Lumps in the lower abdomen are a common occurrence in people of any age. This is understandable, since in the space behind the peritoneum there are many organs and systems (stomach, spleen, colon, gallbladder, ileum, small intestine, upper region of the ureter and kidneys, greater omentum, urinary and digestive systems). Each organ may experience a malfunction, which will manifest itself through swelling, pain, swelling, as well as hardening of a certain part of the abdomen.
It is not dangerous if it is simply caused by muscle strain. However, protrusion may not be so harmless; it is quite possible that the body is giving a signal that urgent measures are required to avoid complications and bad consequences. The seal is most often located on the right side. Let's consider the main causes of pain in the lower abdomen and the formation of a lump from several points of view.
Anatomy of the stomach
The stomach is an extension shaped like a bag, designed for temporary storage and partial digestion of ingested food. It performs important functions. The length of the organ reaches 20-25 cm, volume – 1.5-3 liters. The size and shape of the stomach are determined by its fullness, the age of the patient and the condition of the muscle layer.
The stomach is located above the epigastrium, most of it to the left of the middle plane, and 1/3 to the right of it. The organ in its normal physiological position supports the ligamentous apparatus.
The wall of the stomach consists of three layers, each of which has a specific structure. The gastric walls are protected by an inner epithelial layer - the mucous membrane. Beneath it there is submucosal adipose and epithelial tissue, including capillaries and nerve endings. It contains glands that produce stomach secretions, mucus and peptides.
Food enters the stomach through the esophagus and is digested under the influence of gastric juice and hydrochloric acid over a period of 2-6 hours. Then, thanks to periodic muscle contractions, the food bolus moves to the outlet and is pushed out in portions into the duodenum.
On right
Slightly above the middle abdomen on the right are the ascending colon and the right kidney. Lumpiness in the lower abdomen near the navel on the right, discomfort and pain can occur due to such provoking factors as:
- Appendicitis. When troubles arise, the appendix becomes inflamed and moves to the right. Most often it causes acute pain, accompanied by nausea and fever. Patients need to urgently contact a surgeon for further treatment.
- Lipoma, as a result of blockage of the sebaceous glands or a benign wen. The tumor, soft to the touch, may increase in size and roll slightly under the layer of skin. Surgeon intervention is required.
- Atheroma in the form of a cyst with a diameter of up to three centimeters, in close contact with the skin. A black dot may appear in the middle of the abdomen, indicating a blockage of the gland. Atheroma is inflammatory in nature, so the symptoms are pain in the area, hot to the touch. Surgery required.
- Fibrosarcoma is a malignant tumor with a diameter of up to 2-15 millimeters. It looks like a smooth bump (scar) on the skin, painful and mobile. The area in the middle part of the abdominal quadrate is tense, atrophies over time and can become covered with erosion and crusting. Requires surgical removal.
- Diverticulitis is a type of hernia, characterized by the accumulation of intestinal contents as the inflammation process develops. Pathology can also cause pain in the lower abdomen. Provocateurs are hereditary factors, infection with worms, decreased muscle tone and poor nutrition. Symptoms: stool with blood particles, defecation disorder, painful area with inflammation and fever. Treatment: surgery or antibiotics.
What else can hurt the lower abdomen?
Norm and deviations
Normally, the stomach is located on the left side of the body, but systematic overeating can cause it to shift to the abdominal area of the organ. Near the esophageal opening and the transition to the duodenum there are muscle thickenings in a circular shape. They prevent food from entering the esophagus. When the functions of the alimentary valve are impaired, gastric contents are thrown into the esophagus, causing heartburn. Damage to the sphincter causes bile and pancreatic juice to enter the stomach or, conversely, acidic contents to leak into the intestines, which leads to irritation of the stomach walls and ulceration.
Normally, the position of the cardia is determined on the frontal wall of the abdomen in the area of 6-7 ribs. The vault or fundus of the stomach reaches the fifth rib, the pylorus reaches the eighth rib. The lesser curvature is located below, to the left of the xiphoid process, and the greater projection runs arcuately from the fifth to the eighth intercostal space.
