Menstruation
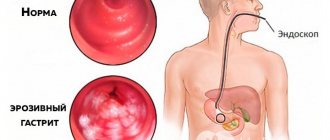
Menstruation is the cyclical, orderly release of the uterine lining in response to the interaction of hormones produced by the hypothalamus, pituitary gland and ovaries. The female cycle is divided into two phases: follicular (proliferative, FF) and luteal (secretory). Its duration is the number of days between the first bleeding and the start of the next.
The average duration of the menstrual cycle is 28–30 days. Patients with MC for less than 21 days are diagnosed with polymenorrhea, and for more than 35 days - oligomenorrhea.
During the menstrual cycle, a woman loses up to 30 ml of blood; if the volume exceeds 80 ml, immediate diagnosis and treatment is required.
FF begins with the first appearance of the critical days and continues until the process of egg release. It is characterized by the formation of follicles, which leads to estrogen-stimulated proliferation of the endometrium (uterine lining).
The LH (lutinizing hormone) wave is initiated by a sharp increase in estradiol produced by the prevulsory follicle and leads to ovulation. At this time, granulosa cells are stimulated and progesterone is synthesized, which is responsible for the surge in FSH (follicle-stimulating hormone) of the middle cycle. In addition, the release of LH stimulates the resumption of meiosis and the completion of division reduction in the oocyte with the release of the first corpus luteum (corpus luteum).
The luteal phase is relatively constant in all women, its duration is 14 days. The variability in cycle length is due to the different onset of the follicular phase, which can vary from 10 to 16 days.
If conception does not occur, the hormone concentration begins to fall and menstrual bleeding occurs.
Influence
17-OHP progestin differs from regular progesterone by an additional hydroxyl radical at the 17th carbon atom in the steroid skeleton of the molecule.
This intermediate product is responsible for attaching the embryo to the mucous membrane of the uterus and regulates the growth of the reproductive organ during gestation. Also, 17-hydroxyprogesterone inhibits the muscle activity of the uterus to prevent spontaneous abortion.
It helps raise blood pressure and prepares the fallopian tubes for the passage of the egg.
This hormone mainly affects the reproductive function of the body, it increases BTT, acts on the central nervous system, causing some behavioral characteristics during the premenstrual period.
Increase
The concentrations of the intermediate product depend on the MC phase and the age of the woman. During puberty, progesterone 17-oh is elevated, the hormone rises rapidly and helps the menstrual cycle normalize.
If 17-OH progesterone is elevated, this condition can be caused by several conditions. The first is the menstrual cycle. 17-oh progesterone in women is increased during pregnancy. These conditions are considered normal.
Also included in the first group is an increase in 17-OH progesterone, the reasons for which may indicate the following conditions:
- impaired functioning of the adrenal glands;
- use of medications based on minor progestins;
- ovarian disorders.
The second group includes reasons indicating physiological reactions of the female body. The hormone 17-OH progesterone is elevated in women who are constantly depressed and fearful, and who regularly experience stress.
During a stressful situation, an ultra-high concentration of minor progestin and other hormones are released into a woman’s blood, which activate the entire muscular system.
Factors influencing the increase in 17-hydroxyprogesterone during FF FF is characterized by low basal temperature and, more importantly, follicular development. Decreased production of the steroid by the corpus luteum and a sharp drop in inhibin A allows FSH to be stimulated during the last few days of the menstrual cycle.
Increasing FSH allows you to recruit the required number of follicles in the ovaries, one of which is intended for ovulation. On day 8 of the cycle, the dominant follicle suppresses the maturation of other ovarian follicles.
During FF, serum estradiol (E2) levels increase and the number of granulosa cells also increases. An increase in FSH during the late luteal phase leads to an increase in the number of follicle-stimulating hormone receptors, and ultimately to an increase in the secretion of estradiol by granulosa cells.
In the presence of E2, FSH stimulates the formation of granulosa cell LH receptors, which allows the release of small amounts of progesterone and 17-OHP, which can have a positive effect on the estrogen-primed pituitary gland to increase luteinizing hormone.
