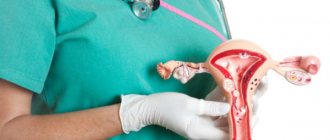
What is an ectopic pregnancy
An ectopic pregnancy is a pregnancy in which the fertilized egg does not reach the uterus and implants outside it. This is a very serious pathology that requires urgent assistance from specialists, otherwise there is a serious threat to further women’s health and even a woman’s life. Where the fertilized egg will continue its short-lived existence depends on the woman’s body and the disease that provoked this pathology. Several types of ectopic pregnancy are classified. Each type hides its symptoms and consequences.
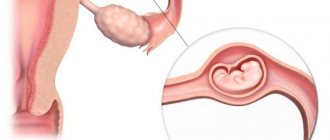
Tubal ectopic pregnancy
The most common “dysfunctional” pregnancy. During ovulation, the egg descends into the fallopian tube and waits there for fertilization. When a sperm penetrates an egg, it descends into the uterus and attaches to its wall. If a woman's tube is blocked, the fertilized egg will not penetrate the uterus and will remain in the tube. In this case, the pregnancy may terminate on its own. After 1-2 months a miscarriage will occur. Another option, which is no less dangerous, is that the pipe ruptures. All this leads to internal bleeding. Urgent hospitalization is required.
Ovarian ectopic pregnancy
The risk of developing this type is very low. The egg matures in the follicle and is fertilized before ovulation, without leaving the ovary. As a result, it attaches directly to the wall of the ovary. Diagnosing this pregnancy is quite difficult; it is often confused with a tumor during ultrasound. In this regard, the embryo can begin to develop and grow in the ovary for several months until the follicle and blood vessels rupture.
Cervical and cervical isthmus ectopic pregnancy.
An even rarer case. Fastening occurs in the area of the isthmus and in the cervical canal. The zygote penetrates the uterus, but due to the looseness of its walls (endometrium) it cannot attach. This pathology is very life-threatening. In some cases, sepsis may develop after bleeding. The uterus may be removed.
Abdominal ectopic pregnancy
Also not a common type.
The embryo is not implanted in the uterine cavity, but on the internal organs, spleen or peritoneum. There are two types - primary and secondary. In primary fertilization, fertilization occurs in the abdominal cavity; in secondary, it is first implanted in the fallopian tube, an abortion occurs, the embryo does not take root, and again tries to implant, but in the abdominal cavity. This type of pathological pregnancy is difficult to determine, especially in the early stages. Pathology is revealed when consequences appear. Damage to large vessels and internal organs occurs.
Causes of pathological pregnancy: why it happens
Fertilization outside the uterus occurs in women with hormonal imbalances, menstrual irregularities, and abnormal development of the internal genital organs.
When ovulation occurs, an egg that is ripe and ready for fertilization is released from the ovary. The egg remains in the tube until fertilization occurs. After conception, the zygote moves through the tube due to wave-like contractions and villi inside the tube and enters the uterus. This process takes about 3 days. During this time, special cells are formed that contain enzymes that help the zygote attach to the wall of the uterus. If at any stage obstacles arise that do not allow the completion of the advancement and attachment of the fertilized egg, the pregnancy will be pathological. We will consider below what reasons this could provoke.
- Inflammatory processes of the uterine appendages.
If one or both pipes are ever subjected to inflammatory processes, their functions will be impaired. Adhesions, fibrous cords, and scars form in their cavity. They prevent the normal passage of the zygote through the tubes to the uterus. As a result, the formed egg is attached to the place where it was able to move.
- Inflammatory processes of the fallopian tubes
. The reason is similar to inflammation of the appendages. The contractility of the tubes is impaired, the villi are not functional and the zygote is not able to move into the uterine cavity.
- Underdevelopment of organs and tissues.
These pathologies arise in the womb. The reasons may be an incorrect lifestyle when carrying a child, or genetics. The most common occurrence is the presence of additional “extra” pipes, unnecessary holes in the appendages.
- Previous operations on the female reproductive organs.
After surgical interventions, an adhesive process appears. It disrupts the patency of the pipes.
- Hormonal disorders.
Disturbed hormonal levels of a woman affect reproductive function. As a result, the menstrual cycle fails and the egg loses its ability to attach and move. This factor is most common among young women.
- One of the pipes has been removed and is missing.
