Etiology
The predisposing causes of the disease depend on the age group of children. Intestinal obstruction in newborns is caused by:
- improper and early feeding of infants, before four months;
- lack of a normal diet in children of the first year of life;
- delayed introduction of complementary foods, as well as prolonged feeding with breast milk only;
- insufficient formation of the gastrointestinal tract;
- structural features of the gastrointestinal tract, in particular the intestines;
- congenital elongation of this organ, as well as a wide range of disorders during the period of intrauterine formation;
- the presence of intestinal diseases of an inflammatory nature.
In children over 2 years of age, among the sources of intestinal obstruction are:
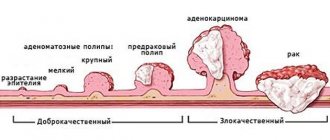
- the formation of benign or malignant neoplasms;
- the presence of fecal stones - the masses harden due to a disturbance in the digestive process or a diet inappropriate for the age group;
- formation of polyps on the membrane;
- entry of a foreign body into the intestine, which leads to blockage of the lumen of this organ;
- the occurrence of adhesive or scar disease, as well as ailments of the genitourinary system;
- volvulus;
- complications after medical intervention;
- immobilization of the large or small intestine;
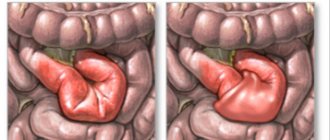
- intussusception is a condition during which the penetration of one part of the intestine into the lumen of another occurs.
Development of intestinal obstruction in children
In some cases, the cause of the disease may be the pathological effect of worms or other parasites.
In some cases, the cause of the formation of the disease may be the pathological effect of worms or other parasites.
Classification
Modern pediatric gastroenterology knows several types of intestinal obstruction in children. According to the nature of origin, the disease is divided into:
- congenital obstruction - occurs as a result of intrauterine pathologies in the development of the gastrointestinal tract in a child, which is why the baby experiences symptoms of the disease from the first days of life. To prevent the recurrence of the disorder, patients are advised to lead an active lifestyle and follow a healthy diet;
- acquired obstruction - the main source of its appearance is intussusception. This form, in turn, is divided into several types. It is diagnosed mainly in infants from the fourth month to one year of life. It differs in that the appearance of symptoms is abrupt and unexpected. In children over 2 years of age, the disease can occur, but is rare.
Acquired intestinal obstruction in children is divided into several types:
- mechanical - occurs due to tumors and fecal stones. In this case, there is a manifestation of severe, cramping pain and disruption of the circulatory process. This may lead to tissue death and peritonitis;
- dynamic - this type of disease develops against the background of previous injuries or operations;
- adhesive - based on the name, the pathology is provoked by the presence of adhesions and inflammation in the abdominal cavity. This is the most common form of this disease in children;
- obstructive;
- strangulation - the main reasons for its appearance are considered to be improper diet, increased intra-abdominal pressure, prolonged fasting, followed by congestion of the stomach.
According to the nature of the spread of the pathogenic process, the disease is divided into several forms:
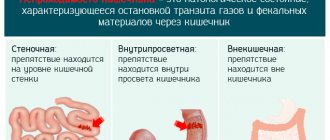
- complete obstruction - often this type is formed as a result of congenital intestinal obstruction and operations designed to eliminate it;
- partial obstruction - differs in that the intestinal lumen is not completely closed. This type can be quite difficult to detect, which is why therapy begins at a later stage.
According to the nature of its course, intestinal obstruction in newborns and children under 2 years of age is divided into:
- acute - is a consequence of various gastrointestinal disorders, hernias and intestinal tumors. Develops to the terminal stage within 24 hours, which is why medical care should be provided as soon as possible after the onset of symptoms;
- chronic – characterized by a milder course. Children suffer from pain in the lower abdomen and constant constipation. The body gradually becomes exhausted.
Depending on the intussusception, acquired or congenital intestinal obstruction occurs:
- small intestinal;
- colonic;
- small-colic – in which part of the small intestine is introduced into the large intestine.
Types of disease
Intestinal obstruction in children is caused by gastroenterological disorders. The degree of development of the disease will depend on the location of the blockage. The higher the education, the more difficult it will be to undergo therapeutic measures. Typically, signs of obstruction appear very quickly and there are noticeable symptoms.
In newborn babies, the pathology appears in approximately 1 case out of 1,500 people. If a child has a stomach ache, bloating, or vomiting, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Gastroenterological problems often lead to intestinal obstruction, and the form and degree of development of the disease depends on where the blockage occurred. Symptoms of this serious disease usually appear immediately.
