How does the gallbladder hurt - symptoms in women
Gallbladder diseases occur more often in women. This is facilitated by the peculiarities of the hormonal system, childbirth, taking contraceptives, antibiotics, weight fluctuations and adherence to strict diets with a sharp restriction of fats. But despite the high prevalence of symptoms of gallbladder diseases, many women do not know how gall bladder hurts or simply stubbornly ignore the first signs of disorders.
Pain syndrome may be associated with nutrition. The gallbladder contracts and releases bile when certain foods, mainly those containing fat, are consumed. And you can’t refuse them at all. This often leads to thickening of bile and the formation of stones, inflammation of the mucous walls of the organ.
Women are very emotional and sensitive. You've probably noticed how your gall bladder starts to hurt, especially if you have cholecystitis and cholelithiasis, if you get nervous. Palpable spasms immediately appear. When under stress, stones can even move, creating the risk of blocking the ducts.
Main symptoms
The main symptoms for pain in the gallbladder:
- nausea, which often occurs after eating fatty and fried foods;
- abdominal pain combined with flatulence;
- dull and bursting, sometimes burning pain under the right rib, radiating to the stomach, collarbone and shoulder;
- decreased appetite;
- yellowing of the skin;
- stool disorders.
Where does the gallbladder hurt?
The localization of pain varies. The pain may be on the right side under the ribs, it seems that the problem is in the stomach or intestines. The pain can also spread to the back, to the area behind the right collarbone, under the shoulder blade, and radiate to the lower back. Many simply do not know whether the gallbladder can hurt in such a way that the discomfort spreads to nearby organs.
Sometimes even experts themselves mistake the symptoms of one pathology for non-existent disorders. Therefore, you should trust only experienced doctors and diagnostic results.
What to do (first aid) when medical intervention is necessary
If the pain syndrome is not very pronounced, then the first step is to take a horizontal position on the right side and place a heating pad under it.
It is better to wrap it in cloth to avoid burns. These measures will ensure relief of tone and improve the flow of bile, which will significantly alleviate the patient’s condition. https://youtu.be/7Ra1fKgzzfE
If the pain is unbearable, you will need to use medications. These are analgesics and antispasmodics that are prescribed by a doctor.
Urgent medical intervention is required under the following circumstances:
- nagging intestinal pain;
- stabbing pain in the stomach radiating to the forearm;
- stabbing pain in the navel with a sharp rise in body temperature, icteric mucous membranes, nausea and vomiting;
- with intestinal bleeding;
- severe pain in the liver area with dizziness, rapid pulse and profuse sweating.
In the absence of timely assistance, complications may develop. These include:
- biliary fistulas;
- purulent-inflammatory processes on the walls of the bladder;
- infection of the bladder contents;
- bile stagnation;
- subhepatic abscesses.
How does the gallbladder hurt - symptoms in men
In men, the symptoms of gallbladder disease are not much different from those in women. But it is not stress that worsens well-being, but rather overeating and drinking strong alcoholic beverages. Smoking also often causes painful cramps.
Men can mistake gall pain for symptoms of gastritis or intestinal diseases, especially with diffuse pain syndrome. But with pathologies of the hepatobiliary system, exacerbations are usually closely associated with a gross violation of the diet. It is difficult for men to comply with dietary restrictions, so abuse of alcohol and fatty foods causes deterioration in well-being.
But if, at the first symptoms, you consult a doctor and follow a diet, then a man’s gallstones begin to hurt less, and the symptoms of other gastrointestinal diseases also gradually subside.
https://youtu.be/eLiCHNIJL1s
Small but very important
There are no unimportant organs in the human body. But still, their role in ensuring the viability of the organism as a whole differs quite greatly. Thus, the liver is one of the vital organs, without which life is completely impossible. The gallbladder is considered an independent organ, but it is extremely closely connected with it. But from an anatomical point of view, it is still part of the liver.
The shape of the gallbladder resembles an elongated pear (or avocado). Its dimensions are small and can vary quite widely. So, its length can be from 8 to 14 centimeters, and its width from 3 to 5 centimeters. Accordingly, the volume can be from 40 to 60 milliliters.
Unlike the liver, which has a characteristic brown color, the color of the gallbladder is greenish, and it is clearly visible against the background of surrounding organs.
