When is cauterization recommended?
Most tumors that appear on the cervix are successfully cured in the initial stages, but the main factor in such cases is to diagnose a cervical cyst in time. Unfortunately, at the beginning of its development the cyst does not show any symptoms, and often it can be diagnosed in the later stages.
The main reason why cauterization is prescribed is the presence of the tumor itself, as well as a number of consequences that negatively affect the reproductive system and the health of women in general.
It is recommended to cauterize the cyst in the following cases:
- In the presence of bacterial damage to the uterine tissue. In such cases, a white and yellow coating can be observed around the tumor, which indicates tissue damage by pathogenic bacteria. Bacteria are formed due to improperly performed surgery on the uterus or lack of proper care in the postoperative period.
- With intense bleeding. Excessive discharge of bloody fluid, similar to menstruation, is direct evidence that the tumor needs to be treated or removed. This is caused by the fact that the cyst reaches an impressive size and begins to put pressure on the tissue of the uterus, exerting a pathogenic effect on the uterus and preventing it from functioning normally.
- Sharp pain in the lower abdomen. It is also recommended to remove a cervical cyst in cases where a woman experiences causeless acute pain in the lower abdomen. As a rule, these pains have nothing to do with the menstrual period, and have an extremely negative effect on the reproductive system due to frequent uterine spasms.
- Pain is felt during sexual intercourse. If acute pain is felt during sexual intercourse, it is recommended to remove the cyst, or, as a last resort, undergo intensive treatment.
- The appearance of pain when urinating. If a woman experiences pain when urinating, this may indicate that the cyst has caused inflammation in the tissues of the cervix.
Preparation before intervention
The main task of treatment is to restore the patency of the gland ducts and remove the accumulated contents. It is equally important to prevent recurrence and the development of complications. Immediately before the operation of cauterization of cysts on the cervix, you should undergo a number of examinations:
- general blood and urine analysis,
- genital smear, including cytological,
- culture tank with antibiogram,
- RW analysis (syphilis), HIV,
- extended colposcopy,
- Ultrasound.
Research will help determine the presence or absence of inflammation of the genitourinary system. Smears include a mandatory examination of the vagina, urethra, and cervical canal of the neck. If an infection is detected, surgery is contraindicated. First, the patient is prescribed a course of treatment, after which an intervention is performed. To accurately determine the correctness of the drug prescription, a tank culture is carried out with a sensitivity test to antibiotics.
Colposcopic examination is carried out to determine the location of cysts and their number. Additionally, the presence of other changes in the cervix is checked. If necessary, a targeted biopsy is performed if atypical formations are suspected.
In the absence of an infectious process, after obtaining a cytological examination and biopsy, the cyst is cauterized. Preference is given to the first half of the menstrual cycle.
It is necessary to remove the cyst by cauterization
If a cervical tumor is diagnosed in late stages, then drug treatment in such cases is ineffective. At best, it can slightly reduce the size of the cystic formation and eliminate some symptoms. Doctors prescribe immediate cauterization of a cervical cyst in the following cases:
- If there is a large amount of fluid in the tumor. An excessive amount of pus accumulates in the cyst, which provokes the appearance of pathogenic bacteria and can cause bleeding.
- The cyst is abnormal. If obvious pathological deviations are observed during the development of the cyst, then it must be cauterized immediately.
- Large tumor sizes. If during an ultrasound it is impossible to examine the size of the cyst and assess the condition it is in, then such a neoplasm is removed.
- Rapid tumor growth. In cases where the cyst has grown to unacceptable sizes over a certain period of time and continues to grow, it also needs immediate cauterization.
Types of cyst cauterization
Cauterization of the cyst is done in several ways. Depending on the severity of the woman’s cyst, the most appropriate method is chosen. The most common and effective types of cauterization are:
- Cauterization with electric current. This method of cauterization of the cervix is one of the oldest, and its essence is contact cauterization of the tumor with an electric current. Recently, cauterization in this way has lost popularity, as it has a number of postoperative consequences.
- Cauterization using a microarc. Unlike electrical contact cauterization, this method does not come into contact with the affected tissue. The cyst is removed using low voltage electric current. This method completely removes cystic formation from the cervix and does not cause relapse of the disease.
