Combination with other symptoms
Cystitis pain occurs in the lower abdomen, side, lower back and urethra. An acute burning sensation occurs when urinating, when the bladder mucosa is irritated. Itching in the intimate area in women is an indicator of the presence of infection in the body, which often leads to the development of dysbiosis.
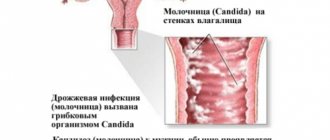
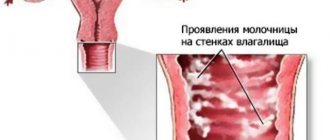
If itching and burning appear in the intimate area not only during urination, then we can talk about the development of some kind of inflammatory pathology. This could be a fungal infection in the vagina (thrush) or vaginitis.
In men, pain from cystitis is localized in the lower abdomen, groin, suprapubic region and urethra. With the urge to urinate, it intensifies. A burning sensation in the urethra occurs due to the accumulation of bacteria in the bladder, which damages its mucous membrane.
In combination with itching and burning, other symptoms indicate cystitis:
- decrease in the volume of urine excreted;
- lower abdominal pain,
- groin;
- frequent urge to urinate;
- no relief after urination;
- the appearance of mucus, pus and blood in the urine.
You may feel unwell, accompanied by weakness, headache, and fever.
Prevention
Relapses and spread of candidiasis in general (no matter where) are a sign of immunodeficiency - temporary and local or general. To avoid them, you should not allow it to decrease - due to frequent colds, physical and emotional stress, exposure to several harmful factors at the same time (city smog, smoking, alcohol abuse, inactivity, excessive or insufficient hygiene, tight synthetic underwear).
The condition of the urinary tract is well affected by not having the habit of tolerating the urge, wearing warm high-waisted trousers or long jackets in winter, and drinking a sufficient amount of fluid (1.5-2 liters, but you should drink more only in hot weather).
Cystitis and thrush are two diseases that almost always occur side by side.
Of course, these diseases are more common in the fair half of humanity, and this is due to the physiological characteristics of the structure of the body.
So what to do if thrush and cystitis occur at the same time? What measures should be taken for a speedy recovery without complications and the disease becoming chronic?
Read more Causes of intrauterine fetal death in late stages
How to properly treat thrush (candidiasis) in men
Candidiasis can occur for completely different reasons, namely: pregnancy or lactation, allergic reactions, serious illness. One of the common reasons for the development of this disease is long-term use of antibiotics, which can disrupt the vaginal microflora and promote the development of Candida fungi.
Yeast-like fungi Candida are found in moderate quantities in any healthy body. They can be found in the mouth, intestines and vagina. However, under the influence of certain factors, fungi begin to multiply and sharply increase in number.
- 1 How to deal with thrush
- 2 Treatment and prevention
- 3 Prevention
In addition to treatment with medications prescribed by a gynecologist, certain recommendations must be followed for a quick recovery. Review your diet and follow a diet. It is strictly forbidden to consume: alcohol, sweets, baked goods and fresh baked goods, salty and spicy foods, yeast dough.
During treatment, avoid douching. It is better to give preference to the use of vaginal gels and ointments. In this way, the natural microflora of the vagina can be restored. You can use an antifungal drug such as Ginocomfort, as well as products based on Miconazole, Nystatin, Nitacymin.
If you notice the first signs of the disease, contact your gynecologist. Do not self-medicate, because without examination you can confuse thrush with other infections.
To treat candidiasis, medications such as:
- Lactagel;
- Livarol;
- Clotrimazole;
- Ginesol;
- Pimafucin;
- Oronazole;
- Econazole
If the symptoms are pronounced, the gynecologist prescribes drugs for oral use, as they are absorbed into the blood and quickly distributed to the necessary parts of the body. The most effective medications are:
- Forkan;
- Mikosist;
- Diflucan;
- Medoflucon.
