general description
First you need to understand what this disease is.
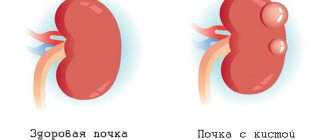
A maxillary sinus cyst is a formation that is pathological in nature. Cysts are located in the maxillary cavity. In the human body there are only two maxillary sinuses: right and left. They are covered with a special protective mucus. Sometimes it happens that these glands become clogged, causing them to become overfilled with mucus. The glands themselves stretch and turn into a ball-shaped tumor. This is what is commonly called a cyst.
The tumor contains fluid inside, which can be purulent or sterile. This will depend on the severity and duration of the disease. As a rule, cysts of the maxillary sinuses, the treatment of which should be carried out only after diagnosis by a specialist, are located on the lower walls. The severity of symptoms will directly depend on the location and size of the tumors.
What is and what does a cyst of the maxillary sinus mucosa look like?
A cyst of the mucous membrane of the maxillary sinus is a benign neoplasm. Localized in any nasal cavity, mixed development is possible. It contains fluid inside, which is a consequence of the inflammatory process. The maxillary sinus has thin and elastic walls and in appearance resembles a filled bladder. The neoplasm occurs when a special secretion from the gland does not pass correctly. Therefore, their stagnation occurs, areas of the sinuses become inflamed, stretched and expressed by some symptoms.
This is what a maxillary sinus cyst looks like
A maxillary sinus cyst (false cyst) has an ICD code of J33.8 or K09, depending on the location and form of development.
Classification and symptoms according to the ICD
The standard classification divides cystic formations in the sinuses of the upper jaw into 2 types:
- true - they are formed by the tissues of the nasal mucosa, such inclusions are localized in the maxillary sinus of the nose, in any of its sections, such neoplasms are characterized by the presence of a two-layer capsule;
- pseudo-formations are cysts that have grown into the sinuses of the upper jaw from other tissues. These can be odontogenic cysts, which are a continuation of gum formations, or inclusions, the development of which is provoked by the characteristics of allergic reactions. That is, these are any cystic tumors in the sinuses that have a different nature of occurrence. Maxillary sinus cysts of this type are characterized by the presence of a single-layer capsule and growth from the inferior sinus wall.
Depending on the affected area, the classification of neoplasms may be as follows:
- cyst of the right maxillary sinus;
- cyst of the left maxillary sinus;
- cyst of both paranasal sinuses.
There are two main types of pathology of the maxillary sinus:
- Odontogenic cyst of the maxillary sinus. It develops in the root of the tooth and is caused by various infections. This type is characterized by inflammation that is attributed to other problems occurring in the oral cavity. This type is very easy to diagnose, especially with radiographs.
- Retention cyst of the maxillary sinus. It consists of a two-layer wall lined with epithelium. Epithelial cells secrete mucus, which accumulates in the cyst cavity. This type of disease is usually detected on MRI.
Location of the pathology.
Types of pathology are also distinguished by location. A cyst is identified in the right maxillary sinus, a cyst in the left maxillary sinus.
In the ICD-10 disease classifier, this form is coded J01.0. It develops quickly, the first signs are detected after a few hours or days. The following symptoms are characteristic of acute sinusitis:
- severe pain occurs in the upper jaw, intensifies during movement or touch;
- moderate nasal discharge, depending on its nature, it can be clear or purulent;
- swelling of the cheek and eyelid on the side of the pathological process;
- general weakness, severe increase in body temperature;
- difficulty in nasal breathing.
In the early stages, some signs of intoxication may be observed - a feeling of nausea, vomiting and a change in appetite, which is associated with severe inflammation of the body. And with palpation (touching) or percussion (pressure) on the affected tooth, severe bursting pain occurs.
Chronic
It occurs more often than the acute form of sinusitis. It develops over a long time, the symptoms are mild. As a rule, the symptoms intensify in paroxysms against the background of thermal, mechanical or chemical effects. Typical symptoms:
- nasal congestion, poor sleep;
- swelling in the cheek area on the affected side;
- moderate pain when pressing on the tooth, while blowing your nose, or when bending over;
- constant weakness and decreased immunity;
- low-grade fever;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- bad breath.
In the disease classifier, chronic maxillary sinusitis has code J32.0. It is difficult to treat and can lead to serious complications.
According to WHO statistics, chronic odontogenic sinusitis is most often diagnosed between the ages of 20 and 35 years.
You may also be interested in what yellow snot in an adult means, you can find out at this link.
Indications and contraindications for endoscopic removal of a maxillary sinus cyst
The indication is a cyst that makes itself felt by the above symptoms.
Or simply a large cyst, since there is a possibility of its rupture, ingrowth into other anatomical areas, destruction of bone walls, etc. Contraindications:
- severe chronic conditions - diabetes, liver disease, kidney disease and some others;
- acute inflammatory diseases;
- oncopathology.
It is performed under general anesthesia, sometimes under local anesthesia. The technique is as follows:
- the assistant raises his upper lip;
- the surgeon cuts the gum, uses pliers to make a cut in the bone and penetrates the sinus;
- with the help of special instruments, the entire sinus is cleaned, the anastomosis is expanded;
- then the mucous membrane is sutured, but not the bone. This is an important point, its significance will be described below.
Advantages of the method:
- Low cost.
- Availability in all hospitals.
- We have accumulated extensive experience in performing the operation.
- Possibility of complete examination of the sinus.
Flaws
- Traumaticity.
- After the operation you need to stay in the hospital for about a week.
- Painful postoperative period.
- The use of anesthesia is contraindicated for certain categories of patients.
Possible complications
This is a rather difficult intervention and requires time and experience of the surgeon. The recovery period is long. Afterwards, complications such as persistent rhinitis and sinusitis are possible, due to the fact that the bone wall of the sinus is removed, so any infection can easily get into the maxillary sinus.
This is the most effective, simple and safe way. It does not damage tissue. Local anesthesia is administered using anesthetic drops in the nose. A special thin microendoscope equipped with a camera and an electric pump is passed through the nasal cavity. The surgeon receives an image of all structures on the monitor screen. Under video control, he penetrates the sinus with an endoscope and performs the necessary manipulations there.
Advantages of the method
- short preparation, as well as the postoperative period;
- the operation takes about twenty minutes;
- there are almost never complications or contraindications;
- bloodlessness and low invasiveness.
Flaws
- high price;
- The equipment is not available in all hospitals.
There are practically no complications; sometimes they occur when the surgeon is insufficiently experienced or when the patient does not comply with the doctor’s recommendations.
Microsinusrotomy
A type of endoscopic surgery is microsinusrotomy.
A puncture is made under the upper lip with a special needle and an endoscope is inserted into it. This method is used for large cysts. There are no complications compared to a radical incision of the walls as in the Caldwell-Luc operation. The advantages and disadvantages of the technique are the same as with conventional endoscopic surgery.
Taking pills or drops to treat a cyst in the nose is pointless - today there is no such miracle drug. But medical scientists are working to create a absorbable phytodrainage spray.
Advances in medical technology make it possible to treat benign tumors, which include cysts, with laser. The method is an alternative for people with respiratory failure and bronchial asthma.
The Internet is filled with folk recipes for treatment. Herbal drops, decoctions and inhalations actually relieve inflammation and improve breathing, but cannot treat a cyst. There are no folk remedies that remove a cyst.
Indications for surgical intervention to remove a cyst from the maxillary sinus using an endoscope are:
- Breathing problems
- Presence of a feeling of a foreign body in the maxillary sinus
- Frequent acute respiratory diseases
- Double vision
- Increased intraocular pressure
- Frequent headaches similar to migraines
- Purulent inflammation of the neoplasm
- Presence of swelling on one side of the cheek
Contraindications include:
- Cysts that have not manifested themselves over a long period of existence, have not begun to actively grow and do not cause discomfort
- Presence of any acute diseases
- Chronic diseases of the cardiovascular system
- Diseases of the liver, kidneys and other vital organs
- Epileptic disease
- Presence of malignant neoplasms
The cost of endoscopic removal of a cyst in the maxillary sinus varies from fifteen to thirty thousand rubles. The final price depends on the level of the clinic, city and qualifications of the attending physician.
Pricing policy for surgical intervention using an endoscope in major cities of the Russian Federation
| City | Price |
| Moscow | From 20 to 30 thousand rubles |
| Saint Petersburg | From 18 to 25 thousand rubles |
| Rostov-on-Don | From 15 to 22 thousand rubles |
| Novorossiysk | From 16 to 27 thousand rubles |
An operation to remove a cyst in the nasal sinus is carried out according to strict indications (if they are absent or the process is asymptomatic, the operation is not indicated):
- Persistent nasal congestion that is not relieved by typical methods.
- Severe headaches.
- Visual impairment (double vision, loss of visual fields).
- Swelling or severe deformation of the face. It occurs extremely rarely, only with large-sized cystic formations.
- Suppurative process. When a secondary infection occurs, typical symptoms of intoxication, pain, and a feeling of fullness in the sinus area occur.
- Size – more than 1.5 cm in diameter (indication for removal in English literature).
Surgical removal of a cystic neoplasm is contraindicated in the following cases:
- acute infectious processes in the body;
- diseases of the cardiovascular system in the stage of decompensation;
- diabetes mellitus type I in the stage of decompensation;
- blood clotting disorder;
- status epilepticus;
- malignant neoplasms.
The method is high-tech; its implementation requires special training (not possible in all clinics).
Endoscopic removal of the cyst is preferable, but not always possible
Causes and risk factors
The etiology of this disease is associated with various chronic inflammatory processes and congenital defects affecting the oral region or nasopharynx. The main reasons why a cyst may appear include the following:
- The presence of chronic nasal diseases, for example, rhinitis, sinusitis, sinusitis, polyps, sinusitis.
