The gallbladder acts as a container for bile in the body. If we talk about a disabled gallbladder, we mean an organ that is not working for some reason. Due to some reasons, bile stops accumulating in it and is discharged into the intestines. This condition greatly harms human health, but also becomes life-threatening, since the place of bile is taken by purulent masses. To avoid this, you need to know the primary symptoms and consult a doctor in time for help.
What is a “disabled gallbladder”?
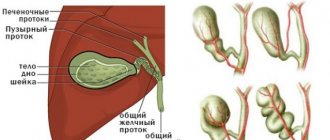
The question of the concept of “disabled gallbladder” was initially raised by radiology specialists. During their examinations, they discovered that when a contrast agent was introduced, which should give a reaction with bile, it was not recognized. Thus, the gallbladder itself was not detected. From this, experts concluded that with such indicators there is a non-functioning organ.
In other words, the gallbladder does not work when bile does not enter it or, conversely, is not released from it. Therefore, it makes its way, bypassing the disconnected organ into the duodenum along the common duct.
Diet
The most important component of the treatment of any disease of the digestive system is diet. A diagnosis such as a disabled gallbladder requires patients to follow a strict diet. Anything that causes a sharp release of bile is prohibited: fried, fatty, hot, spicy, salty, alcohol and anything that causes gas formation (foods that should have been excluded before the ultrasound).
For the first time after surgery, you can eat only foods that are easily digestible: pureed soups in vegetable broths, vegetable purees, viscous porridges, vegetables and fruits - at first only in baked form, compotes and jelly, fresh (non-acidic) fermented milk products. You need to eat food 6-7 times a day, in portions of no more than 300 g.
A disabled gallbladder is a serious complication of almost all diseases of the biliary tract. Modern medicine successfully deals with it, and whenever possible, doctors preserve the diseased organ if it is able to function after treatment. But in case of such a disconnection, it is extremely important not to delay contacting a doctor.
Nutritional adjustments are prescribed for any type of treatment: for surgical treatment - immediately after the operation, for medication - from the moment you start taking medications. Its main principles are:
- eat 4-5 times a day in small portions (200-300 g at a time);
- Dishes are allowed boiled, stewed, baked, fried is prohibited;
- animal fats are limited;
- Only low-fat varieties of meat and fish are allowed;
- for the first time after surgery or during drug treatment, all food should be of liquid or semi-liquid consistency;
- The amount of salt and sugar consumed is limited.
Until the acute stage of cholelithiasis has passed, the diet should include cereals cooked in water, vegetables, fruits, some lean meat and fish. Anything spicy, salty, smoked, sweet, or floury is prohibited. You can drink only freshly squeezed juices and compotes from rose hips and dried fruits. Even after recovery, the attending physician gives lifelong nutritional recommendations.
A disabled gallbladder is a serious pathology that, if not properly treated, can become life-threatening. If you suspect a disease, you should immediately go to the hospital. More often, surgical intervention is required, but with timely treatment you can manage with medication and diet.
A diet for disconnection syndrome, as well as eating without a gallbladder after its removal, is an important component of complex treatment.
The patient's diet should exclude:
- Salo.
- Beef and lamb fat.
- Mayonnaise.
- Fatty fish.
- Fried foods.
- Spicy food.
Following a diet allows you to speed up the process of recovery of the body after surgery and avoid the development of complications.
If the first signs of the disease are detected, you need to contact a doctor who will prescribe a course of treatment, regardless of the stage of the pathology.
It is worth considering that in the presence of this pathology, it is necessary to undergo surgical intervention associated with the removal of the gallbladder organ. The procedure is called cholecystectomy.
Proper surgical intervention is presented in several types: laparoscopy or abdominal surgery.
It is carried out in the form of several incisions, the punctures are miniature, and therefore this type of surgical intervention is tolerated quite well by patients with gallbladder diseases.
Doctors try to make every effort to preserve the organ, but this is not always possible, and therefore, if the gallbladder is not able to recover with the help of treatment, it poses a danger to humans.
