Adhesions in the pelvis: what are they?
Symptoms of adhesions in the pelvis, as well as the process of treating the disease, require an integrated approach, complete mutual understanding between the patient and the doctor. The very essence of the pathology is that the connective tissue located in the pelvic area grows together, where physiologically it should be absent.
The functionality of internal organs is impaired, and concomitant diseases arise.
The main localization of adhesive processes is the lower part of the abdominal cavity, the pelvis. The greatest danger of adhesive disease lies not only in the fact that it causes dysfunction of healthy tissues located in the pelvic area, but also in the fact that it can lead to such serious consequences for the female reproductive system as infertility, as well as obstruction of the fallopian tubes.
Diagnostics
Diagnosing adhesions in the pelvis is quite difficult. At the first visit to a doctor, he can only suspect the disease, based on medical history and typical complaints. With a bimanual examination of the pelvic organs, the gynecologist can determine either their immobility (the uterus and appendages are securely “fixed”) or their limited displacement. In the case of a significantly pronounced adhesive process, palpation of the uterus and appendages is very painful. To clarify the diagnosis, additional studies are prescribed:
- smears on the vaginal microflora;
- PCR diagnostics for latent sexually transmitted infections;
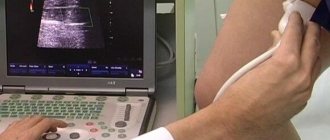
- Gynecological ultrasound;
- MRI of the pelvic organs.
Ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging for the most part, but 100%, allow diagnosing the adhesive process. Hysterosalpingography is also prescribed to determine the patency of the tubes. If their obstruction is detected, we can always talk about the presence of adhesions in the small pelvis, but if they are patency, the presence of an adhesions process cannot be denied.
For reliable diagnosis, diagnostic laparoscopy is used. When examining the pelvic cavity, adhesions are identified, the extent of their distribution and massiveness. In the laparoscopic picture there are 3 stages of the prevalence of the adhesive process:
- Stage 1 - adhesions are localized around the oviduct, ovary or in another area, but do not interfere with the capture of the egg;
- Stage 2 - adhesions are localized between the oviduct and the ovary or between these anatomical structures and other organs and cause difficulty in capturing the egg;
- Stage 3 - the fallopian tube is twisted, the tube is blocked with adhesions, which indicates the absolute impossibility of capturing the egg.
How do adhesions in the pelvis affect the body?
The abdominal cavity and pelvis are lined with parietal tissue, and the outer shell of the internal organs is covered with a visceral layer. If this part of the human body has not been subjected to negative effects in the form of mechanical injuries, surgical operations, inflammatory processes of infectious etiology, then both types of tissues have a perfectly smooth surface.
Under conditions of normal functioning of the parietal and visceral tissues, the synthesis of peritoneal fluid is performed, the main purpose of which is to ensure the movement of organs inside the abdominal cavity and directly in the pelvis. For example, the bladder cavity after filling can move slightly and move the uterus without damaging its walls.
If the internal organs of the pelvis have been subjected to pathological effects, then fibrin begins to form on the surface of the visceral tissue.
This substance should prevent the spread of the inflammatory process to neighboring tissues. Fibrin has a viscous consistency, and its excess amount can cause fusion of parietal and visceral tissues. As a result of this process, adhesions of varying sizes and severity are formed.
Most often, adhesive disease develops in the pelvic area in women, affecting the organs of the reproductive system. For example, if infectious microorganisms entered the cavity of the fallopian tubes, acute inflammation developed, and the patient did not receive adequate drug therapy, then over time the released fibrin forms an adhesive plug, blocking their abdominal opening.
Other internal organs located in the pelvis also undergo pathological changes. As the adhesions grow, a tubo-ovarian neoplasm (pyosalpinx) is formed, which covers the walls of the pelvis, intestinal walls, bladder, and appendages in women.
This type of tumor is difficult to treat surgically, disrupts the blood circulation of internal organs, and also reduces their performance. To achieve a complete cure for the patient, the doctor will need to show skill and put a lot of effort into removing adhesive tissue without disturbing healthy visceral tissue.
Intestinal adhesions
Intestinal adhesions
Intestinal adhesions can be hazardous to health. In places where they occur, a cancerous tumor or other equally dangerous complications can develop. Therefore, a doctor should be involved in their diagnosis and treatment! Folk remedies can only be used as an auxiliary treatment.
- St. John's wort decoction is recommended by almost all folk healers for the treatment of intestinal adhesions. To make a decoction, pour a glass of boiling water over one spoon of herb and place on low heat for a quarter of an hour. Cool and strain. Divide into three parts and drink throughout the day.
- Morinda, or, as it is popularly called, noni, gives a very good result in resolving intestinal adhesions. You need to take its leaves, fruits and roots. Grind everything and mix well. Eat two spoons with each meal. In a month there will be no trace of adhesions left.
Causes of adhesions in the pelvis
There are many factors that can provoke acute inflammation of the connective tissue of the pelvis, causing adhesions.