The LH surge leads to the destruction of granulosa cell junctions, the oocyte is reintroduced into the diploft stage of prophase 1 of meiosis, then the follicle ruptures and the oocyte moves into the uterine cavity. It is in the FF that the egg turns into a developing fetus
The level of secondary progestin at this time should be 0.32–2.23 nmol/l. If 17-OH progesterone is elevated in the follicular phase, this indicates excessive accumulation of the male sex hormone in the body.
If 17-OH progesterone and testosterone are elevated at the same time, the doctor diagnoses infertility. With an increased amount of both hormones, a married couple will not be able to get pregnant naturally; the ovulatory phase may not occur. In this case, the duration of the MC usually increases.
If 17-OH progesterone is increased 5-6 times in the follicular phase, this may mean that there is no menstrual bleeding for 2-3 months. If the concentration is more than 15 nmol/l, immediate contact with an endocrinologist is required.
17-OH progesterone is increased in the follicular phase - reasons:
- tumors of the ovary or adrenal glands;
- infertility;
- acne on the face;
- diabetes;
- hyperhidrosis.
- Additionally, hyperprogesteronemia in FF may indicate CAH.
What does it mean to increase and decrease progesterone levels?
An abrupt and sharp increase in level occurs during the period of ovulation and during the second half of the luteal phase. This is a completely normal and natural process, which is a direct confirmation of the body’s readiness for procreation. This is when the body needs a hormone like progesterone most. This is like a kind of signal for the whole body to prepare, because the likelihood of fertilization is high. Another sharp hormonal surge occurs in the third trimester, during pregnancy. This is already the result of preparation for the birth of a child.
When the levels of such an important hormone seriously exceed the upper limits, this is a reason to think about your health.
So, if 17-OH progesterone is elevated in the follicular phase, then the reasons should be determined as soon as possible. This can cause serious problems with conception, since the process of preparing the uterus and egg will be disrupted - ovulation is suppressed, the egg does not move along the intended route.
One of the first alarm bells indicating this problem is delays in menstruation, which alternate with heavy, painful discharge. Some girls even stop menstruating for several months, despite the fact that they are at the peak age for fertilization and are still very far from menopause.
Incorrect functioning of the ovaries (including tumors), improper absorption of the hormone, and diseases of the urinary and reproductive systems can increase the level of the hormone.
If progesterone is increased in the luteal phase, then there may not be many reasons. According to gynecologists, there are only three of them:
- The body is in peak condition and is ready for fertilization “to the maximum.”
- Pregnancy has already begun.
- Any of the previously taken medications gave this side effect.
Lack of the hormone affects the body extremely negatively. A decreased level of progesterone in the luteal phase is an extremely dangerous trend. It can indicate a variety of hereditary and acquired diseases, and can lead to complications during pregnancy and miscarriage.
As the practice of gynecologists shows, this problem is most often associated with dysfunction of the adrenal cortex. A woman’s body is simply not able to produce the required level of the hormone. This problem is discovered during puberty. It’s good that at this moment the girl still has enough time to prevent unpleasant consequences. If the disorder is discovered later, the therapy may be delayed or may not bring any results at all.
Lack of progesterone leads to untimely or incorrect production of luteinizing hormone in the next cycle. The entire rhythm of the reproductive system is disrupted and, as a result, infertility. This problem is also often associated with Addison's syndrome, in which the adrenal glands cannot cope with the production of all hormones. It is possible to increase the level artificially, but this can have a negative impact on all other organs.
Factors
After ovulation, the remaining granulosa cells that are not released with the oocyte continue to enlarge, become vacuolated in appearance, and begin to accumulate a yellow pigment called lutein. Luteinized granulosa cells combine with newly formed theca cells and surrounding stroma in the ovary to become the so-called corpus luteum. It is a transitional endocrine organ that predominantly secretes progesterone; its main function is to prepare the endometrium for implantation of a fertilized oocyte.
Signs
The nature of the symptoms is individual for each woman, it depends on the concentration of progesterone in the blood and the general condition of the body. With hyperprogesteronemia, increased excitability, irritability, and depressive states are observed.
When 17-OH progesterone is elevated, symptoms may include:
- feeling of breast engorgement;
- the mammary glands become painful and sensitive on palpation;
- a woman's weight increases;
- intestinal problems;
- a previously non-troubling acne appears on the face;
- my legs begin to swell.
During this period, women quickly get tired, experience dizziness, and migraines appear more often. In addition, memory concentration decreases and anxiety appears. The possibility of panic attacks cannot be ruled out.
