Pregnancy occurs as a result of fertilization of a female cell by sperm - male cells. Few people know about an important process that occurs at the very beginning of pregnancy - cell implantation. This is the process when the fertilized egg attaches to the uterus, and this is where the full process of pregnancy begins. The first signs of the birth of a new life appear. You need to know the main points about this phenomenon, because it is one of the most critical moments in bearing a child. We will look at the timing, sensations and signs of implantation.
A little about conception
The time comes and the egg is released from the ovary. Next, it moves along the fallopian (uterine) tube towards the sperm. They are trying to overcome its dense shell. This is a serious obstacle to sperm. Therefore, they begin to secrete a substance designed to dissolve the membrane of the egg. As soon as the membrane weakens, the most agile and powerful sperm will enter the egg through it. This is how fertilization occurs - the birth of life.
Then the fertilized egg, in which cell division has already begun, moves along the fallopian tube closer to the uterus. At this stage, the hormones estrogen and progesterone play a very important role. They regulate the normal movement of the egg through the fallopian tube.
Within a day after fertilization, rapid cell division begins in the egg. After four days, the embryo already contains 32 cells. The embryo will enter the uterus 96 hours (4 days) after fertilization. The embryo attaches to the uterus.
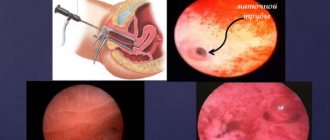
In the case of IVF, the egg is “taken out” from the follicle using a puncture (piercing with a thin needle). This process is described and shown in more detail here. After the egg is retrieved, it is placed in a special environment in which fertilization occurs. The sperm donor can be the husband or the donor material can be provided by a sperm bank.
Embryo transfer occurs only on days 3-5. Then all that remains is to wait for the embryo to attach to the uterus.
Classification options
Depending on the day on which the fertilized egg was attached to the wall of the uterus, there are several types of implantations. In addition to the normal time required for the embryo to attach (1-1.5 weeks), experts highlight:
- Early implantation is very rare. This process is characterized by the fact that the embryo is fixed in the uterine cavity already on the 6th day after fertilization.
- Late implantation - the fertilized egg attaches after 10 days. A similar situation is quite often observed when a woman’s age exceeds 35 years, or assisted reproductive technologies, in particular IVF, are used to conceive.
You can find out about the expected implantation of a fertilized egg by measuring your basal temperature in the morning (before getting out of bed after waking up). To assess it correctly, measurements should be taken daily for a week. When implantation occurs, a woman may notice a slight decrease in basal temperature (up to 0.3 degrees).
https://youtu.be/39DQiJHyRac
Embryo implantation
Implantation is the next stage of pregnancy. As it moves through the fallopian tube, substances accumulate inside the embryo; these substances are needed for successful attachment to the wall of the uterus and subsequent development. The embryo develops villi. The embryo needs the villi for nutrition during the implantation stage. In parallel with the movement and development of the embryo, changes occur in the mother’s body. Hormones begin to prepare the surface (mucous membrane - endometrium) of the uterus for embryo implantation.
The attachment of the embryo to the uterus begins 96 hours after fertilization. Implantation consists of 3 stages.
How exactly does attachment occur, 3 stages of implantation:
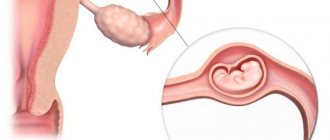
- The embryo enters the uterus and attachment occurs. The embryo clings to the endometrial mucosa of the uterus. Once attached, the uterus fills with fluid. This way the fertilized egg will better press against the wall of the uterus.
- Next, adhesion occurs. The uterus and embryo begin to communicate with each other through the villi on the embryo.
- At the third stage of implantation, invasion (penetration) begins. The embryo joins the mother's circulatory system, thus forming an embryonic kidney.
Attachment of the embryo to the uterus
Symptoms of attachment
Women are often interested in what day the symptoms of the attachment of the fertilized egg to the uterus begin. Most women feel nothing. Embryo implantation is painless. Not everyone is able to notice an increase in the concentration of hormones in the body.
Rarely, but symptoms can be felt, here are some of them:
- The stomach hurts and pulls below. Read more about nagging pain in the lower abdomen during IVF here.
- Slight tingling in the chest.
- During the first week there may be some discharge similar to menstruation. The discharge may be red, pink, brown or yellowish in color.
- Nausea (especially in the morning).
- Sometimes increased body temperature (not higher than 38).
