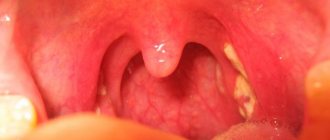
Diseases and pathologies that cause pain
The human esophagus has four layers (mucosal, submucosal, muscular, adventitial); if the function or integrity of at least one of them is impaired, a swallowing disorder occurs. The wall of the organ has nerve endings, but despite this, under normal conditions a person does not feel the movement of liquids and solid food through it.
Pain when swallowing occurs in the esophagus if a pathological process occurs in the tissues. What caused the pain when swallowing can be understood by identifying the accompanying signs:
- nausea and vomiting indicate gastrointestinal diseases;
- heartburn appears if the secretion of hydrochloric acid is increased and it penetrates the esophagus;
- regurgitation occurs with achalasia cardia, tumor, diverticula;
- weakness and pallor are typical if there is internal bleeding, for example, due to a burn or injury to the esophageal mucosa.
With this disease, the acidic contents of the stomach penetrate the esophagus, thereby causing inflammation of the mucous layer. The causes of the pathology are:
- the activity of the antireflux barrier is reduced (the esophageal sphincter relaxes frequently and for long periods of time due to deterioration of esophageal peristalsis);
- acidity in the esophagus is poorly regulated (the neutralizing effect of bicarbonates of esophageal mucus and saliva is reduced);
- decreased protective function of the mucous membrane;
- increased production of hydrochloric acid.
The disease is also indicated by symptoms such as heartburn, belching with sour or bitter smell of food, difficulty swallowing, cough, hoarseness, dry throat, caries, anemia, drooling. Reflux most often occurs when a person is in a horizontal position, so in most cases severe pain and burning is felt when the stomach and esophagus are at the same level (at night, when bending over).
To reduce the likelihood of hydrochloric acid entering the esophagus, it is recommended to sleep with the head of the bed raised by 10–15 cm. If the inflammatory process has begun, then it takes time to restore the mucous tissue. During this period, it is necessary to avoid coarse, spicy, sour, salty, pickled foods, as they greatly irritate the mucous membrane, which causes a burning sensation when swallowing.
The severity of pain is influenced by the stage of the disease. In severe cases, pain may occur even when swallowing water or saliva. The pain syndrome is localized behind the sternum or in the area of the xiphoid process, but can radiate to the back, neck, upper esophagus, collarbone, jaw.
Poultry or fish bones, cartilage, and nut shells can get stuck in the esophagus. Sometimes surgeons remove small objects, such as pins, coins, buttons, and paper clips. Most often, objects are swallowed by children 1–3 years old, which is facilitated by the underdevelopment of the dental system, swallowing insufficiently chewed food, insufficient innervation of the laryngopharynx, and inattention.
The most dangerous are large foreign bodies and sharp objects that get stuck, which can injure or puncture the esophagus. If stenosis of the esophagus occurs, then food begins to get stuck in it, which under other circumstances would easily reach the stomach (this happens if a child is fed and does not pay attention to the fact that it hurts to swallow).
Once inside, a foreign body injures the tissues of the esophagus, which leads to the development of an inflammatory process and increases the risk of bacterial infection. The patient experiences a sensation of a lump in the throat, salivation increases, and pain becomes more intense when swallowing.
Symptoms depend on where the foreign body is stuck in the esophagus:
- if something is stuck in the cervical part of the organ, then the person is forced to tilt his head down and slightly forward, refuses to eat, experiences pain when swallowing, vomiting may begin, and drooling appears. If the object is sharp, then blood is visible in the saliva, and if it is large, then breathing difficulties appear;
- when something swallowed is stuck in the chest part, the clinic is less bright. The esophagus hurts severely when swallowing, the sensation spreads to the area between the shoulder blades or to the arm;
- a foreign body stuck in the diaphragmatic part causes girdling or epigastric pain. Trying to eat solid food results in vomiting. Drooling is not typical.
On the second day, the patient's condition worsens due to the inflammatory process.
Burns can be chemical or thermal. In the first case, the digestive tract was exposed to chemicals, alkalis, acids; in a thermal burn, the mucous membrane was burned by too hot food. Pain occurs along the entire esophageal tube, as well as in the oral cavity, pharynx, and stomach.
It appears immediately after swallowing substances, so making a diagnosis is not difficult. Clinical symptoms are pain, vomiting with blood and mucous particles, drooling, difficulty swallowing, pallor, fever, low blood pressure, weak pulse.
Children often get chemical burns after tasting vinegar or ammonia or household chemicals. The most dangerous are alkalis used in everyday life; detergents with ammonia, bleaching or disinfectants, and some medications are slightly less harmful. Acid is more harmful to the stomach lining than the esophagus.
