Problems with the gallbladder are common today; stones often form in it. Representatives of the fair sex are more susceptible to this disease. Gallstone disease (GSD) is more often detected in overweight people and older age groups, but children almost never encounter this disease. If symptoms of gallstones appear, you should consult a doctor, get diagnosed and immediately begin treatment if the presence of the disease is confirmed.
What is gallstone disease
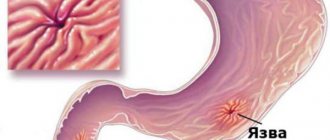
If stones (calculi) form in the gallbladder, its ducts or in the liver, this is cholelithiasis. There are two main factors that lead to the disease: stagnation of bile in the bladder and an increase in the concentration of salts due to impaired metabolism (precipitate precipitates from the bile). Stones can form in the bile ducts, in the liver. The stones have different shapes, sizes, composition, as can be seen in the photo. Sometimes gallstone disease causes cholecystitis, an inflammatory process of the gallbladder.
The main causative agents of their formation of stones include:
unhealthy diet (fasting, overeating, eating unhealthy foods);
- pancreatic diseases;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- bearing a child;
- long-term use of hormonal contraceptives.
- For the second stage, the formation of stones is considered normal: several small stones.
- The third stage of cholelithiasis is the chronic form of calculous cholecystitis. The gallbladder is filled with stones of different sizes, which can deform the bladder.
- Complicated cholecystitis is accompanied by the development of various pathologies.
- nausea, sometimes vomiting;
- bloating, constipation or diarrhea, stools lose color;
- increased body temperature;
- yellowing of the skin, mucous membranes;
- frequent belching of air, a feeling of bitterness in the mouth.
- biochemical blood examination;
- general blood analysis.
Gallstone disease is divided into stages of development (taking into account ultrasound results). The classification looks like this:
Initial (pre-stone) stage. It is characterized by the presence of thick bile and the formation of sand in the bladder. A suspension forms in the bile. This stage can still be reversed if you choose the right method of therapy and adhere to a healthy diet.
Symptoms of gallstones
Almost always, the appearance of gallstones does not have obvious symptoms or clinical signs. This period can last a very long time: approximately from 3 to 10 years. Symptoms of gallstones in women and men depend on the number of stones, their location and size. Signs of gallbladder disease are as follows:
severe, acute attacks of pain, colic under the ribs on the right side and near the liver;
Diagnosis of cholelithiasis
Correct timely diagnosis of urolithiasis (urolithiasis) is a necessary course of therapy and a chance to protect yourself from the consequences of a dangerous disease. There are several ways to detect gallstones:
Why are gallstones dangerous?
If you do not pay attention to the symptoms of gallbladder disease and do not get rid of the stones in a timely manner, then serious exacerbations may occur:
the occurrence of an acute form of inflammation of the walls of the gallbladder;
Complications
The formation of stones in the gallbladder is fraught not only with impaired motility of the diseased organ. GSD can have an extremely negative impact on the functioning of other organs, especially those that are in close proximity to the gastrointestinal tract.
Thus, the edges of the stones can injure the walls of the bladder, causing the development of inflammatory processes in them. In especially severe cases, neoplasms clog the entrance and exit of the bile, thereby complicating the outflow of bile. With such deviations, stagnant processes begin to occur, leading to the development of inflammation. This process can take from several hours to several days, but sooner or later it will definitely make itself felt. The extent of the lesion and the intensity of the pathological phenomenon may vary.
So, it is possible that a slight swelling of the gallbladder wall may form, or its destruction. The consequence of this dangerous process is rupture of the diseased organ. Such a complication of cholelithiasis directly threatens the patient’s life.
The spread of the inflammatory process to the abdominal organs is fraught with the development of peritonitis. A complication of this condition can be infectious-toxic shock or multiple organ failure. During its development, serious disruptions occur in the functioning of the heart, kidneys, blood vessels and even the brain.
If inflammation is too intense and pathogens release excessive amounts of toxins into the blood, ITS may appear immediately. Under such circumstances, even immediate resuscitation measures do not guarantee that the patient will recover from a dangerous condition and prevent death.
Treatment without surgery
Many people are interested in how to dissolve gallstones non-surgically, without medication. There are several effective methods that help eradicate the disease in the first stages of development, when the stones are small. These include a special diet, folk remedies and medications.