The following causes of adhesions are identified:
- infection with a bacterial infection that is transmitted as a result of unprotected sexual intercourse (gonorrhea, syphilis, ureaplasmosis);
Gonorrhea can cause adhesions to appear in the pelvis. Then the symptoms of adhesive disease are added to the symptoms of gonorrhea, and complex treatment is needed
- long-term inflammation of the pelvic organs, which did not receive adequate drug treatment;
- chronic pathologies of the female reproductive system (parametritis, salpingo-ophritis, pelvioperitonitis, endometritis);
- infection with tuberculosis bacillus;
- recently performed surgical operations on uterine tissue in the form of early termination of pregnancy, hyteroscopy, removal of tumor tumors;
- placement of an intrauterine device, which was carried out in violation of medical protocol;
- mechanical damage to the pelvic organs resulting from falls, blows, accidents;
- acute inflammation of appendicitis.
Adhesions in the pelvis (symptoms, treatment of the disease continue over a long period) are most often diagnosed in the female half of the population.
The likelihood of developing adhesive disease increases several times in the presence of factors such as promiscuous sex life, unbalanced nutrition, the presence of reduced immunity, hypothermia, and non-compliance with personal hygiene rules.
In pregnant women, adhesions in the pelvic area may occur in the event of fetal development abnormalities. Quite often, the pathological process manifests itself after a cesarean section, if it is not possible to give birth to a child naturally. In fact, this is a complication of a surgical operation associated with dissection of the walls of the reproductive organ and the anterior part of the peritoneum.
Causes
Adhesion formation refers to the body's defense mechanisms and has the goal of separating the damaged area (inflammation or injury) in the pelvic or abdominal cavity from healthy tissue. The tendency to form adhesions, the intensity of their formation and the prevalence of the process are determined by a number of factors: increased reactivity of the connective tissue, weakened immunity and the individual predisposition of the peritoneum to adhesions. Risk factors for the formation of connective tissue adhesions are divided into 3 groups:
- endogenous, caused by the body’s genetic predisposition to adhesions (reduced or increased production of the enzyme N-acetyltransferase);
- exogenous – affect the body from the outside (trauma, surgery, infection);
- combined, when external and internal factors participate in the formation of adhesions.
The immediate causes of adhesions in the pelvis are:
- Surgical interventions. The intensity of adhesions is directly related to the operation performed in the abdominal cavity. Factors that increase the likelihood of the formation of adhesions include: surgical approach (laparoscopic or laparotomy), the volume and traumatic nature of the operation, its duration, temperature conditions (excessive cooling or heating of intestinal loops), installation of drains in the pelvis that remove blood and peritoneal fluid, used suture material and chemicals (iodine, alcohol, various powders).
- Inflammatory diseases. Acute endometritis, salpingoophoritis, vaginitis, parametritis and other pelvic diseases contribute to adhesions. Hidden sexually transmitted infections that occur with a blurred clinical picture (chlamydia, ureaplasmosis) are the cause of chronic inflammation in the pelvis, which serves as an impetus for adhesions.
- External endometriosis. Regular bleeding from endometriotic lesions into the pelvic cavity leads to aseptic inflammation and adhesions.
- Bleeding into the pelvic cavity. Rupture of the ovary, interrupted ectopic pregnancy such as tubal abortion or rupture of the tube occurs with bleeding into the abdominal cavity, subsequent aseptic inflammation and the formation of adhesions.
- Injuries to the lower abdomen. Bruises, hemorrhages, open wounds of the small pelvis resulting from a fall, blow, or accident.
- Systemic connective tissue diseases. Scleroderma, dermatomyositis, rheumatism and others.
note
In 50 percent or more of cases, the formation of adhesions is caused by the combined action of several factors. Their formation is predisposed by promiscuity, abortion, invasive gynecological procedures, poor intimate hygiene, and late visits to the doctor.
Symptoms of adhesions in the pelvis
Adhesions in the pelvis (symptoms, treatment of the disease should begin immediately after the examination) manifest themselves differently, depending on the scale of the adhesive process, as well as the number of organs that are involved in it.
Signs of the disease are classified according to the characteristic clinical picture:
| Form of adhesive disease | Current symptoms |
| Acute |
|
| Intermittent |
|
| Chronic |
|
Adhesions in the pelvis (symptoms and treatment of the disease directly depend on the form of its course) are most dangerous if an acute type of the disease develops. In this case, the patient is urgently taken to the surgical department of the hospital, where he undergoes emergency surgery to eliminate adhesive foci of inflammation.
Main clinical manifestations
They entirely depend on the stage of the disease and how widespread the adhesions are in the pelvis, so the symptoms can vary quite a lot, thereby significantly complicating diagnosis.
Symptoms of pelvic adhesive disease are not unique, so the disease is easily confused with many others. And if banal poisoning most often does not pose any threat to the body and can be treated at home, then appendicitis (and even more so peritonitis) requires emergency medical care.
- Acute form. It is characterized by pronounced pain, vomiting, fever, nausea and an increase in heart rate (heart rate). If urgent measures are not taken, complete intestinal obstruction occurs, the pressure drops sharply, protein and water-salt metabolism are disrupted, and the patient’s general condition is assessed as extremely severe.
- Intermittent (intermittent) form. The disease may (although not necessarily) be asymptomatic. The pain is mild and intermittent, and the most common complaints of patients are related to various intestinal disorders (diarrhea, constipation, painful bowel movements).
