- Development mechanism
- Reasons for the formation of adhesions
- Classification
- Symptoms of intestinal adhesions
- Diagnostics
- Treatment of intestinal adhesions
The formation of intestinal adhesions is a pathological process, which in most cases is provoked by traumatic surgery on the abdominal and pelvic organs. The lack of adequate treatment can provoke serious complications and negative health consequences, which include mechanical intestinal obstruction.
What is adhesive disease
The disease is characterized by the appearance of fibrous compounds growing between the internal organs and the layers of the peritoneum.
ICD-10 code – K66.0 – peritoneal adhesions.
Narrower classifications:
- N73.6 – pelvic peritoneal adhesions in women;
- N99.4 – postoperative adhesions in the pelvis;
- Q43.3 – congenital anomalies of intestinal fixation.
Adhesions are dangerous because they can form in large quantities and cause the insides to stick together. Often the disease leads to infertility in women: the lumen of the fallopian tubes or uterus is blocked, which significantly impedes the movement of sperm to the egg.
A possible serious complication is the development of partial or complete intestinal obstruction due to overgrown adhesions in the rectum and small intestine.
Reasons for appearance
Most often, the disease occurs after abdominal surgery: severe mechanical damage occurs, which leads to a similar protective reaction of the body.
Fusion can also occur in response to an inflammatory process . This mechanism is also associated with the body's defensive reaction.
Attention! Other, less common causes are injuries, bruises, and malformations of the digestive tract. For example, pathologies of the pancreas, damage to the intestines and gallbladder.
Diagnostics
To diagnose a pathological condition, a number of examinations are required.:
- General initial examination. Depending on the clinical picture, the patient’s condition can be satisfactory (compensatory stage) or unsatisfactory (with exacerbation or development of intestinal obstruction). When superficial pressure is applied to the abdomen, painful sensations may be noted. With deep palpation the pain intensifies.
- Laboratory tests include general tests of urine, blood, and stool. They are necessary to clarify the complete clinical picture, to identify whether there are signs of other hidden pathologies and inflammatory processes.
- An ultrasound of the abdominal organs is required to make an accurate diagnosis.
- Endoscopic examination is necessary to view the adhesions in more detail. Diagnostic methods include colonoscopy, irrigoscopy and FGDS.
- X-ray of the abdominal cavity. It is necessary to identify foci of exudate and other abnormalities.
- Contrast x-ray also allows you to identify the exact location of the adhesions.
- Laparoscopy is a minimally invasive surgical method intended for diagnosis and treatment. During surgery, fibrous tissue can be examined and treated immediately by dissection, if necessary.
Important! An accurate diagnosis is made using several diagnostic methods.
Homeopathy
Treatment of adhesions without surgery using homeopathic remedies can only be used as an auxiliary element of complex conservative therapy. The dosage and regimen of use is calculated individually for each clinical case. Homeopathic specialists recommend using the following herbal preparations:
- Aconitum Napellus C6 (derived from turnip grass extract);
- Staphysagria drops or Arnica Montana granules (active ingredient – larkspur seeds);
- Bellis Perennis drops (active ingredient – daisy extract).
- Siofor for weight loss
- Household milk separator
- Water diarrhea in an adult
Features of manifestation
The adhesive process has some manifestation features that should not be ignored :
- Mood swings: aggressiveness, irritability, nervous and unbalanced state.
- The appearance of severe swelling and problems in the functioning of the kidneys.
- Signs of hypovitaminosis due to problems with the absorption of nutrients.
- Problems in the heart: arrhythmia, tachycardia.
Important! If you start treating the disease, all these signs go away on their own.
Symptoms of adhesions
Symptoms are varied and directly depend on the location of the adhesive process , the duration of the painful condition and the strength of the growth.
At the initial stages, there are problems with the gastrointestinal tract, nothing more. In advanced cases, peritoneal signs and intestinal pathologies develop. Also distinguished :
- latent form;
- predominance of severe pain;
- prevalence of dyspeptic disorders.
If an adhesion occurs in the abdominal cavity, the manifestation of symptoms will depend on the location of the fibrous growths . The pain usually occurs aching and dull. During physical activity or immediately after eating, the pain may intensify. Sometimes stool disturbances occur, but this is not so typical for abdominal adhesions.
In the presence of overgrown tissue in the intestines, the manifestations are more intense. Often observed :
- problems with appetite;
- constipation;
- bloating;
- heartburn;
- flatulence and gas retention.
Important! Lack of treatment often leads to partial or complete intestinal obstruction.
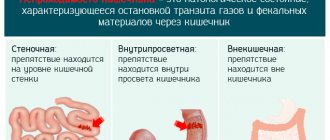
Signs of obstruction include:
- cramping, stabbing pain in the intestines;
- vomiting and nausea;
- absence of stool and gas;
- deterioration, weakness.