Ovulation can occur on the side where the tube was removed, the risk of ectopic pregnancy increases sharply.
- Tumors
. Neoplasms of a malignant or benign nature that have arisen in the appendages will also interfere with the zygote. In addition, tumors can seriously disrupt hormonal levels. Often tumors are diagnosed after the discovery of an ectopic pregnancy.
Causes and pathogenesis
Normally, at the end of the second week of the menstrual cycle, a woman ovulates - the release of a mature egg from the ovary into the free cavity of the peritoneum.
Next, with the help of special villi, the female reproductive cell penetrates the fallopian tube, where it merges with the sperm and forms a zygote. After 1 week, the embryo reaches the uterine cavity, where implantation occurs. If these processes are disrupted, the embryo does not enter it on time, which leads to the development of ectopic pregnancy. The causes of ectopic pregnancy are extremely varied, and they cannot always be identified. The etiology of this pathology is the slow movement of the embryo through the fallopian tube or increased activity of the trophoblast (layer of cells of the embryo), which leads to premature implantation. The most common predictive factors for ectopic pregnancy include 6 diseases and situations:
- Inflammation of the fallopian tube. Due to this disease, the cilia that move the egg to the uterine cavity die. Also, adhesions can form in the fallopian tubes.
- Sexual infantilism. This disease is accompanied by the presence of long and tortuous fallopian tubes; the egg does not have time to reach the uterine cavity in time.
- IVF and treatment with hormonal drugs. Excessive concentration of progesterone in the blood slows down the movement of the egg through the tubes.
- Surgical interventions on the fallopian tubes. Lead to the formation of scars and adhesions on them.
- Tumors of the female genital organs. This group of diseases can lead to anatomical changes in the fallopian tubes.
- Endometriosis. This pathology causes a decrease in the activity of the tubal villi.
In a tubal pregnancy, the embryo is implanted into the fallopian tube, in which bleeding occurs, dissecting its wall. The embryo begins to increase in size, but this happens more slowly than during physiological gestation. Changes characteristic of normal pregnancy are noticeable in the uterus: a slight increase in size, softening of the cervix and isthmus. After some time, the embryo grows to a large size and ruptures the tube; sometimes it is spontaneously expelled into the peritoneal cavity (tubal abortion). The period during which these processes occur depends on the location of implantation; it ranges from 4 weeks to 4 months.
Ovarian pregnancy is rare and occurs as a result of migration of the zygote from the tube to the ovary. Some doctors believe that with such a gestation, fertilization of the egg occurs in the follicle, that is, before ovulation. Abdominal pregnancy is an even rarer pathology; it can occur primarily - with a perverted localization of fertilization, or as a result of a tubal abortion.
How to detect an ectopic pregnancy in the early stages
Ectopic pregnancy in the early stages is similar in symptoms to normal pregnancy. But most often it is recognized at the stage of development of tubal abortion or other types of interruption. Progressive pregnancy in the early stages, with a developing fetus, is recognized by ultrasound.
What indicates abnormal development of pregnancy, signs of ectopic pregnancy in the early stages:
- Spotting.
Before menstruation begins, heavy discharge or light bleeding may occur. During the attachment of the embryo to the wall of the uterus, they do not last long, a few hours. If the embryo is implanted outside the uterus, the bleeding will be more profuse and prolonged. - Drawing or cramping pain.
During the normal development of pregnancy, they occur in the lower abdomen and do not last long. During improper implantation of the embryo, the pain intensifies and becomes cramping and cutting in nature, develops in the area where the embryo was implanted and spreads to the entire abdomen. - Malaise
. In a normal pregnancy, a state of malaise and fatigue are a common symptom, but in a pregnancy that is not proceeding properly, the feeling of poor health intensifies, dizziness and even fainting may occur. - Toxicosis
. Accompanies a woman during a normal pregnancy; during an ectopic pregnancy, nausea and vomiting are more pronounced. - Increased body temperature and chills.
Characteristics of discharge
After conception, the expectant mother needs to closely monitor vaginal discharge, as its regularity, smell and color may indicate the presence of a disease. A successful pregnancy is indicated by the complete absence of any discharge. Only at the very beginning of gestation may mucus of a transparent or white color be observed. This occurs due to changes in hormones, which is considered normal.
Vaginal mucus may be absent during progressive ectopic pregnancy. Only during the expected period are minor spotting discharges that have a brown or burgundy tint.
