Usually, all unpleasant symptoms caused by physiological hormonal changes disappear immediately after menstruation. However, sometimes the symptoms may last longer. When the lower back and lower abdomen hurt after menstruation, treatment is not always required. Sometimes the symptom is caused by physiological processes that take place in the female body. The condition also indicates probable adnexitis. Another possible root cause is endometritis. It is important to pay attention to the additional clinical picture. If you suspect an illness, visit a doctor and attend the recommended examinations.
The lower back can hurt both during and after menstruation
Why there may be pain
Painful sensation after menstruation can be:
- pathological;
- physiological.
Only pathological discomfort needs treatment. The deviation may be of the following nature:
- pulling;
- aching;
- cutting;
- cramping.
If the pain is very severe, it requires medical intervention.
It is important to pay attention to additional signs. This will help establish a preliminary diagnosis, detect deviations in a timely manner and begin to eliminate them.
What to do if you feel unwell?
When the pain does not disappear after the end of menstruation and, in addition, it is accompanied by other symptoms, you need to urgently visit the doctor. The following symptoms should alert you:
- swelling of the mammary glands and the release of clear or white discharge from them;
- after the end of menstruation, spotting is systematically observed;
- the discharge is characterized by a sharp, unpleasant odor;
- the temperature is maintained at 37-37.5 degrees for several days;
- temperature jump above 38 degrees;
- abdominal pain even on the outside.
However, not all women seriously assess their own condition and often resort to self-medication. Hot tea and a warm heating pad may eliminate the spasm, but they do not eliminate the inflammation and only increase bleeding, if any. So you shouldn’t let the problems of the reproductive system take their course, trusting to chance, but it’s better to visit a doctor who will really help eliminate the problem.
https://youtu.be/unLQVqiSVnQ
Physiological reasons
Usually the discomfort is due to hormonal changes. This is explained by the fact that during menstruation the amount of progesterone changes. After the end of the critical days, the indicator returns to normal.
Pain in the abdomen and back can be explained by the special location of the uterus. Symptoms occur in girls whose organ is slightly tilted back. In this case, pressure is exerted on the nerve endings. This provokes periodic discomfort.
During menstruation and for several days after it, discomfort may be due to the natural contraction of the uterus. Only women with low pain syndrome experience unpleasant symptoms.
Pain in the abdominal cavity and lower back is a natural reaction of the body to the start of taking hormonal contraceptives. The condition does not require treatment. The state of health returns to normal without outside help and taking additional medications.
Sometimes ovulation occurs earlier than expected
A girl may also ovulate early. In this case, signs of a natural process can appear already 6-7 days after the end of the critical days.
Pregnancy cannot be ruled out. Successful fertilization is always manifested in the initial stages by nagging discomfort in the lower abdomen. In addition, the symptom radiates to the lower back. The girl complains of nausea and weakness.
Main causes of pain
Aching pain in the groin that persists after the end of menstruation can be caused by:
- sexual, venereal infections;
- formation of an ovarian cyst;
- hormonal imbalance;
- inflammatory diseases of the reproductive system;
- oncological tumors;
- ailments of the nervous system;
- tuberculosis of the genital organs;
- ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome.
Depending on the cause of the pathology, the pain can have varying intensity and radiate to the lower back, hip, and intestines. Bloody, spotting or discharge of a different color, itching of the external genitalia, and a strong odor may appear.
How does endometritis manifest?
With endometritis, the mucous membrane of the uterus and the epithelium, the inner layer lining the organ cavity, become inflamed. This disease is of an infectious nature and develops as a result of:
- caesarean section;
- childbirth;
- instrumental research;
- medical abortion;
- sexual intercourse during menstruation;
- installation of an intrauterine device;
- sexual infections.
In acute endometritis, the duration of menstruation increases, uterine bleeding may develop, the menstrual cycle is disrupted, and the temperature rises to 38°. After the end of the critical days, pain in the lower abdomen persists, which radiates to the pelvis and lower back, and spotting brown or pus-filled discharge is present. In mature women, necrotic masses can accumulate in the uterine cavity, causing an increase in its size.
Chronic endometritis is characterized by a protracted course without hyperthermia. The pain is aching and practically not felt in the lower back. Purulent discharge persists. During menstruation, the groin area hurts, the cycle is disrupted, delays and intermenstrual bleeding appear.
