Can food cause heart pain?
Substernal discomfort in the heart area after eating is most often the result of serious complications of a cardiac, pulmonary, vascular, infectious, gastrointestinal nature that arise in the body, or a consequence of psychological problems. The syndrome that develops at the intersection of cardiology and gastroenterology is called gastrocardial.
The bottom line is that when food is swallowed, mechano- and chemoreceptors are activated in the esophagus, stomach and intestines. This causes irritation to the vagus nerve that controls them, causing heart attack-like symptoms.
In addition, this occurs against the background of coronary atherosclerosis, so food in the stomach, requiring blood flow, aggravates the already insufficient blood supply to the myocardium, causing chest pain.
What is the diagnosis of gastrocardial syndrome?
Basically, the diagnosis of gastrocardial syndrome is based on the exclusion of cardiac pathology and other mediastinal diseases. For this purpose, patients undergo an ECG, and it usually shows no signs of myocardial ischemia. To exclude a hiatal hernia, an ultrasound of the abdominal organs and contrast radiography are performed. These research methods will exclude pathology of the liver and pancreas.
To diagnose gastrocardial syndrome, endoscopic examination is strictly prohibited, since irritation of the receptor zones of the esophagus and stomach leads to excessive stimulation of the vagus nerve, and cardiac arrest is possible. In order to diagnose peptic ulcer disease, such patients are subjected to a urease breath test.
Causes
Among the causes of gastrocardial syndrome are:
- VSD with fluctuations in vascular tone as a result of impaired innervation;
- swallowing air (aerophagia);
- high intra-abdominal pressure due to flatulence and high position of the diaphragm.
It is generally accepted that this is the prerogative of people with a labile psyche, suffering from stomach ulcers, tumors of the digestive system of various origins. In addition, pain in the heart area (stabbing, cutting, aching) associated with eating occurs with the following diseases:
| Name of pathology | Characteristic signs |
| Extracardiac | |
| Gastritis | The causes may be autoimmune processes, Helicobacter pylori, poor nutrition, poor diet, alcohol, smoking. Pain occurs only in the acute phase; the chronic course is asymptomatic. Behind the sternum begins to burn after eating immediately or within half an hour, they resemble angina pectoris, but are not relieved by Nitroglycerin, they respond well to antacids. A distinctive feature is the presence of concomitant symptoms in the form of:
|
| Peptic ulcer of the stomach or duodenum | Provokes substernal discomfort associated with food, accompanied by the following symptoms:
Exacerbation occurs in the autumn-spring period. A distinctive feature is the relief of the severity of manifestations with antacids, but in case of exacerbation, these remedies (like a heating pad on the epigastric area) do not bring complete relief: examination and adequate pathogenetic therapy are needed. |
| Binge eating | Constant gluttony causes increased gas formation, a feeling of heaviness, and discomfort in the chest. Similarly, pain occurs when overeating garlic, onions or foods that a given person cannot tolerate individually. |
| Gastroesophageal reflux or GERD – gastroesophageal reflux disease | Nausea and heartburn are the main symptoms of the pathology; they may be accompanied by chest pain. The essence is a retrograde reflux of stomach contents into the esophagus, while acid from the stomach causes a burning sensation in the sternum area and an unpleasant taste in the mouth. |
| Esophageal hernia | Pain in the heart area, intensifying after eating or lying down, is accompanied by nausea, heartburn, tachycardia or bradycardia, and dizziness. |
| Indigestion | Gives phantom pain in the heart if a block occurs during the passage of food from the esophagus to the stomach, accompanied by difficulties when swallowing. |
| Dumping syndrome | The result is gastric resection, accompanying symptoms:
The point is that the raw food bolus enters the small intestine from the stomach, which stretches its walls and stimulates the synthesis of histamine and kinins, which enhance peristalsis. |
| Pancreatitis | Chest pain is unbearable, girdling, occurs after eating, especially after taking spicy food or alcohol, several hours later, accompanied by nausea, bloating, radiating under the left shoulder blade and shoulder. |
| Biliary tract diseases | Substernal discomfort occurs after eating fatty foods and is combined with heaviness in the right hypochondrium, loss of appetite, and nausea. |
| Heartfelt | |
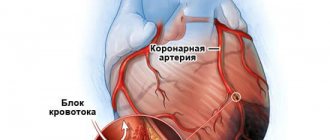
| Angina pectoris | A type of IHD is angina pectoris, which manifests itself as attacks of chest pain after physical activity or after eating heavy food, overeating: the diet should be redistributed in favor of fruits, vegetables, and eating in small portions. |
| Myocardial infarction | This is a gastric type of heart attack, characterized by severe pain in the epigastric region, simulating a stomach ulcer, and requires urgent medical attention. |
| Psychological problems | |
| Cardioneurosis | In the absence of any organic changes in the heart and other internal organs, we are talking about the psychogenic nature of retrosternal discomfort: like a stone on the heart or a lump in the throat after eating, accompanied by tachycardia and arrhythmias. The reason is stress, strong emotions. |
| Panic attacks | Substernal discomfort after eating can be triggered by anxiety, stress, VSD |
In addition, diseases of the lungs and pleura can cause pain in the chest, including after eating, as well as acute respiratory viral infections, acute respiratory infections, and infections. Diagnostics will help determine the exact cause.
