What are HPV types 16 and 18
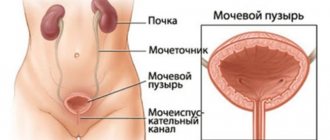
Papillomavirus 16 and 18 increases the risk of malignant tumors in women. Such as dysplasia, cancer of the genital organs, vagina and cervix. Pathology is detected during gynecological screening.
Papillomavirus types 16 and 18 do not yet indicate a cancerous tumor, but increase the risk of its occurrence. The infectious process affects the mucous membranes and deep layers of the epithelium of the genital organs and the cervical canal. As a rule, the pathogen begins to develop in the body of women of reproductive age.
It is quite difficult to say how HPV 16 and 18 differ from other types in women. Externally, they are very similar to other papillomas. The difference exists in the genetic information of the DNA of HPV types 16 and 18.
There are 2 possible outcomes of the disease. Representatives of the fair sex either recover or die. It all depends on the body’s defenses, the stage of the disease at which effective therapy was started. Thus, if we talk about what HPV (papilloma) types 16 and 18 are, it is a pathogen that increases the risk of developing malignant tumors, usually leading to death.
What is HPV?
Papillomovirus is a collection of many infectious strains that have varying effects on human health. Today, more than 100 types of virus of varying degrees of danger are known. Thus, some of them contribute to the appearance of condylomas and papillomas on the body, others provoke the occurrence of malignant neoplasms. Type 18 of the virus is the latter; its effect is especially dangerous for women. Even among highly oncogenic strains, it, along with type 16, is considered the most aggressive.
Probability of infection
According to statistics, papillomavirus 16 causes cancer more often than type 18. The risk of developing cervical cancer when infected with the first type is 50%, with the second - 10%.
Moreover, in men, infection rarely provokes cancer. 90-95% of them are only carriers of pathogenic DNA HPV 16 and 18.
HPV types 16 and 18 may have the following routes of infection in women:
HPV type 16 in women is transmitted sexually
- sexually;
- vertical route of infection (in pregnant women, from mother to child during childbirth);
- through household items (especially personal hygiene products).
Reasons that can cause infection:
- frequent change of sexual partner;
- intimate intimacy without protection;
- from 5 or more sexual partners;
- entering into intimate relationships at an early age (before 16 years).
Factors that increase the risk of infection:
- abortion;
- inflammation in the vagina and uterus;
- STI;
- vaginal dysbiosis;
- gynecological pathologies of a chronic nature.
Experts have noticed that usually females with this pathology have concomitant diseases . Such as chlamydia, ureaplasmosis and others.
HPV type 18: features and differences from other strains
According to the principle of influence on the body, different HPV strains are no different. The HPV type 18 virus invades human DNA and changes it in such a way that growths, mostly of a benign nature, begin to appear on the skin.
In most cases, papillomas are harmless and, if detected and removed in a timely manner, do not cause harm to health. A strong immune system can heal, but it takes time, sometimes years. You can help your body get rid of the dangerous virus by taking immunostimulants and antiviral drugs.
The peculiarity of this strain of the virus is that HPV type 18 in men rarely makes itself felt. The disease in men may not manifest itself in any way, but the carrier remains potentially dangerous to his sexual partner.
The danger of the HPV type 18 virus in women is cervical cancer. According to statistics, in more than 76% of cases of this type of oncology, the cause is the 18th type of human papillomavirus.
Stages of the disease
Papillomavirus in women 16 and 18 has four stages of development:
- Initial (incubation). It is asymptomatic. The exact duration of this stage cannot be determined. It all depends on the type of infection, the individual characteristics of the patient’s body, and the nature of the pathology. The pathogenic microorganism is latent, since it does not change the structure of cells, but is already amenable to diagnostic examinations.
- Second phase. Characteristic formations appear on the skin. During this period, the active development of pathogenic microorganisms occurs.
- Dysplasia. There is a combination of microorganisms that cause pathology and the DNA of human cells. This is a precancerous condition.
- Fourth stage (malignant). This is the final stage of development. During this period, cancerous tumors are already diagnosed.
The earlier the disease is detected, the easier it will be to cure it. Therefore, it is recommended to periodically get tested for the presence of pathogen varieties. Especially those who are predisposed to it.
