Most often, chronic pharyngitis, characterized by alternating periods of remission and exacerbation, occurs due to improper or insufficient treatment of the acute form of the disease. It manifests itself in the development of inflammatory foci on the mucous membranes of the throat.
Forms of the disease
There are several types of chronic pharyngitis.
- Catarrhal (simple) - persistent diffuse venous hyperemia, swelling of the mucous membrane, dilation and stasis of small-caliber veins, dilation of the excretory ducts and hypersecretion of the mucous glands.
- Allergic – the result of a local allergic reaction, there is a cause-and-effect relationship between the allergen and the appearance of symptoms of the disease, while the allergen can be contained both in food and inhaled air.
- Atrophic - characterized by dry throat, difficulty swallowing, and bad breath. The patient drinks a lot of fluid, especially during a long conversation.
- Hypertrophic - there is a release of a large number of mucous clots that settle on the walls of the pharynx, while the palate and uvula become inflamed. In these cases, the patient wants to constantly cough and expectorate. Sometimes coughing occurs with nausea.
In childhood, catarrhal, hypertrophic (granular) and lateral pharyngitis are more common, and atrophic is rare. The latter is often combined with chronic rhinitis. Therefore, how to treat chronic pharyngitis will directly depend on the form of the disease, as well as the corresponding symptoms.
The most striking signs of the chronic form are:
- Dryness, soreness, sensation of a foreign body in the throat, cough.
- Tearing.
- Discharge of viscous secretion, especially in the morning.
- It is not often that complaints do not correspond to the pharyngoscopic picture - they may be insignificant or absent with pronounced changes in the pharyngeal mucosa and vice versa.
Chronic pharyngitis develops slowly over many years. Each exacerbation is replaced by remission, when all signs of the disease are expressed implicitly.
Forecast
The prognosis depends on the form of the disease, the degree of damage to the mucous membrane, the duration of the inflammatory process, the general condition of the patient, as well as the adequacy of treatment. It should be long-term and comprehensive, which will make it possible to reduce the number of relapses or even completely get rid of the disease.
Often chronic pharyngitis is not an independent disease, but a sign of pathology of the digestive system.
If treatment of atrophic pharyngitis is started at an early stage, the structure of the mucous membrane can be completely restored.
Symptoms of chronic pharyngitis in adults
In the chronic form of the disease, complete catarrhal damage to the pharynx, as well as the mucous membrane of the nasopharynx, occurs. Sometimes the auditory tube and paranasal sinuses are affected.
The symptoms of chronic pharyngitis in adults are less pronounced in contrast to the acute form, and the disease is practically asymptomatic - there is no fever, depression, but tickling, dryness, hoarseness of the voice and the sensation of a lump in the throat are constantly present. Patients may be tormented by a dry cough; they want to clear their throat as quickly as possible, but attempts are in vain.
The standard clinical picture of symptoms includes:
- moderate sore throat;
- nausea, the appearance of a gag reflex during expectoration;
- dryness, irritation in the throat, especially when inhaling hot or cold air;
- the presence of viscous discharge in the throat in small quantities;
- feeling that there is a lump or foreign body in the throat (happens occasionally);
- coughing;
- cervical lymphadenitis;
- increased symptoms of the disease in the morning, gradually subsiding during the day;
With an exacerbation of the disease in adults, all the signs of chronic pharyngitis are observed, significantly intensified, supplemented by fever, sore throat, and symptoms of general intoxication of the body.
Complications
If treatment for acute pharyngitis is not started in time, the disease quickly becomes chronic, which in the future can lead to unpleasant complications, including complete atrophy of the pharyngeal tissue or a malignant tumor process. Chronic pharyngitis can eventually develop into tracheitis, laryngitis (inflammation of the trachea and larynx) or cause chronic bronchitis.
Pharyngitis caused by streptococcal infection provokes an abscess, the sign of which is a constant sore throat, erythema and unilateral swelling. Another unpleasant manifestation is the inability to talk for a long time. This becomes a real problem for those patients whose professional activities involve teaching and lecturing.
Treatment of chronic pharyngitis
The question of how to cure chronic pharyngitis worries every patient. This can definitely be done, but only with the right approach. Very often, adults begin to use folk remedies without establishing the cause of the disease.
Various inhalations and even self-prescribed antibiotics may not do any harm, but still the consequences of treatment with improvised means are always unpredictable. Therefore, when starting to treat pharyngitis in adults, you need to clearly understand that you cannot do without a doctor, since the healing process must be comprehensive.
So, how to treat chronic sore throat? It all depends on the cause of the disease. If it is due to allergies, antihistamines are prescribed. If pharyngitis is associated with gastroesophageal reflux disease, you must change your diet and lifestyle. In any case, the patient should take care of good hydration of the mucous membranes of the throat.
Treatment of chronic pharyngitis in adults occurs according to the following scheme:
- The use of medications, when prescribed by a doctor - antibiotics.
- Undergoing physical procedures, for example - warming up, laser or UHF.
- Folk remedies are used - gargling with herbs, washing the tonsils, lubricating with special solutions and irrigating with sprays.
Also, general indications for all types of treatment are to reduce the load on the larynx, for this you need:
- Talk less.
- Eliminate from the diet foods that irritate the mucous membrane of the throat (caffeine, alcohol).
- Do not eat excessively hot or cold food.
- Mandatory long breaks after forced voice strain.
Such a comprehensive treatment will reduce the inflammatory process and improve the functioning of the stomach. This disease must be treated strictly individually, then it will be cured.
On what basis is the diagnosis of “pharyngitis” made today?
In the process of interviewing the patient, you can find out the following symptoms characteristic of chronic pharyngitis in an adult:
- discomfort;
- dryness and sore throat;
- difficulty swallowing;
- feeling of something extra in the throat;
- pain that occurs during the so-called “empty” swallow.
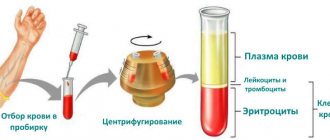
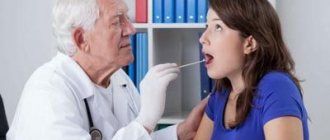
To assess the severity of the disease and its characteristics, the ENT doctor examines the patient’s mouth, throat and pharynx, as we can see in the corresponding photo. If necessary, pharyngoscopy can be performed. To determine the exact cause of the disease, a special study is done in a microbiological laboratory.
Differential diagnosis is carried out mainly with chronic tonsillitis (inflammation of the tonsils):
| Signs for differential diagnosis | Chronic sore throat | Chronic pharyngitis |
| Localization of the inflammatory process | Tonsils and oropharynx | The back of the pharynx, tonsils may be absent if the disease develops after their removal |
| History of the disease | Frequent sore throats, possibly an indication of rheumatic pain | One of the causative factors of pharyngitis (see above) |
| Pain when swallowing | Moderate, with exacerbation strong | Rawness, soreness, discomfort, pain during an “empty” sip. |
| Pharyngoscopy | Typical picture of chronic tonsillitis | Typical picture of chronic pharyngitis |
How to treat pharyngitis with folk remedies
Inhalations and rinses are a good way to treat pharyngitis, but it is worth considering that folk remedies must be taken in combination with drug treatment in order to prevent the development of various complications.
- 30 drops of 30% propolis tincture in 0.5 cups of warm water - use for rinsing.
- For 2 parts coltsfoot take 1 part mint. 1 tbsp. l. pour a glass of boiling water. Use for rinsing and inhalation.
- Take 20 g of buds or just pine needles, pour a glass of boiling water, leave. Use for inhalation.
- Mix 1 part linden and calendula flowers, 2 parts sage. 1 tbsp. l. collection, pour 200 ml of boiling water, leave for 1 hour, use 20-30 ml of infusion for 1 inhalation.
All these remedies are good and quite effective, but still, if there is no relief after the next few days and the condition worsens, be sure to consult a doctor.
Traditional medicine recipes
https://youtu.be/XKoUSAZRnKk
It is known that in order to completely cure chronic pharyngitis, it is necessary to use a whole range of various medicinal and physiotherapeutic procedures, as well as traditional medicine recipes.