After the integrity of the organ in which the embryo is localized is violated, the secretion acquires a purulent odor and contains particles of rejected epithelium, pus, and blood . As to whether there is always blood discharge during an ectopic pregnancy, it is indicated by the fact that sometimes it can be colorless with an unpleasant odor.
https://youtu.be/JpruAI0A6oI
When an ectopic pregnancy occurs, the discharge differs in the amount and color of the secretion. It can be scanty, prolonged, in the form of heavy uterine bleeding. Shades range from dark brown to pink.
In gynecology, contact bleeding is observed that appears after sexual intercourse. This creates a misconception about a possible miscarriage.
During the peeling of the embryo from the walls of the tube, a rich brown and even black secretion occurs. This process takes a long time until diagnosis is made.
With other types of ectopia, bleeding is profuse, which is explained by the rupture of blood vessels during the growth of the embryo. Every woman who is sexually active should know what discharge occurs during an ectopic pregnancy, since this dangerous pathology occurs quite often.
Difference from menstruation
Compared to menstrual blood, discharge during ectopic pregnancy is of a different nature. Their abundance or scarcity depends on the reason why they appeared - detachment of the fertilized egg or rupture of an organ.
Most often, discharge during an ectopic pregnancy in the early stages occurs after a missed period. If the test confirms pregnancy, then you should be examined by a doctor.
The situation becomes more complicated when the appearance of secretion coincides with the menstrual cycle. In this case, you need to pay attention to pain, smell, and color changes.
Ectopic gestation is detected using ultrasound. At the earliest stages, a vaginal sensor helps detect the embryo. In addition, a study is carried out to analyze the presence of chorionic hormone (hCG), which indicates the normal development of pregnancy. Its deficiency is explained by abnormal conception.
Signs of a ruptured fallopian tube
A very life-threatening condition for the patient when the organ is destroyed and the embryo is thrown into the abdominal cavity. are observed :
- Severe pain at the site of the fetus, spreading to the lumbar and anal region.
- Painful sensations on palpation.
- Hemorrhagic shock due to severe internal bleeding: pale skin, profuse sweating, rapid pulse, low blood pressure, fainting.
- The appearance of blood from the genitals.
https://youtu.be/RRFHzYNYcvc
When assistance is provided, the pressure is stabilized, hemostasis is performed, and the tube with the remains of the embryo is removed. In case of heavy bleeding, the abdominal cavity is sanitized and antibiotic therapy is prescribed to avoid the occurrence of inflammatory processes.
If the fetus is detected early, if the tube has not ruptured, there is a chance to save the organ and the opportunity to have healthy offspring in the future.
All women of reproductive age should remember that ectopic pregnancy often occurs as a result of gynecological ailments. Therefore, it is advisable to visit a gynecologist more often and carry out timely treatment of any pathologies.
An ectopic pregnancy is an abnormal condition that poses a serious threat to a woman’s life. The normal location of a fertilized egg is the uterus. If fixation occurs in any other place, this is a pathology and requires immediate intervention from doctors. The first signs of an ectopic pregnancy, if known about them, should alert a woman and encourage her to make an appointment with a specialist.
What will the test show?
Women turn to the test during a missed period.
With an ectopic pregnancy, scanty spotting may appear. With such symptoms, if you take a test, it will show a positive result. But the second stripe will not be clearly defined, pale. There are two types of test, the first is a regular test, available in pharmacies and stores, it is based on detecting the level of the hCG hormone, the second determines the ratio of intact and modified hCG, it can recognize an ectopic pregnancy at 5 weeks.
If the test determines that the embryo is not attached correctly, an ultrasound scan should be performed.
How not to confuse it with menstruation?
Typically, discharge during an ectopic pregnancy is of a different nature compared to menstruation. They can be more scarce or more abundant, which depends on what specific reason provoked their appearance - a pipe rupture or fetal detachment.
Moreover, such discharge most often appears after a short or rather long delay in the menstrual cycle. If your period does not come on time, this is a reason to consider and undergo a pregnancy test or examination by a doctor. If, after taking tests, progesterone or hCG is detected in the blood, it means the woman is pregnant. Discharge indicates either an ectopic pregnancy or a threatened miscarriage. Therefore, in any case, after such “months” you should consult a doctor.