- Severe irritability.
- Weakness.
- Dizziness.
What can you feel during embryo implantation week by week?
These are the most common sensations at the beginning of the attachment of the embryo to the wall of the uterus (endometrium). This stage of pregnancy is very important, like all subsequent ones, but implantation is the most dangerous period for the embryo. It is important to maintain the right attitude, not to be nervous, and to avoid stressful situations.
7 weeks after attachment
During IVF, after embryo transfer, the same symptoms are observed as in a normal pregnancy. Watch the video for transfer tips. In this video, a reproductive specialist will talk in detail about what happens after transfer during in vitro fertilization.
Symptoms
Implantation has no specific signs; in most cases, the woman does not feel anything and has no idea when exactly the embryos began to implant into the wall of the uterus. Some women, after natural conception, experience so-called implantation bleeding associated with disruption of the endometrium of the uterus due to invasion.
After IVF, many women who underwent a stimulated protocol have discharge, but do not differ from usual in the middle of the cycle, and therefore it will be almost impossible to notice implantation bleeding.
Some women note that after implantation, their mood and well-being change, drowsiness appears, appetite increases, and body temperature may also rise. These sensations are subjective and cannot be considered a clinical sign.
Bleeding
During the attachment of the embryo to the uterus, discharge appears, they are called implantation bleeding. Such discharge (similar to menstruation) is normal. Not every woman experiences discharge at the attachment stage. There is no need to be afraid of such discharges. They occur differently for each woman; they can be abundant or small.
The color of the discharge may vary. These can be yellow, red, brown and pink shades. Implantation bleeding should subside within 48 hours . It rarely happens a little later. Often such discharge is simply mistaken for normal menstruation.
Important! The presence of blood clots in the discharge should alert you; with normal implantation they are not present.
If the discharge is red with blood clots, it is better to call a doctor. Bleeding may have started, in which case a miscarriage may occur. Other reasons are also possible: the endometrium has exfoliated, an inflammatory process has begun in the uterine cavity, hormonal imbalance and even oncology.
This is a very serious situation that only a doctor can understand. Only he can correctly indicate the cause, diagnose the disorder and choose the appropriate treatment.
Why doesn't the embryo attach?
It is best to plan and properly prepare for a future pregnancy so that the implantation of the embryo is successful. Pregnancy will go smoothly, without any troubles, if you are ready for it.
Reasons why the fertilized egg may not attach:
- Embryo implantation may not occur after a previous abortion, miscarriage or pelvic inflammation.
- Taking hormonal drugs and subsequent hormonal imbalance.
- Use of an intrauterine device.
- Maternal malnutrition.
- Bad, destructive habits.
For proper preparation, visit a gynecologist. He will create a preparation program for pregnancy. As a result of preparation for conception and pregnancy, the risk of such negative factors can be avoided.
Write comments and ask questions. Don't forget to rate the article with stars under the article, this is very important to us. Thanks for reading. Let your embryo attach to the endometrium without problems.
How to increase your chances?
In fact, a woman cannot significantly influence the possibility of implantation after replantation. In order for the hormonal background to be as close to natural as possible in the second phase of the cycle, she is prescribed progesterone preparations. And this is the only way to make pregnancy more likely.
DETAILS: What antibiotics to give to broiler chickens
In addition, a woman is recommended to follow certain rules after embryo transfer - do not take a hot bath, do not swim, do not take any medications without a doctor’s permission, do not lift heavy objects, and limit physical activity, especially those associated with jumping and sudden bending of the body.
Intrauterine development of the fetus. Possible complications of pregnancy and critical periods.
The fact that an expectant mother should take care of herself is perceived as a truism. But few people know that during pregnancy there are periods when the risk of all kinds of health problems increases significantly. By observing increased caution at “critical moments,” a woman will be able to “safeguard herself” in time and avoid unnecessary problems.
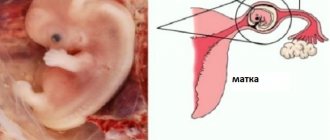
Pregnancy lasts 9 calendar or 10 obstetric months* (its average duration is 280 days from the first day of the last menstrual period until birth). During this time, the most complex process of transforming a fertilized egg into a mature fetus, capable of independent existence outside the mother’s womb, occurs. Over 9 months, rapid cell division occurs, the formation of organs and tissues of the fetus, the maturation of functional systems, the establishment of connections between them, thanks to which the newborn will be able to adapt to the external environment and live an independent life, separate from the mother’s body. * 1 obstetric month consists of 4 weeks.