Important! Treatment of pharyngitis using traditional medicine methods should be carried out exclusively in combination with drug therapy and under the supervision of a doctor.
The most effective traditional medicine recipes for the treatment of pharyngitis include:
- A medicine based on garlic and honey. It’s easy to prepare: chopped garlic (a couple of medium-sized cloves) is mixed with 30 grams of honey. Take this remedy 5 ml three times a day until complete recovery.
- Infusion of spruce and fir buds. To prepare the solution, the indicated ingredients are poured with boiled water at the rate of a kilogram of dry matter per one and a half liters of liquid. The resulting mixture is brought to a boil and cooked for twenty minutes. The broth is infused for at least an hour, filtered, a glass of honey and a drop of propolis tincture are added. Take one tablespoon three times a day.
Important! Before using any traditional medicine recipe used to treat pharyngitis, make sure that you do not have an individual intolerance to each of the components that make up the drug.
- It is known that one of the most effective procedures in the treatment of pharyngitis is rinsing. They use a mixture of chamomile, sage, St. John's wort, linden and eucalyptus flowers, which are poured with boiling water (one part of dry matter to ten parts of liquid) and infused for half an hour. In addition to rinsing, this decoction can be used in the form of tea.
- Also, to treat the inflammatory process in the pharynx, rinsing using ordinary soda or saline solutions (5 grams of salt or soda per 200 ml of warm boiled water) is effective.
https://youtu.be/Ir_LHTT7MPs
Pharyngitis is a disease in which the mucous membrane of the throat becomes inflamed due to a viral or bacterial infection.
In most cases, pharyngitis is a consequence of acute respiratory infections, acute respiratory viral infections or sinusitis; typical symptoms of the disease are:
- Sore and sore throat;
- Hoarseness and dry cough;
- Increased body temperature;
- Swelling and redness of the mucous membrane of the posterior wall of the larynx;
- Enlarged lymph nodes.
Pharyngitis is a very unpleasant disease in itself. But if left untreated, it will become chronic and cause even more trouble. Therefore, it is important to quickly cure it and prevent complications. What means and methods can be used for this?
Chronic pharyngitis
The author of the article is Olga Petrovna Chuklina, general practitioner, therapist. Work experience since 2003.
Chronic pharyngitis is a disease in which constant inflammation of the pharyngeal mucosa develops.
Chronic pharyngitis occurs in adults with periods of exacerbations and remissions.
Acute viral infections, chronic physical and mental stress, and a decrease in the body's defenses can provoke an exacerbation of the disease.
The following reasons for the development of chronic pharyngitis are identified:
- frequent respiratory viral infections;
- untreated cases of acute pharyngitis;
- prolonged exposure to irritating substances on the mucous membrane of the pharynx and upper respiratory tract;
- chronic inflammatory diseases (sinusitis, tonsillitis, dental caries, rhinitis);
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), pancreatitis);
- conditions after tonsillectomy (removal of tonsils);
- alcohol abuse, smoking;
- violation of nasal breathing (deviated nasal septum, polyps and adenoids);
- eating spicy, hot foods.
There are three clinical forms of the disease in chronic pharyngitis:
- catarrhal;
- hypertrophic (granular);
- atrophic.
The catarrhal form of chronic pharyngitis is the most favorable in the course of the disease. In this case, inflammation of the superficial layers of the pharyngeal mucosa develops, characterized by moderate swelling.
The hypertrophic form manifests itself in the form of growths of the pharyngeal mucosa (nodules, tubercles).
The atrophic form is the most unfavorable form of chronic pharyngitis. At the same time, the mucous membrane of the pharynx thins and becomes dry. Treatment of this form takes a very long time.
Causes of the disease
The causative agents of chronic pharyngitis can be various kinds of viruses, bacteria, fungi and intracellular parasites .
Reference! Most of them are classified as opportunistic microorganisms, which under normal circumstances can remain in a person for a lifetime without causing any negative effects.
This microflora is activated, provoking the development of chronic pharyngitis, under the following conditions:
- general weakening of the immune system ;
- lack of adequate nutrition;
- lack of sleep;
- hypothermia of the body;
- smoking;
- alcohol abuse ;
- any concomitant diseases accompanied by inflammatory processes;
- pathological deformations of the nose (they can provoke stagnation of fluid in which pathogenic microflora develops).
But the main cause is still untreated, neglected or unattended acute pharyngitis.
In such cases, changes in the structure of the mucous membrane become permanent, as a result of which the chronic form develops.
Symptoms of chronic pharyngitis
If an adult has chronic pharyngitis, he or she experiences the following symptoms:
- constant sore throat;
- sore throat;
- feeling of a foreign body in the throat;
- painful sensations when swallowing;
- dry, unproductive, frequent cough;
- presence of bad breath.
During the period of remission of the disease, the patient has only local signs of the disease. An exacerbation of pharyngitis is characterized by the development of intoxication of the body (fever, general weakness, malaise), and an increase in local signs of the disease.
The catarrhal form is characterized by the presence of more pronounced pain in the throat, which intensifies after hypothermia, viral infections, and after fatigue. When examining the mucous membrane, its hyperemia and swelling are visible.
When an adult develops a hypertrophic or granulosa form of pharyngitis, complaints about the sensation of a foreign object in the throat come first. In the granulosa form, one can detect disorderly, chaotic growths of the mucous membrane in the form of nodules and elevations. And with the hypertrophic form, thickening of the mucous membrane is observed without the formation of nodules.
In the atrophic form of chronic pharyngitis, the patient has mainly complaints about:
- dry throat;
- hacking cough;
- constant discomfort in the throat.
Upon examination, you can see a thinned mucous membrane of the pharynx, dry mucosa, crusts, and small hemorrhages.
During exacerbations, there may be symptoms of inflammation of nearby organs (laryngitis, tracheitis, tonsillitis).
Major complications
You should not self-medicate, because this often leads to the development of life-threatening conditions for the patient; only a doctor knows how to properly treat chronic pharyngitis.
If medical recommendations are not followed or treatment is prescribed incorrectly, the risk of complications during exacerbation of pharyngitis increases:
- tonsillitis;
- laryngitis;
- tracheitis;
- bronchitis;
- regional lymphadenopathy.
When a chronic course of pharyngitis appears, some patients experience the development of inflammatory diseases of a systemic nature:
- glomerulonephritis;
- myocarditis;
- rheumatism.
The most serious complication is malignancy of the atrophic form.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of chronic pharyngitis is based on a thorough survey and examination of the patient.
The doctor must perform a pharyngoscopy - examination of the mucous membrane of the pharynx.
At the same time, he can detect characteristic signs of any form of chronic pharyngitis.
Thus, with catarrhal form, the following changes in the posterior pharyngeal wall can be detected:
- redness;
- swelling;
- a small amount of mucus.
The hypertrophic form is characterized by the presence of the following changes in the pharyngeal mucosa:
- thickening, swelling;
- developed venous network (congestion);
- in the granulosa hypertrophic form, red nodules up to 0.5 cm are also detected.
In the atrophic form, the following changes are found in the pharyngeal mucosa:
- thinning;
- dryness;
- crusts;
- minor hemorrhages;
- pale pink color.
To determine the causative agent of the disease, a scraping is taken from the mucous membrane of the back wall of the pharynx and a bacterioscopic examination is carried out.
In a general blood test during the period of remission of the disease, there may be no changes, but during an exacerbation, general signs of inflammation are determined (increased leukocytes, ESR).
Consequences and complications of the disease
A person with chronic pharyngitis most of the time may not remember his illness until it begins to worsen (this can happen once or twice a year or more often, especially in spring and winter ).
During exacerbations, the same symptoms appear as in the acute form, but the body temperature may also increase, although not much: only up to 37.5 degrees.
In this case, there is no need to bring down the temperature, and it is recommended to take antipyretics only if the temperature reaches 38.5 degrees or higher.
During periods of exacerbation, it is necessary to pay special attention to treatment and follow all doctor’s instructions , since in its advanced form, chronic pharyngitis can lead to a number of complications:
- development of acute and chronic laryngitis;
- bronchitis;
- tracheitis;
- change in voice timbre;
- complications on the kidneys, joints and heart (typical only for chronic pharyngitis caused by the activity of β-hemolytic streptococci of group A).