It’s another matter when they appeared at the same time when menstruation was supposed to begin, and the woman did not know about the pregnancy. In this case, it is difficult not to confuse them with menstruation. If their color, character, smell have changed, or pain has appeared, it is advisable to consult with specialists.
Why is an ectopic pregnancy dangerous?
If this pathology occurs, the consequences are irreversible. If measures are taken in time, more serious complications can be avoided.
- If the pregnancy is not terminated in time, the tube ruptures. As a result, the movement and attachment of the embryo into the peritoneal cavity.
- Termination of pregnancy naturally or mechanically. A timely diagnosed ectopic pregnancy also has consequences.
- Heavy bleeding may occur upon diagnosis.
- Bleeding due to pipe damage. Difficult to stop, with lethal outcome.
- Development of peritonitis.
- During the operation, the tube can be removed; this option is possible if an abnormal pregnancy is not recognized in time.
- During the operation, the tube is preserved, but the risk of another abnormal pregnancy remains.
When a fallopian tube rupture occurs, its signs
Dark beige
This pathology is not limited to one option. Therefore, discharge during an ectopic pregnancy in each individual case may be of a different nature. Also, there may be no pathological discharge at all, but in very rare cases and only in the very early stages of the pathology.
With an ectopic pregnancy, it is possible to have dark discharge instead of menstruation if the pregnancy test result is negative or weakly positive.
Bloody discharge can be caused by a drop in progesterone levels, a ruptured fallopian tube, or spontaneous abortion. Also in vaginal secretion may be present:
- blood;
- pus;
- rejected mucosal epithelium.
In any case, it is in the woman’s interests to immediately visit a gynecologist to confirm or deny an ectopic pregnancy.
A progressive type of ectopic pregnancy is a process of growth, development, detachment and death of the embryo. Here, there is usually no pathological discharge, and during the period of expected menstruation, scanty bleeding of brown or dark red color may be observed. But in most cases, vaginal secretion mixed with blood occurs after a delay, and a woman can easily mistake it for her regular period.
There is also contact secretion with blood that occurs after sex. For this reason, women often suspect termination of pregnancy rather than pathological implantation of the fertilized egg.
Interrupted WB
Here the detachment of the embryo and its death are noted. It can develop in two ways: with subsequent rupture of the fallopian tube or tubal abortion. In this case, the vaginal secretion has a rich brown or even black color. Moreover, black discharge instead of menstruation may also have a slight spotting character, which indicates the process of rejection of the fertilized egg from the walls of the uterine tube.
It is important to remember that such discharge can be long-lasting, until the pathology is diagnosed.
In such a situation, the embryo over time significantly stretches the wall of the fallopian tube, which leads to its rupture. As a result, the fertilized egg ends up in the abdominal cavity, entering through the resulting hole.
Initially, there is a small amount of dark red vaginal secretion. After a couple of hours, a large amount of blood comes out of the vagina, in which the rejected epithelium of the genital organs is present. In other words, the woman notices blood with clots and pieces of tissue.
Tubal ectopic pregnancy occurs in almost 97% of cases, but there are very rare forms of this pathology, which differ in the place of attachment of the fertilized egg:
- in the abdominal cavity;
- in the body of the uterus;
- in the rudimentary uterine horn;
- in the area of the ovary;
- simultaneous occurrence of intrauterine and ectopic pregnancy.
In each of these cases, there is profuse bleeding caused by the destruction of blood vessels by the embryo. Unfortunately, these types of ectopic pregnancies are difficult to diagnose in the early stages, but the probability of their occurrence is less than one percent.
The timing of damage to the fallopian tube is directly related to the part of the tube in which the embryo is implanted. If it is in the isthmic section, rupture of the fetal sac occurs at 4–6 weeks; when the fertilized egg “occupies” the interstitial section, the period is extended to 10–12 weeks. If the embryo has chosen a place for further development - the ampullary part of the tube, which is located next to the ovary, rupture occurs after 4 - 8 weeks.
Fallopian tube rupture is a dangerous way to terminate an ectopic pregnancy. It occurs suddenly and is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- with severe pain
- drop in blood pressure
- increased heart rate
- general deterioration of condition
- the appearance of cold sweat and loss of consciousness
- pain radiates to the anus, leg, lower back
All of the listed signs of ectopic pregnancy are caused by both severe pain and massive bleeding into the abdominal cavity.