- Abnormalities in the structure of the nose, including an abnormal septum. Such an anomaly can disrupt the normal flow of air, as well as the blood supply to the entire mucous membrane in the nose. Such defects may be acquired or congenital.
- Prolonged exposure to an allergen. In particular, if these allergens have been located in the maxillary sinuses for a long time.
- Chronic dental diseases, as well as inflammation around the dental tissues in the upper jaw.
- Immunodeficiency state.
The main reasons for the appearance of formations
A cyst in the maxillary sinuses appears as a result of complete occlusion or significant problems with the outflow of secretions from the gland (which regularly produces mucus). In the international classification of the disease, a maxillary sinus cyst is classified as a retention disease.
The main reasons for the appearance include:
- inflammatory diseases of the nasal passage or paranasal sinuses;
- diseases of the teeth and upper jaw (this type of cyst is called odontogenic, which means “born by a tooth”);
- severe allergic sensitivity or reactivity of the body (especially when the allergen remains in the maxillary sinuses for a long time after inhalation);
- individual anatomical features;
- poor immune system (this factor has not yet been definitely proven by doctors).
The main etiological cause of the appearance of maxillary sinus cysts is sinusitis. This condition is usually provoked by an inflammatory process, leading to severe swelling of the mucous membrane. Such conditions are favorable for blockage of the excretory ducts and the formation of a large number of cysts in both the right and left sinuses. If sinusitis is detected, the doctor must conduct a radiological examination.
Causes
The upper part of the socket of 5-7 teeth of the upper jaw is also the lower wall of the maxillary sinus. With inflammation in this area, the tissues thicken, and blockage of the sinus anastomosis develops. This anatomical mechanism underlies the development of sinusitis; further infection occurs through the lymphogenous and hematogenous route. The following causes of the disease are identified:
- the presence of a cyst or granuloma in the upper jaw;
- periodontitis;
- illiterate treatment, prosthetics;
- complication after tooth extraction;
- osteomyelitis;
- trauma, mechanical damage.
Sinusitis caused by eruption of molars is considered dangerous. They have long roots that can grow into the wall of the sinus. This problem leads to chronic maxillitis, which is difficult to treat.
You may be interested in the information on how to relieve nasal congestion without drops, which you will learn about here.
A cyst of the upper maxillary sinus is formed due to blockage of the excretory glandular ducts located in the nasal cavity, most often this occurs against the background of sinusitis, sinusitis, polysinusitis and rhinitis of various etymologies, which have a chronic course. The following factors can provoke the growth of such capsules:
- curvature of the septum in the nose;
- carious teeth in the upper jaw, which are a source of constant infection;
- inflammation of the tissues inside the tooth (pulp);
- polyposis;
- broken bite and drooping hard palate;
- allergic reactions;
- personal features of the constitution of the maxillary cavities and facial symmetry.
Cyst of the maxillary sinus is a fairly common benign neoplasm. It primarily occurs when the glandular ducts are blocked.
Since in every person the mucous membrane of the nasal cavity has glands that synthesize secretions throughout life, the development of a maxillary cyst is possible. Because every gland has its own ducts that extend to the surface of the paranasal sinus. Under the influence of frequent inflammatory processes and infectious diseases, the mucous layer begins to thicken and the ducts become clogged, further causing the formation of cysts.
In addition, the causes of neoplasm of the maxillary sinus can be:
- Chronic pathological conditions of the nose (sinusitis, rhinitis, etc.).
- Violation in the structure of the nasal septum. It occurs infrequently, contributes to a decrease in nasal breathing function, and the mucous membrane has insufficient blood supply. May be congenital or acquired.
- Long-term influence of the allergen.
- A strong decrease in the immune status of the body.
- Dental diseases, various inflammatory processes of the tissues of the upper jaw.
- Accumulation of large amounts of lymph in the lymphatic vessels due to acute respiratory viral infections, influenza, and allergic reactions.
Carrying out the operation
There is no specific size of cyst for removal from the maxillary sinus. Everything is individual. Surgery is important to eliminate severe neoplasms. Such a cyst can significantly decrease in size if a puncture is performed, during which its contents are eliminated through a puncture. But the disease will still remain and will begin to appear again over time.
If the formation significantly increases in size, it can completely block the access of air to the cavity of the maxillary sinus, and also worsen the condition of the blood vessels. In this case, the doctor prescribes surgical intervention, since it is impossible to cure such a formation with the help of medications.
The quality of the procedure performed will directly depend on the following factors:
- type of pathogenic formation in the nasal cavity, its size;
- the surgeon’s experience and education;
- using high-quality and modern equipment.
There are several ways to remove a maxillary sinus cyst. Efficiency has been proven by many years of practice. Judging by the reviews, removal of a maxillary sinus cyst has positive results.
How to avoid getting sick?
Before referring the patient for diagnosis, as well as prescribing appropriate treatment for a maxillary sinus cyst, the specialist must verbally interview the patient about any symptoms of this disease. As mentioned earlier, this disease most often occurs without any symptoms and is discovered completely by accident during a medical examination or general examination of the body.
These symptoms include the following:
- Pain in the sinus area, which intensifies when the head is tilted down.
- The appearance of a feeling of heaviness, as well as pulsating pressure near the eye socket.
- Pain in the cheek, radiating to the teeth.
- Viscous mucus that constantly flows down the back wall.
- Facial asymmetry.
- Swelling of the cheeks.
- Attacks of headaches, as well as migraines.
- Discomfortable sensations in the forehead area.
- Nasal congestion on the side where the cyst is located.
- Symptoms of intoxication.
With this pathology, in some cases, symptoms such as double vision and blurred vision appear. This happens because the eyeballs begin to shift and their mobility is limited. In these situations, patients go not to an ENT specialist, but to an ophthalmologist. In some cases, a cyst of the maxillary sinus, the treatment and causes of which we discuss in this article, does not manifest itself in any way, and the main symptoms will be visual disturbances.
In the field of medicine, there is a separate classification of formations on the maxillary sinuses. A cyst of the left or right maxillary sinus can be of the following types: mucocele with mucous contents, hydrocele with serous fluid, and pyocele with purulent contents.
In addition, based on their origin, these neoplasms are divided into three types. Let's look at them separately.
One of the preventive measures for this disease is timely sanitation and treatment of oral diseases. This is due to the fact that in most cases they are odontogenic in nature. In addition, in order to avoid the development of such anomalies, competent therapy for sinusitis, chronic rhinitis and other nasal diseases helps.
If you have symptoms of a maxillary sinus cyst, it is better to immediately use surgical intervention so as not to suffer from possible complications in the future.
Remember that the final decision on the treatment of the disease is made only by a doctor who understands all the features of the pathological process and concomitant human diseases.
Main symptoms of damage
The main reason for the accumulation of thick mucus in the nasal cavity and the appearance of a cyst in it is sinusitis. If a person has a deviated nasal septum or other problems in the structure of the jaws, palate, or maxillary sinuses, then he is at particular risk. In this case, radiography or MRI is used to identify the cyst.
The formation is often discovered by accident, since as long as the sinus cavities are not clogged, the patient does not feel any unpleasant symptoms. As the cyst increases in size, it can cause the following unpleasant symptoms:
- pain spreading in the eye area: when you tilt your head, the pain only gets worse;
- pain in the temples and forehead;
- feeling unwell, worsening condition;
- nasal congestion, in some cases only in the nostrils;
- swelling of the nose;
- thick discharge of pus from the nose;
- feeling of mucus running down the back of the throat;
- frequent and prolonged colds.
If the cyst has managed to grow to a large size, the patient complains of the following problems:
- pronounced facial asymmetry;
- displacement of the eyeball;
- pain in teeth and gums;
- pressure in the eyes and nose.
The cyst itself provokes the appearance of the same symptoms as sinusitis. A small formation can lead to serious complications and endanger the life and health of the patient. But if the size of the formation begins to increase, the doctor will prescribe a mandatory operation to remove the cyst in the maxillary sinus. If the symptoms of the disease are ignored, the patient may experience the following complications:
- meningitis;
- sepsis;
- deformation of the facial structure;
- vision problems;
- necrosis of bone tissue.
If the tumor in the maxillary sinuses has become too large and causes discomfort, then it is important for the patient to undergo surgery to remove the maxillary sinus cyst. Rehabilitation after surgery to remove a cyst does not last long. The cost of the operation varies from 5,000 to 20,000 rubles, depending on the chosen method.
In reviews of the removal of maxillary sinus cysts, patients note the safety and painlessness of the procedure. In case of surgery, the doctor removes all the mucus and phlegm accumulated in the sinuses. The maxillary sinus cyst goes away after the operation, there is no previous discomfort, and the risk of complications in the future is reduced.
Symptoms of pathology
The manifestations of symptoms with a maxillary sinus cyst are not always associated with the size of the capsule, as is the case with tumors in other organs and systems. Large capsules on the upper wall may not show any signs of their presence, while small cysts on the efferent anastomosis, on the contrary, can cause severe pain in the head or teeth.
Symptoms of maxillary sinus cysts may manifest themselves more intensely when acute inflammation occurs, for example, due to an exacerbation of a chronic disease.
One of the main symptoms is a stuffy nose. If a tumor has formed in one of the sinuses, then discomfort and breathing problems will only occur in one nostril; if both sinuses are affected, the person cannot breathe through the nose at all. This situation is possible only when the neoplasm has grown greatly and filled the entire space of the sinuses. At the same time, mucus flows from the nose, the patient suffers from ENT diseases more often, they are more severe and last longer.
Half of the patients who are subsequently diagnosed with a sinus cyst complain not only of nasal congestion, but also of headaches in the area of the eye and temples. In swimmers who dive to depth, this symptomatology may intensify. The headache can be constant and periodic, often this can be a reaction to a stressful situation or climate change. Additionally, dizziness may occur.