So, the following types of this disease are distinguished:
- congenital form;
- acquired form.
The congenital form of intestinal obstruction occurs in the case of anomalies of the gastrointestinal tract, such as stenosis or atresia. This form of the disease can begin to develop even before the baby is born, that is, in the womb. If the onset of the disease is not detected in a timely manner, peritonitis may subsequently develop. By the way, the congenital form of the disease is very common among newborns.
The cause of the acquired form of intestinal obstruction is most often the occurrence of inflammatory processes or surgery. The acquired form is also divided into the following subtypes:
- intussusception;
- mechanical obstruction;
- adhesive form of the disease.
The most common forms are intussusception or mechanical obstruction.
An acquired form of intestinal obstruction, as shown by medical indicators, is often observed in children aged 4 months to a year. The disease occurs completely unexpectedly, and the main accompanying symptoms are severe vomiting and sharp attacks of pain. In some cases, there is stool with blood and mucus.
One of the most common forms of the disease is adhesive obstruction. This disease is very serious and requires immediate hospitalization of the baby.
Complications
It is important to treat this disease promptly and effectively, otherwise you cannot avoid dangerous complications. If the intestinal contents stop passing through obstructions, the body begins to consume too large volumes of fluid from the intestinal lumen. Because of this, the skin in the abdominal area becomes stretched and shiny, and pain occurs on palpation. Due to constant vomiting, the body becomes dehydrated.
An imbalance of fluid provokes an imbalance of important chemical elements contained in the blood. These are electrolytes. Because of this, complications associated with irregular heartbeat appear. If it is not possible to quickly restore the electrolyte balance, there will be shock.
Another dangerous complication is kidney failure. It appears as a result of systemic intoxication due to impaired intestinal integrity or dehydration. Therefore, it is important to identify pathology early in order to carry out effective treatment.
According to reviews from patients who themselves have encountered this problem, in the vast majority of cases, obstruction can be overcome with the help of timely, qualified medical care. Then there is a high chance that the child will recover without consequences for the body. If you do not pay attention to obstruction, it can be very dangerous, even fatal.
One of the consequences of this condition is infection of the entire body. In this case, the intestines lose their integrity or become pinched. There are many tactics for drug treatment of volvulus, but in this case the probability of relapse reaches 80%.
If the contents of the intestine are stopped by a certain obstacle, the child’s body takes more fluid from the intestinal lumen than it should. The tummy area becomes painful. His skin is tight, dry and shiny. In addition to this, frequent vomiting causes dehydration and imbalance of chemical elements in the blood.
The prognosis depends on how quickly the parents see a doctor, correct diagnosis and the completeness of the medical care provided. An unfavorable outcome is possible with late detected pathology or inoperable tumors. With adhesions, relapses in the future are likely.
Symptoms
Acute intestinal obstruction in children manifests itself abruptly and unexpectedly. Each type of disease has a characteristic manifestation, but there is a group of symptoms that accompanies any course of the disease. Symptoms of the disease are:
- pain syndrome is cramping in nature. During an attack, the pain is so intense that children often experience pain shock;
- attacks of nausea with frequent vomiting. Excessive vomiting does not provide relief to the baby's condition. If the large intestine is affected, vomiting may be absent altogether;
- disruption of the process of defecation, or rather, complete retention of stool. Children suffer from constipation, which can only be relieved with an enema;
- increase in abdominal size;
- increase in body temperature;
- increased gas formation;
- decreased appetite;
- the stomach ceases to be soft and elastic, which is why it takes on an irregular shape;
- signs of dehydration.
If help is not provided to the child in a timely manner, the above symptoms become more intense.
- pain syndrome is cramping in nature. During an attack, the pain is so intense that children often experience pain shock;
- attacks of nausea with frequent vomiting. Excessive vomiting does not provide relief to the baby's condition. If the large intestine is affected, vomiting may be absent altogether;
- disruption of the process of defecation, or rather, complete retention of stool. Children suffer from constipation, which can only be relieved with an enema;
- increase in abdominal size;
- increase in body temperature;
- increased gas formation;
- decreased appetite;
- the stomach ceases to be soft and elastic, which is why it takes on an irregular shape;
- signs of dehydration.
Treatment with alternative medicine
If the disease is in a mild stage and clinical recommendations allow treatment outside the hospital, then home methods can be used to eliminate constipation after consultation with a doctor.
