- Pumpkin seeds
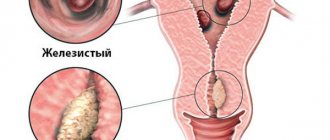
A polyp in the uterus is a benign neoplasm that is formed as a result of the pathological proliferation of endometrial cells. Externally, it is a rounded growth on a stalk, resembling a mushroom, with a porous surface of burgundy-violet or yellowish color.
Polyps in the uterus are the result of pathological proliferation of endometrial cells
The size of the neoplasm can range from several millimeters to three centimeters. Polyps can be single or multiple, and can be localized in different places (for example, on the anterior and/or posterior wall of the uterus).
Most often, this pathology occurs in women 40–50 years old before the onset of menopause, but in some cases, polyps can also form in girls during adolescence.
What are polyps and what do they look like?
Polyps are benign neoplasms that are most often localized in the cervix. They look like warts, and several such outgrowths can appear at the same time.
Polyps differ from each other in size, structure and location. They may develop without symptoms, but more often occur with pain and bleeding.
You can see what a polyp looks like in the photo below:
This is what polyps in the uterus look like in women.
It is worth noting that there are three types of polyps in the uterus - glandular, fibrous and adenomatous. Glandular polyps appear due to high levels of estrogen. Most often they occur in young patients.
The appearance of fibrous polyps is possible due to inflammation.
They occur mainly in women after 40 years of age, when strong hormonal changes occur in the body.
Adenomatous polyps are more dangerous because in adulthood they can degenerate into a cancerous tumor.
Forecast and consequences
The appearance of tumors in the uterus is often associated with ovarian dysfunction, therefore, despite surgical intervention, without appropriate hormonal correction they can grow again.
Adenomatous polyps in some cases degenerate into malignant neoplasms, so when such growths are detected, a woman should closely monitor her health.
A polyp in the uterine cavity can appear during pregnancy. This is dangerous because there is a risk of placental abruption. Through it, the fetus receives oxygen and nutrition along with blood. If the placenta does not adhere too tightly to the wall of the uterus, this can cause fetal hypoxia or a delay in its development.
During pregnancy, treatment is not carried out, and all the doctor’s efforts are aimed at improving the condition of the fetus. In some cases, changes in hormonal levels lead to tumors resolving on their own.
Reasons for their manifestation
The reasons for the formation of growths in the uterus are still practically unknown, but doctors believe that the main factor in their appearance is hormonal disorders. In case of hormonal imbalance, changes occur in the internal structure of the lining of the uterus.
Here are a few more reasons why polyps appear:
- Endocrine diseases (autoimmune thyroiditis, thyrotoxicosis, Down syndrome, diabetic foot, and so on).
- Injuries.
- Infections that are sexually transmitted.
- Erosion.
- Endometriosis of the uterus.
- Poor metabolism.
- Contraceptive IUDs.
- Diabetes.
- Overweight.
- Abortion.
Frequent depression and stress can lead to any changes in the body's performance, including such an unpleasant manifestation as polyps.
Treatment methods for cervical polyps
There is no drug therapy. It is impossible to get rid of pathological growth of the mucous membrane with medications. Traditional methods will also not be effective.
The only treatment option is surgery. Removal is carried out on days 5-7 of the cycle (or after the complete completion of menstruation). During menopause, surgery can be scheduled for any day.
Polyp removal options:
- Classical polypectomy – removal of the formation with a conchotome;
- Loop excision – excision of the polyp with a thin loop (part of the cervix may be captured);
- Laser excision – removal of a formation with a laser beam;
- Conization of the cervix is a cone-shaped excision of tissue (indicated for large and multiple polyps, malignant degeneration).
Loop polyp excision minimizes blood loss and scarring.
The resulting material is sent for mandatory histological examination. The polyp bed is cauterized using one of the available methods:
- Electrocoagulation (electric current);
- Laser vaporization;
- Cryodestruction (liquid nitrogen);
- Radio wave cauterization.
Cauterization is indicated to eliminate bleeding and prevent relapse of the disease. For nulliparous women, radio wave or laser exposure is recommended. After electrocoagulation, the cervical mucosa takes a long time to heal. The formation of scars is possible, which in the future will lead to serious problems during pregnancy and childbirth.
On a note
Based on patient reviews, we can conclude that polypectomy is quite well tolerated, rarely leads to the development of complications and can almost completely eliminate the likelihood of relapse of the disease. After treatment, moderate bleeding is observed, which disappears within 2-3 weeks. Complete healing of the cervical mucosa occurs in 4-6 weeks.
Recommendations after polypectomy:
- Limiting sexual and physical activity for 4-6 weeks;
- Prohibition on visiting the sauna, bathhouse, swimming pool, bathing;
- Compliance with the rules of intimate hygiene.
If the patient refuses surgical treatment, symptomatic therapy is carried out: antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs, immunomodulators, vitamins.
Symptoms that appear
In cases where the polyps are quite small in size, symptoms may practically not appear.