Treatment of chronic pharyngitis
Treatment of chronic pharyngitis is carried out by an otolaryngologist.
Treatment is provided on an outpatient basis; hospitalization is not required.
Treatment should be carried out strictly under the supervision of a specialist, and all prescribed recommendations must be strictly followed.
First of all, it is necessary to eliminate all harmful effects on the pharyngeal mucosa:
- exclusion of spicy, salty, hot, cold foods;
- inhalation of harmful, irritating substances;
- exclusion of alcohol;
- to give up smoking.
For the entire period of treatment, it is recommended to maintain a plentiful drinking regime.
It is necessary to maintain the humidity of the inhaled air in the room at a sufficient level (50-70%).
This can be done using special devices - ultrasonic humidifiers, or using traditional methods - you can hang wet sheets in the room, place containers with water.
Gargling with the following means has an effective therapeutic effect:
- decoction of chamomile, sage, calendula;
- Miramistin;
- Rotokan;
- Furacilin.
To reduce tissue swelling, antihistamines are prescribed:
Pharynx treatments are also used:
Local antiseptics are used:
Antibacterial drugs are taken only during exacerbations of the inflammatory process with a proven bacterial nature. The following antibacterial agents are mainly used:
- Amoxiclav;
- Flemoxin Solutab;
- Chemomycin;
- Klacid;
- Cefixime.
Self-medication with antibacterial drugs can, on the contrary, lead to progression of the disease.
In the presence of granulosa hypertrophic pharyngitis, the following types of treatment are used:
- Cauterization with silver;
- Laser coagulation (laser cauterization of granules);
- Cryotherapy (liquid nitrogen).
It is mandatory to take medications aimed at restoring the microflora of the pharyngeal mucosa:
When treating atrophic pharyngitis, the following methods are used:
- removing crusts from the mucous membrane;
- lubricating the pharyngeal mucosa with sea buckthorn, peach, and apricot oil.
Inhalation of oil solutions is effective for chronic pharyngitis; for this you can use:
- Peach oil;
- olive;
- rose oil;
- menthol oil.
Hardware methods of physiotherapy are also used:
How to cure forever
To get rid of most of the manifestations of this disease, you need to completely get rid of the factors that provoke it. In addition, you need to engage in full therapy for the disease, under the supervision of a doctor.
There are enough treatment methods; various drugs and physiotherapy can be used for therapy. It is acceptable to use some traditional methods, but you should be careful with them.
Hardening the throat for chronic pharyngitis is a controversial technique, the effectiveness of which has not been proven. Therefore, it is not recommended to use it; it is better to immediately turn to conservative treatment. It is better not to further irritate diseased mucous tissues of the nasopharynx.
In general, for chronic pharyngitis, treatment at home is acceptable; observation in a hospital setting is usually not required. However, physical therapy appointments may be required.
Drugs
Depending on the causes and symptoms of the disease, different medications may be required for treatment. The following groups of medications are usually used:
- Local antibacterial therapy. Systemic antibiotics in tablet form are usually not required; specialized antibacterial sprays are used. These include Bioparox, Imudon, IRS - 19.
- Anti-inflammatory painkillers. Typically used in the form of sprays and lozenges. The most commonly used tablets are Grammidin, Yox spray, Faringosept, Hexoral and their analogues.
While taking medications, it is advised to switch to a diet that does not contain food that irritates the mucous membranes. It is not recommended to eat foods that are too hot or cold, or foods that are too spicy or sour. You also need to drink a lot of liquid, preferably plain clean water. In case of exacerbations, bed rest is recommended.
How to gargle
The most common recipe for rinsing is a saline solution; it is advisable to use sea salt to make it. For one glass of warm water, take one spoon of salt, and rinse up to three times a day.
You can also use a light infusion of chamomile, this remedy will help soothe a sore throat. Take one spoon of dried herb per glass of boiling water; before rinsing, you need to cool the infusion.
Treatment with folk remedies
Traditional recipes are also effective in the fight against pharyngitis, the main thing is not to warm a sore throat, high temperatures provoke bacterial activity. It is also worth remembering that it is difficult to completely overcome the disease with the help of folk remedies; they can only represent auxiliary therapy.
The most useful and safe folk remedy for pharyngitis, which will help soften a cough and relieve severe pain, is milk with honey. The milk should be warmed up a little, do not make it too hot. In a glass of milk you need to dilute one spoon of honey, you can add a little cream. You should drink this drink at night.
By combining different products you can achieve the best effect. If your condition worsens, you should consult a doctor.
https://youtu.be/3FOlNQSDgFY
Prevention
Preventive measures include:
- quitting smoking and alcohol;
- avoid inhaling harmful substances;
- promptly and completely treat acute forms of pharyngitis and other inflammatory diseases of the nasopharynx;
- treat concomitant diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- refusal of spicy, hot, cold foods.
Diagnosis by symptoms
Find out your probable illnesses
and which
doctor
should you go to.
Causes
Some of the most important reasons include:
- influence of toxins and other hazardous substances;
- weakened immunity;
- seasonal colds;
- allergies;
- smoking or exposure to secondhand smoke;
- close contact with a sick person.
Separately, it is worth highlighting bacterial pharyngolaryngitis, which was provoked by viral infections. The most common is the acute form of the disease, which occurs as a result of the penetration of various types of infections into the body, provoked by various viruses and pathogens. The inflammatory process is much more complicated if a person has a weakened immune system, since the body does not resist infection well during this period.
https://youtu.be/fXwc6vJMcdg
Symptoms and treatment of chronic pharyngitis in adults
One of the most common pathologies of the larynx and mucous membranes of the throat is considered to be a fairly common disease - chronic pharyngitis. The disease is inflammatory in nature and is distinguished by its duration, with phases of remission and exacerbation included in the process. The latter manifest themselves especially clearly during the period of influenza, ARVI and other colds. Is it possible and how to cure chronic pharyngitis in the shortest possible time? During the period of illness, certain unfavorable symptoms occur, but treatment of chronic pharyngitis in adults and children is possible using a number of existing methods.
Varieties
In accordance with the nature of the morphological changes, chronic pharyngitis has several types.
- The catarrhal form is characterized by inflammation of the external mucous membranes of the pharynx and the appearance of slight swelling;
- The hypertrophic variety is identified by thickening of the mucosa in the area of the posterior wall of the pharynx, as well as the appearance of growths on the palatine arches. This group classifies granular pharyngitis, in which bright red granules with a smooth surface form on the lining of the pharynx (on the back wall). Lateral pharyngitis also stands out with the appearance of bright red ridges behind the velopharyngeal arches (one or both).
- the atrophic appearance is diagnosed by significant thinning of the mucous membranes of the pharynx;
- mixed pharyngitis is a combination of hypertrophic changes with atrophy.
Depending on what provoking factor triggered the development of chronic pharyngitis, its following types are classified:
- viral (the most common form);
- allergic;
- bacterial;
- traumatic;
- fungal.
Treatment of chronic pharyngitis becomes more complicated if a viral infection begins to develop in the throat area, weakened as a result of a bacterial infection.
Causes of chronic pharyngitis
The development of the chronic form of pharyngitis is primarily based on a weakened immune system, a person’s frequent exposure to colds and the occurrence of various kinds of complications that develop against the background of viral infections in the body. The duration of inflammatory processes occurring on the pharyngeal mucosa is also one of the main provocateurs leading to the appearance of an unpleasant disease.
The following unfavorable factors can be identified that can have a direct impact on the progress of the disease and its transition to the chronic stage:
- acute pharyngitis that was not treated in a timely manner,
- recurring infectious diseases: viruses, fungi, bacterial pharyngitis,
- progressive inflammatory processes in the oral cavity, for example, tonsillitis, diseases of the gums, teeth,
- inflammatory diseases in the paranasal sinuses, nose,
- allergic reactions,
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract: pancreatitis, reflux esophagitis and others,
- consumption of excessively hot liquids, tobacco, alcohol, spicy foods,
- laryngeal injuries,
- disturbances in the functioning of the liver, lungs, heart, as well as disturbances in metabolic processes in the body.