Symptoms of oophoritis
Acute inflammation of the ovaries is called oophoritis. The causative agents of the pathological process can be staphylococci, chlamydia, streptococci, tuberculous mycobacteria, and E. coli. Bacteria reach the reproductive organs via an ascending route or through the bloodstream from diseased internal organs.
Reasons for the development of oophoritis:
- weakened immunity;
- hypothermia;
- complication of vaginitis, vulvitis;
- consequences of abortion;
- chronic diseases of other internal organs;
- sexual infections;
- stress, chronic fatigue;
- installation of an intrauterine device.
Most often, inflammation of the ovaries is combined with damage to the uterus and appendages, and andexitis or salpingoophoritis develops. The disease causes destruction of epithelial tissue and the formation of adhesions, which is accompanied by an inflammatory process. Oophoritis can have an acute, subacute and chronic course with periodic relapses.
The acute stage is characterized by the fact that the woman has severe pain in the abdomen and lower back, as during menstruation, the body temperature rises to 38°, the groin area is hard and tense. Hyperthermia is accompanied by symptoms of intoxication of the body:
- headache;
- weakness;
- nausea;
- increased sweating;
- sometimes urination is delayed;
- purulent, foul-smelling vaginal discharge appears.
In the chronic course of oophoritis, the symptoms are less pronounced. The lower back hurts, the stomach aches and pulls, menstruation is painful, and the cycle is disrupted. The duration of critical days increases, the discharge becomes more abundant with clots or, conversely, scanty, spotting, dark brown or black. This condition negatively affects the psycho-emotional state of a woman. Advanced oophoritis can lead to infertility.
Signs of adnexitis
Adnexitis is an inflammatory disease of the appendages. Most often, the pathology is diagnosed in women over 25–30 years of age. The causes of the disease are identical to oophoritis, they have a similar clinical picture, since the fallopian tubes, ovaries and uterus are usually involved in the inflammatory process.
The main symptoms of adnexitis:
- hyperthermia up to 39°;
- acute pain in the lower abdomen;
- menstrual irregularities;
- dysmenorrhea;
- intermenstrual bleeding;
- pain when urinating;
- copious watery or purulent discharge;
- painful sexual intercourse.
The stomach can hurt very badly; the attack is similar to acute appendicitis. Analgesics help little. As the disease becomes chronic, the symptoms become less intense. The stomach worries almost constantly, on menstruation days and when there are no periods. The pain becomes aching, and adnexitis relapses periodically.
Without timely treatment, the pathology can lead to peritonitis, the formation of adhesions, ectopic pregnancy, and infertility.
Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome
With the artificial administration of hormonal drugs that stimulate ovulation, ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome may develop. The complication occurs as a result of a hormonal imbalance in the patient, an allergic reaction, polycystic ovaries, or pregnancy.
As a result of stimulation, the ovaries enlarge, capillary permeability increases, blood thickens and accumulates in the abdominal and pleural cavity. The woman feels slight pain in the lower abdomen, there is discomfort, a feeling of fullness. Patients notice a slight increase in waist size.
Mild forms of OHSS go away on their own and do not cause any particular trouble. The average degree is characterized by an increase in abdominal size, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and flatulence. In severe forms, liver function is disrupted, a lot of fluid accumulates in the pleural area, and the volume of urine excreted decreases. If fluid enters the lungs, shortness of breath occurs.
If severe symptoms of OHSS develop, the woman is treated in a hospital setting. In milder forms of the pathology, the patient should constantly visit a doctor and monitor her health.
Signs of cysts and cystic ovarian tumors
A cyst is a round formation filled with fluid that forms in the ovarian cavity and leads to a significant increase in its size. The cause of the development of pathology is a hormonal imbalance in a woman’s body.
Classification of cysts:
- follicular;
- endometriomas;
- cystic tumors.
Follicular cysts are formed from the ovary's own tissue and appear as a result of a disruption in the ovulation process, during which the follicle continues to grow or fluid accumulates in the corpus luteum. Such cysts do not require any treatment and disappear on their own within a month or two. Endometriomas develop due to damage to the inner layer of the ovary. A capsule filled with blood is formed.
Cystic tumors are cancerous growths that have the appearance of cysts. The correct diagnosis is established after additional research.
In the initial stages, the disease is practically asymptomatic. A characteristic symptom is menstrual irregularities, menstruation is delayed or uterine bleeding develops. Girls begin puberty early.
