Main causes
The causes of gynecological diseases are external and internal. Among the external causes of development, the following factors stand out:
- Regular or periodic stress reflexes on the part of the body to external stimuli.
- Frequent change of sexual partners, unprotected sex.
- Bad ecology.
- Antibiotic abuse.
- Infectious diseases.
- Early onset of sexual activity.
- Inadequate hygiene.
If we talk about internal reasons, they are as follows:
- Hormonal imbalances.
- Abortion or miscarriage.
- Abnormal arrangement of internal organs.
- Pathologies in the formation of the genital organs - a double vagina or a bicornuate uterus.
https://youtu.be/D3EzWZU5OWM
Diagnosis of female diseases
If one or more of the symptoms described above appears, a woman should consult a gynecologist. The specialist will conduct a survey and perform a bimanual gynecological examination, which will partially compile a clinical picture of the pathology.
To establish the cause of changes in the functioning of the reproductive system and identify the disease, a woman needs to undergo a comprehensive diagnosis, which includes laboratory tests and instrumental studies. Many gynecological diseases can be detected using ultrasound of the uterus and appendages. Colposcopy and hysteroscopy also have great diagnostic value.
Laboratory tests make it possible to see changes in the vaginal microflora, identify inflammatory processes and infections that cause diseases of the female organs. Such studies include smear microscopy, PCR, ELISA.
Classification of female diseases by groups
Female gynecological pathologies come in several groups:
- Inflammatory. They are provoked by microorganisms. Inflammatory diseases in gynecology include endometritis, vaginitis, vulvitis, adnexitis, cervicitis.
- Hormonal. They are provoked by problems in the functioning of the endocrine glands. These are uterine fibroids, polycystic ovary syndrome, cycle failure.
- Hyperplastic. A neoplasm in the form of a cyst or tumor is suspected. These are cervical erosion, ovarian cystoma, leukoplakia.
Gynecological diseases manifest themselves with specific symptoms characteristic of genital pathologies. Here are the general symptoms of gynecological diseases:
- Leucorrhoea is a whitish pathological discharge from the vagina.
- Bleeding not associated with menstruation can be spotting, strong, profuse or completely insignificant.
- Burning or itching in the genital area.
- Pain during intimate contact.
- Discomfort when urinating.
- Ulcers or erosions on the genital tract.
- Pressing, bursting or pulling pain in the lower abdomen.
Read about the symptoms and treatment of chronic cystitis in women. You will find an overview of effective drugs and recommendations from doctors!
In the next article, read all about the treatment of uterine fibroids: we have prepared a list of hormonal drugs and traditional medicine recipes.
Do you know that there is an interstitial form of uterine fibroids? In this material we will tell you why it is dangerous and what treatment methods exist.
Uterine fibroids
Myoma is a benign tumor that occurs in the uterus and consists of muscle cells. It is not capable of becoming malignant, but can cause a woman considerable discomfort.
Causes
Most often, fibroids develop against the background of hormonal imbalance, especially with increased synthesis of estrogen and progesterone. That is why most patients with fibroids are women of reproductive age.
After entering menopause, the tumor often decreases as hormone production begins to decline. Another reason for the development of this pathology is therapeutic and diagnostic curettage and abortion, in which damage occurs in the uterus.
Types of uterine fibroids
A provoking factor may be the lack of regular sexual activity, when blood stagnates in the pelvic organs. Myoma can develop in women who do not lead an active lifestyle, which also provokes poor blood circulation in the genitals.
Diagnostics and therapy
Often fibroids do not make themselves felt, and a woman learns about the presence of a tumor only after an examination in a gynecologist. But some women may experience symptoms such as heavy menstrual flow, as well as bleeding on other days of the cycle. Such factors contribute to a decrease in hemoglobin and a deterioration in well-being.
Sometimes fibroids can cause frequent urination and constipation. Some women complain of pain in the lower abdomen.
Fibroids are diagnosed using ultrasound. For small tumors, therapy is not carried out, but the condition of the tumor is regularly monitored. As education increases and health deteriorates, women are prescribed hormonal medications that prevent increased production of estrogen.
If the fibroid is large and interferes with normal urination, a surgical method is prescribed to remove the tumor. Sometimes a gentle method is used, designed to block blood flow, due to which the fibroids are reduced.
Treatment with folk remedies
Since a tumor in the uterus occurs as a result of excess estrogen, therapy with folk remedies is aimed at reducing these hormones.
- Recipe 1. Flaxseed (2 tbsp) is poured with boiling water (500 ml) and boiled over low heat. Take 14 days, half a glass half an hour before meals three times a day.
- Recipe 2. Freshly squeezed potato juice (100 g) is taken on an empty stomach for 3 months. After a four-month break, the course is repeated.
List and review of signs of pathologies in gynecology
There are many gynecological diseases. Let's look at those that occur most often.
Inflammation of the appendages and ovaries
Inflammation of the appendages (salpingitis) and ovaries (oophoritis) are common problems in gynecology. A general inflammatory process of the ovaries and appendages, which is called salpingoophoritis or adnexitis, is also possible.
It occurs most often , since the appendages, ovaries and uterus are in close connection with each other.
The disease develops due to the entry of pathogenic or opportunistic microorganisms into the intimate organs, and a favorable background for this is a decrease in immunity.
A common factor leading to inflammation is hypothermia . Other reasons are the installation of an intrauterine device, abortion, difficult childbirth.
The main symptoms of inflammation of the appendages and ovaries are pain in the lower abdomen, itching, discharge with an odor, increased body temperature, headache, dizziness, and general weakness. Symptoms appear a couple of days after infection. If hypothermia occurs, your health may deteriorate immediately. If the disease is not treated, it can go from an acute form to a chronic one.