In such cases, specialists decide to completely remove it. If the gallbladder is disabled, what to do and what course of treatment to choose should be decided exclusively by an experienced doctor, who is based on the results of the diagnosis of the patient’s body.
It may be that for the purpose of recovery and treatment, therapeutic or medicinal treatment is prescribed, and retrograde cholangiopancretography is performed.
The doctor, first of all, prescribes medications that should help the body strengthen its immune system. These are drugs that have a tonic effect.
Also included here are products with a choleretic effect. Thanks to them, it is possible to remove signs of inflammation, spasms and pain, and improve the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
If the duct is blocked by a stone, the doctor will prescribe a remedy to dissolve the formation.
But when the gallbladder is disabled due to the lack of tone in the muscle layer of tissue, you need to use medications and a special diet.
All methods of treatment, including alternative medicine or recipes for natural infusions, healing decoctions, are best discussed with the treating specialist; self-medication can have a detrimental effect on the patient’s subsequent condition.
Health is no joke, as WHO statistics once again prove.
Therapy for this condition includes several techniques, namely:
- drug treatment;
- use of alternative medicine recipes;
- diet therapy;
- removal of stones using ultrasonic waves;
- surgical intervention associated with organ removal.
Among the medications used for this condition, the following groups can be distinguished:
- drugs from the group of enzymes that improve the digestive process (Creon, Mezim);
- medications that have an antispasmodic effect (No-shpa);
- agents with choleretic effects (Allohol, Cholagol, Cholenzym);
- medications that have a beneficial effect on the autonomic nervous system (Novopassit);
- herbal preparations (ginseng tincture).
In addition, there are a number of drugs whose main function is to dissolve existing stones. However, you should be extremely careful with them, since they do not help with all types. These drugs do not dissolve certain stones.
Tubages with mineral water also have a good effect. But before starting this procedure, you need to make sure that the person does not have gallstones. Otherwise, instead of relieving the condition, tubing will lead to even more severe blockage of the duct lumen with a calculus.
Surgical treatment
Nowadays, laparoscopic-type operations are very common, in which the intervention is carried out through two or three punctures of the abdominal wall without wide abdominal incisions. If dysfunction of the bladder has developed due to the accumulation of stones in it, then there are methods for removing them - either using mechanical action or ultrasonic waves.
When eating when the gallbladder is disabled, you must adhere to table No. 5. This will significantly improve the patient’s condition not only during an exacerbation, but also during the rehabilitation period after surgery.
Since a disabled gallbladder is, as a rule, a consequence of other common diagnoses associated with this organ, therefore, the prevention that needs to be carried out to prevent gallbladder dysfunction is the same as the prevention of other gallbladder diseases.
Firstly, nutrition must be balanced and proper. You shouldn’t get too carried away with unhealthy foods such as fatty, smoked, very salty and very sweet.
The diet should include porridge in water, soups in low-fat broth, meat and fish cooked with steamed vegetables, stewed in water (without oil) or in broth. Among the foods consumed, it is necessary to give priority to lean meat and fish, vegetables, and fruits.
Secondly, measures to prevent a disabled bladder include giving up bad habits, especially excessive consumption of alcohol-containing drinks.
Moderate activity such as walking and light exercise will be useful not only for the prevention of gallbladder diseases, but also for the body in general. And some doctors also say: in order to avoid diseases of the gallbladder, liver and other internal organs, it is very useful from time to time to arrange fasting days for yourself and cleanse the body of toxins.
If, nevertheless, a gallbladder disease has already been diagnosed, the patient is shown a special diet for a diseased gallbladder. In this case, the same nutritional principles described above apply.
Just before eating, food should also be pureed to a puree state, and you should eat in very small portions, increasing the number of meals during the day. You also need to drink more liquid: this can be ordinary purified water, alkaline mineral water, as well as vegetable juices, which help liquefy and remove bile.