Diet
In case of serious gallstone disease, it is necessary to follow a divided diet: five to six times a day. Food allowed on a therapeutic diet has a choleretic effect; eating small portions by the hour promotes the release of bile. This diet is also a disease prevention measure. The menu of a person suffering from ICD must necessarily include animal proteins and products with magnesium. The diet for gallstones, like any other therapeutic diet, divides food into “possible”/“not allowed”. Allowed to eat:
lean meat, fish;
Products that are not recommended for consumption:
fatty meat, fish, liver, lard, offal;
Folk remedies
Treatment of cholelithiasis with folk remedies is aimed at two main goals: getting rid of an attack of colic, as well as preventing the formation of stones in the future. An effective technique for stopping an attack: you need to warm up the camphor oil a little, soak a piece of gauze, and apply it under the ribs on the right side. “Grandmother’s” recipes for removing stones from the gallbladder and for the outflow of bile:
Brew the herb and parsley roots. Drink a strong decoction in any quantity.
Tablets
If the gallbladder hurts, then it can be cured without surgery with special drugs - analogues of the acids found in bile (Henochol, Ursosan, Ursofalk, and so on). Along with this method of treatment, medications can be taken that activate the production of bile (“Holosas”, “Allohol”, “Liobil”). Drugs for the destruction of stones, which are prescribed by a gastroenterologist, are used if the stones are no larger than 2 cm in size. The duration of therapy is at least 6 months.
Treatment of gallstones without surgery
This method of removing gallstones involves physically crushing the formations using electromagnetic shock waves. In theory, this effect crushes the stones to small sizes (3 mm), at which the formations themselves are removed from the body. However, this treatment has its own characteristics:
- therapy is used only for asymptomatic cholelithiasis;
- suitable for crushing single cholesterol stones (maximum 3–4 pieces) with a diameter of up to 30 mm;
- depending on the size of the stones, 1–7 sessions may be required;
- the method is contraindicated in cases of clotting factor disorders, pancreatitis, ulcers and chronic cholecystitis;
- high risk of damage to the walls of the gallbladder, which leads to an inflammatory reaction;
- Most patients experience blockage of the bile ducts after such therapy.
Considering the high risk of complications, this method cannot be called promising.
Methods for removing stones from the gallbladder
When gallstones have grown to large sizes, such a diagnosis cannot be avoided without surgical intervention. Modern medicine offers options for removing stones from the body that are painless and provide more guarantees that the stones will not form again. Surgical intervention is performed according to certain indications. Today, doctors perform classic abdominal surgeries, laparoscopy, and crushing stones with ultrasound.
Operation
The presence of stones is not considered a reason for surgery. The surgeon prescribes it only when there are specific clinical symptoms: biliary colic, aching, dull pain, heaviness under the ribs on the right, frequent belching, bitter taste in the mouth, heartburn. Standard surgery (cholecystectomy) is often performed for emergency reasons. General anesthesia is performed. The patient's gallbladder is removed, and if necessary, the ducts are drained. The wound is sutured, a drainage is placed to the bladder bed.
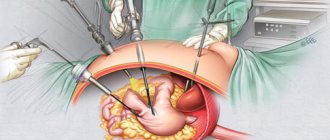
Laparoscopy
Recently, stones are often removed by laparoscopy. The stones are removed using trocars, special metal conductors inserted into the peritoneum. The abdominal cavity is filled with carbon dioxide, and a tube from a device is inserted into the incision, which will transmit the image to the monitor. The doctor pulls out the stones and installs staples on the vessels and ducts of the gallbladder. Indications for surgery: calculous cholecystitis.
Ultrasonic stone crushing
Gallstone diseases are sometimes the reason for referral for ultrasonic crushing of stones (lithotripsy). Ultrasound destroys stones, breaking them into small particles (no more than 3 mm). Small pieces exit into the duodenum through the bile ducts. This type of operation is suitable for those patients who have up to 4-5 large cholesterol stones.
Dissolving stones with medications
At an early stage, it is possible to dissolve gallstones with medication through a course of ursodeoxycholic and chenodeoxycholic acid. However, this treatment is not suitable for everyone, since the following conditions must be met:
- in the gallbladder there are only cholesterol formations up to 15 mm in size;
- stones fill no more than 50% of the gallbladder volume;
- the contractile response is normal, and the bile ducts are patent;
- the patient does not suffer from excess body weight and multiple concomitant pathologies;
- the patient has the opportunity to take prescribed medications regularly and for a long time (0.5–2 years);
- the patient complies with all medical recommendations regarding a healthy lifestyle and proper nutrition;
- Treatment is carried out only for asymptomatic cholelithiasis.