Depending on the specific body type, specific shapes and types of the human stomach are distinguished:
- Horn or cone shape. They occur when a person has a brachymorphic physique. The stomach has an almost transverse arrangement.
- Fish hook shape. Typical for patients with mesomorphic build. The body of the stomach is located vertically, then bends sharply to the right side, forming an acute angle between the evacuation route and the digestive sac.
- Stocking shape. It is recorded when the patient has a dolichomorphic physique. The descending zone of the stomach is low, and the pyloric part is raised steeply, located along the midline or slightly to the side of it.
These forms are inherent to a body in an upright position. When a person lies on his side or back, the shape of the stomach changes. That is why the palpation procedure is carried out in a supine position in order to obtain the correct clinical picture characterizing a certain pathology.
Deviations from these norms and changes in the size of the stomach, as well as displacement of the organ, indicate the presence of pathological processes and may be symptoms of a specific disease.
Women's problems
Pathologies or reasons for the appearance of lumps in women are often gynecological in nature. Doctors advise not to wait for severe colic or other signs of pathology to appear: nausea, bleeding and to go to the clinic.
Provokes tumors in the abdomen in women:
- adhesions in the uterine cavity;
- torsion of the appendages, when a compaction is observed in the left, right part of the navel, in addition there is nausea, vomiting, throbbing pain, when surgical intervention is no longer possible;
- ovarian cyst with compaction as the tumor reaches an impressive size;
- menstrual irregularities.
Treatment will depend entirely on the type and size of the tumor - conservative or surgical.
It is not uncommon for sutures to harden in women after a cesarean section. Of course, the resulting lump does not always indicate pathology. But a caesarean section is a complex operation in which doctors have to cut tissue in the peritoneal area. Next is to seal the honey. materials, and fabrics are sewn with a ligature.
During the recovery period, the sutures are covered with scar tissue, but sometimes a growth appears in the peritoneum due to an autoimmune reaction, the use of low-quality materials, tissue infection, and the development of an abscess under the skin.
It is suppuration that can become a dangerous phenomenon in the event of damage to tissues under the skin, cell death, and mixing of dead tissue with keratinized skin particles. Bacteria may enter, which can lead to infection, modification of structures and compaction of tissues. Additionally, itching, burning, and ichor appear in the middle square of the peritoneum.
Dissection of the lymphatic channels during surgery can also lead to a lump above the suture. In the case of non-fusion of the damaged lymphatic channel, fluid moves into the free space in the peritoneal cavity filled with lymph.
A similar phenomenon can occur after laparoscopy, in the case of poorly performed surgery on the uterus and appendages. One way or another, the dissected tissue in the peritoneal cavity is stitched and secured with threads. Lack of quality or inexperience, the negligence of the surgeon leads to complications, infection of wounds and sutures, and the development of a bacterial infection.
In the best case, scar tissue forms under the skin, in the worst case – active proliferation of cells in this area, the formation of a keloid scar due to infection, the development of inflammation.
Women need to closely monitor their stitches after surgery:
- follow preventive measures and doctors’ instructions;
- Treat seams regularly with antiseptic solutions. Fukortsin, brilliant green);
- stick the patch onto the surface of the seam.
Alarm bells should be a reason for an urgent visit to the gynecologist: severe pain and colic at the incision sites, oozing ichor from the wound with a serous smell of rot, high fever, redness and swelling at the stitching sites, unpleasant vaginal bleeding with itching, burning, pain.
An examination is required and, most likely, an operation to clean the sutures in case of suppuration.
Pregnancy
As the fetus grows, the skin of women during pregnancy stretches, but some tension in the peritoneum does not pose any particular danger. This often happens due to underdeveloped abdominal muscles and excessive tension.
However, sometimes the reasons are:
- appendicitis accompanied by colic, pain;
- gastroduodenitis with pain in the upper quadrant of the peritoneum;
- cystitis with burning sensation, pain when urinating, retention and stagnation of urine;
- umbilical hernia, a common occurrence in the postpartum period with the appearance of protrusion.