The patient may also complain about other unpleasant manifestations of this pathology:
- discomfort and feeling of an extra object in the maxillary area;
- mucus or drainage of pus in the throat;
- pain in the eye area and cheek area, usually one-sided pain;
- increase in temperature;
- nasality occurs;
- partial or complete loss of sensitivity to odors.
The mechanisms of pathology formation have been sufficiently studied by science and doctors have a detailed understanding of all tissue transformations under the influence of probable causes. A true cyst of the maxillary maxillary sinus can form as a result of a deviated nasal septum and an inflammatory process (sinusitis). In both the first and second cases, an obstacle arises to the outflow of the mucous secretion of the glands, which causes the formation of a tumor.
False neoplasms occur when granulomatous tissue grows due to dental diseases.
The probable causes are supplemented by predisposing factors, which include allergic processes and inflammation, infections and metabolic disorders, hypovitaminosis, and immunodeficiency.
The cyst makes breathing difficult as it grows in the respiratory canal. Baggy growths can cause irreversible deformities of the palate, nose and maxillary sinuses. Various additional diseases associated with the formation of a maxillary cyst:
- Kartagener's syndrome;
- Young's syndrome;
- Nasal mastocytosis.
Symptoms of the disease
Symptoms of the disease.
Maxillary sinus cysts are quite rare. It is discovered by chance, after a CT scan, MRI or x-ray for another reason.
At a certain location and large enough size, this formation begins to cause great discomfort. What can indicate its presence?
First of all, the patient will experience the following symptoms:
- a feeling of fullness and pain in the area where the cyst is located;
- mucous discharge from the nose and its constant congestion;
- headache. They can constantly torment the patient or occur periodically under the influence of climatic conditions;
- breathing disorder. Impaired breathing on one or both sides simultaneously affects the quality of sleep.
Important! The cyst may spontaneously rupture. In this case, nasal discharge appears, which is colored orange. This is exactly the shade of the liquid that was in the cavity. There is no need to be afraid; this feature does not cause any harm to health.
Sometimes inflammation may occur, accompanied by suppuration.
At the same time, new symptoms are added to the ones described above:
- increased body temperature;
- runny nose with purulent discharge;
- pain in the cheeks, eyes and teeth;
- weakness and intoxication of the body.
Important! The size of the formations does not always influence the severity of the clinical picture. For example, a large cyst located on the lower wall may not manifest itself for a long time, while a small one located in the anastomosis area, on the contrary, causes severe toothache and headache.
Diagnostic methods
The masses can be seen on physical examination and are often detected when assessing symptoms. Nasal endoscopy involves inserting a small camera with a light source into the nose. The image is projected onto a screen so that the doctor can examine the maxillary sinuses in more detail. The procedure is usually not painful, but the patient may be given a local anesthetic to minimize discomfort.
An MRI will show hidden lesions that cannot be fully appreciated by physical examination alone.
Computed tomography can provide more complete information about the disease. It will show hidden formations that cannot be fully assessed by physical examination alone. Imaging is also required for surgical treatment planning. On CT scan, the cyst usually has a color attenuation of 10-18 Hounsfield units, which is similar to the consistency of mucus.
Other disorders may mimic a cyst in the maxillary sinus, making diagnosis difficult. Examples include glioma, inverted papilloma, and cancer. Early biopsy is recommended for unilateral nasal polyps to rule out more serious conditions such as cancer, inverted papilloma, or fungal sinusitis.
There are currently no methods to prevent maxillary sinus tumors. It is necessary not to be exposed to inflammatory and infectious diseases of the nasal cavity, which serve as the cause for the formation of the disease.
Obstetrician-gynecologist, endoscopic surgeon
More articles
The diagnosis is established on the basis of anamnesis after the implementation of diagnostic methods. For this purpose the following may be prescribed:
- X-ray. In the picture, the cyst looks like a rounded protrusion located on the wall and has clear, smooth contours. This method detects only large tumors.
- Puncture. If during the puncture the specialist receives an orange specific liquid, this indicates a diagnosis. This method is very inaccurate, since the doctor can puncture the protrusion only if the cyst is large.
- CT scan of the maxillary sinus cyst. This method is the most reliable, as it allows you to assess the internal structure of the problem area and determine the presence of pathology.
- Sinusoscopy. An endoscope is inserted into the cavity through the excretory anastomosis or a special hole, allowing you to study in detail the presence of a pathological process in this area, as well as, if necessary, carry out treatment and biopsy.
If it is, it means that the person may have chronic problems with the respiratory system and teeth. Diagnosis of a cyst in the space of the upper jaw is most often carried out using an x-ray, which can be directed by an ENT specialist or dentists. An x-ray can reveal the presence of a large cystic inclusion.
The best results are obtained by magnetic resonance and computed tomography. MRI and CT can establish the exact location of the tumor, the thickness of its capsule and its internal structure. These methods are used for advanced stages of pathology; they make it possible to determine the method in which surgical intervention should be performed.
To clarify the diagnosis, the doctor may prescribe a puncture, during which a puncture is made in the cystic capsule and its contents are pumped out. If the liquid has a specific orange tint, the pathology is confirmed. This is an unreliable diagnostic method, since it only detects large formations that may get in the way of the needle.
One of the most informative diagnostic measures is endoscopic examination - sinusoscopy. It is carried out using a special video device, an endoscope, which is inserted through the excretory anastomosis into the nasal cavity. During the study, an additional biopsy or treatment may be performed. Sinusoscopy allows you to detect polyps in the maxillary sinuses and other pathologies, including cysts.
Typically, treatment of a maxillary sinus cyst is carried out as planned without emergency intervention, but in each specific case, what to do is determined only by the attending doctor, based on the general condition of the patient, the degree of relapse of the disease and the presence of concomitant diseases.
If the tumor is initially small, the advice of ENT doctors boils down to wait-and-see tactics; during observation, it is necessary to determine the rate of growth of the tumor and the nature of the changes occurring in it. Also at this time, additional examinations are carried out, and further treatment tactics are determined.
If an odontogenic cyst is diagnosed, which is a continuation of a tumor in the tooth, then there is a high chance that it can resolve after healing from dental problems. In some cases, additional drug treatment may be recommended.
In any case, only the attending physician can definitely say how to treat a cyst in a given case. If surgical intervention is prescribed, it is impossible to carry out it without first eliminating the inflammatory process. The course of anti-inflammatory therapy will include the following groups of medications:
- saline solutions for washing sinuses;
- medications that help improve the flow of mucus from the sinuses;
- topical corticosteroids;
- antibacterial agents for local and systemic use;
- vasoconstrictors.
The surgical procedure for a GP cyst will depend on the size of the cystic cavity and its location. Surgical intervention is prescribed when the tumor significantly worsens the patient’s life, and specific dimensions for the operation are not established.
Currently, patients can undergo the following types of interventions:
- Denker's maxillary sinusotomy. During the operation, access to the growth is made through the front wall. This method can remove cysts even in hard-to-reach locations. This is the only type of surgery that can remove a tumor on the posterior wall of the maxillary cavity;
- endoscopy. Endoscopic removal does not involve any wounds; an endoscope is inserted through the anastomosis, and all manipulations are performed as painlessly as possible in no more than an hour. This technique does not cause complications, does not damage the maxillary sinuses and does not lead to the development of inflammatory processes;
- puncturing. The puncture is done with a thin needle, which is inserted into the nose and pierces the sinus. This is only a temporary measure that helps to suck out the contents of the cystic capsule, but does not remove its walls. Gradually, the tumor fills up again and begins to cause uncomfortable symptoms to the patient.
ethnoscience
To do this, you can use the following recipes:
- 3 drops of aloe juice are instilled daily into the nose on the side of the affected sinus; the juice should not be concentrated, it is better to dilute it with water;
- take cyclamen roots, grate them, squeeze out the juice, then dilute with enough water. Use the resulting drug to instill 3 drops into the nasal passage on the side where the cyst is located;
- you can perform inhalations using essential oils;
- You can eliminate headaches with the help of black radish juice, you need to instill it in 5 drops. into the nose three times a day;
- combine strong tea leaves, eucalyptus and honey in equal parts, bury the resulting mixture in your nose, 1 drop three times a day;
- You can rinse your nose with an onion-honey mixture. To prepare it, a large onion is grated into a paste. Add 1 tablespoon to a glass of hot boiled water. honey and the resulting onion porridge. The drug is infused for 5 hours, strained and the nose is washed with this mixture twice a day;
There are some traditional medicine drugs that can be taken orally to relieve the symptoms of cystic formation:
- medicinal infusion. Rose hips, lilac inflorescences, wheatgrass and horsetail are mixed in equal proportions. 2 table. lie the resulting collection is poured with boiling water overnight. Take up to 5 r. per day, before use, dilution with water is allowed;
- Grape and aloe juice, as well as honey, are mixed in equal proportions. The resulting drug is taken 1 tsp. before eating;
- A tincture of alcohol or vodka is made from nut shells and taken on an empty stomach, 1 tablespoon.
The use of any folk remedies must be coordinated with your doctor, since their improper use can cause allergic reactions, poisoning, activation of the inflammatory process, or incompatibility with other medications.
Odontogenic sinusitis is at the intersection of the interests of dentistry and otolaryngology. If you suspect this disease, you should first contact a therapist; after collecting an anamnesis, he will refer you to the necessary specialized specialist. The following methods are used for diagnosis:
- radiography of the paranasal sinuses;
- SCT and MRI, CT;
- Orthopantomogram (OPTG) to identify the localization of soft tissue inflammation.
Operation Denker
The Denker operation is a procedure that is not particularly different from the Caldwell-Luc operation. This method is also considered quite outdated and is performed under general anesthesia. During the Caldwell-Luc procedure, an incision is made in the upper jaw under the lip. Denker's operation is characterized by an incision through the frontal facial wall. All other actions will be the same.