It is also possible to use alternative medications made on the basis of Itraconazole. These include Orungal.
Prevention
To prevent candidiasis when taking antibiotics, you must follow simple rules:
- Therapeutic diet.
- Maintaining hygiene.
- Boosting immunity with vitamins.
- Dairy products.
- Healthy lifestyle, moderate physical activity.
Thrush after a course of antibiotics is a fairly common occurrence. Therefore, it is also recommended to take special medications that help preserve the intestinal and vaginal microflora when taking strong drugs.
Optimal therapy for a combination of cystitis and candidiasis
Of course, it is not difficult to cure this kind of disease; it is more difficult to prevent a relapse or the disease becoming chronic.
This is especially important when two diseases occur simultaneously, because if you ignore the symptoms, you can waste time.
Therefore, complex treatment of cystitis and thrush should be thoughtful and balanced.
Basic rules for treating cystitis
- Since thrush is fungal in nature, broad-spectrum antibiotics for the treatment of cystitis are completely excluded. Antibiotics of this type can aggravate the picture of candidiasis.
- Instead of broad-spectrum antibiotics (penicillin, ceftriaxone, amoxicillin and others), drugs with the active substance of the nitrofuran series are prescribed. This could be Furamag, Furadonin, Furagin, Furasol and other medicines with a similar composition.
- Narrow-spectrum antibiotics are also suitable for the treatment of cystitis complicated by thrush. This could be Nitroxoline (5-nok), Monural, Nolitsin (Normax).
- To treat cystitis in combination with thrush, antibacterial drugs are prescribed - Palin, Nevigramon, Rulid.
- For the treatment of cystitis, diuretics and anti-inflammatory drugs of plant origin are prescribed - Phytolysin paste, Cyston tablets, Canephron tablets and drops, kidney herbal preparations.
All of the above drugs do not affect the development of thrush and do not provoke abnormal growth of the fungus. The medications are taken according to the instructions and in doses recommended by the doctor. Typically, treatment of acute cystitis takes up to two weeks; chronic cystitis is treated in alternating courses.
The fact that cystitis is a common disease in women does not give reason to take this disease lightly, because the inflammatory process can lead to unpleasant consequences. Consequences of cystitis in women: who is at risk? Find out all about possible complications.
Read about the causes of burning after urination in women and men here.
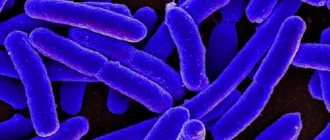
Cystitis can be caused by a variety of pathogenic microorganisms, and before starting treatment, the doctor must find out which microbe or bacterium caused the inflammatory process. Here https://mkb2.ru/tsistit-i-mochevoy-puzyir/kakie-infekcii-vyzyvayut-cistit.html you will learn what infections cause cystitis and how infection occurs.
Medicines for thrush
Thrush can be treated by taking oral tablets and capsules, or by topical application of suppositories and ointments.
Irrigation and douching also have a significant effect. The drug, method of administration and course of treatment are prescribed only by a specialist.
Typically, the course of antifungal therapy lasts up to ten days. An exception may be taking medications containing fluconazole, since the drug can cope with ordinary thrush in 2-3 days.
The following medications are suitable for the treatment of thrush:
- Fluconazole, Difluzol, Mycomax, Diflucan and similar antifungal drugs.
- Narrow-spectrum antibiotics: Nystatin, Nitamycin (Pimafucin, Primafungin).
- Antifungal drugs: Clotrimazole (Canesten, Candide), Ketoconazole (Ketodine, Livarol), Isoconazole (Gyno-Travogen, Travogen), Miconazole (Ginezol, Daktarin, Mycozon), Itraconazole, Hexicon, Borax and others like them.
- Douching with herbal decoctions of yarrow, sage, knotweed, chamomile, nettle and oak.
- Douching with Chlorhexidine, Miramistin and other antifungal and antimicrobial drugs.