If you receive a burn, immediate use of corticosteroids and broad-spectrum antibiotics is necessary. Even with timely medical care, strictures and non-healing bleeding areas can form on the esophageal mucosa over a long period of time (even years).
With a diaphragmatic hernia, the abdominal organs move through the resulting defect or through the enlarged opening of the diaphragm. A hernia appears due to the weakness of the tissues connecting the sections of the diaphragm and increased intra-abdominal pressure (due to hacking cough, severe vomiting, physical exertion, constipation, etc.).
The severity of symptoms depends on the diameter of the hernial orifice, the location of the hernia and its shape, as well as the prolapsed organs. Pain appears not only when swallowing, but also when turning the body. They are intense, often radiating to the left arm, back, and lower jaw.
If the hernia is large, then pain may also be felt in the spine. The clinical picture of the disease is complemented by a feeling of heaviness in the pit of the stomach, shortness of breath, palpitations, and rumbling in the chest area.
What is a sore throat with acid reflux?
Heartburn is the most common symptom associated with acid reflux, but 20 to 60 percent of people develop heartburn symptoms without heartburn.
The most common symptom of sore throat associated with acid reflux is a swelling in the throat.
- angina
- suffocating sensation and tension in the throat.
- chronic cough
- constant throat clearing
- food sticks to throat
- halitosis
- hoarse voice
- burning sensation in the mouth.
- a sour taste, like a mixture of saliva and acid, known as water sass.
- red and irritated voice box
- feeling of mucus in the throat or postpartum drip.
Head and neck symptoms associated with acid reflux can be misleading. For example, chronic sore throat caused by acid reflux is sometimes misdiagnosed as recurrent or chronic tonsillitis.
Laryngeal pharyngeal reflux
When stomach acid hits the vocal cords, significant inflammation can occur. If this happens repeatedly, it can lead to hoarseness, frequent clearing of the throat, coughing, or a feeling that something is stuck in the throat.
These symptoms are sometimes called laryngeal pharyngeal reflux (LPR).
Scientific opinion is divided as to whether PPR is a symptom of acid reflux or is a separate medical problem.
LPR often begins as an upper respiratory tract disorder with symptoms that can linger as a result of irritation of the vocal cords by even small amounts of acid reflux.
Singers, teachers, and people who have to use their voice extensively every day may experience more severe symptoms of sore throat caused by acid reflux.
Diagnostics
A doctor will be able to find out why there is pain in the esophagus when swallowing after conducting the necessary tests. At the initial examination, the gastroenterologist will collect anamnesis, ask in detail about the intensity of pain, its nature, duration, time of occurrence, and palpate the abdomen to check for pathologies in the abdominal cavity.
Instrumental diagnostic methods will help to examine the wall of the esophagus and stomach, as well as evaluate their motor function. The doctor prescribes:
- X-ray examination;
- fibrogastroduodenoscopy;
- daily pH-metry;
- manometry (test with water);
- ultrasound examination.
If a tumor is detected, a biopsy is performed, and the tissue is sent for histological examination, which will determine whether the cells are malignant.
Doctors' answers
To establish the cause, examination and palpation of the abdomen is very important. Most likely, you have chronic gastritis in the acute stage. BUT problems with the pancreas, reflux-esophagitis, and ulcers cannot be ruled out. Without a full examination (ultrasound of the abdominal cavity, biochemical and general blood tests, FGDS), this cannot be established.
The fact is that omez doesn’t help, maybe it’s gastritis with low acidity? What are its symptoms and what is the treatment?
You can NEVER determine from your symptoms whether there is high or low acidity in the stomach or what type of gastritis you have. I repeat once again - for this purpose it is given to do FGDS and, if necessary, pH measurements. Hypoacid gastritis develops quite rarely and often leads to gastric atrophy. It is treated comprehensively and treatment depends on the cause.
Consultation is available 24 hours a day
We need to know your opinion. Leave a review about our service
Treatment
Self-treatment in the event of pain in the esophagus is unacceptable, since very serious complications can develop, including narrowing of the organ and perforation. In most cases, surgical intervention is required (for neoplasms, detection of a foreign body, hernia).
If the cause of pain is a burn to the mucous membrane, then gastric lavage is necessary, and in severe cases, bougienage (insertion of a special instrument to dilate the esophagus). For severe pain, anesthetic drugs will help: Novocaine, Anestezin, Lidocaine. Heartburn will go away after taking medications that protect the mucous membrane from irritation (Almagel, Simethicone).