The gallbladder is located approximately 3 centimeters below the costal arch. It is in close contact with the lower part of the liver and the wall of the peritoneum. The part of the bladder that is adjacent to the liver is connected to the connective tissue that envelops the entire liver. To make it more convenient for the gallbladder, there is a special pit in the liver, which has the Latin name fossa vesicae felleae.
In rare cases, the liver may be lower than it should be. Then the gallbladder is in close proximity to the intestinal loops.
As you might guess, the main purpose of the gallbladder is to accumulate bile and release it into the intestines when there is a need to digest food. If the gastrointestinal tract works without failures, then there should be no bile in the empty intestines.
In just one day, the liver synthesizes almost 2 liters of bile, and the volume of the bladder is only 50 milliliters.
As soon as a portion of food from the stomach enters the desired section of the intestine, a signal is sent through special nerves to the gallbladder, which causes the release of its contents first into the small duct and then into the duodenum. Fatty foods cause particularly active bile movement.
The walls of the bladder have many special folds that help the movement of liquid. In addition, due to its special structure, the bladder is able to make stored bile more concentrated. Therefore, it is called “mature” or “vesical” bile, while the bile directly secreted by the liver is called “young” or “hepatic”. It also enters the duodenum during the digestion process. This mixture of different biles provides the best conditions for processing food and preparing it for absorption in the appropriate parts of the intestine.
Causes of pain in the gallbladder
Only a doctor can say exactly why the gallbladder hurts. But a specialist makes a diagnosis based on ultrasound or MRI data and blood tests. Most often, pain is associated with an inflammatory process, injuries to the mucous membrane from stones, the proliferation of infectious pathogens against the background of stagnation of bile or internal damage.
The main diseases that cause pain in the gallbladder:
- cholecystitis;
- biliary dyskinesia;
- cholelithiasis;
- cholangitis;
- gallbladder tumors.
The basis of most gallbladder diseases is bile stagnation. It provokes the formation of stones, inflammation, and the proliferation of bacteria. But it is important not to forget about the connection of the gallstone with the liver, pancreas and intestines. When one organ malfunctions, a cascade of associated disorders and complications usually appears. Therefore, it is so important to consult a doctor on time and adjust your diet.
Chronic and acute cholecystitis
With cholecystitis, the mucous membrane becomes inflamed, and pain in the gall bladder can be periodic or constant. During an exacerbation, the discomfort increases sharply. Gallbladder pain and other symptoms can appear not only due to poor diet and consumption of fatty foods and alcohol, but also due to stress.
Psycho-emotional stress and nervous experiences often contribute to the exacerbation of chronic gastrointestinal pathologies. During times of stress, most people experience painful spasms in the gallbladder area and their overall health noticeably worsens.
The main symptoms of acute and chronic cholecystitis:
- paroxysmal pain in the right side of the abdomen, which can radiate to the collarbone, shoulder or shoulder blade;
- sweating and physical weakness;
- nausea and vomiting, which most often contains bile impurities;
- flatulence;
- bitterness in the mouth.
Cholecystitis is closely associated with diseases such as biliary dyskinesia and cholelithiasis. Inflammation in the gallbladder is mainly caused by stones. The non-calculous form of cholecystitis is much less common.
Cholelithiasis
The pain caused by gallstones is dull, but almost constant. Acute pain syndrome occurs with biliary colic, when the stone moves and causes blockage of the duct. It is often necessary to urgently seek medical help in this condition.
Gallstone disease is quite dangerous, and if there are stones, you need to get rid of them. It is not always possible to save an organ, and it does not make sense. A gallstone filled with stones cannot perform its functions. In addition, the disease causes pathological changes in both the pancreas and intestines.
Main symptoms of gallstones:
- pain in the right hypochondrium;
- nausea;
- vomit;
- heaviness in the abdomen, increasing after eating;
- increasing weakness;
- yellowing of the skin;
- unstable chair.
During the period of remission, gallstone disease is practically not a concern. Many people live for years with stones and do not know what gallstone pain is and where it is located. But this does not always happen and not for everyone. If a doctor recommends removing an organ, you should study the topic yourself and listen to the opinion of a specialist.
Biliary dyskinesia
Biliary dyskinesia refers to functional disorders of the biliary system. The disease is based on deterioration of motility and bile drainage. Dyskinesia can develop in a hypokinetic or hyperkinetic type.
The main symptoms of gallbladder and duct dysfunction:
- stabbing pain in the right hypochondrium, which radiates to the shoulder blade and shoulder and occurs after physical overload, stress or a diet disorder;
- nausea and vomiting;
- stool disorders.