And you should not neglect folk remedies that dilute, remove bile and maintain the functions of the gallbladder in a normal, efficient state.
Nutritional therapy is always recommended in combination with other means and methods against this disease. The diet has the following features:
- Eat often, in small portions (up to 300 g).
- Do not fry dishes, but boil, stew, steam.
- Consume more plant foods, less animal fats.
- Do not forget about choleretic products, especially vegetable and fruit juices.
- Season vegetables with vegetable oil to stimulate bile drainage.
- Eat more foods with vitamin C.
- In the acute phase of the disease, eat only liquid, semi-liquid food, and pureed foods.
- Reduce the amount of salt and sugar in your diet.
- Drink at least 3 liters of fluid per day.
Causes of pathology
The main cause of the pathology is cholelithiasis. There are several mechanisms for its development:
- Complete filling of the bladder cavity with stones. This situation occurs after a long course of the disease. The organ cannot contract because its walls are greatly stretched.
- Obstruction of the bile duct. A blockage can occur due to a stone lodged in the duct. But in some cases this happens due to the blocking of the lumen of the bile duct with thick bile. Additionally, this is facilitated by the inflammatory process in the neck of the gallbladder.
- Organ calcification. This pathology is characterized by the deposition of calcium on the walls of the gallbladder. This statement is also known medically as the “porcelain gallbladder.” In this case, the risk is mainly not that the organ stops functioning, but that it is more susceptible to cancer pathologies.
- Sclerosis of the gallbladder can be expressed in deformation of the walls of the organ. In this case, it is a wrinkled lump adjacent to the liver.
- Cessation of the ability to contract due to the fact that its muscle structure has been replaced by scar tissue.
- Cholesterosis, which occurred due to the regular deposition of cholesterol on the walls of the bladder.
Complete filling of the bladder cavity with stones is a possible cause of gallbladder disconnection.
A disconnected gallbladder is most often found in pathologies such as biliary dyskinesia, chronic cholecystitis. In this case, the pathological process is irreversible, and the gallbladder becomes an absolutely useless organ, since its ability to receive and release bile is lost.
Sometimes his work can be restored. This applies to cases where the bile duct was blocked by a stone. If he moves it into the gallbladder or into the intestines, the passage for bile is cleared.
How to recognize?
A disabled gallbladder is a serious complication of gallstone disease. Symptoms of cholelithiasis are as follows: pain in the right hypochondrium, flatulence, heartburn, unpleasant taste in the mouth, indigestion. If the stone moves and blocks the duct, then pronounced symptoms of hepatic colic appear: severe pain, vomiting, fever.
If the gallbladder becomes inflamed and bulges, then it may be perforated, then purulent contents will enter the abdominal cavity and if medical assistance is not provided to the patient in time, peritonitis will begin. In this case, you need to urgently undergo surgery.
Another serious complication of cholelithiasis can be obstructive jaundice. If the outflow of bile is disrupted, it can enter the blood. The patient's skin turns yellow, itching appears, the temperature rises, the stool becomes light-colored, and the urine becomes the color of beer. These symptoms cannot be ignored; this condition requires emergency hospitalization.
In some cases, symptoms may not be pronounced. A person may not realize that his gallbladder is not functioning.
Symptoms of the disease
With pathology, the following symptoms are noted:
- heartburn;
- increased gas formation;
- feeling of bloating;
- painful sensation in the right side in the hypochondrium;
- dispersion disorders in the digestive processes;
- feeling of bitterness in the mouth.
In some cases, patients complain of constant itching of the skin. At the same time, the color of the stool changes: urine becomes darker and has a brown tint, feces, on the contrary, become discolored. These signs should concern the patient, as this means that the liver is involved in the pathological process and the body is intoxicated.
If the disease becomes acute, there is a danger of perforation of the gallbladder walls by a moving stone. In addition, the danger lies in the fall of purulent contents into the abdominal cavity, as a result of which peritonitis is possible. This situation requires immediate medical intervention and emergency surgery.
