Every woman notes the presence of vaginal discharge at certain periods of the menstrual cycle. A particularly important type is cervical mucus, which resembles the white of a raw egg. At different phases of the cycle, these secretions have different characteristics and perform different functions to maintain a woman's reproductive health.
What is cervical mucus?
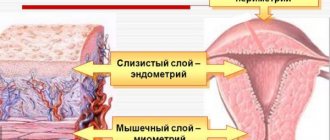
Cervical mucus is a special fluid produced by the epithelial cells of the cervix. The appearance and properties of cervical mucus change during the cycle under the influence of female sex hormones.
The liquid is a viscous transparent discharge, which in some cases has a white or milky tint. Mucus is a product of the cervical glands, which are located on the inner layer of the cervix.
Cervical mucus has an alkaline pH during the period of ovulation; during the remaining periods of the cycle, the balance shifts towards an acidic environment.
The cervical secretion consists mainly of sugars, amino acids, glycoproteins, enzymes, electrolytes and water.
How to thin cervical discharge
To conceive, it is necessary that the cervical fluid be of the desired consistency: viscous, medium thickness. If the secretion thickens excessively, it is necessary to follow the rules for liquefying it. Only the attending physician determines which drug to use to reduce the viscosity of cervical mucus. Self-medication is unacceptable.
The amount of water you drink per day affects the parameters of all biological fluids in the body. The greater the intake of water into the body, the lower the risk of thickening of the secretion. Sometimes simple dehydration reduces fertility.
To change the composition and viscosity of the secretion, oils containing unsaturated fatty acids (primrose oil) are used. Syrups are used that affect the production of secretory substances (guaifenesin). These substances should be used with caution, they can lead to allergic reactions.
To increase the acidic environment of the vagina to a more neutral value, change the diet. To do this, eat more plant foods, minimize meat, dairy products, and coffee. Acid-base properties are improved by products with an antioxidant effect (green tea).
Medicines with probiotics will help improve the vaginal microflora and reduce the risk of proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms. If there is a genital tract infection, a test is taken to determine the pathogen and the disease is treated. Conception should not occur in an infected body, as this may negatively affect the development of the fetus. During pregnancy, many medications cannot be used.
Every woman notes the presence of vaginal discharge at certain periods of the menstrual cycle. A particularly important type is cervical mucus, which resembles the white of a raw egg. At different phases of the cycle, these secretions have different characteristics and perform different functions to maintain a woman's reproductive health.
https://youtu.be/3CisjRRbkaQ
Kinds
The properties of mucus in the cervical canal are determined by traces on underwear, panty liners or toilet paper. If it is not possible to study the nature of the discharge in this way, it is necessary to insert a finger into the vagina and examine in detail the mucus that remains on it. By the appearance of the discharge, you can determine the phase of the menstrual cycle and the possibility of conceiving a child.
During the menstrual cycle, discharge has different appearance and physical properties:
- In the first days after menstruation, the mucus is very thick and does not manifest itself in any way.
- A few days before ovulation, sticky and liquid discharge appears.
- During ovulation, mucus becomes slippery, stretchy and transparent.
- After ovulation, the discharge becomes thicker and takes on a white or milky hue.
What kind of discharge is this?
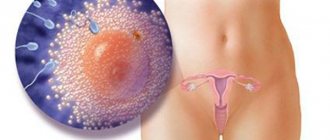
Cervical fluid supports the vital activity of sperm, creating an environment favorable for them. In the vagina it is acidic, so the mucus neutralizes it and helps them move.
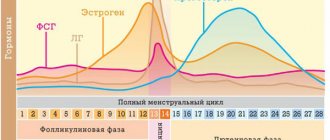
During the menstrual cycle, under the influence of hormones, in particular estrogen, the nature of the discharge changes. If ovulation is not yet expected, then there is no mucus or very little is produced. The closer ovulation is, the more fluid appears.
When you ovulate, your cervical fluid becomes thin and looks a bit like egg white. If there is very little such discharge, then sperm will not be able to live in the vagina and fertilization will not occur. Afterwards it thickens again.