Dyskinesia is chronic. Many people do not consult a doctor and cope with pain in the gallbladder on their own with the help of antispasmodics. But it is necessary to turn to professionals in order to exclude the development of potentially dangerous diseases and begin treatment on time.
Cholangitis
With cholangitis, the bile ducts become inflamed. The disease is accompanied by pain in the right hypochondrium, nausea, yellowing of the skin. Women get sick more often than men. Cholangitis mainly occurs against the background of cholelithiasis or pancreatitis. With these diseases, various pathogens enter the ducts, causing an inflammatory process.
Tumors
Various neoplasms of the gallbladder and nearby organs can compress the tissues, causing disruption of the outflow of bile and causing acute and chronic pain. A tumor can be detected using ultrasound diagnostics and magnetic resonance imaging.
Some neoplasms of the gallbladder and other organs of the digestive tract are prone to malignancy. Therefore, if pain occurs, it is better to immediately undergo a comprehensive examination and seek help from specialists.
Diagnostics
Problems with the gallbladder require mandatory consultation with a specialist (gastroenterologist, surgeon, oncologist).
To find out the cause of the disease, doctors interview the patient, examine him and prescribe tests. These include:
- Complete blood test for the presence of leukocytosis and accelerated ESR. These signs indicate that there is an inflammatory process in the body.
- Fibrogastroduodenoscopy. This method allows you to identify the infectious pathogen, as well as examine the composition of bile. If necessary, perform a test to determine sensitivity to antibacterial drugs.
- Cholecystography.
- Ultrasound. Thanks to this study, it is possible to determine deformation changes in the walls of the bubble and their thickness. It allows you to determine impaired organ motility, dilated bile ducts, the presence of adhesions or polyps.
- Holegraphy.
- Radiography. Allows you to evaluate the size and deformation of the organ.
- Diagnostic laparoscopy with bacteriological examination.
- Magnetic resonance imaging, computed tomography. Pathological changes can be detected even with small inclusions.
Pain after gallbladder removal
Many people are familiar with pain after gallbladder removal. They are a consequence of the restructuring of the entire digestive system. After all, now there is no gallstone, where bile accumulated and was stored.
After surgery, the body is rebuilt within 6-12 months. Bile is no longer stored, but flows directly into the duodenum in a less concentrated form. Not only dull pain may occur, but also flatulence due to changes in intestinal microflora. The stool is also often loose, especially in the first months.
If pain in the gallbladder intensifies after surgery, you should immediately consult a doctor. After cholecystectomy, stones can become stuck in the ducts, causing inflammation.
To prevent the onset of pain, be sure to follow diet No. 5. It involves excluding animal fats and fried foods, and alcohol. But the diet must be complete. Strict prohibitions apply only in the first months after surgery.
In this video, experts describe how the gallbladder hurts with cholecystitis and what kind of disease it is and why it is dangerous to health.
https://youtu.be/u9vBEVbaNo0
Treatment
The gallbladder is treated with pharmaceutical and surgical methods, depending on how advanced the condition is. Also, not all pathologies can be treated with medications.
Drug therapy
The selection of pharmaceutical drugs depends on the causes that led to the disease. For cholecystitis, as well as acute cholangitis, therapy primarily includes anti-inflammatory and painkillers.
Comprehensive treatment includes:
- broad spectrum antibiotics. For example, Cefotaxime, Cefazolin;
- choleretic drugs (Digestal);
- painkillers (Mebeverdine, Duspatalin), for intolerable pain, narcotic analgesics are used;
- Digestive aids. Such as Festal and others.
For cholelithiasis the following is prescribed:
- medicines for the outflow of bile (Choludexan);
- antibacterial drugs (Fortum);
- To relieve pain, Nalbufin or Ketanov are recommended.
If dyskinesia is diagnosed, it is important to normalize the motor function of the bladder and ducts. This is facilitated by cholekinetics. For example, Holosas. As well as medicinal mineral water.
Attention! Above is an approximate set of drugs. Only the attending physician should prescribe medications!
In case of hepatic colic, you should urgently call a doctor. Before his visit, ensure peace, completely refuse food and drink. To relieve severe pain, you can take a No-shpa tablet.
Surgical intervention
Surgical removal of the gallbladder is called cholecystectomy. It is carried out if there is a threat to life. Indications for surgery:
- stones in the organ and ducts cannot be eliminated with the help of medications;
- the gallbladder does not function;
- acute inflammation with destruction of the walls of the gallbladder.