Pain in the lower abdomen or a feeling of heaviness and discomfort may appear after sexual intercourse and persist for a long time. If perforation or torsion of the cyst leg occurs, the pain becomes intense and radiates to the sacrum and rectum. This condition causes intoxication of the body with the appearance of nausea, vomiting, and high fever.
Tuberculosis of the genital organs
Genital tuberculosis is caused by Koch's bacillus; most often the disease is diagnosed in young women 20–30 years old. In 90% of cases, the pathology affects the fallopian tubes, less often the uterus and ovaries. In rare cases, tuberculosis of the external genitalia, vagina, and cervix is diagnosed.
Symptoms of genital tuberculosis:
- no menstruation for several cycles;
- very painful periods;
- intermenstrual bleeding unrelated to regulation;
- heavy menstruation, lasting more than 7 days;
- the nature of the pain is nagging;
- low-grade fever;
- severe weight loss of a woman;
- malaise, lethargy;
- increased sweating.
If the peritoneum is involved in the pathological process, symptoms of an acute abdomen occur. With such signs, appendicitis, ovarian apoplexy, or ectopic pregnancy may be mistakenly suspected.
Pathological causes
Often symptoms accompany pathologies of the reproductive system. In this situation, the signs cause unbearable discomfort. A woman can be diagnosed with:
- vulvitis;
- adnexitis;
- inflammatory process in the fallopian tubes and ovaries;
- endometritis;
- venereal diseases;
- infectious processes.
Pain can occur in the presence of inflammation of the ovary.
The most common options are presented in the table.
| Vulvitis | The most common option is vulvitis. This is an inflammation of an infectious nature. The disease is the result of non-compliance with basic personal hygiene, unprotected sexual intercourse, or fungus. A woman with pathology complains of cloudy vaginal discharge of a purulent nature. The genitals itch and swell. |
| Gastrointestinal diseases | Pain in the lower back and abdomen often accompanies diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Intestinal pathologies make themselves felt with such signs. The condition is additionally accompanied by abdominal bloating, bowel problems such as constipation, nausea and vomiting. |
| Diseases of the genitourinary system | Another root cause is the improper functioning of the genitourinary system. This can manifest itself as pyelonephritis, cystitis, kidney tumors, etc. You should consult a doctor if the pain persists for a long period of time. |
Symptoms may be the result of recent surgery or trauma. The signs are also typical for women who prefer excessive physical activity.
Why does my lower abdomen still feel tight after my period?
The beginning of menstruation in many women is accompanied by pain, which should not be the case when it ends. But this happens. Women experience pain and discomfort in the lower back, lower abdomen and pelvis. This may be a symptom of other, serious disorders. You cannot help but react to such signals from your body.
Especially if the pain does not go away or decreases after taking the pills for a certain time, then you should urgently consult a doctor.
There is no need to panic if you just experience mild pain in the lower back. But you need to know why this happens to your body.
A little about the menstrual cycle
Menstruation is a special type of blood discharge. They may contain impurities, lumps and clots. They are darker in color than the blood from the wound. This is an indicator of the woman’s health and that she is not currently pregnant.
The period from period to period is called the menstrual cycle. There should be at least 21 days and no more than 36 days between bleeding. Previously, unpleasant sensations occur in the lower abdomen, lower back, mild nausea and headache.
Painful sensations arise due to increased load on the organs of the reproductive system and increased irritation of nerve fibers.
How can you relieve pain
To improve your well-being, you need to resort to simple recommendations. First of all, you should give preference to rest. Sometimes it is enough to lie down for a couple of hours to fully recover.
One of the useful recommendations is to play sports.
Doctors also recommend exercising after menstruation. It is best to choose yoga. Such physical activity is beneficial for the female body and helps prevent the recurrence of symptoms.
You should resort to taking painkillers as a last resort. It is better to coordinate medications with your doctor in advance to avoid side effects and contraindications.
Traditional medicine is also useful. A woman is recommended to take tea with mint, chamomile or sage. It is advisable to take a warm bath with sea salt. Discomfort may be psychological in nature. With this pathogenesis, a woman is recommended to surround herself only with pleasant people. You should not be nervous or expose yourself to stressful situations or emotional outbursts.
How to get rid of pain after menstruation
There are several ways to reduce pain.
- The pain may be psychological in nature. Surround yourself with good people and positive emotions. If your job constantly causes stress, then it is advisable to change it. Perhaps you need to go somewhere to relax.
