Vaginal mucus is secreted by a woman throughout her life. Her character changes not only with age, but also during each menstrual cycle. Vaginal discharge is necessary to protect the female organs from sexually transmitted infections and maintain the health of the reproductive system. The change in color of the discharge during ovulation (mucus can be white, brown, bloody, etc.) can suggest pathological changes occurring in the female reproductive system.
What is ovulation
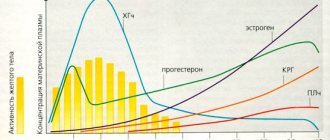
This is the time when a mature egg capable of fertilization leaves the ovarian follicle and enters the peritoneum. In every woman of fertile age, in normal health, ovulation occurs in every menstrual cycle. Moreover, its periodicity is regulated by neurohumoral mechanisms, the function of which in the female body is performed by gonadotropic hormones of the anterior pituitary gland and ovarian follicular hormone. In this case, the discharge of follicular fluid is observed on the day of ovulation of the ovary, the tissue of which becomes thinner.
Can there be discharge during ovulation?
The characteristic cervical mucus is a sign of the onset of ovulation, but it must be borne in mind that discharge cannot be a reliable indicator of egg maturation. So, even a healthy woman can experience anovulatory cycles several times a year. In addition, ovulation may not occur for several months after an abortion or miscarriage and for a year after childbirth.
Ovulatory cycles are influenced by a woman’s hormonal background, so they do not occur during the body’s preparation for the premenopausal period and throughout menopause. This explains the need to pay attention not only to discharge in some phases of the cycle, but also to other signs of ovulation. Under certain conditions, cervical mucus may not be secreted at all, and its absence will not indicate infertility or the presence of sexual diseases. However, fertilization of the egg is difficult, but pregnancy is still possible.
Reasons for deviations of discharge from the norm
Ovulatory mucus should be the same over several cycles; if the color or nature of the discharge changes radically, you need to visit a doctor.
Brown discharge
Brown mucus is not considered a pathology if a woman does not experience other alarming symptoms - the appearance of such discharge is associated with rupture of the follicle, and usually goes away within 48 hours.
Brown discharge appears due to rupture of the follicle
Other causes of dark, thin cervical mucus include:
- increased estrogen levels;
- taking hormonal and other drugs that can affect the female cycle;
- gynecological pathologies of an infectious nature, dysbiosis, candidiasis;
- the presence of an intrauterine device;
- malfunction of the thyroid gland;
- deficiency of rutin and vitamin C, which causes deterioration of the vascular walls;
- severe liver diseases.
Important!
Spotting brown discharge in the middle of the cycle may indicate pregnancy; conception can occur if unprotected intercourse occurs 5 days before the expected date of ovulation.
Bloody issues
The presence of a large amount of blood in the ovulatory mucus is a sign of disturbances in the reproductive system; this phenomenon is called intermenstrual bleeding.
Discharge with blood indicates problems in the reproductive system.
Causes of heavy bleeding:
- polyps, endometrial hyperplasia;
- fibroids, cervical cancer;
- polycystic ovary syndrome;
- hormonal imbalance in girls during puberty, women during menopause;
- hematological pathologies in which platelet levels decrease.
Bloody discharge in the middle of the cycle is a common side effect when taking oral contraceptives.
Yellow and green discharge
Yellow mucus is a sign of bacterial vaginosis - pathogenic microflora multiply on the walls of the vagina, which does not cause an inflammatory process, but can cause itching, burning, and changes in the acidity of the vaginal environment. If such discharge appears, you should not douche or use tampons.
Green discharge appears due to bacterial infections
Yellow, green, watery mucus with a pungent odor is a sign of chlamydia, gonorrhea, curdled discharge indicates thrush. Additional signs are itching, swelling of the external genitalia, discomfort during bladder emptying and sexual intercourse.
The absence of ovulatory discharge may be due to low estrogen levels or individual characteristics.
How to determine ovulation by discharge
Weak pink discharge in the middle of the cycle, approximately 1.5-2 weeks before the start of menstruation, is formed when the follicle of a mature egg ruptures. During this period, the amount of estrogen hormones increases sharply and a slight rejection of the internal uterine tissue (endometrium) occurs, which is accompanied by bloody discharge. Such symptoms of ovulation occur in about a third of women and are considered normal. For other representatives of the fairer sex, the mucus has the consistency of the white of a chicken egg.
