers. In this case, in addition to nausea, vomiting and diarrhea, the temperature rises to about 38 degrees, and the symptoms are not observed constantly, but periodically. The patient also feels severe pain in the stomach area.
- Cholecystitis is a liver disease. At the moment of its defeat, the body begins to poison itself, so vomiting and diarrhea appear, which are accompanied by abdominal pain, fever and general weakness. With this disease, appetite drops sharply and the person loses weight.
- Inflammation of the pancreas also provokes these symptoms, but at the same time there is pain in the left hypochondrium and near the navel, and undigested food particles can be observed in the stool.
- Tumor diseases cause loose stools, vomiting and acute pain that is constantly increasing in nature. Feces with these diseases change color, and the presence of bloody impurities may be observed.
These conditions are quite severe and require immediate medical intervention. With proper treatment, in most cases it is possible to achieve long-term remission of the disease and the patient can lead a full life with minimal dietary restrictions.
Important! The most important assistant in stabilizing the condition is changing your diet. If disorders of the digestive system occur, it is necessary to eat food in small portions at intervals of several hours. At the same time, the menu should include only foods that are easy to digest.
Diagnostic methods
When you contact a doctor, a diagnostic examination will be prescribed to determine the causes of the above symptoms.
Table 1. Diagnostic procedures
| Name | Description of the method |
| Palpation | The doctor examines the patient's abdominal area with his fingers. At the same time, the nature of the pain that occurs during this stage of the examination is determined, on the basis of which a preliminary diagnosis is made. To clarify it, standard tests of blood, urine and feces are prescribed. |
| Coprogram | This diagnostic method helps determine the presence of infections, their type and specific pathogens. Stool samples are also examined for the presence of parasites. It is known that the causes of diarrhea and vomiting can be roundworms, lamblia and pinworms, which easily enter the body with low-quality or unprocessed food, from dirty hands and other sources. In deciphering the coprogram, the density and appearance of feces, coloring, the presence of a specific odor, particles of undigested food and various discharges (purulent, bloody) are analyzed. |
| Hydrogen breath test | Using this diagnostic method, a specialist can obtain information about the presence of bacteria, malabsorption of minerals and nutrients, as well as the prevalence of bacteria in the small intestine. |
| Colonoscopy | The examination is carried out using a fibrocolonoscope, and the inner surface of the intestine is examined up to the colon. The device is inserted through the rectum. |
| Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGDS) | Using this method, a detailed examination of the internal linings of the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum is performed. The study is carried out using a gastroscope inserted into the esophagus through the oral cavity. |
| Ultrasound examination (ultrasound). | This diagnostic method allows a specialist to give an objective assessment of the condition of the gastrointestinal tract and determine the presence of pathological processes that caused diarrhea and vomiting. |
| Irrigoscopy | This diagnostic method is intended for a detailed examination of the colon. The doctor receives images that clearly show defects in the mucous membranes. The results of irrigoscopy completely eliminate the chance of medical error. |
| Sigmoidoscopy | The diagnostic method is aimed at examining the rectum and sigmoid colon. Using a sigmoidoscope, pathologies such as tumors, fissures, polyps and hemorrhoids are detected, which can also cause diarrhea. |
Sometimes one diagnostic method is enough to determine the cause of the pathological condition. In more complex cases, a series of examinations are prescribed to make an accurate diagnosis.
Loose stools and vomiting during pregnancy
At the moment of the birth of a new life, serious changes occur in the female body, which cause many unusual conditions. Diarrhea and nausea occur quite often in pregnant women. In most cases this is the result of toxicosis. This process is caused by a sharp change in hormonal levels.
And in most cases it is observed in the first trimester of pregnancy and in the last stages. In this case, treatment of vomiting and diarrhea is carried out using a gentle method, that is, drugs are not taken to eliminate symptoms, but medications are prescribed to maintain the body. Gradually all the unpleasant sensations go away.
But without consulting a specialist, a pregnant girl should not encounter this condition, since sometimes, due to a sharp change in hormonal levels, a sharp development of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract can be observed. Therefore, only after a careful assessment of the general condition of the expectant mother can the doctor tell about the degree of complexity of the disease and advise what to do with diarrhea and vomiting.
Main causes of diarrhea
Diarrhea, with or without fever, occurs due to a sharp increase in water content in the intestines. With diarrhea, fecal matter contains up to 90% liquid. The volume of stool in combination with other symptoms allows us to establish the approximate nature of the disorder:
- Motor impairment . If peristalsis is impaired, the stool becomes liquid, but its volume does not increase. In this condition, the patient requires drugs that restore intestinal motility.
- Violation of the suction mechanism . In the presence of this pathology, severe diarrhea with water appears. In this case, the volume of feces increases due to the large amount of undigested food.
If the symptom is not accompanied by fever, then the causes of diarrhea in adults may be as follows:
- Dyspepsia . What causes disorder in an adult is elementary “indigestion” caused by excessive consumption of food.
- Impaired enzyme production , caused by both diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and unhealthy eating habits.
- Food intolerance . Also causes distress without fever. We are talking about acquired intolerance, since congenital intolerance is identified in childhood.
- Poisoning by foods , both exotic and familiar, but improperly prepared. Mild poisoning occurs without fever.
- Taking medications . Diarrhea without fever can appear in an adult when taking medications - laxatives, antacids, anticoagulants.
- Helminthic infestations, giardiasis . When infected with protozoa, loose stools are rarely accompanied by fever, although symptoms of common ailments may be present, making diagnosis difficult.
- Pathologies of the gastrointestinal , including those of an inflammatory nature (gastritis, ulcerative colitis), cause chronic diarrhea without fever.
- Stress . It often provokes stool upset in adults. Its distinguishing feature is transience.
- Traveler's diarrhea . Appears when eating unfamiliar unusual foods, contaminated water, raw meat and fish.
Important! On average, diarrhea lasts 3-4 days. Prolonged diarrhea in an adult, not accompanied by fever, indicates a chronic course of the disease.
When to call an ambulance
- Severe symptoms of poisoning. If blood appears in your stool within 24 hours.
- You belong to a risk group.
- If botulism is suspected, life-threatening food poisoning occurs (occurs when botulinum toxin gets into food). It is most often found in home canning, especially green beans and tomatoes.
- blurred vision;
- muscle weakness, even paralysis;
- difficulty urinating;
- difficulty breathing and dry mouth;
- migraine.