Other causes of burning
There are many reasons for the occurrence of painful syndrome in the upper abdomen. Determining their exact location and type of pain can help in determining the causes of pain syndromes.
Gastritis
Gastritis or inflammation of the gastric mucosa is one of the causes of pain in the upper abdomen. In addition, before or after eating, the following symptoms may occur:
- nausea, vomiting;
- fast saturation;
- belching;
- heartburn, a burning sensation in the throat or behind the breastbone;
- darkening of the stool;
- cramps in the upper region of the stomach;
- feverish condition.
The causes of acute gastritis can be:
- food poisoning;
- rotavirus infections (usually in children);
- increased acidity;
- long-term use of painkillers (Aspirin, Ibuprofen), spices, and acidic foods.
The causes of chronic gastritis can be: infections (bacterium Helicobacter pylori), chronic poisoning.
Gastroparesis
Gastroparesis (slowing of the emptying process due to insufficient muscle relaxation), in addition to pain in the stomach after eating or during eating, is characterized by:
- early saturation;
- heartburn;
- bloating in the upper abdomen;
- belching.
Stomach ulcer
Peptic ulcer disease is manifested by characteristic long-term pain in the center of the stomach. During or after eating, dull or burning pain occurs in the upper abdomen, which can be girdling in nature. Pain occurs due to the presence of open ulcers (wounds) in the inner layer of the stomach. If foci of inflammation are located in the first part of the small intestine, then pain can occur between meals or at night.
Stomach cancer
Such a dangerous disease as stomach cancer includes pain in the upper and middle zones of the stomach among its symptoms. In addition, other symptoms of the disease are:
- sudden weight loss;
- lack of appetite;
- change in color of stool to almost black;
- nausea.
Pancreatitis
Acute pancreatitis can cause pain in the center of the stomach or in the upper left. It may also be accompanied by nausea, loose stools, white diarrhea, and poor appetite.
Other diseases
There are other diseases that can cause stomach pain of varying intensity and nature.
- Painful sensations in the central upper zone of the stomach can appear as a result of varicose veins of the esophagus (more often observed in chronic alcoholics).
- All pathologies of organs that are located in the left upper abdomen (spleen, diaphragm, some parts of the intestine) can also be causes of pain: enlargement and rupture of the spleen (additional symptoms include blue discoloration of the peri-umbilical area);
- intestinal dysfunction (accompanied by constipation or diarrhea with bloody discharge, temperature may rise, nausea or vomiting);
- diaphragm hernia. In addition to pain in the upper left abdominal region, pain can occur in the chest area;
- liver pathologies. Additional symptoms may occur, such as increased sweating, nausea, yellowing of the skin and sclera of the eyes. The painful sensations themselves are felt more in the upper zone of the stomach on the right;
- pancreatic diseases. May be accompanied by high fever, vomiting, nausea, pain resistance to antibiotics;
- rachiocampsis. Due to the close location of the stomach to the vertebrae, when nerves are pinched, pain can be felt in the epigastric part on the left or right side;
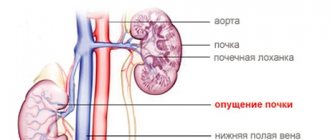
- renal colic. Pain occurs when moving stones.
- eating solid foods;
Video on the topic:
- The protrusion of part of the small intestine through clefts in the upper abdominal muscles can provoke the appearance of unpleasant painful sensations of a cramping nature. In addition to pain in the upper region of the stomach, symptoms of this condition include the appearance of a small bulge that can be felt.
- A fracture of the lower part of the chest leads to pain in the upper, central parts of the stomach, and they can change their intensity while moving, walking, or bending forward; the pain can worsen or go away.
- The presence of constant dull pain in the upper abdomen, which periodically intensifies during or after eating, may indicate a weakening of the aortic wall (in patients over 50 with atherosclerosis or other diseases that contribute to protrusion of the aortic wall or splitting of its layers).
- Heart attack (this may begin with a tingling sensation in the upper abdomen when inhaling or exhaling).
- Excruciating pain in the upper abdomen can be a sign of appendicitis, but it is predominantly localized in the right side of the abdomen and does not affect its central area.
- In women, pain in the upper and central part of the abdomen of a pulling nature can be a symptom of pathologies of the reproductive system - ovarian cysts, ectopic pregnancy, miscarriage and others.
- Abdominal muscle injuries. In addition to the gnawing pain in the upper zone of the stomach, you can observe a small noticeable bulge in the form of a hematoma.
- Pancreatic dysfunction.
- Abuse of coffee and alcoholic beverages, which leads to irritation of the mucous membrane and causes pain in the form of pain in the left intercostal space.
- Smoking, stress and poor diet.
If a person experiences sharp or aching pain under the ribs on both sides, then it may indicate the development of very dangerous pathologies. It is unlikely that a normal physiological phenomenon can be considered as the cause of discomfort in such a situation. That is why people who have pain under the ribs on both the right and left need to go to a hospital for consultation and undergo a comprehensive examination.
Burning and pain under the ribs on both sides may be a sign of the development of the following pathological conditions:
- Diseases developing in the spinal column.
- Heart attack.
- Pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, which usually include cholecystitis, pancreatitis, gastritis, gastroduodenitis, and ulcerative lesions.
- Diseases of an infectious nature, the course of which usually occurs in a chronic form, for example, mononucleosis, tuberculosis.
- Pathologies developing in the genitourinary system, for example, urolithiasis, cystitis.
- Mechanical damage to the liver or spleen, in which the integrity of the organ was damaged.