The partner may not even have thrush, but is a carrier of it. If you neglect the rule of treating both partners, then the risk of recurrence of thrush increases to 70%.
And thrush, as you know, can again cause cystitis.
Take care of your health, lead a healthy lifestyle, follow the rules of hygiene and the recommendations of your doctor. Then thrush and cystitis will remain a thing of the past and will no longer make themselves felt.
Pregnancy and childbirth greatly increase the likelihood of cystitis. Want to know what's the reason? Then read on - cystitis after childbirth: main causes, symptoms, treatment directions and prevention.
Read about the use of chamomile decoctions and infusions in the treatment of cystitis in this topic.
Is it necessary to restore the microflora after thrush therapy and how to do it?
After thrush, regardless of its location, it is usually necessary to restore the normal microflora of the human body, since both the yeast fungi themselves and the drugs that are used for them significantly affect the bacterial background.
Normal microflora is very important for our body: if it is disturbed, the mucous membranes dry out, become irritated, and dysbacteriosis develops, which is fraught with serious discomfort. Therefore, the restoration of microflora after suffering from thrush cannot be ignored.
Microflora of the gastrointestinal tract
You can restore the microflora of the stomach and intestines after thrush and after taking antibiotics by taking probiotics - preparations that contain cultures of lactobacilli and bifidobacteria that normally inhabit our gastrointestinal tract.
- Consume more fermented milk products (except for hard cheeses and blue cheeses - the latter are generally undesirable to eat either during or after thrush).
- Include as many fresh fruits and vegetables in your diet as possible.
- Limit consumption of sweets, yeast products and fermented foods.
- Stop drinking alcohol.
The specific drug will be prescribed by the doctor who treated the thrush. During the treatment period, you should stop taking antibiotics, since they kill not only pathogenic microorganisms in our stomach and intestines, but also beneficial bacteria.
If a course of antibiotic therapy is necessary, during it you should take probiotics to “restore losses” of microflora, and after it, take a full course of probiotics to eliminate dysbiosis.
Oral and nasal cavity
The yeast fungus Candida, which causes thrush, multiplies well in the mouth, disrupting the normal microflora of not only the oral cavity, but also the nose. Dysbacteriosis of the oral cavity and nose is manifested by drying out of the mucous membranes, the appearance of microcracks on them, difficulty in nasal breathing, and the formation of bloody crusts in the nose.
The same symptoms are observed after long-term use of antibiotics or after a course of systemic antibiotics - by the way, it is often antibiotics that disrupt the normal bacterial balance in the body and provoke the pathological proliferation of Candida fungi.
You can also restore the microflora of the mouth and nose by taking and topical application of probiotics (there are special preparations in drops that can be instilled directly into the nasal sinuses). It is also important to exclude from the diet foods that affect the bacterial background and the proliferation of fungi - the list of products is the same as in the case of gastrointestinal dysbiosis.
Women who have encountered thrush often have to restore their microflora after treating a fungal infection. Sometimes the cause of disruption of the bacterial composition of the vagina and the development of fungal diseases is antibiotic therapy.
Taking antibiotics provokes dysbiosis (doctors also call it dysbiosis) of the vagina. Such dysbiosis often leads to the fact that the Candida fungus, deprived of its natural antagonists, begins to actively multiply.
The main “inhabitants” of the vagina are lactobacilli, therefore the main medications used to correct the bacterial background will be preparations of lactobacilli. Such preparations are recommended for use topically, in the form of vaginal suppositories and capsules, or in the form of tampons soaked in liquid probiotic preparations.
Suppositories must be placed 1-2 times a day, the course of treatment usually lasts from 5 to 10 days. Specific suppositories will be recommended by a gynecologist who, after reviewing the test results (smear, culture), will determine the most effective drug in each specific case.
It must be remembered that in the acute stage of chronic candidiasis or in acute forms of thrush, prebiotic preparations are contraindicated.