Attention! If the patient is not helped within 24 hours, sepsis and peritonitis develop with painful death.
Treatment with folk remedies
Folk remedies proven over the years can help in the treatment of intestinal adhesive disease. Let's look at the most effective of them.
Fruit and berry and herbal preparations
Collections made from raspberries, black currants and rose hips have a good healing effect. In addition to the main effect, they also give strength to the body and strengthen the immune system. To prepare a decoction for oral administration, you will need dried berries and fruits in equal proportions. Pour 2 tablespoons of berry picks into 1 glass of boiled water and heat in a water bath for 5-7 minutes. Then let the broth brew, it is better to cover it with a lid. After 2 hours, strain and take 0.5 cups 2 times a day for a month.
In the fight against adhesions, you can use lingonberry-based preparations. It is noteworthy that lingonberries have absolutely no contraindications. The berries of the plant are used to treat adhesive disease. To prepare healing tea you will need 1 tablespoon of dried lingonberries, 2 tablespoons of rose hips and 2 tablespoons of dry crushed nettle leaves. All ingredients are mixed, take 1/3 of the mixture and pour 1 cup of boiling water. The tea is infused in a thermos for 3 hours and then filtered. This amount is enough for 2 doses: morning and evening. It is better to drink warm. The course of treatment is 1 month.
A herbal collection of sweet clover, yarrow and coltsfoot has a good absorbable and anti-inflammatory effect. Dried and crushed yarrow leaves and umbrellas, sweet clover leaves and whole coltsfoot flowers are mixed in equal proportions. 1 tablespoon of the collection is poured into a glass of boiling water and infused in a thermos for 2-3 hours, after which it is filtered. The resulting decoction is divided into 4 parts - this is enough for 1 day. Used before meals, the course of taking the drug is 1 month.
Lingonberries, which are part of medicinal preparations, will perfectly help relieve unpleasant symptoms of the disease.
Decoctions and infusions of medicinal plants
Decoctions and infusions made from bergenia help to cope with the problem of adhesions. This herbaceous plant has anti-inflammatory properties and helps with bloating. You can use the root, flowers and leaves of bergenia.
Decoction recipe: 1 tablespoon of dry crushed plant root is poured into an enamel bowl and poured with 1 glass of boiling water. Next, the container is placed in a water bath for 30 minutes, the product is stirred periodically. The decoction is infused for 4 hours and then filtered. It is recommended to take a decoction of bergenia 1 hour before meals 3 times a day.
Infusion recipe: 1 tablespoon of dried flowers and bergenia leaves is poured with 1 glass of boiling water, heated in a water bath for 15 minutes, then decanted and infused in a thermos for 1 hour. Take this infusion 1 tablespoon 2 times a day.
It is undesirable to use bergenia for a long time for intestinal adhesions, as it has an astringent effect and can cause constipation.
Morinda limonifolia, popularly often called “noni,” will help relieve pain from adhesive disease. You can take the juice from the fruits of this plant orally, although it is not so easy to get. A mixture of dried fruits, roots and leaves of morinda is used as a medicine. This composition is consumed with meals, 2 tablespoons 3 times a day. Most people who have recovered from adhesions note that after 2 weeks the pain disappears completely, and after a month the adhesions themselves go away.
A good painkiller for adhesions is a decoction of St. John's wort, widely known among the people. But you shouldn’t abuse it, because St. John’s wort (along with bergenia) sometimes causes constipation. 1 tablespoon of dry crushed herb is poured into 200 ml of hot water and brought to a boil in a water bath, boiled for 10 minutes, removed from heat and infused for 2 hours. The strained drink is taken once a day, 1 tablespoon.
Maryin root helps to cope with adhesions in the early stages. Tinctures prepared from this plant normalize metabolism, relieve tension, and relieve pain. 100 g of dry ground root is poured with 100 g of alcohol, diluted to 40 degrees. Next, the infusion is left for a week in a dark place (it is recommended to use a dark glass bottle for this). After 7 days you can take: 30 drops 3 times a day before meals for 30 days. If necessary, it can be repeated after a break of 10 days.
A wonderful remedy for intestinal adhesions is aloe infusion. To prepare it, it is recommended not to water the plant for a week, then cut off the large leaves and leave them in the refrigerator for 3 days. The leaves prepared in this way are passed through a meat grinder and mixed with butter and liquid honey. The ratio should be as follows: for 1 part aloe raw material, 6 parts oil and 6 parts honey. The finished infusion is stored in the refrigerator. Take 2 times a day for 1 month, after mixing 1 tablespoon of the resulting product in 1 glass of warm milk.
Plants' seeds
Flax seed is one of the indispensable assistants in the treatment of adhesions.
Rich in useful substances, milk thistle can also be used in the fight against intestinal adhesions. 1 tablespoon of milk thistle seeds is poured into a glass of boiling water and boiled in a water bath for 10-15 minutes. Infuse for 3 hours, strain. The finished decoction is taken hot, a quarter glass, 2 times a day for a month.