For hyperprogesteronemia, make an appointment with a gynecologist and endocrinologist. This disorder can cause numerous endocrine diseases, so you should carefully check the body.
Analyzes
The main test that allows you to see the level of progesterone in the blood is a blood test for hormones. The day of delivery is important. Usually the doctor prescribes such a laboratory test on days 22-23 from the beginning of the menstrual cycle, which is when the full picture of the hormonal status is visible.
At the same time, the doctor can analyze the indicators of other hormones: cortisol, estrogens, testosterone, etc. This can help in diagnosing various diseases when clinical research methods are used, for example, X-rays, ultrasound, endoscopy and others.
Attention! The method for determining the hormone is a blood test, the method for making an accurate diagnosis is a set of diagnostic measures determined by the doctor.
Consequences
If 17-OH progesterone is high for a certain phase, and there are no signs of pregnancy, you should consult a doctor to begin prompt treatment and exclude the development of side effects.
Every woman must know what this minor progestin does. If the hormone 17-OH progesterone is elevated, what does it affect?
This has a very bad effect on human brain activity. An intermediate product synthesized in the adrenal cortex affects the areas of the brain that are responsible for memory, the hypothalamus.
In addition, this hormone has a negative effect on a number of receptors and enzymes responsible for taste, joy, pleasure and enjoyment. If the increase in 17-OH progesterone in the blood continues, the woman begins to suffer from mental disorders, and her depressive state often becomes noticeable.
Where is it produced and what is it responsible for?
The main place where progesterone is synthesized is the zona reticularis of the adrenal glands. The tropic hormone ACTH, adrenocorticotropin, has a direct effect on the production of the steroid.
The 17-OPG hormone is designed to be converted into other hormones:
- In the adrenal glands (and nowhere else) it is synthesized into cortisol by the enzymes 21-hydroxylase and 11-b-hydroxylase.
- There, in the adrenal glands and in the gonads, it is converted into androstenedione, 17-20-lyase is responsible for this.
Since OH-progesterone serves as an important source for the appearance of cortisol, the behavior of this hormone is in many ways similar to that of cortisol. The maximum level of 17-OPG in the blood is in the morning, cortisol works similarly. Hormonal levels decrease during the day, although naps during the day may cause a slight spike.
If there is a decrease in the synthesis of cortisol in the body (due to a lack of a “specially trained” enzyme), then progesterone begins to work on androstenedione, and the level of sex hormones in the blood increases. In addition, the amount of 17-OPG itself accumulates in the body.
Treatment
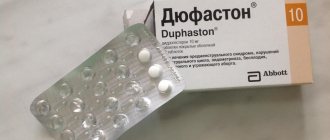
The drug treatment regimen is selected individually; the gynecologist or endocrinologist primarily relies on the test results obtained. Treatment for elevated 17-OH progesterone is often based on the use of oral contraceptives containing a specific combination of hormones.
Representatives of these funds are:
Each drug has some side effects and contraindications. Therefore, the use of medications without medical advice is impossible.
The progesterone inhibitor Epostan is prescribed to correct hormonal levels somewhat less frequently; it is less effective.
Hormonal medications are also prescribed to treat this condition. They should not be taken by pregnant women. Dexamethasone is often prescribed for elevated 17-OH progesterone. Methylprednisolone also has a good effect on lowering.
Drug treatment can be aimed at getting rid of the cause of the disease. For example, for cysts, oral contraceptives are prescribed, and for renal failure and adrenal dysfunction, corticosteroid hormones are prescribed.
Treatment can also be surgical. Such measures are taken if the cyst does not resolve on its own. The doctor removes the formation itself or resects the ovary. Then medication therapy is prescribed to prevent the inflammatory process, infection and restore the woman’s menstrual cycle.
Folk
In addition to medications, if 17-OH progesterone is elevated, treatment may be based on the use of traditional medicine. Nature is rich in medicinal plants that have proven themselves in cases of hyperprogesteronemia of various origins.
Patients often ask doctors the question: “How to reduce 17-OH progesterone with folk remedies? Will they help? It is impossible to give an exact answer, because the body is unique, in one case the recipes will help restore the concentration of the hormone, in another - not.