Even if the protrusion does not hurt or cause any particular discomfort, you should consult a doctor. So, for example, with oncology, the tumor does not hurt and may not make itself known for a long time. Meanwhile, it is dangerous due to its transformation into cancer and a malignant form, when the consequences can become completely irreversible.
It happens that the hernia is reduced on its own when taking a horizontal position. But sometimes it forms as a result of a cesarean section and becomes uncontrollable when medical intervention is already inevitable. Additionally, there is acute cramping pain, high fever, diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting.
Signs contribute to increased intestinal tone together with the uterus and can lead to miscarriage and premature birth.
Any deviations from the norm should be a reason to contact a gynecologist. Women should not ignore even minor unpleasant symptoms or visual changes in the navel area.
In children
The most common occurrence in a child from birth is an umbilical hernia or a hard lump that does not disappear upon palpation in the peri-umbilical area. Additionally, babies kick their legs and refuse to eat. Colic and bloating are observed. There are strangulated and reducible hernias. In boys it is usually the groin, in girls it is usually the umbilical. In any case, treatment and the help of a surgeon are required.
When is palpation performed?
Indications for the procedure are cysts, tumors of various origins, hernias, organ displacement, obesity, and inflammatory processes. The patient may complain of increased flatulence, stomach pain, and a clinical picture of appendicitis may be observed.
During the initial examination, the doctor also records weight loss in patients associated with food restriction, to clarify the presence of pain after eating, pallor of the skin, indicating hidden ulcerative bleeding, or grayness of the skin, which is a symptom of stomach cancer.
Causes
Various factors, even at first glance not related to dermatology, can provoke the formation of a seal. The most common reasons include:
- Changes in metabolic processes, including those associated with the development of chronic diseases.
- Hormonal imbalance. Deviations can be caused by thyroid dysfunction, medications, and other circumstances affecting the endocrine system.
- Infectious, viral pathologies. Infection can occur directly through the skin, where the problem area has formed. Another option is that a small lump under the skin on the abdomen is the result of the spread of pathogenic cells throughout the body.
- Lifestyle, bad habits, poor nutrition.
- Genetic predisposition.
- Injuries.
- Insufficient hygiene.
There are other possible reasons that can trigger the formation of subcutaneous lumps, and a doctor will help you figure them out, as well as choose the appropriate treatment.
Approximate inspection
An indicative examination helps determine the tone of the muscle fibers of the stomach and the possibility of resistance of the organ in painful areas. This type of examination allows you to get a picture of the condition of the organs in the abdominal cavity. Auscultoaffriction is used - light percussion with line movements of the finger. Palpation is carried out counterclockwise, by pressing and circular movements. The examination begins on the left side, then palpates the upper area near the ribs and ends the procedure by pinching the lower right side.
Examination of the small circle of the gastrointestinal tract (around the navel) allows you to clarify the diagnosis. By palpation, the gastroenterologist identifies areas of pain and inflammation. With gastritis, palpation of the stomach causes severe pain, since its walls are inflamed, and even superficial tingling can increase the pain.
Types of bumps on the stomach
Formations under the skin may differ in origin, possible consequences for the body, as well as methods of treatment. Seals are also divided into benign and malignant, which rarely, but still, can form on the abdomen. If we consider the main types of cones, the following groups are distinguished:
- Atheroma. It is a benign type, formed from fat cells due to blockage of the glands. It feels dense, with clear boundaries and painless. Only in case of inflammation and suppuration does it cause discomfort and can open on its own. It is removed by surgical methods; conservative treatment for atheroma does not give positive dynamics.
- Cysts. At the initial stage, the formation does not have any special symptoms, but over time, compaction is noted, and this lump under the skin on the abdomen hurts. The sensation can be pulling, and as the size of the cyst increases, the pain increases. The formation rarely degenerates into a malignant tumor, consists of connective, adipose tissue, and has a cavity in which biological fluid accumulates. Treat exclusively promptly.
