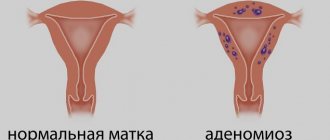
An ovarian luteal cyst is a benign neoplasm that occurs after the release of a mature egg from the dominant follicle.
The dominant follicle, also known as the “Graafian vesicle,” matures under the influence of estrogen, and during the period of increasing concentrations of luteinizing hormone, its membrane ruptures, which facilitates the release of the egg into the fallopian tube.
Cyst on the ovary: what is it?
An ovarian cyst is a neoplasm filled with fluid, located on the surface or in the thickness of the ovary. The size of the body can be insignificant, just a few millimeters, or reach a couple of tens of centimeters. The occurrence of an ovarian cyst is often associated with the normal functioning of the organ, which does not pose a serious danger to a woman’s health. However, in some cases, the appearance of a tumor may indicate the presence of a serious disease that requires special treatment.
How do cysts form? Every month, every woman develops a cyst in one of the ovaries, called a dominant follicle. This is a bubble filled with liquid where the germ cell matures. Its size can range from 0.5 to 2 cm.
On the 15th day after the start of menstruation, the dominant follicle bursts, releasing the egg, which enters the fallopian tube and, if a sperm is present, is fertilized. For unknown reasons, the follicle sometimes does not burst, but accumulates liquid in large quantities. Its diameter can reach 70 mm. This will be a functional or follicular cyst. However, don't panic right away. These types of ovarian cysts are considered harmless and often resolve after a few menstrual cycles.
After the follicle ruptures, a corpus luteum forms in its place. It is a collection of progesterone cells. Again, for unknown reasons, fluid collects in it and leads to the formation of a corpus luteum cyst.
Follicular cyst
Some types of ovarian cysts in women are directly related to persistent hormonal imbalances. Failures in the system can be associated with termination of pregnancy, especially in the later stages, as well as frequent exposure to stress.
All this creates optimal conditions for the development of a follicular cyst.
Doctors associate the appearance of the pathology with a lack of the hormone LH. Due to this rupture of the follicle does not occur.
The process of education formation is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- signs of fever in the form of body temperature above normal, chills, aches in bones and muscles, discomfort;
- discomfort in the back, especially in the lumbar region;
- problems with the cycle;
- presence of spotting.
In general, a follicular cyst is not considered a life-threatening condition. However, its treatment is lengthy and complex. And if the size of the formation is impressive, the doctor will recommend surgical intervention.
Types of ovarian cysts
In addition to the above-mentioned functional formations, which disappear on their own over several weeks or months, there are other types of ovarian cysts that appear against the background of various diseases.
These include:
- An endometrioid cyst is a cavity filled with blood that forms against the background of endometriosis (a gynecological disease in which there is an overgrowth of tissue similar to the mucous membrane of the uterine cavity on various organs).
- Dermoid cyst formed from cells of other organs. Its contents may include hair, bones, and cartilage. It is large in size and can be removed surgically.
- Hemorrhagic cyst resulting from hemorrhage into a functional formation.
- Polycystic syndrome is a gynecological disease accompanied by the appearance of a large number of cysts of different sizes.
- Cystadenoma is a benign formation that grows to a very large size, but does not show any symptoms.
- Mucinous neoplasm filled with mucous contents.
Treatment: is surgery necessary?
For functional cysts, expectant management is used for 2–3 menstrual cycles. The gynecologist monitors the growth of formations.
Several methods are suitable for treating cysts. In order for the cyst to resolve, hormonal therapy is carried out using oral contraceptives: “Yarina”, “Novinet”. Their action is based on suppressing the growth of follicles, as a result of which new cysts do not form, and old ones undergo regression.
If the cyst does not resolve and grows, there is a risk that it will burst. To eliminate risks, surgery is prescribed to remove it.
- During reproductive age, they strive to preserve the reproductive function of the ovary, so surgery is performed using a gentle method using laparoscopy. The intervention is performed through punctures on the abdomen, without making a cavity incision.
- If there is a tendency to growth or if there is a danger of torsion of the pedicle of a mobile cyst, another surgical tactic is necessary - wedge resection of the ovaries. In this case, the cyst is cut out along with part of the ovary.
- During menopause, a total oophorectomy is performed—the entire ovary is removed.
How does a cyst manifest itself: symptoms
The disease does not have any characteristic clinical manifestations. The symptoms are similar to those of many other diseases of the abdominal cavity and pelvic organs. However, some larger cysts may have the following symptoms:
- nagging pain in the lower abdomen;
- short attacks of acute pain with slight bleeding from the vagina;
- irregular menstrual cycle;
- slight spotting between periods;
- pressure or heaviness inside the abdomen;
- pain during and after sexual intercourse;
- pain after physical activity;
- vomit.
These symptoms may be more or less pronounced depending on the degree and type of disease.
Causes of luteal cysts
The formation of a neoplasm can be caused by the following reasons:
- hormonal imbalance that occurred due to any pathology of the endocrine glands (for example, hypothyroidism). This also includes incorrectly administered hormone therapy for the underlying disease, improper use of oral contraceptives, and use of drugs that are involved in stimulating the ovulatory cycle;
- persistent stressful situations;
- physical and/or mental fatigue;
- hypothermia at the time of ovulation;
- occupational hazards and diseases;
- drug abuse;
- sexually transmitted infections;
- bad habits;
- Weight loss, which interferes with estrogen production;
- inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs;
- abortion, which can also cause hormonal imbalance;
- oncological diseases.
