Causes of bleeding in the middle of the cycle
Bloody discharge between periods can be caused by various reasons, including even the most harmless of them (for example, associated with poor nutrition, the predominance of fatty foods, hot seasonings and spices in the diet, bad habits - alcohol, smoking). In women who abuse harmful products, not only the cyclicity of menstruation is often disrupted, but also diseases of the reproductive system are more often observed.
The most common causes of mid-cycle bleeding include:
- hormone fluctuations or disturbances in their levels;
- deficiency of thyroid hormones, diseases of the endocrine system;
- diseases of the cervix, endometrium, benign neoplasms and oncological diseases of the genital organs;
- bends of the uterus;
- cysts in the ovaries;
- decreased blood clotting;
- lack of vitamins (primarily K and C);
- the initial phase of taking estrogen drugs or, conversely, stopping the course;
- taking certain other medications, including birth control;
- use of intrauterine contraceptives;
- vaginal trauma, miscarriage, infections and inflammation of the genital organs;
- some procedures performed during a gynecological examination (cervical biopsy, cauterization);
- severe stress, nervous disorders or depression.
One of the factors why bleeding occurs in the middle of the menstrual cycle may be pathology in the genitourinary system. In this case, bleeding may be more intense and painful.
https://youtu.be/eSRAnlc0E9I
Description
Appearing spots, mostly faint, sometimes even brownish vaginal discharge. Sometimes they disappear after a few hours, and in other cases it lasts for several days. Intermenstrual bleeding occurs regardless of regular menstrual bleeding.
Spots are usually caused by hormonal changes, for example, hormonal contraceptives (pills, IUD, etc.). Additionally, natural hormone changes during puberty and menopause may be a factor when it comes to frequent bleeding. Last but not least, the psyche can influence the subtle interaction of hormones in the female body. Stress, grief, painful loss, as well as happiness sometimes cause bleeding.
Difference with menstrual period
The spot differs from the normal menstrual period both in terms of its onset and the main reasons:
At any time and for various reasons
Bleeding can occur at any time, regardless of the menstrual period. Causes can range from hormonal changes to cancer.
Menstrual cycle - monthly routine
The female cycle is determined by the interaction of different hormones. It begins with the first rule (menarche) at puberty and ends with menopause (menopause). The monthly cycle begins on the first day of the monthly menstrual period and ends one day before the next menstrual period. How long a monthly cycle lasts varies from person to person. On average it is about 28 days.
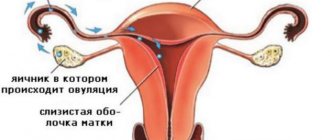
In the first half of the cycle, follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) stimulate the growth of ovarian follicles. As a rule, only one follicle matures completely. It produces more and more estrogen. This causes the lining of the uterus to grow and prepare for the eventual implantation of a fertilized egg.
Around the middle of the cycle, LH triggers ovulation (at this point estrogen levels are highest): a mature egg leaves the follicle, is captured by the fallopian tube and slowly passes through it into the uterus. She gives birth about 24 hours after ovulation.
The membrane of the egg follicle remaining in the ovary meanwhile turns into the corpus luteum. This produces the hormone progesterone and, in smaller quantities, estrogen. Progesterone (also called luteal hormone) is also involved in preparing the lining of the uterus for eventual implantation. In addition, progesterone and estrogen together inhibit further secretion of FSH and LH from the pituitary gland. This prevents the eggs from further maturing in the ovaries.
But if fertilization stops, the corpus luteum will die within ten to twelve days. Thus, the levels of progesterone and estrogen in the blood are significantly reduced. In response, the thickened endometrium and unfertilized oocyte are excreted along with the blood during menstruation.
Causes of mid-cycle bleeding in teenagers
A teenager may experience bleeding between periods during the formation of a cycle, which takes place over six months to a year. Therefore, it is recommended to mark the beginning of the cycle in the calendar every month in which they took place, which will help determine whether the cycle will be long or not. The cycle becomes regular one and a half to two years after the appearance of the first menstruation. If a cycle does not form during this time, you should consult a gynecologist who can prescribe a special hormonal course to normalize cyclicity. Women in the premenopausal period (45-50 years old) may also experience irregular menstrual cycles.
What it is?