Relieves spasms No-Shpa, Nitroglycerin. When taking antacids, proton pump inhibitors, H2 blockers, the production of hydrochloric acid decreases. If peristalsis and spasms are reduced, prokinetics, antispasmodics or calcium channel blockers are prescribed.
Tissue regeneration will happen faster if you follow a diet that excludes any rough, spicy, sour foods, and also give up alcohol and smoking. It is necessary to eat in small portions and preferably pureed food, steamed or boiled. At the first opportunity, you should visit a doctor to find out the cause of pain in the esophagus and receive adequate medical care.
Pain when swallowing in the esophagus indicates impaired functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, which entails a lot of other symptoms and discomfort. When a person is experiencing pain when swallowing in the esophagus, in no case should you self-medicate; you should immediately go for a consultation to a hospital, where qualified specialists can identify and eliminate the true cause of the pain.
Causes
It is quite difficult to name specific reasons that can lead to the development of a disease such as reflux esophagitis, since they are diverse and can be caused by both disruption of the normal functioning of internal organs and systematic exposure to negative external factors on the body. For example, among the most common causes of GERD are the following:
- Constant pressure placed on the stomach, which can occur as a result of pregnancy, when the growing uterus literally compresses the internal organs, or when there is a sufficiently large number of extra pounds.
- Long-term systematic use of certain types of medications, which include antihistamines, antibiotics, anesthetics, that is, pain relievers, and many others.
- Presence of bad habits: drinking drinks containing alcohol, smoking, eating fatty, spicy foods, canning. In addition, this item can include a systematic violation of the diet, expressed in irregular food intake, or in one-time intake in large quantities.
- The presence of pathologies of internal organs, namely the gastrointestinal tract. It is the presence of pathologies in the activity of these systems that provokes the release of stomach contents into the esophagus, leading to damage to the mucous tissues.
GERD develops as a result of problems with the gastrointestinal tract
Esophagitis
Pain in the esophagus when swallowing, or, as this condition is called in medicine, dysphagia, is a consequence of esophagitis, an inflammatory pathology that affects the mucous membrane of the esophagus. The disease can occur in acute, chronic, catarrhal, erosive, hemorrhagic, necrotic and pseudomembranous forms.
Experts have identified a number of factors that cause esophagitis:
- Irritation from hot or cold food;
- Alcohol abuse;
- Acid, alkaline burns;
- Probing;
- Prolonged vomiting;
- Infectious lesions;
- Allergy to certain foods;
- Severe intoxication.
The initial stage of the disease does not show obvious symptoms. A person occasionally experiences slight discomfort in the esophagus during swallowing.
When the disease takes on an acute form, esophagitis is expressed by:
- Burning pain that radiates to the back, sometimes to the neck;
- Increased salivation;
- Swallowing disorder;
- Bloody vomiting.
If you experience pain in the esophagus when swallowing and other symptoms appear, you should go to the hospital to avoid unforeseen consequences.
The chronic form of the disease manifests itself:
- Heartburn;
- Burning behind the sternum;
- Belching with an unpleasant aftertaste;
- Difficulty breathing;
- Bronchial asthma;
- Mild pain in the esophagus when swallowing.
Depending on the form of esophagitis, the patient is prescribed inpatient or outpatient treatment, including:
- Special diet;
- Antacids;
- Medicines that relieve heartburn;
- Agents that neutralize excess stomach acid.
In severe cases, doctors resort to surgery.
GERD
Esophageal pain after swallowing is caused by gastroesophageal reflux disease. The disease provokes the release of stomach acid into the esophagus, which is not adapted to such aggressive chemical influences. The walls of the organ begin to become inflamed, ulcers form on them, which causes excruciating pain when swallowing.
Among the causes of GERD are:
- Improper diet;
- Problems with excess weight;
- Poor gastric motility;
- Problematic saliva production;
- Regular stressful situations;
- Excessive loads;
- Stomach pathologies.
It is simply impossible not to notice the symptoms of the disease. GERD manifests itself:
- Pain in the esophagus, larynx and chest after swallowing;
- Constant heartburn;
- Unpleasant belching;
- Cardiac arrhythmia;
- Asthmatic attacks;
- Cough;
- Burning stomach.
This disease is a very dangerous disease, so at the first sign of symptoms you should immediately go to the hospital.
To get rid of pain when passing food caused by GERD, an individual treatment program is necessary. It is prescribed by specialists based on the diagnostic results obtained.
Therapeutic methods include:
- Special diet;
- Physiotherapeutic procedures;
- Antacids;
- Prokinetics.
Achalasia cardia
Another cause of pain in the esophagus when swallowing food is achalasia cardia - impaired motility of the esophagus. To be more precise, the disease is a poor reflex opening of the opening between the esophagus and the stomach, as a result of which complete swallowing does not occur.