When the stones are still small, they can be removed with medication, but the disadvantage of this treatment is a large number of contraindications and low effectiveness (40–80%). The larger the stones, the more difficult they are to dissolve, as calcium nuclei appear.
There is also a high risk of relapse of the disease - 10-70%, to prevent which it is necessary to constantly follow a diet and take ursodeoxycholic acid in low doses as maintenance therapy.
Considering the high cost of drugs, for example Ursosan, a course of treatment for 1 year will cost approximately $550–600. And since the recurrence rate of cholelithiasis is very high, surgical removal of stones is more profitable.
Although surgery remains the main method of treating cholelithiasis, the development of medications to dissolve stones is becoming more promising.
There are no limits to the variety of folk remedies that promise to dissolve stones in the gallbladder. They are mainly associated with eating plant extracts that “resorb” stones.
Decoctions of knotweed and dill are considered means of rapid dissolution, and you can slowly get rid of the disease by consuming fresh vegetable juices and red beet decoction for months. Many also advise cleaning the gallbladder by using olive oil and apple cider vinegar.
The most harmless of all this are juices and dill water, which even newborns can drink. Research shows that by consuming dill throughout the summer, a person stimulates the cleansing of the gallbladder from small stones.
As for apple cider vinegar, you should not drink it if you have stomach diseases (gastritis, ulcers), and drinking the oil on an empty stomach will only cause severe vomiting in people with the dyspeptic form of cholelithiasis.
Reviews about the treatment
Anna, 34 years old After laparoscopy (removal of the gallbladder), I followed a strict diet for two years: nothing fatty, salty, spicy, smoked. Naturally, alcoholic beverages were excluded from the diet. Now I feel much better, I visit a hepatologist every year. So far I have no complaints about my health.
Ilya, 25 years old It so happened that almost all members of our family have problems with the gallbladder and kidneys. I was also “lucky” to inherit a housing complex. The operation was not needed; the doctor prescribed pills plus diet food, thanks to which the stones dissolved.
Tatyana, 62 years old. For a couple of months I suffered from pain under the ribs on the right side, nausea, and began to have problems with bowel movements. I decided to undergo examination by a gastroenterologist. It turned out that the gallbladder was filled with stones and sand. I got rid of the problem using ultrasonic crushing. Nothing to worry about yet.
A bile stone of any size is an unpleasant phenomenon. For men and women, the reasons for the appearance of gallstones are different, but for both sexes the following statement is typical: treatment of gallstone disease is a complex process, and it is not always possible to do without surgery.
Risk of complications
If you suspect gallstone disease, you should seek professional medical help. Specialists will conduct diagnostics to confirm the diagnosis, after which a course of therapy will be prescribed. Lack of timely measures can lead to the development of dangerous conditions, among which the following complications can be identified:
- Acute inflammation of the gallbladder.
- Rupture of the gallbladder.
- The addition of a secondary infection that can lead to the development of chronic diseases.
- Intestinal obstruction.
- Development of neoplasms in the gallbladder.
Causes of stones
The reasons for the formation of stones or the occurrence of acute attacks when stones form in the gallbladder ducts turn out to be different, each to a certain extent depends on the individual qualities of the patient, from medical history to genetics.
Among the most common reasons are:
- interruptions in food intake: first - overeating (the cause is often accompanied by nausea and vomiting), then, on the contrary, prolonged fasting;
- problems with excess weight, including obesity;
- sedentary work that does not allow movement during the working day;
- side effect of hormonal-based contraceptives;
- pathology of the pancreas.
The occurrence of stones in the gallbladder ducts is an unpleasant thing, not recognized in time, and provokes serious complications. For example, cholelithiasis can easily lead to biliary cirrhosis of the liver.
The composition of the stone stuck in the duct
Based on the nature of the pain, it is impossible to determine the composition of the stone that caused cholelithiasis. Cholesterol stones, for example, often contain an admixture of calcium, which is not fully processed in the body and is forced to be excreted through roundabout routes.
Sometimes lime gets into the stones - a rather rare phenomenon, but known. The presence of a substance in stones is determined using a diagnostic method - cholecystography.
Stones in the liver ducts often appear as a parallel disease: damage to the first organ of the excretory system leads to damage to the second. Of course, treating two diseases at the same time complicates the process; it is better to monitor the timely passage of stones in advance, preventing the appearance of new ones.
Stone formation: causes
The main ones include the body’s production of bile, which is oversaturated with cholesterol.
Such an illness can lead to the manifestation of other diseases in the body. This could be diabetes, anemia, colitis, cirrhosis and others. The most likely factors for the formation of stones are:
- Innateness.