- Chronic (latent) form. The clinical picture is blurry and often does not have any external signs. Sometimes constipation and subtle discomfort in the lower abdomen may occur. Diagnosis (if there is no reason to suspect the presence of adhesions) is difficult, and the only obvious manifestation - the inability to get pregnant for a long time - is simply ignored by many women.
Attention! Patients with a severe attack of pain, accompanied by obvious signs of poisoning of the body (nausea, vomiting, severe fever) need urgent hospitalization, therefore the only correct decision in such a situation would be to call an ambulance.
Diagnosis of adhesions in the pelvis
Determining the adhesive process in the pelvic area is a difficult task even for an experienced surgeon. The primary stage of the examination begins with the doctor performing a visual examination and palpation of the lower abdomen. Then listens to the patient's complaints.
If there is a suspicion of a pathology, additional diagnostics are prescribed in the form of:
- gynecological examination in women, as well as the collection of smears to determine the microflora of the internal genital organs;
- taking venous blood to check whether the patient is infected with dangerous types of infections, including sexually transmitted ones;
- MRI diagnostics of organs located in the pelvis;
- invasive laparoscopy showing uterine torsion, proliferation of fibrous tissue, extensive inflammatory process;
- Ultrasound of the female reproductive system.
It is believed that ultrasound and MRI diagnostics are the two main research methods that provide comprehensive information about the condition of the abdominal cavity and pelvis.
Based on the results of the examination, the attending physician decides to use traditional methods of treatment, using medications, or sets a date for surgical intervention. Surgery is considered the most effective method of completely getting rid of adhesive disease.
Mechanism of development of pathology and clinical picture
At first, the connective fiber is weak and thin; in the first stages of the disease, it is easy to disconnect . Over time, the film thickens, possibly even ossification. In later stages, fibrous tissue can only be excised surgically.
The clinical picture is established based on two criteria : the strength of the lesion (number of growths) and the location. The patient is often tormented by symptoms reminiscent of the progression of intestinal diseases or damage to the gastrointestinal tract. Often a negative condition is preceded by an asymptomatic period when the disease is at an initial stage.
Prevention of adhesions in the pelvis
The formation of adhesions in the pelvic area can be prevented through the timely use of preventive measures consisting of the following:
- prevent inflammatory processes in the lower part of the abdominal cavity and organs of the genitourinary system;
- balance the diet, saturating it only with biologically useful products in the form of cereal porridges, boiled lean meat, ocean fish, fresh vegetables, green fruits, so that a high immune status is maintained;
- always use barrier contraception, or have one permanent partner;
- give up bad habits by eliminating alcohol, tobacco products, and drugs from your life;
- after surgery, undergo a rehabilitation course, starting movements in the first days after surgery;
- Women should visit a gynecologist at least once every 6 months to prevent the occurrence of low-grade inflammation in the appendages and inner layer of the uterus.
All injuries to internal organs located in the pelvis should not be ignored. Ignoring sluggish and constantly disturbing pain in the lower abdomen is fraught with the occurrence of a chronic form of adhesive disease, which in the future can lead to surgery.
Pulmonary adhesions
If you have pneumonia in your legs, adhesions may form between the pleura and the lungs. They make breathing difficult by interfering with the normal movement of the lung during inhalation and exhalation. Pulmonary adhesions respond well to resorption if you use folk remedies.
- Prepare a tasty and healthy tea from two spoons of lingonberries, four spoons of rose hips and two dry nettles. Pour into a thermos and fill with half a liter of boiling water. After three hours the tea will infuse. Drink half a glass of it three times a day.
- Take dried raspberries, black currants and rose hips in equal volumes. Pour two tablespoons of berries into a half-liter thermos and fill with boiling water. After two hours, strain. Take half a glass twice a day.
- Make lotions from flaxseed for 30 days in the evenings and leave until the morning. Place the flaxseed in a gauze bag, tie it and place it in boiling water. Leave until completely cool. Place on the kosha over the area of adhesions, secure and go to bed.
Treatment methods for adhesions in the pelvis
Modern medicine has a large number of techniques and therapeutic regimens that allow effective treatment of patients with all stages of adhesive disease. Let's look at each of the existing methods in detail.
Drug therapy
Adhesions in the pelvis (symptoms, treatment of the disease is possible with medications) can be treated with medications if the disease is at the initial stage of its development. These are medications that prevent the formation of excess fibrous tissue and also relieve the inflammatory process.
At the stage of conservative treatment, the following medications can be used:
- Streptokinase - administered intravenously once a day, 250,000 IU, together with an isotonic solution (50 ml) of sodium chloride, as part of a dropper with a drug delivery rate of 30 drops. per minute (this is a one-time shock therapy drug, after the administration of which other anti-inflammatory drugs, as well as blood thinners, are used);
- Chymotrypsin is administered by injection at a dose of 5-10 mg per day intramuscularly, and the minimum long-term therapeutic course is from 10 to 12 days;
- Trypsin - prescribed intramuscularly 2 times a day in combination with 2 ml of sodium chloride solution, a single dosage of the active substance is 0.005 mg (long course of therapy 7-10 days);
- Longidaza - applied subcutaneously with injection into the area of the adhesive process and a dose of 3000 MO (course of treatment from 5 to 25 injections, and the interval between drug administrations should be at least 3-10 days, depending on the severity of the disease);
- Trental is an intravenous infusion, which is administered in the form of a dropper, observing the ratio of auxiliary drugs - 100 mg of Trental, the same amount of Ringer's solution, 0.9 sodium chloride and glucose solution, 5% concentration (the medication is dripped 1-2 times a day for 60 minutes ., and the general course of therapy is determined only by the attending physician based on the patient’s well-being).