Discharge before and after ovulation by day
Discharge during menstruation in women lasts from 5 to 7 days. Immediately after the end of menstruation, the so-called dry days begin (8-11 days).
12-13 days. A watery secretion is indicated. It is sticky and not abundant (the beginning of the ovulation period).
Day 14 Mucus increases in volume and thins out.
15th day. Vaginal discharge becomes similar to egg white: it has no color and stretches between the fingers. Blood streaks may appear. (ovulation)
16th day. The secretion is still as copious as snot.
17-19th day. The consistency becomes denser. The secretion becomes cloudy and thickens (the fertile period ends).
20-28th day. There are no allocations.
Data by day are approximate and do not reflect the menstrual cycle of all women.
As soon as a mature egg is released into the fallopian tube, the woman’s body is ready for fertilization and pregnancy. If you know which discharge during ovulation is considered normal and which is a symptom of a disease, you can find out how favorable your health is to pregnancy.
What kind of discharge before ovulation
During the first phase of the menstrual cycle, a woman secretes thick mucus, which causes a mucus plug to form in the cervix, which protects the organ cavity from pathogens and sperm. Due to its strong thickness, the mucus does not come out, so during this period the woman notes the absence of discharge before ovulation. Afterwards, the secretion gradually liquefies and it begins to flow out, while the nature of the mucus changes to viscous, transparent (reminiscent of egg white). This sign indicates that ovulation will begin soon.
What type of vaginal discharge is considered normal?
Cervical mucus is a product of glands located in the cervix (cervix). This is where all the secretions come out. Depending on the stage of the female cycle, the content of mucus changes. This is a natural physiological process regulated by hormones.
There are several types of discharge:
- Menstrual - produced not by glands, but by the uterus. The glands begin to produce mucus at the end of menstruation. It is dense and closes the entrance to the uterus like a cork.
- Mucous discharge before ovulation, insignificant, sticky.
- Cervical mucus, similar in viscosity to raw egg white, during ovulation.
- Dense masses immediately after ovulation.
The characteristics of mucus vary significantly in composition and structure in different periods. This is necessary to protect the uterus from sperm penetration when conception is not possible. Another function of mucus is to protect against infection.
Please note: the composition and density of cervical mucus is regulated by the body to facilitate conception and protect against infection.
At a time unfavorable for conception, the mucus composition is slightly acidic. When fertilization becomes possible, the composition changes to alkaline to maintain sperm viability. In addition, a change in the viscosity of cervical mucus helps sperm move better towards the egg.
What kind of discharge occurs during ovulation?
Determining the maturation of an egg by the nature of cervical mucus is not an accurate enough method, which should preferably be supplemented by measuring basal temperature, conducting special tests, and folliculometry. As a rule, discharge during ovulation is abundant and watery, transparent, white or pinkish in color. In rare cases, they have bloody impurities or a yellow tint. If blood is released before the onset of menstruation for several hours, you should urgently visit a gynecologist, since this sign indicates uterine bleeding.
If a woman has recently given birth to a baby, pink discharge may be the reason for the restoration of ovulation. Simultaneously with the change in the characteristics of the secretion, a woman may experience other signs, for example:
- pain in the mammary glands;
- increase in basal temperature;
- pain in different localizations;
- increased libido.
The absence of cervical discharge on the day of ovulation will be normal: many women do not experience any external changes in the body when their follicles mature. Vaginal dryness is a relatively common problem that interferes with normal conception. It is sometimes caused by low levels of the hormone progesterone or estrogen. In addition, dryness is due to the individual characteristics of the female body.
How long do they last?
During ovulation, mucus is released in large quantities for 2-3 days. After the release of the egg, the ovary begins to produce progesterone, under the influence of which the contents of the cervical canal change from a liquid consistency to a denser and thicker one. A sign of the end of this period is white mucous discharge. When using the calendar method of birth control, determining when ovulation is approaching will help a woman identify the days when the probability of conception is highest.