- Inflammation in the ducts that remove bile.
- Obesity.
- Hemicolectomy.
- Pregnancy.
- Cholesterosis.
- Damage to the kidney parenchyma.
- Poor nutrition.
- Starvation.
- Flatulence.
- Use of certain medications.
- Pathologies in the endocrine system.
- Physical inactivity.
Specific symptoms
The first signs of gallstones are the same in men and women. In fact, already formed stones can remain in the gallbladder ducts for a long time, until some trigger mechanism causes the first symptoms of gallstone disease:
- the appearance of hepatic colic;
- the appearance of heaviness in the right side;
- bitter sensation in the mouth;
- belching, nausea, vomiting.
If the time of formation of gallstones is short, the first attack of exacerbation ends within 10-15 minutes; as the disease develops, an increase in the duration of the attack is observed. If the pain does not go away within half an hour, it is better to call an ambulance and provide first aid.
Are common
Signs of gallstone disease are the same for men and women, including symptoms:
- the appearance of heaviness in the abdomen or sides;
- change in skin color: some patients turn pale, others turn yellow and darken;
- increased pain after eating (it is difficult for the gastrointestinal tract to cope with the increased load, difficulties arise in digestion);
- nausea accompanied by heartburn and vomiting;
- changes in stool, excretion - profuse diarrhea or persistent constipation;
- If already digested food returns to the stomach, belching, heartburn, increased gas formation, and, in some cases, vomiting may occur.
Depending on the stage of development of the disease, the severity of symptoms and the duration of attacks during which the patient feels worse differ.
Typically masculine
Men suffer from gallbladder diseases 2 times less often than the opposite sex - the frequency is associated with different biological systems of the body, including the production of hormones. Symptoms of gallstone disease in men do not differ from the general classification; in women, certain nuances are known.
Typically feminine
It is believed that gallstone disease is more common in older women, especially those who are overweight. Symptoms of gallstones in women differ from those of the opposite sex. The pathology is indeed observed in older women, but changes in the body under the influence of the fetus play a significant role.
If a girl had a predisposition to developing the disease before pregnancy, difficulties with the functioning of the liver and problems with bile excretion are quite likely to occur. The occurrence of the disease during pregnancy is more dangerous; it is better to think about timely diagnosis and treatment as soon as possible.
Diagnosis of the disease
The diagnosis of gallstone disease is made on the basis of the symptoms listed by the patient to the attending physician at the first appointment. There are a number of procedures that are mandatory for diagnosis, helping to confirm or refute the diagnosis:
- general blood test (the clinical stage of the disease and the presence of inflammation are established);
- biochemical blood test (for liver stones, the activity of substances directly involved in metabolism is detected);
- cholecystography (helps determine whether the organ has increased in size);
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity (the most accurate analysis to determine the presence and size of stones, possible blockage of the ducts, cholecystitis is diagnosed and pathological complications are identified).
Only after a correct diagnosis has been established is it permissible to begin treatment.
Treatment of cholelithiasis
If the bile ducts are not able to clear themselves due to the patient's inaction, it makes sense to prescribe targeted treatment for gallstone disease. The main methods of combating stones in the gallbladder ducts include:
- Following a special diet.
- Taking special medications that allow you to dissolve stones directly in the internal organ. The drugs are harmless, apart from possible side effects due to contraindications: dissolved substances simply remain in the gallbladder or are excreted along with bile. There is no stone left that impedes the removal of bile; it is easier for the bile ducts to function. The disadvantages of this treatment include the ability to dissolve only small stones, not exceeding 1 cm, and the method does not stop the process of stone formation. After a year and a half of treatment, the stones appear again.
- Lithotripsy is the destruction of stones in an alternative way: using a strong shock wave created by special devices. It is used against cholesterol accumulations not exceeding 3 centimeters in size. The number of accumulations destroyed at a time is three; if there are more stones in the ducts, a different technique is prescribed. Thanks to such a forceful blow, accumulations of substances begin to be crushed into small grains that pass through the ducts with greater ease and are eliminated from the body in a completely natural way: urine and feces. The method does not cause pain and is carried out without hospitalization of the patient.
If the therapeutic course does not help, we are talking about surgery. There is no other way to free the ducts from excess substances and formations. In selected cases, it is necessary to remove the gallbladder; it becomes obviously clear that it is better to forget about the normal functioning of the organ.
Treatment goals include:
- cleansing the bile ducts;
- return to normal liver function;
- normalization of bile production in the body.