What if your heart hurts after drinking coffee?
Scientists have found that coffee cannot affect the functioning of internal organs, in particular the heart, if there were no problems with a person’s health before drinking this drink. But excessive consumption of this drink can affect the functioning of the body as a whole.
As such, caffeine does not have negative properties, but it does have some effects on organs and systems, which can cause detrimental effects on the human body.
So, it is believed that coffee increases blood pressure, but in fact, caffeine prevents it from decreasing, which has unpleasant consequences for people with high blood pressure.
What can cause heart pain and problems with the nervous system.
Scientists have found that coffee cannot affect the functioning of internal organs, in particular the heart, if there were no problems with a person’s health before drinking this drink. But excessive consumption of this drink can affect the functioning of the body as a whole.
As such, caffeine does not have negative properties, but it does have some effects on organs and systems, which can cause detrimental effects on the human body.
So, it is believed that coffee increases blood pressure, but in fact, caffeine prevents it from decreasing, which has unpleasant consequences for people with high blood pressure.
What can cause heart pain and problems with the nervous system.
It should be noted that coffee increases the excretion of gastric juice and can cause exacerbation of gastrointestinal diseases in susceptible individuals. For varicose veins of the lower extremities, coffee consumption is harmful, as it causes blood stasis in the extremities.
- dried apricots;
- kiwi;
- dairy products;
- chocolate;
- pumpkin seeds;
- walnuts;
- baked potatoes;
- raisins.
If heart pain occurs after drinking coffee and its causes are not clear, you should visit a doctor and undergo an examination. In this case, it is worth significantly reducing the amount of drink consumed.
What to do about heart pain after eating
A specific treatment regimen can be selected only after a detailed analysis of the examination results, but there are a number of rules that can make the patient feel better:
- give up caffeine-containing drinks, chocolate, spicy, fatty foods;
- exclude from the diet freshly squeezed and canned juices, which irritate the esophagus;
- eat at the same time, in small portions, at least 4 times a day;
- calculate the correct drinking regime;
- walk regularly after meals, which corrects digestion;
- dinner a couple of hours before bed to prevent night pain.
The symptom of heart pain that occurs after eating cannot be ignored, as it may be a sign of a serious illness. Differential diagnosis, which will help distinguish chest discomfort of cardiac etiology from any other, may be taking a Nitroglycerin tablet.
Diagnostics
In order to determine what exactly caused the pain in the heart after eating, it is necessary to undergo a series of examinations:
- Electrocardiography. The procedure will reveal dysfunction in the heart.
- Ultrasound of the cardiovascular system and gastrointestinal tract. It will allow you to determine whether there are pathologies of the heart, stomach, intestines, and liver.
- Contrast radiography. The procedure is aimed at identifying diseases of the abdominal organs.
The exact diagnostic method is determined individually based on the patient’s complaints. For example, in case of gastrocardial syndrome, endoscopic examinations are not used in any case.
Pancreatitis
This is an acute inflammatory process developing in the pancreas. At the same time, it is not always clear what hurts more: the heart or the stomach.
Since the gland is located immediately under the stomach on the left, the localization of pain will be in this area and above, just where the heart is located.
The pain is sharp and cramping (at the beginning of the process), dull and aching (during the recovery stage).
The inflammatory process engulfs the tissues of the organ, gradually destroying them, and intoxication of the entire body occurs.
Symptoms may be as follows: pain in the heart and left hypochondrium, loose stools with pieces of undigested food, belching, hiccups, pale skin and mucous membranes, symptoms of dehydration. Body temperature may rise.
Such signs appear in acute form of pancreatitis.
The pancreas is very sensitive to alcohol intake. This may be the cause of its inflammation. Alcohol makes her work harder, causing inflammation in her tissues.
conclusions
Patients with pain behind the sternum or in the upper abdomen need to first assess the situation in which the problem arose, remember similar symptoms, if they existed before, and the features of its progression.
