Quick response
If a woman develops thrush while breastfeeding, the doctor prescribes medications that do not pass into milk. In general, gynecologists try not to prescribe medication, limiting themselves to diet, herbal medicine and means to normalize the vaginal microflora.
Read more in the article ⇓
Thrush during breastfeeding is a problem that many women face, especially during the postpartum period. During lactation, the use of most drugs is prohibited, but if you consult a doctor in a timely manner and follow his recommendations, you can get rid of candidiasis while maintaining breastfeeding, which is important for the child.
Risk factors
In first place among the triggers of candidiasis are frequent changes in the concentration of progesterone, prolactin and estrogen, stress, and nervous tension. These factors weaken the immune system. As soon as the functioning of the protective system deteriorates, opportunistic fungi Candida Albicans begin to multiply. They provoke genital thrush (candidiasis) in women in labor and nursing mothers.
After childbirth, candidiasis may develop on the nipples or in the woman’s mouth for similar reasons. This increases the risk of chronic thrush in a child.
Other provocateurs for the development of thrush in women in labor and lactating women:
- psycho-emotional stress, fatigue, sleep disturbances;
- congestion in the pelvic organs;
- decreased local immunity due to postpartum discharge;
- hypothermia;
- rapid weight gain;
- antibiotic therapy due to complications of childbirth (this group of drugs often causes candidiasis);
- metabolic disorders;
- intestinal dysbiosis;
- infection with sexually transmitted infections;
- gastrointestinal diseases;
- diabetes;
- immunodeficiency state;
- infection from a sexual partner (a man may be sick or a carrier of a fungal infection).
Thrush is often caused by excessive consumption of sweets, yeast products, beer, and kvass. Fungi also multiply quickly due to synthetic underwear, the use of low-quality products for the intimate area, tampons, scented pads, condoms, and stimulating gels.
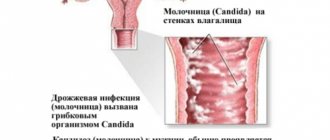
What is candidiasis in a nursing mother?
Often the fungus colonizes on the genitals and manifests itself in the form of vulvovaginitis (candida infection of the vaginal mucosa and labia minora). The main reason for this is changes in hormonal levels and weakened immunity. Indirect reasons are poor personal hygiene, a strict diet that limits a large number of foods, overwork and nervous stress. Candida can settle not only on the mucous membranes - during the feeding period there are often cases of thrush on the nipples of a nursing mother.
Appears in the first days after delivery, when the process of breastfeeding has not yet been established. Its occurrence is associated with improper attachment to the breast, as a result of which infection easily gets into the resulting wounds and cracks. Increased humidity due to frequent sucking and milk leakage also creates a favorable environment for the development of candida.
- Reduced amount of milk produced;
- The fungus can clog the milk ducts, resulting in an increased risk of mastitis;
- The infection is easily transmitted to the newborn in the oral cavity, causing him severe discomfort and refusal to eat.
Manifestations
The lower the immunity, the more severe the candidiasis. Signs and symptoms vary among different forms of the disease. In advanced cases, the fungus spreads through the genitourinary and/or respiratory system and gastrointestinal tract.
The appearance of pain, discomfort, burning sensation in the lower abdomen may occur due to candidiasis or postpartum complications
Symptoms and signs of genital thrush in women with breastfeeding:
- unbearable itching on the labia, in the vagina;
- swelling of the mucous membrane of the genitals;
- burning during urination;
- redness of the vulva, vaginal mucosa;
- discomfort in the lower abdomen, painful sex;
- vaginal discharge with a sour (kefir) odor;
- opaque cheesy lumps (white or grayish clots) on the mucous membrane of the vagina, vulva or underwear.
In the oral form, a white coating covers the mucous membrane of the mouth, pharynx, and lips. Thrush lesions are painful on contact with food. Intestinal candidiasis is manifested by itching of the anus and flatulence.
During breastfeeding, women are also often tormented by nipple candidiasis. The infection may appear nonspecifically as a pinpoint red rash, roughness, or blisters of fluid on the skin of the breast and areola.
Signs and symptoms of nipple thrush:
- inflammation of the areola tissue;
- redness of the nipple;
- itching of fungal lesions;
- nipple pain during feeding;
- swelling, burning, itching of the skin on the chest, areola;
- cracks, scales on the nipple;
- weeping skin (maceration);
- burning inside the gland;
- increased sensitivity of the nipples, discomfort when touched or rubbed by clothing;
- cheesy coating, white bubbles inside the cracks, on the surface of the nipple.