If, at the end of the course, the patient can safely say that digestion has improved and most of the unpleasant symptoms have disappeared, then the treatment was successful. However, a weakened body needs careful care; it is necessary to observe certain preventive measures. The postoperative regimen is prescribed by the doctor, according to the patient’s medical history, and general features are identified.
Preventive measures
After completion of treatment, preventing exacerbations, a special diet is prescribed, the products of which have a positive effect on the gallbladder and gastrointestinal tract without creating unnecessary stress. With gallstones and a high risk of recurrence of deposits, a person’s diet plays a huge role. The patient's condition depends on the type of food eaten.
Gallstone disease is an unpleasant disease, but the disease will recede if you start fighting in time and stop the subsequent occurrence of stones in the bile and hepatic ducts.
The gallbladder performs the functions of storing, concentrating and secreting bile. When bile stagnates, its components precipitate and turn into crystals, after which the gradual formation of stones occurs. This disease is most common among women over forty years of age. In men, the disease is less common. The reasons for the formation of gallstones are varied. What symptoms of gallstones serve as a signal of a progressive disease, we will tell you in this article.
Pharmacological treatment
During an attack of biliary colic, it is recommended to take non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or paracetamol to relieve pain.
If its intensity is strong, opioids are used: pethidine or pentazocine. Drugs with antispasmodic effects are used simultaneously, including papaverine and drotaverine.
In the treatment of patients who, due to contraindications, cannot be treated surgically, ursodeoxycholic acid can be used. It dissolves cholesterol deposits.
However, you should know that the diameter of the stones decreases by 1 mm per month of pharmacological treatment. Treatment is long-term (12-24 months), and its effectiveness is 50-70%.
Ursodeoxycholic acid cannot be used if the diameter of the deposits exceeds 15 mm, also in the case of dye-based stones, obese patients, with liver disease and during pregnancy.
Article for you:
Heartburn - how and what to treat at home
Signs and symptoms of the disease
The formation of gallstones is accompanied by a number of specific symptoms. Let's consider what symptoms are harbingers of cholelithiasis:
- stabbing and paroxysmal pain under the right rib;
- bitterness in the mouth;
- jaundice;
- nausea;
- belching;
- bloating;
- changes in stool (constipation, diarrhea).
Increased temperature, chills, and fever are also symptoms of the development of the inflammatory process and cholecystitis of the gallbladder.
Classification
Gallstone disease is divided into several stages:
- Physicochemical or pre-stone . This is the initial stage of the development of cholelithiasis. During its course, gradual changes occur in the composition of bile. There are no special clinical manifestations at this stage. The initial stage of cholelithiasis can be detected by conducting a biochemical study of the composition of bile.
- The phase of latent (hidden) stone bearing . At this stage, stones in the gallbladder or its ducts are just beginning to form. The clinical picture is also not typical for this phase of the pathological process. It is possible to identify gallstone neoplasms only during instrumental diagnostic procedures.
- The stage when the symptoms of the disease begin to appear brighter and more severe . In this case, we can talk about the development of acute calculous cholecystitis, or state the fact of its transition to a chronic form.
In some sources you can see a four-stage gradation of gallstone disease. The last, fourth, phase of the disease is characterized as such, during which concomitant complications of the pathological process develop.
Causes of the disease
The most common causes of the disease are:
- inflammatory process of the gallbladder;
- the content of bile in increased amounts of cholesterol, bile pigment and calcium serves to convert bile into water-insoluble bilirubin;
- genetic factor is one of the reasons for the formation of stones. The child is likely to develop gallstone disease if one of the parents has had it;
- treatment with drugs such as octreotide, cyclosporine, clofibrate;
- long intervals between meals and fasting foreshadow the formation of stones;
- Crohn's disease, cirrhosis of the liver and Caroli syndrome can lead to the formation of gallstones;
- when the lower part of the intestine is removed, stones form in the bile;
- drinking alcohol in large quantities causes the formation of stagnation of bile, as a result of which bilirubin crystallizes and stones appear.
One of the main reasons for the appearance of cholelithiasis is the intake of large amounts of fatty foods with cholesterol. Due to impaired nutrition, obesity develops, which is a secondary risk factor for the development of the disease. In addition, incorrect functioning of internal organs and liver function failure can negatively affect bile and subsequently lead to the formation of stones.
Stones appear when the walls of the gallbladder contract poorly. The causes of poor bladder contraction may include problems such as flatulence and dyskinesia. Surgeries on the gallbladder can also affect its proper functioning. Another reason may be pregnancy, during which the gallbladder becomes stressed and its functioning is disrupted. Cysts, tumors, adhesions, swelling of the bladder walls, congenital defects - all of this can serve as a factor contributing to stone formation.