Often, achalasia cardia is diagnosed in people over 20 years of age. Unfortunately, to this day scientists have not been able to figure out the causes of the disease.
The main signs of the disease include:
- Impaired swallowing;
- Retention of food in the esophagus;
- Vomit;
- Painful sensations behind the sternum;
- Difficulty breathing;
- Suffocation;
- Cough;
- Significant weight loss.
Initially, difficulty swallowing occurs periodically, resulting from severe stress or hasty eating. But over time, the pain becomes regular, preventing a person from drinking even liquids. Esophageal vomiting is becoming more common, making life unbearable.
Due to the danger of the disease, doctors recommend seeking medical help when the esophagus hurts when swallowing.
Treatment of achalasia cardia consists of three methods:
- Balloon dilatation;
- Botulinum toxin injections;
- Surgical myotomy.
Doctors also recommend avoiding psychological stress, giving up physical activity and unhealthy diet, because a healthy lifestyle is the key to happiness.
Dermatomyositis
Pain in the stomach when swallowing food is caused by dermatomyositis, an inflammation of the connective tissues. The disease can occur as an independent disease, or as a consequence of tumor neoplasms.
Experts have identified some factors contributing to the development of dermatomyositis, including:
- Hereditary predisposition;
- Infectious lesions;
- Various injuries;
- Psychological stress;
- Frequent hypothermia;
- Allergic reactions.
This disease has similar symptoms to other diseases, so you should promptly seek advice from medical institutions.
Dermatomyositis manifests itself:
- Pain in the esophagus and stomach when swallowing;
- Poor passage of food;
- Decreased appetite;
- Peculiar abdominal pain.
Before starting treatment, the patient will have to undergo a number of procedures, including medical history, biochemical and immunological studies, electromyography, magnetic resonance imaging, biopsy, etc.
Treatment of dermatomyositis is a complex process, which is based on:
- Glucocorticosteroid hormones;
- Cytostatics;
- Immunoglobulin injections;
- Plasmapheresis;
- Vitamin complex.
If dermatomyositis is diagnosed as a secondary disease, therapy will consist of treating the primary disease.
Esophageal carcinoma
Pain occurs when swallowing in the esophagus due to a malignant neoplasm. Cancer is the eighth most common cancer, affecting women and men equally.
Among the most common types of the disease are squamous cell carcinoma, which arises from the epithelial cells of the mucous membrane, and adenocarcinoma, which develops from the glands of the organ.
Doctors have identified several factors contributing to the development of esophageal cancer:
- Vitamin deficiency;
- Chronic diseases of the organ;
- Tobacco smoking;
- Alcohol abuse;
- Various internal burns.
The main sign of a tumor is pain in the esophagus during swallowing. At first it is difficult for a person to swallow solid food, but over time it becomes painful to take a sip of water.
The disease also manifests itself:
- Pain in the central part of the chest;
- Vomiting, sometimes mixed with blood;
- Hoarseness of voice;
- Weight loss;
- Black feces.
Small tumors are removed surgically. This is followed by chemotherapy and radiation therapy.
In advanced stages, a stent is installed in the patient - a special tube that allows food to pass through, the esophagus is dilated using bougienage, and radiation therapy is prescribed.
Chemical burn
In the throat and esophagus, pain may indicate a chemical burn, which occurs due to neglect or loss of self-control.
With a chemical burn, not only the esophagus hurts when swallowing, but also the sternum, stomach, shoulder blades, collarbone, and neck. It all depends on the degree and form of the lesion.
Among the auxiliary signs are:
- Visual changes;
- Hoarse voice;
- Swelling of the mucous membranes;
- Shortness of breath;
- Vomiting;
- Intestinal spasms.
If the burn is caused by caustic substances, fistulas will form, which will lead to general malaise or loss of consciousness.
To eliminate pain when swallowing caused by a burn, therapeutic procedures are performed, including:
- Washing;
- Drugs that relieve spasms;
- Medicines to relieve shock;
- Antibiotics;
- Hormonal.
Relationship between stomach and throat pain
It is important to know whether swallowing itself or the passage of food through the alimentary canal is painful.
ARVI or bacteria can cause a sore throat. But if there is a lump in the throat, food gets stuck in the esophagus, nausea and a gag reflex appear, this is a serious symptom and requires immediate medical attention. Problems with ailments that cause inflammation can be the cause of the following diseases:
- reflux esophagitis;
- hiatal hernia;
- allergic conditions;
- organ atony;
- spasm of the esophageal tube;
- esophageal achalasia.