This is explained by the fact that Candida mushrooms feel great in the acidic environment created by lactobacilli, which means that lactic acid creates quite favorable conditions for their life and reproduction.
- Wash yourself twice a day with warm water. And once - with neutral soap, the second - with a decoction of herbs (chamomile, calendula).
- Wear underwear made from natural fabrics and be sure to be loose.
- Follow the same diet as for thrush - no sweets, alcohol, yeast products, or baked goods.
- Change underwear and pads frequently during menstruation, do not use tampons and pads with deodorizing components.
Some doctors believe that after treating thrush, there is no point in restoring the vaginal microflora, since it is only slightly disturbed and can return to normal without additional drug load on the woman’s body.
This point of view has a right to life, so it is recommended to first do a vaginal smear and evaluate the bacterial background, and only then, if problems with the microflora are identified, can restorative drugs be prescribed.
That is why self-medication is unacceptable even in such a seemingly simple case. If you do not need to take probiotics, and a woman independently uses suppositories with lactobacilli, there is a high risk of acidification of the discharge.
That is, discharge appears with a characteristic sour-milk odor, itching and irritation develop. These symptoms may be mistaken for the same thrush, and treatment with antifungal drugs will begin with renewed vigor.
Cystitis: signs and treatment regimen
Cystitis is an inflammatory disease of the bladder. Due to the peculiarities of the anatomical structure, the disease is more common among women. According to statistics, cystitis is the most common disease of the urinary system among the fair sex.
- What causes cystitis?
- Types of cystitis
- Symptoms of acute cystitis
- Chronic cystitis
- Cystitis in men
- Cystitis during pregnancy
- Cystitis in children
- Tests for cystitis
- Possible complications
- How to treat cystitis?
- Antibiotics for cystitis
- Suppositories for cystitis
- Folk remedies for cystitis
- Home treatment
- Bladder instillation
- Prevention of cystitis
The urgency of the problem is increasing, since every year the frequency of initially diagnosed cystitis and exacerbations of the disease is steadily increasing. What will help get rid of the disease? Before answering this question, let's talk about the provoking causes, the mechanism of development of the pathological process, as well as methods of diagnostic examination.
What causes cystitis?
According to experts, there is no single factor that could cause the inflammatory process. Typically, a number of provoking factors lead to the onset of the disease. It is extremely important to identify all these etiological causes in order to prescribe adequate therapy. Knowledge of the etiology will help prevent exacerbation of cystitis and transition to a chronic form, which is much more difficult to cope with.
So, let’s highlight the main causes of cystitis:
- promiscuity in sexual partners. What does the phrase “genitourinary system” mean? The fact that the genital organs are close to the organs of the urinary system and there are high risks of infection. Interestingly, pathogenic microorganisms can penetrate the urethra not only from the vagina, but also from the surface of the external genitalia;
- lack of proper compliance with hygiene standards. If you want to minimize infection of the urinary system, follow simple but effective rules: change your underwear regularly, change your pad every few hours during menstruation, wash yourself after sexual intercourse, as well as defecation, wash your external genitalia daily;
- dysbacteriosis and candidiasis. When the natural balance of microflora is disturbed, opportunistic microflora is activated. Active reproduction of microorganisms that are not characteristic of the genitourinary system leads to the development of an inflammatory process;
- weakening of immune defense. As a result of the fact that the immune system cannot fight pathogenic microflora properly, infectious agents freely penetrate into the bladder cavity;
- infrequent urination. If urine remains in the bladder for a long time, stagnation becomes more active and pathogenic microorganisms begin to actively multiply. This is why you should not be patient, but go to the restroom on time;
- hypothermia weakens local immunity, as a result of which the infection easily penetrates through ascending pathways;
- constipation, improper wiping;
- avitaminosis;
- passive lifestyle;
- microtrauma of the urethra during intimacy;
- allergy;
- wearing tight synthetic underwear, etc.
