Infiltrative gastric cancer is a morphological form of carcinoma, which is characterized by infiltrative growth (growth through the wall of the organ) and the absence of clear tumor boundaries.
- Causes
- Who is at risk
- General clinical manifestations
- Forms of pathology
- Stages of the disease
- Diagnostics
- Treatment options
- Forecast
- Prevention measures
Features of infiltrative cancer:
- It is characterized by a high degree of malignancy - it grows quickly and metastasizes early.
- May occur in young people.
- The hereditary factor is clearly visible.
- As a rule, it manifests with symptoms of dyspepsia.
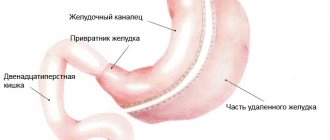
Structure and functions of the stomach
Cancer can form in any part of the stomach. To establish an accurate diagnosis and treatment, it is necessary to know the anatomical features of this organ. The stomach is a hollow muscular organ that can stretch to large sizes. It is located in the abdominal cavity directly between the esophagus and the duodenum.
- food accumulation;
- its mechanical grinding and digestion;
- absorption of certain substances (water, electrolytes);
- thorough mixing of the food bolus;
- movement of food into the underlying sections;
- protective.
The stomach has several sections: cardiac, pyloric, fundus and body. The inside of the stomach is covered with ciliated epithelium. It forms the mucous membrane of the organ. Cancer develops from the epithelial layer itself. In severe cases, cancer can grow into the muscle or submucosal layer.
Physiology of the antrum
The specific function of the antrum is to finally grind food into a pulp state so that the maximum size of a food particle is no more than 2 mm. During mechanical grinding there is also constant mixing of food. After receiving a portion of uniform consistency, the food mass rushes through the pyloric sphincter and undergoes further processing in the duodenum.
The mechanical function of the antrum is not the only one. If the main section of the stomach produces more hydrochloric acid, then the task of the antrum is reduced to neutralizing acidity by producing alkaline mucus, concentrated in the pylorus area. This action is necessary to prepare the food mass for processing in an alkaline environment that will be created in the duodenum. The transition from acidic contents to an alkaline environment should not be too abrupt.
Another function of the antrum should be considered endocrine: individual cells produce the hormone gastrin, which has an effect on hydrochloric acid.
Insufficient gastric peristalsis contributes to food stagnation, fermentation and rotting, which causes the acidity of the environment to increase to a greater extent. The gastric mucosa is designed for a certain acidity level, corresponding to the normal production of hydrochloric acid by the parietal cells. When acidity increases, the mucous membrane is destroyed, which is accompanied by diseases of the entire digestive system of varying degrees of severity. If the effect of too acidic gastric juice is not stopped in a timely manner, the pathological condition becomes chronic.
Classification of types of stomach cancer
1. Depending on the location and place of formation in the organ:
- tumor of the fundus of the stomach;
- body of the stomach;
- cardiac part;
- large curvature;
- small curvature;
- cancer of the antrum of the stomach;
- cardioesophageal;
- gatekeeper parts;
- mucous cancer;
- total cancer - when the entire organ is involved in the process;
- cancer of the pylorus of the stomach.
2. According to the histological form and cellular composition of the changed area:
- epithelial;
- glandular;
- adenocarcinoma;
3. If it is possible to establish the cellular composition at the morphological level, then they talk about:
- highly differentiated form;
If recognition of elements is not possible, we are talking about:
- undifferentiated cancer.
4. According to the type of manifestation of the disease:
- intestinal form - the composition of the tumor can be confused with an intestinal type lesion, elements are disguised as intestinal metaplasia;
- diffuse form - characterized by rapid and progressive damage to other organs.
- mixed type - when elements of the above forms are found.
5. By the nature of growth:
- exophytic – growth outside the organ zone;
- endophytic – formation of a tumor in the lumen of the stomach;
- infiltrative – with a high degree of infiltrative and inflammatory processes;
5. According to the shape of the tumor:
- mushroom-shaped - resembles a mushroom in its outline;
- papillary – formed in the form of papillomas, processes on a stalk:
- polypoid – resembles the structure of a polyp;
- signet ring or signet cell – takes the shape of a ring or ring-shaped;
- saucer-shaped - looks like a flat saucer, rises slightly above the wall of the organ;
- scirrhos - in the form of a thick compacted tape;
- in the form of cauliflower.
For diseases of oncological origin, a specialized TNM classification has been adopted throughout the world. It is convenient because it displays the disease process from all sides, shape, degree, stage of cancer and metastasis.