Reflux esophagitis
With reflux esophagitis, particles of gastric juice enter the esophagus, irritating the pharynx.
After chewing, food is sent to the gastric region for digestion. To prevent food from returning to the esophagus, the junction between the two sections is closed with a valve, which should fit tightly to the walls of the mucous membrane and act as a “door”. When it is imbalanced, a hole is formed that is no longer able to protect the mucous membranes of the upper parts of the digestive system. With intra-abdominal pressure, fine particles of acidic gastric juice rise up the esophagus, irritating the throat. The tongue is covered with a white coating, the throat is red. A burn occurs, which becomes inflamed with each new ejection, and over time degenerates into serious pathologies, for example, ulceration.
Hiatal hernia
The diaphragmatic muscle lies between the abdominal and thoracic cavities. The esophageal tube passes through a small hole in it. Ligaments and connective tissues hold organs together. With strong intra-abdominal pressure or other anomalies, the walls of the esophagus or stomach protrude into the chest area. The disease is common in gastritis and is often asymptomatic. However, without proper treatment, the pressure in the walls increases over time, increasing the deflection of the hernia and rocking the pylorus. The sphincters weaken their work and bile and acid leak into the esophagus, followed by inflammation of the walls of the mucous membranes.
Allergic conditions
Laryngeal stenosis may be a symptom of seasonal allergies.
A clear sign of a sore throat is any type of allergen, including seasonal allergies. Symptoms of its manifestations are:
- feeling of coldness in the throat and esophagus;
- itching and cough with watery eyes;
- laryngeal stenosis;
- shortness of breath with lack of air.
- sneezing.
Organ atony
Violation of peristalsis of the muscular layer of the stomach leads to disruption of its functions. This happens for reasons:
- asthenia;
- strong and prolonged neuroses;
- lesions of the sheath of nerves enveloping the stomach or adjacent to it.
Esophageal tube spasm
With severe anxiety, pathological impulses from the center of the brain travel along the nerve endings to the walls of the esophagus and cause muscle spasm of the tissue. Motor skills are not affected. Stenosis of the larynx and food-conducting pathways occurs for the following reasons:
Psychological illnesses can lead to spasm of the esophageal tube.
- Nervous stress: psychological diseases;
- emotional stress;
- mental disorders in a growing organism.
- burns of the esophageal membrane;
Esophageal achalasia
A decrease in the tone of the esophagus and its peristalsis occurs due to neuromuscular disorders. The cardia is in constant tension and does not relax when swallowing food. This makes it difficult to push the bolus of food through the tube into the stomach. Causes of pathology:
- ARVI;
- lack of B vitamins;
- congenital pathologies of the nerve fibers of the esophagus;
- trauma at the neuropsychic level.
Summarizing
If a person experiences pain in the esophagus when swallowing, they should immediately go to the hospital for diagnosis and appropriate treatment. After all, only a highly qualified specialist will be able to determine the true cause of pain when swallowing in the esophagus. And also do not forget that self-treatment can lead to serious complications in the form of incurable diseases.
Found an error? Select it and press Ctrl+Enter.
Odynophagia is a medical term that describes pain in the esophagus when swallowing. Since it is impossible for food to enter the stomach normally without swallowing, any disorders can lead to exhaustion.
In fact, swallowing involves not only the muscles of the pharynx, but also the entire esophagus. Therefore, pain can occur in the throat, sternum, and upper abdomen. The source of the development of pain when swallowing in the esophagus lies either in mechanical damage to the muscles or in neurological abnormalities.
Possible causes of pain when swallowing
Pain in the esophagus when swallowing food may not be directly related to the swallowing reflex. Only a gastroenterologist can make a final diagnosis and prescribe treatment, so you should not try to use the information below for self-diagnosis. The causes of pain in the esophagus when swallowing can be associated with both gastrointestinal diseases and mechanical damage.
There are 5 most common triggers:
Bacterial and viral infections that affect the mouth, throat, or entire esophagus can cause pain when swallowing. For example, acute or chronic stomatitis, tonsillopharyngitis make the process of contracting the muscles of the pharynx and upper esophagus very painful.
- Presence of a foreign body.
If pain in the esophagus occurs during the passage of food, and not during swallowing, then the cause is more likely to be a stuck foreign body. Foreign objects or particles of solid food that do not reach the stomach can partially or completely block the passage of food through the esophagus.
The presence of a foreign body may be indicated by an additional symptom such as difficulty breathing. Sharp objects (such as fish bones) can scratch the soft walls of the esophagus, which can also make the passage of food painful.
- Inflammatory processes.