Types of cystitis
Depending on the nature of the pathological process, the disease is divided into two categories:
- acute cystitis. It occurs suddenly, causing difficulty urinating and general symptoms such as weakness and increased body temperature;
- chronic cystitis. The process may not manifest itself, but laboratory tests will indicate the presence of an infectious process. However, with an exacerbation of the disease, symptoms characteristic of an acute process appear.
Depending on the etiological factors, cystitis occurs:
- specific. The disease in this case may be a consequence of tuberculosis or sexually transmitted diseases: chlamydia, ureaplasmosis, syphilis;
- nonspecific. The disease occurs as a result of activation of opportunistic microflora: yeast-like fungi, staphylococci, enterobacteria, Klebsiella, etc.
Symptoms of acute cystitis
In each specific case, the signs of cystitis may differ. However, it is possible to identify general symptoms of an infectious process in the bladder:
- pain during urination;
- frequent urge to urinate;
- at the end of urination, the discomfort intensifies, and there is also a feeling that the bladder is not completely emptied;
- general weakness and hyperthermia;
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- menstrual irregularities;
- the appearance of purulent discharge from the urethra;
- the urine becomes cloudy and streaks of blood appear in it.
Chronic cystitis
The chronic form cannot appear out of nowhere; it is a complication of acute cystitis, which can be caused by untimely or illiterate treatment. Patients sometimes have an uncontrollable desire to go to the toilet at night, and during the daytime there is a constant desire to empty the bladder.
During the period of exacerbation of the chronic form, symptoms of acute cystitis occur with high severity. During remission, a woman may experience absolutely no complaints, the only thing being frequent urination, as well as minor pain in the lower abdomen after intimacy or physical activity.
Treatment of chronic cystitis is usually carried out with the use of antibacterial agents. Depending on the type of causative agent of the inflammatory process, antifungal or antiviral drugs may be prescribed. Currently, new generation drugs are used that have a powerful therapeutic effect: Monural, Normax, Tsiprolet A.
Cystitis in men
Although women are more likely to suffer from bladder inflammation, men can also experience the condition. Let's highlight common reasons:
- chronic sexually transmitted infections;
- urolithiasis disease;
- urethral stricture;
- taking hormonal drugs or cytostatics;
- diabetes;
- prolonged stress, lack of sleep.
General treatment recommendations for men include the following:
- fluoroquinoline or cephalosporin antibiotics;
- herbal medicine, which includes herbal diuretics and anti-inflammatory drugs: Phytolysin, Canephron, as well as herbal teas based on lingonberries, bearberry and horsetail;
- analgesics, in particular non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: Nimesil, Diclofenac.
Cystitis during pregnancy
Pregnancy is a pleasant moment in a woman’s life, which cystitis can greatly overshadow. According to statistics, every tenth pregnant woman suffers from this disease. This prevalence can be explained by changes in hormonal levels, as well as weakened immunity.
Cystitis during pregnancy can lead to pyelonephritis, premature birth and the birth of low-birth-weight children.
Let's look at the features of the daily routine for pregnant women with cystitis:
- contacting a urologist;
- You shouldn’t take risks and self-medicate. Folk remedies may not help, but even harm, for example, causing uterine hypertonicity;
- avoid contact with infected people;
- Avoid consumption of spicy, smoked, fatty, fried foods. Eat enough fruits and berries;
- avoid tight underwear;
- Follow your doctor's recommendations.
The treatment regimen includes the use of the following medications:
- antibiotics. Pregnant women are prescribed Monural, Suprax, Amoxicillin;
- herbal preparations: Canephron, Cyston, Urolesan;
- antispasmodics, in particular No-spa.