Preimplantation period - fertilization of the egg
Normally, 12-14 days before the expected menstruation, ovulation occurs, that is, an egg that has reached a large size leaves the ovary and enters the fallopian tube, where fertilization most often occurs. From this moment pregnancy begins. The fertilized egg continues its journey through the fallopian tube for 4 days towards the uterine cavity, which is facilitated by:
- contraction of the smooth muscles of the fallopian tube wall. These contractions normally occur in a unilateral direction - towards the uterine cavity from the end of the tube facing the abdominal cavity;
- movement of the cilia of the mucous membrane that covers the fallopian tube from the inside. The liquid in the tube begins to move, and with the flow of this liquid, the fertilized egg enters the uterus;
- relaxation of the sphincter (circular muscle) at the junction of the fallopian tube and the uterus. This sphincter is designed to prevent a fertilized egg from entering the uterine cavity prematurely, before the uterus is ready to receive the fertilized egg.
The movement of the egg through the fallopian tube occurs under the influence of the female sex hormones estrogen and progesterone. Progesterone is a pregnancy hormone that is produced in the ovary in the early stages of pregnancy (at the site of the burst follicle, a corpus luteum is formed, which produces this hormone in large quantities and contributes to the onset and maintenance of pregnancy). If there is not enough progesterone produced, the egg from the fallopian tube will enter the uterine cavity late. With increased peristalsis of the fallopian tube, the fertilized egg will enter the uterine cavity before it can penetrate the mucous membrane, as a result of which the egg may die. Since in this case the pregnancy will not take place, there will be no delay in the next menstruation, the pregnancy will remain undiagnosed and unrecognized.
The period of movement of a fertilized egg through the fallopian tube is considered the first critical period of pregnancy (from 12-14 to 10-8 days before the start of the next menstruation). As a result of disruption of the complex mechanisms regulating the functioning of the fallopian tube, the egg after fertilization can also implant into the wall of the tube (ectopic pregnancy).
Conditions for successful implantation after ovulation
In order for the embryo to easily overcome its path and penetrate into the wall of the uterus, certain conditions are necessary:
- The thickness of the endometrium is no more than 13 mm. Therefore, pregnancy is impossible with endometriosis.
- Sufficient progesterone levels.
- Patency of the fallopian tubes.
- A sufficient amount of nutrients necessary to nourish the embryo.
Sometimes pregnancy does not occur even after fertilization. There may be several reasons for this:
- A thick layer of the embryo's protective membrane.
- Obstruction of the fallopian tubes.
- Endometriosis.
- The uterine epithelium is too thin.
- Lack of progesterone.
- Low amount of nutrients.
- Damage to the DNA structure of the embryo due to gene mutations.
- Increased maternal blood clotting.
Implantation period - attachment of the fertilized egg to the wall of the uterus
This period also passes even before the expected menstruation, most often when the woman is not yet aware of her pregnancy. Once in the uterine cavity, the embryo already consists of 16-32 cells, however, it does not immediately penetrate into the uterine mucosa, and remains in a free state for another two days. These two days from the moment the fertilized egg enters the uterine cavity until it attaches to the uterine wall constitute the implantation period. The location of insertion depends on a number of circumstances, but most often it is the anterior or posterior wall of the uterus.
Nutrition of the fertilized egg during this period occurs due to local dissolution of the mucous membrane of the uterine wall with the help of enzymes secreted by the fertilized egg. After 2 days, the fertilized egg implants into the uterine mucosa, which contains large quantities of enzymes, glycogen, fats, trace elements, protective antibodies and other biologically active substances necessary for the further growth of the embryo.
The second critical period of pregnancy is implantation, that is, the attachment of the fertilized egg to the wall of the uterus. If implantation fails, then the pregnancy ends under the guise of menstruation (in fact, this is an undiagnosed miscarriage at a very short time). Since there is no delay in menstruation, the woman does not even assume that she is pregnant.
The implantation process is greatly influenced by hormonal factors: the concentration of hormones such as progesterone, estrogens, prolactin (a hormone from the pituitary gland, a gland located in the brain), glucocorticoids (adrenal hormones), etc.