Consequences and prevention
If therapy is not carried out, organ dysfunction leads to inflammation, the formation of pus and its spread into the abdominal cavity - peritonitis. Large stones can cause the bladder to burst. This condition is life-threatening.
If removal has been performed, you must follow a diet, eat often and in small portions. In the absence of a storage organ, bile is constantly present in the intestines in small quantities. During fasting, it irritates the intestinal walls, and when eating difficult-to-digest foods, it becomes insufficient.
To prevent gallbladder diseases, it is recommended to follow a diet that excludes alcohol and heavy foods. If the outflow of bile is difficult, take choleretic drugs (magnesia, sorbitol, plant extracts - immortelle, rose hips, barberry) provided that there are no stones in the bladder.
Diagnosis of the disease
Initially, when contacting a specialist, he conducts an anamnesis and an external examination. In addition, he refers for ultrasound examination and x-rays. X-rays require the introduction of a special contrast agent, which will not be visible during the examination if the gallbladder is disconnected.
However, the survey data is not 100% accurate. The results shown may be unreliable as a result of various technical errors, incorrect examination, or other diseases (stomach, liver, intestines).
If this disease is suspected, the patient is referred for an ultrasound. Thanks to this study, it is possible to detect stones in the organ, the degree of blockage of flows, and identify possible changes that lead to cancer.
In a pathological condition, a shadow will be observed behind the lower liver on ultrasound images. If there is even a small amount of bile in the bladder, the image will reveal anechoic zones that look like a double arch.
Ultrasound is a method for diagnosing gallbladder shutdown
If the bubble has adhesions or a wrinkled structure, then its cavity will not be detected on ultrasound. The specialist conducting the examination notes the uneven enlargement of the walls and the irregular shape of the boundaries. If the organ works, but intermittently, then its contents can be recorded. It may contain bile, pus or stones.
Preventive actions
It is not difficult to avoid the formation of stones, gallbladder shutdown, cholecystitis and other ailments. To do this you need:
- Healthy food;
- to refuse from bad habits;
- avoid intense physical activity;
- lead a calm lifestyle;
- maintain the required level of physical activity;
- periodically arrange fasting days to completely cleanse the gallbladder and other digestive organs of toxins and accumulations.
For a preventive examination, it is necessary to visit a general practitioner, hepatologist and gastroenterologist 1–2 times a year. This will help keep the gallbladder, liver and other important organs in perfect order.
Treatment options
If after diagnostic examinations the diagnosis is confirmed, the attending physician decides to prescribe a further treatment plan. First of all, it depends on the reasons that caused this pathology.
There are basically 2 types of therapy used for a disabled gallbladder:
- medicinal;
- surgical intervention.
Drug treatments
If the original cause of the disease is impaired motility of the bile ducts, then the following medications are used:
- drugs that improve the functioning of the digestive system on an enzymatic basis - Festal, Pancreatin, Mezim and others;
- choleretics (Allohol, Holagol, etc.);
- antispasmodics (No-shpa, Spazgan, etc.);
- tonic preparations (tincture of Eleutherococcus, ginseng, etc.).
For pathologies associated with bile stagnation, the following treatment regimen can be used. In the morning, a choleretic agent (magnesium sulfate, xylitol) is taken on an empty stomach, after which a hot heating pad is applied to the right hypochondrium. The procedure can be carried out only after consultation with your doctor. The main contraindication to it is the presence of stones in the bladder, since in this case they can move and block the duct, which will require urgent medical attention.
Surgery
In some cases, when a disabled gallbladder is detected, the attending physician decides to perform surgical intervention.
The gallbladder is removed if multiple stones, sclerotic phenomena, acute inflammatory processes and accumulation of purulent masses in the organ cavity are found in it.
Indications for the operation include:
- gangrene of the gallbladder, that is, tissue death (necrosis);
- large stones, more than 15 mm;
- the threat of complete blockage of the gallbladder or intestinal ducts with stones;
- complete failure to fulfill one’s functions – dysfunction;
- the formation of polyps and their rapid growth in the organ cavity;
- cholesterosis – accumulation of large amounts of cholesterol on the walls of the bladder;
- cholecystitis is an inflammatory process of the organ.