Cystitis in children
Cystitis in children is as common as among adults. According to experts, more than thirty percent of young children have suffered from cystitis. The main provoking factors of childhood cystitis are:
- developmental anomalies of the urinary system;
- hypothermia;
- dehydration of the body;
- improper hygiene of the external genitalia;
- swimming in dirty ponds;
- frequent use of soaps for bathing;
- weakened immune system;
- artificial feeding.
Young children cannot explain their complaints, but parents can pay attention to fever, lack of appetite, sleep disturbances, and whims. These symptoms are similar to other diseases, for example, ARVI, so it is better not to self-diagnose, but to consult a doctor and take the necessary tests.
The daily routine for children with cystitis is as follows:
- compliance with bed rest;
- heating pad on the lower abdomen;
- sitz baths based on medicinal herbs;
- compliance with dietary nutrition;
- drink plenty of fluids: cranberry juice, rosehip decoction, still mineral water.
Antibacterial agents are used to treat childhood cystitis, namely:
- Augmentin;
- Cefodox;
- Furadonin;
- Co-trimaxozol.
Tests for cystitis
Diagnosis of absolutely any disease begins with a person’s own observations of changes in his condition, which prompts him to consult a specialist. At the doctor’s appointment, the patient reports his complaints, when they appeared, whether they arose before, what diseases he had, etc. Next, the patient is examined and the abdomen is felt, during which pain is detected.
For cystitis, the following laboratory tests are performed:
- a general blood test, in which the erythrocyte sedimentation rate increases and leukocytosis is detected;
- general urine analysis. Protein is detected in the urine, and microscopic examination reveals a high content of red blood cells, white blood cells, and bacteria;
- bacteriological analysis of urine. The study allows you to accurately identify the causative agents of the disease. The results help in prescribing antibiotic therapy;
- Cystoscopy is performed for a chronic process. In acute cystitis, the procedure is very painful and can even lead to the spread of the infectious process;
- Ultrasound examination shows the condition of the urinary tract, and also identifies stones and neoplasms.
Possible complications
Cystitis can lead to the following consequences:
- bleeding;
- impaired functional activity and shrinkage of the bladder;
- pyelonephritis.
How to treat cystitis?
Treatment for cystitis begins after undergoing diagnostics and making an accurate diagnosis. In order to get rid of the disease completely, a comprehensive approach is taken to eliminating it.
Antibiotics for cystitis
The main task in an acute process is to prevent the spread of infection; antibacterial agents perform this role well. It is better to start with a bacteriological test to determine the sensitivity of pathogenic microorganisms.
An important rule in antibiotic therapy is strict adherence to dosages, frequency of use and duration of the treatment process. Remember, the entire treatment course should be completed to the end, even if the condition has returned to normal, do not stop therapy under any circumstances. Ignoring this rule threatens the development of resistance of microorganisms, as well as the transition of the disease to a chronic form.
Let's consider several antibiotic treatment regimens:
- Monural. Treatment is carried out for three days. The dosage is three grams - once a day;
- Norfloxacin. For three days, four hundred milligrams are taken twice a day;
- Ciprofloxacin. Again the treatment is three days. Dosage two hundred and fifty milligrams twice a day.
Suppositories for cystitis
Suppositories are a convenient, and most importantly, effective form for treating bladder inflammation. Let's highlight the main advantages of candles:
- local effect and bypass of the digestive tract, thereby eliminating toxic effects on internal organs and the development of intestinal dysbiosis;
- suppositories are administered either vaginally or rectally, due to which the medicinal substance is quickly delivered to the affected area and the therapeutic effect is immediate.
Suppositories for cystitis are divided into categories:
- antibacterial. Prescribed in the acute phase of the disease, as they are able to suppress the growth and reproduction of pathogenic microorganisms;
- anti-inflammatory. They contain a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory component;
- antispasmodic. They relieve spasm of the smooth muscles of the bladder and, as a result, have an analgesic effect;
- hematogenous. Prescribed if bladder spasm affects blood vessels. Such suppositories improve blood circulation.