Some experts adhere to the theory of a genetic predisposition to the formation of luteal cysts. That is, the neoplasm may never appear, but may arise under the influence of any of the above agents. The frequency of menstruation also has an impact on the development of this pathology. Thus, the average woman who gives birth to more than three children is much less at risk of developing cysts in the ovaries than someone who has never given birth at all.
In most cases, luteal cysts are benign. Despite this, the patient should regularly visit a gynecologist, especially if the tumor does not disappear within several months, but on the contrary begins to grow.
Detection of a cyst
In order to detect an ovarian cyst, it is necessary to undergo a gynecological examination, during which tenderness in the lower abdomen or enlarged appendages may be detected. Ultrasound allows you to painlessly and reliably determine the size of the tumor and its location.
A puncture of the posterior fornix will help detect the presence of blood or fluid in the vagina. This method is often used in case of complications.
It would be useful to donate blood for a test that will determine the markers of malignancy, hemoglobin level and the ability of blood to clot.
MRI allows you to determine the size, structure, contour, nature of the contents and how the cyst affects neighboring organs.
To rule out an ectopic pregnancy, you need to take a pregnancy test.
Drug therapy for cysts
This is the only method that has proven results and has the right to exist. Conservative treatment is always prescribed if the cyst is detected for the first time and is not classified as cancer, dermoid or endometrioid. Drug therapy is aimed at treating functional formations and includes drugs that act on the main causes of the appearance of such cysts. This means that the treatment will:
- anti-inflammatory;
- hormonal.
In addition, enzyme preparations that should help the cyst resolve and vitamins can be used.
Expert opinion
Daria Shirochina (obstetrician-gynecologist)
The duration of conservative treatment should not exceed 3 months (the basic regimen is about 10-14 days), after which its effectiveness is assessed. Presence of the cyst is an indication for its surgical removal.
Anti-inflammatory treatment
It is prescribed taking into account the fact that cysts can be a consequence of a chronic inflammatory process. This treatment is especially advisable in the presence of a large number of leukocytes in flora smears, when sexually transmitted infections are detected or clinical signs of adnexitis during examination.
First of all, antibacterial drugs are prescribed; it is advisable to choose them based on cultures of the vaginal microflora and determination of sensitivity. This will avoid unnecessary stress on the body and liver with ineffective medications. Either one group or a combination of several antibiotics can be used. The most commonly used are the following:
- Tetracyclines: "Doxycycline";
- Macrolides: Azithromycin, Erythromycin, Clarithromycin;
- Cefazolins: Cefepime, Cefotaxime;
- Cephalosporins: "Zinnat".
Often Metronidazole is added to regimens, which is not an antibiotic, but has antimicrobial activity, including against Trichomonas.
Antibacterial drugs are prescribed orally or in the form of injections or droppers. If inflammation is detected in the vagina or there is some kind of genital infection, local sanitation with suppositories, also containing antibiotics, is prescribed.
Basic therapy is supplemented by the use of painkillers that can reduce the intensity of inflammation. These can be injections or tablets, but more often rectal suppositories based on indomethacin or diclofenac are prescribed.
Hormonal treatment
Oral contraceptives are usually used for therapy for a period of at least 3 months, after which the effectiveness is monitored. These can be either combined preparations based on estrogens and gestagens, or containing only progesterone or its analogues. The medicine is selected by the doctor taking into account the woman’s constitution, bad habits, age and some other indicators.
When hormonal contraceptives are prescribed (most often these are pills, but there may also be vaginal rings, patches, etc.), the woman’s ovaries go into “hibernation”, due to which the functional cysts regress. But such treatment does not affect other cysts and, on the contrary, can enhance their growth. The most commonly used drugs are:
- "Regulon";
- "Jess", "Midiana", "Dimia";
- “Yarina”, “Diane-35” and others.
The use of only progesterone-containing hormonal drugs has a slightly different direction of action and is prescribed for severe insufficiency of the second phase of the cycle. The following medications may be used:
- "Duphaston", "Utrozhestan";
- "Norkolut";
- "Orgametril" and others.
These medications help restore the balance between estrogens and gestagens, improve the function of the pituitary gland, which leads to the normalization of ovarian function and the disappearance of cysts.
Cysts on the ovaries can be the result of a malfunction of the thyroid gland and pituitary gland with excessive production of prolactin. To correct such disorders, hormonal drugs of another class are used:
- dopamine receptor agonists: Bromocriptine, Cabergoline and others;
- thyroid hormones: “Thyroxine”, “Euthirox” and others.
Ultrasound of the thyroid gland
After normalization of the level of basic indicators, cysts on the ovaries disappear on their own.
Separately, it should be said about hormonal treatment of endometrioid cysts. First of all, they must be removed, and, if possible, all other existing foci of endometriosis. And only after this, hormonal treatment is prescribed to prevent relapse. The most commonly used drugs are:
- Agonists and antagonists of hypothalamic releasing hormones: Buserelin, Zoladex and others. They can be in the form of injections, which are given once a month or even every 3 months, a spray for nasal use, or patches.
- Preparations based on dienogest. For example, Mirena (intrauterine device), Visanne and other drugs.
Conservative treatment of endometriosis/endometrioid cysts
The course of treatment and regimens are prescribed only by a doctor.
Ovarian cyst: why is it dangerous?
In most cases, the disease is considered harmless, and treatment of ovarian cysts without surgery is quite possible. But in some cases, complications can lead to irreparable consequences.
Twisting of the cyst stalk is dangerous for the ovaries. This can happen under the influence of intense physical activity or during vigorous sexual intercourse. This is fraught with tissue necrosis, since twisting makes it difficult for blood to access part of the ovary. This process is expressed by severe sharp pain in the abdominal area. This cannot be done without surgical intervention.