The primary focus of a malignant tumor is usually designated by the Latin letter T.
TX – there is no complete information for diagnosing cancer;
T0 – the primary focus could not be identified;
TIS – precancerous form, or carcinoma in situ;
T1 - the process is localized in the mucosa to the muscle layer;
T2 – damage to the muscle layer;
T2a – changes in the muscular plate to the basal layer;
T2 in – deeper than the basal layer;
T3 – damage to all layers of the organ without damage to nearby neighboring organs;
T4 – involvement of other organs and systems in the process.
The Latin letter N reflects the stages and coverage of regional lymph nodes in the process.
NХ – there is not enough information to assess the condition of the lymphatic system;
N0 – lymph nodes are not affected;
N1 – there are signs of cancer in the nearby group;
N2 – changes in 2 or more groups;
N3 – distant groups of lymph nodes are involved in the process of metastasis;
Latin M informs about the presence of metastases.
Mx – not enough information to clarify;
M0 – no metastatic foci were identified;
M1 – metastatic lesions of other organs were detected.
The designation G stands for the degree of malignancy.
There are medium, high and undifferentiated degrees.
Let's talk in more detail about some types of stomach cancer.
Features of stomach cancer
Stomach cancer is common in almost all countries of the world. This disease occurs in men and women. The peak incidence occurs between 50 and 70 years of age. Women get sick 2 times less often than men. Recently, the disease is often detected in people at a younger age.
The highest incidence rates are observed in the following countries: Japan, Korea, Mexico, Chile, Finland and some others. Every year, low-grade cancer or other forms of cancer kill about 1 million people worldwide.
In the field of oncology, this pathology ranks 4th in terms of frequency of occurrence. As for Russia, stomach cancer ranks 2nd here. In Ukraine, when talking about stomach pathology, they mention the schluka. Shlunka is “stomach” in Ukrainian.
What are the causes of this disease? Today, the following etiological factors are of greatest importance:
- poor nutrition;
- infection of the gastrointestinal tract by Helicobacter pylori;
- burdened heredity;
- smoking;
- presence of chronic infectious diseases;
- exposure to carcinogenic substances;
- alcohol abuse;
- hormonal disorders;
- features of the constitution;
- presence of chronic gastritis;
- disruption of the production of hydrochloric acid and gastric juice.
This malignant neoplasm of the stomach is formed not without the participation of external factors. There is a connection between the incidence of cancer and the content of certain chemical elements (cobalt, copper) in the soil. In addition, the environmental situation, the quality of consumed water, and harmful occupational factors are of no small importance.
Diagnostics
Accurate diagnosis is necessary to select the correct treatment tactics. The first step is to go to a gastroenterologist, who will perform an initial superficial examination. This will be followed by tests and examination procedures:
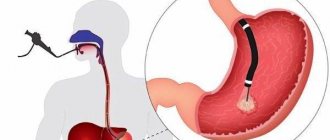
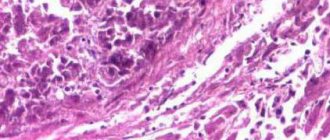
- Biopsy of stomach tissue using FGS followed by microscopy of the taken material.
- Tests for gastric acidity and enzyme ratios.
- Blood test for Helicobacter pylori.
- Blood chemistry.
- Urinalysis, coprogram.
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs.
It is extremely important to distinguish gastropathy from various forms of gastritis, gastric ulcers, pancreatitis, and gastrointestinal neoplasms.
Glandular stomach cancer or adenocarcinoma
This is the most common type of cancer of the organ. This form accounts for about 80% of all morbidity cases. Why does the disease have such a name? It all depends on what type of tissue it was formed from.
In this form of pathology, the primary focus of transformation was a glandular tissue cell, which subsequently gave rise to growth and damage to other cells of the same group.
There are two types of it:
- Tubular adenocarcinoma, which is formed from the ducts of the glands.
- Undifferentiated adenogenic gastric cancer. When morphologists cannot figure out from which element the focus primarily developed.
The causes of the pathology are not fully known, however, it is generally accepted that the disease is caused by precancerous processes such as stomach ulcers, polyps, Menetrier's disease, atrophic and hopoacid gastritis.
Clinical manifestations of the disease can remain hidden for a very long time and not manifest themselves in any way. In later stages, all this may be accompanied by symptoms:
- constant nausea;
- loss of appetite;
- vomiting of eaten food;
- sudden weight loss;
- general weakness;
- hallucinations, dizziness, fainting;
- anemic syndrome of unknown origin.