Happy men continue to be blissfully ignorant of women's health. They sincerely believe that pads and tampons are essentially useless things, produced solely for the sake of women's whims. And they consider PMS to be our whims. Sometimes we ourselves feel uncomfortable because during this period we so want warmth, care and attention. A strong woman does not show her weaknesses. But intermenstrual bleeding is an alarming symptom. It warns not only about any problems in the health of the female body. But it may be a bell indicating various diseases. Have you noticed unusual intermenstrual bleeding? There is no need to panic - this is a fairly common phenomenon that may be a variant of the norm. Maybe you fell from a great height the day before? Or did you have an overly active intimate relationship? Yes, yes, sometimes sex can have such consequences, so notifying your partner about possible problems is a very good idea. Of course, intermenstrual bleeding can indicate tears in the vaginal area, but this is already a factor that needs to be reported to the police. If a woman has gaps, then she may have been a victim of rape.
Causes of intermenstrual bleeding when taking hormonal drugs
Intermenstrual bleeding can occur when taking hormonal drugs that change a woman's hormonal levels. This type of blood loss is especially common in the first weeks after starting to take the drug. Experts do not consider this phenomenon as a pathology, because it takes time to adjust the hormonal levels - the body’s adaptation to new conditions occurs gradually. But if spotting continues for more than 5 months, this is a reason to consult a doctor, who will stop taking this medication or correct its effect with the help of other special medications (for example, Duphaston).
Quite often, intermenstrual bleeding is a side effect of the contraceptive drug. By taking birth control medications, you can avoid additional protection against unwanted pregnancy. Such tablets are easy to use and can stabilize the menstrual cycle. But the female body does not always tolerate the effects of contraceptives equally well; in some cases, bleeding may occur.
Oral contraceptives should be taken from the first day of the cycle (or as prescribed by your doctor). Stopping taking the drug before completing the course (3 weeks) can provoke heavy bleeding from the uterus - the so-called “withdrawal bleeding” - which will require serious gynecological procedures (vacuum aspiration or curettage) to stop.
You should know: Some emergency contraceptives can cause heavy bleeding. When starting to take such drugs, a woman should be observed by a doctor for the first two weeks.
Causes of bleeding between periods with a cyst
A tumor on the ovaries (cyst) can cause fluctuations or disturbances in hormone levels. A cyst is a formation filled with fluid or blood, and has two types - functional cyst and non-functional. The first type is mostly harmless, the second requires mandatory examination and often surgical intervention. Dangerous cases are when there is a possibility of rupture of the tumor, twisting or suppuration of the cyst. In addition, the possible degeneration of the cyst into a malignant formation poses a great danger.
When should you worry?
If intermenstrual bleeding occurs regularly and is not accompanied by severe discharge and pain in the lower abdomen, there is no need to worry too much. But for any abnormalities during menstruation that are atypical for a particular woman, it is important to visit a gynecologist to exclude the possibility of developing pathology or prescribe the necessary therapy.
Constant delay of menstruation, disturbances in its duration and intensity, pain syndromes are a cause for concern and a visit to the doctor. It should be remembered that any disease detected at an early stage can be treated quite effectively.
It happens that, a couple of days after a visit to the gynecologist, a woman begins to have spotting. This phenomenon may be due to the use of instruments or doctor’s manipulations. If it lasts more than two days, you should also visit a gynecologist.
Diagnosis and treatment of disorders
Diagnosis and treatment of any menstrual irregularities should be carried out only by a medical specialist. Intermenstrual bleeding is no exception. Self-diagnosis and therapy are unacceptable. Also, the causes of this phenomenon cannot be attributed solely to any nervous shocks or consequences of changes in diet or medication. Only a gynecologist, after conducting an examination, can determine the true cause of the discharge and, if necessary, prescribe the correct treatment. After all, not only physiological processes cause intermenstrual bleeding, but also a serious pathology, which is impossible to establish and treat on your own.
After a visit to the gynecologist, examination and conversation with him, you may need to conduct additional research. Diagnostic methods include:
- smear microscopy;
- Ultrasound of the thyroid gland, pelvis;
- blood test for hormones;
- histological and cytological examination of scrapings and aspirate.
After a thorough diagnosis and examination of all symptoms, treatment will be prescribed by a doctor if necessary.
Treatment methods for intermenstrual bleeding are directly related to its causes and the woman’s age. First, the patient takes hemostatic drugs and restorative drugs. In this case, anemia is often observed; women are prescribed medications containing iron and vitamin complexes. Such types of treatment for bleeding caused by hormonal imbalance and ovulation are called conservative. Bleeding caused by stress and nervous disorders is treated with sedatives and antidepressants. For inflammation and infections of the genital organs that cause intermenstrual bleeding, appropriate drug therapy is also used.