Therefore, to find out whether a woman has a tumor or not, it is worth visiting a gynecologist every 3 months.
The clinical signs of this disease are worth considering in more detail. Here are a few symptoms that appear with polyps:
- A nagging pain appears. They intensify before menstruation. Some patients experienced “cramping-like” pain.
- Bleeding may recur a few days after your period ends.
- Painful sensations during sexual intercourse. In this case, bloody discharge may appear after it.
- There is a disturbance in the menstrual cycle.
- Weakness and dizziness appear. The skin may also become pale and look sickly.
- Endometrial polyposis can cause infertility or miscarriages.
Treatment tactics
In treating the disease, you should adhere to some important rules:
- The surgical method is the main one in the treatment of polyps of the body and cervix;
- Removal of the formation should be carried out as soon as possible after diagnosis;
- Surgery is not performed during pregnancy;
- The removed polyp must be sent for histological examination to the laboratory;
- It is necessary to remove uterine polyps even if they do not grow, do not bother or interfere with a full life.
Indications for surgical treatment:
- The appearance of polyps during menopause (in older women there is a high probability of malignant degeneration of the polyp);
- The size of the formation is more than 1 cm;
- Infertility;
- Suspicion of malignant degeneration.
For confirmed cancer, the scope of the operation is determined based on the severity and extent of the process.
Regarding small polyps (about 4-5 mm), gynecologists do not have a consensus. Some experts believe that any pathological formations are a risk of cancer and bleeding, so polyps need to be removed. This is especially true for women who have entered menopause, because after 45 years, the likelihood of developing oncological processes increases significantly. Other gynecologists suggest observing small polyps in women of reproductive age (if they do not interfere with conceiving and bearing a child).
Do polyps lead to cancer?
Malignancy (spontaneous degeneration of benign cells into malignant ones) can occur with polyps that are of the adenomatous type.
This process not only complicates therapy, but also destroys tissue located in close proximity to the growth, and also increases the risk of bleeding in the uterus.
Malignancy poses a direct threat not only to the health, but also to the life of a woman.
What are the causes of endometrial polyp?
Endometrial polyp is a very common gynecological pathology, ranging from 10 to 25% in all cases and from 40 to 70% after menopause.
The causes of polyps are varied:
- hormonal imbalance, especially excess estrogen and lack of progesterone in the second phase of the menstrual cycle;
- chronic inflammatory process in the uterus, its cervix or appendages;
- endometriosis;
- diseases of the adrenal glands, pancreas (diabetes mellitus);
- long-term use of glucocorticosteroids or sex hormones;
- obesity, hypertension - increase the risk of developing polyps by 10 times;
- frequent abortions, miscarriages, curettages;
- incomplete removal of the placenta after childbirth or abortion (placental polyp);
- surgical interventions on the uterus and ovaries;
- long-term intrauterine device
- and many others.
Surgeons Euromed In Vitro
Possible dangers
When polyps are detected in the uterus, it becomes necessary to remove them due to the fact that they are dangerous to the woman’s health.
Among the possible troubles that a woman may encounter are:
- Uterine bleeding. If therapy is not carried out in a timely manner, the polyp develops internal small vessels. But due to the fact that its walls do not have a dense structure, there is a possibility of injury. Because of this, bleeding may occur even in the middle of the menstrual cycle. They are completely insignificant and the woman will not notice it. But even small blood losses, when repeated systematically, “threaten” to manifest as anemia. However, large polyps when injured lead to quite heavy bleeding. It will not stop on its own.
- The possibility of conception becomes difficult. The larger the tumors, the more serious the possible problems. A fertilized egg will not be able to penetrate inside the uterus and, naturally, gain a foothold there. On its way there will be a polyp, which is a mechanical obstacle.
- Complications may also arise when carrying a child. If there are polyps, miscarriages and placental abruption may occur. The pregnancy itself may be ectopic.
- The polyp may appear as a source of infection. If a pathological agent enters the uterine cavity, then it will “begin” its destructive effect near the polyp. This effect occurs due to the fact that the polyp shell is not able to resist infection.
These possible complications can lead to major health problems for the woman. Because of this, there is a recommendation from gynecologists to remove detected formations immediately after their identification.
Symptoms
You can suspect that a neoplasm has appeared in the uterine cavity if the following symptoms occur:
- menstrual irregularities, heavy uterine bleeding;
- spotting between periods;
- pain in the lower abdomen or lumbar region;
- mucous discharge from the vagina.
Very often, there are no symptoms of polyps in the uterine cavity at all and neoplasms are detected accidentally during an ultrasound examination.
How are polyps detected?
Neoplasms can be detected in several ways:
- During a routine gynecological examination of the vagina. This procedure is carried out using mirrors. In this case, the gynecologist is able to see any protruding formations. They are usually distinguished by color; both pink and bright red growths can appear. The shape of polypous formations can be either grape-shaped or round. When the polyp becomes keratinized (thickened and covered with stratified epithelium), its color may become white. If it is colored burgundy or purple, this may indicate a violation of blood circulation in it. Usually the structure of such a neoplasm is soft to the touch, and it itself is elastic.