The most popular are:
- Plum juice or fresh berry puree. Give the product 2-3 tbsp. spoons before meals, diluting a little with water.
- Pumpkin puree or baked vegetable pieces.
- Prune decoction.
- Sea buckthorn oil. Half a teaspoon of it is taken 3 times a day in its pure form or added to porridge, compote, or vegetable salad. For home cooking, fresh berries are poured into an enamel bowl and mashed with a wooden spoon. After this, let it brew for a day and collect the resulting oil from the surface of the berries.
Taking such drugs can only help in certain conditions and only with partial blockage.
If complete obstruction is detected, then this method will only aggravate the patient’s condition. Also, medications will not help with severe intestinal volvulus or developmental anomalies. That is why self-medication is categorically unacceptable.
Such therapy may take place if the obstruction is caused by improper nutrition to clear the intestinal tract of fecal stones.
Light laxatives can be replaced with certain products, for example, kefir or beets, which are more beneficial for the baby. Therefore, drugs are prescribed only in extreme cases. These can be glycerin suppositories.
Forecast
Intestinal obstruction in a child is considered a dangerous pathology that can lead to death. There are a lot of factors for its formation, both acquired and innate. Therefore, during pregnancy, the expectant mother needs to lead a healthy lifestyle, eat right, and exercise.
Timely detection and a favorable prognosis will occur only with the initial development of the disease. Therefore, it is important in case of various digestive disorders, in case of severe pain, not to hesitate, but to immediately go to the doctor.
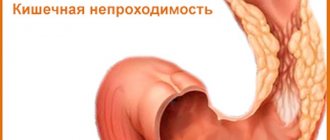
Signs of intestinal obstruction in children and treatment methods
Intestinal obstruction in children is a complex disease in which partial slow movement of feces occurs, and in especially severe cases, its complete cessation. The reasons for this phenomenon may be various malformations of the intestine, in which the motor activity of this organ is disrupted.
Such a pathology requires immediate medical intervention, as it can lead to very serious consequences for the child’s health, even death. In some cases, even surgery may be required.
Stages of pathology development
The main common causes of intestinal obstruction in children should still be mentioned. This:
- some disturbances in the functioning of internal organs;
- existing inflammatory processes;
- accidental entry of foreign objects;
- some parasites and worms;
- adhesive clusters;
- neoplasms;
- hernias;
- formation of gall and fecal stones.
It is worth considering the stages of the disease. According to medical practice, it has three stages:
- The initial stage of the disease lasts about 3-12 hours, and is usually accompanied by pain in the abdomen, severe rumbling and flatulence.
- The duration of the intermediate stage of the disease takes about 13-36 hours. The patient feels some relief, but this is just an imaginary sensation. During this period, intoxication of the child’s body and partial dehydration occur.
- Terminal is the third stage of the disease, which occurs two days after the onset of the disease. The patient's condition deteriorates sharply. All symptoms of dehydration appear, and damage to other internal organs is possible.
Causes
A number of reasons can provoke the occurrence of the syndrome:
- congenital gastrointestinal diseases;
- pathologies of the mesentery;
- functional disorders of the digestive system;
- presence of foreign bodies;
- accumulation of parasites;
- volvulus;
- inflammatory processes;
- high mobility of the cecum;
- immature peristalsis;
- gallstones;
- strangulated hernias;
- intussusception;
- adhesions;
- formation of fecal stones;
- neoplasms.
Intestinal obstruction causes a buildup of stool and gases. With a long process, toxic substances are absorbed into the blood, resulting in the development of intoxication of the body.
Cystic fibrosis
The disease is caused by a defective gene that controls the body's absorption of salt. As a result, a large amount of salt and little water enters the cells. This causes the fluid that lubricates our internal organs to become thick and sticky. This pathological mucus clogs the lumen of the glands of the digestive tract and blocks the airways.
Most often, symptoms of cystic fibrosis are detected at an early age. In twenty percent of cases, newborns have meconium ileus. The child is not gaining weight well. Sticky mucus can cause serious damage to your baby's lungs. Children often suffer from chest infections. They are worried about shortness of breath and wheezing.
Thick mucus interferes with the normal movement of the food bolus through the intestines and complete digestion. Children experience bloating and abdominal pain. The only thing that specialists can currently do is to alleviate the manifestations of the disease and also slow down its progression.