Treatment depends on the form, severity, and course of the disease. There are radical (surgical) and conservative (chemotherapy, radiation therapy) methods. Usually these two groups are combined. If the tumor is not amenable to surgical intervention, then palliative chemotherapy is resorted to.
For inoperable stomach cancer, life expectancy is usually no more than 1 year. The prognosis also depends on tissue differentiation. With a highly differentiated form, the tendency to recovery is higher.
The five-year survival rate is more than 70%. For undifferentiated gastric cancer, the prognosis at this stage of medicine is unfavorable. Survival rate is no more than 2–3 years.
Errors in nutrition
Cancer of the antrum of the stomach or any other most often occurs due to malnutrition. It is difficult to find a person who eats right and follows a routine. Cancer develops rapidly under the following conditions:
- eating too hot food;
- excess of smoked, salty and fatty foods in the diet;
- eating poor quality food;
- non-compliance with the diet (intervals between meals).
Today, stores have a wide range of products. Cancer of the cardial part of the stomach or antrum most often occurs with regular consumption of canned food. Such products contain various food additives (preservatives, dyes), which in high concentrations can cause damage to the gastric mucosa.
An interesting fact is that a lack of certain vitamins (vitamin C) in the diet significantly increases the risk of developing cancer in a person. The situation is aggravated by regular alcohol consumption. Ethyl alcohol and its breakdown products have an irritating effect on the gastric mucosa. Over time, this leads to the development of atrophic or erosive gastritis.
Prevention measures
It is much easier to prevent stomach diseases than to cure them. This applies to absolutely all its departments, including the antrum. As a rule, prevention consists of regular examination by doctors in order to identify possible disorders in the early stages of development. We are talking about specialized specialists, that is, you need to contact not a therapist, but, for example, a gastroenterologist.
There are also other preventive measures, including:
- healthy and balanced diet. First of all, all harmful foods (fried, fatty, spicy foods) should be excluded from the diet. The quantity of some products needs to be reduced. This applies to sweets, coffee, carbonated drinks. Add more vegetables and fruits, lean meats and fish to your diet. This will help improve the functioning of the digestive system;
- Avoid stressful situations. If you work in a stressful job, change it;
- give up smoking and other bad habits that negatively affect the health of the gastrointestinal tract and the entire body as a whole;
- all gastrointestinal pathologies must be treated on time, that is, as they appear. You cannot ignore the symptoms of a particular disease and let everything take its course. This can lead to serious complications.
If you follow all these recommendations, you can prevent diseases not only of the stomach or its antrum, but also pathologies of the entire gastrointestinal tract. And constant adherence to a diet will allow you to get rid of extra pounds (if any) and tone your body.
Video - Gastric antrum cancer
Gastric squamous cell carcinoma or epithelial carcinoma
This form of the disease is formed from epithelial cells that form and line the mucous layer of the organ. In practice, this type is quite rare.
A distinctive feature of this pathology is the organ obstruction syndrome. Patients complain of impaired passage of food, a feeling of a foreign body, pain in the form of a spasm, and vomiting with blood.
It is possible to diagnose epithelial cancer using fibrogastroscopy, ultrasound, and x-ray methods. However, the diagnosis is confirmed only by histological and pathomorphological examination of a piece of tissue from the affected area.
If the disease is detected early, the prognosis for life and work ability is favorable. Combination therapy in the form of surgery and chemotherapy makes it possible to achieve remission and recovery in 85% of cases.
When cancer is detected at stages 2–3, the prognosis for remission is reduced, but combined treatment provides a chance for survival and recovery.
At grade 4, survival is minimal; all treatment is aimed at improving the patient’s quality of life and palliative care.
Types of cancer
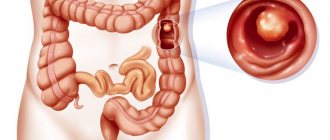
It has been established that the pyloric and antral parts of the organ are most often affected, and less often the body of the stomach. Depending on the growth of the tumor, infiltrative and exophytic cancer are distinguished. In the first case, the tumor grows outward, that is, into the lumen of the organ. At the same time, it has the appearance of cauliflower, saucer or ulcer. Infiltrative tumor growth is characterized by damage to a large area of the mucosa. In this case, the tumor spreads throughout the stomach.
In some cases, when examining a patient, gastric leiomyoma may be detected. It should not be confused with cancer. Leiomyoma does not metastasize to other organs. It belongs to benign tumors of the stomach. Signet ring cell cancer of the stomach is distinguished by the fact that histological examination reveals atypical cells resembling rings. It is very rare. The most dangerous is undifferentiated stomach cancer.