This method of removing a cyst from the maxillary sinus is chosen when the formation requires radical intervention, for example, when it forms on the back wall of the sinus. In this case, only Denker’s operation allows free manipulation and complete elimination of the formation. Of course, such a procedure is quite traumatic. Its main disadvantages include the following:
- general anesthesia is used;
- the patient is in the hospital for seven days until his stitches are removed;
- the rehabilitation period can last for a month;
- swelling on the face, bleeding, discomfort on the lips and gums;
- problems in the sinus wall.
The main advantages of the procedure include:
- easy access to the cyst, good overview;
- during the procedure, you can remove not only the cyst, but also eliminate part of the mucous membrane in which a large number of harmful microorganisms have accumulated;
- the procedure can be carried out in any public clinic - there is no need to look for hospitals with special expensive equipment.
Most often, Denker's operation is the only method to eliminate a large cyst in the maxillary cavity. Doctors advise removal of the maxillary sinus in Moscow.
Maxillary sinus retention cyst or false structures
This tumor is formed due to obstruction of the excretory gland, which produces mucus. This obstruction can be caused by swelling, scarring, or hyperplasia or blockage. However, the gland continues to work and produces mucus. Over time, the walls begin to expand, and the entire space fills, closing the gap.
Location of sinuses
There are true and false cysts of the maxillary sinuses. True cysts are formed when the excretory duct of the gland in the mucous membrane of the nasal passages and sinuses is blocked. The secretion of the gland (mucus) constantly accumulates without an outlet and a capsule of epithelial tissue forms around it. This is the so-called retention cyst of the maxillary sinus, which gradually increases and fills the space of the maxillary sinuses. Usually, cyst blockage occurs with long-term and poorly treated chronic sinusitis.
False cysts of the maxillary sinus are formations from other tissues. Most often they are of dental origin and develop from fibrous or bone tissue, and can also be presented in the form of cholesteatomas, or keratocysts containing cholesterol crystals, horny structures and epithelium. Predisposing factors in this case are chronic periodontal inflammation, caries, and severe chronic diseases.
Progress of cyst removal using an endoscope
Endoscope
During endoscopic removal of a cyst in the maxillary sinuses, I use a device - an endoscope. It consists of a flexible tube and a video camera built into the end, capable of transmitting an image to a monitor screen. During surgery, the doctor sees the whole picture and monitors the progress of the surgical intervention.
With the help of an endoscope, any operation is carried out with millimeter precision. The risk of bleeding and damage to large vessels is reduced and makes even the most serious surgery safer. During the initial examination, it helps to accurately determine the location of the benign neoplasm and step-by-step think through the tactics for removing the cyst.
- When performing an operation using an endoscope, the operating specialist penetrates to the location of the cyst through the natural anastomosis.
At this point, the maxillary sinus joins the entire nasal cavity. Endoscopic removal of a maxillary sinus cyst through a natural anastomosis - If it is not possible to reach the tumor in this way, the doctor can make an additional puncture or incision if necessary.
Endoscopic removal using hole drainage
Having reached the cyst, using surgical instruments, the specialist cuts it off under the full control of an endoscope. Then the tumor is removed through the anastomosis. Surgery is performed under local anesthesia. If the patient has contraindications to its use, the anesthesiologist administers general anesthesia.
There are a number of advantages when using endoscopic equipment to remove cysts in the maxillary sinus:
- The surgical intervention lasts no more than thirty minutes
- The operation is carried out with low pain sensations
- There is a short recovery period following the surgical procedure.
- The tissue where the tumor was located remains healthy
- Safe cyst removal
- Breathing returns to normal immediately after surgery
- Mucus comes out of the sinuses better
- Sense of smell returns
- The operation can be performed on an outpatient basis
- After surgery there are no external signs of surgery, scars, incisions, etc.
On the appointed day of surgery to remove the cyst using an endoscope, the doctor explains the course of the upcoming procedure and places the patient on the floor in a supine position.
Progress of surgical intervention:
- The nasal passages of the nose are treated with a gel with an anesthetic.
A cyst is removed from the maxillary sinus. - Vasoconstrictor drops are instilled into the patient's nose.
- Using a reusable syringe and a sterile needle attached to it, the mucous membrane of the nasal passages is injected with ultracaine
- The endoscope tube is inserted through the lower or middle passage of the nose
- It enters the sinus through the anastomosis, which must be expanded using surgical instruments
- When the endoscope enters the sinus, under control visible on the monitor, the doctor punctures the cyst, then cuts it off from the mucous membrane at the base and completely removes it
- If necessary, a specialist can make an incision from the side of the oral cavity, above the upper row of teeth, and remove the cyst from the resulting hole.
- After removal of the tumor, the nasal passages are subject to tight tamponade
- The removed cyst is sent for bacteriological analysis
- After the operation, the patient spends an hour and a half in the hospital department or in the treatment room under the supervision of medical personnel. After this time, if there are no complications, he is sent home for a further rehabilitation period.
What is the threat and what can it lead to?
It is important to know why a cystic tumor in the cavities of the upper jaw is dangerous and what complications it can provoke.
Even if the capsule remains intact, it can cause complications and deteriorate the patient’s quality of life. When it grows and occupies the entire sinus in the upper jaw, this leads to difficulty breathing through the nose and to the following equally serious consequences:
- severe pain in the head;
- spasm of blood vessels, including cerebral vessels;
- reduced oxygen content in the body, which is fraught with complications for expectant mothers and their fetus;
- development of heart and vascular diseases;
- breathing may stop during sleep;
- the image before the eyes may double;
- the patient's general well-being worsens.
The pressure inside the skull may also increase, the body temperature rises, and inflammatory processes spread to nearby tissues, which in an old state leads to necrotization of the bone.
Preventive measures
A cyst in the maxillary sinus appears as a result of complications from diseases of the nose and nasopharynx. To avoid this condition, it is important to carefully monitor your health and begin timely treatment for colds, runny nose and sinusitis. You should not put off visiting the dentist.
Simple caries can provoke the appearance of pulpitis or suppuration. If the patient is concerned about chronic diseases, then it is important to keep them under control and prevent complications. If there is a deviated septum, it is important to correct this problem. If there are polyps in the nose, they are removed. To prevent cysts you need:
- exercise;
- Healthy food;
- regularly ventilate the room;
- to harden;
- avoid stressful situations.
If a cyst does occur, you should immediately seek help from a doctor and carefully monitor the treatment process. If discomfort or discomfort occurs, it is important to remove the cyst immediately.
Odontogenic cyst
An odontogenic cyst of the upper jaw, that is, a cavity that is formed from tooth tissue, is a false form. It is usually located in the lower parts of the maxillary sinus and is formed during dental disease from follicle tissue.
By location, lesions are identified on the left and right sides, as well as:
- Incisive foramen (nasopalatine);
- Radicular;
- Follicular;
- Retromolar;
- Nasoalveolar;
- Globulomaxillary.
The most common form of all types of cysts of the upper and lower jaw is radicular. It is formed from the structures of the tooth root after an inflammatory process with the formation of granulomas. Usually its size does not reach more than 1 cm, but sometimes large ones are found - up to 3 cm. It is thin, consists of fibrous tissue in which plasma cells and lymphocytes are found, and is lined inside with multilayered epithelium. The inflammatory process leads to hyperplastic processes with the development of processes directed into the capsule.
When the epithelium is completely melted, the formation cavity can be completely filled with granulomatous tissue. Such neoplasms tend to suppurate and can cause destruction of adjacent bone tissue and bone plate. Xanthoma cells and cholesterol crystals may be found inside the cavity. The location of radicular cysts can lead to displacement or growth into the maxillary sinuses.
Nasoalveolar occurs at the junction of the upper jaw and nasal bones at the border of three processes (nasal, frontal, maxillary). Such a tumor forms in soft tissues and can be lined with any type of epithelium: flat, cylindrical, transitional, cubic.
The incisive canal cyst, with gradual growth, destroys the palatine bone and can be lined with flat or cylindrical epithelium.
Follicular arises from the enamel of underdeveloped incisors, molars and premolars and may include one or more tooth germs or formed teeth. Its thin capsule consists of squamous stratified epithelial cells.
Globulomaxillary - forms between the canine and lateral incisor, grows slowly and can grow into the nasal cavity or upper jaw. The fluid contains cholesterol crystals, and the cavity is lined with flat, columnar or cubic epithelium.
Such neoplasms form at the inflamed tooth root; they are filled with pus. They are divided into radicular and follicular. Follicular ones are formed in children from the follicles of baby teeth that are inflamed. Radicular ones form at the very root of the tooth affected by caries. After this, it breaks through the bone jaw tissue and thus enters the sinus.
How to remove a cyst in the maxillary sinus using an endoscope?
This type of intervention is one of the classic options for removing large cysts (Caldwell-Luca operation).
Anesthesia: local or general. It is better to use endotracheal anesthesia; with it the patient does not experience any discomfort.
Technique:
- Position – lying on your back with a cushion placed under your neck, head thrown back.
- Using a scalpel, the gum tissue in the vestibule of the mouth is cut layer by layer, the incision is 1-2 cm below the transitional fold.
- The mucosa and periosteum are separated from the bone structures of the upper jaw.
- Using a chisel, trepanation of the bone is performed, exposing the sinus. The hole in the bone is expanded to 1.5-2 cm.
- All altered tissues and the cyst itself (granulation, liquid) are removed from the sinus.
- A hole of no more than 1 cm is made in the area of the medial wall of the sinus (lower nasal meatus). The sinus will be tamponed through it (the tampon is moistened in an iodine-containing substance). The tampon is removed after 24 hours.
- The wound is sutured in layers and tightly. Everyday dressings are indicated.
The operation is traumatic and requires a long healing period (3-4 weeks). Refers to radical operations, since all components of the cyst are removed (wide access ensures adequate sanitation of the cavity).