- Chemical cauterization. The procedure is carried out exclusively with the use of painkillers. Special dilators provide access to the uterus, after which it is dried with a sterile swab. Next, a tampon soaked in the Solkovagin preparation is applied to the cyst. This tampon must lie on the cyst for some time, after which it is removed. After the procedure, the affected area is lubricated with a special solution.
- Laser cauterization. The laser cauterization procedure is painful, but very effective. During the procedure, a special laser is used, which is directed at the cyst and, thanks to high temperatures, cauterizes the cyst, preventing bleeding and postoperative inflammation. After surgery, small scars remain on the cervix, which completely resolve over the course of several months. This method is recommended for those women who have not yet given birth.
- Cauterization by radio waves. During cauterization using this method, a special radio wave knife is used to cut off the cyst and cauterize the place to which it was attached. This procedure is the most gentle, which does not have a negative effect even on pregnant women.
- Cryotherapy. During cryotherapy, the cyst is cauterized with liquid nitrogen. The good thing about this method is that it completely cauterizes and freezes the postoperative wound, preventing relapse. A relatively new and very effective cauterization method. The main disadvantage of this procedure is the large scars that remain on the cervix. In some cases, it is impossible to get pregnant after such a procedure.
Conization for cervical diseases
Conization of the cervix is the excision of a part of the organ in the shape of a cone. Retention and endometrioid cysts are rarely an indication for such surgery. Conization is prescribed when cysts are combined with other cervical pathology:
- Dysplasia II and III degrees,
- Erosion of the cervix, in which it is impossible to clearly identify the transformation zone and carry out targeted cauterization of tissues,
- Cicatricial deformity of the cervix.
Conization of the cervix in the treatment of cysts is used in exceptional cases, namely, when combined with other serious pathologies.
Surgical treatment options:
- Knife excision. The surgeon excises part of the cervix with a scalpel. This is the simplest, most accessible and at the same time dangerous method of treatment. Conization with a scalpel leads to profuse bleeding. After surgery there is a high risk of complications,
- Loop electroconization (LEEP, LLETZ). Performed using an electric knife. The loop grabs a section of the cervix and excises it, the vessels are cauterized with electric current. This simple and cheap method has its drawbacks and is not used in nulliparous women. After loop electroexcision, there is a high probability of cicatricial deformation of the cervix and postoperative bleeding,
- Laser conization. Excision of the cervix is performed with a laser scalpel. If the lesion is deep, several approaches are required. Healing of the cervix after laser exposure occurs without scars,
- Radio wave conization. It is carried out using the Surgitron or Fotek apparatus. The negative impact of heat on fabrics is minimal. Scars are not formed after the procedure. Recommended for nulliparous women.
On a note
Laparoscopy, laparotomy and other interventions that involve opening the abdominal wall are not performed for cervical cysts.
The cost of conization of the cervix using radiosurgical method is 30-40 thousand rubles. Prices for other treatment options are slightly lower. In public medical institutions, under the compulsory medical insurance policy, if indicated, the operation is performed free of charge for the patient.
Conization is a painful procedure. It is performed under anesthesia. The woman falls asleep and does not experience pain.
Since conization of the cervix is a painful procedure, it is done under anesthesia.
In such conditions, the doctor can safely perform the operation without fear of complications due to the patient’s reaction. The procedure can be performed in a hospital for one day. If the woman feels well, she goes home the same day.
Consequences of cauterization of a cervical cyst
Cauterization is an effective method of getting rid of a cyst, which is in many ways better than surgical intervention. But even this method has a number of disadvantages:
- high risk of bleeding;
- postoperative scars;
- reduction in the diameter of the cervix;
- possible complications in future pregnancies.
More and more often, cauterization is being used in public medical institutions, which makes this procedure even more accessible. After cauterization, a woman may feel a dull pain in the abdominal area, her temperature may rise and discharge of different colors and consistency may appear. In addition, after the operation, the woman should be in a state of complete rest for 2-3 days. If at the end of the period the patient does not experience any complications, she is discharged from the hospital. Recovery after burning can be done both in the clinic and at home.