Chronic salpingoophoritis does not manifest itself so clearly . Possible pain in the lumbar area. Stronger pain may occur when pressing on the appendage area. They intensify before menstruation. Sometimes there is a low-grade fever. An inflammatory gynecological disease - adnexitis - is usually diagnosed during the first examination by a gynecologist.
Learn about the symptoms of adnexitis and the features of its treatment from the following video:
Uterine fibroids
Fibroids are a benign tumor that arises in the uterus and consists of muscle cells. It does not transform into malignant, but can cause significant discomfort.
Often fibroids appear due to hormonal imbalance , especially if the production of progesterone and estrogen is increased.
The disease mainly affects women of reproductive age. After the onset of menopause, the tumor decreases, since hormones are not produced as actively.
Another cause of pathology is abortion and diagnostic curettage, due to which the uterus can be damaged. The reason may be the lack of regular sex, which provokes stagnation of blood in the pelvis. A passive lifestyle can also cause fibroids due to poor circulation.
Often this disease does not manifest itself at all. A woman learns about it only during an examination by a gynecologist. But symptoms such as too heavy menstruation and bleeding on other days of the cycle are possible. These factors provoke a decrease in hemoglobin and weakness. Sometimes the tumor provokes constipation and frequent urination. Possible pain in the lower abdomen.
Fibroids are diagnosed using ultrasound . If the tumor is small, sometimes no therapy is performed, but the tumor is constantly monitored. If the size of the tumor grows, the state of health worsens, hormonal drugs are indicated that normalize the production of estrogen.
Endometriosis
Endometriosis is the process of growth of endometrial tissue in the uterine area. The pathology has many causes . Experts often associate it with hormonal imbalances, deterioration of immunity, and heredity.
Upon examination, an enlargement of the appendages is revealed . Colposcopy can detect small bluish areas.
Ultrasound is used to diagnose the disease. Sometimes laparoscopy or CA-125 analysis is needed.
There are many symptoms of endometriosis , which often complicates diagnosis. Often women complain of pain in the lower abdomen, lower back, changes in cycles, and general weakness.
There may be excessive menstruation and bleeding on other days of the cycle. For treatment, hormonal drugs are used in the form of tablets or injections.
Cervical erosion
Cervical erosion refers to a disruption of the mucous membrane of the uterine cervix. This is one of the most common female diseases.
The phenomenon is benign, but it must be constantly monitored.
The causes are often inflammation of the female genital organs , early onset of sexual activity, trauma, weakened immunity, and hormonal imbalances. Endocrine pathologies can contribute to erosion.
Often the disease is detected only upon examination . Sometimes minor bleeding is possible, especially after intimate intercourse. Soreness may occur. If an infection occurs, itching and discharge with an odor are possible.
The doctor takes a scraping and a smear. Colposcopy or biopsy can be used for diagnosis if there is a suspicion of a malignant course of the disease.
On our website you will also find out what are the signs of infertility in a woman! We will talk about diagnostic measures and methods of treating the disease.
Inflammation of the ovaries and appendages
One of the most common problems in the field of gynecology is inflammation of the ovaries (oophoritis) and appendages (salpingitis).
With a general inflammatory process of the ovaries and appendages, the disease is called salpingoophoritis. It is this disease that occurs most often, since the uterus, appendages and ovaries are closely connected.
Causes and symptoms
Salpingoophoritis usually develops as a result of pathogenic and opportunistic microorganisms entering the genitals against the background of reduced immunity. Often the trigger for inflammation is hypothermia.
Salpingo-oophoritis
Sometimes the development of the disease can be facilitated by the use of intrauterine devices, childbirth with complications, or abortions.
The main signs of salpingoophoritis are pain in the lower abdomen, discharge with odor, pus, itching, general weakness, fever, headaches, and dizziness. Symptoms usually appear two to three days after infection. With hypothermia, pain and deterioration in well-being may appear immediately.
If treatment is not carried out, the acute form turns into subacute, and then into chronic.
The signs of chronic salpingoophoritis do not appear so clearly. Pain may be felt in the lumbar region. More severe pain usually appears only when pressing on the area of the appendages and intensifies before menstruation. Sometimes a low-grade fever is observed.
Diagnosis and treatment
Inflammation of the ovaries and appendages in a woman, as a rule, is determined during the first examination by a gynecologist. But to identify the cause, additional studies are always carried out, the material for which is taken from the vagina and cervical canal. Treatment is prescribed after determining the sensitivity of the pathogen to antibacterial drugs.
In the acute form of salpingoophoritis, therapy is carried out in the gynecology department for a week. For mild inflammation, therapy is prescribed at home.
The doctor prescribes antibiotics, topical anti-inflammatory drugs, and analgesics to the woman. Dosages and treatment regimens must be followed in full, since if the medication is not taken, inflammation usually begins again. If necessary, the sexual partner is also prescribed examinations and therapy.
Folk recipes
Inflammatory processes in the ovaries and appendages have been treated with folk remedies since ancient times. Plant tinctures, douches and tampons dipped in prepared herbal decoctions were commonly used and are still used to this day.
- Recipe 1. Bergenia root (50 g) is poured with a glass of boiling water and left for 8 hours. For douching, the infusion is diluted with warm water (2 l) and the procedure is carried out twice a day.
You can also make tampons from cotton wool and gauze, soak them in incense and insert them into the vagina. At the same time, it is good to take this remedy orally, 1 tsp. an hour before meals three days.