Infections that enter the bladder through the lymphatic or bloodstream may be one of the causes of cholelithiasis. Inflammation of the gallbladder and its canals is caused by any infection that gets into it. In the future, this leads to cholangitis and cholecystitis, and subsequently to the development of cholelithiasis. In medicine, stone formation is divided into two types:
- primary – the formation of stones occurs slowly and without any signs for a long time;
- secondary – the cause of stones is congestion in the gallbladder.
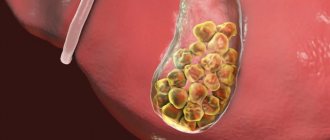
Bile contains various components and, therefore, the stones that form have a distinctive composition. Stones are classified into the following types:
- round cholesterol stones with a diameter of 16-18 mm;
- limestones containing large amounts of lime;
- mixed stones - have a layered structure, and sometimes have a cholesterol shell and a pigmented center, ranging in size from 0.1 to 5 cm;
- pigment stones - appear due to an increase in water-soluble bilirubin. They contain substances from calcium salts and bilirubin. In addition, there is a possibility that small bilirubin stones may appear in the bladder, which are located in the ducts and sac.
Pathanatomy
Gallstones are varied in size, shape, there can be different numbers of them (from one stone to hundreds), but they are all divided according to their predominant component into cholesterol and pigment (bilirubin).
Cholesterol stones are yellow in color and consist of undissolved cholesterol with various impurities (minerals, bilirubin). Almost the vast majority of stones are of cholesterol origin (80%). Pigment stones of dark brown to black color are formed when there is an excess of bilirubin in the bile, which happens with functional liver disorders, frequent hemolysis, and infectious diseases of the biliary tract.
Diagnosis of cholelithiasis
If the above signs are detected, you should consult a physician or gastroenterologist.
The doctor will draw up a general picture of the disease and determine the exact cause of its occurrence. When examining the patient, a general blood test for biochemistry, blood glucose levels, and an analysis of excrement are prescribed. Another way to determine the disease is an ultrasound of the liver and gallbladder. An ultrasound shows an enlarged gallbladder and the presence of stones in it. The presence of stones can be detected by the following echo signs:
- solids in the bladder;
- movement of stones;
- an increase in the thickness of the bladder wall by more than 4 mm;
- white mark on the bottom of the stone.
An X-ray of the abdominal cavity clearly identifies stones consisting of calcium salts. Cholecystography is also performed using contrast to better view the gallbladder. To detect cholecystitis, computed tomography is prescribed. And to identify the location of the stone in the bladder, endoscopic cholangiopancreatography is required.
Asymptomatic cholecystitis is common and lasts a long time. This form of cholecystitis is called chronically calculous.
In addition, another type of cholelithiasis is microcholelithiasis, in which stones with a diameter of 0.1-0.2 cm are present in the gallbladder. Such microliths can be detected through endoscopic ultrasonography. The cause of microcholelithiasis is jaundice, postcholecystectomy syndrome.
The main task of the differential diagnosis of cholelithiasis is to establish the reality of the disease, and not its similarity with any other diseases. Gallstone disease requires a scrupulous and serious approach, otherwise, if diagnosed untimely, it can cause harm to health, and in some cases, the consequences of cholelithiasis can put a person’s life at risk.
Gallstones: types and their composition
Cholesterol gallstones
Cholesterol stones, the most common type of gallstones, are either made entirely of cholesterol or are the main constituent of the stones. Gallstones, consisting only of cholesterol, are usually large in size, white or with a yellowish tint, soft, crumble quite easily, and often have a layered structure. Microscopically, pure cholesterol stones are represented by many thin long monohydrate crystals of cholesterol, which are interconnected by mucin glycoproteins with dark fibers consisting of calcium salts of unconjugated bilirubin
Mixed cholesterol stones contain more than 50% cholesterol and are somewhat more common than pure cholesterol stones. They are usually smaller in size and often multiple.
Pigmented gallstones
Pigment stones account for 10-25% of all gallstones in patients in Europe and the USA, but their frequency is much higher among the population of Asian countries. As with cholesterol stones, pigment stones are more common in women and are usually small, fragile, black or dark brown in color, and their incidence increases with age.