Radiosurgical removal of cysts, papillomas, neoplasms
| Gynecology (from the Greek “gyneko” - woman and “logos” - study) is a branch of medicine that studies diseases characteristic only of the woman’s body. The most important area of study in gynecology is diseases of the female reproductive system. Gynecology is closely related to obstetrics, but it was and remains a separate science, since a woman’s sexual function affects the state of the body not only during pregnancy, but throughout a woman’s life. |
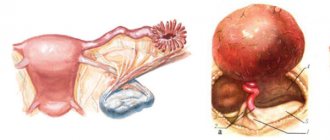
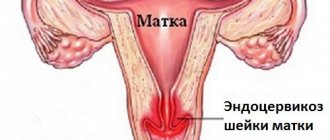
Uterine cyst, cervical cyst (Nabothian cyst, retention cyst of the cervix) are closed and dilated glands in the cervix with secretions accumulated in them.
Due to the inflammatory process in the vaginal part of the cervix (cervicitis) and in the cervical canal (endocervicitis), inflammation and blockage of the excretory ducts of the mucus-producing glands of the cervix occur. The gland filled with mucus increases in volume and is detected during examination, colposcopy and ultrasound examination of the pelvis. Thus, the cause of uterine cysts, cervical cysts (Nabothian cysts, cervical retention cysts) is an inflammatory process on the cervix and in the cervical canal due to trauma and infection during abortion, childbirth, instrumental examinations (hysteroscopy, diagnostic curettage). In a cervical cyst, in some cases, bacteria persist / persist /, multiply and accumulate (infection), which are the source of recurrent / regularly recurring / inflammatory processes of the cervix / cervicitis, endocervicitis/, vagina / colpitis/, uterine mucosa / endometritis/, uterine tubes and ovaries /salpingitis, salpingoophoritis, oophoritis/. It is the inflammatory process that can be one of the causes of ectopic pregnancy and infertility. In the presence of large (1.0 cm or more) cervical cysts, narrowing (compression) of the cervical canal is possible, which is a mechanical factor of infertility. However, uterine cysts, cervical cysts (Nabothian cysts, cervical retention cysts) are not the main or only cause of infertility. The presence of a cervical cyst does not interfere with pregnancy and childbirth. If a cervical cyst is detected during pregnancy, treatment (opening and drainage of the cervical cyst) is preferably carried out after the complete cessation of lochia. As a rule, lochia (sacral discharge from the genital tract) stops by the 40th day after birth. The presence of a single cyst or multiple cysts of the cervix is not a contraindication for the insertion of an IUD /intrauterine device, “spiral”/. Thus, uterine cysts, cervical cysts (Nabothian cysts, cervical retention cysts) deserve attention and treatment.
Symptoms
There are no symptoms of a uterine cyst or a cervical cyst (Nabothian cyst, retention cyst of the cervix).
Examination for uterine cysts, cervical cysts (nabothian cysts, cervical retention cysts)
The examination is carried out in order to detect infection in the vagina, cervix and cervical canal and prevent relapse (recurrence) of uterine cysts, cervical cysts. The examination includes a bacterioscopic examination of a smear from the vagina, cervix and cervical canal for flora, PCR examination of smears for chlamydia, ureaplasma, mycoplasma, trichomonas, gardnerella.
Treatment of uterine cysts, cervical cysts (Nabothian cysts, cervical retention cysts)
Visually accessible (visible) uterine cysts are subject to painless radio wave treatment, and inaccessible ones, located deep in the cervical canal, are observed 2 times a year.
Opening and drainage of cervical cysts, uterine cysts (Nabothian cysts, cervical retention cysts) is performed on any day except the days of menstruation and 3 days before it. This limitation is explained by the reduction in the risk /prevention/ of cervical endometriosis.
If there are clean vaginal smears for flora and there are no hidden infections in the cervical canal, no additional special preparation is required.
If smears reveal an increased number of leukocytes, candida / yeast /, gardnerella, leptothrix, chlamydia, ureaplasma, mycoplasma, preliminary treatment is required. Treatment is outpatient (hospitalization is not required).
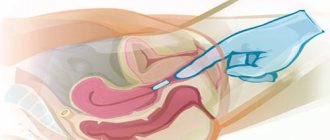
Treatment of uterine cysts, cervical cysts (Nabothian cysts, retention cysts of the cervix) is carried out under aseptic / germ-free / conditions, once and painlessly using the radio wave method (Fotek device). The procedure takes 1-2 seconds, no anesthesia is required. The principle of treatment is non-contact vaporization / evaporation / of the finest passage, reminiscent of the excretory duct of the gland, with ultra-high sound vibrations / radio waves / - so the person does not feel them. Next, vacuum drainage is performed, after which the uterine cyst (cervical cyst) is emptied and collapses, the walls of the cyst stick together and then, as a rule, the cyst does not fill again. The contents of old uterine cysts, cervical cysts (nabothian cysts, cervical retention cysts) are a viscous jelly-like mass.