The use of laser is considered the most modern surgical method of all. The equipment consists of a thin flexible wire at the end of which there is an LED. The essence of the treatment is to cauterize the walls of the cyst using high thermal laser energy.
The method has the following advantages:
- minimal blood loss;
- painlessness;
- minimum duration (10 minutes on average);
- minimal risk of relapse.
Negative sides:
- It is not suitable for everyone, since it requires a superficial location of the cyst (directly near the walls of the sinus); if the formation is localized somewhat deeper, the effect of treatment will not follow.
- Large neoplasms require a more radical approach to treatment (endoscopic or open method). In this case, the laser does not affect all tissues of the cyst (small diameter of action).
At the moment, it does not apply to universal methods of treatment; its use is permissible only for small lesions.
Endoscope
Are there effective methods of prevention?
For a long time, the pathology can develop without any symptoms; in some cases, it may gradually decrease in size, until it disappears completely.
At the moment, there are no specific preventive measures that could protect a person from the development of cysts in the cavities of the upper jaw, so doctors recommend, if possible, timely treatment of all diseases of the nasal cavity - sinusitis, rhinitis, sinusitis, etc. Some experts consider allergic reactions to be one of the main factors in the occurrence of cystic capsules in the nose, which means their occurrence should be avoided if possible.
Possible complications after surgery
Any surgical intervention always carries certain risks. The patient must understand that even a professional cannot guarantee 100% success during the operation. After surgery, there is a risk of the following complications:
- heavy bleeding;
- accumulation of pus;
- sinusitis;
- otitis;
- meningitis;
- damage to the nerves (infraorbital or trigeminal).
The rehabilitation period after removal of a cyst in the maxillary sinuses continues for several weeks. It is important to clean the stitches and rinse the sinuses daily. The treating specialist also prescribes antibiotics, antihistamines and painkillers. The stitches are allowed to be removed after a week. The rehabilitation itself can last a month.
Features of therapy
So, we have discussed the symptoms, types and causes of maxillary sinus cysts. Treatment will only be carried out surgically. In this case, such manipulation cannot be avoided. Neither physiotherapeutic measures, nor heating, nor any medications can eliminate the cyst of the left maxillary sinus or the right. In addition, physiotherapy is contraindicated, as the disease can develop into extensive sinusitis.
There is no specific size of a maxillary sinus cyst that suggests its removal. Indications for surgical intervention are the presence of complaints and complications in the patient. Surgery for maxillary sinus cysts is carried out in any clinic specializing in this. In public clinics this is done absolutely free.
In private medical institutions, removal of a retention cyst of the maxillary sinus, as well as its other types, will depend on certain conditions. As a rule, the cost of such an operation is about 40 thousand rubles. However, before this, the patient must undergo some diagnostic measures described above.
Laser removal of a cyst in the maxillary sinus
Laser for cyst removal
Cysts in the maxillary sinus can be removed using laser radiation. This method is less effective than endoscopic removal of tumors. In order to get to the cyst, it is necessary to puncture the sinus.
The temperature of the laser beam can reach up to three hundred degrees Celsius. The radiation diameter is six hundred microns. To eliminate a cyst of even the smallest size, you will have to work with laser equipment for quite a long time. In some cases, the beam cannot penetrate to the localization of tumors at all.
During surgery using laser equipment, the patient feels pain from the procedure. When the cyst is set on fire, an unpleasant, burning smell emanates from it.
Postoperative period
After removal of a cyst or mucocele of the nasal sinuses, the patient should be monitored in the hospital for several more days. Depending on the intervention methods, the patient may experience swelling, pain and discomfort. If necessary, drainage is installed and painkillers are prescribed. In some cases, patients develop a fever.
Classic surgery is very traumatic, which is why specialists have recently given preference to endoscopic techniques and microsinlusrotomy.
Contraindications
Laser surgery is suitable for most patients with formations in the maxillary sinus. It is prohibited to carry out it only when:
- epilepsy;
- diseases of the heart and blood vessels;
- pregnancy and lactation;
- detection of malignant tumors;
- poor blood clotting.
These contraindications are common for all types of interventions. You also need to understand that removing a cyst using a surgical laser is a full-fledged operation that requires preparation.
Treatment with home remedies and medicines
If a person does not have any symptoms of the disease, then they can simply be observed over time. In such situations, they engage in therapy with folk remedies and medications, for example, Sinuforte is effective. Before use, be sure to read the instructions for use of Sinuforte. Reviews about the price of this drug indicate that it justifies its high cost. To purchase it you will have to pay 2500 rubles. average.
As for traditional medicine recipes, a maxillary sinus cyst can be treated in the following ways:
- Mix one spoon of vegetable oil with six drops of freshly squeezed aloe juice. Use the resulting product to instill a whole pipette into your nose 3 times a day for a month.
- Cyclamen drops have also proven themselves in the fight against this disease. You can make them yourself at home or purchase them ready-made at the pharmacy. After using them, the patient actively sneezes and blows his nose. This causes the walls to rupture, allowing fluid to leak out of the nose.
Please note that if you use traditional medicine recipes for therapy, there is a risk of developing an allergic reaction and some side effects. If signs of the disease begin to bother the patient, his chronic inflammation has worsened, then this becomes a reason for surgical intervention.
As mentioned earlier, no drug can completely rid a patient of the disease. The drugs only suppress the symptoms, but the consequences of the disease always remain.
Endoscopic surgery
Endoscopic removal of a maxillary sinus cyst has its advantages compared to other types of surgery:
- the operation is performed not through an incision, but directly through the nasal sinus;
- after the operation, the patient is left with no visible scars or incisions;
- the procedure takes a little time;
- after the operation, the patient’s condition quickly returns to normal, and the rehabilitation period does not last long;
- local anesthesia is used;
- hospital stay lasts no more than 4 days;
- there is a small one that quickly disappears;
- There are no adverse reactions.
Before surgery, the patient is prohibited from eating for seven hours and drinking for two hours. Endoscopic removal of a maxillary sinus cyst is performed under local anesthesia. In rare cases, specialists use general anesthesia. The operation time is approximately 30 minutes. The puncture diameter is minimal - only 5 mm.
An endoscope is inserted through the puncture and the maxillary cyst in the maxillary sinus is removed. The procedure is monitored by the doctor on the monitor. The cost of such an operation varies from 10,000 to 20,000 rubles. The price includes hospital stay and collection of all necessary tests. Removal of a maxillary sinus cyst in Moscow may cost more. It all depends on the choice of clinic.
After removal of the maxillary sinus cyst, the patient should be observed every month by an ENT specialist. The specialist prescribes medications that will help the patient’s body recover quickly. During the recovery period, the patient is prohibited from eating hot, spicy, smoked or too cold food. It is prohibited to visit the swimming pool, bathhouse and sauna. It is recommended to spend time in a medical sanatorium.
How are they treated?
Treatment directly depends on the size of the tumor. If the cyst is small in size and the disease has not progressed, it may be quite sufficient to instill and rinse the nose. However, such measures do not radically solve the problem, but only reduce the severity of symptoms.
There are three main methods of eliminating cysts through surgery:
- Endoscopy. The safest procedure with minimal risk of complications in the postoperative period. It is performed using an endoscope under anesthesia. After the procedure, the patient is sent home on the same day.
- Denker's method. Consists of trepanation of the anterior section of the maxillary sinus. The method is traumatic, but effective in the presence of complications. After the procedure, a course of antibiotics is prescribed.
- Caldwell-Luc method. During the operation, a tissue incision is made above the upper lip, after which the sinuses are opened and the cyst is removed. The disadvantages of the method are: trauma, the appearance of scars that provoke rhinitis and sinusitis in the future, and a long recovery period after surgery.
Causes of maxillary cyst
The appearance of cysts in the maxillary sinus is provoked by chronic inflammatory processes or congenital defects in the nasopharynx or oral cavity. The main reason for the development of the disease is due to the fact that the excretory duct of the gland, which secretes a specific secretion, is clogged.
The causes of the formation of maxillary cysts include:
- Chronic nasal pathologies: sinusitis, sinusitis, rhinitis, polyps and similar ailments.
- Anomalies in the structure of the nose or septum, as a result of which the air flow is disrupted and disruptions occur in the normal blood supply to the mucous membranes. Defective changes can be congenital - in this case, a hereditary predisposition plays a role - or acquired, caused by injury.
- Anatomical defects, such as facial asymmetry, malocclusion or drooping hard palate.
- Pathological processes in teeth, alveolar bays and gums on the upper jaw. Examples of chronic inflammation are caries, periodontal disease and other diseases.
- Granulomas on teeth. Over time, perihilar cysts grow from them, which can in the future reach the bottom of the upper jaw and lead to disruptions in the normal functioning of the gland.
- The presence of immunodeficiency virus in the human body.
- Exposure to the allergen for a long time. This is especially true in situations where the allergen gets into the maxillary sinuses.
- ORZ. As a result, lymph accumulates in the lymphatic vessels and leads to an increase in the amount of interstitial fluid.
Of all the causes, sinusitis is considered the most likely. The chance that a cyst of the maxillary sinus will develop greatly increases if this disease is not treated in the left, right maxillary sinus, or both.
Cysts develop as a result of blockage of the excretory duct of one or more glands. The development of this condition can be facilitated by almost any inflammatory process localized in the nasal cavity or its paranasal sinuses (rhinitis, sinusitis, especially if it lasts for a long time).
The following factors can also contribute to the formation of cysts:
- Deviation of the nasal septum and other irregularities in the shape of the cartilaginous or bone formations of the nose.
- Dental lesions, primarily pulpitis and caries.
- Prolapse of the hard palate.
- Deformation of the bones of the facial skull.