Black pigment stones
Black pigment stones consist either of a black polymer - calcium bilirubinate, or of polymer-like compounds of calcium, copper, and a large amount of mucin glycoproteins. Does not contain cholesterol. It is not possible to identify a clear crystalline structure in the stones. They are more often found in patients with cirrhosis of the liver, in chronic hemolytic conditions (hereditary spherocytic or sickle cell anemia, vascular prostheses, artificial heart valves, etc.). They make up approximately 20-25% of gallstones and can migrate into the bile ducts.
In the mechanism of formation of black pigment stones, a certain role is assigned to the supersaturation of bile with unconjugated bilirubin and changes in its pH.
Brown pigment stones
Brown pigment stones are composed primarily of calcium salts of unconjugated bilirubin (calcium bilirubinate, less polymerized than in black pigment stones) with varying amounts of cholesterol and protein included. The formation of brown pigment stones is associated with the presence of infection (cholecystitis, ascending cholangitis); microscopic examination reveals bacterial cytoskeletons in them. Stones can form both in the gallbladder and in the ducts, and in the latter they form more often than stones of other composition. In recent decades, a decrease in the incidence of pigmented gallstones has been noted, which many researchers associate with a decrease in the level of infectious diseases of the biliary tract.
Treatment
Depending on the number and size of stones, the treatment method is determined. Treatment is divided into 2 types: surgical and conservative.
Non-surgical
If stones are detected in the bladder, in many cases drug treatment is carried out without surgery. In such cases, according to the indications and prescription of the doctor, the following drugs are prescribed:
- ursofalk, lyobil (normalize the composition of bile);
- Creon (improves digestion, especially lipid absorption);
- plataphylline, drotaverine, no-spa, metacin, pirencipin;
- phenobarbital, zixorine (stimulate the secretion of bile acids).
In modern conditions, the following methods are used to treat the gallbladder and its ducts:
- dissolving stones with medications;
- invasive method (percutaneous cholelitholysis);
- crushing stones with ultrasound or laser.
Currently, drugs that actually dissolve stones are expensive and need to be taken for a long time without interruption. If you stop taking such drugs, the stones will form again, since the causes of the disease have not been eliminated. Dissolving stones with drugs is only 50% effective, for example, in patients with X-ray negative stones (not visible on X-rays). But if the stones are pigmented or X-ray positive, then it is difficult to achieve a positive result.
Surgical removal of an organ
There are two methods of cholecystectomy (organ removal):
The main method of removal is abdominal surgery (opening the abdominal cavity). This method is now rarely used, as complications subsequently arise after surgery. Laparoscopy is performed using a laparoscope apparatus, which consists of two parts:
- video camera that zooms in to large sizes;
- set of various tools.
The advantage of laparoscopy is the small incisions. After this procedure, the patient recovers quickly and there are practically no complications observed.
Indications for surgical removal of stones are:
- the volume of stones is over 33% relative to the gallbladder;
- frequent attacks in the form of colic that are not eliminated by medications;
- formation of blockage of the bile ducts.
Mandatory surgical treatment is resorted to for the following exacerbations:
- inflammation of the abdominal cavity (peritonitis). Here, surgery is necessary to remove the gallbladder and disinfect the abdominal cavity;
- narrowing of the bile ducts, which are formed during the inflammatory process. Due to the narrowing of the channels, the outflow of bile is difficult and stagnation begins;
- accumulation of pus in the gallbladder. When pus accumulates inside an organ, empyema begins, and if pus accumulates next to the organ, then such a disease is called paravesical abscess;
- the appearance of biliary fistulas - holes between adjacent organs and the gallbladder;
- biliary ileus (cholelithiasis).
It should be noted that, despite the stage of the disease, when choosing treatment, it is necessary to take into account age and possible side effects. Sometimes, due to drug intolerance, contraindications to drug treatment may occur. Treatment for cholecystolithiasis is selected depending on the situation, and only the attending physician can determine the method of treatment after a thorough examination.
Use of traditional medicine
Cholecystolithiasis is also treated with folk remedies. To dissolve the stones, you need to take a glass of hot water with the juice of one lemon squeezed into it. When using this method of treatment, the stones begin to slowly dissolve. You need to use this product for a long time. In addition to this, you can take other juices from:
- Cucumber, beets, carrots;
- Juice of parsley, carrots, celery.
To treat this disease, other means are also used, for example, tincture of pine nuts or a mixture of Borjomi mineral water and raisins with holosas.
Folk remedies help only if the gallstones are in small quantities and small in size, and the dissolution of large stones can cause rupture or blockage of the canals.