- Take a horizontal position and apply a very warm, but not hot, heating pad to the painful area. This will bring blood flow to the painful area and reduce pain.
- Feet should always be kept warm. Protect them from excessive moisture and hypothermia.
- Temporarily avoid drinking coffee and tea. Give your preference to lemon balm, St. John's wort, chamomile, that is, natural ingredients.
- There is one good painkiller, although it is not very pleasant to use. This is wormwood. Take 2 teaspoons of wormwood and pour 2 glasses of hot boiled water. This is one serving. You need to drink at least two drinks a day: morning and evening.
- If the pain is of such intensity that you cannot tolerate it, then you can turn to medications.
- Play sports. This will help improve the structure of muscle tissue. Recommended especially for people who lead a sedentary lifestyle. Perhaps you will choose yoga. It helps to train the muscles of the pelvic organs well.
DETAILS: Etiology of pain in various areas of the knee
The causes of pain in the lower abdomen can be different. Consult a doctor, establish a diagnosis and then decide on a method of treatment and prevention.
How to exclude pathologies
Exclusion of pathology is possible only in a medical institution. Self-diagnosis is ineffective. The woman must go to the hospital. The doctor will conduct a preliminary examination and analyze the signs present.
You can find out the cause of pain using ultrasound
The girl is given directions to:
- Ultrasound;
- MRI;
- blood analysis;
- Analysis of urine.
Additional consultation with specialists may be required.
Other reasons
Often the lower abdomen begins to pull due to disturbances in the woman’s mental state. This is due solely to external irritating factors.
It's all about emotions
Prolonged stress, neuroses, depression, panic attacks - all this affects a woman’s reproductive system. Very often, pain in the lumbar region and abdomen does not occur out of nowhere, but due to weakened immunity during menstruation, as well as due to severe emotional depression. The combination of unfavorable factors results in a persistent pain syndrome, which can be difficult to relieve. In such a situation, you should learn to relax, cope with your emotions, and not take the critical comments of others to heart. If necessary, you should seek help from a good psychologist.
A bit of everything
Banal hypothermia of the body (for example, walking in the cold in short skirts and thin tights), immunodeficiency virus, various sexually transmitted diseases, constant change of sexual partners, and an intrauterine device not replaced in time are a favorable environment for the development of pathogenic bacteria. Therefore, in addition to cramping pain in the abdomen, nagging pain in the lumbar region, the legs hurt, the temperature rises, and the general condition sharply worsens. If measures are not taken in time, serious consequences cannot be avoided.
When you need to see a doctor urgently
An urgent visit to a doctor should be if:
- bleeding;
- pathological discharge with an unpleasant odor;
- high pain intensity;
- discharge from the mammary gland;
- elevated body temperature;
- fever;
- fainting;
- intense vomiting.
From this video you can learn about the main causes of pain:
The listed signs indicate the course of dangerous diseases in the body. Self-medication is contraindicated. Taking painkillers is prohibited until an ambulance arrives or a doctor is consulted.
Why does inflammation occur?
Inflammation is caused by bacteria and viruses that enter the body and wait for the right moment to begin to multiply.
Causes of pelvic inflammatory diseases:
- hypothermia;
- stress;
- HIV;
- use of an intrauterine device;
- promiscuity;
- venereal diseases;
- viral infections caused by herpes simplex.
Each of these factors is favorable for the growth of bacteria. Usually, if the disease occurs for the first time, along with lower back pain, the body temperature rises and the condition worsens.
Not all women pay attention to this, mistaking the symptoms for a common cold. The causes of the disease remain unattended, and it becomes chronic. That is why pain radiating to the lower abdomen can appear not only during menstruation, but also be permanent.
DETAILS: Driving a car after endoprosthetics
Diseases that manifest themselves in this way
There are diseases of the female genital area, the symptoms of which are pain after menstruation. When notifying women of these diagnoses, doctors warn women about the possibility of such attacks. If a diagnosis is not made, perhaps the disease occurs in a latent or chronic form, so you should pay close attention to your health, get examined and completely exclude their possibility.
Such diseases mainly include inflammatory processes of the female organs, such as:
- Endometritis is an inflammation of the mucous membranes of the uterus, usually occurring after a traumatic intervention: abortion, curettage, childbirth, cesarean section, mechanical examination, etc. This condition is often chronic and the most indicative symptom is brown discharge.