To prevent the onset of severe consequences for the female reproductive system, the development of adhesions in the appendages and fallopian tubes, mineral oils, as well as dextran in combination with glucocorticoid drugs, are injected into the pelvic area. The appendages are enveloped in a liquid polymer film, which, after completely getting rid of adhesions, dissolves on its own.
Physiotherapy, balneotherapy
The following treatment methods can be used as physiotherapeutic procedures aimed at treating adhesive disease
- electrophoresis of the anterior wall of the abdominal cavity, which is performed in combination with basic drug therapy;
- soft tissue massage in the area of adhesions;
- baths with mineral fashion;
- ultrasound treatment.
The peculiarity of physiotherapeutic procedures is that they are effective as an auxiliary element in the main treatment regimen (postoperative recovery period, preparation for surgery, taking medications).
Traditional methods
There are traditional medicine recipes that can stop the development of adhesions in the pelvis and also promote the resorption of fibrous tissue.
Here are several methods of therapy, the basis of which are decoctions and extracts of medicinal plants:
- pour 50 ml of black cumin and olive oil into a clean vessel, moisten a hygienic tampon in it, and insert it into the vagina overnight (the method is effective in the presence of adhesions in the fallopian tubes, and the course of therapy lasts from 7 to 10 days);
- take 1 tbsp. l. dried chamomile, coltsfoot and plantain, pour them into a metal container, pour 1 liter of water and boil for 10 minutes, leaving to infuse for another 2 hours (douche the vagina and uterus in the morning and evening for 12 days) ;
- you will need to take 1 tbsp. l. marsh cinquefoil, pour it into a glass vessel, pour in 250 ml of vodka or moonshine and leave for 10 days (the procedure for taking home medicine is 20 drops 3 times a day, diluted in a glass of warm water, and the general course of therapy is 25 days);
- collect it yourself or buy a medicinal plant at the pharmacy - boron uterus, take 2 tbsp. l. raw materials, pour into a thermos, and then add 1 liter of boiling water to it, tightly closing the lid (infuse for 3 hours, and then take 150 ml 3 times a day 15 minutes before meals, the total course of therapy is 15 days).
Before using folk remedies as a method of treating adhesions in the pelvic area, it is recommended to consult a surgeon or gynecologist if the pathology is localized in the organs of the reproductive system. Unauthorized therapy can lead to complications and deterioration of well-being.
Candles for spikes
In addition to injectable medications that are administered intravenously, subcutaneously and intramuscularly, suppositories can be used, namely:
- Longidaza - relieves the inflammatory process, swelling, stops further growth of fibrous tissue (administered rectally or vaginally at the rate of 1 suppository for 3 days, and the total course of therapy is 10 suppositories);
- Heparin - have anti-edematous and anti-inflammatory properties, improve tissue blood circulation, are administered intravaginally 2 times a day, morning and evening for 10 days (it is advisable to perform the procedure at the same time).
If adhesive disease has developed in the pelvis in men, then suppositories are administered rectally. They are actively used to restore damaged tissues of the genitourinary system. At the discretion of the doctor, the duration of treatment can be extended by 7-10 days.
Surgical intervention
Surgery is the most effective and frequently used method in the treatment of pelvic adhesions. The surgical intervention is performed in a sterile operating room, the patient receives general anesthesia, and the duration of the procedures ranges from 1.5 to 4 hours.
Depending on the complexity of the adhesive tumor, the number of organs involved in the pathological process.
After making an incision in the anterior wall of the abdominal cavity and entering the internal space of the small pelvis, the surgeon cuts out the overgrown fibrous tissue, restoring the normal position and functionality of the organs. Upon completion of the procedure, the wound surface is sutured and a sterile dressing is applied. The recovery period is 10-15 days.
Other methods
In addition to methods of drug therapy, surgery and the healing properties of medicinal herbs, an alternative method of treating adhesions in the pelvis is used. This is egg rolling, which is practiced by traditional healers. The patient lies on his back, and a chicken egg is placed on top of the skin surface of the abdominal cavity and rolled in a clockwise direction.
At this time, the traditional healer reads special prayers and conspiracies aimed at getting rid of adhesions in the pelvic area. This is an alternative method of alternative medicine, which is also popular among the general population.
Treatment of adhesive disease of the pelvic organs
Treatment of the pathology is carried out conservatively and surgically . Conservative therapy is carried out at stage 1 of plastic pelvioperitonitis and includes:
- Antibiotics. Identification of an infectious agent requires antibiotic therapy; the selection of drugs is carried out based on the results of the study. sowing and taking into account the resistance of bacteria to them.
- NSAIDs. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs include indomethacin and diclofenac, which relieve pain, eliminate swelling of inflamed tissues and resolve loose adhesions (the initial stage of the disease).
- Hormonal agents. Treatment with hormones is carried out when endometriosis is detected.