Method of contraception
Some women use cervical mucus to identify dangerous and infertile days of the cycle. This method of contraception has the right to life, but requires precision and absolute discipline. Any external factors, such as exercise, diet, medication, can affect the condition of the mucus, creating confusion.
It is important to observe the nature of the discharge every day in order to create your own calendar of dangerous and non-hazardous days. If you are not planning to become pregnant in the near future, it is better to use additional methods of contraception.
What does the nature of the discharge indicate?
To determine ovulation, you need to learn to distinguish cervical fluid by day of your cycle. It can be of several types, depending on the proximity of ovulation.
The first two days after menstruation are called dry days. The vagina feels dry or slightly wet. These days it is almost impossible to get pregnant. After a few days, the amount of mucus increases; its consistency resembles glue. Spermatozoa can exist in such an environment, but these conditions can hardly be called ideal for them.
When the liquid thins and resembles a cream, this indicates that ovulation will occur soon. Its color becomes yellowish and slightly cloudy. There is moisture in the vagina, and there may be marks on the underwear. Such secretions are suitable for sperm and promote their movement. These days are considered favorable for conception.
When the egg is released, there is a lot of mucus, it becomes viscous and watery. After the amount of liquid decreases, it thickens.
If a woman knows her body, she will be able to recognize deviations. This will help diagnose diseases at an early stage, determine the presence of infections or an inflammatory process.
Important Rules
In order for the observation to give reliable results, it is necessary to follow the basic rules:
- Each cycle, on the day of the end of menstruation, determine the nature of the fluid, 3 times a day. To do this, wash your hands thoroughly and take a vaginal sample with your finger;
- Determine the quality of mucus: liquid, sticky, dry;
- To check the ductility, simply spread your fingers;
- Check the dryness of your underwear every time you go to the toilet;
- Record the results of your own research.
What functions does it perform?
To figure out what kind of liquid it is in the cervical canal, you need to know its main functions:
- Provides penetration of sperm to the egg;
- Gives male reproductive cells additional strength and energy;
- Protects sperm from leukocytes and the acidic environment of the vagina;
- “Filters” male cells, selecting the strongest.
After a man has an orgasm, the sperm mixes with the lining of the cervix. There, sperm can live for several days, gradually moving to their “destination.” Those cells that could not survive dissolve in the endometrium. When progesterone is produced, the mucous membrane cannot accept “guests”.
Why is there no mucus?
Some women complain that they experience a lack of cervical fluid during ovulation or have difficulty determining its nature.
This can be caused by a number of factors:
- Vaginal infections;
- The presence of seminal fluid;
- Sexual arousal;
- Ointments and spermicides;
- Antihistamines.
The fluid in the cervical canal removed during menopause should not dry out on your finger until you wash it off. When there is no discharge or it is too dry and in small quantities, even if the woman is in menopause, this may indicate abnormalities.
This phenomenon occurs after therapeutic and surgical interventions, due to hormonal imbalance, endocervical problems. After an examination, the doctor will correct it with estrogen or prescribe another treatment.
In the absence of pregnancy, cervical fluid appears completely normal. Conception may not occur if a woman’s body produces antibodies to male sperm - this is the so-called immunological incompatibility. A woman's antibodies deprive a man's reproductive cells of mobility. In this case, it is necessary to carry out the necessary examinations, determine the disorders that have arisen in the cervical canal, and be treated both with medication and with an auxiliary method, for example, artificial insemination.
What functions does it perform?
The product of the cervical glands performs several important functions:
- Sperm survival. The most important function of mucus is to provide sperm with a suitable environment to survive and remain active. The fact is that the vagina is characterized by an acidic environment, and sperm is alkaline. Cervical mucus during ovulation, unlike the vagina, has an alkaline environment, which protects sperm from death in the aggressive acidic environment of the vagina.