- Diseases affecting the respiratory tract, which can be either infectious or viral in nature.
The patient should monitor the intensity of pain.
If they can be described as acute, then you must immediately call an ambulance, which will transport him to a hospital facility.
On site, highly specialized specialists will examine the patient and then prescribe him a course of drug therapy. If it is determined that the cause of the pain is a life-threatening pathology, the patient will undergo unscheduled surgical treatment.
Ulcerative pathology is most often detected in the stomach, as well as in the duodenum. If a person does not undergo drug therapy in a timely manner, the disease will progress. The result may be perforation of the lesion, as a result of which a hole is formed at the site of its localization, through which the contents of the organ begin to penetrate into the retroperitoneal zone.
People who have encountered such a problem give the following description of painful sensations: pain of a dagger type, occurs suddenly, the attack lasts a short time. The localization of the source of pain is initially the solar plexus area. After some time, it begins to move to the subcostal zones.
With the development of inflammation in the pancreas, people experience painful sensations of a girdling nature. Their intensity increases with any tension or movement of the body. Most often, patients turn to specialists with complaints after heavy meals, which included sweet and fatty foods.
Excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages can also provoke an exacerbation of the disease. If a person encounters inflammation of the gland for the first time and promptly turns to a hospital for help, then he has a chance of recovery. In the case where drug therapy was not carried out in a timely manner, the disease will quickly become chronic and will periodically remind itself of relapses.
With the development of inflammation in the gallbladder, people experience painful sensations that are initially localized in the right hypochondrium, but in the absence of timely drug therapy they can radiate to other areas of the peritoneum. At the same time, characteristic symptoms appear:
- feverish condition;
- there is a drop in pressure;
- cold sweat appears;
- the skin may become icteric;
- suffers from constant nausea;
- severe vomiting occurs, etc.
To reduce the intensity of discomfort in this category of patients, experts recommend applying a heating pad filled with ice to the source of pain during an attack. They should also adhere to bed rest for several days and limit their diet. In the case when the acute form of cholecystitis is accompanied by very intense pain, people can alleviate the condition through analgesics or antispasmodics.
With the development of this pathology, people experience painful shooting or tingling sensations. Their intensity increases with any tension or movement of the body. Some patients feel as if there is a foreign object in the peritoneal area. In parallel, the following symptoms develop:
- hiccups occur;
- a dry cough begins;
- shortness of breath appears.
Pain in the right hypochondrium and back
Pain syndrome of such localization always becomes the reason for a thorough examination of the kidneys. And if it appears frequently under the shoulder blade, the doctor suspects lung damage. This usually indicates the development of an inflammatory process of bacterial, viral or fungal origin. But the formation of malignant neoplasms in them, which reduce functional activity, is also possible.
Pneumonia
Pain under the right rib does not appear immediately. Several days pass from the moment infectious pathogens penetrate the pulmonary pleura. Pneumonia often becomes a consequence of not seeing a doctor for tracheitis, bronchitis, tonsillitis, or influenza. It is also predisposed to congestive heart failure, chronic bronchitis, chronic nasopharyngeal infection, congenital malformations of the lungs, severe immunodeficiency conditions, prolonged immobilization, elderly and senile age. The disease manifests itself with the following symptoms:
- Increasing temperature.
- Severe pain behind the sternum on the right.
- Shortness of breath, feeling of lack of air when inhaling.
- Pale skin, blue discoloration of the nasolabial triangle.
- Excessive sweating.
In children and weakened patients, digestive and peristalsis disorders are common - diarrhea, attacks of nausea and vomiting, suppression of appetite.
After the introduction of microbes or viruses into the lungs, their active growth and reproduction, general intoxication of the body rapidly develops. It is this that leads to severe complications that can cause death.
Pleurisy
Soreness at the bottom of the ribs located on the right may indicate pleurisy - the formation of an inflammatory focus in the area of the pleural layers. This leads to the deposition of fibrin fibers on the pleura with further formation of adhesions. Accumulation of purulent, serous or hemorrhagic effusion inside the pleural cavity is also possible.
If the patient complains of pain in the right hypochondrium, the doctor may suspect pleurisy
In most cases, patients are diagnosed with infectious pleurisy: parasitic, bacterial, fungal, viral. But it also develops as a result of malignant pleural tumors, breast cancer, lymphoma, ovarian tumors, systemic vasculitis, lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, myocardial infarction. In addition to pain on the right side, pleurisy is characterized by:
- cough;
- temperature rise to significant levels;
- decreased appetite;
- earthy skin tone;
- bad breath.
Simultaneous therapy is carried out for both pleurisy and the pathology that provoked it. Systemic antibiotics, antimycotics or antivirals are used. In severe cases, glucocorticosteroids are used in the form of injection solutions.
Description of pain
“It hurts between the ribs” - this is how people usually talk about the unpleasant sensations that appear in the chest. The epicenter of this discomfort is in the following places:
- muscles;
- fascia;
- intercostal nerve;
- bone or cartilage.
Discomfort in the intercostal space prevents a person from living fully.
Pain in the ribs can be long-lasting, acute, pulling, aching, or stabbing. This ailment worries either constantly or in specific situations, for example, when being in the same position or when doing work that requires serious physical exertion.
Features of pain in the upper abdomen in the middle
Periodic pain in the upper abdomen cannot be a separate disease.