When trying home remedies, you should rely on reviews from women who have tried them. You will also need to have your blood tested to check the effectiveness of the medicine. If necessary, the recipe can be replaced with another one.
17-OH progesterone and treatment of increase with folk remedies - recipes:
- Take 15–20 g of rowan flowers, pour 370 ml of boiling water. The medicine is infused for 60 minutes, then filtered. Drink 120 ml after a meal.
- Rowan berries in the amount of 2 dessert spoons are boiled over low heat for 25 minutes. The decoction is filtered and taken on a full stomach, 100 ml 2-4 times a day. The duration of treatment is 14 days.
- Clove flowers and buds, properly prepared, have a positive effect on the body in the treatment of skin pathologies caused by hyperprogesteronemia. First, prepare a mixture consisting of equal numbers of clove flowers and buds. A tablespoon of the mixture is poured into 350 ml of boiling water. The medicine is infused for a quarter of an hour. Drink 3 tsp. on an empty stomach 3-4 times a day. Treatment with this remedy should be for at least 7 days.
- Grind 4 dessert spoons of carrot seeds, pour in 650 ml of boiling water. Infuse the medicine in a dark place for 24 hours. Afterwards, filter the solution and drink 200 ml several times a day.
- The stem of the uterus normalizes the production of sex hormone. It is ground in a coffee grinder and brewed in the proportions of 1 tbsp. per glass. Drink 100 ml twice a day.
17-OH progesterone, if elevated, can be lowered using folk remedies. However, the exact process of preparation, application and dosage of medicinal herbs should be followed.
Reasons for increasing the concentration of 17 oh progesterone
All reasons for an increase in 17-OH concentration are divided into pathological and physiological. The first group includes:
- congenital hyperplasia (excessive tissue formation) of the adrenal glands;
- deficiency of enzymes involved in the synthesis of cortisol, steroid hormones aldosterone (21-hydroxylase, 11beta-hydroxylase);
- tumors of the ovaries and adrenal glands.
An increase in hydroxyprogesterone during pregnancy is a normal physiological phenomenon. The placenta begins to produce it. But, the norms of the active substance are determined depending on the week of pregnancy.
A significant increase in the substance in the first trimester, in the last weeks leads to self-abortion, intrauterine fetal death.
Deviations from the norm
Doctors prescribe a test for 17-on-progesterone to patients quite often - both during routine pregnancy planning and during the diagnosis and treatment of infertility. Therefore, doctors very often have to explain why elevated 17-OPG is dangerous for women and how to cope with the problem.
The normal limits for OH-progesterone are quite wide, and if 17 progesterone is slightly increased, it is quite safe for a woman. Normally, substance 17 is always elevated during pregnancy and in the second half of the monthly cycle. Constant stress, depression and other disorders can provoke a hormonal surge.
A serious increase in 17-OPG levels is usually observed with:
- menstrual irregularities;
- infertility in women;
- lack of enzymes 21-hydroxylase and 11-b hydroxylase;
- tumors of the ovaries and adrenal glands;
- congenital hyperplasia of the adrenal cortex.
In adolescence, such a hormonal imbalance can cause hirsutism (male-pattern hair growth) in girls, and later – menstrual cycle disorders and abnormal blood sugar levels.
If the level of progesterone 17 is significantly lower than normal, the following pathologies are possible:
- Addison's disease (adrenal cortex insufficiency);
- in men - false hermaphroditism.
Before deciding how to lower 17 he progesterone, it is first important to make a diagnosis. There is only one way to return the hormone to normal levels - treatment with hormonal drugs.
Increased hydroxyprogesterone levels during the follicular phase of the cycle
The level of 17 oh progesterone in the blood depends on the phase (day) of a woman’s menstrual cycle. The first is follicular (FF). It begins on the first critical day and continues until ovulation. This period is characterized by low basal temperature (lowest values at rest) and maturation of follicles.
Against the background of a significant increase in estrogen and FSH (follicle-stimulating hormone) during this period, a very small amount of progesterone and 17-OH is released, but it is enough to trigger the active secretion of luteinizing hormone. It, in turn, ensures that the egg is ready for fertilization .
If 17 OH progesterone is elevated in the follicular phase, this is an indicator of an excess amount of the male hormone in the blood. If the concentration of testosterone and 17 oh progestin is simultaneously exceeded, the doctor makes a conclusion about infertility.