Inflammation of the epiglottis (epiglottitis) and inflammation of the esophageal tube (esophagitis) are fairly common causes of pain in the esophagus when swallowing food. Additionally, the patient may notice dysphagia (impaired swallowing) and expectoration of pus. How to eliminate pain in the esophagus when swallowing, the causes of which are already clear, we will consider further.
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease.
But the most common reason why the esophagus hurts when eating is reflux disease. Unpleasant sensations arise due to regular regurgitation of gastric contents, including acid into the distal part of the esophageal tube. In the early stages of the disease, unpleasant symptoms can only be felt in the morning: pain in the esophagus appears even when swallowing saliva.
- Tumors, cancers.
Fortunately, malignant diseases are not a common cause of deviation. However, if you feel like something is pressing in the esophagus when swallowing (perhaps even without acute pain), then you need to contact an oncologist.
It is likely that a benign or malignant tumor on the wall of the esophageal tube is interfering with the normal passage of food. Sudden weight loss may indicate cancer. Smokers, as well as people who have suffered from other types of cancer, are at risk.
Traditional medicine for aching pain
To get rid of aching pain in the upper part of the stomach, it is not necessary to use chemicals, because in folk medicine there are many methods to relieve the symptoms of the disease. It is worth using a simple and common method - a warm compress.
You need to heat the water, soak a cloth in it, and then apply it to the area that hurts the most. It is advisable to carry out this procedure in the morning or evening.
After regular procedures, nausea will go away, belching and heaviness will disappear, the stomach will seem to become light, and the lump in the throat will go away on its own.
You can treat aching pain with herbal teas, decoctions, and infusions.
Cumin decoction
Compound:
- 1 tsp. seeds;
- 1 glass of water.
Preparation:
- place cumin seeds in water;
- bring the broth to a boil;
- remove from the stove;
- cool to room temperature;
- strain;
- drink 0.5 cups in the morning and before bed.
Chamomile tea
Compound:
- 1 tbsp. l. chamomile flowers (dry, fresh);
- 1 glass of water.
Preparation:
- bring water to a boil;
- pour boiling water over chamomile;
- leave for 20 minutes;
- strain;
- drink 4 times a day before meals, 0.5 cups;
- You need to make tea immediately before drinking, preferably in the morning;
St. John's wort tincture
Compound:
- 4 tbsp. l. St. John's wort;
- 0.5 l of vodka.
Preparation:
- place the herb in a glass jar;
- pour vodka;
- leave for two days;
- Dilute 30 drops of infusion with a glass of water, drink half an hour before meals 3 times a day.
Compound:
- 1 tsp. plants;
- 200 ml boiling water.
Preparation:
- pour boiling water over the plant;
- leave for half an hour;
- strain;
- consume 3 times a day, 1 tbsp. l.;
- The infusion has analgesic properties, so it is an excellent substitute for pills; it is best to drink it in the morning.
Experts also recommend going to the gym. Therapeutic exercise will help tighten muscles, restore your back and improve your health. Of course, you shouldn’t get involved in sports at first, so as not to aggravate the situation.
Aching pain in the stomach, in its upper region, nausea and heaviness can cause deterioration in performance and general health. If a person faces such a problem regularly, it is imperative to seek help from a specialist and not start treatment on your own.
Ignoring the problem can only make it worse, which may require medication or surgery.
As usual, most people, when pain occurs in the upper region of the gastrointestinal tract, are in no hurry to consult a specialist. Many people begin treatment with painkillers, especially if discomfort, a lump at the top of the throat, nausea, belching, or heaviness appears only in the morning and does not bother them during the day. A constant and unpleasant lump in the throat is not taken seriously, and for self-medication, those drugs that are at hand are used.
If discomfort occurs regularly, and not just in the morning, then the reasons may be different, including the manifestation of inflammatory processes in the stomach and intestines. If the pain is concentrated only at the top, then a simple ultrasound of the abdominal organs can show accurate results. Spasms that radiate to the back may indicate a problem with the liver or kidneys; it is strictly forbidden to trigger such a condition. In this case, painkillers will be useless, and self-treatment will only worsen the problem.
If pain in the upper part of the esophagus and nausea do not leave a person for several days, concentrating in one area, then you should definitely consult a doctor. If a specialist suspects diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, tests will be required to help identify the cause.
The daily diet should be as balanced as possible. A person should eat small meals 5 times a day. Dairy products help relieve the causes of pain due to their gentle effect on the stomach. If pain occurs at the top of the esophagus, then you need to pay attention to the level of stomach acidity. The specialist prescribes a number of drugs that neutralize hydrochloric acid, thereby eliminating heartburn.