During an objective examination, pale and cold extremities, increased heart rate, rapid and weak breathing are determined. The abdomen is soft, painless, and may be slightly swollen.
Massive hemorrhage contributes to the appearance of signs of peritoneal irritation, as well as muffled percussion tone (blood in the abdomen).
A gynecological examination reveals cyanosis of the cervix, an enlarged, soft uterus that is shorter than the expected gestational age, pastiness or a formation similar to a tumor in the groin area on the right or left. An impressive accumulation of blood in the abdomen and pelvis leads to the fact that the posterior fornix becomes flattened or protrudes, and its palpation is painful. There is no bloody discharge from the uterus; it appears after the operation.
Puncture of the abdominal cavity through the posterior vaginal fornix allows obtaining dark, non-coagulating blood. This procedure is painful and is rarely used for pipe rupture (pronounced clinical picture: sharp pain, painful and hemorrhagic shock).
Attachment of the fertilized egg outside the uterine cavity is caused by impaired peristalsis of the fallopian tubes or a change in the properties of the fertilized egg. Risk factors:
- inflammatory processes in the pelvis
Inflammatory processes of the appendages and uterus lead to neuroendocrine disorders, obstruction of the fallopian tubes, and dysfunction of the ovaries. Among the main risk factors is chlamydia infection (salpingitis), which in 60% of cases leads to ectopic pregnancy (see chlamydia in women: symptoms, treatment).
Intrauterine contraceptives lead to ectopic pregnancy in 4% of cases; with long-term use (5 years), the risk increases 5 times. Most experts believe that this is due to inflammatory changes that accompany the presence of a foreign body in a woman’s uterus.
Abortions (consequences), especially numerous ones, contribute to the growth of inflammatory processes of the internal genital organs, adhesions, impaired peristalsis and narrowing of the tubes; 45% of women after artificial termination of pregnancy subsequently have a high risk of developing an ectopic pregnancy.
- malignant neoplasms of the uterus and appendages
- hormonal disorders (including stimulation of ovulation, after IVF, taking a mini-pill, impaired production of prostaglandins)
- fallopian tube surgery, tubal ligation
- abnormal development of a fertilized egg
- sexual infantilism (long, crimped tubes)
- endometriosis (causes inflammation and adhesion formation)
- stress, overwork
- age (over 35 years old)
- congenital malformations of the uterus and tubes
- genital tuberculosis
Ectopic pregnancy is scary due to its complications:
- severe bleeding – hemorrhagic shock – death of a woman
- adhesions in the pelvis
- secondary infertility
- inflammatory process and intestinal obstruction after surgery
- recurrence of ectopic pregnancy, especially after tubotomy (in 4–13% of cases)
Girls who are afraid of encountering this pathology usually ask questions: where does it hurt, or what kind of pain occurs during an ectopic pregnancy. In fact, everything happens individually. And the nature of pain when an ectopic pregnancy occurs can be different. In some patients, the malaise resembles a normal pregnancy, but in many patients, especially in an advanced stage, their health worsens day by day, which is not surprising, since the fetus grows in the wrong organ, which is contrary to nature. Pain after detection of an ectopic pregnancy can be localized in certain organs and it is worth talking in more detail here.
I would like to note once again that in each patient, pain during pathological pregnancy manifests itself to varying degrees and at different times, sometimes they are not noticeable at all, while discharge after detection of an ectopic pregnancy is present in most patients. Spotting or heavy vaginal discharge is due to the fact that the embryo was implanted in an area where there are many blood vessels.
Bleeding most often resembles coffee grounds in color. Brown discharge during an ectopic pregnancy is quite rare, but can still be the beginning of continuous bleeding that poses a threat to the life of the pregnant woman. Sometimes doctors need to completely remove the uterus to avoid death.
It is very difficult to recognize a pathological pregnancy on your own. Many patients treat discharge during an ectopic pregnancy as the onset of another menstruation. Unfortunately, the signs of pregnancy that occurs in the uterine cavity are the same as during normal pregnancy. Bloody discharge in the early stages of pregnancy may not indicate the presence of pathology.
Light discharge in early pregnancy may indicate fetal implantation. It should be noted that implantation bleeding may not occur. It also does not signal the attachment of a fertilized egg in the uterine space. Therefore, at the first symptoms of pregnancy, even with a weakly positive pregnancy test, and any bleeding from the genital tract after an ectopic pregnancy, you should definitely consult a specialist.