A single detection of a high concentration of 17-OH in FF is not always associated with reproductive dysfunction. The cause of hormonal imbalance can be severe stress . After a while, you need to retake the blood test and find out the real picture.
What to do if 17-OH progesterone is elevated in the follicular phase
The result of the analysis showed an increase in 17-OH progesterone in the follicular phase. Don't panic. This is not a guarantee of serious problems; the increase can be one-time without a tendency to repeat. A sharp deviation in 17-OH progesterone can occur as a result of a serious stressful situation, when the level of blood flow to the heart should be maximum. Over time, it is necessary to conduct additional research that will show the real picture.
If the problem persists or begins to worsen, the woman is prescribed hormone therapy. Dexamethasone is relevant in such a situation, but only your attending physician has the right to prescribe this kind of drugs, who at the same time pays attention to additional preceding factors. A normal reaction of the body is a slight increase in weight, since the components of the medicine retain water in the body.
Ways to reduce 17 oh progestin levels
If you have symptoms of high 17-OH, your doctor will order a blood test. After laboratory testing, treatment is determined. To lower progesterone 17 oh, hormonal medications are used. Dexamethasone and Methylprednisolone are most often prescribed. During therapy, women notice weight gain. It is explained by the ability of these drugs to retain large amounts of water in the body.
When treating problems with conception and infertility, high concentrations of hormones are not used. The doctor determines the treatment regimen taking into account the symptoms of the disease and the phase of the menstrual cycle. Medicines are taken several times a day, taking into account the permissible daily concentration of the active substance.
If there are problems with the digestive system, medications are taken after meals. The duration of treatment is 3-6 months. To monitor the effectiveness of treatment, the doctor periodically orders laboratory blood tests.
Therapy for elevated hydroxyprogesterone may include combined oral contraceptives : Zhanin, Yarina, Anteovin and others. They contain a combination of female sex hormones and have a beneficial effect on hormonal status in general.
Drug therapy is designed to eliminate the main cause of the increase in the amount of 17-OH. For ovarian cysts, oral contraceptives are effective; corticosteroids are prescribed for adrenal dysfunction. In some cases, surgery is used.
For example, ovarian resection is performed if the cyst does not resolve on its own. Drug therapy prescribed after surgery is designed to prevent inflammation, infection and restore the uterine cycle.
Elevated 17 oh progesterone is treated with folk remedies. The effectiveness of such treatment depends on the individual characteristics of the woman’s body. Traditional medicine has a sufficient number of recipes. Monitoring the concentration of the hormone will help draw a conclusion about the effectiveness of the drug. If necessary, you can try a different recipe. The following medicinal plants are used to reduce hydroxyprogesterone levels:
- rowan flowers and fruits;
- carnation flowers and buds;
- carrot seeds;
- stem of uterine hogweed.
To prepare decoctions and infusions, it is necessary to purchase high-quality and correct raw materials and strictly follow the recommendations for the preparation and administration of the medicine. Before using any folk medicine, you should consult your doctor.
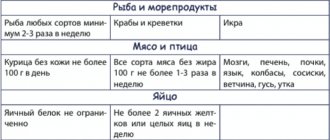
Dietary nutrition gives positive results only with an integrated approach to therapy . During the treatment period, it is recommended to reduce the amount of protein foods in the diet and increase the carbohydrate content. The menu includes potatoes, carrots, beets, parsley, peas, and onions. Eating fruits and dried fruits is allowed
High 17 oh progesterone, confirmed by several blood tests taken during the follicular phase, is an indicator of pathologies in the body. For this reason, there are problems with conception and pregnancy.
Normally, 17-OH progesterone is increased towards the end of the cycle, during pregnancy, stress and in the first days after birth in children. In other cases, an abnormally high concentration of the steroid hormone accompanies adrenal dysfunction and malfunction of the ovaries. A persistent increase provokes infertility, stillbirth, miscarriages and other pregnancy pathologies, and hirsutism in women.
Progesterone increases during stressful situations
What is 17 OH progesterone and its age norms
17 OH progesterone is an important element not only for the menstrual cycle, but also for conception. The substance is interdependent with the follicular phase.