In addition to the above points, not the least influence on the delicate mucous membrane is exerted by irritants that prevail in the external environment: cold air, unfavorable ecology, polluted environment, hazardous production.
Symptoms of chronic pharyngitis
Speaking about signs that can indicate the presence of such a disease of the pharynx, it should be noted that the chronic stage of pharyngitis is very different from its acute stage. The course in a chronic form most often does not cause a deterioration in the patient’s general well-being, the body temperature does not rise, but there is a certain set of symptoms that can lead to the idea of the presence of pathology.
As signs of the formation of chronic pharyngitis, the following group of general symptoms should be distinguished:
- sensation of a foreign body in the throat, the so-called lump,
- dry throat,
- sore throat, itchy throat,
- nasopharyngeal congestion,
- the appearance of hoarseness in the voice,
- constant desire to cough,
- dry cough,
- displacement of painful sensations in the ear area,
- discomfort when swallowing,
- inflammation, burning in the throat,
- accumulation of mucus on the walls of the larynx, which entails the appearance of a constant swallowing reflex,
- an increase in discomfort in the throat in the morning and a gradual easing during the day.
In addition, the transition of the disease into a chronic form is characterized by several stages or types of pharyngitis. Each has a simpler or more severe form of occurrence. The main thing here is to remember that an illness that is not treated at the initial stages of development can lead to the formation of more dangerous types of the disease, the healing process of which will be much more difficult and lengthy than in its early stages. That is why symptoms and treatment of chronic pharyngitis in adults should be determined by a competent doctor.
So, among the main types of chronic pharyngitis, the following forms can be noted:
- Catarrhal pharyngitis. The mildest form of chronic pharyngitis. The main point here is the presence of a sore, dry throat, as well as a constant desire to cough. This stage most often worsens during severe cold snaps or when a person finds himself in unfavorable conditions, for example, in a smoky room or in a hazardous industry.
- Atrophic pharyngitis. This form is characterized by thinning of the laryngeal mucosa, which leads to an increase in its sensitivity. The course of the stage is also characterized by a constant feeling of dryness in the throat, burning, the presence of a foreign body, as well as a more severe form of dry cough, which torments the patient almost constantly, causing quite painful sensations. Here you can note the appearance of an unpleasant odor from the oral cavity.
- Hypertrophic pharyngitis. The stage is characterized by such signs as thickening of the mucous membranes of the throat, accumulation of mucus or pus on the back wall. Characterized by a constant desire to cough, as well as soreness, dryness and worsening bad breath.
Separately, it is worth mentioning another type of chronic pharyngitis - an allergic form of the disease caused by the presence of a certain allergen in the environment or food, which provokes irritation of the pharynx and causes symptoms characteristic of the disease.
It should be noted that the chronic stage of the disease can proceed quite calmly and manifest itself exclusively when coughing, provoking a kind of attack. But such a condition always passes and a person’s well-being improves. This is precisely why the disease is dangerous, since delaying a timely visit to a specialist can lead to the development of more serious stages of pharyngitis. Of course, various types of inflammatory processes in the body, decreased immunity and infections can also provoke an exacerbation.
In any case, the presence of any discomfort in the larynx that has not been eliminated for a long time should prompt a person to visit an appropriate specialist. Otherwise, the mucous membranes of the larynx will undergo negative changes and acquire the status of a permanent focus for the development of infections, which, in turn, can lead to quite serious complications and health problems.
Causes of the disease
Chronic pharyngitis does not occur as often as an independent disease. In most cases, its development occurs as a result of reduced immunity of the pharyngeal mucosa, which is influenced by various external and internal factors.
Among the main reasons are:
- ARVI;
- sinusitis, tonsillitis, which can recur frequently;
- dust, chemicals that have a negative effect, thereby causing irritation of the mucous membrane for quite a long time;
- relapses of inflammatory processes in the nose and sinuses;
- other pathologies of the body.
Often the pathology develops against the background of:
- allergic reaction;
- diseases of the digestive system;
- cholecystitis;
- inflammatory process of the pancreas
- genetic predisposition;
- impaired blood circulation in the respiratory system.
Provoking external factors include:
- unfavorable environment;
- excessive consumption of spicy and hot foods;
- alcohol;
- smoking.
We must not forget about working conditions, which are sometimes not so favorable, as well as environmental pollution. All these are reasons under the influence of which the mucous membrane begins to become irritated.
The risk of pharyngitis also increases when the body is hypothermic.
Treatment of chronic pharyngitis
Practice shows that recovery from such an unpleasant disease as chronic pharyngitis is quite possible and the healing process has been successfully completed by many owners of the disease. The main point here, undoubtedly, is a timely visit to a specialist, since first of all it will be necessary to identify the causes of the disease, and only a physician can do this. Having clarified the symptoms of chronic pharyngitis, and treatment will be prescribed to them. That is, an action plan will be drawn up to eliminate irritants and prescribe appropriate medications for treatment. There are a number of general medical recommendations that can help improve the patient’s condition:
- reduce the activity of the vocal cords, in other words, talk less,
- take breaks in verbal speech,
- limit intake of excessively hot or cold food, liquids,
- exclude irritating factors: smoking, alcohol, spicy food, carbonated water, polluted atmosphere.
But as for more specific treatment methods prescribed exclusively by a doctor, here most often there is a treatment plan of the following type:
- taking medications of an antiseptic, anti-inflammatory, antibacterial nature, possibly antibiotics,
- physiotherapy: heating, UHF, laser,
- use of solutions, sprays, inhalations, rinses, syrups.
The above points are considered a mandatory basis in the procedure for treating chronic pharyngitis. Knowing how to treat chronic pharyngitis in adults, it is important to remember that the process must include various healing methods, since only an integrated approach, coupled with eliminating the causes of the disease, can lead to positive results and get rid of the unpleasant pathology. In addition, you should undergo additional examination, because the cause of the development of pharyngitis and its transition to the chronic stage can be various disturbances in the functioning of the stomach or all kinds of allergens. In such cases, therapy should include parallel treatment of the identified disorders.
Treatment
In case of exacerbation of chronic pharyngitis without deterioration in general well-being, symptomatic treatment and local antimicrobial therapy (inhalations, rinsing with solutions, lozenges) are indicated.
Local medications may include:
- Essential oils.
- Antibiotics.
- Antiseptics.
- Sulfonamides.
- Bacterial lysates.
- Natural antiseptics.
- Deodorants.
- Antiviral agents.
- Vitamins.
The main requirements for such drugs:
- Low allergenicity.
- Low rate of absorption from mucous membranes.
- No toxic effect or irritation of mucous membranes.
- Wide spectrum of action - drugs should affect not only microbes, but also viruses.
A treatment regimen for chronic pharyngitis should be prescribed by a doctor after a face-to-face consultation.
In case of exacerbation of chronic pharyngitis, in addition to the main methods of therapy, it is necessary:
- Follow a diet. Hot, salty, spicy, and solid foods are excluded from the diet.
- Apply warm compresses to the front of the neck and hot foot baths.
- Stop smoking.
If the disease develops as a result of pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, then without eliminating the underlying cause, any methods of treating chronic pharyngitis can only give a short-term effect.
Treatment of catarrhal pharyngitis
The mildest degree of chronic pharyngitis, namely the catarrhal stage, in the treatment process involves, first of all, the elimination of various kinds of irritating factors. This includes smoking, spicy foods, and drinks that irritate the mucous membranes, such as carbonated or alcohol-containing liquids. In addition, hours-long conversations should be eliminated and the load on the ligaments should be reduced. On top of that, you will need to stay as little as possible in places where gas, dust and other unfavorable environmental conditions accumulate.
General recommendations include frequent intake of warm liquids, such as milk and soda, as well as ventilation of the room in which the sick person is located.
As for chronic pharyngitis treated with medications, this stage does not involve the use of antibiotics. Most often, experts recommend taking antiseptics, anti-inflammatory and topical painkillers. These can be sprays, lozenges, inhalations, rinses. In case of a more serious course of the disease, if chronic granulosa pharyngitis has already appeared, various physical procedures can be prescribed.