Disease on the nipples first occurs due to oral candidiasis in a child undergoing breastfeeding. Improper treatment leads to re-infection of the baby's mouth and woman's breasts with fungus.
Thrush during breastfeeding: symptoms and treatment
Candidiasis during lactation, or more simply explained, thrush during breastfeeding, this diagnosis can be heard by a breastfeeding woman at an appointment with a gynecologist, after examination in a gynecological chair, and taking tests (smears).
Table of contents
|
And what is this same candidiasis, which is known in everyday life as thrush? For what reason does it appear, what are its symptoms? How to cure the disease without harming the child?
Causes of candidiasis (thrush)
Every human disease has its own dominant, main pathogen. Thrush during breastfeeding also has such a pathogen - a yeast-like, microscopic fungus “Candida”.
According to the Latin pronunciation of the fungus (candida), the disease it causes is called candidiasis.
The disease is called thrush because the fundamental symptom of candidiasis is cheesy, abundant milky discharge that appears at the site of the inflammatory process in the woman’s body.
Microbiologists remind that candida fungus belongs to the natural innate gastric microflora with which a person is born.
But such a favorable mass of microflora, which includes candida fungus, does not pose a danger if it corresponds to a healthy biochemical balance in the human body.
Control over this microbiological ratio is exercised by the immune system.
When the immunity of the same nursing woman is sharply weakened due to the fault of:
• difficult pregnancy, childbirth;
• if a woman suffers from chronic diseases of the liver, kidneys, and gastrointestinal tract;
• either the mother of an infant is susceptible to frequent colds (flu, bronchitis, sore throat);
• or the causative agent of thrush has entered the female body through external contact through infection, through microcracks in the nipples, or during sexual intercourse;
In such cases, conditions are created for candida (yeast-like bio-fungi) to “reincarnate” into an aggressive pathogen.
What other causes of thrush in a nursing woman exist?
The list-table attached below will help women remember these risk factors during breastfeeding, and avoid infection, infection with yeast, fungal pathomicroflora.
| Causes | Description |
| Drug overdose | Sensitivity to penicillin drugs, antibiotics that the woman took during a cold - Ampicillin, Ampiox, Tetracycline and similar ones. |
| Household unsanitary conditions | Before feeding, a woman does not wash her hands or wash her breasts with warm water. The milk remaining in the breast is expressed irregularly, not completely: it leaks, soaking the breast pads and bra. If the underwear is not changed for a long time, a pathogenic microenvironment develops in the textile fabric of pads and bras, in which the “candida” fungus predominates. |
| Sexual intimate life of a woman (breastfeeding) | A man with whom a woman has sexual relations can be infected with thrush fungus. Signs of male candidiasis manifest themselves as minor symptoms; the man may not even know about the disease. A woman should be wary of a man’s cheesy discharge after sexual intercourse, which does not resemble ordinary sperm. And, also whitish bubbles on the inside of a man’s lips and gums (when kissing). |
| Dental surgical interventions (extraction, dental prosthetics) Gynecological examinations (insertion of coils into the uterus to prevent another pregnancy) | Most often, this situation occurs when a woman goes to unlicensed private dental offices or to practicing private gynecologists (outside hospital institutions). |
| Swimming in a public bath, in open, polluted waters | Thrush is characterized as an extremely infectious, contagious disease. The causative agent of the disease, a fungus, multiplies stably in a humid, warm environment. |
| Underwear (panties, bras) purchased in thrift stores, second-hand in spontaneous markets | Unfortunately, such products do not always undergo thorough disinfection, or they are worn underwear from sick people. |
Dermatologists add their reminders about the causative agent of thrush during breastfeeding - candida fungus.
Skin diseases such as weeping dermatitis, psoriasis, and dry eczema often provoke the activation of painful candidiasis in women.
Useful tips for mothers: NURSING HEALTHY AND BEAUTIFUL MOTHER
Therefore, treatment of such “joint diseases” in sick women (breastfeeding) is carried out by both dermatologists and gynecologists.
Types of thrush that can occur in a woman during breastfeeding
The infectious disease clinic divides thrush (candidiasis), especially in women who are breastfeeding, into common types and rare ones.
The most common ones include:
- Genital candidiasis.
- Dental thrush.
- "Nipple" candidal dermatitis.