- Recipe 2. Boil an onion (onion) in 1 liter of water to soften and filter. Douche with warm broth three times. As a rule, odor-bearing discharge and discomfort go away after several procedures.
- Recipe 3. Chop the garlic and add warm water for a while. Soak a tampon in this infusion and insert it into the vagina for 2 hours. The procedure is performed until the symptoms completely disappear.
Features of treatment
Gynecologists and venereologists treat women's diseases. All medications and other methods of therapy can be prescribed after examination and an accurate diagnosis.
Antibiotics are prescribed to destroy pathogens . Itching, burning, and discharge can be combated with the help of local medications - suppositories, tablets.
After the course of treatment, vitamins and immunomodulators are indicated. Sometimes magnetic and laser therapy, UHF, and electrophoresis are prescribed.
If treatment was carried out using antibiotics, therapy against intestinal dysbiosis is necessary after it.
Numerous female pathologies are asymptomatic, developing and progressing. Gynecological examinations for preventive purposes are very important.
Women's diseases and their symptoms - we talk about this in detail on our website. Well, now we will present to your attention a short overview of the most common female diseases.
In the modern world, in caring for their family, women often stop paying attention to their women's health. The asymptomatic course of some female diseases and untimely access to a doctor can play a fatal role in the future, and medical care may no longer be effective. Therefore, while caring for her family, a woman should not stop thinking about herself, showing the same concern for her women's health. In medicine, problems of the female genital area are dealt with by gynecologists, who recommend that women undergo regular preventive examinations for the purpose of early detection and treatment of a particular disease.
Most female diseases may have one of three main symptoms as they progress:
- -menstrual dysfunction (absence of menstruation, irregular menstruation, prolonged menstrual bleeding, pathological menstruation, dysfunctional uterine bleeding, etc.),
- - pathological vaginal discharge,
- - pain in the lower abdomen.
Each of these signs, and even more so their combination, indicates the need to visit a doctor. Based on these symptoms, we will consider the most common diseases of the female genital area.
Infectious diseases
The causes of inflammation in the genitals are often coccal infections, E. coli, chlamydia and other microorganisms.
Many sexually transmitted diseases often occur in a hidden (latent) form. The first signs of infection are itching in the vagina, pain during urination, and discharge with an odor. Possible rashes on the vaginal mucous membranes, hyperemia, and enlarged inguinal lymph nodes.
The discharge may be yellow or green, with or without an odor. The menstrual cycle may be disrupted. Sometimes the temperature rises slightly. A woman feels itching, pain in the groin, and also during sexual intercourse.
Infection with chlamydia and ureaplasmosis contributes to the development of diseases such as salpingoophoritis and cervical erosion. When infected with the papilloma virus, the likelihood of developing cancer increases.
Treatment of sexually transmitted infections
Treatment of sexually transmitted infections is carried out by a gynecologist and venereologist. All drugs are prescribed only after a thorough examination of the patient.
The causative agents of the disease are destroyed by antibiotics, which are selected after their type is determined. Signs such as itching and odor-bearing discharge are removed with the help of local medications: suppositories, tablets.
After the course of treatment, the woman is prescribed a course of immunomodulators and vitamins. It is also possible to use laser, magnetic therapy, electrophoresis, and UHF. After a course of antibiotic therapy, it is imperative to treat the resulting intestinal dysbiosis.
Do you still think that it is completely impossible to heal your body?
Uterine fibroids.
Myoma is a benign tumor of the muscle fibers of the uterus. Its size can range from several millimeters to several centimeters, which can give rise to different clinical manifestations, but the main symptom with which people consult a gynecologist is excessively heavy and prolonged menstruation.
The main cause is considered to be an increased level of female sex hormones (estrogens) and chlamydia, which occurs in every fourth woman on the planet aged 16 to 45 years. Depending on the size of the tumor, menstrual-like bleeding may occur 2 or several times a month. Constant and significant blood loss leads to the development of anemia, which is manifested by pallor of the skin and mucous membranes, increased fatigue and weakness. Only very large or multiple fibroids cause pain.
Diagnosis of female diseases
To determine a specific disease in gynecology, an integrated approach and differential diagnosis are used.
In gynecology, there are a large number of different dysfunctions of the pelvic organs; for this reason, differential diagnosis is used, which consists of the following methods:
- Personal inspection. A mandatory procedure in which the doctor independently evaluates the appearance of the genital organs, the amount and color of discharge, and performs palpation.
- Blood analysis. Depending on possible deviations, general and biochemical laboratory tests may be prescribed.
- Transvaginal ultrasound. It will allow you to accurately see what cannot be assessed using other methods: changes in structure, the presence of tumors, their size, etc.
- Laboratory examination of a smear. Biomaterial is taken during the examination. Allows you to evaluate microflora.
- Testing for the presence of tumor markers, pathogenic microorganisms, determination of hormonal levels.
- MRI of the pelvic organs.
- Cytological examination of the contents of the cervical canal.
Treatment depends on the specific gynecological disease in women. It can only be prescribed by the attending physician based on the examination results. We strongly do not recommend using traditional methods or taking any medications on your own. You should not experiment with your own health.
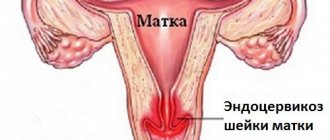
Cervical erosion (endocervicosis).
It is one of the most common diseases among the female population. Almost 40% of all women experience erosion, of which 55% are women under the age of 25. Cervical erosion is a defect in the mucous membrane of the outer part of the cervix, the triggering point of which is most often an infectious inflammatory process.