There are several types of surgical intervention that help with this pathology:
- Cholecystectomy. Radical removal of the gallbladder.
- Cholecystolithotomy. It involves removing deposits from the organ, while using a minimally invasive type of penetration into the cavity and preserving the gallbladder.
- Lithotripsy. Crushing stones using laser or ultrasound with further elimination of fragments.
- Contact type litholysis. Dissolution of stones using special acids that are injected directly into the gallbladder.
The most common procedure is complete removal of the gallbladder – cholecystectomy.
In this case, cholecystectomy and cholecystolithotomy can be performed laparoscopically or through an incision. The first method is preferable, since all manipulations pass through a puncture and the tightness of the body cavity is not broken.
Surgery is a method of treating a disabled gallbladder
Lithotripsy is used in cases where the stones are small, up to 20 mm. The doctor makes sure in advance that the functionality of the bladder, the patency of the biliary tract, and the ability to contract are preserved.
Contact lipolysis is used quite rarely, in particular when it is impossible to use other treatment methods or when they are ineffective. It is most often used in Western countries. In Russia, there are isolated cases of successfully performed procedures.
Reasons for gallbladder shutdown
In order to help such a patient and prevent the negative consequences of the disease, it is necessary to understand the causes of such severe gallbladder pathology. As a rule, patients suffer from the following deviations, which lead to the blocking of the bladder:
- cholelithiasis with an active process of stone formation;
- abnormal contractile activity of the biliary tract - dyskinesia;
- chronic inflammation of the gallbladder - cholecystitis;
- blockage of the main bile duct - common bile duct;
- adhesive process in the walls of the organ;
- deposition of salts on the walls of the gallbladder with their infiltration of all layers - porcelain;
- scarring of the bladder walls due to the adhesive process.
All these reasons can be present either individually or in combination. This depends on how prone the patient is to certain processes in the body: the formation of scars, stones, precipitation of salts. Lifestyle and diet in the presence of liver problems play a huge role in the development of these processes.
Diseases of the biliary tract and the bladder itself are typical for middle-aged and older people, since one of the determining factors for the development of pathology of the liver and nearby organs is lifestyle and diet.
The symptoms of disconnection depend on the cause that caused the disconnection and on the characteristics of the pathological process that occurs in this area. A disabled gallbladder manifests itself in the same way as cholecystitis:
- Pain in the right hypochondrium (hepatic colic).
- Flatulence, belching, bloating.
- Heartburn and reflux of bile into the stomach, esophagus and oral cavity.
- Vomiting.
- Sometimes - an increase in temperature.
- Sometimes - jaundice (yellowing of the sclera and skin, itching, darkening of urine and lightening of stool).
Disconnection can manifest itself simply as unpleasant sensations on the right side, or indigestion in the intestines.
Nuances of a therapeutic diet for pathology
The diet for a disabled gallbladder corresponds to the nutritional rules for pathologies of this organ.
- Meals should be frequent (at least 4-5 times a day) and in small portions.
- Regularity is no less important. It is best to eat on a schedule, that is, at the same time, with equal intervals between meals. This way, bile will be produced in a timely manner, in the right quantity, and the likelihood of stagnation will be reduced. The intervals between meals should not exceed 7-8 hours.
- The temperature of the food should not be too cold or, on the contrary, hot, as this can cause spasm of the gallbladder ducts.
- It is prohibited to consume foods that burden the gastrointestinal tract.
- Products that provoke increased bile formation are also prohibited.
- Monitor the total caloric content of food. You need to eat the number of calories per day that help ensure normal functioning. Overeating leads to deterioration in the performance of internal organs due to the accumulation of fat mass.