- Fibrinolytic enzymes. Longidase, lidase, terrilitin promote the dissolution of adhesions due to the cleavage of glycopeptide bonds. Enzymes are prescribed in rectal suppositories, for intramuscular administration and during physiotherapy.
- Physiotherapy, gynecological massage, exercise therapy. Among the physiotherapeutic procedures, electrophoresis with enzymes, paraffin therapy, and SMT are effective.
- Vitamins, immunomodulators. They improve general condition, normalize blood flow and metabolism in tissues, and stimulate the immune system.
Surgical treatment is indicated when conservative therapy is ineffective, as well as in the case of acute and intercurrent forms of the disease.
Important
If serious complications develop (ectopic pregnancy, intestinal obstruction), emergency surgery is performed.
Dissection of adhesions is performed endoscopically (laparoscopy):
- laser therapy (adhesions are cut with a laser beam);
- electrosurgery (unions are cut with an electric knife);
- aquadissection (dissection of adhesions is performed with water under high pressure).
Sozinova Anna Vladimirovna, obstetrician-gynecologist
14, total, today
( 73 votes, average: 4.36 out of 5)
Pyoderma in children: symptoms and treatment
Cleft palate in humans: causes of the defect, methods of correction
Related Posts
Complications
Depending on the location of the adhesive process, as well as in the absence of drug or surgical treatment, the patient can expect the following types of complications:
- infertility in women caused by obstruction of the fallopian tubes;
- menstrual irregularities;
- bending of the cervix, as well as deformation of the organ itself, which will make it impossible to bear a healthy child;
- lack of normal digestive function, which is expressed in intestinal obstruction.
Ignoring the symptoms of adhesions in the pelvis, as well as the lack of treatment for the disease, can provoke an acute inflammatory process in the internal organs. Ultimately, it can spread to the upper abdominal cavity, causing suppuration, blood poisoning and death.
Article design: Mila Friedan
Consequences and complications of the adhesive process
The formation of adhesions is a rather serious process and ultimately provokes many complications and negative consequences.
If not treated in a timely manner and the adhesive process is not dealt with, they provoke the following negative consequences:
- Female type of infertility and menstrual cycle disruption.
- Abnormal bending of the cavity in the structure of the uterus and complete/partial obstruction of the fallopian tubes.
- Complete or partial obstruction of a woman’s intestines, as well as ectopic pregnancy.
Adhesions can provoke negative symptoms such as constipation and chronic types of abdominal pain, as well as dysbiosis and damage to the bile ducts.
The most dangerous adhesions for girls are when the body grows and develops, and treatment is not prescribed, this can provoke abnormal skewness and infertility, and an increased risk of ectopic pregnancy.
Chronic pelvic pain syndrome
Painful sensations are associated with the tension of the adhesions when the pelvic organs are displaced. In this case, there is irritation of the receptors that are responsible for pain, and disruption of blood supply.
Chronic pelvic pain is characterized by:
Treatment
Conservative treatment includes suppression of inflammation and infection and symptomatic therapy. To reduce inflammation, they resort to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for a course of 7-14 days: Nimesulide, Ibuprofen, Ketoprofen, Etoricoxib. The drugs are administered parenterally for the first three days, and then switched to oral administration. To protect the gastric mucosa, it is recommended to take Omeprazole or another proton pump inhibitor for 2-3 weeks. In case of exacerbation of peptic ulcer, high blood pressure, bleeding, as well as decompensation of the liver and kidneys, NSAIDs should not be taken.
Antibiotics are used to eliminate the infection. Before culture results, broad-spectrum antibiotics are prescribed: protected penicillins, cephalosporins, macrolides. In gynecology, cephalosporins and fluoroquinolones are most often used: Ceftriaxone, Moxifloxacin, Ciprofloxacin. If anaerobes are suspected, Metronidazole is used, which also acts on protozoa. For ureaplasmosis and chlamydia, Doxycycline is used. The course of antibiotics is 10-14 days. During treatment, you should take probiotics to maintain the intestines: 2 hours after taking the antibiotic Bifiform, Linex, Bion-3 and others.
The following groups of medications help reduce pain:
- antispasmodics (No-shpa, Drotaverine, Buscopan, Papaverine, Platiphylline);
- analgesics (Analgin, Paracetamol, Ketanov, Ketorol);
- prokinetics (Itopride);
- enemas;
- anti-flatulence agents (activated carbon, Smecta, Polysorb, enzyme preparations).
To normalize excretory function, herbal preparations are sometimes prescribed: Canephron, Urolesan and others.
Hormonal therapy plays a key role in the treatment of gynecological pathologies. Combined preparations of estrogen (estradiol, ethinyl estradiol) and gestagens (norgestrel, desogestrel and others) are used. Medicines are prescribed in a continuous or cyclic mode, starting with small doses.
To eliminate adhesions, specific enzymes are provided that break down proteins. The drugs Longidaza, Lidaza, Trypsin, Terrilitin are used rectally in the form of suppositories and intramuscularly in courses of 1-2 weeks. Enzymes can also be used for physical therapy.
Physiotherapy
Mud therapy and applications with paraffin have a good effect. To reduce adhesions, phonophoresis and electrophoresis with anti-inflammatory and enzymatic agents are indicated. Adhesions resolve well with this treatment at the first and even second stages of the process. UHF therapy, diathermy, and iontophoresis have a general strengthening effect.