In the body of a healthy woman, the concentration of the steroid hormone is normal. This means she is ready for pregnancy. Gynecologists prescribe an analysis for ON progesterone to patients planning to conceive, since during the period of gestation it loses its information content.
There are the following standards for progesterone OH (nmol/l):
- Newborns: from 0.23 to 0.75; from 0.70 to 2.30.
- Children (pre-puberty, early puberty): from 0.03 to 0.90; from 0.10 to 2.70.
- Male audience: from 0.07 to 1.70 (13-17 years old); from 0.20 to 5.30 (from 17 years old).
- Female: from 0.03 to 2.30 from 0.10 to 7.00 (13-17 years); from 0.07 to 2.90 from 0.20 to 8.70 (from 17 years old).
- Pregnant women: from 0.66 to 4.00 from 2.00 to 12.00.
- Luteal phase: from 0.90 to 8.70.
What is 17-OH progesterone responsible for?
The hormone 17-OH (17-OPG) is an intermediate element of the steroid group, which is produced during the metabolic transformation of 17-hydroxypregnenolone and progesterone. It is produced from cholesterol by the adrenal cortex and gonads (testes in men, ovaries in women); during pregnancy, 17-hydroxyprogesterone is also produced by the placenta. Cortisol or androstenedione (precursor of estradiol and testosterone) is synthesized from this hormone.
The main function is the synthesis of other hormones. 17-OHP is found in the body of men and women and is responsible for puberty, a stable menstrual cycle, the possibility of conception and sexual activity.
What is the difference between progesterone and 17-OH progesterone?
17-hydroxyprogesterone and progesterone have a number of differences:
| Features | 17-OPG | Progesterone |
| Biochemical structure | Metabolite of cortisol synthesis | Steroid substance |
| Synthesis | Mainly the adrenal glands, to a lesser extent – the placenta and gonads | Corpus luteum, in a smaller volume – adrenal glands, gonads. |
| Functions | Source material for the production of other hormones | Basic hormone for pregnancy, affects conception |
General information about the hormone
17-OH-progesterone or hydroxyprogesterone is one of the intermediate products of hormone metabolism that belongs to the group of steroids.
It is formed from two precursors - progesterone and 17-hydroxypregnenolone, through complex transformations in the adrenal glands into the hormone cortisol.
Hydroxyprogesterone can also be produced in the placenta and genitals, where it is also converted into androstenedione (this substance is the starting point for the synthesis of either the male sex hormone testosterone or the female sex hormone estradiol).
When to take a blood test?
Indications for testing, in particular when planning pregnancy:
- infertility in women due to hormonal imbalance;
- as part of a comprehensive examination for an ovarian tumor;
- disruption of the menstrual cycle.
A blood test for progesterone is prescribed during periods of infertility or ovarian problems.
In newborns, analysis is prescribed to exclude adrenal hyperplasia. In men, the study allows us to determine the cause of hormonal imbalance.
The study in women is carried out on days 2–4 of the cycle, in children and men - on any day in the morning on an empty stomach. Blood is taken from a vein on an empty stomach.
A comprehensive analysis is also used to determine the multisteroid profile - a highly accurate study that determines different types of disorders in the synthesis of adrenal hormones and sex hormones. The analysis is performed by mass spectrometry.
What do the results mean?
There may be three analysis options:
The level of 17-OH-progesterone is normal.
This means that hormonal abnormalities are not associated with the adrenal cortex or ovaries,
The hormone level is increased.
Hormone levels may increase with tumors of the ovary or adrenal glands.
Mild forms of hormone elevation usually result in menstrual irregularities and infertility.
An increase in the level of 17-OH-progesterone occurs with congenital adrenal hyperplasia in children and adults.
In children, this is usually a genetically determined pathology, transmitted in an autosomal recessive manner as a defect in one of the enzymes that allows hormones to be actively metabolized. As a result of a failure in this chain, testosterone synthesis and accumulation occurs. At birth, signs of virilization are revealed - an increase in male sexual characteristics in boys, with an enlargement of the penis and scrotum; in girls - signs of false hermaphrditism - an increase in the clitoris and labia, mistakenly taken for the penis and scrotum. Children of both sexes also develop metabolic disorders with severe losses of potassium and sodium salts.
The level of 17-OH-progesterone is reduced.