If the initial phases of thrush are missed, or a woman self-medicates (with incorrectly selected medications), rare but very dangerous types develop:
• Candidal vaginitis – acute inflammation of the vaginal mucosa;
• Candidiasis vulvitis is a pathological degeneration of the deep muscular tissues of the vagina;
• Candidal endocervicitis – penetration and infection by the thrush fungus of the internal (endogenous) area of the woman’s genitourinary system (urethra, bladder, uterus, ovaries).
Thrush during breastfeeding in women is not limited to these types.
In the practice of gynecology, there are known cases of symptoms in women (who are breastfeeding children) that are similar to vaginal thrush - leucorrhoea with white flakes.
But, during laboratory examination of vaginal discharge, thrush fungus is not detected.
Doctors call this “type” of thrush – pseudocandidiasis.
As a rule, this is how side clinical effects appear when diabetes begins in a breastfeeding woman.
Or these are consequences after intensive treatment (for a nursing mother) with corticosteroids, pharmacological hormonal drugs, or seasonal allergies.
Areas affected by thrush in a nursing woman
The causative agent of thrush primarily affects and is based on the mucous surfaces of the female body.
Ideal conditions for the rapid proliferation of Candida fungal masses are anatomical places of the body where there is high humidity, temperature, and numerous large and small folds of internal surfaces. For example, the walls and vault of the vagina, or the oral mucosa in women.
If a woman is breastfeeding a child and has problems feeding - little milk, blockage of the milk ducts (alveoli) due to compaction in the mammary gland (mastopathy), the nipples of such a woman will be covered with microcracks, and there will be blisters on the areas near the nipples.
A similar picture appears because the child, not receiving free and abundant milk from the mother’s breast, intensively sucks the milk, leaving “wound” marks on the nipples.
On such inflamed nipples, the causative agent of a fungal infection, thrush, easily attaches and penetrates further into the body of a nursing woman.
Symptoms, treatment of thrush during breastfeeding
The main pathological symptoms of thrush, which cannot be confused with other gynecological diseases, are the appearance of itching and cheesy, flaky discharge at the site of initial penetration of the causative agent of the fungus “Candida” into the woman’s body.
Symptoms
If a woman's thrush has penetrated through cracks in her nipples while breastfeeding, the initial symptoms will begin to appear in the form of painful swelling of the nipples, and curdled clots will appear along with breast milk.
A woman is bothered by itching and burning in her nipples during and after feeding.
In advanced cases of breast thrush, when a woman consults a dermatologist late (after 5-6 days from the date of the first appearance of suspicious signs), the symptoms are much more severe - extremely painful sensations in the nipples, in the breast itself.
A nursing woman's general body temperature rises (above 39 degrees), chills and fever appear.
There may be a phenomenon such as “burnt milk”, blockage of the milk ducts due to high temperature.
The genital route of infection with thrush is manifested by symptoms - copious, curd-like vaginal discharge, itching, burning sensation in the vagina.
In the future, without timely treatment, pain inside the vagina intensifies and becomes debilitating (both day and night).
The “milky” type of discharge causes acute inflammation and irritation on the labia minora, the mucous membrane of which becomes covered with ulcers and cracks.
The same ulcerative lesions cover the internal mucosa of the genitourinary sectors - the walls of the vagina, fornix, and cervical urinary canal.
Treatment
At the first symptoms that indicate a possible thrush, women should not waste time.
It is necessary to urgently contact a antenatal clinic with a gynecologist.
The faster the results of laboratory tests are received, the more successfully and quickly the doctor will cure thrush in a breastfeeding woman.
The gynecologist introduces the proven and safe Pimafucin into the drug treatment plan. Fluconazole and Candiston spray demonstrate the same safe effect.
Prescribes douching with healing herbal disinfectant solutions - from calendula, chamomile, string.
In conclusion, we cannot do without useful advice for women who are breastfeeding their baby.
Do not risk your health, the health of your child, who may prematurely lose an invaluable source - mother's breast milk, due to thrush (on a woman's chest). And the woman herself may lose healthy genital and reproductive organs for many years if vaginal candidiasis is not cured
- about the author
- Recent publications
Tatiana Vasilyeva
author of the publication (site editor)
NURSE Mother of two daughters and grandmother of wonderful grandchildren.
Tatyana Vasilyeva recently published (see all)
- Artificial feeding of a child at 5 months - 08/01/2019
- When does colic begin in a newborn - 06/01/2019
- Frequent regurgitation in infants - 05/21/2019
Prevention methods
During the period of therapy, sexual contacts are stopped. To avoid re-infection, the man is also recommended preventive treatment.