To get rid of aching pain in the upper part of the stomach, it is not necessary to use chemicals, because in folk medicine there are many methods to relieve the symptoms of the disease. It is worth using a simple and common method - a warm compress. You need to heat the water, soak a cloth in it, and then apply it to the area that hurts the most.
It is advisable to carry out this procedure in the morning or evening. To keep the temperature of the compress warm for a long time, the fabric can be wrapped in cling film or a towel. It should be noted that the water for compresses should be made comfortable so that it is not too hot or cold. After regular procedures, nausea will go away, belching and heaviness will disappear, the stomach will seem to become light, and the lump in the throat will go away on its own.
You can treat aching pain with herbal teas, decoctions, and infusions.
St. John's wort tincture
To get rid of aching pain in the upper part of the stomach, it is not necessary to use chemicals, because in folk medicine there are many methods to relieve the symptoms of the disease. It is worth using a simple and common method - a warm compress.
You need to heat the water, soak a cloth in it, and then apply it to the area that hurts the most. It is advisable to carry out this procedure in the morning or evening.
After regular procedures, nausea will go away, belching and heaviness will disappear, the stomach will seem to become light, and the lump in the throat will go away on its own.
St. John's wort tincture
Treatment of the main causes and symptoms of odynophagia
To treat odynophagia, medical professionals use a two-step approach. The essence of the method is that before identifying the underlying disease that provoked pain in the esophagus when eating, treatment is aimed at eliminating or reducing the intensity of unpleasant symptoms.
Regardless of the exact diagnosis, anyone who experiences discomfort in the esophagus when swallowing needs to adhere to a certain diet. Firstly, it is forbidden to eat hot, salty and spicy foods. Secondly, it is recommended to avoid caffeinated drinks and alcohol.
However, to prevent pain in the esophagus from occurring again and again after eating, it is imperative to eliminate the trigger. For example, odynophagia, which is associated with cancer, will disappear only after a course of chemotherapy or radiotherapy. And if something interferes with the esophagus when swallowing, you will have to perform a diagnostic endoscopy and remove the stuck foreign body or tumor.
Since the most common diseases that provoke odynophagia are reflux disease and esophagitis, maximum attention should be paid to the methods of their treatment (especially since they are very similar).
Medications for the treatment of reflux disease and esophagitis help:
- relieve pain when swallowing;
- reduce the intensity of stomach acid production;
- protect the esophageal mucosa.
Despite their safety and effectiveness, uncontrolled use of proton pump inhibitors and H2 receptor blockers can lead to complications and side effects. At a minimum, there may be problems with nutrient absorption.
If it is not possible to consult a gastroenterologist, then it is better to give preference to antacids (especially if the pain is accompanied by heartburn). Drugs in this group neutralize stomach acid, so even if the patient develops regurgitation, it will not cause much harm.
You also need to know that the main components of antacids are chemical compounds such as:
- calcium carbonate;
- sodium bicarbonate, aluminum;
- Magnesium hydroxide.
The accumulation of the above components in the body can also inhibit the absorption of nutrients.
Diagnosis and treatment of gastroesophageal reflux
If the symptoms discussed above are present, it is necessary to seek advice from a therapist, who, if necessary, will give a referral to a more specialized specialist - a gastroenterologist, as well as an otolaryngologist to determine the cause of the sore throat.
To make a diagnosis of gastroesophageal reflux, the doctor must find out the full picture of the disease: when pain occurs, its nature and location, what serves as a provoking factor for the pain, whether there are chronic diseases of the throat and stomach; what food the patient eats, in what cases a lump in the throat or heartburn appears.
Therefore, before going to the doctor, it is a good idea to study your symptoms.
To confirm the diagnosis, additional examination is prescribed:
- FGDS - detects inflammation, erosion and other changes in the stomach and esophagus
- An x-ray of the esophagus will show the presence of a hernia
- a study of changes in the acidity of gastric juice will indicate a possible cause of the disease
- examination using radioisotopes is very expensive and is prescribed in cases where other methods do not bring results
- biopsy – if cancer is suspected
Treatment of uncomplicated forms of reflux is possible at home. To alleviate the condition, antacid medications are prescribed to relieve heartburn and eliminate throat discomfort (Almagel, Rennie, Gastal); prokinetics to improve peristalsis (Motilium, Motilak, Perinorm).
If it is determined that a sore throat is caused by reflux, there is no need for additional treatment with special medications; neutralizing the stomach acid will be sufficient.
Folk remedies also give good results. If you use them at the very beginning of the disease, while changing your diet and regimen, you can avoid many health problems.
At the initial stage of the disease, herbal medicine can be used: yarrow, chamomile, St. John's wort, calendula, plantain herbs. Infusions and decoctions of these herbs will relieve stomach pain, nausea, and help digestion.