Routes of transmission of the virus
All types of HPV, including type 18, are introduced into the carrier’s DNA upon contact with an infected person. Routes of transmission of the virus:
- urogenital;
- from mother to child;
- domestic.
The easiest way to become infected with HPV is through unprotected sex. Women are more susceptible to infection than men, which is due to the large area of the mucous membrane that comes into contact with a potential carrier of the virus during unprotected sexual intercourse.
In this case, a man can act as a carrier of infection without knowing it. This is due to the fact that in men the virus rarely manifests activity, provoking the formation of condylomas and papillomas on the genitals.
Infection of a child during passage through the birth canal occurs only if the woman has an active virus. Such cases are rare, but every woman should be tested for HPV before planning a pregnancy.
The virus can be transmitted through household contact only in cases of severely reduced immunity. This is due to the fact that HPV is concentrated in saliva, blood and genital secretions. Thus, if you are immunodeficient, you can become infected by using someone else's towels or cups.
Speaking about the sexual transmission of the virus, it should be borne in mind that it is concentrated in fluids produced by the human body. This creates a risk of infection through oral sex or even through a kiss, since HPV can be detected in saliva in high concentrations.
The virus is transmitted through contact of mucous membranes
Symptoms
Manifestations of a pathological condition in a person can be different. It all depends on the strain. As a rule, in humans, when the papilloma virus begins to develop in the body, warts appear in the external and internal genital organs. During intimacy, bleeding is observed. All this is accompanied by the following signs:
Symptoms of HPV type 16 in women may include burning and itching during sex
- burning and itching in intimate places;
- disruption of urine output;
- pain during intimacy.
However, these symptoms may indicate the presence of many diseases (cystitis, urethritis, etc.). Without special tests, the disease cannot be distinguished from other pathologies of the genitourinary system. Only after a complete diagnosis can a doctor make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe the necessary treatment.
What to do after treatment?
After the therapy, a woman should understand that now she will have to especially carefully monitor her health. This involves the need to undergo regular examinations with a gynecologist every six months to monitor possible changes. In addition, it is necessary to retake HPV tests once a year to monitor viral activity. Such measures can prevent the reactivation of strain 18 and keep its number under control.
However, it is important to remember that a person can be sick with several types of the virus at the same time. Successfully getting rid of one does not guarantee complete protection against other strains. The only barrier on their way is a strong immune system that can suppress activity at an early stage.
To avoid infection with other types of virus, you should use only personal hygiene products and use condoms during sexual intercourse. After all, prevention is always easier and cheaper than treating the consequences of the disease.
https://youtu.be/eedhuihKHKc
Diagnostics
If you suspect papillomavirus types 16 and 18, you should consult a gynecologist for diagnostic tests. First of all, the doctor collects an anamnesis of the disease (how long ago the symptoms appeared, what pathologies close relatives suffer from, etc.). After this, an examination is carried out on a gynecological chair (external manifestations are examined). Using special mirrors, the cervix and vagina are examined. In addition, biomaterial is collected for analysis.
Screening is performed to detect infected cells. This analysis of HPV 16 and 18 allows you to detect pathological changes even without external signs. After this, PCR is prescribed - this is an analysis to detect the DNA of an oncological virus. The purpose of the polymerase chain reaction is not only to identify the pathogen, but also to typify the infection. It is important to know how the analysis is taken. It is collected using a smear from the cervix. 2 hours after your last trip to the toilet. A negative indicator means that no pathogenic microorganisms were detected. Positive that you may be infected.
Quantitative reference values may be shown erroneously. Additionally, the following diagnostic examinations may be prescribed:
- colposcopy (examination of the cervix);
- special tests with ethanoic acid, Lugol's solution;
- digene test (test rate is below 100 thousand pathogen copies/1 ml of material).
If the presence of a pathogen is detected, the woman is prescribed an additional examination to identify concomitant diseases that are sexually transmitted.
Modern diagnostic methods
The presence of skin growths or formations on the genitals should suggest the possibility of infection with HPV type 16. What to do in such cases? Of course, you need to go to the doctor. What diagnostic methods are used in modern medicine? There are several basic procedures that will help determine the presence of the papilloma virus.
- A basic examination, during which the doctor examines skin tumors, collects anamnesis, etc.