- Pimples. One of the harmless types of bumps that can form on the stomach. If you do not make efforts to squeeze out, but carry out the correct treatment, you will get rid of the problem area relatively quickly and without scars. Usually pus accumulates in pimples and if opened independently, there is a possibility of infection spreading to other tissues.
- Lipoma. Often called a wen, it forms in the subcutaneous layers, can have different sizes, and grow into other tissues. The compaction at the initial stages is soft, as it develops it can become denser, and practically does not degenerate into cancer mutation cells. The lump does not lead to pain; discomfort begins to appear when neighboring tissues are pressed, especially when nerve endings are pinched. If there is a need for this, it is recommended to remove the fatty tissue in a medical institution; opening it yourself can aggravate the situation, for example, the tissue becomes infected.
In addition to benign neoplasms, some of which are listed above, there is a possibility of the formation of a lump, indicating the appearance of mutating cancer cells. There are relatively many types of cancer and they can manifest themselves in the abdomen in different ways.
Despite the possibility of developing cancer, in most cases, tumors on the abdomen under the skin are benign. They are treatable, but it is first important to find out the reasons why the lump formed.
Comparative method
The method is used to diagnose symmetrical zones of the abdominal cavity and examine the epigastric area. The procedure allows you to determine the correct location of the organ and deviations in its size from the norm, if any anomalies exist.
The procedure is performed from the lower abdomen, comparing the iliac areas. The diagnostic process includes examination of the navel and groin area. The comparative type of palpation differs in the technique of the procedure. During palpation, the patient is in a sitting position, which makes it possible to identify pathological changes in the abdominal walls. The procedure makes it possible to determine whether the stomach is in the right place and what the degree of change in the size of the organ is.
Superficial palpation
In the presence of a pathological condition, palpation is accompanied by pain. The procedure allows you to determine the size and shape of the stomach, the level of tension in the abdominal muscles (under normal conditions it should be insignificant), detect pain points and the lower border of the stomach. The method helps to make a tentative diagnosis of appendicitis with a painful abdomen and muscle tension on the right side.
Superficial palpation is carried out by gently pressing the fingers of one hand on the abdominal wall in specific areas. The procedure begins on the left, in the groin area, after which the hand is moved to the epigastric area, to the right iliac region. The patient's position is lying down, arms should be at their sides. Throughout the procedure, the doctor checks with the patient exactly where he feels pain in the stomach upon palpation.
Deep sliding
The examination is scheduled after a visual examination. The procedure is carried out with the fingers slightly bent along the middle phalanx, which are placed parallel to the stomach. As the patient exhales, the hand slowly plunges into the abdominal cavity, the doctor’s fingertips slide along the back wall of the stomach, which helps to establish mobility, pain and structure of the organ. You need to exhale 2 to 4 times per press from the doctor. Deep palpation of the stomach is carried out starting from the intestine and ending with the pylorus. When pain appears, their nature and location are determined. During the procedure, the position of the organs relative to each other, their sizes and the possibility of displacement, the nature of the sounds, the presence of seals or tumors are also recorded by determining the lower border of the stomach.
The procedure can also be performed while the patient is standing. In the vertical state, it is possible to feel the lesser curvature and highly located neoplasms of the pylorus.
Left
If you divide the abdominal cavity into 4 zones, then on the left side there are: the renal gate, ureter, omentum, intestine, intestinal loops.
Why is there a lump near the navel on the left:
- Intestinal obstruction with the appearance of persistent asymmetrical bloating, vomiting, gas formation in the walls of the large intestine, and stool retention.
- Abdominal aortic aneurysm with protrusion and expansion of the walls. More common in men. Causes: hypertension, atherosclerosis, bad habits, infection. There is a dull pain in the left peritoneum radiating to the lower back. Treatment is medication; in advanced cases, surgery.
- Hydronephrosis is a kidney disease that leads to accumulation of urine in the pelvis. Causes: urolithiasis, tumor, prostate adenoma in men, gynecological pathologies in women. Left-sided hydronephrosis is diagnosed taking into account the affected kidney on the left. Symptoms are increased blood pressure and temperature, colic in the lower back, difficult outflow of urine with stinging and burning.