As medical practice shows, this is always a sign of a developing pathology. That is why, at the first manifestations of this symptom, it is recommended to consult a doctor as soon as possible and carry out diagnostic procedures. In most cases, the cause of pain with this localization is pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, which are located in this part of the abdominal cavity. At the same time, it is worth noting that sometimes under this sign there may be diseases not related to the gastrointestinal tract, which are accompanied by vague, radiating pain (when it hurts under the ribs, in the chest, radiates to the back, etc.). This, in turn, may indicate neuralgia or a hernia.
In medicine, cramping severe pain has a common name - “acute abdomen”. In this condition, the patient usually requires urgent medical care and hospitalization.
It is especially important not to delay calling a doctor if the patient suffers from severe chronic pathologies or if the patient is a child. Pain in the upper abdomen in the middle part is a sign that can indicate very different diseases. That is why, in addition to him, the doctor needs to pay attention to the patient’s complaints:
- This could be nausea after eating or on an empty stomach, diarrhea and bloating, vomiting, etc.
- How often and with what intensity does pain occur (what provokes it). Thus, pain most often develops when coughing, after drinking alcohol, or after nervous or physical stress.
- The nature of the pain (bursting, dull aching, cutting, etc.).
Only by taking into account all the signs together will the doctor be able to correctly identify the cause of the disease and select the necessary treatment.
Diagnosis of pain between ribs
Pain occurs due to the influence of numerous factors. As a rule, these can be diseases of the heart, trachea, and gastrointestinal tract. However, only a specialist will be able to name the exact cause of the discomfort.
Frequent causes of this disease will be described below.
Pinched nerve
A pinched nerve is the first reason that a person feels pain symptoms in the intercostal space. This usually happens with the following diseases:
- osteochondrosis;
- protrusion;
- intervertebral hernia.
Excessive stress on the spine, hypothermia, infection, injury - all this can cause a pinched nerve. In addition, multiple sclerosis or polyneuropathy can also become irritants.
A pinched nerve is a common cause of discomfort.
A person may also experience intercostal neuralgia. It causes pain in all parts of the chest. The pain during its development is so “burning” that it resembles an electric shock. Moreover, it becomes stronger when a person changes position, takes a deep breath or makes a sudden movement. He has to choose a position in which the pain bothers him the least. Because of the discomfort, the person must tilt their torso in an attempt to put less “strain” on the source of the pain.
During the palpation procedure, the doctor determines the development of the disease and the presence of tingling and numbness in the chest based on the activity of the nerves in the intercostal space.
The symptoms of pain between the ribs make it clear that you need to see a doctor as soon as possible.
Diagnosis begins with examining the patient and collecting anamnesis, but this is not enough to make an accurate diagnosis. The doctor will be able to indicate recommendations for treatment and the choice of appropriate therapy after the patient undergoes the following diagnostic procedures.
| Diagnostic technique | Description | Accuracy |
| Ultrasound of the heart | A standard diagnostic procedure that can be performed in any medical institution. Prescribed for suspected heart problems. | 40-60% |
| EGDS | This diagnosis is prescribed by a doctor for possible diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. | 0.5 |
| Electrocardiography | A diagnostic method prescribed for symptoms suggestive of heart disease. | 50-80% |
| MRI | A type of minimally invasive diagnostics that allows you to obtain information through magnetic resonance. Does not negatively affect health. | 75-85% |
| CT | The most informative diagnostic procedure, by which you can immediately determine the root cause of pain between the ribs. | 85-90% |
These examinations will help the doctor identify the root cause of pain between the ribs and make a final diagnosis.
Diagnosis of pain in the intercostal space helps to find a treatment method as quickly as possible
The patient usually needs help in the form of consultation with the following doctors:
- neurologist;
- traumatologist;
- gastroenterologist;
- cardiologist.
They assess the patient’s health status, the severity of the disease and the speed of its development.
Nature of pain
Before defining the characteristics of pain, you need to find out:
- What time of day does it occur?
- Where exactly does it hurt and how?
- What did you do before the pain appeared under the diaphragm, in the middle?
- Have there been any injuries or are there ongoing acute illnesses?
Now let's go through each of the points.
- Pain between the ribs below is indignation of the solar plexus. They can come at you at any time of the day. According to statistics, pain occurs in the evening or during sleep.
Why is this happening?
We perform a large number of actions during the day. Work, children, everyday life take away your strength and ROUTINE. A disrupted diet, sleep, incorrect loads during possible training - all these are signs that the body will soon fail. An unhealthy diet is added to the regime - it is this that most often leads people to acute pain. Fatty, fried, heavy, spicy food for dinner inflames the entire digestive system. As a result, it hurts between the ribs, in the middle, in the front when compressed.
- The nature of the pain depends on the diseases that caused the solar plexus to malfunction. Most often they manifest themselves as: sharp, pressing, sharp, burning, pulling.
They are divided into: chronic and permanent/local and spasmodic. Chronic pain is constant, severe and does not go away on its own. They develop into serious diseases of the digestive system, and can lead to heart problems.
- You need to find out, remember, identify what you did before the onset of illnesses.
Hard evening workouts. It's no secret to many that training in the gym with weights can cause muscle injuries. But, training after work, carrying heavy weights and persistently squatting after 21.00, not only muscle structures are tense, but also nerve endings. The result is a malfunction in the body's systems, problems with sleep, a general disruption of the daily routine, a burning sensation under the ribs, in the center, and the inability to sleep.
Meals for the night. Imagine, your body is already ready for sleep, all its work slows down, your metabolism is about to go to rest. And you offer him a piece of fatty pork with fried potatoes. Then you go to bed. And all systems are trying to digest what they have eaten. As a result, food stagnates and gastric juice cannot cope with the volume. Digestion is no longer in working tension, but in nervous tension. With such actions, burning, sharpness, baking, spasms, and pain just above the stomach occur.