- Colposcopy or cervicoscopy. Cervicoscopy is performed using a hysteroscope. The presence of a video camera makes it possible to examine even the smallest neoplasms, the focus of inflammation that has arisen near them, or, especially, ulcers around the growths. In order to exclude the presence of degeneration of the polyp into a low-quality neoplasm, a biopsy is performed during the procedure. Moreover, if the growth is small in size, then it is possible to remove it at the same time. Colposcopy is performed using a special binocular with built-in lighting.
- Diagnostics using ultrasound. If a polyp is detected in the cervical area, then its appearance is possible in the endometrium. Using ultrasound, you can obtain information not only about the thickness of the endometrium, but also about the structure of this layer. In addition, data will be obtained on the condition of both the ovaries and tubes.
Classification of neoplasms
According to localization, all formations are divided into two large groups:
- Cervical polyp – located on the surface of the columnar epithelium of the cervical canal;
- Polyp of the uterine body - located in the endometrium (mucous layer of the uterus), most often localized in the fundus.
On a note
Large polyps of the uterine body can extend beyond the internal os and imitate formations of the cervical canal. During a gynecological examination, the doctor will see a round formation hanging from the external pharynx. This can be either a cervix polyp or a long growth coming from the lower part of the uterine body. It is quite difficult to determine the type of polyp without special research.
| Type of polyp | Fabric structure | Size | Woman's age | Risk of degeneration into cancer. tumor | Probability of relapse |
| Glandular | Formed from the mucous layer and contains glands | Up to 1.5 cm | More common during reproductive age | Minimum | Practically not observed |
| Glandular fibrous | Consists of glandular cells and stroma (connective tissue) | Up to 2-3 cm | Occurs at any age | Minor | Relapse is possible; after removal, hormonal therapy is indicated |
| Fibrous | Consists of connective tissue cells | From 2-3 cm | More often found during menopause | High | Frequent relapses |
| Adenomatous | Originate from glandular epithelium and may contain atypical cells | From 2 cm | More often found during menopause | Very high, considered a precancerous condition | Frequent relapses |
Based on their structure, polyps of the body and cervix are divided into several types. Characteristics of formations are presented in the table.
Glandular polyps are similar to fluid cysts, while fibrous polyps are dense because they are based on connective tissue.
The placental polyp deserves special attention. This formation is detected only in the body of the uterus and is a growth formed from the remains of the placenta. It is discovered after childbirth or late abortion. Requires urgent removal.
Treatment without surgery
Combating polyps with surgery has always been considered the most effective method.
But many women, for various reasons, do not want to be treated in this way and refuse surgery. Therefore, doctors offer drug therapy.
There are three types of drugs for treating polyps:
- Oral combined contraceptives are prescribed to girls, as well as women under 35 years of age. This treatment is effective for existing glandular polyps and allows you to avoid the unpleasant curettage procedure, which, moreover, can be painful.
- Gestagens. These are steroid sex hormones that restore the endocrine system and regulate the functioning of endometrial cells.
- GnRH drugs (GnRH agonists). Prescribed to women most often after they turn 35 years old.
In addition to hormones, doctors also prescribe vitamins. During therapy, a woman’s body must receive both vitamin B and iron. However, if after treatment there is no positive effect, then surgical intervention is recommended.
Traditional medicine also helps treat polyps. However, it is worth keeping in mind that these remedies can only be used after consultation with a specialist.
You can take infusions of blackcurrant and rose hips daily. Decoctions for douching should be prepared from rosemary, sage and oak bark.
These ingredients are crushed and then filled with water. Then they must be boiled for at least half an hour. Next, cool the broth, strain and use for douching.
Tampons can be inserted into the vagina, which should first be dipped in a mixture of the following components:
- aloe juice or its crushed leaves;
- honey (must be only natural);
- sour milk.
Once the milk has started to sour, place it on the fire in a small saucepan and then warm it up a little. At the moment when flakes form, the fire must be turned off.
Then crushed aloe leaves and natural honey are added to the pan.
You can use clean gauze as a tampon, into which the resulting mixture is placed. For the treatment of growths, this is one of the best traditional medicines.
Diagnostic methods: how to detect a polyp in the uterus
To identify pathological formations, the following methods are used:
Gynecological examination
When examined in the mirrors, the doctor may see a polyp hanging from the cervical canal. It is a red or pink formation on a thin stalk. Polyps located far in the body of the uterus cannot be seen.
Laboratory research
Since the appearance of a polyp can be caused by infectious diseases, you should undergo the following tests:
- Flora smear;
- Bacteriological culture from the cervical canal;
- Screening for STIs (if indicated).
Colposcopy
Examination of the cervix under high magnification allows you to determine the nature of the polyp and decide on further tactics.
On a note
During pregnancy, a decidual polyp may appear - a growth of the membrane formed from endometrial tissue and intended to nourish the fetus. This formation is not dangerous, but may bleed during gestation. No treatment is required - during childbirth the polyp will come out along with the decidua.