Protrusion and pain when urinating are often observed in men with urinary tract infections and the development of diseases - cystitis, prostatitis, urethritis, pyelonephritis. Possible irritation of the gastric mucosa due to bloating and colic in the left quadrant of the abdomen.
Colic, nausea, vomiting, and fever may indicate problems with the pancreas. Hardening in the peritoneum indicates:
- hernia;
- umbilical ring fistula;
- cyst development;
- swelling of the walls of the small intestine;
- metastasis to the navel in stomach cancer.
Such hardening can be extremely dangerous. Doctors do not advise letting the situation take its course and delaying the examination. Especially when special discomfort and characteristic signs appear, regardless of the location in the abdomen.
Ausculto-percussion, ausculto-affrication
The purpose of these examinations is to determine the size of the stomach and its lower border. During ausculto-percussion of the stomach, the doctor, using one finger, makes superficial blows in a circular motion relative to the phonendoscope.
During ausculto-affrication, a finger is passed along the abdominal wall, making raking movements. As long as the finger passes over the stomach, noise is heard in the instrument; when it goes beyond these boundaries, the rustling stops. The area where the noise has disappeared indicates the lower limit. From this point the doctor begins to do deep palpation. Detection of a hard stomach on palpation indicates a tumor. Very often, a large curvature of the epigastrium is felt under the fingers.
Percussion
The manipulation is carried out by superficial finger strikes, starting from the navel and moving towards the lateral areas of the abdomen. The patient is placed on his back. The method makes it possible to determine Traube's space, that is, the presence of a gas bubble at the bottom of the epigastrium. Palpation of this type is carried out on an empty stomach; if the volume of gas on an empty stomach is insignificant, a preliminary diagnosis of pyloric stenosis is made.
This method also detects the presence of fluid in the stomach. The patient is asked to lie on his back. The doctor also asks the patient to breathe deeply, involving the stomach in the breathing process. The gastroenterologist makes quick, short pushes in the epigastric zone with four half-bent fingers of his right hand. With his left hand, the specialist fixes the abdominal muscles in the lower region of the sternum. If there is liquid in the stomach, a gurgling sound appears. The procedure makes it possible to determine the lower border of the stomach and the tone of the organ.
From below
A seal near the navel from below is observed if it is:
- pinched hernia;
- protrusion of the sigmoid colon;
- rupture of the walls of the diverticulum;
- inflammation of the pelvic organs in women;
- intestinal obstruction in the lower sections;
- increased gas formation in the walls of the large intestine;
- localization of the tumor in the genital organs of men.
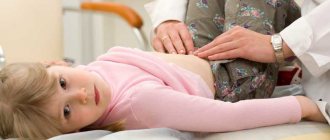
Specifics of palpation in children
To perform the procedure on infants, the following requirements must be met:
- the child should lie on his back, the baby’s muscles should be relaxed;
- Before performing the procedure, the doctor needs to warm his hands;
- If pain appears, to which the child reacts by crying, the procedure must be stopped immediately.
The palpation procedure allows you to determine the lower border of the stomach in young children, as well as identify the syndrome of the greater curvature of the stomach. It is necessary to pay attention to the thickness of the child’s skin and muscle elasticity.
Diagnosis in children begins with the stomach area and ends with the navel, where the intestines are palpated. Palpation of the stomach is an important link in the process of diagnosing gastrointestinal diseases. Correct implementation of the procedure allows you to make an accurate diagnosis and promptly begin treatment therapy.
Differential diagnosis
Symptoms characteristic of gastritis can also appear in other gastrointestinal diseases. To differentiate from similar diseases, the result of a blood test is an alpha-amylase test. The results will show what kind of disease is developing in the body. If you suspect acute gastritis, you need to do an electrocardiogram. Only according to its data will it be possible to distinguish gastritis from myocardial infarction. This type is similar to food poisoning. To exclude the latter, rinsing is done and after that the doctor should check the symptoms again. In chronic gastritis, it should be differentiated from ulcers, cancer or atrophy of the gastric glands.
Return to contents