Symptoms
If a disabled gallbladder is diagnosed, the symptoms in the initial stage will be weak and insignificant. Only over time does a person complain of the following phenomena:
- metallic taste in the mouth;
- pain in the hypochondrium on the right (pulling nature);
- flatulence;
- changes in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract;
- bloating;
- hepatic colic when moving stones;
- heartburn.
If the stones move, this process brings a lot of discomfort. The person feels terrible pain, his temperature rises and he begins to vomit.
In the absence of timely assistance, the neglected organ releases pus into the peritoneum. The patient develops peritonitis. Without treatment in a medical institution, it will not be possible to surgically save the patient’s life.
Sometimes a person experiences yellowness of the skin, urine and feces. At the same time, the skin is itchy and the temperature rises. This indicates a disruption in the process of bile outflow when it enters the blood. The patient is diagnosed with obstructive jaundice, which is a complication of cholelithiasis.
Possible complications
With prolonged disruption of the functionality of the gallbladder, it leads to disturbances in the functioning of the biliary system. Due to the fact that bile does not enter the duodenum or does not enter in sufficient quantities, a disruption occurs in the process of digestion and extraction of nutritional components. Also, with prolonged inactivity, the inflammatory process of the pancreas can join the listed problems.
If there is a sudden disruption of the outflow of bile due to blockage of the duct with stones, it leads to acute cholecystitis, which is accompanied by colic.
Even in the complete absence of disturbing symptoms, a non-functioning organ carries a threat: tissue death and changes in structure occur, as a result of which malignant neoplasms may appear.
Treatment and possibility of restoration of function
The fundamental principle for alleviating the patient’s condition is to find out the reason that led to this state of affairs. Restoration of the gallbladder is possible if the process of stone formation is still reversible, or their number is small and there is a possibility of normalizing the situation. For this condition, medications are prescribed that can dissolve existing stones and prevent the formation of new stones. This will improve the movement and formation of bile.
If it is not possible to restore stable functioning of the bladder, and it becomes a source of infection in the abdominal cavity, then a decision is usually made about surgery. Surgical treatment allows you to avoid complications from a non-functioning bladder clogged with stones: gangrene, pancreatitis, peritonitis, hepatitis.
A prerequisite for improving health is proper nutrition. This is a separate diet for diseases of the liver and bile ducts. In addition to following the principles of proper nutrition, it is necessary to take antispasmodics - drugs that relieve spasm of the ducts. In complex treatment, agents that stimulate the motility of the biliary tract are necessary.
Etiological factors in the development of the process
There are many reasons that lead to organ shutdown, namely:
- lack of free space inside for the accumulation of bile;
- the entrance to the organ cavity is closed;
- the gallbladder does not have the ability to adequately change its volume.
The lack of free space in the cavity of an organ can be caused by factors such as its complete filling with stones, damage to the wall, as well as neoplasms of malignant or benign origin localized inside the organ. As a result of these reasons, the organ cannot work as usual. The entrance directly to the bladder can be blocked in two places - at the mouth or at the level of the duct. The reason for the closure of the lumen of the duct is a stone, deformation in the form of an inflection, or an area of scar tissue.
The organ may lose its contractility due to the replacement of a section of the wall with connective tissue. In addition, a large number of lipid plaques on the surface of the wall can lead to contraction disorders. Their basis is cholesterol. With biliary dyskinesia of the hypotonic type, problems also arise with contraction; the bladder cannot adequately perform its functions.
Diagnostic procedures
The first stage of diagnosis is a thorough interview of the patient and his general examination. After this, a qualified specialist can make a preliminary diagnosis and refer the patient for additional diagnostic procedures - ultrasound examination and cholecystography.
An ultrasound can determine the reasons for organ shutdown. This study visualizes very well stones in the cavity of the organ and its various deformations. In difficult to diagnose cases, an MRI may be required.
Important! After discovering the cause that led to the development of the pathology and making a final diagnosis, the question of choosing one or another treatment method is decided. Experts also determine whether surgery is needed or whether at this stage we can limit ourselves to conservative methods of therapy.