Ultrasound of the pelvic organs
Ultrasound examination can detect up to 90% of all endometrial polyps. The presence of menstrual blood or serous fluid in the uterine cavity facilitates diagnosis, due to which contrast is carried out. Cervical polyps are not so visible on ultrasound.
Ultrasound diagnostics of the pelvic organs is a highly accurate and absolutely safe research method.
Ultrasound signs of a uterine polyp:
- Local thickening of the M-echo (endometrial shadow);
- The appearance of foreign inclusions in the shadow of the endometrium;
- Detection of a round or oval formation.
Glandular polyps are difficult to identify with ultrasound, since their sound conductivity is close to that of the endometrium. Fibrous formations are clearly visible during the examination.
In recent years, hydrosonography - ultrasound with contrast of the uterine cavity - has become very popular. The method is quite complex, therefore it is not used as a screening method and is prescribed when a diagnosis has already been established to confirm it, clarify the location of the polyp and identify concomitant pathologies.
Hysteroscopy
It is a study of the uterine mucosa under high magnification using special endoscopic equipment. The procedure is performed under general anesthesia or local anesthesia and takes place in several stages:
- The patient is positioned on a gynecological chair;
- The doctor exposes the cervix in the speculum and grasps it with bullet forceps;
- The cervical canal is dilated;
- An endoscope is inserted into the uterine cavity - a thin tube with a video camera;
- All information is displayed on the screen, and the doctor can assess the size and shape of the polyp, see the condition of the uterine mucosa, and identify concomitant pathologies;
- The study ends with a biopsy - tissue sampling for histological examination.
On a note
Histological verification is the only method to accurately determine the structure of the polyp and distinguish benign from malignant formations.
When performing hysteroscopy, a test with the supply of gas or liquid into the uterine cavity helps to distinguish polyps from other phenomena. Polyps flatten, elongate and increase in size.
During hysteroscopy, the examination of the uterine cavity and the identification of a polyp in it occurs using a hysteroscope - a flexible tube with a video camera at the end that transmits an image to a monitor.
Hysteroscopy can be not only a therapeutic, but also a diagnostic operation. The doctor removes small polyps directly during the examination. According to indications, the operation is completed by curettage of the uterine cavity and/or cervical canal. The scraping is also sent to the laboratory for examination.
Preventive measures
To prevent cancer caused by the degeneration of polyps, it is necessary to undergo a gynecological examination in a timely manner. An antenatal clinic should be visited at least twice a year. Timely diagnosis will help avoid not only infertility, but also cancer.
If you experience any discharge or blood clots, you should consult a doctor. Any inflammation that occurs must be cured completely. Mechanical damage to the genital organs should be avoided when performing douching and washing. Injury can also occur during curettage or abortion.
In case of endocrine diseases, hormonal levels must be corrected with prescribed special medications. If ruptures or cracks occur during childbirth, they must be healed immediately and thoroughly.
Frequent abortions can cause growths to appear. Because of this, you should use contraception during sex. It will also allow you not to get sick during sexual intercourse with a new partner.
Menstruation should occur at a time known to the woman. If the cycle is disrupted, its normalization must be carried out immediately.
It must also be remembered that long-term use of hormonal contraception leads to various imbalances in the body.
If you are overweight, you should take care of yourself. This requires diet and exercise.
If you follow these recommendations, the appearance of polyps can be avoided.
Diagnostics
To make a diagnosis, you must consult a doctor at the gynecology department. He will conduct an examination and prescribe the necessary examination.
Transvaginal ultrasound is usually prescribed to detect tumors.
The most accessible and at the same time painless method for diagnosing neoplasms is transvaginal ultrasound. It is carried out using a sensor that is inserted into the vagina.
In some cases, hysteroscopy is performed to examine and subsequently remove the growth. A tube with a micro-video camera is inserted into the uterine cavity.
Sometimes X-rays with contrast are taken to diagnose pathology of the uterus and fallopian tubes.
Causes of endometrial polyposis
The main cause of the formation of uterine polyps are neurohormonal factors and inflammatory endometrial changes.
- Conditions such as hyperestrogenism or hormonal ovarian dysfunction provoke the appearance of polyps. These conditions are accompanied by hyperplastic endometrial changes in the form of polypoid growths. Such conditions are often accompanied by pathologies characteristic of high estrogen levels, such as uterine fibroids, mastopathy, or glandular endometrial hyperplasia, adenomyosis, or polycystic ovary syndrome.
- Chronic pathological processes contribute to endometrial polyposis: female inflammation such as oophoritis, adnexitis or endometritis, genital infectious lesions, damage to the uterus during abortion and curettage, long-term wearing of an intrauterine device.
- At risk for endometrial polyps, experts include women with obesity, neuropsychiatric disorders, immune disorders, thyroid pathologies, hypertension or diabetes.
- Vascular growths can also cause the development of polyposis. When vascular channels become blocked or grow around them, active proliferation of epithelial cells begins.