Often this disease is asymptomatic, but if the cyst reaches a significant size or compresses adjacent anatomical structures, the following symptoms may appear:
- Painful sensations in the projection of the sinus, and the pain can radiate to the temple or forehead; when pressing in the area of the projection of the cyst, the pain intensifies.
- Painful sensations in the wings of the nose.
- A persistent sensation of the presence of a foreign body in the right maxillary sinus (or in the left, depending on the location of the pathological process).
- Nasal congestion, in most cases on the affected side.
- Feeling of pressure, fullness under the eye.
If you have similar symptoms, the best option would be to seek help from an otorhinolaryngologist, since only a doctor can make the right decision about the need for observation or surgical treatment.
If, during a survey of a patient, an otolaryngologist discovers, for example, cysts of the right maxillary sinus that are suitable for the clinic, then the preliminary diagnosis must be confirmed by an instrumental research method, since the manifestations may be similar in different pathologies, for example, with the same sinusitis.
In most cases, one of the following methods is used:
- Radiography. Allows you to obtain information about the localization, shape and size of the pathological process. It is accessible both in terms of the cost of the procedure and in terms of the availability of equipment in almost every medical institution.
- Magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography - methods are more accurate, but also more expensive for diagnosis. Not all hospitals have such equipment, and the queue to perform the procedure may require a fairly long waiting period.
- Fiber optic endoscopy is a fairly accurate method that allows you not only to examine the paranasal sinus from the inside, but also to take material from the suspicious area for additional research.
The etiology of this disease is associated with various chronic inflammatory processes and congenital defects affecting the oral region or nasopharynx. The main reasons why a cyst may appear include the following:
- The presence of chronic nasal diseases, for example, rhinitis, sinusitis, sinusitis, polyps, sinusitis.
- Abnormalities in the structure of the nose, including an abnormal septum. Such an anomaly can disrupt the normal flow of air, as well as the blood supply to the entire mucous membrane in the nose. Such defects may be acquired or congenital.
- Prolonged exposure to an allergen. In particular, if these allergens have been located in the maxillary sinuses for a long time.
- Chronic dental diseases, as well as inflammation around the dental tissues in the upper jaw.
- Immunodeficiency state.
There are various ways to remove maxillary sinus cysts. The classic version looks like this: the surgeon makes an incision under the patient’s upper lip, opens the wall of the bone cavity with a chisel and excises the cyst.
In our clinic, operations on maxillary sinus cysts are performed using endoscopic technologies. Under visual control, the doctor makes a small (several millimeters in size) puncture in the gum and through it removes the pathological formation.
Recovery of the body after endoscopy occurs very quickly, so we do not hospitalize patients. You are allowed to leave the clinic on the same day.
- Congenital or acquired as a result of injury, deviated nasal septum: In this case, the cold air does not warm up enough in the nasal passages and causes cooling of the maxillary sinus, which in turn creates favorable conditions for the development of infection with the subsequent formation of a cyst.
- Expansion of the opening of the maxillary sinus into the nasal cavity (congenital or acquired after illness or injury), which also disrupts the bacterial balance in the sinus and leads to an inflammatory process with excessive secretion of mucus, which then becomes covered with elastic tissue and turns into a cyst.
- Complications after acute or chronic diseases of the nasopharynx, paranasal sinuses, oral cavity, teeth.
- Immunity disorders, weakening of the body.
Classification
Based on the nature of the sinus discharge, cysts are distinguished:
- With serous contents - hydrocele,
- With mucous membrane - mucocele,
- With purulent - pyocele.
By origin:
- Retention cysts are true cysts that form as a result of complete or partial obstruction of the excretory ducts of the glands that produce mucus. The reasons for their obstruction are: swelling, blockage, scarring or hyperplasia. The gland continues to function and produce secretions. Over time, the walls stretch, it overflows and closes the lumen of the sinus. True cysts are lined with mucosal epithelium.
- False cysts are cyst-like formations, the origin of which is not fully understood. They usually occur in men. Possible causes of pseudocysts are: exposure to allergens or infectious agents, as well as pathology of the upper teeth. False cysts form in the thickness of the mucosa and do not have an epithelial lining.
- An odontogenic cyst forms around the inflamed root of the upper tooth and is filled with pus. They are radicular and follicular. The first ones form near the inflamed root of a carious tooth, gradually grow through the atrophied bone tissue of the jaw and penetrate into the sinus. The latter arise from the follicle of an inflamed milk tooth.
According to the localization of the pathology:
- Right sinus cyst
- Left sinus cyst.
Surgical removal methods
For maxillary sinus cysts, surgery is the most effective method of treatment. Today, the following treatment methods exist:
- Puncture. It is a puncture of the maxillary sinus with a medical needle using local anesthesia. After this, the surgeon pumps out the fluid filling the cyst. The procedure helps to significantly reduce the size of the tumor, as a result of which the bursting pain goes away. However, the method is not the most effective, because it gives only a short-term effect. The walls of the cyst remain in the same place and after a while are filled with liquid contents again.
- Caldwell-Luc method. A very complex and painful, but effective surgical technique. A hole is made in the bone located above the upper jaw, and then the part covering the sinus cavity is removed using a chisel. The attending physician removes the maxillary cyst using a sharp medical spoon. The recovery period after this type of intervention is quite long. The hole in the bone heals and becomes covered with scars. In addition, patients may develop various disorders in the nasal paranasal sinus, accompanied by frequent sinusitis and rhinitis.
- Endoscopic. The most preferred method of tumor removal today. It is not only the safest among all methods, but also has a number of advantages. Damage to the mucous membrane and bone tissue is minimized, so no pronounced scars remain on the skin. The tumor is removed using an endoscopic device inserted through the anastomosis. The device is equipped with a camera, which allows you to carefully examine the adnexal cavity and carry out the intervention with extreme precision. The neoplasm is eliminated along with the membrane. This prevents recurrence of the pathology. In addition, after an intervention of this type, the recovery period is limited to a short period.
Why do they appear
The main reasons for the appearance of maxillary cysts include:
- Recurrent or chronic maxillary sinusitis (sinusitis). Inflammatory changes in the mucous membrane lead to blockage or scarring of the excretory glandular ducts. The produced secretion has no outflow, accumulates and stretches the gland. This is how true mucous and serous cysts are formed.
- Chronic non-infectious inflammation (usually of an allergic nature), accompanied by hyperplasia of the mucous membrane of the nose and paranasal sinuses.
- Dental pathology, the resulting cysts are called odontogenic. The most common reason for their appearance is inflammation around the root of a carious tooth or near the tooth germ of the upper jaw. The purulent process leads to atrophy and destruction of bone tissue, spreading to the walls of the maxillary sinus. More rare causes include abnormally deep tooth roots and excessively traumatic tooth extraction.
- Predisposing factors are injuries to the facial part of the skull, congenital anomalies with asymmetry of the hard palate and nasal bones, and immunodeficiency states. Occasionally, a cyst in the sinus is formed against the background of a congenital defect in mucus production, when the secretion of the glands has an excessively viscous consistency.
Appearance mechanism
Cystic neoplasm has a fairly simple mechanism of appearance. The paranasal sinuses are lined with a mucous membrane, which has glands that produce a specific secretion (mucus) throughout the entire life period. The glands are penetrated by excretory ducts that open on the surface of the mucous membrane of the paranasal sinuses.
In the event that a person often suffers from inflammatory diseases, the mucous membrane thickens over time, and the outlet openings become clogged. Despite this, mucus production continues, because the gland continues to function as usual. Due to the fact that mucus cannot leave the sinuses, deformation of the walls of the gland occurs. This is how a maxillary sinus cyst is formed.
The arrow indicates a cyst in the maxillary sinus.
Signs and symptoms to watch out for
In the initial stage of development, a cyst in the maxillary sinus does not produce symptoms, but there are signs that you should pay attention to for a timely examination. At first, this may be a slight elevation above the surface of the upper jaw, adjacent to the tooth, if it is an odontogenic pathology. And if a true cyst develops, then the symptoms will resemble the clinical picture of sinusitis: headache and pain in the jaw on the affected side, nasal congestion, as with a runny nose, chronic rhinitis.
With odontogenic development of the formation, patients are bothered by pain when chewing and biting. If the tumor has reached visible size, round, painless formations of varying density can be felt on the upper jaw or in the nose area. When suppuration occurs in the area of formation, there will be swelling and inflammation, pain when touched.
If the tumor is located close to the exit of the second branch of the trigeminal nerve, that is, in the upper part of the air sinuses, even a small tumor will cause severe pain. In this case, a large cyst in its lower parts may be painless. In addition, for people who are fond of scuba diving, the disease causes discomfort and headaches when diving to depth.
If an opening occurs, the fluid that filled the cyst flows out of the nasal cavity on the side of the rupture.
To confirm the diagnosis of a false or true maxillary sinus cyst, it is necessary to take an x-ray or computed tomography scan of the nasal sinuses. From the image, you can determine the location, size, shape and nature of the surrounding bone structures.
Cyst of the right and left maxillary sinus: how to treat?
These formations may not manifest themselves throughout life or may manifest with unpleasant symptoms and pain. The disease is monitored dynamically and treated surgically if necessary.
What it is?
A cyst is a benign formation that resembles a cavity with walls and contents. It is very often found in the paranasal sinuses, and especially in the maxillary sinuses, but never goes beyond them.
The size of the cyst varies greatly: from small and tiny to gigantic, filling the entire cavity. There are two types:
- true. They are lined with epithelium;
- false. They do not have a special lining.
According to the development mechanism, it happens:
- Retention cyst. It develops when the excretory ducts of the glands of the mucous membrane are blocked.
- Odontogenic cyst. The cause is dental pathology.
In addition, they can be single or multiple, as well as congenital and acquired. Depending on the location, there may be a cyst of the frontal sinus, maxillary sinus, and others.