- Help with penetration into the uterus. Another obstacle for seminal fluid on the way to the egg is the cervix, the internal diameter of which is only a few millimeters. It is not easy to overcome such a bottleneck, and cervical mucus again helps with this: in the middle of the cycle it becomes very slippery, which facilitates the fastest passage of sperm through the narrowest part of the woman’s reproductive system.
- Uterine protection. During periods when a woman is not ready to conceive, the mucus becomes acidic and becomes very dense, clogging the cervix. This happens in order to protect the uterus from infection and pathogenic bacteria and maintain its sterility.
- Fetal protection. After pregnancy, under the influence of the hormone progesterone, the cervical secretion becomes even thicker and denser. To protect the unborn child from pathogens, mucus concentrates and thickens in the cervix. This plug also helps to securely close the internal os of the uterus and retain the fetus.
Changes in mucus during pregnancy
In early pregnancy, cervical mucus thickens. It forms a dense plug that prevents infection from entering the uterus. This protects the fetus from environmental influences and infectious agents.
When the body prepares for childbirth, the plug comes out. This may happen several weeks before or just before delivery.
Liquefaction of the plug means the appearance of pathological reactions. There are several possible reasons:
- risk of miscarriage;
- the appearance of an infection that is mixed with the mucous component.
Both conditions are dangerous for the fetus and require immediate medical attention.
Problems and diseases
Many problems of a woman’s reproductive health are associated with the secretion of the cervical glands:
- The properties of cervical secretion depend on hormonal levels. Sometimes the cervical glands do not respond to changes in the dominant hormone during the monthly cycle. In this case, during ovulation, the cervical fluid remains thick and does not allow sperm to enter the uterus, which prevents conception. This problem most often occurs after surgical treatment of the pelvic organs, or severe inflammatory disease of the uterus and isthmus.
- Hormonal imbalance also affects the condition of cervical secretions. With a lack of estrogen or progesterone, mucus does not change its character in the middle or in the second half of the cycle, and its amount remains unchanged.
- If the amount of cervical mucus is not enough, the barrier between the vagina and uterus is destroyed. This leads to the penetration of bacteria from the vagina into the uterus and the development of inflammatory diseases such as endometritis, endometriosis, and inflammation of the appendages.
- Due to the advanced inflammatory process in the uterine cavity, cervicitis occurs. This inflammatory disease of the cervical canal is characterized by copious cervical mucus with an unpleasant odor and uncharacteristic color (green, yellow), as well as bloody discharge after sexual intercourse.
- After cervicitis, in very rare cases, cervical secretions may contain antibodies to sperm - proteins that deprive sperm of activity and prevent pregnancy. This problem leads to pleukolny infertility of the couple and requires treatment.
- A large amount of brown, green or yellow mucus in menstrual blood may indicate the presence of polyps in the uterus, a cyst on the ovary, or a severe sexually transmitted infection.
Causes of thick mucus consistency
When diagnosing an excessively viscous state of discharge, fertility decreases. This may prevent the desired pregnancy from occurring.
There are several reasons for the thick consistency of mucus:
- an increase in viscosity immediately after sexual intercourse (therefore, doctors recommend abstaining from them before the analysis);
- ovulation has already occurred;
- hormonal imbalance;
- vaginal candidiasis;
- inflammation of the fallopian tubes;
- sexually transmitted diseases;
- endometritis (inflammation of the uterine wall).
Important! Changes in the quality and quantity of discharge can lead to infertility. Therefore, before planning a pregnancy, it is necessary to donate cervical fluid for examination.
Before ovulation
For several days after the last day of menstruation, cervical fluid is acidic, thick in consistency, and white or milky in color. Cervical secretion is concentrated in the area of the cervical canal, preventing the penetration of pathogens and sperm into the uterine cavity. Mucus does not move towards the vaginal opening, so this time is called the “dry period” due to the feeling of dryness in the genitals.
2-3 days before ovulation, cervical fluid changes its structure: it becomes more watery, and the color changes from white to transparent.