Measures to prevent thrush in nursing women and infants:
- nipples are washed with soda or manganese solution before and after feeding;
- During treatment, they use silicone pads or switch the baby to infant formula;
- They carefully monitor hand and body hygiene and the cleanliness of things.
If you have candidiasis, it is recommended to wash yourself after each trip to the toilet. Hands are disinfected before applying medications and after treatment. It is better to wash towels and linen with chlorine in hot water. Panties and pants should not be too tight. Clothes are worn from natural fabric.
To prevent thrush, it is useful for a nursing woman to:
- get enough sleep, rest more often;
- walk in the parks;
- control negative emotions (psychotraining);
- drink a lot of green tea;
- exclude sweets and other foods that provoke the development of fungi from the menu;
- adjust weight with nutrition and exercise (during breastfeeding, diets and intense training are not recommended for weight loss).
Recurrence of thrush is prevented by strengthening local immunity. Upon completion of therapy, continue to wash with a decoction of calendula and chamomile. Soda baths are used periodically. It is advisable to use colorless, non-flavored condoms, avoid soap and douching.
To prevent thrush, all provoking factors are eliminated. During antibiotic therapy, it is recommended to take antifungal agents .
What do you need to remember?
- Thrush develops due to decreased immunity and hormonal fluctuations.
- When breastfeeding, it is possible to develop candidiasis on the nipples.
- Gentle medications and traditional medicine are recommended for nursing mothers.
- The basics of prevention are personal hygiene and nutritional correction.
Literature:
- Kozlova V.I., Puhner, A.F. Viral, ■ chlamydial and mycoplasma diseases of the genitals. M.: Avicenna, 2000. P. 228-267.
- Burduli G.M., Frolova O.G. Reproductive losses. - M.: Triada-X, 1997. - 190 p.
- Ailamazyan E.K. Obstetrics: Textbook for medical students. universities - St. Petersburg: Special Literature, 1997. - 496 p.
- Dmitriev G. A. Laboratory diagnosis of bacterial urogenital infections. -M., 2003.-336 p.
- Keshishyan E.S., Ryumina I.I. Feeding children in the first year of life // Russian Bulletin of Perinatology and Pediatrics, supplement (appendix). - 2007. - No. 1. - 46 p.
- Korsunsky A.A., Abolyan JI.B. Organization of work to protect and support breastfeeding in children's medical institutions // Russian Bulletin of Perinatology and Pediatrics. - 2004. - T. 49., No. 6. - P. 54-61.
- Kulagina N.V. Psychological and physiological features of the course of the postpartum period when postpartum women and newborns stay together: Abstract of thesis. dis. . Ph.D. honey. Sciences.- St. Petersburg, 1996.-25 p.
- Lipova E.V., Khrzayan R.S. The effectiveness of monotherapy for bacterial vaginosis and urogenital candidiasis with terzhinan, a combined local drug.//Russian Bulletin of Obstetrician-Gynecologist.-2006.-T.6, No.5.- P.66-68.
- Mokhova E.F., Sysoeva V.V., Lobach S.V. Assessing the effectiveness of active tactics for managing postpartum women with postpartum complications. // Advances in modern natural science. M., 2004.-P.227-228.
Folk remedies
For 500 ml of warm boiled water you should take 1.5 tbsp. spoons of soda, stir until completely dissolved. Lubricate the affected areas with the solution applied to a gauze pad 3-4 times a day.
- Herbal infusion baths.
Decoctions of oak bark, calendula and chamomile flowers, as well as eucalyptus and sage leaves (you can prepare a collection of all these ingredients by mixing them in equal proportions) are used for baths at night, washing and wiping the affected areas.
Green tea is a healthy tonic drink, but its abuse can lead to insomnia.
You should drink it daily, if possible several times a day. It helps control excess yeast and speeds up recovery. But you should avoid black tea.
Hydrogen peroxide is used quite often as a treatment for thrush during breastfeeding. This antiseptic effectively kills fungus, but it must be used correctly. Hydrogen peroxide in its pure form should never be used for douching. You should prepare a solution: add 2 tbsp to 1 liter of warm boiled water.
Douching with hydrogen peroxide should be done twice a day at the beginning of treatment. If the clinical manifestations of the disease decrease, you will need to switch to a regimen of one douching per day. In the future, as you recover, douching with hydrogen peroxide should be done once every 2 days. Douching with hydrogen peroxide should be prescribed by a doctor according to indications; self-medication here can cause significant harm.