Surgery
If these methods are ineffective and the process is widespread, they resort to surgery: destruction of adhesions using various physical methods. In patients with adhesive disease, surgery is performed according to the following principles:
- the cuts are made wide;
- prevent drying of the peritoneum (treatment with solutions);
- completely stop bleeding;
- completely remove blood and all clots;
- polymers are used for suturing;
- do not use dry formulations of antibiotics and antiseptics.
The separation of adhesions by such methods as:
- laser beam;
- electric knife;
- aquadissection - pressure of water under pressure.
These methods are less traumatic, with the exception of water pressure, and help avoid relapse of the disease.
In the surgical approach to the treatment of adhesions, the postoperative period plays an important role. Patients must strictly observe restrictions on the motor regimen, take all prescribed medications, avoid getting the sutures wet and overloading the postoperative wound.
To improve healing, taking multivitamin complexes containing vitamins A, D, E and nicotinic acid is recommended. Anti-inflammatory and antibacterial therapy is also carried out. In a hospital setting, detoxification treatment with solutions of Reamberin, Reopoliglyukin, Poliglyukin is indicated.
Is it possible to get pregnant
If there are first-degree adhesions in the pelvis, pregnancy and pregnancy are possible even without treatment. The second stage requires treatment before planning a pregnancy. And with the third, the success of childbirth is unlikely due to irreversible changes in the internal organs.
How adhesions and scars form
However, our fabrics have one natural, irrevocable property - they strive to protect our body. And sometimes the development of so-called protective factors after damage occurs intensively - with a reserve.
In practice, it looks like this: in places where the serous membrane is damaged, collagen and elastic fibers and connective tissue cells are intensively produced. If at this time any internal organ (for example, a loop of intestine) touches the area of the damaged serosa, it is involuntarily involved in this process. A cord of connective tissue is formed, which leads from the wall of the internal organs to the inner surface of the abdominal wall. This is called adhesions.
Adhesions can also connect internal organs to each other. Each of them is also covered by a serous membrane. During the operation, micro-tears are not excluded. And these places of microtrauma can also subsequently become a source of the formation of adhesions between this organ and the organs adjacent to it.
Also, at the site of contact and healing of tissues after their dissection or rupture, a scar may form, in which the normal tissue is replaced by a more rigid and inelastic connective tissue. Scars can be on the skin, or they can be on internal organs.
What causes adhesions?
Adhesive disease is a condition that occurs when a large number of individual adhesions are formed or a significantly pronounced adhesive process is formed, which leads to disruption of the functioning of internal organs.
In most cases, intestinal adhesions occur after surgery. Most often they appear after major operations performed by laparotomy (through a large incision in the abdominal wall).
Doctors who operated at the dawn of surgery noticed that when repeated operations were necessary, adhesions between individual organs were found in the abdominal cavity. Even then, it was clear to surgeons that numerous complaints presented by patients after surgical interventions on the abdominal organs were associated with adhesions. Since then, the complex history of studying this problem began.
The adhesive process (intestinal adhesion) is currently one of the most studied pathological processes in the human body. The main reactions of the internal environment that play a decisive role in the occurrence of adhesions include:
- inflammatory tissue reaction;
- coagulation of blood and the proteins it contains;
- anti-coagulation.
During surgery, trauma to the peritoneum is inevitable. In the event that only one of its leaves was damaged, and the one with which it is in contact remained intact, adhesions will not form. But even if such an injury causes a fusion between organs, it will be superficial, easily stratified and will not lead to dysfunction of the organs.
If 2 adjacent leaves were injured, then a whole cascade of pathological reactions is triggered. Due to a violation of the integrity of the blood capillaries, the release of individual blood proteins occurs. Globulins (namely coagulation factors) play a major role in the adhesion of organs. When these proteins come into contact with exposed intestinal tissue, a cascade of clotting reactions is triggered. The outcome of this cascade is the precipitation of fibrinogen in the form of fibrin. This substance is the universal “glue” of our body, which leads to the formation of early intestinal adhesions after surgery.
In the process of blood clotting, the anticoagulation system plays a significant role, which is activated somewhat later than the coagulation system. In most cases, blood that gets onto the peritoneum of the intestinal loops first coagulates and then returns to the liquid phase precisely thanks to the fibrinolysis system (dissolution of precipitated fibrin). But sometimes, upon contact with the peritoneum, this process can be disrupted, and fibrin does not dissolve. In this case, polar cods may appear.
Classification
The clinical classification of plastic pelvioperitonitis is based on the characteristics of its course. The following forms of pathology are distinguished:
- Spicy
. The disease manifests itself with severe clinical symptoms with pain, temperature, drop in pressure, nausea and other signs of increasing intoxication. In some cases, intestinal obstruction develops. - Intermittent
. The phasic flow is noted. During exacerbation, characteristic pain occurs and intestinal disorders may occur. During remission, symptoms are minimal or absent. - Chronic
. The disease is asymptomatic or its manifestations are mild. The patient periodically experiences constipation and pain in the lower abdomen. Usually the reason for visiting a doctor is the inability to get pregnant.