Reasons for the absence of cervical discharge
There are natural reasons when the discharge stops for a short period of time. For example, the period after ovulation, temporary dehydration of the body due to insufficient water intake. In such conditions, specific treatment is not required; secretion will be restored after the cessation of the factor.
The first reason for a pathological decrease in secretion is a hormonal imbalance. Secretion is produced under the influence of sex hormones. If their number is insufficient, the indicator is at the same level or does not stand out at all. Cervical mucus is often released before ovulation.
In a healthy woman, the vaginal microflora is represented by lactobacilli and opportunistic microorganisms. They develop in a slightly acidic environment. If hormonal levels, diet, or acid-base status change, the microflora balance is disrupted. Opportunistic microbes multiply and become pathogenic. This leads to inflammatory reactions. To eliminate the possibility of their penetration into the uterine cavity, the secretion ceases to be produced. This prevents the passage of bacteria. The lumen of the canal narrows.
To timely identify the appearance of the pathogen, a woman must respond to the occurrence of painful symptoms. Abdominal pain appears and spreads down to the genitals. Unpleasant sensations, itching, burning occur in the vagina. The discharge takes on an unpleasant odor.
Under the influence of prolonged stressful situations, hormonal imbalances occur in the body. The production of adrenaline increases, which reduces the activity of the genital organs. The longer this condition lasts, the more exhausted the body becomes. This can lead to infertility. If a woman cannot cope with this condition on her own, she should consult a psychologist.
When using cosmetics for intimate hygiene or lubricants (lubricants), a cessation of secretion is often observed. This is due to the effect of chemicals on Bartholin's glands. Their effect is suppressed during the use of the cosmetic product. The condition is reversible and can be corrected by discontinuing the drug.
During ovulation
When the egg is ready to unite with the sperm, the cervical fluid changes its pH from acidic to alkaline so that the male seed does not die and does not lose its activity. The physical properties of the cervical secretion also change: it becomes very slippery, viscous and easily permeable, and its quantity increases. The discharge looks like egg white. The changes are associated with a sharp increase in the hormone estradiol.
The permeability of mucus is due to an increase in the distance between liquid molecules. In this state, the cervical secretion is like a sieve through which male reproductive cells penetrate absolutely unhindered.
During this period, women notice wet spots on their underwear or sanitary pads - this sign indicates the onset of the fertile period.
Self-assessment of mucus properties to determine ovulation and fertile days
Based on the consistency of cervical mucus, you can try to determine the most fertile days yourself. To do this, put on medical gloves and place two fingers deep into the vagina to extract a small amount of secretion. Now evaluate the consistency:
- Dry. There is almost no mucus, it is impossible to get pregnant on such days.
- Watery. The mucus is very thin, which indicates that ovulation has not yet occurred.
- Slimy and viscous. If the mucus stretches several centimeters between the fingers, this indicates maximum fertility.
- Creamy. The mucus becomes thick and not sticky after ovulation. The chances of conception are minimal.
Cervical mucus performs important functions and determines a woman's fertility. And now you know everything about her.
(voted: 1, rating: 5.00 out of 5)
Share the news on social networks
Ask a Question! You have questions? Feel free to ask any questions! And our staff specialist will help you. Go>>
- Recommended Articles
- Hormones when planning pregnancy
- Utrozhestan when planning pregnancy
- Nutrition when planning pregnancy
« Previous entry
After ovulation
After the death of an unfertilized egg within a few hours, the hormonal background changes sharply, and the hormone progesterone comes into force. Under its influence, the cervical secretion changes its properties: the reaction of the medium returns to acidic, it becomes thicker and denser, becomes white, its permeability gradually disappears, and the amount of liquid decreases. 2 days after ovulation, the cervical fluid completely loses its permeability properties and again reliably protects the uterus from the penetration of bacteria and sperm. The cervical secretion retains this state until the onset of menstruation.
If fertilization has occurred, the fluid gradually becomes very dense and forms a white mucus plug, which comes out only during childbirth.