All this leads to the fact that the structure of the mucous membrane of the cervix changes, its multilayered epithelium at the site of damage disappears, and the surface of the mucous membrane is exposed. As a result, true erosion of the cervix is formed.
Usually, after 1-3 weeks, true erosion heals or turns into pseudo-erosion of the cervix, when the stratified epithelium of the erosion is replaced by columnar epithelium from the cervical canal of the cervix.
Typically, erosion is asymptomatic and is detected during a gynecological examination; very rarely it can manifest as bloody discharge after sexual intercourse. If left untreated, erosion can develop into an oncological process.
Colpitis
Colpitis is one of the most common diseases that affects exclusively women. Colpitis affects the vagina. According to statistics, an average of 60% of females suffer from this disease.
Vaginitis is the second name for this disease; it can be classified as the most common in gynecology. The inside of a woman's vagina is a cavity and is constantly in a moist state. Based on this, we can conclude that there is the most suitable environment for the proliferation of various microbes.
Vaginal candidiasis, or thrush.
Vaginal candidiasis, popularly called thrush, is one of the common diseases in women, which gives them a lot of discomfort. The cause of the development of the disease is fungi of the genus Candida, which enter the human body at birth when passing through the birth canal and remain with us for life, showing their aggressiveness only when immunity decreases. Many women—about 75%—have encountered thrush at least once or several times in their lives.
The main signs of vaginal candidiasis are itching in the vaginal area, cheesy discharge and an unpleasant sour odor. In addition, women may be bothered by burning and pain after intercourse, which is why they prefer to avoid sexual relations.
Thrush can last a long time, with periods of exacerbations and remissions, so you should not put off going to the doctor. Strengthening the immune system and treatment prescribed by a doctor will help you quickly cope with such an unpleasant disease.
Types of gynecological diseases and their manifestations
There is a wide variety of diseases unique to the female sex. The course of each of them has its own distinctive characteristics. Some appear immediately, while others can wage a silent war for years and lead to infertility or even death.
| Disease | Localization |
| Vulvitis, cervicitis, candidiasis | Affects the external organs of the reproductive system, the cervix |
| Endometriosis, adnexitis, fibroids, ovarian cyst | Affects the uterus and its appendages |
| Dysplasia, cervical cancer | Affects the cervix |
Regardless of age, certain gynecological diseases occur in women, the list and symptoms of which you will learn below.
Colpitis
Colpitis is an inflammatory process affecting the mucous tissues in the vagina. The disease develops against the background of the proliferation of pathogenic microflora: fungi of the genus Candida, staphylococcus, streptococcus, E. coli.
The course of the disease can be acute or chronic. Colpitis occurs most often in women of fertile age, but can also develop in children and the elderly.
Symptoms:
- pain and discomfort in the vagina and labia area, burning sensation;
- copious discharge, sometimes with a characteristic smell of rot;
- painful urination;
- swelling and redness of the genitals.
Vulvitis
Vulvitis is an inflammatory disease affecting the female genital area. The following areas are affected by infection: the clitoris, labia, and vaginal opening. The disease develops against the background of a weakening of the immune defense with a concomitant violation of the integrity of the skin of the area.
The cause of the development of vulvitis is most often pathogenic organisms: yeast, E. coli, streptococci, etc. Sometimes inflammation can develop against the background of an STD.
DETAILS: Malavit - instructions for use, indications, doses, composition
Symptoms:
- swelling in the area of the external genitalia;
- redness, itching and burning when touched, after urination or sexual intercourse;
- purulent vaginal discharge.
Cervicitis
Cervicitis is an inflammatory process affecting the tissue of the cervix. The disease is accompanied by purulent or cloudy discharge, discomfort during sexual intercourse, and nagging pain in the lower abdomen. Chronic cervicitis leads to cervical incompetence and the spread of the inflammatory process higher.
Cervicitis rarely occurs as an independent disease; most often it occurs due to acute vulvitis, vaginitis, colpitis, etc. The disease is provoked by pathogenic flora that reaches the cervix.
The risk of developing cervicitis is increased by certain factors: trauma during childbirth, a history of abortion, installation of an intrauterine device, and use of contraceptives.
Symptoms:
- Acute cervicitis is accompanied by cloudy discharge. Swelling of the cervix and minor hemorrhages appear.
- Chronic cervicitis is accompanied by cloudy mucous discharge, and pseudo-erosions form on the cervix. Its surface becomes thicker, and cysts may form. Swelling and redness in the chronic form are not so pronounced.
Candidiasis
Candidiasis (thrush) is the most common disease of the female reproductive system. Its causative agents are fungi called Candida. Candidiasis is not a sexually transmitted disease. Develops due to increased proliferation of fungi, against the background of weakened immunity.
Symptoms:
- white discharge with a sour odor and a curd-like consistency;
- swelling of the genitals;
- increased discomfort upon contact with water after sexual intercourse.
Uterine fibroids are a common and complex disease. It is a neoplasm consisting of benign cells. Fibroids are nothing more than overgrown muscle fibers.
Symptoms of uterine fibroids:
- increase in the menstrual cycle;
- excessive bleeding during menstruation, the appearance of blood clots;
- pain in the pelvis, back, legs;
- frequent urination;
- pain during sexual intercourse;
- increase in abdominal size.
Adnexit
Adnexitis is an inflammatory process that occurs in the appendages. The causative agents of the disease are various microorganisms and bacteria. The process can occur in both acute and chronic forms, with frequent relapses possible.
Endometriosis
Endometriosis is a disease in which the endometrium, lining the inner surface of the uterus, grows beyond its limits. New cells undergo the same changes during the menstrual cycle as the endometrium itself.