But you should avoid alcohol-containing tinctures. They will irritate the already damaged mucous membrane and do more harm than good.
A very useful recipe for flax seed: 2 tablespoons per glass of boiling water, leave for 8-9 hours, strain.
Drink half a glass before meals for a month. For heartburn, raw potato juice will help if you take it 20 minutes before meals, ¼ cup for three weeks. You need to make fresh juice every time.
Also, calamus root, milk at room temperature, and slightly alkaline mineral water without gas will relieve heartburn.
But all these measures will not bring the desired result without changing your lifestyle, eating habits, bringing your weight back to normal, if it exceeds it, and adjusting your physical activity.
Therefore, along with taking medications and folk remedies, the following recommendations must be followed:
- exclude foods that provoke heartburn - fried, fatty, spicy, smoked, pickled, baked goods and fresh bread, cakes, pastries, chocolate, citrus fruits;
- split meals are recommended - 5-6 times a day in small portions;
- food should be amenable to gentle methods of heat treatment - boiling, stewing, steaming, baking without a crispy crust;
- last meal – 3 hours before bedtime;
- wear looser clothes, avoid wearing tight corsets, bandages, weights, belts and girdles;
- during sleep, the head should be slightly elevated so that the acid that enters the esophagus cannot enter the throat;
- exclude physical exercise and hard work associated with bending forward, especially after eating;
- eliminate alcohol and smoking;
- if you are overweight, contact a nutritionist to choose an individual diet;
- eliminate psycho-emotional overstrain, stress, stress.
Only if you take all the measures together, you can cope with the disease and improve your quality of life.
So, you should know that sore throat with gastroesophageal reflux differs from pain with diseases caused by damage to the ENT organs.
Useful video
There are many patients who feel pain in the esophagus when food passes. It is quite possible to get rid of pain in the esophagus when swallowing food, the causes of which are varied, by taking the necessary actions in time. If you have pain when food passes through your esophagus, you should watch this video.
The safest drugs among those prescribed for the treatment of GERD and esophagitis are alginates. A prominent representative of this group is Gaviscon. The drug does not contain components characteristic of antacids. The main active ingredient is alginic acid.
Alginates work by creating a mechanical barrier against stomach acid. After taking the drug, a foamy gel forms on the walls of the distal esophageal zone and the upper part of the stomach.
Thus, even if regurgitation occurs, the stomach contents do not in any way damage the esophageal walls. This is especially important for those patients who have ulcers or erosions on the tissues of the esophageal tube. Alginates are also suitable for those for whom synthetic drugs are contraindicated, because the main active ingredient (alginate) is extracted from brown algae.
A piece of tissue is wrapped around the lower part of the esophagus and secured with a small suture. As a result, regurgitation becomes almost impossible.
Having learned why it hurts to swallow in the esophagus, the patient will be able to undergo timely prevention of diseases of this organ, and also not worry about the development of complications.
Therapy
You can find out why there is pain behind the sternum, get advice, and find out what approach is needed to provide treatment at an appointment with a gastroenterologist. The patient undergoes a complete examination. The safest method is gastroscopy, which provides information about the condition of the organ. Gastroscopy is prohibited for esophageal cancer.
After conducting an ultrasound examination, X-ray examinations, and taking into account the results of gastroscopy, the doctor makes nutritional adjustments. Spicy, fatty foods, frequent snacks are excluded from the patient's diet; overeating is unacceptable.
The prescribed diet does not bring the desired result - it is necessary to treat with medications. The main task of the medicine is to relieve pressing pain and improve the process of food intake. The specialist prescribes a medicine that treats acidity by suppressing hydrochloric acid (Phosphalugel, Ranitidine, Cerucal). To relieve dyskinesia and restore muscle tone, the drug Metoclopramide is prescribed.
You can find out why there is pain behind the sternum, get advice, and find out what approach is needed to provide treatment at an appointment with a gastroenterologist. The patient undergoes a complete examination. The safest method is gastroscopy, which provides information about the condition of the organ. Gastroscopy is prohibited for esophageal cancer.
After conducting an ultrasound examination, X-ray examinations, and taking into account the results of gastroscopy, the doctor makes nutritional adjustments. Spicy, fatty foods, frequent snacks are excluded from the patient's diet; overeating is unacceptable.
The prescribed diet does not bring the desired result - it is necessary to treat with medications. The main task of the medicine is to relieve pressing pain and improve the process of food intake. The specialist prescribes a medicine that treats acidity by suppressing hydrochloric acid (Phosphalugel, Ranitidine, Cerucal). To relieve dyskinesia and restore muscle tone, the drug Metoclopramide is prescribed.