The role of the cervix in fertilization
Cervical mucus consists mainly of glycoproteins like mucin. It is rich in carbohydrates, and is a hydrogel similar to the hydrogel of the umbilical cord.
In the period after ovulation, the amount of cervical mucus is reduced to 50 ml, and by the time of ovulation it can increase to 600 ml. In clinical studies, it was found that the amount of cervical mucus increases in proportion to the increase in the titer of 17B-estradiol in the blood. The increase occurs due to an increase in water content in the mucus. Thanks to this, cervical mucus changes its rheological properties, and by the onset of ovulation, normal conditions for conception are created.
At the same time, a continuous flow of mucus is provided in the cervical canal, associated with the movement of microvibrations on the surface of epithelial cells. The fluid flow goes from the internal pharynx to the external pharynx, and it is more pronounced near the walls of the cervix canal. This is considered one of the biological mechanisms that prevents an incompetent sperm from fertilizing an egg.
Mucus has the following properties:
- Consistency, viscosity - changes throughout the menstrual cycle. Depends on the concentration of ions and proteins in the mucus. After menstruation, the viscosity of mucus decreases and its wateriness increases until ovulation occurs. Progesterone in the luteal phase of the cycle reduces the secretory activity of the epithelium, and the concentration of ions, globulins and cellular elements increases due to this. The maximum density of mucus is observed before menstruation.
- Extensibility – indicators of the elasticity of cervical mucus. Peak elasticity occurs during ovulation. The length of the threads can reach 12-14 cm, and on ordinary days this figure does not exceed 3-4 cm.
- Crystallization is a property that is exhibited when dried on glass. Normally, cervical mucus during the ovulatory period forms a pattern reminiscent of fern leaves.
The mucus of the cervical canal is represented by a hydrogel containing low molecular weight (electrolyte ions) and high molecular weight structures (HMS) - mainly mucin molecules that form the mucus matrix, and immunoglobulins that play a protective role. Mucus consists of fibrillar (protein) threads, in which protein molecules are located in the center, surrounded by oligosaccharides.
During the period of ovulation, the glycoprotein systems of the matrix are located at a distance of approximately 3.21 microns from each other, which is necessary for the normal passage of sperm through the cervical canal (the diameter of their head is 2.5-3 microns). In case of infertility, this indicator during the period of ovulation is only 1.4 microns. Normally, with a 28-day cycle, favorable rheological properties of mucus for conception appear from the 9th to the 15th day of the cycle.
Why is the analysis done?
In the clinic, you can do an analysis that comprehensively shows the state of the cervical secretion. This test is called the "cervical number".
The result of the analysis is expressed in one number, which evaluates the quality of the cervical fluid. A referral for analysis is usually issued when the causes of infertility in a woman are diagnosed. This analysis also reflects the condition of the ovaries.
The quality of cervical secretion is determined by the following criteria:
- Amount of liquid in ml.
- Drying pattern: When the mucus dries, a special pattern is formed on the glass slide.
- The number of leukocytes in 1 ml of liquid (from 0 and more).
- Consistency of cervical secretion (watery or viscous).
- Extensibility of liquid. Extensibility is determined by the distance that mucus can stretch between two glass slides.
The value of each parameter is assessed in points, which are then summed up.
The overall score is a very informative indicator of a woman’s hormonal health:
- 0-8 points – low level of estrogens (female sex hormones) in the blood,
- 9-11 points is the norm,
- 12-15 points – increased level of estrogen in the blood.
Both increased and decreased amounts of estrogen in a woman’s blood adversely affect overall health and the ability to become pregnant.
There is also an analysis that shows the ability of cervical secretion to pass sperm and maintain their activity. Material for analysis is taken during ovulation 9-24 hours after sexual intercourse and examined using a microscope.
Sperm found in cervical mucus are divided into:
- with fast forward movement,
- with a slow forward movement,
- chaotically moving,
- motionless.
The presence in the sample of at least a minimal number of sperm with rapid forward movement signals that the cervical fluid is correctly performing its functions, and infertility (when diagnosed) is not due to this factor.