- It happens that polyposis in the uterine cavity is caused by genetic predisposition, a sedentary lifestyle, or long-term use of Tamoxifen. This medication is used in antitumor therapy to block hormone-sensitive receptors. As a result, in some patients, polypous formations begin to actively grow.
What it is
A polyp is a benign formation that appears on the walls of the cervix. Under unfavorable conditions, growths with thin stalks appear on the walls of the uterus and its mucous membrane, with which they are attached to the epithelium. These growths are also called endometrial polyps. Each growth has a network of vessels that connects to the stalk, and through it to the bloodstream. Thus, nutrition occurs, which subsequently leads to an increase in size of the formation.
The size of polyps can vary from a few millimeters to several centimeters. In most cases, the problem is diagnosed in women 35-45 years old. If treatment is incorrect or untimely, benign tumors may develop into a malignant tumor. It is worth noting that a woman does not always have only one polyp; as her height increases, the number of formations may also increase.
Effect on pregnancy
The situation here is ambiguous.
Cases of favorable conception, gestation and childbirth with a polyp are far from uncommon.
However, this depends on the location of the tumor, its type and size.
If pregnancy does occur in the presence of a polyp, treatment and removal are carried out only if the formation is larger than 1 cm, if it is inflamed and if it will interfere with natural childbirth (cervical canal polyp).
In all other cases, treatment is postponed until after childbirth and the end of lactation.
In some cases, a polyp can of course lead to complications during pregnancy, so the woman should be under the strict supervision of a gynecologist throughout her pregnancy..
What can trigger growth?
As a rule, the growth of a polyp is provoked by hormonal changes in a woman’s body.
In addition, the impetus for the growth of a neoplasm can be:
- low immunity;
- stressful situations, depressive states;
- age-related changes.
IMPORTANT!
The growth of a polyp also depends on many individual characteristics of the body - the presence of underlying diseases, medication use, emotional state, inactive lifestyle, and so on.
Reviews about the treatment
Victoria:
I had a uterine polyp removed by curettage. They gave me anesthesia, scraped out the area where the polyp was located - and that’s it. It's OK. A couple of hours after the procedure I went home.
Anastasia:
I have already had my polyp removed by hysteroscopy twice and it relapsed again. After each removal, she underwent a course of hormone therapy. Still, after 1.5-2 years the polyp appears again. I did it in different clinics.
Treatment
Removal of the polyp is recognized as the most effective treatment method. If pathology is detected early, hysteroscopy or uterine curettage is sufficient. In the future, the condition of the organ is monitored. The reappearance of organ body polyps serves as a reason for complete removal of the endometrium (resection). This type of operation allows you to completely eliminate the modified structures. It is performed only for women who are not planning to have a child (over 35 years old). The appearance of polyps after a surgical procedure and against the background of conservative treatment of polyposis is the reason for removal of the uterus. Also, the organ is eliminated if atypical cells are detected.
Conservative methods
In addition to surgical treatment, there are methods to maintain the process at a safe level and prevent complications.
Considering the high dependence of the development of the disease on disruption of the endocrine system, the main remedy in the treatment of polyposis will be a group of hormonal drugs.
- Combined oral contraceptives. After determining a woman’s hormonal background, the doctor selects a remedy that can restore normal levels. The course of treatment lasts from 21 days to 3 months.
- Progestins help regulate the balance of hormones in the body. They have a hemostatic effect. Used for 5-6 months in the second phase of the cycle.
In addition to hormonal therapy, non-hormonal agents are also used.
Women during and before menopause are prescribed GnRH antagonists. These drugs can not only stop the process of polyp growth, but also reverse it.
Folk remedies
Traditional medicine methods are an auxiliary therapy against the background of treatment. To effectively eliminate endometrial polyps, herbal decoctions and infusions are used both for oral and local consumption (baths, tampons and douching).
Important! When treating pathological growth using exclusively traditional methods, the healing process will be delayed, since herbal therapy takes a lot of time. It is permissible to carry out only in case of uncomplicated pathology at an early stage of the disease and under the supervision of a doctor (examination every 1.5 months).
Possible complications and prognosis
Endometrial polyps, for the most part, are benign in origin and do not pose a great danger to a woman’s health. Although there are exceptions in which a certain number of them contain adenocarcinoma cells and malignant indicators. Endometrial polyps can have a negative impact on IVF, causing the threat of miscarriage.
Located next to the fallopian tubes, they prevent pregnancy. Treatment with medications and hysteroscopy can alleviate the course of the disease, but after this there is often a danger of complications in the form of their reoccurrence.
There is a possibility that polyps that have not reached large sizes can regress on their own without the use of therapeutic methods. A positive effect on suppressing the disease and limiting the growth of the endometrial polyp is facilitated by taking the drug Tamoxifen, prescribed by a gynecologist.
How to treat uterine polyp
If formations are detected in the uterus, their mandatory treatment is indicated. If treated with medication, the growths will not disappear completely. There is always a risk of re-growth of endometrial cells and their degeneration into malignant ones. You can completely get rid of polyps only through surgery.