An increase in body temperature and pain in the lower abdomen is accompanied by suppuration. If it ruptures, it will be impossible to treat the ovarian cyst without surgery.
Physical activity can also lead to cyst rupture. This happens when the tumor grows, its walls become thinner, and more and more fluid accumulates. When ruptured, the contents of the tumor can enter the abdominal cavity and cause peritonitis. Surgical intervention will be less traumatic than when twisting the cyst.
Only a functional ovarian cyst can resolve without complications. The consequences of, for example, endometrioid and dermoid formations can be disastrous, as they can degenerate into a malignant tumor.
Every woman should think about the question of how to treat an ovarian cyst, since a constantly growing tumor, even if it is not malignant, can lead to disruption of the functioning of neighboring internal organs as a result of compression. And another extremely unpleasant consequence of a cyst can be female infertility.
An ovarian cyst, the consequences of which can be very different, requires immediate consultation with a doctor and immediate treatment to avoid serious conditions and complications.
Features of a serous cyst
Another type of benign formation is considered to be a serous cyst or cystadenoma. Externally, it is represented by a single-chamber bubble with light contents and non-elastic walls.
They are localized on one of the ovaries. If the conditions are right, the growth can grow up to 30 cm in diameter. The pathology is most often diagnosed by ultrasound, when women come with complaints of problems with the menstrual cycle and pain during sexual intercourse.
In addition to this disease, it also has other symptoms:
- painful sensations in the lower abdomen and lower back even at rest;
- a feeling of squeezing affecting the bladder, rectum and nearby internal organs;
- difficulty with bowel movements;
- increased nausea and vomiting;
- neuralgic disorders in the form of sleep problems, decreased performance, causeless lethargy and weakness;
- with a large cyst, a protrusion on the abdomen on the side of the formation becomes noticeable.
If treatment is not started in time, the growth will fester. Because of this, an inflammatory process will begin, accompanied by a sharp jump in body temperature.
It is also possible for the stem to twist, and in rare cases, rupture of the formation. As a result, signs of peritonitis and sepsis will be observed. The probability of transition to a malignant form is 10-15%.
Conservative methods of therapy
How to treat an ovarian cyst depends on its origin, size, dynamics of development and age of the patient. If hormonal levels provoke the appearance of a cyst, then the use of oral contraceptives is prescribed for several months. This will block the functioning of the ovaries, normalize the production of hormones and the menstrual cycle, which will lead to a decrease or complete disappearance of the tumor.
Treatment of ovarian cysts without surgery is possible by taking tablets containing progesterone. In a healthy body, this hormone is produced in the second half of the cycle and during pregnancy. However, an insufficient amount of it against the background of excess estrogen leads to the formation of a cyst. The tablets will help reduce the size of the tumor.
How is it formed
Normally, during the follicular phase, the formation of the corpus luteum occurs in place of the Graafian vesicle, which carried the egg within itself for two weeks. The corpus luteum begins to produce progesterone (the pregnancy hormone), which is necessary to ensure conception.
If fertilization does not occur, then the VT regresses and turns white. In case of conception, the corpus luteum grows even more and begins to produce progesterone with redoubled force. With pathology, VT does not disappear after ovulation, but begins to accumulate a transparent or hemorrhagic secretion, turning into a luteal cyst. In addition, theca lutein cysts of the ovaries, unlike luteal cysts, develop due to underdevelopment of the follicle - ovulation does not occur. This is an important diagnostic criterion between two seemingly similar neoplasms.
Luteal cysts differ from other ovarian cysts in their ability to resolve on their own within a few months after their appearance and in their purely functional nature. Moreover, an interesting fact is the formation of the formation in the right ovary due to better blood supply.
Treatment of cysts with Duphaston
"Duphaston" is one of the drugs prescribed for the treatment of ovarian cysts. The active substance is an analogue of progesterone - dydrogesterone. Despite its chemical nature, it is an excellent substitute for natural progesterone, performing its functions well. It affects the walls of the uterus and has no side effects.
“Duphaston” is mandatory for follicular ovarian cysts, as it promotes the timely transition of the 1st phase of the menstrual cycle to the second, while preventing the endometrium from growing. Moreover, long-term use of Duphaston is prescribed for endometrioid cysts, since the drug can prevent the appearance of new tumors. In this case, the medicine is combined with surgical treatment. "Duphaston" for ovarian cysts is often the only medicine that can help in the fight against neoplasms.
Why is it better to see a doctor?
In addition to the fact that the cyst may turn out to be malignant initially or acquire signs of oncogenic growth within 5-10 years, the following complications of such neoplasms on the ovaries are possible:
- Gap . This is one of the common situations that is provoked by physical activity, intimate relationships, sudden movements and other situations that lead to changes in intra-abdominal pressure, the field of which the cyst capsules may not withstand and rupture.
According to ultrasound: rupture of hemorrhagic ovarian cyst
- Torsion of the legs . By “pedicle” we mean a complex of vessels and nerves that approach the cyst. As a result of the tumor rotating 180 or 360 degrees, the flow of blood to and outflow from the cyst is disrupted, which leads to the development of peritonitis.
- Hormonal disorders . Cysts are often accompanied by menstrual irregularities, infertility and other problems.
- Inflammation of the cyst with progression . Infection of the formation can occur both in the presence of the genital tract and in the activation of its own opportunistic flora, and abscesses can form and, as a consequence, peritonitis.
All these conditions pose a threat to a woman’s life and require urgent surgical treatment with removal of the cyst or the entire ovary.