Stress is the cause of all our diseases. Because of it, the body is in constant tension. Pain can appear anywhere, of a completely different nature. Lead you to weakness, emotional loss of strength, diseases of neurology, digestion, heart.
- Injuries, chronic diseases. One of the most common causes in the solar plexus area. Having received a blow between the ribs, the largest nerve node will become sharply inflamed and will respond as sharp, severe pain. A blow delivered with great effort will cause nausea, burning, and dizziness. In cases of such actions, it is necessary to help the victim straighten up, or even better, lay him on his back in an even position.
Why does a burning sensation occur in the hypochondrium on the right?
A burning sensation is a type of pain that occurs with severe irritation and acts as a danger signal that mobilizes the body to eliminate the causes of the disease. Pain can be true (felt in the diseased organ) and reflected, when a person feels it on areas of the skin remote from the source.
A burning sensation in the right hypochondrium is disturbing in cases of pathology of the liver, gallbladder, and kidneys. Pain on the left occurs with diseases of the stomach or pancreas. Referred pain is a common symptom of spinal diseases: spondyloarthrosis, spondylitis deformans (Bechterew's disease), intervertebral hernia. A burning sensation in the left hypochondrium in front may be a consequence of herpes zoster, intercostal neuralgia.
The most common cause of burning in the right hypochondrium is cholecystitis. The following may cause discomfort:
- gallstones;
- enteritis, gastritis;
- low acidity of gastric juice;
- stagnation, changes in the chemical composition of bile;
- eating disorders;
- neuroses, neurotic states.
If the cause of the burning sensation is kidney pathology, the problem may develop as a result of the following provocateurs:
- unbalanced diet;
- hereditary factors;
- metabolic pathologies;
- inflammation and abnormalities of the genitourinary system;
- taking certain medications.
The cause of a burning sensation in the left hypochondrium can be gastritis, gastroduodenitis, or a stomach ulcer. These diseases develop under the following circumstances:
- infection with bacteria Helicobacter pylori;
- eating low-quality products;
- drinking alcohol;
- the presence of purulent infection in the oral cavity (dental caries) and pharynx (tonsillitis);
- leakage of duodenal contents due to impaired motility of the digestive tract.
Referred pain and burning in the right side occur due to diseases of the spine: spondyloarthrosis, spondyloarthritis (Bechterew's disease), intervertebral hernia cause the growth of bone tissue of the vertebrae - osteophytes, which irritate the spinal roots. Painful impulses radiate (reflect) along the nerve trunks in the hypochondrium, causing burning pain.
Causes of spinal pathology:
- injuries, damage;
- great physical activity;
- impaired blood supply due to atherosclerosis, vascular pathology;
- metabolic diseases and endocrine problems;
- systemic connective tissue diseases - rheumatism, scleroderma.
Shingles is caused by a virus that affects the nerve trunks, along which pain is reflected in the hypochondrium. The pain is always one-sided - either in the left hypochondrium or the right.
Intercostal neuralgia causes reflex pain in the hypochondrium and burning sensation. Causes:
- injuries;
- colds;
- long stay in a static position for transport drivers and office workers;
- hypothermia.
Depending on the problem area, other symptoms also appear, which undoubtedly need to be taken a closer look at. The nature of the unpleasant sensations and accompanying manifestations indicate which organ needs examination.
A burning sensation in the right hypochondrium is a fairly common complaint of patients when visiting a therapist. Moreover, this applies to people with previous diagnoses, and people without health problems who engage in frequent physical activity. And despite the fact that the symptom does not cause much concern, such a signal from the body cannot be tolerated.
A burning sensation in the right side under the ribs in front is a cause for concern about many organs.
They are much less common, but it is also advisable to be aware of them:
- For intercostal neuralgia. Intercostal neuralgia belongs to the list of neurological diseases. Its symptoms are periodic burning pains under the ribs or in the area (between the ribs).
- In case of rib bruises, the directly damaged ribs will hurt. The pain will be constant and aching. This is not the most dangerous type of burning that could be. But an examination by a traumatologist and neurologist is necessary.
- For osteochondrosis of the lumbar region. This disease differs in symptoms from all previous ones. Considering that the musculoskeletal system is affected, the pain moves in the direction from the lower back (on both sides) to the legs. It appears during physical activity or just walking.
- For herpes zoster. The likelihood that the burning sensation in the right side under the ribs in front from shingles is small. Its symptoms are easy to distinguish. The pain will not come from the inside, but only the upper layers of the skin will hurt.
- With thrombosis of the vena cava. With this problem, you will feel not only a burning sensation in the ribs area. The entire lower part of the body goes numb and fails.
- Heart diseases. Oddly enough, with some heart diseases, such as, for example, an attack of angina, the symptoms can also be reflected far from the source. An attack will provoke only one wave of pain and burning from the lower part of the left rib to the right region of the chest. In this situation, call an ambulance or go to the hospital yourself immediately.
- Lungs. Diseases associated with the lungs also include diaphragmatic pathologies. They are more of a mechanical damage. The symptom is painful discomfort in the radius of the liver, on the left.
- Stomach diseases. The main and most common stomach diseases are gastritis and ulcers. Often, patients initially do not distinguish them from liver pathologies. The distinctive character is that the discomfort begins after eating heavy food.