The disease is common in women of childbearing age and is second only to uterine fibroids in frequency of cases.
Doctors and scientists cannot yet name the exact cause of the disease. There is an opinion that endometrial cells enter the nearby genital organs along with blood clots.
Therefore, this disease is often associated with operations, difficult childbirth and abortions.
Symptoms:
- pain in the lower abdomen, radiating to the sacrum and lower back;
- excessive bleeding during menstruation;
- thick, staining discharge after the end of menstruation.
Endometriosis is dangerous because in 40-43% of cases it leads to infertility. Another complication of the disease is various inflammatory processes, due to the fact that blood can accumulate in one area and not come out, as in a normal cycle.
Cervical dysplasia
Dysplasia is a pathological condition in which the number of layers and the structure of the cellular structure covering the epithelium of the cervix changes.
A common cause of the development of dysplasia is HPV (human papillomavirus), or, more precisely, certain strains of it, which belong to the highly oncogenic risk group.
It can take about 10 years from the time the disease develops until it degenerates into cancer. During this time, there may be no symptoms.
Symptoms:
- copious, odorless discharge with a light milky color;
- discomfort and pain during and after sexual intercourse, discharge of blood streaks after intimacy;
Cervical cancer
Cervical cancer is one of the most common malignant diseases. There are two groups of women at risk: those aged 40-50 years and those aged 55-65 years.
It is possible to prevent the disease because it is preceded by various precancerous conditions.
Symptoms:
- vaginal discharge streaked with blood;
- aggravated cervicitis, colpitis;
- purulent discharge;
- violation of the monthly cycle;
- pain during and after sexual intercourse.
Ovarian cyst
An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac located in one or both ovaries. Its dimensions can be several centimeters or up to 25 cm in diameter.
It is formed when a mature egg cannot leave the ovary during ovulation. As a result, it begins to stretch and fill with liquid.
Multifollicular ovaries, or polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS).
This diagnosis is made to perhaps every fourth woman when visiting a gynecologist. According to statistics, this disease affects from 2.5 to 8% of women, mainly aged 25-30 years. Polycystic ovary syndrome is a disease in which the maturation of follicles is disrupted, ovulation does not occur, and the eggs that remain in them turn into numerous cysts.
Often the disease develops spontaneously, but the main cause is still considered to be a hereditary factor, in which there is an increased production of androgens (male sex hormones) with a decrease in the formation of progesterone. A predisposing factor is excess weight, so the most effective way of prevention is to normalize body weight.
The main and only symptom of this female disease is an irregular menstrual cycle. Several months may pass between periods. Recently, in the West, there has been a tendency that doctors regard this condition as a variant of the norm and are in no hurry for a woman to restore her menstrual cycle. Recent studies have concluded that PCOS is not a clear cause of infertility, as previously thought.
Endometriosis.
It is important to know that not only polycystic ovary syndrome is sometimes the cause of menstrual irregularities. This symptom may be a sign of another female disease, such as endometriosis.
The uterine cavity is lined with special mucous cells that make up the inner layer - the endometrium. The peculiarity of endometrial cells is that they respond to cyclical changes in hormonal levels. In particular, if the endometrium grows, thickenings appear, and blood vessels proliferate, then the uterus is thus preparing for fertilization. If this does not happen, then most of the endometrium exfoliates on certain days of the cycle, and menstrual bleeding occurs.
However, sometimes, for an unknown reason, the endometrium appears not only in the uterus, but also outside it, which is medically called endometriosis. The same changes occur in these cells as in the cells of the uterine cavity, however, the clinical manifestations of this process can be different, up to disruption of the function of a particular organ. Mostly, endometriosis occurs in women of reproductive age between 25-30 years; in postmenopause, it practically does not occur.
The causes of endometriosis are still not fully known; it is common to think about genetic mutations, changes at the level of cellular enzymes and hormone receptors. Risk factors include surgical manipulation of a woman's genital organs. Endometriosis can be genital, within the genital organs, and extragenital, in other areas of the body.
Genital endometriosis is characterized by the growth of endometrial cells on the ovaries, outside the uterus, in the cervix or cervical canal. A typical symptom is spotting that appears a few days before menstruation, which may continue for some time after menstruation has stopped. The second most common symptom is pain in the pelvic area, which can be constant, intensify before menstruation, after going to the toilet, sexual intercourse, and sometimes for no apparent reason.
Extragenital endometriosis is difficult to diagnose because it may have no signs or be disguised as another disease, depending on the area where the endometrial cells are located. The only sign that helps in diagnosis may be pain and exacerbation of the condition depending on the day of the menstrual cycle.
The most common female diseases
Vaginal candidiasis
Vaginal candidiasis or simply - thrush Our list of “Women's diseases” begins with probably the most common female disease - vaginal candidiasis or, as it is more often called, thrush.
Thrush is a gynecological disease caused by fungal microflora, namely yeast fungi of the genus Candida.
Vaginal candidiasis affects the mucous membrane and skin of the female genital organs.
Vaginal candidiasis occurs most often if the immune system is severely weakened, and your body is exhausted by diseases, diets, nervous exhaustion, etc.
This female disease can appear after long-term use of antibacterial drugs, hypothermia, hormonal imbalances, anemia and diabetes.
Women also suffer from thrush during pregnancy and menopause. The most unpleasant signs of vaginal candidiasis are itching, cheesy discharge and a sour odor.
If left untreated, the fungus can affect not only the female genital organs, but also spread to the intestines, bladder and even kidneys.
Cervical erosion
The second disease on the list of “ The most common female diseases ” was cervical erosion.
