Intestinal flu occurs much more often in children than in adults, and is severe with the development of dehydration. But sometimes it is difficult to differentiate between a viral and bacterial infection based only on clinical symptoms. Laboratory diagnostics are not always available, and results may take some time to arrive. A decrease in immune defense leads to the development of complications. In this regard, for rotavirus infection in children, Furazolidone is prescribed, an intestinal antimicrobial drug to suppress bacterial flora.
About rotavirus
The pathogen belongs to the RNA-containing type of pathogens. The disease is caused by several serovars of the virus; those who have recovered from the disease develop type-specific immunity. The microbe is quite adapted to a variety of environmental conditions. It lives and reproduces well at high and low temperatures.
The causative agent of rotavirus infection spreads from a source to susceptible people in two ways - fecal-oral and household contact. There is insufficient data on the likelihood of an airborne mechanism.
Rotavirus infection is suspected when signs of acute gastroenteritis (nausea with vomiting, diarrhea, cramping abdominal pain and rumbling), intoxication syndrome (chills, increased temperature, weakness) and catarrhal symptoms (running nose, coughing, sore throat) appear.
https://youtu.be/k9aPPL2ETlY
In what cases is it used?
Parents should know exactly when to use Furazolidone. Full information on this issue is given in the instructions for the drug, but it is better to repeat it again and remember it.
Furazolidone tablets are used for gastrointestinal infections of various natures
Indications for use:
- Gastrointestinal infections of various natures, including rotavirus, food, paratyphoid, dysentery. With severe symptoms of poisoning (diarrhea, vomiting).
- For giardiasis and other diseases caused by parasites.
- Infections of the genitourinary system, which include pyelitis, cystitis, Trichomonas urethritis.
- Wounds and burns infected with infection.
Numerous studies have revealed the active destructive effect of the product on the following bacteria and parasites:
- Gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, including salmonella. Consequently, the drug successfully fights intestinal infections, typhoid fever, paratyphoid fever, and salmonellosis.
- Shigella, which is the culprit of dysentery (we recommend reading: how is dysentery treated in children?).
- Giardia, parasites that live in the rectum and lead to a dangerous disease, giardiasis.
- Trichomonas, causing infection in the child’s genitourinary system.
Principles of treatment of rotavirus infection
To date, there is no specific medicine against the causative agent of the disease. For rotavirus gastroenteritis the following is used:
- solutions for oral rehydration (restoring water balance in the body) - Regidron, Gastrolit, Oralit;
- antiviral - Kipferon, Genferon, Arbidol, Tamiflu;
- enterosorbents - Activated carbon, Smecta, Enterosgel, Sorbex;
- antiemetics - Cerucal, Motilium, Metoclopramide;
- medications for diarrhea in case of rotavirus disease are prescribed with caution - Loperamide, Imodium, Uzara;
- probiotics - Lactobacterin, Bifiform, Linex, Acipol;
- enzymes for impaired digestion of food - Festal, Creon, Mezim.
Diet is important for rotavirus infection. Food for babies should be served boiled or baked, in fractional portions, excluding fried, spicy, smoked, fatty and sour foods. Porridges for rotavirus disease are prepared in water, without adding butter. You can eat meat, fish, white bread, vegetables from the oven. It is important not to forget about the drinking regime; fruit drinks, weak tea, jelly, and still water are recommended.
Indications for use
The active component of the medicine is a substance similar to the name of the drug, a derivative of nitrofurans, as well as a number of additional elements that help in the fight against the root cause of loose stools.
Furazolidone tablets for children with diarrhea will be effective if the problem is caused by the following factors:
- Worms, giardiasis.
- Rotovirus infection.
- Salmonellosis.
- Dysentery.
- Food poisoning.
- Disturbance of microflora.
- Inflammation of the gastrointestinal mucosa.
The list of indications is quite extensive, but despite the effectiveness of the drug, it should only be used under supervision and on the recommendation of a doctor.
Are antibiotics effective against rotavirus?
Rotavirus infection cannot be treated with antimicrobial agents, since the latter have a detrimental effect only on the bacterial flora. However, prescribing synthetic antibiotics will help prevent the development of another infection and speed up the healing process.
When should you take Furazolidone?
With rotavirus infection, symptoms of gastroenteritis (vomiting, nausea and diarrhea) usually bother a person for several days, then the symptoms gradually decrease. If a child’s diarrhea continues for more than 5–6 days, a bacterial infection should be suspected. In such situations, with rotavirus, the prescription of the synthetic antimicrobial agent Furazolidone is justified. An antibacterial drug from the nitrofuran group is active against gram-positive cocci and gram-negative bacilli, as well as protozoa. Furazolidone is practically not absorbed from the intestinal lumen, and resistance to the drug develops slowly.
The drug is approved for use in children over 1 year of age in an amount of 10 mg/kg body weight - this is a daily dose, which should be divided into three or four doses at equal time intervals.
The duration of use of Furazolidone for rotavirus infection should not exceed 10 days. If there is no positive dynamics of the disease, you should stop taking the medication and consult a doctor.
Furazolidone analogs
If for one reason or another it is not possible to use the medicine, on the recommendation of a doctor it can be replaced with substances similar in mechanism or composition.