Types of chronic forms of pharyngitis
Subatrophic pharyngitis
Chronic pharyngitis can be:
- catarrhal;
- hypertrophic;
- atrophic.
An intermediate form may be subatrophic pharyngitis. Of particular note is pharyngitis in older people, which is associated with an age-related decrease in local immunity, as well as fungal forms, which are often associated with chemotherapy for cancer.
The peculiarities of the course of each form of the disease determine the doctor’s tactics when choosing certain means and methods of therapy.
Treatment of chronic pharyngitis at home
Of course, any stage of chronic pharyngitis requires a hasty visit to the otolaryngologist. Otherwise, there is a high probability of getting a complication, for example, chronic nasopharyngitis, and its treatment will be much more difficult. But to alleviate the condition at home before visiting a doctor, you can also use some methods available to anyone.
Among the most optimal home treatment options are the following well-proven methods:
- foot baths with hot water,
- inhaling hot steam, for example, over freshly boiled potatoes,
- gargling with herbal decoctions of chamomile, sage, rose hips, eucalyptus, calendula,
- rinsing with soda,
- drinking warm milk with honey,
- Warming compresses placed on the neck area.
The use of the above methods provides quite significant assistance in eliminating the symptoms of the disease and generally alleviating the patient’s condition forever, but it should be remembered that the true healing process is possible only with a complex effect prescribed by a specialist in his field.
To summarize, it should be noted that the occurrence of any disease occurs due to reduced immunity, so any person needs to treat their own health with special attention and care. And, of course, you should always remember that self-medication or delaying a visit to the doctor can only lead to a worsening of the condition and a smooth transition of the disease to a more severe stage, which is fraught with various kinds of negative consequences.
Modern aspects of therapy: how to cure chronic pharyngitis once and for all
So, let’s try to answer the question of how to treat pharyngitis, the chronic nature of which significantly reduces the quality of life of patients, because in every fourth patient the disease is susceptible to chronicity. It would seem that many procedures, for example, irrigation and inhalation, are quite feasible at home, decoctions of medicinal herbs for rinsing can be prepared with your own hands, but it is necessary to take into account that treatment should be carried out under the constant supervision of specialists who know exactly how to treat patients diagnosed with pharyngitis chronic".
There can be no talk of self-medication here, since the choice of medicine cannot always be made correctly, guided by the affordable price or by independently studying the indications for use in the drug instructions.
Only if you carefully follow all your doctor’s prescriptions can you say that chronic pharyngitis is curable. The prognosis is all the more favorable the earlier the correct diagnosis of “chronic pharyngitis” is made and a list of measures is determined, which will allow a timely decision on how to cure the disease in each specific case.
Drug treatments
At the present stage of development of therapeutic methods of treatment, it is quite possible to say that in most cases the diagnosis of “chronic pharyngitis” is curable, especially if the patient himself is determined to get rid of the disease and eliminate the constant source of infection in the body.
Currently, it is very important to correctly and timely prescribe antibiotics, taking into account the sensitivity of microbes to them. In addition to eliminating pathogenic microorganisms, it is necessary to repopulate normal microflora, otherwise dysbacteriosis may occur, which will contribute to relapses of pharyngitis.
Preference is still given to local forms of medicinal substances, which allows them to be delivered to the site of chronic inflammation without saturating the blood and the entire body, which is usually not necessary.
Some remedies for topical treatment of pharyngitis
It is also necessary to stimulate the activity and enhance the activity of cells of the immune system and its other factors, which is especially important in elderly patients. Once again, it is worth noting that if you have been diagnosed with “chronic pharyngitis,” only a competent specialist should decide how to treat this disease, otherwise it is quite difficult to get rid of it.
So, medications for the treatment of pharyngitis belong to several main groups:
- antibiotics;
- antiseptics;
- herbal preparations;
- probiotics;
- means that improve general and local immunity;
- antifungal agents;
- antiviral;
- corticosteroids;
- adaptogens.
Sprays and aerosols
Methods of administration of therapeutic agents:
- Inhalations.
- Irrigation.
- Aerosol therapy, including using a nebulizer.
- Sprays.
- Rinse.
- Tablets and lozenges.
Intravenous laser irradiation of blood
Non-drug treatments
In identifying the disease “chronic pharyngitis” and developing a plan for how to treat it, the use of non-drug treatment methods, in particular physical factors, sanatorium-resort treatment, where there are ample opportunities for the prevention and treatment of the underlying disease and general improvement of the body, is important.
Physical factors in pharyngitis produce a whole range of influences:
- prevent the spread of inflammation;
- relieve tissue swelling;
- improve their nutrition;
- strengthen immunity;
- have a healing effect;
- help eliminate chronic infection;
- reduce the risk of allergic reactions.
Types of physiotherapeutic interventions that are preferable to choose for chronic pharyngitis:
- short wavelength ultraviolet irradiation (SWI);
- use of low-energy lasers locally and intravenously;
- ultrasound therapy;
- medicinal electrophoresis;
- alternating magnetic field.
Salt caves
Visits to the so-called “salt caves” have proven themselves to be excellent, helping to eliminate discomfort in the throat, freeing breathing, alleviating the chronic runny nose that such patients often have. Special reflexology techniques, which can be performed by an appropriate specialist, help reduce the negative impact of a chronic source of infection on the immune system.
In addition, it is necessary to give up all bad habits that aggravate the course of the disease, such as smoking, drinking strong alcohol, eating too hot food or drinks. It is important to sanitize other foci of infection, especially those located in the immediate vicinity (dental diseases, sore throats, sinusitis, rhinitis).
https://youtu.be/QjsjGiAMLN0
The video in this article will help you understand what “chronic pharyngitis” is and how to treat it correctly, timely and efficiently, avoiding relapses.
Pharyngitis is an infectious disease, the source of inflammation of which is localized mainly on the pharyngeal mucosa, often spreading to the lymphoid apparatus. The main symptoms of the disease at the initial stage are similar to the symptoms of a common cold. There are acute and chronic stages of the disease.
Chronic pharyngitis is characterized by a slow course of the disease and includes periods of exacerbation and remission.
Often, an exacerbation occurs against the background of a decrease in local and general immunity, for example, as a result of viral diseases or severe hypothermia.
Treatment of chronic pharyngitis in adults is determined by the form of the disease, the general condition of the patient and the presence of accompanying symptoms.
Physiotherapy
Depending on the symptoms and treatment in adults, the appropriate one is selected. Many patients are interested in how to treat pharyngitis and how effective physiotherapy is.
Physiotherapy for pharyngitis can give very good results. In particular, ultrasound, electrophoresis, and inhalations are performed. It is worth noting that ultrasound is used to treat the pharynx area and helps treat even prolonged chronic pharyngitis.
For inhalation, drugs should only be selected by a doctor, as they can provoke an allergic reaction. Reviews from patients indicate that with the help of inhalation it is possible to eliminate the manifestation of this disease and achieve long-term remission.
Drug therapy
Treatment of chronic pharyngitis takes longer and requires a special approach, compared to therapy for the acute stage of the disease. The fundamental approach to treating this disease is to eliminate the cause that caused the inflammation. Whereas in the chronic form of the disease it is extremely difficult to determine the causes.
Patients are often interested in how to treat chronic pharyngitis and whether it can be cured completely? Doctors agree that it is not only possible, but also necessary to treat this form. Moreover, most often this can be done outside the hospital, strictly following the instructions of a specialist. The attending physician, based on examination of the patient, history taking, test results (blood, urine) and other diagnostic measures, will select adequate and effective treatment.
Most often, therapy for chronic pharyngitis includes drugs and procedures such as:
- Treatment with antimicrobial and antiviral drugs depending on the causative agent of the disease. So, if pharyngitis is caused by a bacterial infection, then treatment is carried out with antibiotics (Augmentin, Amoxiclav, Sumamed). If the cause of the disease is viruses, then the patient should use antiviral drugs (Groprinosin, Arbidol, Amiksin, Ingavirin).