Antibiotic therapy helps remove thick mucus. Children are prescribed a high-calorie, balanced diet high in protein and pancreatic enzymes. At the same time, the fat content in the diet is sharply limited.
Ascariasis
Roundworms reproduce in the small intestine. While their larvae can move to various organs of our body, for example, to the heart, liver, lungs. The main route of transmission of parasites is fecal-oral. A child can become infected through contact with soil or sand. Infection also occurs when eating unwashed vegetables and fruits.
After entering the intestines, the eggs turn into larvae, which spread through the bloodstream. Ascariasis causes fever, chest pain, and dry cough. Once the larvae are swallowed, they return to the digestive tract. Already there they develop and turn into adults. This process lasts about three months.
During this period, children are worried about the following symptoms:
- weakness;
- nausea;
- irritability;
- stomach ache;
- dyspeptic disorders;
- weight loss;
- bloating;
- the appearance of roundworms in feces;
- stool disorders;
- nausea and vomiting;
- temperature increase.
To confirm the diagnosis, a blood and stool test is prescribed. Drug therapy includes the use of antiparasitic drugs, as well as immunomodulators, antihistamines and restorative drugs. During treatment, foods that provoke the proliferation of pathogens, such as sweets and baked goods, should be excluded from the diet.
Antiparasitic drugs inhibit the movement of roundworms by affecting their muscles. The worm is paralyzed and leaves the body naturally. In order to prevent ascariasis, parents need to thoroughly wash all vegetables and fruits. It is necessary to teach your child not to put dirty hands in his mouth.
Crohn's disease
The exact causes of this disease are not fully known, although scientists have identified a hereditary predisposition in the mechanism of chronic inflammation. An outbreak can be caused by viruses and bacteria, antibiotic therapy, and increased intestinal permeability.
First of all, attentive parents can pay attention to weight loss and the occurrence of problems with physical development. The disease affects the entire gastrointestinal tract, including the oral cavity. The pathology causes constipation, pain, nausea, and lack of appetite. The goal of the treatment process is to reduce clinical manifestations and achieve stable remission.
Drug therapy includes taking cytostatics and anti-inflammatory drugs. In some cases, the doctor may decide to perform surgery. This may include the formation of fistulas and abscesses, severe stenosis of the intestinal wall, and lack of results from drug therapy.
Symptomatic manifestations
As mentioned earlier, the symptoms of the disease appear sharply, and often parents can name not only the day, but also the time when the disease began to develop.
So, the main symptoms that parents of children with intestinal obstruction encounter:
- sharp and very severe abdominal pain in a child of a cramping nature;
- severe nausea;
- presence of vomiting;
- complete refusal of the child to eat;
- possible absence of stool;
- manifestation of flatulence;
- noticeable bloating.
It is worth remembering that the pain that arises can be so strong that the child is simply unable to endure it, and he begins to scream. If the child is very small and cannot express his condition in words, parents notice his severe anxiety. The baby is constantly spinning, trying to find a body position in which the pain would subside a little.
Some obvious symptoms can help determine the exact type of intestinal obstruction. If the blockage has formed closer to the stomach, vomiting will appear instantly and will be very intense.
If the problem occurs in the large intestine, vomiting, as a rule, does not appear in the baby, and the main accompanying signs will be:
- severe bloating;
- tormenting child's urge to go to the toilet.
All these symptoms are naturally accompanied by loud crying of the child.
During intussusception, blood may come out of the rectum, and this is due to the fact that this organ is irritated and its tissues are damaged.
If you do not call a doctor in time when observing such signs and do not provide first aid, intestinal necrosis may develop very quickly. Although the pain sensations are reduced to some extent, the general condition of the children worsens sharply. The probability of death is very, very high.
Intestinal obstruction in children is a disease that is simply impossible not to notice. The symptoms of the disease are always pronounced, and any parent will notice them and be able to recognize them.
Symptoms
Each of the listed types of intestinal obstruction in infants and older children has characteristic symptoms, but there are common signs of pathology, such as:
- Damage to the small intestine is provoked by repeated vomiting.
Pain syndrome. The sensations are cramping and often coincide with the rhythms of peristalsis. During an attack, the pain intensifies to the point of shock. Changing body position does not bring relief. - Vomiting reflex. The symptom occurs repeatedly and abundantly, does not bring relief if the small intestine is affected. If the functioning of the colon area is disrupted, vomiting is not so frequent.