Since adhesions play a significant role in the development of infertility, it is important to take into account the features of damage to the uterine appendages. Specialists in the field of gynecology and reproductive medicine distinguish the following stages of the process, determined laparoscopically:
- Stage
I. _ Single thin adhesions are localized near the ovary, fallopian tube, uterus or other organs, but do not interfere with the movement of the egg. - Stage
II . The ovary is connected by dense adhesions to the fallopian tube or other organs, while more than 50% of its surface remains free. Adhesions interfere with the capture of the egg by the fimbriae. - Stage
III . More than half of the ovary is covered with numerous dense adhesions. The fallopian tubes are impassable due to deformation and blockage of the lumen.
Results
One of the causes of female infertility is synechiae in the fallopian tubes, which fuse the organ.
Most often, the pathology is the result of other gynecological diseases and is asymptomatic, diagnosed during a routine examination by a doctor or during pregnancy planning. The adhesive process often becomes the cause of female infertility and requires mandatory treatment. For synechia, the following are used: conservative therapy, surgery and traditional medicine. It should be remembered that you should not self-medicate, as you can harm yourself, cause the disease and waste valuable time on treatment.
Education mechanism
The abdominal cavity is lined from the inside by the peritoneum, a serous membrane that forms a closed space where the abdominal organs are located. The peritoneum is represented by 2 layers: parietal, lining the abdominal cavity, and visceral, enveloping the internal organs. Both layers of the peritoneum are connected to each other and pass into one another. The main functions of the peritoneum are to create mobility of organs, prevent their friction against each other, protect against microbial agents and limit the infectious process when microorganisms penetrate into the abdominal or pelvic cavity.
Preventive measures and prognosis
After operations, doctors recommend walking around after the first day, since blood circulation should not slow down. When there is insufficient oxygen in the tissues, toxins begin to accumulate, which contribute to the appearance of adhesions.
A sedentary lifestyle causes congestion in the pelvic area, so if pain occurs, it is recommended to devote 30 minutes a day to gymnastics. Particular attention should be paid to the abdominal muscles. Swimming is a universal method, as it gives an even load on all muscles.
Timely treatment of diseases of the female genital area and adherence to personal hygiene rules when communicating with partners of the opposite sex will reduce the risk of infection in internal organs.
If the disease is detected at the first or second stage, a woman has a chance to get pregnant safely, carry and give birth to a healthy child, because the damage is not so significant. At the third stage, in which the internal lumen of the fallopian tubes and ovaries are affected, urgent measures and financial expenses are required. Treatment is long and expensive. If the villi that propel the egg into the uterus are damaged, an ectopic pregnancy may occur, after which the only way to give birth to a child will be through in vitro fertilization.
What are intestinal adhesions?
Intestinal adhesions are formations of connective tissue (cords) between the abdominal organs and intestinal loops, leading to fusion or gluing of the serous membranes of the organs to each other. The adhesive process is facilitated by the natural ability of the peritoneum to adhere (adhesion).
As you know, the peritoneum is a thin film that envelops the internal organs. If for some reason an inflammatory focus forms in the abdominal cavity, the peritoneal film sticks to the inflamed area and prevents the spread of the pathological process to other organs.
But there is another side to this useful protective function. Sometimes the adhesion process can proceed too intensely, which leads to dysfunction and deformation of the organs enclosed in such a peritoneal membrane. Blood vessels may be pinched, and the intestine often narrows due to compression of its walls by adhesions.
Why do intestinal adhesions form?
Doctors identify several main reasons leading to the formation of adhesions:
- Open or closed injuries to the abdomen and abdominal organs. In this case, the formation of adhesions can occur a significant period of time after the injury (up to six months).
- Surgical intervention on the abdominal organs.
- Inflammatory or infectious processes in the peritoneum (peritonitis, acute appendicitis, perforation of a gastric or duodenal ulcer). Particularly extensive adhesions occur in diffuse peritonitis, when the infection breaks through into the abdominal cavity.
- In women, adhesions can form as a result of inflammation of the appendages or as a result of cesarean section.
- Hereditary predisposition. It is associated with increased synthesis of enzymes that provoke the proliferation of connective tissue, which manifests itself in the fact that with any, even minor damage to the epithelial cells of the peritoneum, adhesions are formed.
- Radiation therapy in the treatment of cancer. During its implementation, radiation damage to the peritoneum occurs, leading to the formation of adhesions.
Doctors admit that most often the cause of the formation of adhesions is surgical operations. According to statistics, they form in 15% of patients, and the more severe and extensive the surgical intervention, the greater the risk of adhesions forming between internal organs.
Symptoms of the formation of intestinal adhesions
Since the formation of adhesions is a rather long process, its symptoms do not appear immediately. Sometimes the pathological process does not manifest itself in any way and is discovered by chance during an examination. This becomes the reason that patients seek medical help with a complicated adhesive process. So, what are its main symptoms:
- Periodically occurring nagging pains that are localized in the area of the postoperative scar. Pain may intensify after physical activity, especially those associated with sudden turns of the body and lifting heavy objects.
- Dysfunction in the gastrointestinal tract, expressed in bloating, flatulence, a tendency to constipation, and a feeling of fullness in the navel.