This condition occurs with Addison's disease, congenital or acquired adrenal insufficiency. In addition, a decrease in the level of the hormone in men occurs in a state of false hermaphroditism - when the synthesis of progesterone is disrupted and because of this, the normal formation of the body according to the male type is disrupted.
Norm 17-OH progesterone
The norm for women by cycle phases:
| Period | Minimum (nmol/l) | Maximum (nmol/l) |
| In the follicular phase | 1,24 | 8,24 |
| In the ovulatory phase | 0,91 | 4,24 |
| In the luteal phase | 0,99 | 11,51 |
| Menopause | 0,39 | 1,55 |
Blood test results for 17-OH progesterone
Normal for children:
| Age | Normal (nmol/l) |
| Up to 1 month | 3,03–51,5 |
| Up to 2 months | 4,8–29,7 |
| 2–3 months | 1,5–12,4 |
| 3–4 months | 0,6–13 |
| 1 – 10 years | 0,24–7,8 |
| 11–14 years old | 0,21–4,06 |
| 15–18 years old | 1,2–6,8 |
Normal for pregnant women:
| Term | Normal (nmol/l) |
| First trimester | 3,55 –17,03 |
| Second trimester | 3,55 – 20 |
| Third trimester | 3,75 – 33,33 |
The norm for men over 18 years of age: 1.52–6.36 nmol/l.
Normal levels of 17-OH progesterone during the follicular phase
To determine 17-OH progesterone in the follicular phase, a hormone test is prescribed. First of all, it is appropriate in the following situations:
If signs of hirsutism are detected
When adrenal dysfunction is suspected
As one of the tests for adrenal tumors.
Causes of elevated steroid hormone levels
The physiological norm is considered to be an increase in levels after successful conception; no analysis is prescribed during this period. The concentration also changes after sleep, eating, depending on the period of the cycle, under the influence of stress.
High levels are observed in some diseases and conditions:
- malfunction of the adrenal glands, often due to the absence or deficiency of 21-hydroxylase;
- ovarian dysfunction;
- taking hormonal drugs.
https://youtu.be/6S25U_N6z0w
17-OH is closely related to other hormones:
- Cortisol and 17-OH progesterone are 2 interrelated substances . The first is synthesized from the hormone 17-OH, their volume in the body increases in parallel.
- If testosterone and 17-OH progesterone are increased simultaneously in the follicular phase, infertility is diagnosed . The ovulatory phase is disrupted or absent, and the cycle length increases. An increase in the volume of 17-OH provokes a rise in testosterone, which can cause not only infertility, but also miscarriages and fading of pregnancy.
- Increased prolactin and 17-OH progesterone . The level of prolactin determines the possibility of conception and ovulation. Its concentration increases along with the hormone 17-OH during pregnancy and stress.
- 17-OH progesterone and LH (luteinizing hormone) . The volume of 17-OH begins to increase a day earlier than the LH level, and the peaks in hormone levels coincide.
Functions and mechanism of action
17-OPG is traditionally considered a male hormone, while progesterone is an exclusively female hormone. The main functions of 17-one-progesterone in the body are the synthesis of cortisol and androstenedione (later testosterone and estradiol).
In addition, like any sex hormone, 17-OPG regulates puberty in women and affects the menstrual cycle (ensures correct alternation of phases and the onset of ovulation). And also, among other sex hormones, it affects the reproductive function of women, the ability to conceive and bear a healthy child.
As the main product for the synthesis of cortisol, 17-one-progesterone ensures that the body is prepared for stress and unforeseen situations. Being one of the sources of testosterone and estradiol, it is responsible for puberty, sexual behavior and reproduction.
The effect of 17-OH-progesterone in the body is invisible at first glance. The concentration of free hormone in the blood is quite small; most of the substance is immediately exposed to enzymes. But if the slightest malfunction occurs, for example, the number of enzymes decreases or the synthesis of androstenedione increases sharply, and cortisol decreases, the dangerous influence of the hormone OH-progesterone immediately appears.
Symptoms of high 17-OH progesterone
The reaction to an increase in 17-OH concentration is individual for each person.
With an increased level of 17-OH progesterone, blood sugar levels increase
Main features:
- cycle failure (when the level exceeds the norm by 5–6 times, menstruation is absent for several months);
- overweight;
- breast swelling or tenderness;
- gastrointestinal dysfunction;
- pimples, acne, urticaria;
- increased sugar levels;
- swelling;
- body hair.