The preparedness of the uterine mucosa for implantation and its readiness to accept the fertilized egg are also of great importance. After abortion, curettage, long-term wearing of an intrauterine device, infections, inflammatory processes, the receptor (perceiving) apparatus of the endometrium may be disrupted, that is, hormone-sensitive cells located in the uterine mucosa do not respond correctly to hormones, which is why the uterine mucosa is not sufficiently prepared for upcoming pregnancy. If the fertilized egg is not active enough and does not promptly release the required amount of enzymes that destroy the uterine mucosa, then it can penetrate the uterine wall in the lower segment or in the cervix, resulting in cervical pregnancy or abnormal placentation (the placenta blocks the exit from the uterus partially or completely ).
The presence of adhesions (synechias) in the uterine cavity after inflammatory processes, curettage, as well as uterine fibroids can also prevent normal implantation.
The period of organogenesis and placentation - the laying of all organs and tissues of the fetus
This period lasts from the moment the fertilized egg is implanted into the uterine mucosa until 10-12 weeks of pregnancy, when all the organs and tissues of the fetus are fully formed, as well as the placenta (the baby’s place is the connecting link between the fetus and the maternal body, through which nutritional processes occur, metabolism and respiration of the fetus in the womb). This is a very important period of intrauterine life, because At this time, the formation of all organs and tissues of the fetus occurs. Already on the 7th day after fertilization of the egg, the mother’s body receives a signal of pregnancy thanks to the hormone chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), which is secreted by the fertilized egg. HCG, in turn, supports the development of the corpus luteum in the ovary. The corpus luteum secretes progesterone and estrogens in quantities sufficient to maintain pregnancy. At the initial stage of pregnancy, before the formation of the placenta, the corpus luteum takes on the function of hormonal support of pregnancy, and if for one reason or another the corpus luteum does not work fully, then there may be a threat of miscarriage, miscarriage or a non-developing pregnancy.
The entire period of organogenesis and placentation is also a critical period of intrauterine life of the fetus , because the fetus is highly sensitive to the damaging influences of the environment, especially in the first 3-6 weeks of organogenesis. This critical period of pregnancy is especially important because... under the influence of unfavorable environmental factors, the embryo may die or develop developmental abnormalities.
During these periods, the influence of environmental factors on the embryo is especially dangerous, including:
- physical (ionizing radiation, mechanical effects); this may be the effect of ionizing radiation, for example in the conditions of a man-made disaster at nuclear facilities, mechanical effects in the form of vibration, etc. in relevant industries or during sports training;
- chemical: phenols, nitric oxide, pesticides, heavy metals, etc. - these substances can also enter the body of a pregnant woman if she works in relevant industries or when carrying out repairs in a room where the woman stays for a long time. Chemicals include nicotine, alcohol, certain medications such as those used to treat cancer, etc.;
- biological (for example, herpes virus, cytomegalovirus, rubella virus, etc.).
It must be emphasized that during critical periods, harmful effects lead to the most severe consequences - the death of the embryo or the formation of gross malformations.
Fetal period
From 12 weeks of pregnancy, the fetal period of intrauterine life begins, which lasts up to 40 weeks. At this time, the fetus is already fully formed, but physically immature.
Pregnancy periods of 13, 20-24 and 28 weeks are critical for patients with hyperandrogenism - increased levels of male sex hormones - due to the onset of fetal hormone production. During this time, it is necessary to check the level of hormones and adjust the dose of drugs prescribed to reduce the amount of male sex hormones (dexamethlzone, metip-red, etc.). At the same time, the doctor monitors the condition of the cervix, since an increase in the amount of male sex hormones can lead to its premature opening.
At 13 weeks of pregnancy, the male fetus begins to produce its own testosterone - the male sex hormone; at 20-24 weeks, the production of cortisol and male sex hormones by the fetal adrenal cortex begins, as a result of which a woman with hyperandrogenism may experience another rise in male sex hormones, which will lead to termination of pregnancy.
At 28 weeks, the fetal pituitary gland begins to synthesize a hormone that stimulates the adrenal glands - adrenocorticotropic hormone, as a result of which the production of male sex hormones increases, which can also lead to termination of pregnancy. If necessary, at this time the doctor will adjust the dose of medications.
So, the effect of unfavorable factors during critical periods of pregnancy can lead to the most unfavorable consequences. Therefore, during the entire period of waiting for a child, and especially during critical periods, a woman needs to avoid the effects of unfavorable factors and consult a doctor in case of any “problems”. I would like to advise expectant mothers to take care of themselves, especially since pregnancy lasts only 9 months, and the health and life of your baby depends on its course.
