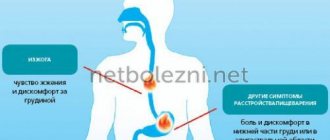
Many people experience heartburn from time to time, but most simply try to ignore this phenomenon. Moreover, it passes quite quickly. But heartburn occurs due to the fact that gastric juice rises to the throat, which in itself is incorrect.
In addition, this symptom may indicate quite serious problems in the body. Therefore, it is desirable for everyone to know what the reasons for the release of acid from the stomach are, why this phenomenon is dangerous and what to do to avoid its occurrence.
Features of the pathology
When food enters, a release of hydrochloric acid occurs, which is necessary for the breakdown of products during digestion and assimilation. Due to the normal functioning of the intestinal tract, food enters the stomach. In case of violations, undigested food, bile and hydrochloric acid are thrown into the esophagus. The ingress of gastric juice provokes the appearance of scar deformities, ulcers, and erosions on the mucous membrane. With the regular release of bile into the esophagus, the space between the organs of the intestinal tract may narrow, which can lead to the development of a cancerous tumor.
Traditional methods for removing mucus from the throat
Alternative medicine offers many ways to combat this disease. They need to be viewed critically. For example, decoctions of medicinal herbs with antiseptic properties will help well with inflammatory diseases, but will be powerless for allergies or will aggravate them.
Chamomile, sage, licorice, thermopsis and others will help cope with inflammatory mucus. If the patient doubts that he can properly prepare the tinctures on his own, then you can buy ready-made mixtures and tinctures at the pharmacy.
Warm milk with honey has a good calming effect. This drink washes away pathological secretions, disinfects and has restorative properties. Contraindicated for allergy sufferers and young children.
Causes of the disease
The factors causing the constant reflux of bile into the esophagus are internal (physiological) and external (nutritional) reasons.
Internal:
- stomach pathologies: reflux esophagitis, gastritis, ulcer;
- chronic inflammation of the duodenal mucosa;
- gallbladder disease;
- diaphragmatic hernia;
- accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity;
- structural features of the sphincter between the stomach and duodenum;
- cardiovascular diseases;
- oncological neoplasms in the abdominal cavity;
- obesity;
- pregnancy.
External:
- unbalanced diet;
- drinking water at the same time as eating;
- dry food, snacks;
- binge eating;
- tobacco and alcohol abuse;
- long course of taking painkillers and analgesics;
- playing sports after eating;
- lifting heavy objects;
- uncomfortable posture during sleep;
- stress;
- passive lifestyle.
Symptoms
When bile and acid flow from the stomach into the esophagus, signs are observed that cause discomfort after eating food:
- belching with a bitter taste;
- heartburn;
- secretion of vomit along with bile;
- hiccups;
- pain, stomach cramps;
- feeling of a lump in the throat;
- dry mouth;
- yellow coating on the tongue;
- decreased appetite.
When bile is released into the esophagus, bitterness is necessarily observed in the oral cavity. This occurs due to the seepage of accumulated fluid through the damaged mucous membrane. An unpleasant taste is observed in the morning on an empty stomach.
Heartburn is a burning sensation behind the breastbone that occurs due to the release of undigested food and gastric juice into the esophagus. The acid is released and the pH level rises.
Nausea can be caused by alcohol abuse or overeating fatty foods. Vomiting with bile is a symptomatic sign indicating serious disorders of the gastrointestinal tract. Due to irritation of the nerve of the diaphragm of the esophagus, prolonged hiccups begin. When bile is refluxed from the stomach, moderate pain is observed. The regularity of spasms depends on the time of day: most often the syndrome occurs at night.
The release of hydrochloric acid and bile from the stomach affects the functioning of the body. With esophagitis the following are noted:
- changes in the structure of tooth enamel;
- pain in the heart area;
- cough;
- hoarseness;
- hoarseness of voice.
Regardless of the cause of bile reflux, symptoms that cause discomfort occur. Therefore, if symptoms appear regularly, you should contact a gastroenterologist to avoid progression of the disease.
Which doctor should I contact?
Since phlegm often accumulates in the throat with a mild cold, you should first consult a physician. He is a general practitioner and can make a diagnosis on his own. If necessary, he will refer the patient to a specialist - an otolaryngologist. This doctor specializes in pathologies of the upper respiratory tract (sinusitis, sinusitis, laryngitis, pharyngitis).
If you suspect damage to the lower respiratory tract (pneumonia, lung cancer), the patient should consult a pulmonologist.
First aid
Impaired functioning of the esophageal sphincter leads to unpleasant symptoms that can cause burns to the mucous membrane of the intestinal tract. To prevent serious damage to the internal walls, you must follow the first aid rules:
- drink enough liquid in small sips (at least 1 liter);
- use medications for acute pain - antispasmodics;
- drink alkaline mineral water or milk to neutralize hydrochloric acid if a burning sensation occurs.
After providing first aid, an urgent medical examination is necessary.
Diagnostics
A correct diagnosis confirming the cause of bile entering the esophagus can be made by a doctor only after laboratory tests (blood, urine) and instrumental examination. Modern diagnostic methods help to establish the origin of clinical signs:
- radiography;
- endoscopy;
- gastroscopy;
- manometry;
- pH-metry;
- choledoscintigraphy;
- ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs;
- biopsy.