The cause of development is a blockage of the excretory duct of the gland, which secretes a special secretion. When blocked, this secretion begins to stretch the walls of the duct and slowly fills with serous fluid.
The following factors contribute to the appearance of such pathological protrusions of the mucous membrane:
- chronic processes in this area (sinusitis);
- hereditary predisposition;
- injuries;
- abnormalities of bone structure and excretory ducts;
- diseases of the upper teeth and gums (caries, periodontal disease, etc.).
It is known that the roots of the upper teeth, usually 5 and 6, can protrude into the lower wall of the sinus or they are separated by a very thin septum. With the development of dental pathology in this area, so-called odontogenic protrusions develop. They are:
- Radicular. This means that they come from the root of the tooth.
- Follicular. They were based on a displaced tooth germ.
Cystic protrusions are discovered during a random routine examination in almost every fifth patient. In some people they resolve on their own and unnoticed, while others live with them all their lives and don’t know about it.
When they reach a certain size and begin to bother the patient, the doctor recommends surgical treatment.
In most cases, a maxillary sinus cyst does not manifest itself in any way. Its presence is discovered by chance during a CT scan, MRI or x-ray for another disease.
First of all this:
- Distension and pain in the area where it is located. The patient complains of discomfort in the cheek area on the right or left.
- Frequent nasal discharge and congestion.
- Headache. They can be permanent or periodic, often associated with changing climatic conditions and stress.
- Breathing problems. Lack of breathing from one or both halves of the nose, depending on its location.
When it spontaneously ruptures, the orange liquid that was in the cavity begins to flow out of the person’s nose. This feature does not pose any harm to human health, but can greatly frighten him.
When it suppurates and becomes inflamed, other symptoms appear:
- temperature rises;
- a purulent runny nose appears;
- cheeks, eyes, teeth hurt;
- there are signs of intoxication of the body.
Size does not always affect the severity of symptoms. A large formation on the lower wall is asymptomatic for a long time, and a small one near the excretory anastomosis or on the upper wall sometimes leads to terrible pain in the head and teeth.
Diagnostics
- X-ray of the paranasal sinuses. In the picture, it resembles a rounded protrusion on one of the walls with smooth, clear contours. In this way, only sufficiently large variants are determined.
X-rays with contrast are also used, which will help determine a protrusion of any size. If the patient has an odontogenic cyst of the upper jaw, the dentist chooses other projections for the images.
- Diagnostic puncture. If during a puncture the doctor receives a specific orange liquid, then this confirms the diagnosis. This method is very inaccurate, since the doctor can only get into a protrusion that is large and located along the trajectory of the puncture.
- CT scan. This is a reliable method that allows you to assess the internal structure of this zone and the presence of pathology.
- Diagnostic sinusoscopy. An endoscope is inserted into the cavity through the excretory anastomosis or a special hole, which allows you to study in detail the presence of pathological processes in this area and, if necessary, immediately carry out a biopsy and treatment.
This method also makes it possible to diagnose polyps of the maxillary sinus and pathological processes.
In most cases, this problem does not have any consequences for the patient, since it rarely manifests itself with significant symptoms.
Negative consequences are observed with inflammation and suppuration of this formation. In such cases, the inflammatory process can not only cause sinusitis or frontal sinusitis, but also spread to the external soft tissues.
What complications are sometimes observed:
- Nasal cavity: sinusitis, chronic inflammatory process.
- Orbit: phlegmon, abscess, thrombosis of the cavernous sinus.
- Intracranial consequences: meningitis, encephalitis, thrombosis, brain abscess, etc.
The risk of these complications forces people with this disease to periodically (once a year) visit a specialist and monitor the dynamics of the development of the process.
When there are no symptoms and the disease does not manifest itself in any way, then it is simply observed over time. In these cases, they treat this disease with folk remedies.
Alternative medicine suggests treating it in this way:
- mix a tablespoon of vegetable oil with 5-6 drops of fresh aloe juice. Drip a whole pipette 2-3 times a day for a whole month;
- Cyclamen drops, prepared at home or purchased at a pharmacy, will help solve the problem. After using them, the patient begins to actively blow his nose and sneeze, which can lead to a rupture of its wall and fluid flows out of the nose.
If the symptoms begin to bother a person and his chronic inflammation often worsens, then surgical treatment is performed.
No drug can completely relieve the patient from it. Drugs can suppress the symptoms, but it itself and its consequences will remain until the patient decides to remove it promptly.
Where are such cysts removed? In any specialized otorhinolaryngology department in the clinic. The patient himself chooses to go to a private medical institution or have an operation in a public hospital. According to indications, in public clinics they are removed free of charge.
The price for cyst removal in a private institution depends on the level of the clinic and staff, as well as the volume of intervention and other factors. On average, such an operation costs 35-40 thousand rubles.
This is an operation in which the cavity of the maxillary sinus is opened through an opening in the upper jaw. After opening, the mucous membrane is cleaned with a special curette, removing all pathological contents from it.
Microsinusrotomy
Less traumatic intervention compared to classical surgery. The formation is removed through the nose using special instruments.
Thanks to such minimally invasive interventions, the patient endures the postoperative period easier, and the mucous membrane heals faster.
After removal, the patient is under observation in the clinic for several more days. Depending on the method of intervention, the patient may experience swelling, pain and discomfort in the postoperative area.
The classical operation is very traumatic, so recently preference has been given to microsinusrotomy and endoscopic techniques. After modern operations, the postoperative period is easy and after a couple of days the person can be transferred to home mode.
One of the measures to prevent this disease is timely sanitation and treatment of oral diseases, since most cases are of odontogenic nature. In addition, competent treatment of sinusitis, chronic rhinitis and other nasal diseases will help to avoid the development of such anomalies.
The final decision on the treatment of this disease should be made by a doctor who knows all the features of the pathological process and concomitant human diseases.
Question: I have been diagnosed with a cyst of the right maxillary sinus and my cheek hurts very much. The doctor made a puncture and punctured it, the pain went away, but he advised us to have an operation. Why perform the operation when it has been pierced?
Answer: It remained in place, the walls simply collapsed after the puncture. It may fill with fluid again and the symptoms will return, so it is better to remove it.
Question: My son has a cyst in the left maxillary sinus and it causes snot, pain and swelling in the nose. What drops or tablets will help remove it?
Answer: No drops, tablets or procedures can remove it, so if there are indications, it is better to get rid of it surgically.
Question: The picture revealed thickening of the mucous membrane and a cyst, which does not bother me in any way. There were problems with admission to the Ministry of Emergency Situations. How will it interfere with service and work?
Answer: Certain types of professional activities require ideal health. Even if it does not bother you now, there is still a danger of its rupture or suppuration in an extreme situation. If choosing a profession is important to you, you can delete it promptly and then try to apply.
Diagnostics
In addition to the above symptoms, radiography of the paranasal sinuses, if necessary, using a contrast agent, may be useful in diagnosing a cyst of the left maxillary sinus. This allows you to determine the exact location of the tumor and its size, as well as outline treatment tactics.
Endoscopies are also used, i.e. insertion of a probe with fiberglass optics through the nasal cavity into the sinus. With this method, it is possible to obtain a sample of cyst tissue for examination.
A certain result is obtained by puncture of the paranasal sinus by puncturing the sinus wall and suctioning out the contents of the cyst. Computed tomography is very informative, i.e. layer-by-layer computer images of the affected area or the skull as a whole. Magnetic resonance is sometimes used, but in the case of a cyst it is not as useful
Due to the absence of characteristic signs, the disease is poorly diagnosed. If a cyst is suspected, the following instrumental studies are performed to establish a diagnosis:
- X-ray of the sinuses. In the picture, the cyst is a round-shaped formation that protrudes on one of the walls of the examined maxillary sinus. It has a clear, smooth contour. However, such a diagnosis is effective only if the size of the cyst is large. Another option for making a diagnosis is an x-ray using contrast. With its help you can detect formations of any size.
- Taking a puncture. To do this, a puncture is made in the sinuses, and if a secretion (a specific orange liquid) was found in them, then the presence of a cyst is confirmed. This technique is inaccurate, since it all depends on the size and location of the formation. You can get into it in cases where it is large and is located on the trajectory of the puncture.
- CT scan. This alternative method for detecting cysts provides a complete picture of the structure and physiological characteristics of the sinuses, which plays an important role in preparing the patient for surgery if removal of the formation is required.
- Sinusoscopy. Using a device such as an endoscope, all abnormalities and pathological processes in the area under study are studied, and it is also possible to carry out a biopsy and treatment, that is, endoscopic removal, if necessary.
The diagnosis is established on the basis of anamnesis after the implementation of diagnostic methods. For this purpose the following may be prescribed:
- X-ray. In the picture, the cyst looks like a rounded protrusion located on the wall and has clear, smooth contours. This method detects only large tumors.
- Puncture. If during the puncture the specialist receives an orange specific liquid, this indicates a diagnosis. This method is very inaccurate, since the doctor can puncture the protrusion only if the cyst is large.
- CT scan of the maxillary sinus cyst. This method is the most reliable, as it allows you to assess the internal structure of the problem area and determine the presence of pathology.
- Sinusoscopy. An endoscope is inserted into the cavity through the excretory anastomosis or a special hole, allowing you to study in detail the presence of a pathological process in this area, as well as, if necessary, carry out treatment and biopsy.
Antibiotic treatment of the maxillary sinus
Until recently, a diagnosed cyst was an unquestioning indication for surgical treatment. Now the practice continues, but doctors are first trying to cope with conservative methods of treatment.
If the cyst does not cause any discomfort or impede nasal breathing, then surgical intervention is not required. But this does not mean that you can forget about it. Patients diagnosed are under special care and undergo regular examinations to monitor the development and growth of the cyst. If conservative therapy fails, a planned operation to remove the cyst is prescribed.