Reviews from doctors and patients about the drug
Most gynecologists and obstetricians turn to hormone therapy in the course of their work, and in particular to the new generation drug Duphaston. Experts say that the effectiveness of such a medicine is undeniable, but you should be careful about the individual characteristics of the body, the diagnosis and the pill regimen. The dosage of Duphaston can be determined exclusively by the attending physician after studying the general picture of the disease, all test results and direct examination of the patient.
After taking the pills, women note a normalization of their cycle, an improvement in hormonal levels, and evidence that the diagnosis of “threatened miscarriage” has been removed. Being a new generation drug, Duphaston does not contribute to weight gain, body hair growth, or changes in voice timbre.
Diagnostics
The following examination options are used:
Upon consultation with a doctor, manual examination reveals additional parts of the ovaries exceeding 20 cm; they do not cause pain. Pregnancy or hydatidiform mole are determined by special tests.
Ultrasound of the pelvic organs confirms the presence of cysts with a multi-chamber structure, homogeneous contents without inclusions, and a bilateral location.
In some cases, diagnostic laparoscopy is indicated.
During a cesarean section or abdominal surgery, these cysts are easily identified. They are a structure with thin walls in the form of a bunch, which has a stressed state. When cut, a yellow lining of the inner layer with yellow liquid is visible.
Stopping the medication
Hormonal treatment can only be started under the supervision of a doctor. Self-administration can cause considerable harm to a woman’s body, so starting and stopping a course of therapy should be agreed upon with a doctor, especially if the woman becomes pregnant during the period of use. The doctor must develop a plan for completing the medication, which should not be abrupt. Typically, during pregnancy, Duphaston is taken until the 12th week, after which the dose is gradually reduced and reduced to a minimum until treatment is completely stopped.
Can a cyst resolve on its own?
Spontaneous resorption of cysts is not excluded, but most often this phenomenon is observed in the case of the formation of a neoplasm due to ovarian dysfunction.
As soon as the functioning of the organs is normalized and stabilized, the cystic formation may regress.
Doctors identify only one type of cyst, which is prone to disappearing on its own - functional ones.
This type of cystic formation includes:
- corpus luteum cyst;
- follicular cyst.
Quite often these cysts resolve while waiting for the baby.
CAREFULLY!
If there is no positive dynamics within three cycles, it is necessary to begin treatment measures.
Folk remedies
Women often wonder how to cure an ovarian cyst with folk remedies? In this case, there are many options. To treat a neoplasm, you can use honey, which is inserted into the vagina as a tampon. You can mix honey and viburnum, which is famous for its healing properties, in a 1:1 ratio, and take the mixture on an empty stomach for three months intermittently.
It is recommended to use soda from available means. A tablespoon of powder, slaked with vinegar, is mixed with a glass of vodka and three liters of water. You will also need a glass of vinegar. First we extinguish the soda, then add the rest of the products. Flaxseed oil in general has a beneficial effect on the female body and directly normalizes hormonal levels. Walnuts, or rather, the partitions of its shell cope well with hormonal imbalances. Infusions from the herbs of boron uterus and elecampane are considered good helpers in the fight against ovarian cysts.
Treatment of ovarian cysts without surgery is a completely doable task. The main thing is to consult a doctor in time, follow his recommendations and not delay treatment if symptoms are identified.
Traditional methods of treatment
Alternative treatment should be approached with caution and only in accordance with the doctor’s recommendation. In no case should you try to get rid of long-existing formations in this way or those that are suspicious according to ultrasound or tests for tumor markers. Alternative treatment can be used in combination with the main one.
Special compositions for tampons
To use them, it is necessary to prepare, in addition to the healing composition, the tampons themselves from gauze or bandage. Then apply the medicine to them and lay them down, usually overnight.
The recipes are as follows:
- Honey onion . You need to take a small onion and place it in a preheated oven for 10-15 minutes. Then you should dip the onion in honey and leave for a couple of hours to soak it. Subsequently, wrap the bulb with gauze or a bandage and insert it into the vagina at night. The course is at least 7-10 procedures.
- Mumiyo with honey . You need to take 3-4 g of mumiyo and dissolve it in a small amount of water. Add honey, but it should not be fresh, but slightly sugared. Mix with mumiyo. Soak a gauze pad and insert it into the vagina at night. Course - 14 days.
- Nettle juice. You need to take fresh leaves and squeeze the juice out of them. Soak gauze swabs and place them in the vagina overnight for at least 7 days.
- Kalonchoe with honey . It is necessary to take Kalanchoe juice and fresh honey in equal proportions. Also apply to tampons. The course is at least a week.
- Aloe leaves . You need to take old fresh leaves of the plant, chop and squeeze the juice out of them. Use to soak tampons immediately before insertion. Treatment for at least a week.
- Ointment based on sea buckthorn oil . You need to take a tablespoon of beeswax, one boiled yolk, a teaspoon of fresh aloe juice. Mix and add sea buckthorn oil until you obtain a jelly-like consistency. Apply to a gauze pad and then into the vagina at night. If you add more wax, you can form unique candles and use them separately.
Decoctions and infusions
Traditional recipes for the treatment of cysts also include various healing solutions that can be taken orally. Here are some:
- Borovaya uterus . You need to take one tablespoon of dried herb and pour a glass of water that has just been brought to a boil. You can place it in a thermos or simply wrap the jar and let it sit for 3-5 hours. Take 3 tablespoons orally 3-5 times a day.
- Red brush. You need to take 3 tablespoons of the dried plant and chop it. Add four glasses of alcohol or vodka. Leave for 14 days in a dark place at a temperature of no more than 20 degrees. Take a teaspoon three times a day before meals.
- Burdock . You need to take a fresh plant and squeeze the juice out of it. Take 2-3 teaspoons for 3 weeks.