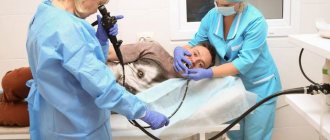
Endoscopy and gastroscopy are aimed at visual examination of the stomach, esophagus, and duodenum. The procedure involves swallowing a probe with an installed optical camera, which displays an image on a monitor. The introduction of a gastroscope makes it possible to identify cicatricial deformities and visible damage to the mucous membrane due to the ingress of hydrochloric acid and bile. X-rays are aimed at detecting a hiatal hernia or tumor. Manometry is a study of the functioning of the motor function of the sphincter.
Measuring the level of hydrochloric acid in the body throughout the day allows you to determine the severity of reflux disease. Choledoscintigraphy is aimed at studying the tone of the gallbladder. Ultrasound is an indirect diagnostic method that allows us to identify pathologies of the abdominal organs that affect the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. Biopsy is the collection of cells from the gastric mucosa during endoscopy to detect cancerous tumors.
Treatment of pathology
Complex therapy includes medication, diet, and traditional methods. Strict adherence to the treatment course will allow you to get rid of unpleasant symptoms and avoid the recurrence of reflux disease.
Medications
It is necessary to treat bile reflux with medications:
- antisecretory drugs;
- proton pump inhibitors;
- blockers;
- antacids;
- prokinetics;
- antispasmodics.
Medicines are aimed at eliminating symptoms and treating the cause of the pathology. To neutralize the increased level of gastric juice, inhibitors are prescribed: Omeprazole, Omez, Pantoprazole. The drugs promote rapid healing of damaged cells when ulcers and erosions are detected. Blockers Ranitidine and Famotidine reduce the aggressive effect of hydrochloric acid on the mucous membrane of the digestive organs. Antacids help normalize the acid-base balance thanks to magnesium and aluminum contained in the drugs: Gaviscon, Maalox, Phosphalugel.
Prokinetics improve the functioning of the sphincter and the motor function of the esophagus. The drugs Motilium and Ondansetron normalize the process of digestion, the passage of food from the stomach to the intestines. If pain occurs, it is recommended to take antispasmodics. For rapid recovery and regeneration of damaged areas of the epithelium, you should use products that have an enveloping, protective effect - Venter, De-Nol.
Diet
Adjusting the diet is a mandatory method of therapeutic therapy for pathologies of the digestive tract. The diet includes:
- exclusion of spicy, smoked, fried, fatty foods, legumes;
- consumption in small portions up to 200 g per meal;
- refusal of fermented milk products, semi-finished products, fast food;
- eating large amounts of food containing plant proteins;
- avoiding overeating, fasting, snacking on the go, dry food;
- giving up bad habits in the form of alcoholic beverages and tobacco products;
- The last meal is 2-3 hours before bedtime.
For reflux disease, the diet should be balanced and include foods high in proteins, vitamins, minerals, and amino acids.
ethnoscience
Recipes using simple ingredients are an effective addition in the treatment of pathologies associated with the reflux of bile and hydrochloric acid from the stomach. Herbal medicine involves taking single- or multi-component decoctions and infusions. Popular medicinal herbs and plants are:
- linen;
- St. John's wort;
- calendula;
- plantain;
- menthol mint;
- licorice;
- calamus
Medicinal drinks relieve the burning sensation, envelop the walls of the stomach, protecting against the aggressive effects of food when it enters the body. It is recommended to drink decoctions and infusions before meals. Effective remedies are sea buckthorn and rosehip oil. A mixture of milk and tomato juice in a 1:1 ratio, oatmeal or flax porridge cooked in water help to quickly eliminate heartburn.
Operation
If there is no positive dynamics after taking medications or following a diet, surgical intervention may be necessary. The operation involves changing the size of the esophageal sphincter, through which bile and food from the stomach are refluxed.
Indications for use are serious damage to the mucous membrane detected during endoscopic examination:
- Barrett's esophagus;
- profuse bleeding;
- adhesive stenosis;
- oncological disease.
When a cancerous tumor is detected, the tumor and lymph nodes are removed, through which metastases can spread throughout the body.
Symptomatic therapy
Among home methods, drinking plenty of warm liquid will help relieve the condition. This is an effective way to thin mucus and wash away excess mucus.
However, this is only a temporary measure: exudate production will continue as the underlying cause has not been eliminated.
Treatment of the root cause begins after diagnosis and prescription of appropriate medications. There cannot be a single list of drugs, since treatment regimens vary from disease to disease.
Recommendations
To prevent the reflux of gastric juice into the esophagus, it is necessary to take preventive measures:
- lie on a raised pillow while sleeping;
- eat healthy, wholesome food;
- do not engage in vigorous activity, do not lift weights after eating;
- wear loose clothing;
- do not take sedatives or antibiotics for a long time;
- monitor body weight;
- visit a medical facility regularly.
We recommend: What is esophageal cardiospasm and how to treat it?
What to do if your child has phlegm?
Treatment of sputum in a child is complicated by the small range of products approved for use in childhood. Children under 3 years of age are recommended to be treated primarily with folk remedies.
Medicines allowed from 6 months:
- "Stoptussin."
- Linkas.
- "Ambroxol".
- "Alteyka".
Products for children over 3 years of age:
- "Dr. MOM."
- Codelac Broncho.
- "Herbion".
- "Amtersol".
It is difficult for young children to cough up mucus on their own. You can help them using massage. The child is placed on his stomach with a pillow placed under his hips. Using stroking movements, massage the back along the spine (from bottom to top). After stroking, light pats, rubbing with knuckles, and kneading movements are performed.