Gastropathy of the antrum mucosa
This type of pathology accompanies chronic forms of gastritis and is not an independent disease according to the medical classifier. The mucous membrane of the entire antrum becomes covered with redness, which is why it is often called erythematous gastropathy. Massive redness of the antrum mucosa has the same causes as the disease itself. Doctors ascertain the condition of the mucous membrane as an endoscopic finding.
When eliminating provoking factors, antacids and (or) astringent drugs are prescribed. The radical method of treating antral gastropathy is surgery.
Anton Pavlovich Chekhov, through the mouth of his hero, the secretary of the congress Zhilin, stated that “the doctors invented catarrh of the stomach. This disease comes more from freethinking and pride.” In Chekhov’s times, “cathars” were the name given to the entire spectrum of stomach diseases. People suffered from them until death, which came much earlier than expected. Medicine of the 21st century has learned to diagnose and heal the ill-fated catarrh, one of the varieties of which is gastropathy.
Signet or signet ring cell carcinoma
The disease is not called so because the growth of the tumor resembles the appearance of a ring. It's much deeper here. The mechanisms are embedded in the cell. The thing is that with tumor damage, metabolic processes are disrupted at the lowest level.
A special substance enters the cell - mucin, which is capable of oppressing the nucleus. Under a microscope, this phenomenon looks like a ring. Hence the name.
The clinical picture is similar to previous forms. All the differences are only at the morphological level.
There are 4 stages of the process. The most dangerous and critical of them is degree 4. With it, distant foci of metastasis are formed, damage to the entire organ, and disruption of other vital systems.
In this form, surgical intervention must be performed. If this is not possible, cytostatic therapy is carried out. The prognosis for stage 4 signet ring cancer is critical.
It is believed that it cannot be cured. Therefore, for statistical assessments, doctors take a survival period of 5 years. Of this interval, the survival rate at stage 4 accounts for no more than 4%.
Reasons for appearance
The development of pathology can be provoked by the uncontrolled use of medications that can change the internal environment of the organ. Mesotherapy also affects the appearance of shoots. In addition, the following negative factors lead to the manifestation of papules:
- stomach injuries;
- regular smoking;
- chronic liver pathologies;
- bile in the mouth;
- increased acidity in the stomach;
- exhaustion of the body;
- being under stress;
- burns of mucous structures;
- diseases of the vascular system.
Return to contents
Stages of the disease
In oncology, it is customary to distinguish several stages of tumor development. This division is based on the following criteria:
- presence of a primary tumor and its size;
- presence of regional metastases;
- the presence of distant metastatic foci.
Regional metastasis refers to the penetration of cancer cells into regional lymph nodes. These cells provoke the appearance of new lesions. Distant metastases can occur in any organ. Most often they are found in the liver and lungs. Infiltrative gastric cancer or any other cancer with distant metastases is difficult to treat.
There are 4 main stages of cancer. At stage 0, cancer is detected in situ. In this case, the mucous layer of the organ is affected, but the tumor does not grow into the tissue. At stage 1, damage to the submucosal layer without the presence of metastases is observed. Stage 2 is characterized by germination of the muscular layer of the organ. At the same time, the mobility of the stomach and its function are practically not affected.
At stage 2, single metastases may appear in regional lymph nodes. It is important that treatment measures are most effective at stages 1 and 2 of cancer. Poorly differentiated gastric cancer or any other form of it at stage 3 is characterized by the fact that all layers of the stomach are affected (epithelial, submucosal and muscular).
Cardioesophageal cancer
The disease is not isolated. The process involves the lower parts of the esophagus and the upper parts of the stomach.
A precancerous disease is most often gastroesophageal reflux disease with a long and chronic course, especially if adequate therapy has not been carried out.
Predisposing factors are:
- bacterial lesions of the gastrointestinal tract, especially contamination of the mucous membrane with Helicobacter pylori infection;
- eating unhealthy unbalanced food;
- frequent stressful situations;
- excessive fasting;
- chronic diseases;
- genetic family predisposition.
Symptoms of the disease
Clinical manifestations do not differ much from other forms of cancer. Particular attention is drawn to debilitating heartburn, belching of rotten air, and bad breath.
All this is accompanied by signs of general intoxication, weakness, and asthenovegetative syndrome. The patient becomes unable to work, spend a long time on his feet, and in extreme cases, get out of bed.
A diagnostically significant procedure is fibrogastroduodenoscopy followed by histomorphological analysis.