In case of diseases of the digestive tract, the occurrence of discomfort is a reason to consult a doctor, since taking painkillers “blurs” the picture of the pathology, which complicates diagnosis.
The following sources of information were used to prepare the material.
Painful sensations in one organ periodically radiate to another. “The stomach and heart hurt” are often said by people with ordinary gastritis. This is a typical situation in an internal medicine clinic. The causes of stomach pain are varied, but they rarely affect the cardiovascular system. Confusion occurs due to the close anatomical location of both organs. Therefore, high-quality differential diagnosis and timely treatment provide a good result and the absence of complications.
Nutrition rules
Pathology of the gastrointestinal tract, gall bladder, and heart requires mandatory adherence to a diet. The basic principles of nutrition are:
- Fractional meals. The number of receptions is 5-6 per day.
- Eating food warm.
- Exclusion of fatty, spicy, smoked, salty foods.
- Steaming dishes.
- Replacing fresh bread with yesterday's bread, crackers.
- Exception of chocolate and baked goods.
- Inclusion of sweet fruits and vegetables in the diet.
Walking in the fresh air, following a daily routine and healthy sleep, which should last at least 8 hours, will help maintain health.
The appearance of periodic attacks of tachycardia or extrasystole after eating is a signal:
- possible failure of the cardiovascular system;
- insufficient interaction of organs and systems of the body;
- constant overload of the digestive system with the need for additional oxygen and energy to completely digest food;
- insufficient oxygen supply to organs;
- overstimulation of the autonomic nervous system.
If arrhythmia appears after eating, it is necessary, first of all, to make changes to your diet and lifestyle.
Basic nutritional rules include:
- You cannot eat a large amount of food at one time - meals should be fractional, distributed throughout the day;
- Do not go to bed after lunch or dinner;
- Adhere to the principles of a balanced diet:
- It is advisable not to eat large amounts of salt, sugar, sweets, fatty meats and fish, fried and spicy foods, smoked foods, marinades, heavy and difficult to digest dishes (noodles, pancakes, dumplings, dumplings), foods with a long shelf life, fast food;
- increase fermented milk products, cereals, herbs, vegetables, fruits, and fiber-rich foods in your diet.
- Organization of fasting days if you are overweight.
- More often eat well-heat-treated foods and warm liquids.
- After eating, it is advisable to take a walk in the fresh air.
Where does it hurt?
With heart problems, the most common pain is behind the sternum (that is, in the center of the chest). The interweaving of nerve endings located in this zone creates the most sensitive zones that subtly react to cardiac problems.
How does it hurt? A heart attack is characterized by squeezing, pressing, burning, sometimes tearing pain. “The pain started in my right shoulder... Then it crawled up to my chest and got stuck somewhere under my left nipple. Then it was as if someone’s calloused hand penetrated my chest and began squeezing my heart like a bunch of grapes. She squeezed slowly, diligently - one-two, two-three, three-four... Finally, when there was not a blood left in the squeezed out heart, the same hand indifferently threw it away...” - this is how the writer Nodar Dumbadze .
How long does it hurt? With a developing heart attack, an attack of heart pain lasts much longer (15 minutes or more) than with angina pectoris, often provoked by physical activity or stress, but can also occur at rest, for no apparent reason.
Where does it give? Most of all, cardiologists are alarmed by complaints of pain behind the sternum, which radiates to one or two shoulders and especially to ... the jaw. Some people mistake this kind of pain for a toothache and, after the attack ends, even go to the dentist, unaware that they were halfway to a heart attack. The fact is that in the projection of the cervicothoracic spine there are nerves that supply the innervation of the heart, the chin area, and the area of the shoulder joints. Therefore, the pain impulse from the heart muscle is often transmitted to a neighboring node. If at the same time a person’s left arm also goes numb (from the shoulder to the elbow or to the little finger), and the body is covered in cold sweat, there can be no two opinions: you urgently need to dial “03”.
Does pain depend on movement? By answering this question, we can assume what the resulting pain syndrome is associated with - a cardiovascular problem or intercostal neuralgia, diseases of the spine (osteochondrosis). If a person’s pain changes or intensifies when inhaling, exhaling, or moving his arm, then it is most likely not of a cardiac nature. If pain appears during an ordinary walk around the apartment or at rest, this is a sure sign of acute coronary syndrome and a reason to call an ambulance.