Required behavior
Among women planning a pregnancy, there is an opinion that it is necessary to limit physical activity as much as possible (even to the point of bed rest) in order for the fetus to become well established and continue to develop normally. However, this is not true.
At 1-2 weeks of pregnancy, genetic factors in the formation of the embryo and the preparedness of the endometrium to accept the embryo are important for its preservation. Therefore, a woman, preparing for conception, can continue her usual lifestyle without any fear. The only exceptions are those representatives of the fair sex whose fertilization was carried out using artificial methods.
https://youtu.be/1FXsgDZ5-U4
What should be a cause for concern?
If the effect of unfavorable factors in a critical period has led to the threat of termination of pregnancy, women complain of pain in the lower abdomen, pulling or cramping pain in the lower back. The pain may be accompanied by bloody discharge from the genital tract. Such symptoms cannot be left without due attention, because... they may be followed by massive bleeding due to incomplete spontaneous miscarriage, in which the pregnancy cannot be saved.
It is very important at the first symptoms of a threatening miscarriage to immediately contact a gynecologist, undergo the necessary tests, including an examination in a chair, ultrasound, hormonal blood tests for female sex hormones, male sex hormones, and thyroid hormones.
The most significant transformations of the fetus occur in the early stages of pregnancy. Within a few days from the moment of conception, it turns from one cell - a zygote - into a millimeter-sized embryo. The formation of the fertilized egg begins immediately after the fusion of the sperm and egg in the fallopian tube. After this, the fertilized egg attaches to the wall of the uterus. Is it possible to feel the moment of implantation of an embryo into a woman’s body?
Signs of a successful process
Also, a woman planning a pregnancy is interested in whether she will be able to feel the attachment of the embryo in the uterus, because it is from this moment that the development of her unborn baby begins. There are certain symptoms that indicate dramatic changes in the female body, and these are:
- During early pregnancy, small discharge from the genital tract may sometimes appear, having a pinkish or light brown color. If conception is planned, this sign should not cause concern, but with a fairly long break in intimate relationships, it may indicate the development of inflammatory processes in the reproductive system;
- You may experience mild pain in the lower abdomen that has a pulling nature, as well as a slight tingling sensation in the mammary glands;
- a feeling of nausea, especially pronounced in the morning;
- the appearance of a metallic taste;
- short-term low-grade fever (increase in body temperature to 37.5 degrees);
- emotional lability – a woman during this period begins to react very sharply to any external stimulus;
- periodic attacks of dizziness, development of general weakness.
You should be attentive to any signs that may indicate that the embryo has attached to the wall of the uterus, because this period is considered one of the most dangerous throughout pregnancy. Any psycho-emotional overload can provoke a breakdown. In addition, it is necessary to carefully monitor the appearance of genital discharge and its characteristics. If they are bloody, profuse and last more than 2 days, you should consult a gynecologist.
How does conception occur?
In order for conception to occur, the participation of two gametes is necessary - a sperm and an egg. In the first half of the menstrual cycle, the oocyte matures - under the influence of the gonadotropin FSH, it is formed in the ovarian follicle. Around the middle of the cycle, usually on the 14th day, the dominant follicle ruptures and a mature egg is released. This phenomenon is called ovulation.
After leaving the ovarian follicle, the egg travels into the fallopian tube. If sexual intercourse occurred on this day or 2-3 days before, then some of the sperm could reach the fallopian tube. It is there that the male gametes wait for the female gamete to fuse with her and fertilize her.
If there are no sperm in the oviduct, the egg continues its movement, descends into the uterus, dies and comes out along with menstrual blood. If male gametes are present, then they all together begin to attack the surface shell of the egg - the corona radiata. One sperm cannot destroy it; the effort of several is required. However, only the one who first manages to reach the inner layer - the zona pellucida - fertilizes the oocyte.
Zygote implantation during natural conception and IVF
As a result of the fusion of a sperm and an egg, a zygote is formed. This is the one-cell stage of the embryo's existence, which lasts 26–30 hours. Then, as a result of mitotic division, the zygote begins to fragment. By the 4th day of pregnancy, the embryo consists of 12–16 cells, and by the 5th day it already consists of 30. At this stage of development, it is called a blastocyst.
At what time does the blastocyst attach to the uterine wall? During the first 5–6 days, the embryo moves along the fallopian tube and descends into the uterine cavity. During this time, progesterone, which is secreted by the corpus luteum, manages to prepare the endometrium of the uterus for implantation of the fertilized egg - it becomes more loose. The cells of the surface layer of the blastocyst - the trophoblast - throw out finger-like processes and cling to the endometrium. This is how the embryo is implanted.