Treatment includes various types of surgical interventions, installation of a gastrostomy tube, and intestinal anastomoses. They combine all this with chemotherapy. In the early stages, radiation therapy is an effective treatment method.
The tumor is exposed to harmful effects of gamma rays. After which it breaks down and is removed from the body. The prognosis for life at stages 1 and 2 is positive.
When a tumor is detected late, therapeutic manipulations are not always effective enough. The main goal is to create favorable living conditions for people.
Treatment options
The main treatment method for infiltrative cancer is surgery. For common forms of neoplasm, it is supplemented with chemotherapy. If surgery is not indicated, only chemotherapy is performed.
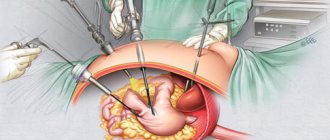
Surgery
When treating infiltrative forms of gastric cancer, the following types of operations are used:
- Gastrectomy.
- Subtotal gastrectomy.
In this case, the affected part of the stomach or the entire stomach is removed en bloc with the surrounding tissues, which includes the greater and lesser omentum, fatty tissue and regional lymph nodes of the 1st-2nd order. The intersection of the organ in case of infiltrative cancer is carried out no less than 7 cm from the defined edge of the tumor. To confirm the radicality of the operation, the removed fragment is immediately examined for the presence of tumor cells at the cutting edges.
If cancer spreads to neighboring organs, the scope of the operation may increase and include resection of the affected tissue.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy can be used as part of a combination treatment, in conjunction with surgery, or as a stand-alone treatment for unresectable tumors.
The following types of chemotherapy are used as part of combination treatment:
- Perioperative. This type of treatment involves 3 cycles of chemotherapy for 8-9 weeks before surgery, then diagnostic tests are performed, and if there are no signs of unresectable surgery and 3 cycles of chemotherapy after it. The regimens used are CF - cisplatin fluorouracil, and ECF - epirubicin, cisplatin, fluorouracil. This treatment can increase 5-year disease-free survival and generally prolong the life of patients with advanced gastric cancer.
- Adjuvant chemotherapy. This treatment is prescribed 4-6 weeks after surgery if no complications have arisen. Oral forms of fluoropyrimidine are used for 12 months or the XELOX (CAPOX) regimen for 6 months. If the tumor is HER-2 positive, treatment may be supplemented with trastuzumab.
For unresectable forms of stomach cancer, chemotherapy is the main treatment method. As the first line of therapy, regimens including platinum drugs and fluoropyrimidines are prescribed. Three-drug regimens that are supplemented with docetaxel improve overall survival but are more toxic. Therefore, they are prescribed only to healthy patients. If there are bone metastases, bisphosphonates (zoledronic acid) may be prescribed.
The first line of chemotherapy is carried out for 18 weeks, after which the patient is observed until the disease progresses. If it occurs within 3 months after the end of first-line chemotherapy, second-line drugs (taxanes) are used; if more than 6 months have passed after progression, first-line drugs can be used again. With a positive HER2 status, treatment is supplemented with targeted drugs.
In weakened elderly patients with concomitant diseases, gentle treatment is prescribed, and when their condition improves, they switch to the XELOX regimen. Symptomatic treatment is indicated for severely ill patients.
Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy is not used as an independent treatment method. For some time in the United States, adjuvant chemoradiation therapy was the standard of care for locally advanced forms of infiltrative cancer. But prospective studies have shown that this tactic does not improve the prognosis of patients, and the treatment is more toxic compared to adjuvant chemotherapy. Therefore, this approach is not currently recommended.
The main use of radiation therapy is palliative treatment to relieve symptoms of the disease. For example, it is used in the presence of bone metastases to reduce pain.
Symptomatic treatment
The following categories of patients are subject to symptomatic treatment:
- At stage 4 of the disease.
- Patients with locally advanced unresectable forms of cancer.
- Patients with severe concomitant pathology that makes it impossible to perform surgery or use cytostatics.
Symptomatic therapy is aimed at alleviating the patient’s condition and combating complications:
- Elimination of bleeding - often stomach tumors are complicated by heavy bleeding. Patients, in this case, experience vomiting of bloody or scarlet blood, melena in the stool. Endoscopic operations are performed to stop bleeding.
- Combating tumor stenosis - various technologies are used here, from stenting to bypass anastomoses and gastrostomy removal below the site of the lesion.
- Treatment of pain - drug therapy, regional anesthesia, radiation therapy.
- Treatment of ascites is intra-abdominal chemotherapy, laparocentesis, and installation of drainage.
Symptoms of gastritis
Gastric ulcer is a chronic disease caused by several causes, with the characteristic formation of ulcerative defects in various parts.