- Colposcopy is prescribed to women for a more thorough examination of the cervix for the presence of viral lesions.
- Cytological studies, which consist of laboratory examination of tissue taken during scraping (for example, from the cervical canal). This test helps determine the presence of abnormal cells.
- PCR diagnostics are quite accurate, which makes it possible to detect the genetic material of the papilloma virus in almost any material, including scrapings from mucous membranes, tissue of warts and condylomas.
Treatment
Treatment of papilloma viruses (HPV types 16 and 18) must be carried out. Even if there are no clear symptoms of the pathological condition. If you do not start the necessary therapy, the risk of cancer increases significantly. Therapeutic measures are aimed not only at eliminating external signs, but also at suppressing the activity of the pathogen.
Complex therapy is used to treat human papillomavirus. If a pathogen is detected, the following techniques are used:
Complex therapy is used to treat human papillomavirus
- Medication. Local and general medications are prescribed. The specialist determines what to treat based on the degree, progression of development and individual characteristics of the woman. The list of drugs for HPV is extensive.
- Invasive. The method is based on surgical removal of growths.
- Folk. These methods can be used only after the recommendation of a doctor. He will tell you what you can do and what not, based on your individual characteristics.
Patients often worry whether human papillomavirus types 18 and 16 can be cured. It is completely impossible to get rid of the disease. But if therapy is started on time and the treatment regimen is correctly selected by a specialist, then the pathology will not provoke the development of oncology.
Classification
There are 2 clinical forms of HPV infection:
- 1Anogenital form: skin papillomas, condylomas form on the skin and mucous membranes of the genital organs, perineum, anus and perianal area.
- 2Non-genital form: damage to the skin of the head, neck, torso, limbs, palms and soles.
Table 1 - Types of HPV that lead to damage to the skin and mucous membranes.
Table 2 - Types of HPV leading to damage to the genitals and perianal area
Along the flow they distinguish:
- 1Asymptomatic infection (the presence of infection is confirmed only by PCR and DNA hybridization methods). In most cases, the infection occurs latently and is not accompanied by any symptoms: no complaints, no skin manifestations. However, the patient is contagious to his sexual partner.
- 2Subclinical (damage to the epithelium is determined only after treatment with a solution of 3-5% acetic acid and microscopy).
- 3Clinically pronounced infection (various skin neoplasms - papillomas - can be detected with the naked eye).
Sexually transmitted HPVs are divided into 2 categories:
- 1 Strains of low oncogenic risk - viruses of this group do not cause cancerous transformation of the epithelium, but only lead to the appearance of condylomas and papillomas.
- 2High oncogenic risk strains can lead to the development of cancerous tumors. There are approximately 12 strains, most often detected in cancer (including 31, 35, 33, etc.). 2 of them (types 16 and 18) are responsible for the majority of cancers caused by HPV.
Consequences of deletion
Surgery is usually prescribed for grade 2 and 3 dysplasia. At stage 1, conservative methods are used. In women with stage 2 HPV, treatment is also carried out with medications. If therapy does not bring any results, surgery is prescribed. The following methods of mechanical removal of growths can be performed:
- cryodestruction;
- radio wave therapy;
- diathermocoagulation.
Patients are very worried and ask the doctor what danger lies behind surgery. At stage 2 of dysplasia development, 2/3 of the epithelium is affected. The operation will not cause loss of reproductive function. At stage 3 of pathology development, most of the cells are affected. In this case, the reproductive organ may be completely removed. As a result, the woman will not be able to get pregnant.
Treatment methods for papillomavirus type 16
Important! Treatment for HPV type 16 involves a combination approach that includes eliminating the virus, strengthening the immune system, and surgical removal of growths.
General therapy
The first stage in the treatment of HPV is aimed at destroying the virus. For this purpose, medicinal antiviral drugs are used - Cycloferon, Amiksin, Interferon (and other variations), Inosiplex. These medications not only effectively fight the multiplication of the virus, but also help strengthen the body’s protective function.
To treat cells that have been damaged by the HPV 16 virus, specialists prescribe the following drugs:
- Kondilin;
- Podophyllin.
The effectiveness of these drugs is due to the cauterizing effect on condylomas. The active substance causes necrosis of affected tissues and relieves the inflammatory process.