Let's look at the most popular and effective suppositories for cystitis:
- Hexicon. The active ingredient of suppositories is chlorhexidine, which has pronounced antibacterial properties. Hexicon can be used for both medicinal and preventive purposes. This is a safe remedy that has virtually no contraindications or side effects, which is why it is safely used at any stage of pregnancy. The course of treatment ranges from five days to two weeks. One suppository is administered twice a day;
- Palin. Pipemidic acid is the main active ingredient of suppositories. Palin sometimes causes unwanted side effects, so it should not be used by women with kidney or liver problems, or by pregnant women;
- McMiror. The active substances are nifuratel and nystatin. Suppositories are intended for vaginal administration and are used for various forms of the disease. Women are usually prescribed one suppository before bed for eight days;
- Diclofenac. These suppositories belong to the group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Diclofenac has analgesic properties. It is not recommended to use suppositories for pregnant women;
- Polygynax. The active ingredients – neomycin and nystatin – have a wide spectrum of antibacterial action. The drug should not be used during lactation or pregnancy.
Can thrush occur from birth control and hormonal pills?
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QJLuU43MuVg
It has also been proven that the effect of hormones on immunological reactions depends on their concentration: high levels have an immunosuppressive effect, and low levels have an immunostimulating effect. Thus, the ratio of sex hormones may be one explanation for the incidence of candidiasis. Thrush from hormonal pills can occur if the drugs contain high doses of estrogen or progesterone. Female hormones can increase the saturation of vaginal tissues with glycogen, which mushrooms feed on, or reduce immune responses. This is why hormonal thrush occurs.
Thrush often occurs after Duphaston and Utrozhestan. These drugs are prescribed to women with problems conceiving to maintain the corpus luteum phase. If the level of progesterone is insufficient, the fertilized egg cannot attach to the wall of the uterus. After taking one of the drugs, changes occur in the endometrium that help the fertilized egg to attach normally to the endometrium and develop.
Symptoms of candidiasis may appear after using emergency contraceptives. These are drugs with pronounced gestagenic and antiestrogenic characteristics. One of the popular means of emergency contraception is Postinor. It has a significant effect on hormone levels and has many side effects. Thrush often appears after Postinor due to the high concentration of the hormone.
In women who use the Nuvaring vaginal ring, thrush is a frequent companion. The drug contains derivatives of the hormones estrogen and progesterone. The main mechanism of Nuvaring is inhibition of the synthesis of active substances in the pituitary gland and prevention of ovulation. Against the background of increased levels of the hormone estrogen, the accumulation of glycogen in vaginal cells increases, which promotes the growth of candida. After Escapel, thrush may appear due to the high content of hormones with antiestrogenic effects, which reduce the body's immune responses.
Genferon is an immunomodulatory drug and does not contain hormones. It is actively used for chronic inflammatory and fungal diseases. The drug copes well with dysbiosis, which develops against the background of a long-term illness or the prescription of large doses of antibiotics. However, thrush sometimes occurs after Genferon.
Patients who treat inflammatory diseases of the urinary tract with Monural may experience the occurrence of candidiasis. The drug inhibits the synthesis of bacteria and is classified as an antibiotic. Thrush after Monural is a side effect of the drug, since, acting on a wide range of microorganisms, the drug disrupts the normal biocenosis of the vagina. As a result, active growth of yeast fungi occurs, and symptoms of vaginal candidiasis appear.
To regulate vaginal microflora, patients are prescribed the drug Vaginorm. It contains a “shock” dose of ascorbic acid, which reduces the pH of the vaginal environment and helps suppress the growth of anaerobes. But the drug does not inhibit the growth of fungal flora. Therefore, there may be thrush after Vaginorm. If the disease is asymptomatic, the use of the drug may increase the growth of a fungal infection. One of the contraindications of Vaginorm is vulvovaginal candidiasis, so before prescribing it, cultures must be done to check for a fungal infection.