Structure of the stomach
The stomach is located between the esophagus and the duodenum. The organ has three sections:
- Cardiac – next to the esophagus.
- Pyloric – located close to the duodenum.
- Antral (prepyloric) - between the cardiac and pyloric sections.
In the body of the stomach, food is crushed and turned into pulp under the influence of hydrochloric acid. Food in the antrum is gradually mixed until a homogeneous mass is obtained, then it enters the pylorus and the duodenum.
A healthy stomach produces some hydrochloric acid necessary for digestion. With slow peristalsis, food is retained in the stomach. This increases the formation of hydrochloric acid, leading to irritation of the mucous membrane. Inflammation occurs, first gastritis, then an ulcer.
Most often, the disease is caused by a pathogenic microbe - Helicobacter pylori, which parasitizes the stomach. The microbe's enzymes produce ammonia, which reacts with hydrochloric acid, interfering with digestion. Bacteria multiply in the gastric mucosa, causing inflammation and later the formation of a defect.
Clinic
The main complaint of patients is pain that appears after eating food. Pain occurs from 20 minutes to 1.5 hours after eating, most often “in the pit of the stomach” - above the navel, in the epigastrium. The time when pain appears after eating depends on the location of the ulcer. The pain, which appears early, begins within 20-30 minutes after eating.
Early pain develops when the ulcer is located high - at the level of the cardiac region. The pain sometimes appears delayed, several hours after eating. This sign is typical in the presence of an ulcer in the pyloric area. Pain on an empty stomach appears with ulcers of the antrum and pylorus, caused by the aggressive effect of hydrochloric acid on the mucous membrane of an empty stomach. Acute pain is an ominous signal indicating the appearance of a complication - organ perforation. For ulcer bleeding, on the contrary, pain is not characteristic.
The location of the pain depends on the location of the ulcer. Pain from a cardiac ulcer appears in the pit of the stomach. Antral ulcers are characterized by pain to the left of the middle of the abdomen. With a pyloric ulcer, the pain is located on the right. It goes away after consuming dairy products, soda or medications that reduce the formation of gastric juice. Excess hydrochloric acid enters the esophagus, causing heartburn and sour belching.
The disease worsens in the spring and autumn with the attenuation of the clinic in the summer and winter. Simultaneously with the onset of pain, nausea and vomiting of eaten food occurs. After the end of vomiting, complaints of headaches are possible, the cause of which is a sharp outflow of blood. Appetite is not impaired, constipation appears periodically.
Gastritis is inflammation of the stomach lining. Because of this, the normal functioning of the gastrointestinal tract is disrupted, and an imbalance appears in its work. Gastritis, the symptoms of which we will discuss in detail, leads to the fact that food is digested much worse. Therefore, the patient may suffer from a deficiency of microelements and vitamins and begin to lose weight.
Such patients often complain of general weakness; they lack energy even to carry out their usual daily activities. Soon other organs and systems begin to suffer. Therefore, gastritis requires attention. It needs to be treated, not cured. It is important to know the symptoms of gastritis. As soon as you suspect something is wrong, it is better to immediately consult a gastroenterologist. We will explain in detail what gastritis is, symptoms, treatment and types of this pathology.
In fact, our general condition and the health of the gastrointestinal tract are directly affected by the food we eat daily. In urban conditions, unfortunately, both water and food are far from ideal and healthy. That is why the morbidity rates of the urban population are off the charts. The body tries with all its might to cope with food prepared using modern technologies from modern products.
Unfortunately, he succeeds with difficulty. A huge problem at the current stage of development of civilization is all kinds of “improvers” of our food. We eat foods that contain a huge amount of preservatives, dyes, flavor enhancers, stabilizers, etc. Even ordinary bread today cannot do without such “charms of civilization.”
Symptoms of gastritis of the stomach are very debilitating and exhausting for the body. But we can still help our stomach a little. The main thing is to improve your food culture. You need to make sure that your diet is balanced. It should consist of high-quality products with a minimum content of all kinds of additives.
It is best to eat about five times a day, in reasonable portions. This kind of nutrition is called fractional. It allows you not to overload the gastrointestinal tract and ensures normal metabolism. Believe me, the symptoms of gastritis are so unpleasant that you will soon want to give up harmful foods and alcohol yourself.
Some disappointing facts:
- According to statistics, since the middle of the 20th century, the total number of gastrointestinal pathologies has doubled;
- About 90% of the total population of civilized countries suffers from some kind of gastrointestinal disease;
- Gastritis remains the leader among gastrointestinal pathologies.