- Sometimes the cause of pharyngitis can be an allergic reaction of the body to dust, wool, certain foods, strong odors, etc. In this case, it is necessary to exclude the cause of the allergy and simultaneously use antihistamines (Loratadine, Suprastin, Diazolin, Zodak).
- At elevated body temperature (above 38 degrees), it is necessary to use antipyretic drugs. The most commonly used drugs are those based on ibuprofen (Nurofen, Ibuprofen) and paracetamol (Efferalgan, Paracetamol, Grippostad, Coldrex), which not only reduce the temperature, but also have an analgesic effect for severe sore throats.
- Hoarseness in the throat can be reduced with the help of antiseptic drugs produced in the form of lozenges, lozenges, sprays (Ingalipt, Hexoral, Chlorophyllipt, Collargol, Septolete).
- Gargling with antiseptic solutions (Chlorhexidine, Chlorophyllipt), which help moisturize the throat mucosa, liquefy viscous secretions, exfoliate and remove crusts.
- Steam inhalations and nebulizer inhalations also have a positive effect, improving the general condition of a patient with pharyngitis. To carry out the procedure, antiseptic (Dekasan), alkaline (Borjomi) solutions are used, as well as saline solution to moisturize the pharyngeal mucosa.
- If chronic pharyngitis is diagnosed, treatment can be supplemented with physiotherapeutic procedures. This can be electrophoresis, ultra-high frequency therapy (UHF), ultrasound therapy.
- In the treatment of sluggish pharyngitis, it is advisable to use vitamin complexes and drugs to strengthen the immune system (Undevit, Virum, Duovit, Imudon, IRS-19).
- A proper diet, excluding salty, spicy, sour, very hot and cold foods will help to quickly cure a chronic disease.
How does the disease manifest?
The disease is characterized by signs of laryngitis and pharyngitis. Acute pharyngolaryngitis is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- dryness and burning in the throat;
- pain when swallowing;
- labored breathing;
- temperature increase;
- dry cough.
Patients may feel an accumulation of thick mucus in the throat; when coughing, it begins to separate over time. As a rule, sputum has an unpleasant odor caused by the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms. Usually in children, pharyngolaryngitis is accompanied by pronounced symptoms - the temperature rises significantly, and the child’s general well-being worsens. Among the complications of this disease in children, inflammation of the nasopharynx and acute rhinitis are often observed; in such cases, experts also make diagnoses such as nasopharyngitis and nasopharyngitis.
Based on the fact that the symptoms of pharyngitis are practically no different from colds, many people confuse it with a sore throat, flu or acute respiratory viral infection. With chronic pharyngolaryngitis, less pronounced symptoms are observed, so the disease often takes on an advanced form, causing complications on other organs of the respiratory system. Headache, drowsiness and lethargy are signs of intoxication of the body, which occurs in the absence of proper treatment.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of the disease is based on examination of the pharynx by an otolaryngologist. The presence of slight swelling and thickening of the mucous membrane, covered with a cloudy viscous substance, indicates the development of catarrhal pharyngitis. Severe redness of the pharyngeal mucosa, through which veins begin to appear, and inflamed lymphoid granules, increased in size, indicate hypertrophic pharyngitis. If the mucous membrane of the pharynx has acquired a pale pink color, has become thinner and is covered with a crust of dried mucus, then atrophic pharyngitis is diagnosed.
To determine the causative agent of inflammation, a throat swab may be taken for subsequent bacteriological or virological examination. To find out the cause of the disease, you may need to be examined by other doctors, including a gastroenterologist, dentist, and endocrinologist.
Types of disease
Types of chronic pharyngitis
Chronic pharyngitis can occur in a variety of forms, which have varying degrees of intensity and symptoms. The catarrhal form is characterized by mild inflammation with a large number of leukocytes. As the disease worsens, the lymph nodes become inflamed.
The hypertrophic form is characterized by the fact that all mucosal structures grow, become swollen and have a thickened shape. In the atrophic form of the disease, on the contrary, the walls of the mucous membrane become thinner.
There may be other forms of the disease, it all depends on the complexity of the pathological process and its duration.
Important! Any form of pharyngitis must be treated comprehensively, including the use of antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, antitussive drugs, adherence to a special diet and the use of medicines.
Procedure for providing medical care
The diagnosis of acute pharyngitis and its treatment are carried out on an outpatient basis. After examining the patient, the otolaryngologist draws up a treatment plan and prescribes the patient a list of necessary pharmaceuticals.
According to modern standards of specialized medical care, doctors give preference to complex therapeutic agents that eliminate pain, inflammation and disinfect the mucous membrane of the pharynx and larynx. Medications are taken only after prior consultation with an otolaryngologist.
What is tonsillitis
Chronic tonsillitis and pharyngitis affect the throat, but not in the same place. Tonsillitis primarily affects the pharyngeal tonsils, also known as tonsils. This important system of the body is not least responsible for the immune system and acts as a kind of protective barrier against infection in the body.
Chronic tonsillitis, like pharyngitis, develops against a background of weakened immunity, when not all pathogens are neutralized by lymphocytes. This happens as a result of a sore throat. This is how chronic tonsillitis is formed. Pharyngitis owes its birth to streptococci, staphylococci, diseases in the oral cavity and sinusitis.
Clinical picture of tonsillitis:
- the size of the tonsils increases noticeably;
- the surface of the tonsils becomes loose;
- tonsils become purple;
- lymph nodes swell noticeably;
- the sky swells;
- there is an unpleasant odor from the mouth;
- there is pain when swallowing;
- voice changes;
- breathing is difficult;
- the temperature rises significantly.
Chronic tonsillitis only gets worse without medical intervention.
An otolaryngologist will conduct an examination, prescribe tests and establish the correct diagnosis.
The primary task at this stage is to prevent tonsillitis or pharyngitis from becoming chronic. If you experience any of these symptoms, you should see a doctor immediately.
Complications from these seemingly innocent ailments can affect the activity of the heart, kidneys, and skeletal system.
Treatment of tonsillitis
To begin treatment of tonsillitis, it is necessary to determine the diagnosis, for which the patient’s blood and urine are sent for analysis. At the initial stage of treatment, they practice rinsing the tonsils with iodine and salt, which should prevent the spread of infection. Salt fights infection, and iodine has an antiseptic effect on the surface of the tonsils.
Sometimes doctors prescribe treatment of the mucous membrane with Lugol and the use of local antibiotics. If the temperature is very high, you should take an antipyretic. Antibiotics should be taken if the temperature lasts more than three days. There is no need to repeat that all drug prescriptions are carried out by a doctor.
As practice shows, removing tonsils leads to a significant reduction in the number of throat diseases. After treatment, it is necessary to take a course of medications and vitamins to tone the immune system.
What is pharyngitis
To succeed in treatment, you need to understand exactly what chronic pharyngitis is and how it differs from tonsillitis. Unlike tonsillitis, with pharyngitis, the causative agents of the disease do not affect the tonsils, but directly the mucous membrane of the throat itself. Like many other diseases, pharyngitis can occur in two forms:
- in acute form;
- in chronic
The cause of the disease is respiratory pathogens:
- rhinoviruses;
- adenoviruses;
- parainfluenza virus;
- coronavirus;
- cytomegalovirus;
- sore throat;
- dry cough;
- lymph nodes are enlarged and painful;
- elevated temperature;
- redness of the back of the throat;
- loss of strength, muscle aches and sweating.
Despite all the obviousness of the manifestations of pharyngitis, only a doctor can understand its nuances. Therefore, do not try to diagnose yourself, much less treat the disease.
Treatment of pharyngitis
Before starting treatment, you should decide what form of the disease you have: bacterial or viral. If the diagnosis indicates a viral form of the disease, then treatment will be as follows:
- proper nutrition;
- drinking plenty of water;
- local antibiotics;
- regular gargling;
- treatment of the larynx with inhalers.
In case of chronic pharyngitis, you should not abuse food that will irritate the throat: sour, spicy, hot foods should be excluded from the diet. With a viral form of pharyngitis, you should drink as much as possible so that the infection is quickly eliminated from the body.