- Adnexitis is an infectious or inflammatory disease of the fallopian tubes or ovaries. Other names are oophoritis or salpingitis. It is caused by infections: candida, ureaplasma, chlamydia, mycoplasma, which subsequently results in a significant inflammatory process, in which nearby organs can also become ill. It is insidious with subsequent infertility.
- Vulvitis is an inflammation of the outer membranes of the external genital organs, caused by yeast-like microorganisms or sexually transmitted infections.
- The progressive inflammatory process causes significant pain, especially after menstruation, pulling in the lower abdomen.
- Cercycitis - inflammation of the cervix, provoked by a virus or infection, can give rise to the spread of inflammation to nearby tissues, in which the symptoms are purulent and mucous discharge and a painful pull in the lower abdomen and lower back.
Non-inflammatory diseases manifested by postmenstrual syndrome include cysts or tumors of the genital organs. The nature of the increase in tumors is always accompanied by a feeling of compression, disruption of the blood supply to organs and nerve endings, which cannot but be accompanied by pain of varying intensity. In these cases, the lower back often hurts.
How to eliminate nagging pain in the lower abdomen and lower back after menstruation
If no serious deviations are detected, use the following methods:
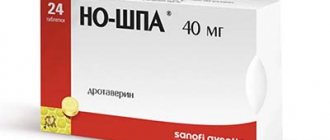
- taking antispasmodics that eliminate increased tension in the muscles of the uterus and vascular endothelium (Spazgan, Spazmalgon);
- taking a hot shower, which improves systemic circulation;
- adequate physical activity that improves muscle tone and increases blood flow (yoga, Pilates, swimming);
- physiotherapy aimed at enhancing metabolism and regeneration at the site of damage (using magnets, electrophoresis, UV irradiation, laser).
After the discomfort ends, the procedures continue to be performed continuously to prevent the condition from reoccurring.
If diseases are identified, the method of therapy is prescribed only by a gynecologist, endocrinologist, or other specialist:
- Conservative methods. It is recommended to take NSAIDs, steroids, hormones, and analgesics. For infection, antibacterial and antiviral agents are used. Physiotherapy is prescribed.
- Radical methods. Recommended when tablets and injections do not work. With the help of surgery, tumors, cysts, and benign tissue growths are removed.
Appointments are strictly adhered to. During therapy, the dosage is not changed; a doctor is consulted about analogues. This will reduce the risk of complications.
Pain after menstruation - treatment
If your stomach hurts after menstruation, it is usually not a physiological process, but a pathological one. Therefore, it is necessary to detect the cause as early as possible and immediately begin to eliminate it.
For diagnosis, effective modern methods are used - ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging, sometimes, if necessary, a puncture is taken, and a thorough anamnesis is collected. After making a diagnosis, the doctor prescribes treatment.
If your breasts hurt after menstruation and the diagnosis is mastopathy, conservative treatment is initially prescribed. It depends on age, the form of the disease, general condition and many other individual factors. Anti-inflammatory and homeopathic drugs, hormonal and iodine-containing, diuretic. If drug treatment does not have the desired effect, surgery may be required.
Infectious and inflammatory diseases cannot be cured without antibiotics, and fungal diseases cannot be cured without special creams and ointments. If, after menstruation, the lower abdomen hurts, and the doctor has diagnosed a cyst or neoplasm, surgery will most likely be needed.
However, do not rush to get upset - such a decision is made only taking into account all factors and strictly individually. It is quite possible that conservative therapy will be the most effective for you.
In addition to drug therapy, there are many folk recipes that can relieve pain after menstruation if the attending physician does not object.
If your stomach hurts after menstruation, it is usually not a physiological process, but a pathological one. Therefore, it is necessary to detect the cause as early as possible and immediately begin to eliminate it.
For diagnosis, effective modern methods are used - ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging, sometimes, if necessary, a puncture is taken, and a thorough anamnesis is collected. After making a diagnosis, the doctor prescribes treatment.
Infectious and inflammatory diseases cannot be cured without antibiotics, and fungal diseases cannot be cured without special creams and ointments. If, after menstruation, the lower abdomen hurts, and the doctor has diagnosed a cyst or neoplasm, surgery will most likely be needed.
However, do not rush to get upset - such a decision is made only taking into account all factors and strictly individually. It is quite possible that conservative therapy will be the most effective for you.