With high concentrations of 17-OH in children:
- abnormal size of the genital organs;
- electrolyte imbalance.
With prolonged disruption of the level, fatigue, migraines, dizziness, anxiety, panic attacks, mood swings occur, attention and memory suffer.
Treatment for elevated 17-hydroxyprogesterone
If the hormone concentration increases significantly, glucocorticoid therapy is prescribed. If there is a slight deviation from the norm, the diet is changed, stressful situations are eliminated, and the regime and lifestyle are normalized. One-time fluctuations in 17-OPG due to depression and stress do not require treatment and are not of diagnostic value.
Medicines
If the analysis shows an excess of 17-OH-progesterone, the following drugs are prescribed:
- COCs (contraceptives) – Yarina, Jess, Diane-3. The products normalize the cycle and reduce the volume of discharge.
- Provided that infertility was diagnosed more than 12 months ago against the background of non-classical CAI (congenital adrenal dysfunction), glucocorticosteroids are prescribed - Metipred, Prednisolone, Dexamethasone.
Yarina - a contraceptive to reduce discharge
Glucocorticosteroids act as functional analogues of natural human hormones produced in the adrenal cortex. The drugs reduce the manifestations of hirsutism in women and improve fertility.
How to lower it using folk remedies?
You can reduce the level of the hormone using folk remedies:
- Take 1 tbsp. l. crushed mint and rowan leaves. Brew the mixture in 1 glass of boiling water, leave for at least half an hour in a thermos. Take the infusion in equal parts three times a day for a month.
- Take 1 tbsp. l. wild carrot seeds, grind in a blender, pour 3 cups of boiling water. Then leave in a thermos for 1 day. Take 1 glass of infusion twice a day.
- 1 tbsp. l. Pour half a glass of boiling water over dry crushed stems of the boron uterus. Boil in a water bath for 15 minutes, cool. Strain, bring the volume to 100 ml with clean boiled water, divide into 2 doses and take twice a day.
- Grind 10 g of cloves, pour a glass of boiling water, leave for half an hour in a thermos. Then strain, take 50 ml of infusion 4 times a day.
- Grind the rowan berries, take 25 g of raw material, boil for 5 minutes in half a liter of water. Cool, strain. Drink the decoction during the day in 3-4 servings.
Dairy products and eggs help normalize progesterone in the blood
Balance your diet, add more nuts, seeds, and olives to your menu. Eggs, poultry, dairy products, fish, and avocados help stabilize hormone levels.
How to correctly take a blood test for 17 progesterone and decipher it?
What kind of analysis is this?
First of all, the doctor prescribes a blood test. After a detailed laboratory examination of the body, appropriate treatment is prescribed.
In severe cases, surgical intervention is indicated. Resection of the gonads is performed if the tumor does not go away on its own and tends to increase. After the operation, medications are prescribed to restore the patient's hormonal levels.
To obtain medicine from rowan, you need to brew 2 tsp. flowers and berries of this plant in a glass of boiling water and leave for 30 minutes. Drink three times a day in equal portions.
- 40 g of seeds are crushed, poured with 3 cups of boiling water, and left for 24 hours in a dark place. Drink a glass several times a day.
- 10 dried clove buds are cut, pour a glass of boiling water, leave in a water bath for half an hour. Drink 4 times a day, 70 ml.
1 tbsp. the stems of the boron uterus are poured with half a glass of boiling water and boiled in a water bath for 15 minutes. Then the volume of the medicine is adjusted to the original volume. This amount is taken 2 times a day.
Why are high rates dangerous?
The danger of increasing the level of 17-OH-progesterone:
- lack of ovulation, cycle disruption, inability to conceive;
- in the first weeks after conception, an increase in concentration can cause spontaneous abortion;
- at any stage of pregnancy, a high level provokes the threat of premature birth, bleeding in the uterus, and placental abruption.
Hormonal levels are directly dependent on lifestyle, nutrition, and emotional stability. Medicines to reduce hormones are prescribed if the level exceeds the norm by more than 2 times. If there is a slight increase in indicators, a gentle diet, psycho-emotional rest, and sometimes taking sedatives are recommended.
Rate this article ( 1 ratings, average 5.00 out of 5)