How to prevent ectopic pregnancy?
Every year, after the start of sexual activity, a girl needs to be observed by her gynecologist.
Get tested and have a colposcopy. Visit an endocrinologist to monitor your hormonal levels. Get tested for hormones.
Monitor your sex life, take precautions, and avoid sexually transmitted diseases.
Pregnancy planning plays an important role. If a couple wants to have a child, both partners must first undergo examination.
Treat in a timely manner all diseases affecting the female reproductive organs and not only the body as a whole.
What to do if you have an ectopic pregnancy if you consult a specialist
Going to the hospital in time and recognizing the anomaly is the main factor in avoiding big problems in the future and avoiding serious consequences.
At the moment, there are two ways to treat ectopic pregnancy - medication and surgery.
In recent times, the only way out was to completely remove the uterus and tubes, which was a death sentence for a woman.
Modern medicine allows us to avoid such consequences and puts the preservation of a woman’s reproductive capacity first.
Many drugs have been developed to treat ectopic pregnancy without surgery. The drugs stop the development of the fetus. But there are disadvantages to this treatment. There are many consequences. Kidney and liver damage, baldness.
At what stage can an ectopic pregnancy be detected?
The disease is most easily diagnosed after the pregnancy is terminated (either a tubal rupture or a completed tubal abortion). This can happen at different times, but usually within 4 to 6 weeks. In case of further growth of pregnancy, it is possible to suspect its ectopic localization if the probable period is 21–28 days, the presence of hCG in the body and the absence of ultrasound signs of intrauterine pregnancy. A pregnancy that has “chosen” a place in the embryonic horn of the uterus can be interrupted later, at 10–16 weeks.
Help with ectopic pregnancy
Several types of laparoscopic operations are used for treatment - tubectomy (removal of the fallopian tube) and tubotomy (preservation of the fallopian tube).
The choice depends on the type of pathology and stage of pregnancy. If there is large blood loss, abdominal surgery (laparotomy) and removal of the fallopian tube are performed.
If the second tube is healthy and the woman’s reproductive function is not damaged.
Ectopic pregnancy occupies a leading position among pathologies of the female reproductive system. It is important to contact specialists in a timely manner. To avoid this anomaly and maintain your health, you need to follow the necessary preventive measures, do not delay the treatment of diseases, and listen to your body.
Causes of pathology formation
As a rule, the disease manifests itself under the influence of certain factors. Doctors identify the main reasons for the formation of the disease. These include:
- The appearance of an inflammatory or purulent lesion in the genital structure. (Due to their action, the structure of the mucous membrane in the conducting path is disrupted, and the contractility of the muscle fiber in the tube decreases. All this leads to disruption of the natural movement of the egg into the uterus, it is retained in the uterine tube. Due to the presence of inflammation in the reproductive system, inflammation can form blockage of pipes, which will lead to serious complications).
- Anatomical structure of the fallopian tube (These tubes can be long or curved, which, as a rule, will interfere with the normal development of pregnancy).
- The occurrence of adhesions in the abdomen after surgery. (Due to adhesions, normal fetal dislocation does not occur.)
- Constant use of contraceptives.
- Pathological process in the fertilized egg (fetal anomaly or disorder at the genetic level).
- Detachment during in vitro fertilization.
- Infection in the genital structure.
- Violation of hormonal levels.
- Constant hypothermia.
In addition to the main reasons that provoke the pathology, there are also some factors (the pregnant woman may not even be aware of them). Such factors are characterized by insignificant movement of sperm cells, an innate constitutional feature in the structure of the genital organ. Also affected by the presence of abortions in women in the family, inflammation in the appendages. If the mother of a pregnant woman had adhesions, scars, or kinks in the fallopian tube. In medical practice, it is noted that the older a woman is, the more likely she is to acquire an anomaly in the reproductive system.
Important! Pathology is much more often recorded in patients over 36 years of age. This category is considered a risk group and women are urgently prescribed an ultrasound examination to make sure that the fertilized egg has attached to the uterine cavity.
You should be attentive to your health and if you detect pregnancy, see a specialist. If a disorder in the system is detected in the form of an ectopic pregnancy, then quickly eliminating the pathology will help avoid complications and will not affect the normal development of the unborn child.