- Dandelion. You need to take one teaspoon of crushed dandelion root and pour a glass of water at 100 degrees. Leave for half an hour and take 50 ml orally 2 times a day.
Douching
To do this, you can use the following recipes:
- Infusion from mantle . You need to take 3 tablespoons of the herb and pour 500 ml of red wine. Heat, but do not bring to a boil. After this, leave for another day and use for douching twice a day.
- Infusion of celandine . You need to take fresh celandine (10 g) and add 200 ml of hot water. Leave for 24 hours, strain and use for douching in the morning and evening.
We recommend reading about the manifestations of ovarian cyst inflammation. From the article you will learn about the causes and symptoms of inflammation of the ovarian cyst, possible complications without treatment, drug therapy and surgery. And here is more information about the features of ovarian laparoscopy and the postoperative period.
An ovarian cyst, even if it does not have warning signs at first glance, can hide dangerous diseases and complications. Therefore, any formations on the ovaries require careful attention and timely treatment. If there is no effect, they must be removed.
Features of cysts of the right and left ovary
It is the right ovary that is more susceptible to various diseases and inflammations. This is explained by its greater activity compared to the left.
If we talk about the formation on the right ovary, then there are characteristic symptoms:
- signs of intoxication;
- an increase in abdominal volume, and it is often asymmetrical;
- decreased blood pressure;
- patient complaints of constipation;
- feeling of tension in the abdominal muscles;
- tachycardia.
The peculiarity of the cyst on the left ovary is that the disease develops much faster.
Such a formation can lead to new tumors on healthy organs, as well as diseases of the urinary system and abdominal cavity.
Experts believe that the main reason for the appearance of a tumor on the left side is that less blood enters this part during ovulation and menstruation.
Malignant neoplasm
If we look at the classification of ovarian cysts, we must take into account that they can be malignant. The tumor grows very quickly and reaches a significant size. Some individual types of cysts, in particular mucous cysts, have a tendency to malignancy, gradually degenerating into a malignant neoplasm.
Cystoma provokes menstrual irregularities, constipation, abdominal pain, and infertility. It often occurs with torsion of the leg, rupture with internal bleeding, and suppuration with the formation of peritonitis.
Ultrasound and tomography are used to diagnose cystoma. The diagnosis is confirmed by laparoscopy with biopsy. This intervention is often therapeutic in nature.
Sometimes there is a need for laparotomy. In this case, a small piece of tissue is taken from the woman and sent for histology. When cancer cells are damaged, the scope of the operation expands somewhat. Malignant cystomas are also treated with hormonal drugs, chemotherapy, and radiation methods.
Feature of treatment
Depending on the type and symptoms of the ovarian cyst, treatment is selected strictly individually, and only the doctor decides on the method of therapy. Treatment can be carried out conservatively and through surgery. In order to prevent torsion and rupture of the cyst, the following recommendations should be followed:
- reduce physical activity;
- refuse physiotherapy and spa;
- do not take hot baths.
In addition, you need to limit your exposure to the sun, and also not visit the solarium, as this can only aggravate the condition.
Basic information about pathology
A luteal cyst is one of the types of functional benign formations on the ovaries. It is formed after the egg has left the follicle. At this moment, the woman ovulates. After this, a corpus luteum is formed from the remaining capsule of the follicle, which, if the outcome is favorable, will be responsible for the safety of pregnancy. If conception does not happen during this cycle, then it simply resolves.
If a hormonal imbalance occurs, then a cyst may grow in place of the corpus luteum. It will be expelled inside by luteal cells. Fluid may accumulate in the cyst, this is normal. Most often, luteal tumors resolve on their own. This type of cyst forms only in the 2nd half of the menstrual cycle. If a woman has one follicle that has matured, then the neoplasm will be the only one.
Causes
It is clear that the etiology of occurrence for each type of neoplasm in the female reproductive system is different.
However, bringing all the main reasons into a general list, you can see the following :
- Disruption of the endocrine system - pituitary gland, hypothalamus, adrenal glands and thyroid gland. All this leads to disruptions in the menstrual cycle and hormonal imbalance.
- A girl's puberty is too early, accompanied by menstruation.
- Abortion or miscarriage.
- Infection in the female reproductive system - from cystitis to STDs.
- Excess body weight.
- Lack of regular sex life.
- A woman is taking a number of medications.
CAREFULLY!
The drug Tamoxifen, prescribed for breast cancer, can cause the formation of a tumor in the ovary.
Classification of ovarian cystic formations
There are several main classifications of ovarian cysts. Depending on the time of occurrence:
- Functional cysts . This is a temporary type of cyst (they exist for several menstrual cycles). The cause is a disruption of the normal course of menstruation and, in particular, the ovulation process. They are not dangerous and disappear spontaneously; no treatment is required.
- Anatomical cysts . Their occurrence is often associated with an abnormal structure of the ovaries (congenital tissue defects). In rare cases, their appearance is preceded by large functional cysts. In this case, the normal structure of the ovaries is destroyed. Requires medical or surgical treatment.
Depending on the size there are:
Requires only observation
Requires drug treatment and ultrasound monitoring
Require surgical treatment
As a rule, all types of ovarian cysts are asymptomatic. In case of complications (leg torsion, rupture), symptoms of an acute abdomen occur, which require emergency hospitalization and hospital treatment, and in 90% surgery is required.
Follicular cyst
It belongs to the type of functional neoplasms and is often detected accidentally by ultrasound. Only instrumental diagnostics can make a diagnosis, since it rarely manifests itself clinically.
- Occurs at a young age.
- Associated with ovulation disorders (the follicle does not burst and the egg does not come out of it). The cavity of the follicle begins to fill with fluid, as a result of which it increases.