Is there shortness of breath? Shortness of breath, which requires serious attention, is characterized by a sudden, acute onset. Especially if the feeling of lack of air arose for the first time, at rest or during the person’s usual physical activity (cleaning the apartment, walking, on the way to work), and decreases when the person sits down or lies down. Sometimes coronary heart disease (CHD), pulmonary hypertension, acute coronary insufficiency, a painless form of myocardial infarction, and pulmonary embolism can occur in this type.
However, shortness of breath can also be of neurotic origin, after emotional stress, when stress hormones are released into the blood, increasing the number of respiratory movements. So it is better to consider this symptom in conjunction with others.
Treatment
The specific course of therapy is determined based on the diagnostic results. Depending on the identified disease, the patient may be prescribed the following treatment:
- Modern measures to combat gastrocardial syndrome include psychotherapy and proper nutrition. The patient must adhere to a diet and eat small portions, excluding overeating. A very important step is to stop consuming chemical products and foods that lead to excessive gas formation. Before eating, the patient must take antispasmodics. If such treatment does not produce results, an operation is performed to suturing the hernial orifice and strengthening the stomach.
- For gastritis, the patient is prescribed diet and drug therapy. A set of physiotherapeutic techniques may also be carried out.
- An ulcer requires immediate treatment. If the disease is in an advanced state, then the only way to get rid of the disease is surgery.
Therefore, if a patient experiences pain after eating in the heart area, the cause of this is most often a pathology of the gastrointestinal tract. To determine a specific disease, consultation with a specialist is necessary. Treatment will depend on the type of disease and the characteristics of its manifestation. In most cases, a person will simply need to normalize their diet and lead a healthy lifestyle.
Diet is the best treatment for gastrocardial syndrome
Therapy for this pathology consists of proper fractional nutrition and psychotherapy. Meals should be in small portions, avoiding overeating. It is important to limit the consumption of harsh chemical products and products that lead to excess gas formation. If you are overweight, it is recommended to normalize it.
It is recommended to take antispasmodics before meals. In the absence of organic pathology, psychotherapy is carried out, which is the most effective method of treatment. Drug treatment of gastrocardial syndrome involves the use of sedatives and sedatives.
If drug treatment of organic pathology is ineffective, surgical treatment is performed, which is aimed at suturing the hernial orifice, fixing the stomach and strengthening the esophageal-diaphragmatic ligament.
You should not ignore such symptoms, because pain in the heart after eating, which occurs for the first time, does not always indicate gastrocardial syndrome.
A situation in which the heart hurts after eating occurs in many people. Almost every person experiences this feeling at least once in their life, it’s just that most people don’t pay any attention to it. It should be understood that the occurrence of pressing pain in the middle of the sternum cannot be a consequence of banal overeating.
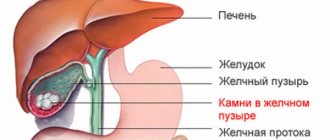
Biliary colic
The formation of stones in the gallbladder as a result of disruption of its functioning contributes to the disruption of the outflow of bile. Accumulated bile leads to inflammation of the digestive organs and intoxication of the body.
The following symptoms will be observed:
- severe pain in the heart;
- pain in the stomach and liver (in the right hypochondrium);
- tachycardia up to 100 beats per minute;
- intestinal dysfunction;
- vomiting pieces of undigested food, and then bile.
Increased pain is observed upon palpation of the right side below the edge of the costal arch. This is the difference between stomach pain and heart pain.
The effect of cholecystitis on the heart
Cholecystitis is an acute inflammatory process that affects the gallbladder. As a rule, with this pathology, pain initially occurs in the stomach area, but if it is not relieved, it goes into the stage of exacerbation and rapidly spreads to neighboring organs located behind the chest: heart, lungs, bronchi, etc.
Cholecystitis
The nature of pain in cholecystitis is often aching, dull, significantly different from the pain that occurs with any cardiac disease. Additional symptoms that help distinguish abdominal pain due to inflammation of the gallbladder from characteristic heart pain are:
- Accelerated heart rate (with this symptom the patient may often have a headache).
- Involuntary belching, after which the taste of bile remains in the mouth.
- Itching of certain areas of the skin.
- Constant nausea, which is replaced by vomiting when drinking alcohol or prohibited foods.
- The occurrence of constipation or diarrhea (depending on the level of acidity of the patient’s stomach).
If you start treating the pathology at an early stage of development, when the pain does not yet radiate to the heart, then in a short period of time you can get rid of pain completely. Otherwise, cholecystitis will go into a chronic stage, in which the stomach and heart can become ill at any time, regardless of the negative impact on them.