This female disease is very dangerous, because in the early stages it does not make itself felt with any special symptoms, except that the stomach may hurt a little and the discharge is much more abundant than usual.
Such female diseases can only be determined by a doctor, so only by visiting a gynecologist can you find out whether you have cervical erosion.
As doctors comment during the examination, the cervix should have a soft pink color, and the epithelium should be smooth.
The cervical canal has a brighter pink color of the epithelium. Due to the emergence of cylindrical epithelium on the outer surface of the uterus, erosion of the cervix is formed.
The causes of erosion can be very different. This could be mechanical damage to the cervix, infections of the reproductive system, trauma received during childbirth, dishormonal factors.
Cervical erosion is a very insidious disease for women, because if left untreated, it can develop into cancer.
Endometriosis
The gynecological disease endometriosis is a fairly serious disease in which uterine tissue grows outside the internal endometrium.
Women's diseases such as endometriosis cause disruption of the menstrual cycle; periods are not only longer, but also very painful.
In addition, with endometriosis, even between menstruation, spotting may appear, the stomach hurts, and pain occurs during intimacy.
Foci of endometriosis can appear not only in the genitals ( genital endometriosis ), but also outside them, for example in the intestines ( extragenital endometriosis ).
Endometriosis can cause infertility, because with its appearance many adhesions are formed in the pelvic area. Endometriosis is treated with both medication and surgery.
Ovarian cyst
Next on our list of “The Most Common Women’s Diseases” is ovarian cyst.
An ovarian cyst is a gynecological disease that is a benign formation of a liquid or dense consistency.
A gynecological disease such as an ovarian cyst can occur for various reasons, for example, due to hormonal imbalance.
The origin of a benign ovarian cyst determines its future fate, that is, the cyst will resolve on its own, or you will be prescribed surgical removal of this formation.
Ovarian cysts must be monitored by regularly visiting the gynecologist's office.
Such female diseases can develop into a malignant tumor. An ovarian cyst is characterized by aching pain in the lower abdomen.
There will also be back pain and the menstrual cycle may be disrupted. It is better not to rush to remove a cyst on the ovaries if it is not growing, because the integrity of the ovary can be damaged.
In adulthood, the ovary with a cyst is most often removed to avoid cancer.
Menstrual irregularities
Menstrual irregularities are also among the most common female diseases
It would seem that this might not be the case. Maybe! If the menstrual cycle is disrupted, menstruation may not last 3-7 days, but, for example, two weeks.
Infections, ovarian pathologies, endocrine diseases, decreased immunity, neurological diseases, etc. can cause disruption of the menstrual cycle.
To cure menstrual irregularities, treat the cause that provoked this failure.
Colpitis (vaginitis).
Vaginitis is an inflammation of the vaginal mucosa, caused by a bacterial infection - staphylococcus, chlamydia, mycoplasma, gonococcus, Haemophilus influenzae, etc. Colpitis (vaginitis) is one of the most common diseases of the female genital organs, affecting mainly women of reproductive age who are sexually active, especially with frequent changes of sexual partners.
Typical symptoms of colpitis are mucous, mucopurulent, sometimes bloody discharge in large quantities from the vagina with an unpleasant odor, itching and burning in the genital area, pain when urinating, swelling and redness of the external genitalia.
In a chronic process, the symptoms may not be clearly expressed, and the process itself is sluggish. Lack of timely treatment can contribute to the spread of the inflammatory process upward and lead to inflammation of the uterine cavity (endometritis), fallopian tubes (salpingitis) and ovaries (oophoritis). Therefore, you should not postpone treatment until later, and consult a doctor at the first symptoms.
Diseases of the uterus and appendages
These are inflammations and tumor formations (benign and malignant) on the ovaries, uterus and tubes. The consequences for the female body can be very different - partial or complete removal of organs, infertility, ectopic pregnancy.
Inflammatory diseases of the cervix most often occur as a result of genital infections, the causative agents of which are chlamydia, trichomonas, streptococci, staphylococci, gonococci, fungi and other bacteria.
Among the most common female diseases, cervical erosion comes first. It is diagnosed in every third to fifth woman. Erosion is a small wound that, as it develops, can affect the entire epithelium of the uterus (dysplasia) and lead to its tumor.
In second place is the cyst. The disease is a blockage of the glands of the uterus or ovaries. Outwardly, it looks like small tubercles. Unlike erosion, a cyst does not develop into a tumor. However, it can grow. Increasing in size, it can deform the cervix and disrupt the structure of the epithelium. This is why treatment for this disease is mandatory.
Erosion, like a cyst, is diagnosed using colposcopy. Treatment is carried out by cauterization (laser or radio waves).
Diseases of the appendages include salpingitis (inflammation of the fallopian tubes), oophoritis (inflammation of the ovaries) and salpingo-oophoritis (inflammation of both the tubes and ovaries).
Symptoms of inflammation:
- Fever.
- Sharp pain in the lower abdomen.
- Nausea, vomiting.
- Increased number of white blood cells in the blood and urine.
- Disturbed menstrual cycle.
Inflammation of the appendages can be caused by pathogenic bacteria (staphylococci, streptococci, chlamydia, gonococci), abortion, biopsy, curettage and other mechanical damage.
In case of any ailments, you should immediately consult a doctor. Diseases of the uterus, as well as the appendages, are a serious threat to reproductive health. Under no circumstances should you delay treatment.
Menstrual irregularities.
Menstrual irregularities in themselves are not a disease. This is primarily a symptom indicating that there are certain problems in a woman’s body.