In addition to drug therapy, there are many folk recipes that can relieve pain after menstruation if the attending physician does not object.
Symptoms
If your stomach feels tight after menstruation has passed, then the pain can manifest itself in completely different ways.
To determine why such discomfort occurred, the specialist evaluates the complaints, and then carries out a clinical and gynecological examination.
Painful sensations in the lower abdomen after menstruation have the following characteristics:
- Sharp or dull.
- Aching, pulling, stitching.
- Various intensities.
- They manifest themselves sporadically or constantly.
- Caused by specific circumstances or appear with general well-being.
Direct pain in the lower abdomen should alert a woman and raise the question of why problems are occurring.
However, when other symptoms are added, you should immediately contact a specialist.
Pain after menstruation - we treat it with folk remedies
1. Breast pain after menstruation - drink more fluids. The volume of ordinary water should not be less than 2 liters per day.
2. Herbal tea helps a lot if your stomach hurts after your period. To prepare it, you need to take lemon balm leaves, thyme, St. John's wort and chamomile in equal proportions. It’s good to add a spoonful of honey and lemon to your tea.
1. Breast pain after menstruation - drink more fluids. The volume of ordinary water should not be less than 2 liters per day.
https://youtu.be/a5gGDu11fnM
Non-hazardous reasons
From time to time a woman feels that her lower abdomen hurts after her period. This is observed as a result of normal functioning of the body.
In this case, the symptoms are not considered critical and do not require any medical intervention.
These include:
- Ovulation. Maturation of the bulb with further release of the egg. Lasts from 12 hours to 2 days. Sometimes this process is associated with pain and light bleeding. Pulling sensations during ovulation begin approximately on days 12-18.
- Premenstrual syndrome. Mostly discomfort is noted a week before the start of the menstrual cycle. But in women with cycle instability, who have suffered from inflammatory or viral diseases, they may encounter cyclical disruptions. Menstruation is delayed or comes early.
- Pregnancy. After menstruation, there is a pulling in the lower abdomen and in the lumbar region during earlier fertilization. This is associated with the gradual growth of the embryo. Due to increased protein synthesis, the woman feels spasms. Then other symptoms of pregnancy become more pronounced: toxicosis, delayed menstrual cycle, pain in the mammary glands. The lower abdomen can only tighten during the 1st trimester of pregnancy.
- Hormonal imbalance. Due to improper functioning of the endocrine system, the content of hormones changes dramatically. The condition can be controlled through the use of special medications.
Appears as a result of the use of oral contraception, various diseases, and deviations from the diet.
After menstruation, the lower abdomen also feels tight as a result of various pathologies. Unpleasant sensations can be triggered by gynecological problems and other diseases. Eg:
- Diseases of the genitourinary system. They are often provoking factors that cause pain in the lower abdomen. The disease is associated with an increase in temperature, a constant urge to urinate, discomfort during it, and malaise. During kidney damage, pain is concentrated mainly in the lumbar region.
- Gastrointestinal diseases. As a result of the close proximity of the gastrointestinal tract and reproductive system, in some cases it is not possible to determine the source of pain without visiting a specialist.
Causes of discomfort: inflamed appendicitis, intestinal obstruction, intoxication or an infectious disease.
Gynecological problems
When a woman’s lower abdomen feels tight after menstruation, it is necessary to rule out gynecological diseases.
If therapy is started at the wrong time, it can cause adverse consequences or disruption of reproductive function in the body.
Discomfort in the lower abdomen after menstruation is typical for the following diseases:
- Endometriosis. It is an abnormal pathological increase in the size of cells of the muscular layer of the uterus. At this time, the woman experiences pain that increases after intimate intercourse. Symptoms of the disease include intense bleeding. Often the result of using hormonal drugs over a long period of time.
- Vulvitis. An inflammatory process that is localized on the vaginal mucosa. Often occurs after an infectious lesion and sexually transmitted diseases, as a result of fungal growth. It is characterized by special gray discharge that is purulent in origin. There is a burning sensation, itching, and swelling.
- Adnexitis. Inflammation that affects the uterine tubes and ovaries. Associated with discharge and heat.
- Cyst in the ovary. It is formed as a result of disruptions in blood flow inside the ovarian follicle. Leads to a gradual increase in the corpus luteum and pressure on the organs. In many situations it is not dangerous, but requires medical supervision.
- Malignant neoplasms. The appearance and formation of cancer provokes painful sensations.