Hardware treatment
When removing genital warts, hardware techniques . These include the following procedures:
- electrocoagulation or cauterization of formations with electric current;
- laser removal;
- radio wave removal;
- cryodestruction.
Surgical intervention
Due to the increased traumatic nature of this method, surgical removal of condyloma is extremely rare. The only indication for surgery is the proliferation of cancer cells , which must be immediately removed from the body.
Is treatment possible with folk remedies?
Traditional medicine recipes can be used in the treatment of HPV type 16 only when combined with drug therapy.
Note! Self-medication can backfire and only make the situation worse. Under no circumstances should folk remedies be used to treat oncogenic papilloma without consulting an oncologist.
Celandine juice has cauterizing and disinfecting activity. To heal the wound surface after cauterization, you can use Kalanchoe or aloe juice.
In addition to the direct impact on the growth, it is necessary to strengthen the immune system. To do this, it is recommended to inhale essential oils of lemon, tea tree, cedar and eucalyptus.
Prevention of HPV 16 infection in women
Note! The most effective way to protect the body from HPV type 16 is vaccination with drugs such as Gardasil and Cervarix.
In addition to this method, you can reduce the risk of infection by following these rules:
- visit a gynecologist at least once every 6 months;
- use condoms during sexual intercourse;
- limit promiscuous sexual intercourse;
- treatment of chronic diseases;
- maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
https://youtu.be/VJ7Efq5j2Rg
How to live with this virus
Many patients who have been diagnosed with a pathogenic microorganism do not know how to live with it further, because it is not completely curable. Don't despair and give up. Despite the fact that papilloma 16 and 18 is a terrible disease that can lead to dire consequences, it is still possible to avoid cancer with adequate treatment.
After treatment has been carried out and pathogenic microorganisms have been suppressed, the following recommendations must be followed to prevent the risk of relapse:
- Eat rationally. Consume foods that contain beneficial elements. To strengthen the immune system, take vitamin complexes.
- To increase the protective functions of the body, do morning exercises and hardening procedures.
- Treat all diseases in a timely manner. Do not let them become chronic.
- Regularly attend antenatal clinics.
- Lead a measured intimate life. Select sexual partners carefully. Use contraception.
Although there is no way to cure the pathology completely, malignant neoplasms form only under certain circumstances. If you follow all the recommendations listed above, you will be able to reduce the risk of cancer to a minimum.
If you have not been infected but are concerned that you will, you are advised to routinely get vaccinated against the pathogen. Follow all the recommendations described earlier. All diseases in the human body develop due to weakened defenses of the body. Strengthen your immune system, watch your lifestyle, and then you won’t be afraid of any infection.
HPV 16: treatment
After making a diagnosis, the doctor will draw up a treatment regimen. Under no circumstances should you try to cope with the problem on your own, especially if we are talking about HPV 16. Treatment is extremely important and can only be entrusted to an experienced specialist.
This infection is quite difficult to treat. However, it is possible to reduce the risk of developing cancer. So what does the treatment process look like after being diagnosed with HPV 16? Treatment includes several important points - strengthening the immune defense, reducing the activity of the virus and removing existing growths.
So, patients with a similar diagnosis are primarily prescribed antiviral drugs. Inosiplex is considered to be quite effective, as it suppresses the proliferation of viral particles. Interferons, in turn, have antiviral, immunostimulating and antitumor properties. Patients are often prescribed drugs such as Amiksin and Cycloferon, which activate the body’s production of its own interferons. Also, the treatment cycle may include drugs that suppress the division of cells already affected by HPV. Podophyllin and Condilin are considered effective.
Treatment of HPV 16 in women also includes regular gynecological examinations and repeated tests until the activity of the virus is suppressed. Naturally, sick people are advised to have proper nutrition, sleep and rest patterns, and physical activity, since all this strengthens the immune system and, accordingly, accelerates the healing process.
What to do if you have been diagnosed with HPV 16? How to live further? With proper therapy, the risk of developing cancer is minimal. And if you undergo regular examinations, cancer can be diagnosed at an early stage, which gives a good chance of a favorable outcome. By the way, carriers of the virus should not have unprotected sex - using a condom is mandatory.