Symptoms of gastritis of the stomach bother almost nine out of ten people. Oddly enough, gastritis remains a disease that affects mostly the middle class of the population. Most of them are residents of large cities and so-called white collar workers. But the poorest segments of the population suffer more from terrible epidemics and infectious diseases than from gastritis. Therefore, gastritis, the treatment and symptoms of which we will consider in detail, bothers relatively wealthy people more.
Unfortunately, gastritis incidence rates continue to rise in developed countries. This is explained by the direct relationship between the level of income and the development of gastritis. The problem is that if the poor are forced to eat simple food in the form of cereals and soups, then the same “white collar workers” sin by constantly visiting fast food and regularly drinking alcohol.
Therefore, gastritis can also be perceived as a tribute to globalization. After all, the plant of the Earth is constantly growing, and it becomes more and more difficult to feed it. Therefore, food manufacturers regularly reduce the quality of their products. But in addition to objective factors, there are also subjective factors. This is our attitude towards our own health and nutrition.
Agree that we ourselves can control what products we consume – relatively safe or potentially dangerous. You should not chase the simplicity and attractive taste of fast food products or ubiquitous semi-finished products. It is better to spend a little of your time and effort, but prepare a healthy and fresh dish at home.
First symptoms
Gastritis of the stomach, the symptoms of which we list below, may be only the first link in a chain of diseases. Unfortunately, we begin to change something in our diet and general lifestyle only after we encounter the first symptoms of the disease. So, with gastritis, what symptoms should you be wary of? You should be concerned if:
- Constriction and a feeling of discomfort appear. This feeling intensifies immediately after eating and is observed in the epigastric area (this is the upper abdominal cavity).
- Pain appears in the same area.
- Heartburn or belching with a sour taste.
- A thick white coating appears on the tongue.
- Dyspeptic symptoms (stool upset, nausea and vomiting) are observed.
- The temperature may rise to 37.
Alone, these symptoms can still signal a simple disorder in the gastrointestinal tract. But if you notice a combination of several at once, this may signal the development of gastritis. In this case, it is better to immediately consult an experienced gastroenterologist. Do not underestimate the danger of this disease. Gastritis can be the starting point in a long chain of dangerous pathological conditions. Therefore, it is better to start treating it immediately.
Gastritis with varying degrees of acidity is also distinguished:
- normal;
- reduced;
- elevated.
Gastritis is acute. In this form of the disease, inflammatory processes in the gastric mucosa are most often caused by a single exposure to a certain irritant. Moreover, such an impact should be quite strong. This could be food poisoning or exposure to harsh chemicals such as medications.
Gastritis is chronic. This is a long-term pathological condition that developed in the patient over some time. In this case, a structural restructuring of the entire gastric mucosa is observed, as well as its gradual atrophy.
Do not underestimate the danger of gastritis! Of course, when the first signs appear, symptomatic treatment can be undertaken, and they will soon go away. But at the same time, the root cause that provoked the development of the disease will remain. It is very important to eliminate it so that there is no relapse of the disease. The danger also lies in the fact that if the treatment is incorrect, it can even provoke the development of ulcers and even cancer.
Causes
Acute and chronic gastritis may have different causes.
Causes of acute gastritis;
- eating low quality food. Moreover, it can be infected with dangerous microorganisms and contain hazardous substances;
- infection. Relatively recently, the bacterium Helicobacter pylori was identified, which most often provokes the development of gastritis. It has been scientifically proven that this bacterium provokes the development of gastritis with an increased level of acidity;
- if toxins have entered the stomach. Penetration of irritating chemicals into the stomach is very dangerous. They can quickly damage the mucous membrane and cause irreversible changes.
- strong alcoholic drinks (provided they are consumed regularly). Alcohol negatively affects the condition of the mucous membrane. He is annoying to her;
- a number of medications also have a bad effect on the stomach. First of all, these are drugs from the group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Indomethacin, Diclofenac, Ketoprofen, Acetylsalicylic acid, Ibuprofen, Aspirin);
- as a consequence of other diseases;
- dysbacteriosis;
- impaired metabolism.
Structure of the stomach
Characteristic signs of stomach cancer in women
- 1Clinical picture of the disease
- 2Local symptoms
- 3Manifestations in later stages
Cancer is a tumor that has malignant growth. The following factors may contribute to the development of the disease:
- bacteria Helicobacter pylori;
- toxic and chemical substances;
- some medications;
- radiation;
- alcoholism;
- the presence of ulcers and atrophic gastritis;
- overeating and lack of fresh fruits and vegetables in the diet.