As for high temperatures, in this case drinking plenty of fluids is necessary as a remedy for dehydration. At high temperatures, the body begins to produce a hormone that destroys viruses and bacteria.
If pharyngitis is bacterial, then you cannot do without antibiotics. Their use will avoid many complications that affect adults much more often than children.
Prevention of tonsillitis and pharyngitis. In order to encounter these diseases as rarely as possible, you need to pay attention to preventive actions.
It will hardly surprise you that the main factors of prevention should be a healthy lifestyle and compliance with hygiene rules.
Given that pathogens are all around us, regular hand washing can cut your chance of getting sick by half.
In order not to get sick, you need to harden the body, not drink cold liquids during the summer heat and constantly replenish the reserves of vitamins in the body.
There is an opinion that if you eat three kilograms of strawberries over the summer, this will be enough for the body to gain the ability to cope with any infection throughout the winter. Citrus fruits also keep the body fit due to its abundance of vitamin C.
Therefore, if you like to drink tea with lemon in the morning, then you are much less likely to get an infection.
How is pharyngitis and laryngitis treated?
During the autumn-winter period, many people may notice how their immunity has weakened and colds have become more frequent. Nasal discharge, sore throat, and cough do not always indicate a cold, because sometimes after a visit to the doctor, a specialist makes diagnoses such as “pharyngitis” or “laryngitis.” At the same time, the treatment of pharyngitis and laryngitis is practically no different from therapy for colds, what are the differences between these diseases?
How are the diseases different?
- sore throat;
- dry cough;
- temperature increase.
Source: https://neb0ley.ru/tonzillit/faringit-laringit-tonzillit-otlichie.html
Basic principles of treatment of pharyngolaryngitis
So, pharygolaryngitis, what is it? The disease can be caused by viruses and bacteria. Only the infectious origin of inflammation requires the use of antibacterial agents.
In case of acute and exacerbation of chronic damage to the tissues of the pharynx and larynx, which are not accompanied by a violation of the general condition of the patient, doctors recommend limiting oneself to symptomatic therapy, a gentle diet, local inhalations and compresses. According to most experts, uncomplicated forms of pharyngolaryngitis do not require systemic antibiotics.
Pharmaceutical preparations for local therapy must meet the following requirements:
- have a wide spectrum of action against bacterial, viral and fungal infections;
- have a low absorption rate through the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract;
- be safe for the human body and not have a toxic effect on the patient’s internal organs and systems;
- the pharmaceutical product should not cause allergic reactions;
- do not cause irritation to the mucous membrane of the upper respiratory tract.
In each clinical case, how to treat pharyngolaryngitis is determined exclusively by an otolaryngologist who has conducted a comprehensive and comprehensive examination of the patient.
Bed rest for pharyngolaryngitis.
Basic medications for the treatment of pharyngolaryngitis
When treating inflammatory diseases of the pharynx and larynx, specialists use the following medications:
- Bioparox is an aerosol with complex effects that has an antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effect. This inhaled antibiotic penetrates into all hard-to-reach areas of the respiratory system. Bioparox exhibits its activity against most pathogens in the upper respiratory tract. It also enhances the body's local defenses and blocks the formation of inflammatory mediators, thereby preventing soft tissue swelling.
- Imudon. The fundamental difference of this drug is that it includes lysates of 10 types of bacteria that most often provoke the inflammatory process. Lysates are small fragments of the shell of a pathological microorganism. After applying imudon to the surface of the mucous membrane, a protective barrier is formed and local immune cells are activated. Chronic pharyngolaryngitis must be treated with immunomodulatory agents.
- Hexetidine or hexoral. This pharmaceutical product is available in the form of an aerosol or rinse solution. Unlike similar antiseptics, hexetidine is practically non-toxic. In addition to its disinfectant effect, the drug has a hemostatic and analgesic effect.
- Octinisept, which is considered an antiseptic with the widest spectrum of effects. It breaks down gram-negative and gram-positive microorganisms, mycoplasmas, hepatitis, herpes and HIV viruses. The instructions for the drug indicate that after external use, octinisept begins to act within 1-2 minutes. In this case, the drug is not absorbed through the mucous membrane of the respiratory canal. The disadvantage of the drug is its release form, which provides for the ease of use of octiisept at home and significant difficulties in using the drug in a medical hospital.
https://youtu.be/SDHy_cQ9kFg
Drug therapy for pharyngolaryngitis.
What is the disease
The back wall of the pharynx in humans is called farings in Latin. Inflammation of the mucous membrane and lymphatic follicles in this area is referred to as “pharyngitis.”
Conditional classification divides the disease according to the stage of its course. Accordingly, they talk about its acute or chronic form.
In the first case, it bothers the patient with sharp pain in the throat, high fever, and cough. During treatment, recovery occurs within 7-10 days, after which the mucous membrane is restored and nothing else reminds of the disease.
A completely different situation is observed in the chronic form of the pathology. In the absence of adequate treatment or in the presence of concomitant factors, irreversible changes and restructuring of the mucosa occur.
The process becomes chronic and it is impossible to cure such pharyngitis. The task of an ENT doctor is to transfer the disease to a stage of long-term remission, when the problem does not bother the person for 2-3 years.
Important:
The ICD-10 code for chronic pharyngitis is J31.2. This includes all forms of this disease: hyperplastic, atrophic and others, with the exception of acute processes.
Causes of the disease
The main cause of the development of pharyngitis is almost always prolonged exposure to one or more traumatic factors.
The cause of inflammation is bacteria, viruses, fungi or the introduction of combined microflora into the body.
Among the mechanisms of transition to a chronic form, experts highlight several key points:
- The existence in the body of a constant source of infection in the immediate vicinity of the pharynx, for example, chronic sinusitis, adenoids, tonsillitis, carious teeth, etc.
- Digestive tract disease (GERD). The mechanism of development of this form is explained as follows: hydrochloric acid, which is contained in the stomach, enters the mucous membrane of the esophagus and the back wall of the pharynx.
- Prolonged irritation by such an aggressive factor causes a chronic inflammatory process.
- Lack of physiological breathing through the nose. Normally, passing through the nasal cavity, the air is cleaned, warmed and moistened. If a person breathes through the mouth (chronic rhinitis, deviated septum), then the air, without the preliminary stages of cleaning and moisturizing, immediately enters the mucous membrane of the pharynx and irritates it.
- Occupational factors: working in gas-filled conditions, as well as dust, flour and other hazards.
- Allergy. In such situations, predisposed people with hypersensitivity reactions develop chronic changes in the mucous membrane of the posterior pharyngeal wall.
- Stress, hormonal disorders.
Interesting:
With age, our mucous membranes undergo irreversible involutional changes: they become thinner, and the number of cells secreting protective mucus decreases. This condition is regarded as chronic atrophic pharyngitis.
Features of treatment
Traditional medicine recommends the use of remedies aimed at local treatment and eliminating the causes of inflammation. Before starting treatment for pharyngolaryngitis, its etiology should be determined. Even if it is known that the disease is bacterial in nature, it is necessary to establish which bacteria caused the inflammation, since treatment will not be effective.
Antiviral and immunostimulating drugs are actively used, which are indicated for the treatment of adults and children. As a local therapy, gargling with various anti-inflammatory solutions and decoctions of medicinal herbs is considered effective. Antibacterial and antiviral agents can be used in the form of inhalations, tablets, solutions or aerosols.
For successful treatment of pharyngolaryngitis, it is important to promptly determine the presence of symptoms of the disease. That is why it is so important to know what signs the inflammatory process of the pharynx and larynx manifests itself.
If you have questions for your doctor, please ask them on the consultation page. To do this, click on the button:
Ask a Question
Features of therapeutic approaches depending on the type of disease
Treatment is based on general and local effects on the affected tissue. The use of antiviral, antibacterial, and antifungal agents is indicated when one or another pathogen is identified.
It is necessary to minimize the impact of factors that aggravate the course of the disease and maintain a gentle vocal regime. In case of allergic processes, it is important to completely eliminate contact with the allergen and carry out specific and nonspecific antiallergic therapy under the supervision of an allergist. For chronic pharyngolaryngitis, it is advisable to use immunomodulatory agents that help the body's defense systems resist infectious effects.