Treatment without surgery
The conservative method can be used to remove single small growths. The gynecologist prescribes drugs that can stop their growth and activate independent resorption:
- If infectious diseases of the uterine cavity are detected, antibiotics are prescribed.
- For small formations, women under 35 years of age are prescribed combined oral contraceptives (Zhanin, Regulon, Yarina).
- After 35 years, gestagens are prescribed - Duphaston, Norkolut, Utrozhestan. Such medications will prevent prolonged and severe bleeding and stop the blood supply to the growths through the vessels.
- During menopause and for patients over 40 years of age, it is ideal to take releasing hormones, such as Leuprorelin, Zoladex, Diferelin.
- If polyposis is accompanied by anemia, it is advisable to prescribe iron replacement therapy together with sedative medications and diet.
The duration of the treatment course usually reaches six months. If necessary, therapy continues.
Surgical intervention
Removal of polyps in the uterine cavity is possible in several ways. When choosing a method, the woman’s age, her state of health, the location of the growths, and plans for a future pregnancy are taken into account. If a single polyp is found, it is cut out; in case of polyposis, the upper layer of the uterine mucosa is scraped out.
Indications for surgical treatment:
- the patient's age is over 40 years;
- lack of positive dynamics with hormonal treatment;
- the presence of a growth of more than 1 cm;
- the presence of atypical cells detected during histology.
Now almost all clinics offer to remove polyps in the uterine cavity through laparoscopy and hysteroscopy.
The hysteroscopic method is a low-traumatic procedure, which is performed under general anesthesia and lasts approximately 20 minutes. It is prescribed 2-3 days after menstruation stops, when the uterine lining is thin and the polyp is clearly visible. Hysteroscopy has several advantages:
- no incisions or surgical sutures;
- safety;
- absolute painlessness;
- the ability to remove even the smallest polyps.
During hysteroscopy, a special instrument with a video camera and lighting is inserted into the uterine cavity through the vagina and cervix. Removal of the growth can occur through cryodestruction (cauterization with liquid nitrogen), electrocoagulation, excision with a scalpel, or twisting.
To perform laparoscopy, a small hole (0.5-1.5 cm in length) is made in the lower abdomen. Its advantages:
- complications are practically excluded;
- no scars;
- postoperative pain rarely occurs;
- the body recovers quickly.
Laparoscopy is performed to remove the entire uterus when numerous polyps with a risk of degeneration into a cancerous tumor are diagnosed.
Regardless of the chosen method for removing polyps in the uterine cavity, all materials are sent to the laboratory for histology (examination under a microscope).
Alternative medicine
Benign neoplasms can be eliminated using non-traditional methods of influence. However, such a measure can only be used with the permission of a doctor. Douching is most often used to treat tumors:
- Mix equal amounts of sage, rosemary, oak bark and yarrow. Prepare an infusion (four tablespoons of the mixture are required per liter of water). Strain the cooled liquid and douche with it every day for two weeks.
- Tincture of propolis, calendula and rotokan. Mix the product with water (use a teaspoon for half a glass). Alternate douching of tinctures every ten days.
What else to read:
- What to do if you have a malignant tumor in the ovary: symptoms and treatment of gynecological cancer Contents of the article:1 Classification of ovarian cancer2 Stages of the oncological process3 Why do malignant tumors occur4 First signs and long-term symptoms of ovarian cancer5 Diagnosis5.1 Gynecological examination5.2 Instrumental methods5.3 Blood tests5.4 Biopsy6 Treatment……
- Why you need to be checked regularly by a gynecologist. Causes and symptoms of uterine cancer Contents of the article:1 Why a cancerous tumor appears2 Types of uterine cancer3 Stages4 How oncology manifests itself4.1 First signs4.2 Symptoms in later stages5 Diagnosis of a neoplasm6 How to treat a cancerous tumor of the uterus6.1 Chemotherapy6.2 Surgery6.3……
- A polyp was discovered on the cervix of the uterus: is a neoplasm dangerous and how to get rid of it Contents of the article:1 Causes of the appearance of neoplasms2 Types of growths3 Symptoms of a cervical polyp4 Is it dangerous5 Diagnostic methods6 Conservative treatment of a cervical polyp7 Modern methods of radical removal of polyps8 Treatment prognosis9......
How dangerous is the disease?
Despite their benign origin, polyps can pose a threat to women's health. Among the most “harmless” consequences, experts highlight chronic failure of menstruation.
But endometrial polyposis can also provoke more serious problems such as complicated pregnancy, infertility, or the birth of a polyp. The latter case may lead to removal of the uterine body.
The most dangerous consequence of a polyp can be malignancy, when the tumor degenerates into a malignant formation. Therefore, polyps require mandatory medical supervision.
Traditional medicine recipes
Those who are interested in how to get rid of a polyp in the uterus without surgery should consult a doctor. Only a doctor can decide whether surgical intervention is necessary in each specific case. The growth can go away much faster if you use folk remedies along with hormone therapy.