Discharge after ovulation
Sometimes mucus continues to come out even after the end of the ovulation period, and the secretion acquires a sticky, sticky consistency. Before menstruation occurs, the fluid becomes watery again. It is important for a woman to monitor the nature of the cervical secretion, since this is the only way she can assess the health of the genital organs. For example, if there is abundant mucus after the release of an egg, which is accompanied by an unpleasant odor, thrush should be suspected. Other symptoms of the disease:
- copious discharge of a cheesy consistency;
- the disease is accompanied by itching and burning.
In addition, the color of the secretion plays an important role: if it is grayish, bloody, yellow or green, this is not a good sign, indicating the presence of pathology. In this case, you need to consult a doctor and take a smear for flora. This diagnostic measure will help to establish the type of opportunistic pathogen of the infectious disease. It could be gardenella, candida or another.
Pathological changes
The appearance of unusual symptoms is a reason to immediately consult a doctor. The nature of mucous discharge remaining unchanged for a long time, bleeding in the middle of the cycle is a bad sign that indicates diseases of the genital organs such as:
- detachment of the endometrium of the uterus;
- hypothyroidism;
- cervical cancer;
- side effects caused by taking hormonal contraceptives;
- decreased platelet count in blood diseases;
- polycystic ovary syndrome.
Bloody issues
Some women notice slight bloody marks on their underwear that are brownish (dark) in color rather than bright red. In most cases, ichor is not a sign of a pathological process. The main reason for spotting during ovulation is the rupture of the follicle, which leaves the mature egg soon after. A red secretion is observed several hours before the start of the ovulation period and lasts for 48 hours.
Yellow
As a rule, this color indicates the development of bacterial vaginosis, a pathology in which pathogenic microorganisms multiply on the vaginal mucosa. Bacteria do not provoke inflammation, but lead to itching, unpleasant odor, burning sensation, and problems with conception due to changes in the acidity of the internal environment of the woman’s genital organs. If you are ill, it is not recommended to douche or use tampons. Doctors with vaginosis advise using sanitary pads and frequently performing hygiene procedures.
Infections such as:
- gonorrhea;
- chlamydia;
- candidiasis.
Brown
Vaginal secretion with a brown tint is a frightening factor for women. Its cause may be pregnancy due to unprotected intercourse in the middle of the cycle. In this case, slight brown spotting (dark blood) appears. Another reason why brownish discharge occurs in the middle of the cycle is hormonal/intrauterine contraception. The vaginal ring and oral contraceptives can cause this side effect during the first 3 cycles of use, which is due to an imbalance of sex hormones.
However, you cannot let your guard down, since brown mucus can be a sign of serious pathologies such as oncology or erosion of the uterine cervix. If the secretion is released very abundantly and looks unusual (brown color, the consistency of the vaginal fluid is thick or heterogeneous), this is a good reason to contact a gynecologist and do an ultrasound to make sure there are no pathological processes.
Ovulation without discharge
Some women are sure that they do not have ovulatory discharge, so perhaps they are not ovulating. This conclusion is erroneous. A minimum of leucorrhoea during ovulation does not mean that the oocyte has not been released. As a rule, this is fraught with problems with conception, but it is possible.
Ovulation without discharge also happens. The absence of discharge at this moment indicates hypoestrogenism. “Smears” on your daily routine occur due to hormonal imbalance, but the causes may not be “reproductive” factors, such as changes in diet or stress.
If the secretion is abundant only for a few days, and then it goes away, then there is no need to worry. Only slightly white or transparent mucus indicates a favorable course of the ovulatory process.
- When it comes to saturated white or gray color, it means that there is a violation of the vaginal microflora.
- What is worth remembering is that even if everything is fine with secretion, but there is pain in the pelvic area and other discomfort, this indicates unfavorable processes.
- If the discharge is scanty or, on the contrary, abundant, then the matter is most likely a hormonal imbalance.
Any suspicious symptoms should not be ignored; timely consultation with a doctor is the key to recovery. The phenomenon of “no discharge during ovulation” is more typical for pre-menopausal age, and in this case this is not a reason for panic, but you can consult a doctor to correct the situation.