- Constipation, accumulation of gases in the lumen. If the patency of the colon is impaired, gases and stool may not pass for up to several days. If there are problems with the small intestine, then defecation is possible on its own or with an enema. But if this does not happen, then the symptom indicates the terminal stage of the process.
- Additional signs by which one can understand that patency is impaired are thirst, bloating, hyperactivity of intestinal peristalsis, turning into atony (complete relaxation of motor skills).
Return to contents
Diagnostic measures
When contacting a medical institution, the only doctor who can correctly and accurately make the correct diagnosis is a surgeon. Of course, many parents immediately run to the pediatrician, and this would also be correct. In any case, independent diagnosis and self-medication is inappropriate here.
So, the parent takes the child to the doctor. The following methods for diagnosing the disease will be used:
- anamnesis;
- medical examination of the patient;
- X-ray of the abdominal organs;
- in some cases, an ultrasound is performed, but it is not mandatory and indicative;
- blood analysis.
Diagnostics
If disturbing symptoms appear, the child should visit a pediatrician and then a surgeon. Specialists will collect complaints and medical history, conduct a general examination of the patient, and palpate the abdomen. After clinical diagnosis, the doctor will prescribe additional studies:
- general blood analysis;
- clinical examination of urine;
- X-ray examination of the abdominal cavity with the introduction of a contrast agent;
- ultrasound examination of organs located in the abdominal cavity.
After the doctor examines the results of the studies performed on the child, a final diagnosis is made and appropriate treatment is prescribed.
Therapeutic actions
It should be noted that if intestinal obstruction was determined in the first 6 hours, then it will be possible to do without surgical intervention, that is, conservative treatment will follow. This therapy is aimed at eliminating all existing stagnation in the intestines and eliminating the possibility of poisoning the body. The little patient should fast for a while and be at rest. The following treatment is carried out:
- Using a tube that is inserted into the stomach through the nose by a doctor. Thus, the upper parts of the digestive tract are freed from food stagnation, thereby stopping vomiting.
- Special solutions are administered intravenously, the main effect of which is aimed at restoring the water-salt balance.
- Mandatory gastric lavage.
- Droppers.
- Enemas with sodium chloride are administered.
- Use of painkillers and antiemetics.
- In case of pronounced intestinal peristalsis, the doctor prescribes antispasmodic medications.
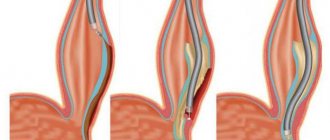
If in this case there is no improvement in the patient’s condition, then proceed to the surgical method. The operation is performed to remove part of the damaged intestine, and in particularly severe situations, the doctor performs a colostomy.
After surgery, the child will have a recovery period. Here it is necessary to observe a special diet. It is worth considering that you cannot eat any food for half a day after the operation. Drinking is also prohibited. After this time, it will be possible to consume fermented milk products or infant formula.
After some time, easily digestible foods are introduced into the patient’s diet. You can’t eat fatty, spicy, salty, smoked foods.
The result of untimely treatment and ignoring the disease can be the death of the patient, therefore, for any, even the most insignificant signs, a trip to the doctor is mandatory.
Surgical intervention
If medical efforts fail to improve bowel function, surgical intervention is indicated. It is usually required for absolute obstruction and involves removing the affected intestinal area. When the cause of the disease is polyps or neoplasms, they are removed. In serious situations, a series of sequential operations may be performed. This is necessary to prevent relapses of the disease.
Before and after surgery, the child is advised to take antibiotics. With the help of droppers, fluid balance is restored and nutrients are replenished (glucose, microelements, vitamins). During the recovery period, the baby needs rest and fasting. The doctor will prescribe him a special diet that will help improve motor skills and restore intestinal microflora. After surgery, medications may be administered to stimulate motor skills. You will be allowed to eat in small portions.
Why is intestinal obstruction dangerous?
Parents often encounter abdominal pain in their children. As a rule, unpleasant sensations quickly pass after a light massage, but you should not be too careless about them. If symptoms occur frequently, it may be intestinal obstruction in children - a serious problem that requires treatment.
This problem needs to be addressed as soon as possible. Otherwise, dynamic intestinal obstruction in children can cause dangerous complications that pose a real threat to life:
- Peritonitis. It begins against the background of perforation of the intestinal walls and the development of infection. Inflammation in the abdominal cavity can lead to sepsis.
- Necrosis of the affected area of the organ. If the blood flow to a certain area of the intestine stops, tissue death will begin, which can cause perforation of the walls and release of contents into the abdominal cavity.