If a burning sensation in the right side under the ribs in front bothers you precisely after eating a heavy meal, its possible causes may be problems with the abdomen:
- pancreatitis;
- ulcer;
- gastritis;
- diaphragm pinching;
- hernia and other diseases of the stomach, intestines or duodenum.
This “bell” should make you think about your health.
- severe pyelonephritis: if a burning sensation appears and is present non-stop and the symptom becomes more noticeable during blows in the area of the ribs of the back.
- chronic pyelonephritis: periodic discomfort, aching, but tolerable. It worsens during the rainy seasons or simply when the weather is humid.
- renal colic: pain is caused by the movement of the stone through the fluid outlet channels. The pain is severe, often blocking the movement of the entire body due to an unbearable burning sensation.
- urolithiasis: the intensity of pain depends on the size of the crystal in the flows. It worsens when jumping, turning the body and after drinking liquid.
- acute pancreatitis: a burning sensation under the ribs is more like a strongly compressive belt. Accompanied by a burning sensation, nausea and vomiting. It becomes more noticeable when lying down.
- osteochondrosis: a disease of the musculoskeletal system. Sharp stinging and burning are replaced by dull pain. They constrain the body in the lumbar area, but do not allow you to stay in one place for a long time.
- retroperitoneal hematoma: manifests itself as a consequence of a back injury, because cracking of the vessel is possible. Therefore, the heavier the bleeding, the more intense the burning sensation.
It can result in shock, complications and even death.
This article provides information for your reference, but an accurate diagnosis, specific and most importantly effective treatment can only be prescribed by a physician and a good examination.
Causes of pain between the ribs in the middle
Pain between the ribs in the middle in the front can be caused by a large number of different triggers. The most common abnormalities in the functioning of the body deserve special attention.
Chest injuries
A common cause of rib fractures is transport accidents.
Traumatic injuries are a violation of the integrity of bone fragments, bruises, compression and concussions. They are diagnosed after mechanical impact in the sternum area as a result of domestic or industrial injuries, natural disasters, criminal actions of other persons, car accidents.
Most often, the examination reveals fractures of one or more ribs, which, depending on the complexity of the fracture, can lead to internal bleeding and damage to internal organs and systems. The clinical picture is pronounced and is accompanied by acute pain, compression of the sternum towards the back, difficulty when trying to inhale and exhale.
The treatment regimen will depend on the complexity of the damage. Can be performed on an outpatient basis or in a hospital setting.
Intercostal neuralgia
Intercostal nerve entrapment can cause chest pain in the front
Due to compression of the nerves, a person develops severe pain in the sternum area. This develops as a result of developmental pathologies or diseases of the spinal column, dysfunction of the endocrine system, and the development of infectious diseases. Intercostal neuralgia can be triggered by stressful situations, hypothermia, disturbances in the functioning of the immune system, and chronic fatigue syndrome.
The clinical picture is severe and manifests itself in the form of intense dull or sharp pain, aching or piercing painful sensations mainly on the left side of the body, which intensify with movement, coughing or sneezing. The person sweats profusely, has difficulty breathing, and has numbness and/or twitching of the chest or back muscles.
The diagnosis can be made based on the results of a bacteriological blood test, x-ray, magnetic resonance imaging, ultrasound and FGS.
Angina pectoris
Angina is caused by atherosclerotic plaques inside the heart vessels
Pain in the chest area can be caused by insufficient blood supply to the muscle fibers. The pain is accompanied by a burning sensation and heaviness, squeezing and general discomfort of the neck, arms, shoulders and back. In most cases, it is paroxysmal in nature; attacks develop in stressful situations or during excessive physical exertion.
The development of angina pectoris can be triggered by emotional instability, lack of physical activity, obesity, bad habits, a predisposition to the formation of blood clots, and high cholesterol levels in the blood.
Shingles
The herpes virus causes vasospasm and muscle pain in the ribs
The disease develops as a result of herpes zoster virus particles entering the human body. If a person's immune system is weakened, pathogens begin to multiply rapidly, attacking healthy tissue. The development of the disease is accompanied by a strong increase in temperature, general malaise and headaches. Characteristic rashes appear on one side of the chest and abdomen, which bring pain and unbearable discomfort to a person.
Painful sensations persist for a long time. It is important to make a correct diagnosis as early as possible and begin proper treatment, otherwise serious complications may develop - arthritis, hepatitis, myocarditis, meningitis, kidney failure, pneumonia, complete paralysis.
Tietze syndrome
Inflammation of the cartilage at the front of the breastbone
This is a pathological process accompanied by inflammation of the costal cartilages and the connecting part of the sternum. The disease causes pain and swelling of the soft tissues. The disease develops against the background of excessive emotional or physical overload, prolonged cough syndromes and due to chest injuries.
A correct diagnosis can be made after a clinical examination, as well as magnetic resonance imaging, ultrasound and x-rays. The basis of the therapeutic course is the use of painkillers and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, ointments and topical creams.
Pleurisy
Fluid accumulation in the lung causes chest pain and cough
This pathological condition is accompanied by inflammation of the serous membranes of the lungs. It develops against the background of injury or infectious lesions, developmental pathologies or diseases of the digestive system, under unfavorable living conditions and toxic effects. Pleurisy is characterized by the appearance of shortness of breath and cough, acute attacks of pain between the ribs, displacement of the trachea and increased body temperature.
It is possible to make a diagnosis based on the results of a clinical and microbiological blood test, x-ray and analysis of pleural biomaterial. The basis of therapy is courses of antibiotics and anti-inflammatory medications with strict adherence to diet.
Osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine
Damage to the thoracic vertebrae leads to spasm of the rib muscles
This disease is accompanied by sharp and/or aching pain in the area of the shoulder blades and sternum, while the legs may go numb, and the muscle fibers of the back and chest are in constant tension. As the pathology develops, disturbances in respiratory processes and heart rhythm disturbances are observed.
Osteochondrosis develops with a genetic predisposition, insufficiently active lifestyle, metabolic disorders and excess weight.
A correct diagnosis can be made using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), radiography, ultrasound and ECG. The therapeutic course is determined by a neurologist; the basis of treatment is analgesic and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, chondroprotectors. In the absence of contraindications, a course of therapeutic massage, physiotherapeutic procedures and physical therapy are prescribed.
First aid
Only a doctor can determine the exact cause of the pain. If you have any problems with going to the doctor, you can do the following:
- As soon as pain appears between the ribs, you need to immediately take a position in which there will be no discomfort. Discomfort tends to increase with sudden movements, such as bending and turning. Changing positions helps normalize your well-being. Lying on a hard surface can alleviate the condition.
- To relieve pain, you need to take painkillers. These include “Analgin”, “Ketonov” and others. However, if the pain remains as severe, it is better to wait for an ambulance to arrive.
- If pain is felt on the left (which is a clear sign of angina), you should cancel any work that requires physical activity. Instead, it is better to lie down and drink Nitroglycerin.
- If you feel discomfort in the stomach, extending into the intercostal space, you need to drink more water and temporarily not eat.
Causes
The causes of any pain in the hypochondrium from the back are natural and pathological. The latter include acute, subacute and chronic diseases affecting the spine and internal organs, as well as injuries of varying severity. Not only its localization, but also a complex of accompanying symptoms helps the doctor make an initial diagnosis and quickly discover the cause of the pain. For example, stiffness, increased local body temperature, crunching when bending and turning the body clearly indicate progressive osteochondrosis.
There are not so many physiological causes of pain under the ribs that radiate to the back. They are natural for beginner athletes who immediately began active training. Unprepared muscles do not have time to adapt to increased loads, so they hurt for several days. Similar discomfort is typical for the entire period of bearing a child.
It is provoked by various factors:
- constant fluctuations in hormonal levels;
- deficiency in the diet of foods high in vitamins and minerals;
- compression of organs located in the abdominal cavity by the growing uterus.
In clinical practice, cases of pain occurring due to stress, emotional shock, and depression have been reported. To save patients from them, doctors included in treatment regimens not analgesics, but antipsychotics, tranquilizers, and antidepressants.
Back pain under the ribs can be side effects of pharmacological drugs that are quite toxic to the human body. Sometimes this is how a long course of taking glucocorticosteroids, cytostatics, antibiotics, and antimicrobial agents manifests itself.
Symptoms
Clinical manifestations depend on the underlying pathology. A burning sensation in the hypochondrium on the right in diseases of the liver and gallbladder is combined with the following symptoms:
- unpleasant taste in the mouth;
- vomiting occurs after eating;
- icteric coloration of sclera, skin;
- dark urine;
- low-grade fever;
- constipation or diarrhea.
Kidney disease is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- hematuria - red blood cells in the urine;
- painful, frequent urination;
- cloudy urine with flakes;
- increased body temperature due to kidney inflammation.
A burning sensation in the left hypochondrium occurs with gastritis. The symptoms are as follows:
- heaviness, pain 5–10 minutes in the epigastric region after eating;
- diarrhea and constipation;
- poor appetite;
- weight loss;
- heartburn;
- unpleasant taste in the mouth.
Inflammation of the pancreas is accompanied by burning pain and symptoms of pancreatitis:
- uncontrollable vomiting;
- loose stools;
- flatulence - bloating;
- rapid pulse;
- weight loss;
- dry pale skin;
- signs of vitamin deficiency.
Referred pain in diseases of the spine is associated with pathology of the musculoskeletal system. They intensify with movements, turns, and bending of the body. When radicular syndrome appears, the burning sensation is combined with other neurological symptoms - “pins and needles”, numbness of the fingers.
Causalgia - the term translates as “burning pain”, a characteristic symptom of herpes zoster. The presence of a rash and blisters along the nerve trunks, combined with a burning sensation in the hypochondrium, allows one to confidently diagnose this disease. Causalgia is typical for neuralgia. Characterized by increased pain with movement and coughing.
Burning does not become the only symptom of the disease, but is combined with a large number of clinical manifestations of other pathologies of internal organs, therefore it is necessary to conduct a complete and detailed examination of patients with this syndrome.
Pain in the left hypochondrium and back
Pain in the back and under the left rib is much less common and is characteristic of pathologies of internal organs. At the initial stages of their development, they are localized only in a certain area. But as the inflammatory or degenerative process progresses, the pain radiates to the thoracic or lumbar spine. What pathologies may be indicated by constant or temporary pain in the left side:
- pancreatitis;
- glomerulonephritis;
- angina pectoris;
- splenic abscess.
Soreness on the left is one of the typical symptoms of a pre-infarction condition. Therefore, immediate hospitalization of the person is necessary, otherwise the risk of severe, irreversible damage to the heart muscle is high.
Even mild, rarely occurring pain in the hypochondrium and back should be a signal to consult a doctor. Pathology detected at the initial stage is much easier to treat. If a person suppresses pain by taking analgesics and ignores their intensification, complications develop. Therefore, soon the doctor has to treat not only a pathology of high severity, but also get rid of its consequences.
When to see a doctor?
You should consult a doctor if you have the following complaints:
- prolonged pain;
- limited movement;
- chest injury.