Along with this, there are surgical methods of therapy (curettage or cleaning of the uterine cavity, removal of female organs). These radical measures are used if the results of cytology and histology indicate the presence of tumor processes. In this case, the woman’s age and her desire to have children are taken into account (for example, for young girls who have not yet given birth, curettage is performed only in emergency cases).
Pathology and norm
If a girl is very young, then she really does not want to see a doctor and therefore will first self-medicate. This is almost always a wrong decision, which can almost lead to death, especially when it comes to bleeding. If the problem lies in the uterus, you won’t be able to see it with your own eyes, but you can figure it out. If a woman had an abortion, and then pain began and the temperature rose, then we can assume that endometritis is occurring, that is, inflammation of the inner layer of the uterus. If left untreated, the disease will reach a new level and become chronic. Intermenstrual bleeding with endometriosis is the body’s cry for help, as it cannot cope with the burden of problems that have fallen on it.
Polyps may appear in the endometrium after abortion. Of course, you can’t make a diagnosis by eye, but based on the results of hysteroscopy, ultrasound and histology, everything becomes clear. Treatment can only be done surgically followed by taking COCs.
You need to pay attention not only to the character, but also to the color of the discharge. If they are brown, it looks like endometriosis. Much has already been said about this disease, but the consequences are often hushed up. But endometriosis may well result in infertility.
So, we need to summarize all of the above. First, intermenstrual bleeding should never be ignored. Even in the most harmless cases, this symptom forces you to pay attention to your health, calm down morally, and stabilize your sex life. You cannot tolerate bloody discharge and leave your partner in the dark, because perhaps their appearance is his fault and a consequence of violent sex.
Secondly, you should definitely go to the gynecologist at the first symptoms of bleeding. In the best case, this will simply be a routine inspection, which, by the way, is recommended to be carried out a couple of times a year in order to prevent possible troubles in time. A gynecologist can already suggest the cause of bleeding and, for example, give a referral to an appointment with a neurologist or psychologist if it’s all about stress.
Thirdly, you cannot self-medicate and prescribe pills recommended on the Internet. It is impossible to diagnose yourself based on your own pain sensations. You won’t even be able to pinpoint the exact location of the pain.
Finally, fourthly, when you see a specialist, give him as much information as possible. Does bleeding cause discomfort? How long does it last? By “long” we mean a period of more than three days. Is the bleeding getting worse? Do you have a regular menstrual cycle? Are there any pain sensations, and what is their nature? It’s good if you can talk about the color and nature of the bleeding, and remember the stressful situations you’ve experienced. Of course, ideally, you need to establish contacts with your own gynecologist in order to be seen by one person and have before your eyes the entire history of your visits to this office.
Doctors' opinion
As mentioned above, intermenstrual bleeding can be caused by both physiological and pathological factors. Often this is only one of the normal variants, but there are also more serious deviations in the functioning of the reproductive system, the development of malignant tumors. Only a doctor can correctly determine the cause of intermenstrual bleeding and prescribe the necessary course of treatment. Self-diagnosis and self-medication are strictly prohibited. If you experience regular irregularities in the menstrual cycle or experience pain during menstruation, you should not postpone a visit to a specialist.
In addition to medication and restorative therapy, doctors recommend that patients also pay more attention to their diet and lifestyle. You should eat more fresh fruits, vegetables, legumes, beef, and liver. It is necessary to take walks in the fresh air more often and devote at least 8–9 hours to proper sleep.
Systematic examinations by a gynecologist, a healthy diet, a mobile and active lifestyle, controlling your own weight and the absence of bad habits will preserve the beauty and youth of a woman for a long time and help avoid many health problems, one of which is bleeding between periods.
What kind of prevention
Prevention of intermenstrual discharge includes timely examination by a gynecologist, good nutrition, moderate physical activity, adherence to work and rest, and protection from infectious diseases.
Every healthy woman has experienced intermenstrual bleeding. In most cases, during reproductive age they are a natural physiological process. If this problem occurs in adolescence or in women over 45-50 years old, you should consult a specialist. This will help avoid the development of infertility, pathologies of the genital organs and malignant neoplasms.
Already from the first menstruation, the following are important:
- daily regime;
- proper nutrition;
- adequate rest;
- physical activity;
- protection against STIs;
- strengthening the immune system.
https://youtu.be/zvRurunAelY
For patients of reproductive age, doctors additionally advise the following:
- regular sex life;
- correct contraception;
- no abortions.
Women who have given birth to more than one child are less susceptible to developing fibroids and endometriosis. And with regular use of oral contraceptives, the risk of developing uterine cancer is significantly reduced.
Tags: bleeding, middle, cycle
About the author: admin4ik
« Previous entry