On what day of ovulation does implantation occur?
It is impossible to accurately determine in advance the day of embryo implantation after ovulation. The situation develops according to an individual scenario.
The zygote appears in the uterus 4-6 days after ovulation. After 1-2 days it begins to penetrate the endometrium. This lasts about 40 hours. The process may periodically pause and intensify.
The zygote is implanted into the uterus - implanted 7-10 days after ovulation
In most cases, implantation occurs 7-10 days after ovulation.
As medical practice shows, approximately 2% of women experience this event on the 5-6th day, 2.8% on the 12th. Many gynecologists consider the completion of implantation to be the formation of a functional placenta at the 20th week of gestation.
How to understand that the embryo has attached to the wall of the uterus?
Are there certain signs of implantation of the fertilized egg into the endometrium? Despite the fact that this stage of gestation may be asymptomatic, some women, based on certain signs, can determine that they are pregnant even before their period is missed. The process of embryo implantation is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- bloody issues;
- nagging pain in the lower abdomen;
- change in basal temperature.
Bloody discharge not of a menstrual nature
The nature of the discharge during embryo implantation:
- scanty, spotting bleeding;
- last no more than 48 hours;
- color of varying intensity - from pink to brown;
- There is no unpleasant odor.
Why is the attachment of the embryo to the uterus accompanied by bloody smears? This is due to the fact that during the implantation of the blastocyst into the surface layer of the uterus, the smallest capillaries of the endometrium are injured. There is no need to worry, microtraumas heal very quickly.
Not all women experience implantation bleeding, but this does not mean that implantation of the fertilized egg did not take place. Women who have gone through the IVF procedure eagerly await these signs, but ultrasound diagnostics can more accurately determine whether the embryo has taken root.
When will the pregnancy test show?
How long is it better to wait before the test and on what day can it be done? A week after unprotected coitus, it is too early to do the test, because the concentration of hCG will not be sufficient to be detected by reagents.
There are several types of pregnancy tests:
- Stripes. The cheapest and most accessible test, at the same time it is one of the most unreliable. However, this does not mean that the strip gives false results; the probability of error is only 4–5%. It has low sensitivity; in order for the strip to detect hCG in the urine, the hormone concentration must be at least 20 mIU/ml, which is achieved 2–3 weeks after sexual intercourse.
- Tablets. This test consists of a cassette with a urinal hole and a window on which the results are displayed, and a pipette for collecting urine. This analysis is close to laboratory ones and detects the hormone at a concentration of 15 mIU/ml.
- Electronic device. It is considered the most accurate method of testing pregnancy at home. Susceptibility – 10–15 mIU/ml. It is allowed to carry out the analysis 10 days after intimate contact, but the more time passes between coitus and the test, the higher its accuracy.
Is it possible to feel and know by some signs that the embryo has attached to the uterus? During pregnancy, hormonal levels change dramatically. Some women feel these changes. However, for most there are no tangible signs.
A medical symptom of the attachment of a developing embryo to the uterus is an increase in the synthesis of the hormone hCG, which serves as a marker of pregnancy. Its stable growth occurs during the first weeks of the term. Pregnancy tests work on its determination.
After ovulation, some signs of successful attachment of the embryo to the uterus can be expected after 7-12 days. Usually at this time, the most impatient ones take pregnancy tests and find out about their condition.
What may be the sensations indicating the attachment of the embryo to the uterus:
- for those who keep a graph of basal temperature - it increases to 37-37.5° at the time of ovulation and decreases by 1-1.5° when introduced into the endometrium, subsequently the temperature will rise again and will persist for the first half of the period;
- sometimes there is increased sensitivity and mild soreness of the mammary glands;
- damage to the endometrial layer by the implantation of the embryo is sometimes characterized by mild pain in the lower abdomen, similar to premenstrual pain;
- changes in hormone synthesis in some women lead to dyspeptic disorders - nausea, vomiting;
- metallic taste on the mucous membranes of the mouth;
- photosensitivity and odor aversion;
- sudden weakness and increased fatigue.
Vaginal discharge usually does not change its nature when the embryo attaches to the wall of the uterus. Some may have a small spot of blood, as well as pink or red-brown smears. In most cases, it is impossible to detect a change in condition from the discharge.