- Violation of the act of defecation, which manifests itself in persistent constipation. This is due to a slowdown in the passage of intestinal contents through areas compressed by adhesions.
- Nausea and vomiting may occur after eating.
- With a chronic course of the process, the patient may experience weight loss.
In some cases, serious complications may occur that pose a threat to the patient's life and require immediate surgical intervention.
Photo: Acute intestinal obstruction
Acute intestinal obstruction develops as a result of compression of the intestinal tube by adhesions, which becomes an obstacle to the passage of intestinal contents. Adhesive obstruction is manifested by attacks of acute pain, vomiting, accumulation of gases and lack of stool. These symptoms may be accompanied by tachycardia and a sharp decrease in blood pressure. In this case, you must immediately call an ambulance.
- Intestinal necrosis . As a result of disruption of the blood supply to the intestinal walls due to arteries pinched by adhesions, their necrosis occurs. This condition requires surgical intervention and removal of necrotic areas of the intestine.
- Ultrasound (ultrasound examination) of internal organs. Allows you to visually detect the presence of adhesions during the examination.
- X-ray with contrast agent (barium salt). The patient must drink the contrast agent on an empty stomach, after which x-rays are taken. They will show defects in intestinal filling, allowing one to judge the presence of formed adhesions.
- Laparoscopy ( diagnostic). During the examination, a flexible fiber-optic tube with lighting and a camera at the end is inserted into the abdominal cavity through a small puncture, which allows you to see the presence of adhesions and even, if necessary, dissect them.
- CT (computed tomography). A modern method that is highly accurate and allows you to visually determine the presence of an adhesive process.
Diagnostics
Characteristic complaints of pain and intestinal disorders help to suspect an adhesive process in a patient. The doctor must conduct a thorough examination and question the patient about the nature of the pain, and clarify whether there have been surgical interventions or abdominal injuries in the past. After a digital examination of the rectum, the patient is prescribed laboratory tests and instrumental examinations.
Treatment of intestinal adhesions
Treatment of adhesions is carried out using conservative methods, folk remedies and surgery.
Treatment with conservative methods
In approximately half of the cases, when diagnosing an adhesive process, it is possible to do without surgical intervention, using conservative treatment methods in conjunction with traditional medicine and a special diet. If adhesions do not manifest themselves in any way and there is no pain, no special treatment is required. Observation and preventive examinations by a doctor are sufficient.
For minor pain and minor functional disorders, the patient is prescribed antispasmodics and analgesics. The doctor may prescribe injections of enzymes, vitreous, aloe preparations, splenin, which promote partial resorption of adhesions. For chronic constipation, it is necessary to take laxatives prescribed by your doctor.
Diet and proper nutrition for intestinal adhesions
If you suspect an adhesive process, you must adhere to a special diet. In no case is it recommended to starve or overeat, this can lead to aggravation of the problem and the development of complications. It is highly desirable to adhere to the regime and eat at certain times.
Meals should be fractional, in small portions, you need to eat 4-5 times a day. Heavy and fatty foods, foods rich in fiber and causing flatulence and bloating are excluded from the diet. These include:
It is not recommended to consume whole milk, any carbonated drinks, hot seasonings, sauces. The menu must include foods containing calcium, eat more cheese and cottage cheese. Fermented milk products, especially kefir, are very useful. They help move contents through the intestines.
It is better to drink kefir at night; it must be fresh, since three-day kefir, on the contrary, has a fixing effect. Food should not be hot or cold, it should be taken warm. This will help relieve intestinal spasms.
Patients with adhesive disease can eat:
- low-fat broths,
- steamed or boiled fish,
- soft-boiled eggs or in the form of an omelet,
- boiled chicken meat,
- dairy products,
- small amount of butter.
The following products are strictly contraindicated:
- strong coffee,
- tea,
- rich meats,
- mushroom and fish broths.
The patient must avoid marinades, smoked meats, spicy seasonings, and canned food. Following such a diet helps prevent exacerbations of the disease and serves as a kind of prevention of adhesions.
Surgical treatment: removal of adhesions through surgery
If the doctor suspects a patient has a disturbance in the blood supply to the intestines due to adhesions, surgery should be performed immediately. Surgery will be aimed at removing obstructions and restoring normal passage of intestinal contents. The essence of the operations comes down to cutting adhesions, for which two types of operations are used: through an incision in the peritoneum and minimally invasive laparoscopic surgery.
The main problem of surgical treatment of adhesions is the fact that any abdominal surgery can again cause the formation of adhesions. Therefore, they try to carry out operations with minimal trauma: adhesions are separated with an electric knife or laser. Another method is hydraulic compression of adhesions and injection of a special liquid under pressure into the connective tissue.
Risk factors for developing pathology
The abdominal cavity is covered inside with a specific membrane consisting of two sheets. If damaged, they can stick together, forming adhesions. This is a kind of adaptation mechanism of the body, the main purpose of which is to distinguish inflamed areas from healthy ones.
The tendency to develop pathology and the level of its manifestation are individual and depend on many reasons, for example, heredity. The main prerequisites for the appearance of adhesions, established by medicine at the present time, are excessive activity of the connective tissue membrane and a decrease in the body’s immune forces.
Risk factors for the disease also include:
Most cases of adhesions occur under the combined influence of negative factors.