Nutrition
When the first signs of cholelithiasis are detected, the patient is recommended a special diet that must be followed continuously. This diet is called diet No. 5. Patients with gallstones should limit themselves to the following products: margarine, strong coffee, fatty meats, spicy seasonings, carbonated drinks, smoked products, canned meat and fish, alcohol, yeast baked goods, fresh bread, hard-boiled eggs, meat broths, fish, mushrooms, pickled foods.
Food for a patient with cholecystolithiasis is prepared by boiling or baking. You need to eat food 5-6 times a day. The diet should include as many vegetable oils and vegetables as possible. Vegetables absorb excess cholesterol.
Video on the topic:
Dietary recommendations
How to treat gallstones, symptoms and treatment without surgery, diet, which is a mandatory component of therapy prescribed by a doctor.
In the case of patients whose gallstones are asymptomatic, a rational diet is recommended. It is necessary to include fiber in the diet, as it improves the functioning of the intestinal tract.
In addition, in the liver it stimulates the production of chenodeoxycholic acid, which helps dissolve cholesterol deposits.
A good source of dietary fiber are vegetable and fruit salads, and bran (read about the benefits and harms of bran here). Particular attention should be paid to the hygiene of consumed foods to prevent food infections and diarrhea.
This can be facilitated by the consumption of food that has been stored in the refrigerator for a long time or has been reheated several times.
Diarrhea promotes the loss of salts in bile, and with their deficiency, the formation of cholesterol deposits occurs more easily.
First of all, avoid fried, fatty foods (meat and fish), smoked foods, eggs, fatty sour cream, mayonnaise, legumes, fried potatoes, chips, mushrooms, fried onions.
Avoid margarine, refined sugar, chocolate, whipped cream, puff pastry and cakes, wheat bread, coffee, alcohol, carbonated drinks, canned food and preservatives.
Eat 4-5 small meals a day and drink at least 2.5 liters of water. The menu may include vegetable soups, lean grilled or boiled meat, lean poultry without skin and lean fish (perch, pike perch, pike).
Add low-fat cottage cheese to the menu. For dessert, eat boiled fruits, fruit purees, juices and fruit salads. Drink fennel tea, apple, grape or orange juice.
Reducing the amount of fat in the diet reduces the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins, so the following foods should be included in the diet:
- rich in beta-carotene (pumpkin (butter), chard, broccoli, chicory, carrots, peppers, green lettuce, green onions, spinach, apricots, peaches, plums, cherries),
- vitamin D (fatty sea fish: salmon, mackerel, sardine, herring),
- vitamin E (green parsley, spinach, lettuce, asparagus, black berries (honeysuckle), nectarines, wheat bran, vegetable oils)
- vitamin K (spinach, lettuce, Brussels sprouts, green tea, cabbage, cauliflower).
Article for you:
Should you have periods during early pregnancy or not?
The following oils can be used in the diet: rapeseed, olive, sunflower, soybean and corn. Butter can be consumed in limited quantities.
Your diet should include foods rich in vitamin C. It has a beneficial effect on the immune system, stimulating it to produce antibodies that facilitate the treatment of inflammation. It contains parsley, red pepper, green pepper, Brussels sprouts, broccoli, cauliflower, spinach, black currants, strawberries, wild strawberries, kiwi, lemon, grapefruit, oranges.
Exercising when sick
If cholelithiasis is detected, you should limit yourself in physical activity. This also implies the exclusion of household physical activity. Physical activity during the course of the disease can help:
- rapid formation of bilirubin (this is dangerous for people with bile stagnation);
- movement of stones (if there are stones, then physical activity will move them out of place);
- likelihood of complications of cholelithiasis;
- complications after surgery.
According to the doctor's indications, daily 30-60 minute walks, gymnastics without stress on the abdominal area and sudden movements, swimming without diving are allowed. These loads are considered to prevent the occurrence of gallstones and also promote recovery after surgery. Professional sports involving heavy loads are prohibited for patients with cholelithiasis.
Prevention
To prevent the manifestation of stones, you need to lead a healthy lifestyle and eat right. You need to give up foods that are rich in cholesterol, do not fast for a long time, and stop taking medications that cause the appearance of stones.
If you follow a few simple vital rules, you can reduce the likelihood of stone formation:
- choose the right diet (excluding foods rich in cholesterol, enriching with vegetables and fruits);
- follow a diet (breakfast, lunch and dinner);
- reduce body weight if you are overweight;
- to live an active lifestyle;
- often spend time in the fresh air;
- fight infections in a timely manner;
- watch your stool (fight constipation);
- Be careful with hormone therapy.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_3x1Rpu0WDY