It is important to know that the lack of treatment will sooner or later provoke various kinds of complications.
Seeing a doctor about pain between the ribs means taking the first step towards recovery.
For example, angina pectoris leads to a heart attack, pleurisy leads to pneumonia or lung abscess, cancer leads to internal bleeding or even death.
Pathological processes that were not given timely attention lead to long and difficult treatment, which is rarely successful. In the most complex and advanced cases, the disease progresses so quickly and severely that it can be fatal for the patient.
Considering that there are too many diseases that can cause this symptom, it will not be possible to solve the problem on your own. It is imperative to see a doctor; he will correctly determine the cause and prescribe proper treatment.
Otherwise, the development of pathological phenomena may begin. You can independently determine only the burning sensation from physical activity, food or something else. Therefore, if the cause of the burning sensation under the ribs is food, then before visiting the doctor, arrange a gentle diet for yourself.
If physical activity is an aggravation, limit yourself from it.
The main thing is not to delay your visit to the doctor, but to contact the doctor as quickly as possible in order to identify the problem “without delay”.
Etiology
Pain in the hypochondrium is one of the most ambiguous signs, as it can indicate the development of any pathological process in the body. If it hurts on the left or right in the hypochondrium, this may be a consequence of the following etiological factors:
- inflammatory processes localized in the pancreas;
- gastroenterological diseases;
- dysfunction of the pancreas;
- pathological processes in the liver, including benign or malignant formations;
- pathological processes in the spleen, including its enlargement.
In addition, pain in the right or left hypochondrium, and in some cases on both sides, can be a consequence of the following diseases:
- retroperitoneal hematoma;
- dystonia of neurocirculatory type;
- infectious or inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system;
- liver or spleen injuries;
- myocardial infarction, but only the type that occurs in the gastralgic form;
- abscess of subphrenic location;
- osteocondritis of the spine;
- some diseases of the upper respiratory system - pleurisy, pneumonia localized in the lower lobe of the lung.
Pleurisy
In addition, heaviness in the right hypochondrium may be symptomatic, and the predisposing reasons for this may be the following:
- excessive amounts of fatty and rough foods;
- late dinners (less than an hour before bedtime);
- excessive amounts of alcohol consumed;
- the presence of chronic diseases of a gastroenterological nature or in the genitourinary system and non-compliance with the prescribed diet;
- excessive physical activity;
- prolonged stay in an uncomfortable position.
In any case, only a doctor can establish the exact causes of pain in the back and hypochondrium by carrying out the necessary diagnostic measures and collecting a personal – and in some cases, family – history.
Diagnostic methods
The examination begins with an examination by a doctor, clarification of complaints, medical history, working and living conditions, and heredity. The data obtained allows you to make a preliminary diagnosis, continue diagnosis, and draw up a treatment plan.
Mandatory laboratory tests:
- Counting the number of red blood cells, platelets, and leukocytes in the blood. The amount of hemoglobin and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) are determined.
- Urinalysis - measure specific gravity, study the presence and number of epithelial cells, sugar, bile pigments.
- Using biochemical studies, the state of protein, carbohydrate, and mineral metabolism is assessed.
- Wasserman reaction to exclude syphilis.
If there are medical indications, additional laboratory tests are performed. In case of liver pathology, the content of bilirubin and bile pigments in the blood and urine is determined. If a patient has inflammation of the pancreas, amylase and other pancreatic enzymes are examined. In case of kidney pathology, the creatinine content in the urine is studied.
Instrumental studies are carried out taking into account the nature of the underlying pathology. For diseases of the spine and osteoarticular system, radiation methods are used - radiography, computed tomography. Soft tissues and internal organs are studied using ultrasound.
Endoscopic methods are used to examine hollow organs, gastroscopy to examine the gastric mucosa, and cystoscopy to examine the bladder. If necessary, patients are consulted by specialists from related medical specialties: neurologist, urologist, orthopedist, gastroenterologist. A comprehensive examination allows for effective therapy.
Burning in the hypochondrium is a symptom, the elimination of which without affecting the cause and mechanisms of development of the pathology will not lead to a radical cure. First of all, it is necessary to treat the underlying disease.
For liver diseases use:
- hepatoprotectors - “Legalon”, “Methyluracil”, “Lipoic acid”;
- for viral hepatitis - Interferon and its analogues;
- Dietary food is required.
Patients with calculous cholecystitis should be recommended surgical treatment - removal of stones. For infectious etiology of gallbladder inflammation, antibiotics are prescribed.
For kidney diseases use:
- broad-spectrum antibiotics - Gentamicin, Levofloxacin, Norfloxacin, Ceftriaxone;
- uroseptics - “Furadonin”, “Furazolidone”, “Nitroxoline”, “Khinozol”;
- painkillers - Paracetamol, Ibuprofen.
Pancreatitis is treated with:
- diet therapy - it is forbidden to eat fatty, fried, spicy foods;
- enzyme preparations - “Festal”, “Digestal”, “Mezim Forte”;
- drugs that suppress fibrinolysis - “Kontrikal”, “Gordox”;
- for pain, Atropine, Ranitidine, and Platifillin are prescribed.
Therapy of gastritis and gastric ulcer:
- drugs to reduce the acidity of gastric juice - “Almagel”, “Phosphalugel”;
- to increase acidity - “Apilak”, “Plantain juice”;
- enveloping agents - “Decoction of flax seeds”, “Smecta”;
- enzyme preparations - “Festal”, “Mezim Forte”;
- Amoxicillin and Tinidazole are used to suppress Helicobacter pylori bacteria.