The organ is removed in two ways. Abdominal surgery or laparoscopy is performed. The latter method has a number of advantages. It gives fewer complications and shortens the recovery period.
When the gallbladder is partially functioning, retrograde cholangiopancreatography is prescribed. Using an endoscope, stones are pushed from the duct into the bladder and broken down with pharmaceutical agents. The following complications are possible after surgery:
- bleeding;
- inflammation of the bile ducts (cholangitis);
- pancreatitis;
- damage to the gallbladder wall;
- infection.
The above complications are quite rare. They depend on the disease that led to the operation and general health. Usually, after surgical manipulation, the patient is discharged home within a couple of days.
The recovery period for laparoscopy takes several more days. After abdominal surgery it takes a little longer. In the treatment of gallbladder diseases, diet plays a decisive role.
The diet depends on the stage of the disease. During exacerbations, only liquid food is allowed: weak tea without sugar, pureed vegetable soups.
After the attack has passed, or in case of chronic forms of illness, the following products are allowed:
- berry and fruit juices diluted with water;
- liquid porridges (oatmeal, rice, semolina);
- rabbit meat;
- fermented milk products (no more than 15% fat content);
- lean soups;
- beef;
- chicken and turkey;
- still mineral water;
- low-fat fish;
- white bread croutons.
All food should be steamed or boiled. Fried foods are prohibited.
In addition, the following should be excluded from the diet:
- pork;
- radish;
- sauces (ketchup, mayonnaise, etc.);
- onion;
- canned food;
- smoked meats;
- garlic;
- mushrooms;
- baked goods;
- caviar;
- ice cream;
- pickles;
- fruits;
- greenery;
- fats;
- spices and herbs;
- soda.
Attention! You need to eat in small portions: about six times a day in small portions. It is advisable to eat at the same time. You can alleviate the condition at the beginning of an attack before visiting a doctor at home.
Folk remedies
Therapy is prescribed taking into account the disease and the changes that have occurred in the gallbladder.
But in any case it is necessary:
- Dieting. You need to exclude fatty meats (pork, lamb), rich broths, smoked foods, fried and spicy foods from your diet. It is better to give preference to turkey, chicken and fish, dairy products, fruits and vegetables. Meals should be frequent - about 5-6 times a day, and the amount of food eaten at one time should be very small.
- You should avoid sweets and flour products.
- Avoid eating hot peppers, onions and vegetables.
- It is important to drink plenty of water for better flow of bile.
To improve the functioning of the digestive system, you need to take enzymes (Pancreatin, Mezim Forte, Penzital, Creon).
Special medications are also prescribed to stimulate bile formation and promote its active secretion.
What to do if you have pain in the gallbladder
Gallstone pain is usually sudden. Often people do not even know that they have stones in the bladder; the doctor accidentally finds them during an ultrasound. What to do and how to treat it?
Which doctor should I contact?
The first thing to do when your gallbladder hurts is to contact a hepatologist or therapist. The doctor will order an examination. This usually includes blood tests, ultrasound of the gallbladder and liver. According to indications, an MRI examination is prescribed.
Drugs and diet
Treatment usually depends on the diagnosis and includes the following procedures and methods:
- compliance with diet No. 5;
- taking medications that relieve inflammation and destroy infectious pathogens;
- prescribing drugs that normalize bile removal and synthesis;
- pain relief, spasm relief.
You should not go to extremes and choose only one treatment method. An integrated approach is the most effective. Diet is the main way to get rid of constant pain. If your gallbladder hurts and there are no serious diseases that require surgery, then first of all pay attention to your diet.
Anatomy and location of the organ
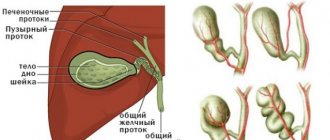
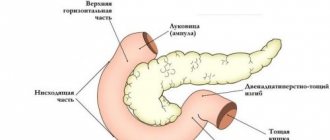
The gallbladder is shaped like a pear and is located on the visceral surface of the liver in a special depression that separates the two lobes of the liver. In the anatomy of the gallbladder, there are three sections: the bottom, the body, and the neck. The bottom of the organ is located near the lower edge of the liver, and the neck faces the gate of the gland and is located together with the ducts in the duplication of the hepatoduodenal ligament.