- It has a direct connection with disruption of the hormonal system.
- Rarely reaches large sizes. Most often diagnosed within 4-6 cm (can reach up to 12 cm).
The clinical picture occurs when cysts are larger than 8 cm, since in this case there is a high risk of torsion and rupture with the development of clinical peritonitis (pain, intoxication, cardiovascular disorders).
If the neoplasm is hormone-producing (no more than 5% of all cases), estrogens are additionally released into the blood, which lead to premature puberty, problems with conception, and bleeding from the uterus.
- single-chamber;
- single;
- round with clear contours;
- thin-walled;
- the contents are homogeneous.
There are no histological features.
Corpus luteum cyst
The corpus luteum is formed in the ovaries under the influence of luteinizing hormone from the pituitary gland. The formation of a cystic cavity is based on impaired blood and lymph circulation, which leads to the accumulation of serous fluid. Corpus luteum cyst also refers to functional formations.
- It is formed by a temporary secretion gland (the corpus luteum forms and involutions monthly).
- Occurs at a young age (not typical during menopause, since ovulation does not occur).
- The name is determined by the lipochrome pigment in the cavity of the gland.
- It is a hormone-producing formation - it secretes progesterone.
- Occurs during ovulation and ensures implantation of the fertilized egg into the endometrium.
- During pregnancy, the regression process occurs between 1 and 12 weeks.
In rare cases, the cyst cavity may be filled with hemorrhagic contents. The diameter usually does not exceed 6-8 cm. It is discovered accidentally on ultrasound. The clinical picture of the disease occurs extremely rarely, only in the event of complications.
- has a cellular structure;
- wall thickness reaches 2-4 mm;
- good blood supply to surrounding tissues;
- has a round or oval shape;
- the contents are homogeneous (echo signs of microhemorrhage into the cyst cavity may be added).
Histologically, the homogeneous structure is represented by cells of the corpus luteum, which are located in several layers.
The cyst goes through several stages of development:
- Proliferation.
- Vascularization.
- Bloom.
- Reverse development.
Depending on the phase, according to ultrasound, cysts differ slightly in size, density and content.
Paraovarian cyst
It arises from a retention formation - epioophoron. This is the embryonic remnant of the primary kidney, which lies between the ligaments of the uterus, the ovary and the fallopian tube. It does not come out directly from the ovarian tissues, but is located in nearby tissues.
- Large sizes (up to 15-20 cm).
- Occurs in adulthood.
- Clinically expressed by pain and pulling sensations in the lower abdomen.
- Affects nearby organs (bladder - causes frequent urination, rectum - false urge to defecate).
- There is a high risk of developing torsions and ruptures, which leads to emergency indications for hospitalization.
- Motionless.
- Does not regress on its own.
Diagnosis of formations
In order to accurately determine the treatment regimen, it is necessary to correctly determine the type of disease.
A gynecologist will tell you how to identify an ovarian cyst. First, inspection and palpation are carried out. Further diagnostics are carried out using several methods at once:
- Clinical analysis of plasma. Laboratory testing determines the presence of inflammation and anemia. When it is normal, another disease is causing the symptoms.
- Ultrasound of the ovaries. Refers to instrumental diagnostic methods, which allows you to see the size of the formation, hyperechoic inclusions and determine its location. If ovarian enlargement is diagnosed on ultrasound, the reasons for this can be determined with high accuracy. Ultrasound data helps determine how quickly the disease is progressing.
- Laparoscopic surgery. A fiber optic tube with a camera and light is inserted into the abdominal cavity, allowing the mass to be seen. In the case when it is located on the surface, it becomes possible to take a piece of tissue, if a neoplasm is located on the ovary, for histological examination. This is necessary to exclude cancer. Diagnosis is carried out, treatment is determined by the doctor.
- Ovarian puncture. It is carried out only under the control of ultrasound of the ovaries. During the procedure, the wall of the abdominal cavity is punctured and a special needle is inserted into the tumor, with which the fluid inside the tumor is taken for analysis. This diagnostic method allows you to determine the type of formation.
One of the most informative ways to determine the disease is an ultrasound of the ovaries, especially when the procedure is performed using a transvaginal sensor, where you can see how enlarged the ovary is.
Hysteroscopy.
Increase. The use of all diagnostic methods allows you to accurately establish a diagnosis and prescribe treatment. The treatment regimen and time depend on the accuracy of the diagnosis. If the type of disease has been incorrectly determined, treatment will not bring the desired result and the risk of developing serious consequences will increase.
Diagnosis of pathology
To determine that the neoplasm is indeed a luteal cyst, you must first contact a specialist. Do not self-medicate under any circumstances .
The gynecologist will first conduct a visual examination. After this, the doctor prescribes a series of tests and an ultrasound examination for the patient.
These measures are considered the main diagnostic methods. An additional research method is laparoscopy.
Causes
The cause of the development of pathology may be inflammatory processes in the organs of the genitourinary system, hormonal imbalance.
Risk factors include:
- frequent stressful situations;
- hypothermia or overheating of the body;
- excessive physical activity;
- abortions;
- endocrine diseases;
- bad habits;
- underweight or obesity.
Injuries, surgical interventions, and uncontrolled use of oral contraceptives can contribute to the development of the pathological process.
What kind of discharge can there be and how dangerous is it?
When an appendage cyst is formed, including a hemorrhagic type, discharge of varying intensity is noted. Due to hormonal disorders (lack of estrogen and progesterone), discharge may also be observed. Yellow-green discharge may indicate the presence of an infectious-inflammatory process.
Damage to blood vessels with an ovarian cyst is accompanied by acute pain. In certain cases, brown discharge occurs with an ovarian cyst from the vagina or may leak into the abdominal cavity. In some cases, uterine bleeding is detected, which begins as a result of uneven exfoliation of the endometrium.