With the help of flaxseed lotions, you can overcome pain in the abdominal area. First, 2 tablespoons of seeds need to be steamed in boiling water. For convenience, you can place them in a fabric bag while boiling. The cooled seeds are applied using a gauze compress to the places where pain is felt. In addition, dry ground flax seeds can be consumed with food in the amount of 1-2 tablespoons per day. This helps cleanse the body of waste and toxins, and also relieves constipation.
Plantain seeds used to prepare the decoction have a good anti-inflammatory effect. 1 tablespoon of seeds is poured with boiled water and simmered over low heat for 10 minutes, then infused for 1 hour and filtered. The finished decoction is drunk 1 tablespoon 3 times a day 30 minutes before meals for 1-2 months.
Therapy methods
In case of formation of adhesive growths, conservative therapy is ineffective . Medicines are needed for temporary use to relieve some symptoms. Medicines are part of complex therapy and serve to alleviate the symptoms of concomitant conditions.
The most effective and radical method of treatment is surgery with dissection of the fused areas around the organs. Laparoscopy is especially popular, since the intervention is minimally invasive, and the recovery period is easier to tolerate compared to traditional surgery. Surgery is prescribed for female infertility, intestinal obstruction and severe dyspeptic symptoms that interfere with the patient’s normal life.
Depending on the situation, the following manipulations may also be prescribed::
- Gradual adhesive excision followed by separation of organs from adhesions. It is performed by laparoscopy.
- If there is occlusion of the intestinal lumen, torsion or necrosis, resection is required. The intestine is partially removed, and the remaining areas are stitched together. If it is not possible to connect the tissues, a stoma is placed to connect parts of the intestine.
- If extensive intestinal damage occurs, anastomoses must be performed.
Attention! In approximately 20% of cases, surgical dissection leads to regrowth of adhesions, so careful prevention is necessary.
Traditional methods using herbs are ineffective, but you can try doing exercises to stretch the tissue. Home remedies can only help with fresh adhesions in the peritoneal area, when only a film forms there. As you exhale, try to stretch them with your fingers.
Diet recommendations include split meals, avoiding fatty, fried, and floury foods . Food is boiled or steamed. You need to eat plenty of vegetables and fruits to avoid constipation. Bonding products are contraindicated.
Best food
Nutrition for intestinal adhesions should be balanced, including plant fiber, easily digestible proteins, and complex carbohydrates. The menu must use all recommended products, making it as varied as possible. The patient receives food in small portions, this facilitates digestion and allows all nutrients to be absorbed. The healthiest dishes include:
- soups with vegetable or chicken broth;
- porridges cooked in water (oatmeal, semolina, barley, wheat, buckwheat);
- wholemeal bread and pasta;
- lean poultry (chicken and turkey fillet);
- sea fish (cod, hake, pollock, flounder);
- chicken and quail eggs;
- cottage cheese, homemade yogurt, low-fat kefir, Varenets, fermented baked milk, soft cheese;
- green and herbal teas;
- soy products (tofu, milk).
Instead of industrial sweets, oversaturated with sugar, preservatives and processed vegetable fats, you can include fruit purees, nuts, dried fruits, homemade fruit drinks and jelly on the menu. They are tasty, rich in essential vitamins, easily digestible and do not irritate the intestinal walls.
An obligatory component of the therapeutic and preventive menu is a variety of vegetables. Leaf and head salads, broccoli, cauliflower and Brussels sprouts, kohlrabi, pumpkin, green peas, green beans, carrots, potatoes, tomatoes, cucumbers, zucchini, and eggplants are especially useful. Vegetables are used to prepare pureed or poured soups, stews, and pancakes. It is advisable to bake food in the oven, cook in a double boiler or microwave. The amount of salt is kept to a minimum; herbs will help enhance the taste: dill, parsley, celery, thyme, basil, rosemary. You must consume at least 500 g of fresh, boiled or baked vegetables and the same amount of fruits and berries per day.
Proper drinking regimen will help improve digestion. Patients benefit from dried fruit compotes, herbal decoctions, homemade fruit drinks, green tea, pure drinking or still mineral water.
Prognosis and prevention
With timely treatment, the prognosis is favorable in most cases . The only danger is the development of complications. For example, with complete occlusion of the intestine, the chances of an unfavorable outcome are high.
To prevent the disease from occurring due to inflammation in the organs, you need to lead a healthy and calm lifestyle and avoid contracting infectious diseases.
If you need to perform an operation, it is recommended to give preference to laparoscopy - a low-traumatic method. Other preventive measures during manipulation include:
- reduction of operation time;
- stopping bleeding;
- careful handling of organs;
- use of gloves not treated with starch or zinc oxide;
- Irrigation of organs with saline solution.