In the area where the body meets the neck, a bend is formed, so the neck lies at an angle to the body. Between the transition to the cystic duct there is a depression called Hartmann's pouch. The normal size of the gallbladder in adults is: length 8–14 cm, width 3–5 cm. The organ holds 60–100 ml of liver secretion. In children, normal organ sizes are in an even larger range.
So, in a child 2–5 years old, the gall bladder is 3–5.2 cm long and 1.4–2.3 cm wide, and in a teenager it is 3.8–8 cm long and 1.3–2.8 cm wide. If the organ is larger, then this indicates obstruction of the bile ducts or acute cholecystitis. A decrease in size occurs with viral hepatitis (liver inflammation) or chronic cholecystitis. The organ wall includes the mucous membrane, muscular, subserous and serous layers. The mucous tissue is sensitive to adverse events occurring in the body, which is why it looks swollen and flaky.
Bundles of muscle fibers are located in the longitudinal and circular directions. There are gaps between them, and then in these places the mucous tissue connects with the serous tissue. This structure of the gallbladder increases the risk of bile leaking into the abdominal cavity (peritonitis) without compromising the integrity of the organ. There is less muscle tissue in the bottom area, and more in the neck area.
The photo shows the location of the organ relative to the liver
The blood supply to the organ occurs through the cystic artery, which comes from the right branch of the hepatic artery and at the neck of the bladder divides into two branches, one of them goes to the upper surface of the bladder, and the other to the lower. Lymph nodes are located to the left of the bladder neck and near the duodenum. When the bladder becomes inflamed, the nodes enlarge and block the common bile duct.
The innervation of the biliary system comes from the celiac, inferior phrenic plexuses and the anterior trunk of the vagus nerve. This means that diseases of the stomach, small intestine or irritation of the vagus nerve (which happens with a diaphragmatic hernia) can provoke malfunction of the sphincter of Oddi and inflammatory disorders in the bladder itself, and vice versa.
Patients often ask which side the gallbladder is on. The gallbladder is located on the right side of the body, under the ribs. In front of the gallbladder is the liver, on the left side is the pylorus, and on the right are the loops of the small intestine.
The bottom of the bladder, as a rule, extends from under the lower edge of the liver closest to the peritoneum by 2–3 cm and touches the anterior abdominal wall. This arrangement of the gallbladder and its ducts gives a projection of pain to the right hypochondrium and epigastric region.
Diet for pain in the gallbladder
There are no fundamental differences in diet for different gallbladder diseases. It is recommended to avoid all fried foods. You can't even fry vegetables. It is better to stew or bake them. A multicooker with a double boiler function would be a good purchase. This device saves time and allows you to prepare truly healthy dishes, which you cannot do without if you have diseases of the gallbladder and other organs of the digestive tract.
Basic principles of nutrition for pain in the gallbladder:
- eat often, but in small portions, so that the bile constantly circulates and does not stagnate;
- give up alcoholic beverages, especially strong alcohol;
- do not consume aggressive animal fats, duck and goose meat, pork, it is better to give preference to domestic chicken, rabbit, turkey;
- Avoid overeating.
Follow your diet constantly. Additionally, follow your doctor's instructions. It is better to combine traditional methods of treatment with folk ones, but with a sense of proportion.
The nature of the pain and its localization
Gallbladder diseases occur without symptoms. The person feels well, but from time to time he is bothered by discomfort in the right hypochondrium.
As gall pathologies develop, the symptoms intensify and begin to bother you more often. In addition to pain, bitterness in the mouth, redness of the tongue, dyspepsia, and jaundice appear.
The disruption of the organ in question is caused by a temporary accumulation of a certain amount of bile. First it must go through the stage of concentration and then crystallization.
Basically, bile accumulates in the area of cholesterol, which is why stones are formed - one stone clot or a cluster of small tumors. When stones pass through the ducts, a person begins to experience severe pain attacks. They can last from 5 minutes to several hours.
The pain is sharp and cutting in nature in the acute form of the disease, pulling and aching in the chronic form. In medicine, attacks of pain are called colic.
Traditional methods
If your gallbladder hurts and other symptoms appear (nausea, vomiting), only a doctor can tell you how to treat specific diseases. Traditional methods are more suitable for preventing exacerbations and maintaining good health.