Copious brown discharge from an ovarian cyst, as well as bleeding, occurs during the transition of the disease to the acute or oncological stage. If there is discharge from an ovarian cyst, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Corpus luteum cyst
The corpus luteum is a temporary gland that develops at the site of a follicle that has burst. The purpose of the corpus luteum is to produce progesterone for possible conception and further pregnancy. The cyst appears in the part where the corpus luteum is located.
A corpus luteum cyst can appear not only in the second half of the cycle, but also during an existing pregnancy. The main cause of the pathology is considered to be poor circulation. An important role in the appearance of cysts is played by the functioning of the endocrine system and chronic inflammation in the woman’s genital organs.
A corpus luteum cyst is often discovered by chance during an examination, because at the initial stage it does not manifest itself in any way. But some patients complain of nagging and aching pain on one side of the abdomen, which radiates to the lower back. Sometimes there is intermenstrual bleeding and a complete absence of menstruation.
The danger of a corpus luteum cyst is that it can burst or twist its stem. A burst cyst can cause bleeding. Without medical care, a woman may die.
Symptoms of a ruptured cyst:
- Sharp cutting pain around the abdomen.
- Nausea, vomiting.
- Dizziness.
A partially twisted leg interferes with the normal outflow of blood, which causes problems with venous circulation. When the cyst is completely twisted, blood circulation stops at the site of the cyst and it dies. Necrosis of the cyst causes an inflammatory process in the surrounding tissues, which can develop into peritonitis (inflammation of the abdominal cavity).
Before surgery, the cyst is observed for a long time.
After removal, it is sent for mandatory histological examination to exclude the presence of malignant cells.
Do not ignore the symptoms that appear. Early detection of a corpus luteum cyst is a guarantee of successful treatment without serious consequences.
Carrying out prevention
Preventive measures are very important. Considering that the causes of cyst formation in many cases are associated with inflammation, prevention includes:
- reduction in the number of abortions;
- sufficient physical activity;
- weight normalization;
- using a condom.
Ovarian cysts are quite common in women. It can be benign or malignant. Before treatment, it is imperative to undergo a full examination to determine the type of pathology and prescribe therapy.
The most effective types of diagnostics
The best types of studies of ovarian tumors include instrumental studies - ultrasound and CT. With their help, you can determine all the main characteristics of the pathology. The remaining tests are more necessary to determine the cause of the development of the tumor.
Ultrasound
A completely safe research method. It is considered the most common type of diagnostics of the genital organs. To increase the information content of ultrasound, the following preparation is necessary:
- Transabdominal ultrasound. It is performed through the anterior abdominal wall. Requires a full bladder. To do this, you need to drink a liter of any liquid an hour before the test.
- Transvaginal. With this type of ovarian diagnosis, the bladder must be emptied.
During an ultrasound scan of any pelvic organs, you should avoid taking gas-forming products for several days. If there is bloating, you should drink a sorbent.
Sometimes, when organs are poorly visible, both types of ultrasound are performed. In most cases, transvaginal ultrasound diagnosis is sufficient. The doctor’s report specifies the following parameters:
- ovarian size;
- number of cysts and their diameter;
- type of capsule;
- the presence of other diseases of the genital organs.
To monitor the growth of the formation, the diagnosis should be repeated after a few weeks. Subsequently, during treatment, examinations are carried out periodically until complete recovery.
If a ruptured ovarian cyst is suspected, differential diagnosis by ultrasound with appendicitis, acute inflammation of organs in the pelvis, or peritonitis is necessary.
CT scan
It is performed instead of ultrasound or when its information content is low. Due to layer-by-layer scanning of the pelvic area, it allows you to evaluate the structure of the ovarian cyst, its size, type, presence of a pedicle and other parameters.
Due to the presence of radiation, CT scanning is prohibited during pregnancy, renal failure, and endocrine diseases.
Before the study, you must empty your bowels and fill your bladder. For 2-3 days, gas-forming products are excluded from the diet. If there is no stool, it is recommended to do an enema or take a laxative.
To perform a CT scan, the patient lies down on a special table placed in the tomograph. The procedure is absolutely painless and requires only complete immobility. Its duration is up to 25 minutes. After the examination, the doctor receives several images, based on which he determines the diagnosis.
Laparoscopy
Laparoscopy for ovarian cysts is rarely used. This is carried out in the presence of the following indications:
- unknown type of neoplasm;
- lack of results from drug treatment;
- the need for diagnosis with immediate elimination of pathology.
To begin the operation, several small punctures are made in the abdominal wall, through which instruments are inserted. The peritoneum is filled with carbon dioxide to increase visibility of the organs. The inspection takes place using a small camera, the image of which is displayed on the monitor screen. The course of the intervention depends on the type of pathologies detected and the availability of the possibility of their immediate elimination.
Puncture of the posterior vaginal fornix
Using only puncture of the posterior vaginal fornix it is impossible to conduct a detailed examination of the ovary. The procedure is considered auxiliary and requires placing the patient under anesthesia or performing local anesthesia. Before the puncture, you should empty your bladder and bowels.
To perform the diagnosis, a puncture is made with a special needle under the cervix. The method involves collecting the contents of the cyst or fluid in the retrouterine space for further examination. The presence of purulent fluid indicates peritonitis or purulent inflammation, blood - the presence of bleeding.
Puncture of the posterior vaginal fornix when diagnosing ovarian cysts is rarely used due to low information content and complexity of execution.