The technique is approved by the Ministry of Health for use even by nulliparous women, because it does not cause burns or scars that prevent the cervix from opening during childbirth, and is classified as a gentle method of surgical treatment. Healing of the cervix after radio wave opening and drainage of cysts occurs within 3 days. After radio wave treatment of cervical cysts for 1-3 days, in some cases, scanty yellow discharge from the vagina may be observed. For recurrent /newly emerging uterine cysts, cervical cysts (Nabothian cysts, retention cysts of the cervix), a combination of homeopathic medicines, herbal medicine in the form of rectal and vaginal suppositories / suppositories / with painless physiotherapeutic procedures is used: vacuum sanitation of the cervical canal and vaginal thermal irrigation solutions sanitizing substances (more about physiotherapy).
The course of treatment is usually 7 days. The effectiveness of a single course of treatment is high. The persistence of the effect depends on the presence and treatment of concomitant sluggish endocervicitis. Prevention of the formation of cervical cysts is timely diagnosis and treatment of colpitis, endocervicitis and other inflammatory diseases of the genitals. There are no restrictions and features of nutrition, sexual intercourse, physical activity for uterine cysts, cervical cysts (nabothian cysts, retention cysts of the cervix). Visiting the solarium, swimming in the pool, river reservoirs and the sea are not contraindicated.
Recommendations after cauterization
Cauterization is an operation that can be compared to surgery. As with conventional operations, a number of complications can occur after cauterization, and to prevent this, you should follow some recommendations.
- Refusal of sexual activity. During sexual intercourse there is a risk of damage to the postoperative wound. In addition, pathogenic bacteria and microorganisms can enter the wound, which can cause serious inflammation. It is recommended to abstain from sexual activity for 2 months. This factor is very important and should absolutely not be violated.
- Personal hygiene items. After the cauterization procedure, tampons should not be used. A tampon can cause damage to the wound, thereby causing inflammation. In addition, the accumulation of fluid in the vagina has an extremely negative effect on the rate of wound healing. The best choice in such a situation would be to use gaskets.
- Vaginal suppositories. Just like tampons, vaginal suppositories can break the scab and cause infection and inflammation. Suppositories after cauterization of a cervical cyst can be used only after the scab has been rejected by the tissue on its own.
- Physical labor. Heavy physical activity negatively affects the weakened reproductive system and can cause a dry crust to separate from the wound, causing complications. It is strictly forbidden to perform physical activity for 30 days after surgery.
- Visiting the sauna and bathhouse. High temperatures warm the body, speeding up bleeding and increasing blood pressure. High pressure in the uterine vessels can cause the scab to pull away from the wound, causing severe bleeding and infection.
- Swimming pools and lakes. When immersed in water, water may enter the vagina, which can result in infection of the wound. In addition, water can wash away the crust on the wound, causing bleeding.
- Exposure to high temperatures. With prolonged exposure to the sun, blood pressure rises, and the chance of the scab coming off the wound is extremely high. Therefore, after cauterization, it is strictly forbidden to sunbathe or take a solarium.
The following restrictions apply:
- significant spread of dysplasia on the tissues of the cervix;
- suspicion of tumor degeneration of the cyst;
- the presence of polyps in the cervical canal;
- concomitant inflammatory lesions of the reproductive system.
The procedure must be carried out in the first week after menstruation. In the absence of concomitant pathology, the patient does not need hospitalization. After surgery, after some time the woman can go home.
Before re-examination by a doctor, it is important to adhere to the following rules:
- maintain hygiene;
- refuse to take baths, visit the bathhouse, sauna, swimming pool;
- Avoid training and heavy physical activity.
Laser removal can be called the most promising method in gynecology in the treatment of cystic formations, taking into account the advantages of the procedure - high accuracy, painlessness, and rapid recovery of the body. The main task of the doctor is to conduct a high-quality diagnosis of the condition in order to perform surgical intervention with the least risk for the patient.