The normal menstrual cycle is characterized by regular menstruation, which occurs every 21-35 days and lasts 3-8 days. If the menstrual cycle is too short or long, and the periods themselves are scanty (less than 20 ml) or heavy (blood loss more than 150 ml), or last 1-2 days, then they speak of a violation. If menstruation is absent for 6 months or more, then they talk about amenorrhea.
There can be quite a few reasons for menstrual irregularities, ranging from gynecological problems to disruption of the pituitary gland, thyroid gland, or constant stress experienced by a woman. Depending on the causes, treatment will also differ, but in no case should you ignore menstrual irregularities, since malignant diseases may be hidden behind this condition.
Mastitis (inflammation of the mammary gland).
Inflammation of the mammary gland, or mastitis, occurs mainly during breastfeeding; at other times it is extremely rare. In most cases, women of reproductive age - 30-50 years are affected. The incidence is 1-16% depending on the region, of which 85% are primiparous women.
The reasons for the development of the inflammatory process in the mammary gland in nursing mothers is lactostasis (milk stagnation), which creates ideal conditions for the proliferation of bacteria. In other cases, the cause is also a bacterial infection, most often staphylococcus.
Mastitis is characterized by redness, swelling and a feeling of tension in the mammary gland on the affected side, an increase in body temperature up to 39C. At the same time, there is a risk of developing an abscess or fistula in the affected area. As a rule, if you consult a doctor in a timely manner, treatment brings quick results.
Causes of inflammatory diseases of the female genital organs
Almost always, the inflammatory process in the genital organs occurs under the influence of a number of different factors - thermal , chemical , mechanical . But the main factor that directly affects the development of inflammation is the influence of infections. Depending on which pathogen provokes the development of inflammatory diseases of the female genital organs, they are usually divided into nonspecific and specific . The latter include tuberculosis , gonorrhea , and diphtheria .
Nonspecific inflammatory diseases are provoked by a wide variety of pathogens: chlamydia , candida fungi , ureaplasma , mycoplasma , trichomonas , E. coli , Klebsiella , corynebacteria ( Gardnerella ), etc.
Opportunistic microorganisms also play a role in the occurrence of such diseases. Most often, transmission of pathogenic pathogens occurs during sexual contact; more rarely, household transmission occurs. In order for inflammation of the female genital organs to be provoked by opportunistic microorganisms, certain conditions must be met. In particular, the vaginal microflora, which creates an acidic environment, prevents the entry and further activation of infection by opportunistic microorganisms.
In addition, the process of shedding the endometrial layer during menstruation is an obstacle to the spread of infection. Along with this layer, microorganisms are also rejected. And thanks to the plastic properties of the pelvic peritoneum, inflammation in a woman affects only the pelvic area.
A factor that protects against the risk of recurrent inflammation of the genital organs is also the use of certain oral contraceptives.
There are active and passive spread of infection to the upper genital tract from the lower. The lymphogenous or hematogenous route is considered passive, as well as spread into the tubes and uterus, into the abdominal cavity through the cervical canal. Active spread of infection occurs with Trichomonas and sperm.
Mammary cancer.
Breast cancer is a malignant tumor of the glandular tissue. Worldwide, it is one of the most common forms of cancer among women, affecting 1/3 to 1/9 of women aged 13-90 years. Among all cancers, it ranks second after lung cancer. According to WHO data, from 8 thousand to 1 million new cases of the disease are registered annually in the world. It also ranks second in terms of cancer deaths in women.
The risk of developing breast cancer after age 65 is almost 6 times higher than before that age, and 150 times higher than before age 30.
Among the main causes of this female disease is a hereditary predisposition to the development of the disease. Predisposing risk factors are quite diverse - lack of pregnancy and childbirth, lack of breastfeeding or too short a period of breastfeeding, obesity, smoking, diabetes, early onset of menstruation (before 12 years) and late menopause (over 55 years), arterial hypertension, alcohol abuse and other.
Vaginitis
Statistics indicate that every third woman has experienced and knows what kind of pain occurs with gynecological diseases. Symptoms of vaginitis that cause discomfort appear in the form of:
- changes in vaginal discharge in character, color and smell;
- feeling of fullness in the vagina;
- itching and burning;
- the appearance of pain when urinating and during sexual intercourse;
- minor bleeding.
The nature of the discharge depends on the following factors:
- age - in girls, in women, in the postmenstrual period;
- time of onset and duration of the disease; vaginitis can be acute, subacute, chronic;
- causes: abortion, childbirth, allergic reactions.
Depending on what pathogen causes the inflammation and the nature of the discharge, there is specific vaginitis (syphilitic, gonorrheal, chlamydial, trichomonas, tuberculosis) and nonspecific (bacterial, fungal).
During an exacerbation of the disease, the symptoms are more pronounced, subsiding as the disease becomes chronic.
Vulvitis
The inflammation is localized in the area of the woman’s external genitalia and can spread to the inner thigh. Manifests itself in the form of small ulcers and erosions in the labia and clitoris.
Severe swelling and redness and serous-purulent discharge may occur. If you have vulvitis, you cannot have sex due to increased pain with movement and touch.
Colpitis
The vaginal mucosa is affected. It manifests itself in the form of the same symptoms as other inflammatory diseases (itching, burning, pain in the lower abdomen).
Only depending on the nature of the pathogen, the appearance of copious white foamy discharge is possible. If a woman has colpitis, then the discharge has a rotten smell.
Cervicitis, endometritis and adnexitis
When cervicitis occurs, the vaginal segment of the cervix suffers. Cloudy discharge in the form of mucus appears, with the appearance of small ulcers and hemorrhages at the site of inflammation, sometimes a dull pain appearing in the lower abdomen.