Diagnosis and treatment of cervical factor infertility
Making any diagnosis begins with collecting anamnesis and clarifying complaints:
- the presence of adhesions and scars after interventions, abnormalities in the structure of the uterus, the growth of tumors - often do not cause complaints from patients;
- infectious processes - characterized by the presence of minor nagging pain, painful menstruation, severe PMS, changes in the appearance or smell of discharge;
- hormonal imbalance - has typical complaints for this pathology, and patients may note that during the period of ovulation there is no increase in the amount of discharge.
After this, the doctor proceeds to an external examination.
The doctor notes the examination data in general, which may indirectly indicate the presence of endocrine disorders. The doctor must also obtain gynecological examination data:
An external examination may reveal obvious signs of hormonal disorders - a moon-shaped face and the presence of striae with hypercortisolism, tachycardia and exophthalmos, increased excitability with thyrotoxicosis, excess body weight, edema and lethargy with hypothyroidism, hirsutism as an indicator of hypoestrogenemia or increased levels of testosterone and androgens.
When assessing the condition of the genital organs during an examination, the doctor notes the condition of the mucous membrane of the vagina and external pharynx (its size, condition, the presence of cysts and neoplasms in this area, scarring and adhesive changes).
During the examination, the doctor takes a smear from the vagina to identify pathogenic flora.
If a pathology is detected at this stage, the patient is prescribed a set of blood tests for hormones, if the cause is an endocrine disorder. After the results of the smear are obtained, if there are structural changes in the cervix, the doctor determines the treatment tactics: prescribing antibiotics to eliminate the infection or surgery to excise the pathological structures.
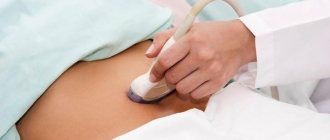
If the above diagnostic procedures do not provide enough information, the doctor prescribes a woman an ultrasound of the pelvic organs. Ultrasound allows you to visually assess the condition of the uterus, cervix, fallopian tubes and ovaries in real time. Ultrasound reveals pathologies such as:
- The presence of neoplasms in the area of the cervical canal and internal os.
- New growths of the uterus that cover the internal os - endometrial polyps, myomatous nodes, etc. They can act as artificial contraceptives, acting on the principle of an intrauterine device.
- Anomalies in the structure of the uterus and its cervix (double uterus, inverted uterus).
If there are structural changes, the patient is prescribed hysteroscopy with a biopsy, if they are caused by the growth of neoplasms, to clarify the nature of the neoplastic process. Further treatment is carried out taking into account whether a benign or malignant neoplasm covers the cervix, the likelihood of its growth due to endocrine pathology is assessed, etc.
In the absence of structural abnormalities, the doctor prescribes a blood test for the presence of ASAT. Cervical mucus is also collected during the period of expected ovulation for a laboratory study of its rheological properties.
If ASAT is present, desensitization therapy can be performed, the regimen of which is selected individually by the doctor. If functional disorders are not associated with organic or endocrine pathology, then artificial insemination or IVF is possible, which avoids the need for sperm to pass through the cervical canal, as happens during natural fertilization.
https://youtu.be/564n-SRbVAk
Is cervical discharge possible during pregnancy?
During pregnancy, a woman’s body undergoes a global restructuring associated with bearing a baby and a large number of hormonal changes. No one can say whether there will be discharge in the canal or whether such a phenomenon will be postponed until better times. The thing is that a woman’s body is very individual, and therefore develops according to its own laws.
Is pregnancy possible after an abortion: 4 dangers
The absence of such a phenomenon is due to:
- A woman's lifestyle;
- Gestational age;
- Diet;
- State of health.
If no discharge is observed, a woman should not worry ahead of time. The urogenital canal, of course, undergoes changes due to pregnancy, but sometimes this can be avoided.
You should consult a doctor who will probably find an appropriate explanation for this phenomenon. This means that the pregnancy process will proceed without complications and the female genitourinary system will not be affected.