To identify a tumor on the appendage, it is necessary to conduct a comprehensive study. It includes several types of laboratory and instrumental diagnostics. Usually, an ultrasound or CT scan is sufficient to determine the type of ovarian cyst; the reasons for its occurrence are blood donations for hormones and tumor markers.
Video
We offer you to watch a video on the topic of the article.
Education: Rostov State Medical University, specialty “General Medicine”.
Found an error in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
During operation, our brain expends an amount of energy equal to a 10-watt light bulb. So the image of a light bulb above your head at the moment an interesting thought arises is not so far from the truth.
Dentists appeared relatively recently. Back in the 19th century, pulling out diseased teeth was the responsibility of an ordinary hairdresser.
Besides people, only one living creature on planet Earth suffers from prostatitis - dogs. These are truly our most faithful friends.
Smiling just twice a day can lower your blood pressure and reduce the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
Even if a person's heart does not beat, he can still live for a long period of time, as the Norwegian fisherman Jan Revsdal demonstrated to us. His “engine” stopped for 4 hours after a fisherman got lost and fell asleep in the snow.
You are more likely to break your neck if you fall off a donkey than if you fall off a horse. Just don't try to refute this statement.
Many drugs were initially marketed as medicines. Heroin, for example, was originally brought to market as a cure for children's coughs. And cocaine was recommended by doctors as an anesthesia and as a means of increasing endurance.
Millions of bacteria are born, live and die in our intestines. They can only be seen under high magnification, but if they were put together, they would fit in a regular coffee cup.
Over the course of a lifetime, the average person produces no less than two large pools of saliva.
According to many scientists, vitamin complexes are practically useless for humans.
There are very interesting medical syndromes, for example, compulsive swallowing of objects. One patient suffering from this mania had 2,500 foreign objects in her stomach.
If your liver stopped working, death would occur within 24 hours.
In 5% of patients, the antidepressant Clomipramine causes orgasm.
According to WHO research, talking on a mobile phone for half an hour every day increases the likelihood of developing a brain tumor by 40%.
When we sneeze, our body stops working completely. Even the heart stops.
Most people do not attach much importance to such a symptom as the flow of fluid from the nose. A common runny nose does not cause concern, even if it is accompanied by p.
The ovaries determine a woman’s reproductive ability; in addition, they are responsible for normal hormonal levels. When these organs malfunction, certain types of ovarian cysts occur in women, which, if left untreated, can cause negative consequences.
Symptoms and signs of ovarian luteal cyst
Since the corpus luteum is the result of transformation of the tissues of the Graafian vesicle released from the mature egg, a luteal cyst can form only in the second half of the menstrual cycle.
A luteal cyst is a single formation. During a time equal to one intermenstrual interval, in the ovary only one follicle (and one egg, respectively) is able to complete the full maturation cycle, therefore, after ovulation, one corpus luteum remains, which can become the source of cyst formation. At one time, only one luteal cyst of the left ovary or luteal cyst of the right ovary can be present in the ovary.
Since the function of the capsule of the luteal cyst is performed by the thin shell of the corpus luteum, which is not capable of stretching too much, the luteal cyst is characterized by a relatively small (usually 4-8 cm) size, as well as the absence of any clinical symptoms.
Luteal cysts are rarely diagnosed. Obviously, this is due to their asymptomatic course and the ability to self-reduce over two or three subsequent cycles.
In rare cases, especially against the background of existing local infectious inflammation, the presence of a luteal cyst in the ovary can provoke a number of symptoms:
— Pain in the projection of the cyst localization. Sometimes instead of pain there is a feeling of fullness, heaviness or discomfort. Similar symptoms appear when the cyst becomes large, or when the ovary is inflamed.
- Hormonal dysfunction. The long-term presence of a luteal cyst in the ovary can lead to excessive accumulation of progesterone and, as a result, a delay in the next menstrual bleeding. Menstruation against the background of cystic transformation of the corpus luteum sometimes becomes longer and/or more abundant.
Complications of a luteal cyst are rare. These include:
— Torsion of the pedicle of the cyst. The luteal cyst is attached to the surface of the ovary through a small outgrowth - a stalk, which is not able to hold the cyst in one position and ensures its mobility. If the cyst rotates around its axis, it drags the leg with it. As a result, due to torsion of the legs, the vessels feeding the cyst are compressed, and a necrotic process develops.
- Cyst rupture. During the formation of the corpus luteum (second phase), vascularization processes may be disrupted. As a result, the vessels located in the cyst shell are destroyed, and blood enters the cyst cavity and accumulates in it. An increasing amount of blood in the cystic cavity leads to the formation of a hematoma; it increases until both the cyst and, accordingly, the ovarian capsule rupture.
Methods of drug treatment
It is worth noting that this method of therapy is prescribed by the doctor only when the source of the cyst is a normal macula or a mature follicle that has not ovulated.
There are some contraindications to treating ovarian luteal cysts with medications:
- exacerbation of a chronic inflammatory process in the area of the appendages, especially if the doctor suspects a suppurating cyst;
- cyst rupture with internal bleeding;
- female infertility;
- cases where cysts appeared due to a tumor.
As soon as the gynecologist has carried out a full diagnosis and is convinced that the cyst is not a tumor formation, he prescribes hormonal drugs.
Basically, the main active ingredient of these drugs is progesterone - this is a hormone whose main function is to ensure the normal course of the second half of the menstrual cycle..
Oral contraceptives are considered another good drug for the treatment of ovarian luteal cysts.
Taking them not only ensures a reduction in the size of existing tumors, but is also a good prevention of the formation of new cysts.
Drug treatment also includes taking anti-inflammatory drugs . Antimicrobial agents can also be added to this list.
In rare cases, the gynecologist may prescribe antidepressants.