The safest remedies include oat infusion and decoction. It has a mild choleretic effect, but at the same time quite effectively prevents stagnation of bile and relieves constant dull pain in the area of the right hypochondrium. You can read more about it in the article The healing properties of oat decoction
You can drink a decoction of rose hips and chamomile. These products are safe even in the presence of stones. But if the gallstones are small and can get stuck in the ducts, it is better to conduct an ultrasound examination first.
You may be interested in the following topics: How to properly clean the gallbladder What is tubage and how to do it correctly Useful herbs for the liver and pancreas The best choleretic herbs and features of their use Why milk thistle oil is useful and how to take it
ZhKB
Gallstone disease is provoked by stagnation of bile and a malfunction in the metabolic processes occurring in the organ. More often, the disease affects women over 40 years old. Usually the disease is asymptomatic. It becomes very painful if the stone gets into the bile duct. Small stones can pass out of the body naturally with feces. If the stone is large, surgical removal is required.
The nature of the pain in cholelithiasis is diffuse, that is, spreading to the entire abdomen with a gradual concentration in the area on the right side and hypochondrium. Additionally, patients experience:
- severe nausea leading to vomiting;
- chronic constipation.
With cholelithiasis, gallstones are formed, which, depending on the composition, can be:
- pigmented;
- cholesterol;
- limestone;
- mixed.
Different methods are used to remove each type of stone, so it is important to undergo an ultrasound of the gallbladder. Provocateurs of the appearance of cholelithiasis:
- improper diet and regimen;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- overweight;
- long-term use of hormonal drugs;
- pathology of the pancreas (pancreatitis).
Causes of the painful condition
Many patients who are faced with gallbladder diseases are interested in the question of why the gallbladder hurts. Main causes of diseases:
- Infectious diseases that are provoked by pathogens (staphylococcus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Proteus, streptococcus). These bacteria provoke inflammation of the walls of the gallbladder.
- Organ innervation disorders. Disturbances in the nervous system occur, as a result of which the nerves do not control processes in the tissues of the body. That is, the liver secretion enters the intestine at the wrong time and in insufficient volume due to problems with contraction of the walls of the gallbladder.
- Changes in the chemical composition of bile. Because of this, calculi (stones) form in the bile duct and its ducts. Due to the fact that the amount of one component exceeds the others, the structure of the liver secretion is disrupted and compactions are formed. One of the pathologies is the accumulation of cholesterol on the walls of the gallbladder.
- Oncological diseases. Due to disorders in the genome of cells, benign or malignant tumors develop.
- Congenital pathologies are rarely diagnosed. One of the variants of such anomalies is stagnation of liver secretion in the gallbladder due to its bending.
Pain in the gallbladder provokes cholelithiasis and other pathologies
Now you know why your gallbladder hurts. The main thing is to identify the disease in time and consult a doctor.
Cancer
The result of prolonged cholelithiasis is cancer. Tumors in the gallbladder can appear in late stages:
- chronic pain in the right hypochondrium, which is not relieved by conventional antispasmodics;
- nausea, vomiting and other dyspeptic disorders;
- rapid weight loss.
The insidiousness of the disease is the asymptomatic nature of the early stages, even without the occurrence of jaundice. In 30% of people, the tumor is palpable in the form of a dense, lumpy, practically painless formation, which is located below the rib. The outcome of treatment depends on the timeliness of diagnosis of the pathology. Early detection gives a 100% chance of cure.
How to treat?
To select a method for treating the gallbladder, the patient undergoes an examination to identify the cause of the disease.
Pain in the area of the gallbladder projection and other manifestations can be deciphered by an experienced gastroenterologist. You can learn from him how and for how long to treat the disease, what medications to use, after a full examination and identification of the root causes of discomfort.
Diagnosis is often carried out using ultrasound, which allows you to obtain data on the condition of the organ:
- presence of stones, sand;
- inflammation;
- increase in size;
- consistency of bile.
The general course for all types of gallbladder pathologies includes:
- A strict diet with the exception of fatty foods, peppers, smoked foods, fresh baked goods, spices, sweets, marinades, gas-forming foods, alcohol, etc.
- Drug therapy with:
- antiparasitic, antibacterial drugs;
- antispasmodics to relieve pain;
- choleretic drugs to improve bile flow;
- enzymes to increase the motor activity of the organ, its ducts and the gastrointestinal tract as a whole.
- Physiotherapy.
- Traditional treatment with infusion of rose hips and viburnum, which help reduce pain within a week.
- Therapy with mineral waters.
The last two points are applied after the exacerbation of the disease has ceased.