Local therapy in adults includes:
- gargling;
- use of aerosols;
- irrigation, washing of mucous membranes.
The impact is carried out with antibacterial, antiseptic, antifungal agents, as well as medicinal plant preparations.
In young children, local therapy for the disease is limited by the child’s inability to rinse his mouth and possible anxiety during a number of procedures. Starting from school age, all methods can be used. If mouth rinsing, aerosols and sprays can be used at home, then irrigation and rinsing should be carried out in medical institutions.
Subatrophic pharyngolaryngitis must be treated with the use of drugs that improve nutrition, blood supply to tissues, and mucus formation (aloe, menthol oil solution, potassium iodide). In case of hyperplastic processes with significant tissue growth, surgical correction is possible.
Thus, the peculiarities of the conditions for the occurrence, symptoms and course of pharyngolaryngitis determine the need for timely detection, careful monitoring and treatment of the disease. Effective therapy not only prevents the development and progression of chronic forms of the disease, but also prevents consequences. This helps to avoid negative effects on the patient’s health and maintain the performance of representatives of “voice” professions.
Photo of pharyngolaryngitis
Pharyngolaryngitis is commonly called diffuse inflammation of the mucous membrane of the pharynx and larynx. In 70% of clinical cases, the disease is caused by a viral infection, which predominantly spreads downward through the respiratory system.
This inflammatory process is characterized by acute pain, bouts of dry cough, increased body temperature and a sore voice. How to treat laryngopharyngitis depends on the pathogen, the severity of symptoms and the prevalence of inflammation of the mucous membranes. The prognosis of the disease is usually positive and the patient’s recovery is observed after 5-7 days.
Laryngitis and pharyngitis: what is the main difference between the two diseases?
Laryngitis is an acute or chronic inflammation of the mucous membrane of the larynx. Pharyngitis is essentially an inflammation of the pharyngeal mucosa.
There is a distinction between acute and chronic forms, each of which have very different causes and forms. Accurate identification of the disease plays a decisive role in the success of treatment.
The prognosis depends on concomitant diseases and the patient’s health status. Laryngitis and pharyngitis sometimes require different treatments.
What is laryngitis
Acute laryngitis is part of a viral infection of the upper respiratory tract, which “descends” from the nasopharynx all the way to the larynx. In adults, laryngitis is accompanied by a sore throat or inflammation of the trachea. Cold, damp ambient air, as well as inhalation of a decongestant, reduces symptoms of the disease.
https://youtu.be/gLQKGyCtWRs
In addition to viruses, sometimes bacterial pathogens can cause acute laryngitis. Infectious diseases have become less common among children since the introduction of appropriate vaccinations in Russia. While cold-related laryngitis occurs primarily during cold periods, epiglottitis does not depend on the season.
Mild laryngitis can be treated on its own with anti-inflammatory medications. If symptoms quickly worsen or fever or difficulty breathing occurs, victims should consult a doctor.
If severe respiratory distress or choking occurs, contact an emergency physician immediately. Especially in children, life-threatening conditions quickly develop when the larynx or epiglottis swells.
Alcohol may cause chronic laryngitis
Chronic laryngitis is caused by environmental influences - nicotine or alcohol products. The causes of prolonged hoarseness - more than 3-4 weeks - should always be clarified by an ENT specialist, since a tumor disease (larynx cancer) must be excluded.
What is pharyngitis
Acute pharyngitis is an inflammation of the throat and a common symptom of a flu or cold infection, so it is almost always caused by viruses. A sore throat greatly interferes with the patient's eating, drinking, and often even talking. However, pharyngitis is generally harmless and can be treated with bed rest, home remedies, and possibly pain medications.
Rarely, bacterial infections occur in the throat, usually caused by streptococci. This form is much more serious because it tends to be purulent and cause serious complications. Therefore, in case of severe pain, high temperature and noticeable accumulation of pus in the neck area, you should visit a doctor.
Most patients experience throat discomfort ranging from scratching to severe sore throat with severe dysphagia. The lining of the throat appears very red, swollen and clogged.
If the throat is constantly inflamed for more than 3 months, it is called “chronic pharyngitis.”
Unlike acute microbial inflammation, chronic pharyngitis is caused by external factors that damage the delicate mucous membrane in the long term.
Depending on the symptoms, the otolaryngologist distinguishes between atrophic (with tissue) and hypertrophic (with tissue swelling) chronic pharyngitis.
Main differences between pathologies
Not everyone knows what the difference is between laryngitis and pharyngitis. Laryngitis is an inflammation of the larynx, while pharyngitis is an inflammation of the pharynx. The causes of diseases vary significantly. In case of bacterial genesis of diseases, therapy is aimed at eliminating the main pathogen.
Etiology of diseases
Strep throat is usually caused by a cold or flu infection. The disease is almost always caused by typical respiratory viruses. Sometimes pharyngitis is caused by systemic diseases: glandular fever, measles or rubella viruses. Rarely, herpes simplex viruses are the cause. A purely bacterial infection very rarely causes inflammation of the pharynx.
Treatment of pharyngitis with antibiotics
Antibiotics for pharyngitis
are prescribed only when the disease is caused by pathogenic bacteria, or when a bacterial infection occurs. In other cases, antibacterial therapy will not be effective. Only a qualified specialist can tell you how to treat pharyngitis in adults.
, the following drugs are used for bacterial etiology
:
- Macrolide antibiotics. Effective against various microorganisms and in cases of intolerance to drugs of the penicillin group. The most commonly prescribed are Sumamed, Erythromycin, Spiramycin, Azithromycin, Zitrolide.
- Penicillins. Treatment in adults is based on the use of drugs such as Trifamox, Flemoclav, Augmentin, Ecoclave, Flemoxin, Amoxicillin.
- Cephalosporin series. For pharyngitis, antibiotics from this group include Suprax, Zinnat, Ceftriaxone, Cephabol, Cefuroxime, Cephalexin. These drugs are
especially in cases of complications and advanced disease. - Tetracyclines. They are used when the bacteria that cause the disease are resistant to drugs from other groups. Used only for the treatment of pathology in adults.
When the disease occurs, these medications are usually prescribed in tablet form, sometimes prescribed as a suspension or in an injection solution. Usually only acute pharyngitis is treated with antibiotics.
If a patient takes antibiotics for pharyngitis, then to prevent the dysbiosis that these drugs provoke, it is necessary to take probiotics.
These include Bifiform, Lactobacterin, Yogurt, Bifidumbacterin, Linex, Laktovit.
When treating a throat in adults, local antibiotics are prescribed, for example, Bioparox or Fusafungin.
Features of the course of the disease
A feature of pharyngitis in the chronic stage is its cyclical nature, that is, periods of exacerbation are certainly replaced by remissions, when the features characteristic of the disease may be absent or mildly expressed.
In children
The immune system of babies is weaker, and therefore they are more prone to the appearance of pharyngitis in the chronic stage. But most often it develops not as a primary disease, but as a secondary disease caused by another ailment (problems with the gastrointestinal tract or respiratory system).
The disease is more severe in children under 2 years of age, when the mucous membrane of the nose and pharynx becomes severely inflamed, causing acute catarrhal rhinitis. In older children, during periods of remission, the disease proceeds unnoticed, its symptoms are practically absent. Sometimes there may be a sore throat and cough.
In this case, the following rule applies: the older the child, the more obvious the disease during the period of remission. When an exacerbation begins, the child’s age ceases to matter, all signs of the disease intensify several times.
During pregnancy
The course of the disease in pregnant women does not differ from its manifestations in men and non-pregnant women. But the likelihood of a chronic form of the disease occurring in pregnant women is much higher, since their immune system is weakened due to the woman's pregnancy.
The risk of the disease in pregnant women is also higher than in other people. If the disease worsens during pregnancy, there is a possibility of miscarriage or premature birth of a child, and there may be a negative effect directly on the fetus (fetal hypoxia). This necessitates the need for timely consultation with a doctor in the event of any inflammatory diseases in order to avoid adverse consequences.