With acute endometritis, women have pain in the lower abdomen, since the inflammation is localized in the uterus itself. The pain increases with palpation. There is a temperature that rises quickly and purulent discharge.
With adnexitis, the fallopian tubes become inflamed. The following types of adnexitis are distinguished: chronic, acute, subacute, depending on the side of the lesion, and bilateral.
Both women and girls may complain that the lower back and abdomen hurt, and the pain is cramping. Urination becomes difficult, watery discharge appears, and symptoms of intoxication appear, as the body temperature rises above 38 degrees.
Types of inflammatory diseases of the female genital organs
Depending on which area of the woman’s genital organs is affected by a nonspecific infection, the disease of the genital organs is determined. If inflammation of the vaginal mucosa develops, colpitis . This inflammation can be diffuse or focal, and can spread to the vulva and part of the cervix.
If the inflammation affects the external genitalia, then we are talking about vulvitis . This disease can develop in a woman as a consequence of trauma to the mucous membrane due to scratching, abrasions, etc. The injured surface becomes infected. Sometimes secondary vulvitis , which is a consequence of inflammation of the internal genital organs.
Inflammation of the cervix is called cervicitis , and the large gland of the vestibule of the vagina is called bartholinitis .
If inflammation affects the inner lining of the cervical canal, then the patient is diagnosed with endocervicitis . Endometritis is an inflammatory process in the inner lining of the uterus. The occurrence of acute endometritis is mainly observed after difficult childbirth, abortion, and curettage.
With inflammation of the uterine corpus, the patient develops salpingitis . The inflammatory process affecting the ovaries provokes the development of oophoritis . Inflammation of the walls of the uterus is called myometritis , and the pelvic peritoneum is called pelvioperitonitis .
Salpingo-oophoritis ( adnexitis ) is an inflammatory process in the uterine appendages, which is provoked by an infection spreading from the vagina in an ascending manner. Usually occurs as a consequence of abortion or difficult childbirth. In more rare cases, infection can occur from the rectum or sigmoid colon, or appendix.
Pathological diseases of the cervix and neoplasms
Erosion can be true or pseudo-erosion. It can occur without any symptoms, only in rare cases does pinkish or brown discharge appear. Abdominal pain localized below is usually not a concern, but may occur spontaneously after sexual intercourse.
Dysplasia, leukoplakia, papillomas and cervical carcinoma. These diseases are considered precancerous; they change the cervical mucosa. Symptoms may not appear for a long time, but if bloody discharge, swelling of the lower extremities and severe pain in the lower abdomen appear, a tumor can be suspected, which requires immediate intervention. Depending on the degree of limitation of life activity in this insidious disease, disability is given.
What gynecological diseases occur with HIV? It is when the human immunodeficiency virus is detected that the risk of developing dysplasia, cervical cancer, infectious diseases and neoplasms increases markedly.
Myoma and fibromyoma
One of the most common benign formations. Depending on the location of the fibroid nodes, women may not feel pain, or, on the contrary, the fibroid becomes the cause of a serious condition. Types of uterine fibroids depending on the nodes:
- subserous;
- intramural;
- submucosal nodes.
Myoma manifests itself in the form of bleeding, independent of menstruation, pain and a feeling of pressure in the pelvis. The nodes put pressure on nearby nerves, resulting in pain in the limbs, back and buttocks.
It is not difficult to determine which gynecological diseases the abdomen grows in; these include benign and malignant neoplasms, including cysts, the etiology of which is different.
Cysts of various origins
Hydrotax (fluid accumulation) can be observed with neoplasms in the ovaries, especially in an advanced form. The following types of cysts are distinguished:
- follicular;
- hemorrhagic;
- Corpus luteum cyst.
What does a follicular cyst look like?
In addition to the most common, other types of cysts are noted:
- endometrioma;
- cystic adenoma;
- dermoid;
- paraovarian.
In various forms, there is pain and a feeling of pressure on the bladder and lower intestines, resulting in increased urination and constipation. The menstrual cycle changes when there are no periods at all, or their rare and irregular appearance.
Sex hormones begin to be produced too intensely, which leads to a change in voice and growth of facial hair. With a significant size of the cyst, asymmetry of the abdomen appears.
Cancer
Malignant tumors in women most often form in the breast, uterus, ovaries and appendages. The main reason is the lack of timely treatment of less serious diseases (for example, advanced erosion). An important influence is exerted by heredity, mechanical damage to the uterus, reduced immunity, and hormonal imbalances.
In the early stages, the tumor is almost impossible to detect. As a result, treatment becomes difficult and often ends in death.
Symptoms of tumors:
- New growths that can be felt with your fingers.
- Swelling of the affected areas.
- Discharge from the genitals with pus or blood.
- Abdominal and back pain.
- Painful intercourse.
- Irregular menstruation.
- Weakness, malaise, weight loss.
Oncological diseases are diagnosed using:
- Ultrasound.
- Biopsies.
- Cytological studies.
- Computed tomography.
- Tests for tumor markers.
Of course, in most cases, tumor formation can be avoided. To do this, you need to consult a doctor in a timely manner. Any diseases and infections should not be brought to an extreme state.
Infertility
The psychology of women with gynecological diseases plays an important role in their lives. The question of infertility, stress, worries, possible depression and anxiety disrupt the normal course of life and change the response to the question of a woman’s sexual function. This can lead to depression and hysteria. Classification of infertility:
- primary, secondary;
- physiological, voluntary;
- temporary, permanent.
The main sign of infertility is the inability to conceive a child. Further, other causes and treatment of possible concomitant diseases are clarified.