Degenerative-dystrophic disease of the spine, spondyloarthrosis, is treated with drugs that improve tissue nutrition:
- chondroprotectors - “Teraflex”, “Arthra”, “Rumalon”;
- vitamin and mineral complexes - “Complivit”, “Vitrum”.
Today, there are the following types of diagnostics for abdominal discomfort:
- ultrasound diagnostics of the abdominal cavity;
- CT;
- MRI (liver, lungs, vertebrae);
- palpation;
- laboratory testing of material (blood, feces and urine).
The primary diagnostic method is palpation of various areas of the abdomen to look for areas of inflammation and swelling. Further diagnostics includes the following research methods:
- MRI, CT, ultrasound, radiography (these methods will help diagnose possible fractures, ruptures, swelling and growths);
- colonoscopy (examines the inside of the colon and intestines);
- endoscopy (pathologies are detected in certain parts of the esophagus and stomach);
- blood, urine, and stool tests (to identify possible parasitic, viral and bacterial infections).
Based on the results of the study, a diagnosis is made and treatment is prescribed.
Diagnostics
To slightly reduce the list of pathologies that can provoke pain under the ribs, it is necessary to detail the unpleasant sensations that arise as much as possible:
- Determine the most precise localization of the pain syndrome;
- Establish the exact paths of pain irradiation - that is, the points to which it spreads;
- Determine the strength of pain;
- Assess the nature of the pain - paroxysmal or constant, aching, pulling, sharp or dull, girdling, shooting;
- If possible, identify factors that increase pain - coughing, sneezing, deep inhalations/exhalations, sudden movements;
- Determine what reduces the intensity of pain or completely relieves it - heat, cold, antispasmodics, analgesics, a certain body position;
- If you have back pain in the rib area, this may recur at regular intervals. You can try to establish what exactly contributes to the appearance of pain - time of day, physical activity, connection with food intake.
It should be added that when the back hurts under the ribs, other signs also play an important role in the diagnosis. These include increased body temperature, fever, nausea, and vomiting.
In addition, by examining in detail all the features of the painful sensation and describing them to the doctor, you can significantly help him make an accurate diagnosis.
The first stage of diagnosis is palpation of the abdomen
If pain of this nature occurs, you should consult a therapist. He will conduct an initial examination and, if necessary, refer you to another highly specialized specialist - a gastroenterologist, cardiologist, or surgeon. To make an accurate diagnosis, the patient is prescribed a number of studies:
- general and biochemical blood test;
- PCR diagnostics of infectious diseases;
- general urine analysis;
- stool examination to determine the effectiveness of the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
If necessary, ultrasound and endoscopic diagnostics of the digestive organs and ECG are prescribed. In false cases, the doctor issues a referral for an MRI or CT scan.
If you are suffering from rib pain, contact the CELT Pain Clinic. We employ doctors of various specialties who will use the entire arsenal of diagnostic and treatment capabilities of our multidisciplinary clinic to solve your problems. Since there are many reasons that cause pain in the ribs, it is very important to correctly diagnose. This is the only way to correctly diagnose and prescribe treatment.
The most dangerous consequences
Perforation of a stomach ulcer - a peptic ulcer destroys the wall of the stomach, and all the contents leak into the peritoneum. Peritonitis occurs. It is characterized by paroxysmal cutting pain in the lower abdomen, intensifying when lying on the left side, symptoms of intoxication of the body, severe weakness, increased heart rate, and sticky sweat. Emergency hospitalization and immediate treatment are indicated.
Perforation of stomach ulcer
Diagnosis of the causes of intercostal pain
As I said earlier, diagnosing intercostal pain is quite difficult due to the large number of possible causes. Therefore, before visiting a doctor, it is recommended to write down the answers to a number of questions regarding the characteristics of the intercostal space. Moreover, the doctor, in most cases, does not have the opportunity to directly observe a painful attack, therefore, there is no way to see the full clinical picture.
What to write down and tell your doctor about intercostal pain
- Where is the pain located: If it is located in the upper part, it can be associated with stomach problems such as ulcers or heartburn, but also heart problems.
- Intercostal back pain, in the area of the shoulder blade, can be caused by muscle tension, pneumonia, embolism or cancer.
- Below, on the side, on the right under the ribs - these are probably problems with the liver and biliary tract; if on the left, then problems with the spleen or descending colon.
- It is important to note that if the pain is widespread, that is, for example, starting from the chest and spreading to the arm, this may indicate a myocardial infarction.
- The pain occurs when you stand, sit or lie down. For example, pain due to pericarditis, that is, inflammation of the pericardium, is relieved by sitting or standing and worsened by lying down.
How is intercostal pain diagnosed?
The doctor, having studied the medical history and symptoms, formulates a hypothesis regarding the causes of pain, which is then confirmed through a series of clinical studies.
Below are the most common ones:
- ECG. To confirm or exclude the presence of heart disease: heart attack, valve dysfunction.
- Blood analysis. In addition to general tests, they examine, in particular, markers of heart damage that indicate a heart attack.
- Transesophageal ultrasound. Allows, using ultrasound, to detect an aortic aneurysm.
- Chest X-ray. May shed light in cases of pneumonia, pleurisy, tumor.
- CT scan of the chest using contrast. Allows you to confirm pulmonary embolism. Show the location of the blood clot that is blocking the artery.
- Gastroscopy. To identify possible reflux disease.
- RX of the stomach. To confirm an ulcer.
- CT scan of the abdomen. To identify problems of the biliary tract and pancreas.