If we talk about the formation of an odontogenic cyst, then antibiotics alone cannot be dealt with; surgical treatment is most often carried out, and the causative tooth is often removed.
What to do to avoid illness?
One of the preventive measures for this disease is timely sanitation and treatment of oral diseases. This is due to the fact that in most cases they are odontogenic in nature.
If you have symptoms of a maxillary sinus cyst, it is better to immediately use surgical intervention so as not to suffer from possible complications in the future.
Remember that the final decision on the treatment of the disease is made only by a doctor who understands all the features of the pathological process and concomitant human diseases.
Despite the fact that the diagnosis of a cyst does not mean the emergence of a serious problem that requires complex and lengthy treatment, it is better to take simple preventive measures to prevent the development of pathology.
The fundamental preventive measures for the appearance of such pathological formations are:
- Timely and high-quality treatment of dental diseases. Cysts are often caused by untreated oral diseases.
- Correct and complete treatment of problems such as sinusitis, rhinitis and other infectious and inflammatory processes in the nasopharynx.
- Elimination of anomalies in the anatomical structure of the nasal cavity and bone tissues of the facial part of the skull.
- Rejection of bad habits.
- Proper nutritious nutrition. A person's diet should be balanced, rich in vitamins and minerals. Meals should be regular.
- Physical exercise. Moderate exercise is required in life to keep the body in good shape.
- Hardening. These can be water procedures, air or sun baths. This approach will ensure good functioning of the immune system, which is especially important for a small child.
- Conducting preventive medical examinations. They can detect the disease at an early stage.
- Reducing the likelihood of an allergic reaction.
When deciding on treatment for a cyst, an ENT specialist usually takes a wait-and-see approach. The fact is that the growth of education has been going on for decades. Therefore, as long as it is small and does not cause any discomfort, there is no need to touch it.
They do rinses, drop herbal decoctions into the nose or lubricate the mucous membranes with them. There is no point in such procedures, since they only temporarily make breathing easier, but do not reduce the size of the formation.
The main symptoms of the presence of a tumor in the sinus
Signs of a cyst begin to appear only after it reaches a certain size or acute inflammation does not occur, for example, an exacerbation of chronic sinusitis occurs. for a maxillary sinus cyst to fill depends on many factors, but, above all, on the frequency and intensity of inflammation and the individual characteristics of the patient.
Attention
Sometimes they grow very slowly and do not manifest themselves at all, and therefore are discovered only during routine examinations or by chance during an examination for another reason.
As the pathological cavity increases, patients may experience one or more symptoms:
- Pain radiating to the forehead, temple and eye socket. Often it is one-sided and appears on the affected side.
- Discomfort in the wings of the nose
- Possible increase in temperature
- The presence of a feeling of the presence of a foreign body in the maxillary sinus.
- Regular or constant feeling of stuffiness in half (with a unilateral process) or the entire nose (with a bilateral lesion).
- An increase in the frequency of exacerbations of chronic ENT diseases, and they are much more severe and longer than before the formation of a cystic cavity.
Source: nasmorkam.net Since the maxillary sinuses have certain areas responsible for detecting smells, breathing and voice formation, when they are damaged, the following may occur:
- partial or complete loss of smell;
- nasality.
Thus, the manifestations of the pathology are in many ways reminiscent of the signs of sinusitis. And since these diseases often accompany each other, the patient may not realize for a long time that he has a cyst in the nose.
In addition, some patients complain of ear congestion and discomfort. This may be a consequence of swelling in the nose. That is, there is some relationship between the cyst and the ear.
Drug treatment
How to cure a cyst in the maxillary sinus? The fact is that the causes, symptoms and treatment of nodules in the nasal cavities are directly related to each other, and methods of treating growths on both sides are determined only by a doctor, taking into account all the features. If the pathology proceeds without producing pronounced symptoms, then doctors suggest a wait-and-see approach and constant monitoring of the formation, while treatment of the maxillary sinus cyst may not be required at all.
It should be understood that it is not yet possible to completely get rid of maxillary sinus formations without surgery using medications alone. But medications help prevent the progression of the inflammatory process, relieve swelling and pain, and slow down the growth of formation.
With sinusitis, a cyst is easily formed under the influence of the inflammatory process and swelling of the glandular ducts, leading to their narrowing and blockage, so medications are also necessary to eliminate bacterial sinusitis. Several drugs of different groups are usually used to mutually enhance their therapeutic effect:
- Antibiotic agents for infectious processes and bacterial sinusitis: Macropen, Suprax, Augmentin, Azithromycin (Zitrolide).
- Antibacterial local agents (drops, sprays): Bioparox, Isofra, Polydexa.
- Mucolytic drugs that help reduce the viscosity of mucus and improve its outflow, relieve swelling and ease breathing: Rinofluimucil, Mucodin, Fluditek, as well as Oxymetazoline, Leconil, Nazol.
- Antiallergic medications that relieve swelling and inflammation: Suprastin, Desloratadine, Tavegil.
- Means for washing the nasal passages: Aquamaris, Aqualor.
- Hormonal medicinal products - Nasonex, Avecort - reduce the effects of allergens, toxins, relieve inflammation and swelling.
What to do if medications don't help? Then experts recommend removing the cystic node in the nose.
Contraindications for surgery
Surgical removal of a cystic neoplasm is contraindicated in the following cases:
- acute infectious processes in the body;
- diseases of the cardiovascular system in the stage of decompensation;
- diabetes mellitus type I in the stage of decompensation;
- blood clotting disorder;
- status epilepticus;
- malignant neoplasms.
The operation is a planned one (an emergency occurs when a massive purulent process is suspected); if there are a number of contraindications, it is postponed until complete somatic well-being.
Prevention
An important condition for the prevention of maxillary sinus cysts is maintaining oral hygiene. It is recommended to treat caries and periodontal disease in a timely manner and regularly visit the dentist. Additionally, to prevent the formation of cysts in the maxillary sinuses, the following must be done:
- promptly treat runny nose, rhinitis, sinusitis and other respiratory diseases;
- avoid long-term allergies and eliminate them by taking antihistamines;
- Be sure to seek help from a doctor if you have a deviated nasal septum.
Possible complications after a cyst of the maxillary sinus
After removal of a cyst or mucocele of the nasal sinuses, the patient should be monitored in the hospital for several more days. Depending on the intervention methods, the patient may experience swelling, pain and discomfort.
Classic surgery is very traumatic, which is why specialists have recently given preference to endoscopic techniques and microsinlusrotomy.
In advanced cases, the consequences of a maxillary sinus cyst can be very serious for human health. Complications can occur during the inflammatory process or suppuration of this formation.
- Nasal cavity: chronic inflammatory process, sinusitis.
- Orbit: abscess, phlegmon, thrombosis of the cavernous sinus.
- Inside the skull: encephalitis, meningitis, brain abscess, thrombosis.
The risk of these complications forces patients with this disease to periodically visit a doctor and also monitor the development of the process.
In the case of a sharp increase in the size of the cyst, its inflammation and suppuration, complications can be very diverse, including damage to the meninges. It depends on the location of the cyst and the degree of activity of the process
There are specialists who believe that a cyst should not be removed if, regardless of its size, it does not cause problems for the patient and does not cause pain. Other experts, on the contrary, talk about the silent sabotage of this education.
We suggest you read: The best way to treat toenail fungus
That even a painless cyst causes inflammation of the surrounding tissues, causing respiratory defects. There is an opinion that a maxillary sinus cyst can cause pneumonia
The patient should carefully choose a specialist for treatment, and if in doubt, it would not be a bad idea to see another doctor.
After all, this formation can provoke the following complications:
- an infection can penetrate into the cavity of the cyst, pathogenic organisms will begin to multiply intensively in the body of the formation, this often happens with sinusitis;
- it is possible for a polyp to grow, such a formation grows quickly and can penetrate into the nasal cavity, creating additional problems for the patient; if only the polyp is removed and the cyst is left, it will grow again;
- the presence of a polyp makes the body less resistant to viruses and infections that attack the respiratory system, the patient begins to get sick more often and takes longer to recover.
Endoscopic surgery is the most modern method
Despite the fact that the pathology is not dangerous and does not pose a threat to human life, and the formation is benign, there are a number of indications when it is better to remove the cyst.
Among the complications that the presence of cysts in the sinuses can lead to without proper treatment:
- chronic rhinitis;
- chronic sinusitis or sinusitis;
- education gap.
The most dangerous are cysts with purulent contents. They can become a source of eye problems such as:
- abscess;
- sinus thrombosis;
- phlegmon.
If purulent cysts have spread inside the head, then there is a risk of developing:
- encephalitis;
- meningitis;
- brain abscess.
In this case, endoscopic removal is necessary.
Reasons for education
The reasons for its formation are quite varied. Very often, a maxillary cyst is a consequence of:
- rhinitis;
- anatomical features of the facial structure;
- inflammatory process in the oral cavity (upper teeth and gums);
- poorly performed dental procedures;
- facial asymmetry;
- sinusitis and sinusitis.
It happens that the appearance of a tumor in the sinus becomes the cause of the flow of one disease into another. For example, from a common runny nose to chronic sinusitis.
Examination before surgery
The very fact of the presence of a cyst is usually revealed by radiography of the paranasal sinuses. In the picture, the cyst looks like a darkening in the sinus with clear rounded contours. But to clarify the diagnosis and determine the scope of the operation, this study is not enough.
Additionally, the following may be prescribed:
- Computed tomogram of the paranasal sinuses.
- Examination of the nasal cavity and sinuses using an endoscope.
- X-ray contrast examination of the sinuses.
- Microbiological examination of sinus discharge in the presence of inflammation.
Usually 2 weeks before surgery the following are prescribed:
- General blood and urine tests.
- Biochemical analysis.
- Electrocardiography.
- Blood for clotting.
- Fluorography.
- Examination by a therapist.
- Dentist examination.