Furagin and Furamag are analogues of Furazolidone in terms of their mechanism of action and belong to the nitrofuran antibiotic series. Approved for use for rotavirus infection in children from the age of three at a dose of 25–50 mg three times a day for a week. The drugs are classified as cheap analogues of Furazolidone.
Nifuroxazide is an intestinal antiseptic from the nitrofuran group, often prescribed for rotavirus infection. The drug is available in capsules and suspensions; it can be used by babies who have reached the age of one month. For rotavirus, the daily dose for children up to 2.5 years is 100 mg, and then 200 mg three times a day.
Furadonin is another analogue of Furazolidone from the nitrofurans, which is sometimes prescribed for intestinal infections. The medicine is not the drug of choice for rotavirus, as it is mainly indicated for inflammation of the urinary tract (uroantiseptic). Furadonin can be prescribed to infants from the age of one month at a daily dosage of 5–7 mg/kg body weight, divided into 4 times.
Enterofuril is a close analogue of Furazolidone with the active substance nifuroxazide, available in the form of a suspension (from 1 month of life) and capsules (after reaching 3 years). The drug is successful in treating rotavirus in young children due to the absence of serious adverse reactions.
Fthalazole is a synthetic antibiotic with antidiarrheal properties from the sulfonamide group, an analogue of Furazolidone in action. The drug can be prescribed to children with rotavirus disease from birth.
Furazolidone - contraindications
The attending physician is obliged to take into account all the characteristics of the patient’s body and warn about situations where the use of an antibiotic is undesirable or prohibited. All people with diseases of the nervous system and glucose-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency should take the pills carefully. Furazolidone contraindications include:
- cannot be used while breastfeeding;
- during pregnancy;
- under 3 years of age (tablets);
- in the presence of severe kidney or liver failure;
- hypersensitivity.
Precautionary measures
Before starting treatment with Furazolidone, it is important to carefully read the instructions for the medicine and study the recommendations given by your pediatrician.
In case of rotavirus pathology, the correctly selected dose of antibiotic also plays a significant role. In children, it depends on age and body weight.
Furazolidone should not be combined with the antibiotics Chloramphenicol and Ristomycin, which may impair the formation of blood cells. For rotavirus, nitrofuran should not be used together with ephedrine, tetracyclines and aminoglycosides.
Furazolidone for children
The drug is not prescribed until 1 year. Furazolidone for children should not be combined with other medications, for example, Chloramphenicol, Ristomycin may, when interacting with the drug in question, cause inhibition of hematopoietic function. It is forbidden to give a child Furazolidone and Amphetamine, Ephedrine at the same time. The antimicrobial activity of the drug substance increases when taken simultaneously with tetracyclines and aminoglycosides. The dosage of the medication should be prescribed by the attending physician.
Side effects
Furazolidone is a relatively harmless drug and does not pose a threat to the health of the baby. The antibiotic is not toxic, but is only capable of causing slight changes in the normal state:
- dyspeptic symptoms - loss of appetite, nausea with vomiting, abdominal pain;
- signs of anaphylaxis - skin rash, hives, swelling of the eyes, itching on the body.
To reduce the risk of developing adverse reactions from using Furazolidone, pediatricians advise giving the baby the medicine before meals and then washing it down with a glass of warm boiled water.
In case of pronounced consequences of treatment of rotavirus disease with an antimicrobial substance, the prescription of antiallergic drugs (Fenkarol, Suprastin), B vitamins with mandatory discontinuation of the drug is indicated.
Composition and release forms
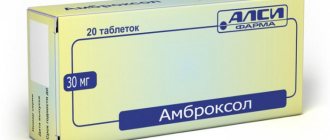
The drug Furazolidone contains:
- polysorbate, calcium stearate;
- lactose, sucrose;
- potato starch;
- 50 mg of the active substance furazolidone.
The list of ingredients and their concentration may vary slightly - they vary depending on the form of release of the medicine.
There are 2 types of funds:
- Furazolidone tablets. They resemble a flat cylinder, are made in yellow, sometimes turning into a green tint. Packaged in blister packs of 10 pcs, a cardboard pack can contain from 1 to 2 blisters.
- The granules used to create the suspension are placed in 150 ml glass jars. The kit includes a dosing cup with which you can dilute the drug with clean water.
The release form is selected depending on the preferences and age of child patients and the concentration of the nitrofuran derivative they need.
The content of furazolidone in granules is less than in tablets, so they are more often used to treat children.
What medications is the drug incompatible with?
The information is very important because Furazolidone is not compatible with some drugs. Let's list them:
- Ethanol. Association with this drug provokes acute intoxication, manifested by vomiting, headache, fever, nausea, problems with heart rhythm, and difficulty breathing.
- Antidepressants and monoamine oxidase inhibitors. If the baby takes a medicine with phenylephrine, which constricts blood vessels, simultaneous use of Furazolidone will cause a sharp increase in blood pressure.
- Antibiotics of the aminoglycoside group can enhance the antimicrobial effect of Furazolidone.
- Foods and medications that can alkalize urine. Entering the body along with Furazolidone, they accelerate the process of drug elimination, reducing its therapeutic effectiveness.