If you know what causes polypous formations, you can use a traditional method to prevent the problem. Effective recipes include:
- Pumpkin seed. For 12 teaspoons of dry raw materials, crushed in a coffee grinder, there are 7 boiled chicken yolks. The resulting mixture must be filled with half a liter of vegetable oil. Then the composition is heated over a water bath for a quarter of an hour. Drink the medicine half a tablespoon per day before meals. Treat for five days. After five days, take a break for five days. They complete the course until the prepared product runs out.
- Microscopic enemas based on herbal preparations. You need to purchase an infusion of calendula flowers, tincture of rokotan and propolis at the pharmacy kiosk. Prepare an enema liquid: half a tablespoon of infusion is dissolved in 100 ml of liquid. The mixture is divided equally. Used twice a day. The medicine is injected into the anus using a syringe. Tinctures alternate. First, they are treated with calendula infusion (10 days). Then rokotan (10 days). Therapy is completed with microenemas with propolis (10 days). At the end of the course, a break is taken (20 days), then the treatment is repeated. You need to do 3 courses.
- Infusion of golden mustache. Take 2 dozen golden mustache joints. The raw materials must be filled with vodka (2 glasses). Infuse the mixture for 10 days in a place protected from light. They drink the product like this: add 20 drops of tincture to 100 ml of liquid twice a day. They take the course for a month. Then the break lasts for 10 days. After which therapy is resumed. Treat in this way for 6 months.
Possible signs
Formations often do not give manifestations. The first symptoms of a uterine polyp appear when the growth has reached a large size. A woman experiences:
- uterine bleeding not during menstruation;
- various disruptions of the menstrual cycle;
- bleeding during menopause;
- discomfort and pain during sex, as well as the presence of spotting after it.
If the growth is formed as a result of injury or an inflammatory process, the following clinical symptoms are possible:
- blood in discharge not associated with menstruation;
- nagging pain in the lower abdomen (with a significant increase in the polyp);
- anemia due to regular blood loss;
- infertility;
- miscarriage;
- uterine cancer.
Types of polyps
There are several main types of polyps. Histologically they are divided into three types:
- adenomatous;
- glandular-fibrous;
- fibrous.
Adenomatous does not develop very often. Such tumors often have focal adenomatosis. In this case, intensive growth of the glandular component is observed. The glands are irregular in shape and small in size.
Tumor-like formations have vascular tangles located near the stalk and thick walls. This type of polyp is the most dangerous, as over time it becomes malignant. This often occurs with neuroendocrine and metabolic disorders. In most cases, during menopause, formations develop in parallel with atrophic processes.
Glandular polyp of the endometrium is often found in young girls under 35 years of age. Much less common during menopause. This type has some morphological features that are manifested in the location of the formations. They are located very unevenly. At the same time, they are directed in different directions.
The upper layer of the formations has many cells. Near the base, the structure is composed of fibrous tissue and becomes much denser. The vascular walls are thickened. They are located in different parts of the uterus and look like balls. Endometrial polyp of the glandular-fibrous type is often accompanied by problems with blood circulation and inflammation.
A fibrous endometrial polyp is formed using connective tissue cells. It contains a lot of collagen fibers. There are single vessels with sealed walls. This type of neoplasm most often appears in women during menopause and premenopause.
Prevention
Since polyps are formed due to a malfunction of the ovaries (mainly caused by excess estrogen), preventive measures include:
- refusal to eat meat products and products that contain hormones;
- active lifestyle and exposure to clean air;
- prevention of hypothermia of the genitourinary system;
- consultations with a gynecologist before choosing hormonal contraception;
- regular medical examination by a female specialist (at least 2 times within 12 months).
An important factor in the prevention of the disease is personal intimate hygiene, avoidance of synthetic underwear and aggressive chemicals used to care for the external genitalia, and frequent changes of pads or tampons during menstruation.
Uterine polyposis neoplasms are focal hyperplasia of endometrial cells. These are benign growths. However, they require mandatory treatment. The most unpleasant symptom of the disease is bleeding from the uterine cavity. In addition, the growths can cause periodic pain in women and lead to infertility.
How it manifests itself
An endometrial polyp can develop for a long time without any symptoms. Most uncomplicated processes are discovered by chance during routine examinations by a female doctor. However, uterine polyposis (multiple formations in the organ cavity) or a polyp that has reached enormous sizes, as well as complicated by inflammation or bleeding, can cause a number of unpleasant symptoms in a woman.
Menstruation disorders
Endometrial polyp affects the course of the menstrual cycle. Most women turn to a gynecologist with complaints of irregular periods, accompanied by heavy bleeding and severe pain. Between menstruation, spotting may occur in the middle of the cycle.
Pain
Large and multiple polyps are manifested by severe pain in the lower abdomen of a pulling nature.
Uterine bleeding
Women during menopause often end up in the hospital with uterine bleeding. Damage to the polyp (severation of the stalk, ulceration, inflammation) can cause this pathology. Chronic nature is possible with erosion of the polyp. This disorder can cause anemia.