Symptoms of cancer in the early stages are not always pronounced. They often resemble simple inflammation of the stomach. The tumor gradually increases in size. When it becomes large, a person’s well-being worsens. There are general and local symptoms of the disease. Common symptoms include loss of strength, weakness, decreased performance, and loss of body weight. In advanced stages of cancer, fever may occur.
All these signs are nonspecific. They are characteristic of any malignant tumor. At stage 1, there are no complaints about stomach problems. During this period, only the mucous layer is affected. In most cases, signs of the disease appear when the tumor grows into the submucosa.
2Local symptoms
Some experts highlight a list of minor symptoms of stomach cancer. It includes discomfort in the upper abdomen, bloating (flatulence), sudden loss of appetite, nausea, hypersalivation, heartburn. Their appearance is due to disruption of the stomach. Bloating occurs after eating. It is caused by the accumulation of gases in the abdominal cavity due to disruption of the digestive process.
When the upper part of the organ is affected, heartburn is a common symptom. The tumor can disrupt the process of moving the food bolus. Its delay can cause acidic contents to reflux into the esophagus. Heartburn is manifested by a burning sensation in the chest. It occurs when the esophageal mucosa is irritated. With prolonged heartburn, esophagitis may develop.
Local symptoms of stomach cancer in women include pain, difficulty swallowing, belching, and heaviness in the abdomen. The pain syndrome has no distinctive features. The pain can be different (aching, cramping, pulling, dull). Most often it is felt in the epigastric zone or hypochondrium on the left. At first, it bothers a person periodically, but then it becomes constant.
Its intensification may indicate tumor invasion of adjacent organs. Local symptoms are most pronounced when the antrum (located closer to the duodenum) of the stomach is affected. Cancer pain is often accompanied by nausea and vomiting. Sometimes nausea is accompanied by drooling. Vomiting indicates a violation of the process of evacuation of chyme from the stomach.
This happens when the tumor blocks the exit from the organ. Vomiting occurs after eating. In this case, the vomit contains food. In severe cases, vomiting occurs like coffee grounds. This is a sign of stomach bleeding. The appearance of such a symptom requires emergency help. Other manifestations of cancer in women include early satiety. The person eats very little. Normally, the feeling of fullness appears only after 20-30 minutes.
The appearance of this symptom is associated with a full stomach and retention of food in it. If the neoplasm is localized in the initial part of the organ, then dysphagia is observed. It manifests itself as difficulty swallowing food and even water. Many patients experience a change in taste preferences. It is possible to refuse meat.
The overwhelming majority of patients go to the hospital to see a doctor already at the 3rd or 4th stage of the disease. An experienced doctor can feel a large tumor through the abdomen.
At stage 3 cancer, more than 7 lymph nodes may be affected. Most often, nodes in the supraclavicular and axillary region are affected. Ascites develops. It is manifested by an increase in the volume of the abdomen. The reason is a disruption in the absorption of water and its accumulation in the abdominal cavity. Pale skin is a sign of advanced anemia.
Symptoms of intoxication are clearly expressed. Asthenic syndrome is manifested by severe weakness, insomnia, and chronic fatigue. Such sick women are unable to do their usual work. A serious complication of a stomach tumor is bleeding. It is observed during the germination of blood vessels. With gastric bleeding, vomiting with blood appears or the nature of the stool changes.
Stage 4 cancer always metastasizes. The following organs are most often affected:
- liver;
- lungs;
- bones;
- kidneys;
- pancreas.
In this situation, symptoms characteristic of damage to these organs are observed. The prognosis for stages 3 and 4 is disappointing. For stage 3 cancer, the five-year survival rate ranges from 15 to 40%. In a more severe case (stage 4 of the disease), less than 5% of sick women survive for 5 years. Thus, the clinical picture of stomach cancer in women is similar to other diseases (gastritis and ulcers). About 80% of patients visit a doctor at stage 4 cancer.
An experienced doctor should know not only the causes of stomach cancer, but also the symptoms of damage to one or another part of the organ. When the tumor affects the initial part of the stomach (cardia), the following clinical symptoms come to the fore:
- difficulty swallowing food;
- nausea;
- vomit;
- regurgitation of food.
Such symptoms appear due to difficulty in the passage of food from the stomach to the underlying sections of the gastrointestinal tract. Pyloric cancer is characterized by difficulty in evacuation of the food bolus. In this case, patients complain of pain after eating, heaviness in the stomach. Frequent symptoms are belching and vomiting.