Pain during sexual intercourse
Sexual intercourse is accompanied by pain when the formation is injured. Small bloody or spotting discharge may occur after sexual intercourse.
Infertility
For women of reproductive age, there is a high risk of developing pathology, which is manifested by the inability to conceive a child (if the endometrium changes) or spontaneous termination of pregnancy.
Discharge
The discharge is bloody and occurs in the middle of the cycle. Over time, the symptom intensifies. Uterine bleeding may develop.
Important! Any change in the reproductive system should be a reason to visit a doctor and undergo all prescribed diagnostic procedures.
About relapse
There is no method of treating uterine polyposis that would 100% protect against recurrence of the pathology. In almost every 10 patients, after successful removal of the growth, its re-formation occurs.
Sometimes recurrence of endometrial polyposis indicates poor-quality removal of the formation or a high probability of its malignancy. To determine the causes of relapse, the patient usually undergoes diagnostic curettage, according to the results of which further therapy is prescribed.
Surgery
Surgical removal of a polyp can be carried out using various methods, the most important thing is that the neoplasm is completely removed, otherwise a relapse of the disease is possible.
Polyp removal options:
- polypectomy;
- laser;
- radio wave method;
- cryodestruction;
- hysteroscopy;
- scraping;
- electrocoagulation and others.
Surgeries, as a rule, are well tolerated by women, and although the recovery period can last up to six months, in general it is not accompanied by any special difficulties .
If a woman plans to have children later, she needs to inform the doctor about this so that he can choose a more gentle method of surgery.
The interventions are carried out under anesthesia, and most often, after a few hours the woman can be discharged home.
Complications in the postoperative period will not arise if the woman strictly follows all the doctor’s recommendations.
Reasons for formation
The exact reason is not known for certain. However, it has been proven that an imbalance in the estrogen-progesterone system is a risk factor. At the same time, a decrease in the amount of progesterone entails an increase in the proliferative effects of estrogens and, as a consequence, activation of endometrial cell division. Most often, polyps are identified in patients with the following “problems”:
- polycystic ovary syndrome;
- chronic anovulation and functional disorders in the ovaries;
- chronic endometritis, frequent medical abortions, curettage and other manipulations inside the uterus;
- hyperplasia of the adrenal cortex;
- extragenital problems: diabetes mellitus, thyroid disease, obesity, liver pathologies;
- inadequate, uncontrolled treatment with sex hormones;
- constant stress;
- inflammatory chronic pathologies of the genital area;
- endometrial trauma during surgical interventions.
If the diagnosis of “endometrioid polyp” is confirmed, its cause is determined in accordance with the patient’s medical history, that is, the presence of a particular past or present disease that has led to hormonal imbalance.
Complications of polyposis
The presence of several neoplasms (polyposis) harms the condition of the reproductive system. Tumors disrupt the structure of healthy tissue and cause discomfort, bleeding or blood clots, which cause the development of anemia. In addition, there are cases of prolapse of growths in cavity , leading to severe pain and uterine bleeding.
The most common fibrous tumor tissue blocking the fallopian tubes or cervix. In addition, as the disease progresses, anovular cycles may predominate in women.
Modern treatment methods
The earlier a disease is diagnosed, the easier it is to get rid of it, and the less harm it will cause to the body. A small formation can be cured by undergoing a course of anti-inflammatory or hormonal therapy. If the situation has gone too far, the polyps are removed surgically.
Modern techniques are low-traumatic and effective. Polyp removal can be done using hysteroscopy. A special tube is inserted into the uterus, at the end of which there is a microvideo camera. Tweezers are inserted through a special channel, through which the formation is excised; in some cases, instead of tweezers, a loop is used to grasp the polyp around the stalk. This leads to separation of the formation from the uterus. After removal, the place where the tumor was located is cauterized with liquid nitrogen.
When a large cluster of tumors is diagnosed or their size is too large, an additional curettage procedure is performed. This guarantees the complete destruction of such a formation as a uterine polyp. The causes and consequences of surgery have been studied in detail in modern medicine. The risk of relapse remains minimal.
Symptoms
Every woman should undergo regular gynecological examination (at least once a year). This is especially true if there is at least one risk factor for the development of the disease. You should carefully listen to the state of your body, since polyposis manifests itself as follows:
- Inability to conceive.
- Violations, cycle failures, in particular towards polymenorrhea. During this period, abnormally heavy bleeding occurs.
- Irregular ovulation.
- Excessive uterine bleeding or discharge (spotting with bloody stains).
- Dyspareunia is pain during sexual intercourse.
- Discomfortable sensations in the abdominal area, pulling, grasping pain.
- In rare cases - general intoxication symptoms.
Possible complications
If treatment is started at the wrong time (too late), the course of the polyp may become more complicated. The most common of these complications are:
uterine fibroids;
- strangulation of the polyp;
- bleeding and posthemorrhagic severe anemia;
- endometrial cancer;
- growth of education to large sizes;
- necrosis of the polyp with ischemia.
In order to prevent the development of these pathologies, it is necessary to start treatment of polyps as early as possible.