Every woman can experience thick periods. Sometimes this is the norm - and there is no reason to worry. But in some cases, dark, high-density blood during menstruation indicates problems with the reproductive system. They can arise for various reasons.
Bloody, appear monthly in women. Their absence is normally observed only before the onset of puberty, during pregnancy, lactation, menopause and menopause.
The nature of menstruation may change under the influence of various factors. Thick blood appears for both physiological and pathological reasons. During menstrual periods, the uterus contracts intensively and thus pushes out the rejected endometrium. This is what causes the appearance of menstruation.
Cycle disturbances, coagulated blood, the presence of clots - all of these can be considered alarming symptoms. Such changes cannot be ignored. Only a doctor can accurately determine what caused the malfunction of the reproductive system.
Reasons for changes in discharge
A change in the color and consistency of menstruation can normally be observed only if there are no long delays, pronounced pain during menstruation and other uncharacteristic symptoms. Such disorders can be provoked by enormous stress, hormonal imbalance and pathology developing in the genitourinary system.
Pathology
Thick, dark-colored periods that acquire the consistency of mucus may indicate the development of the following pathologies:
- inflammation of the reproductive organ. At the same time, the regula darken and may contain an admixture of pus. Hyperthermia, causeless weakness, pain in the lower abdomen and malaise are also often observed. At the initial stage of development of the pathology, the clinical picture is weakly expressed, but the color of menstruation and changes in their consistency are observed immediately;
- hormonal imbalance. Changes in hormone levels can be triggered by surgery, diseases of the genitourinary system, taking hormonal medications, diseases of the appendages, thyroid gland and adrenal glands;
- malignant tumors in the organs of the reproductive system. When they grow excessively, the nature of the regula undergoes changes;
- intestinal pathologies;
- . Thick, dark blood is released in large volumes. Associated symptoms are abdominal pain, dizziness, excessive fatigue and weakness;
- bend of the uterus.
All these pathologies require treatment. For this reason, the appearance of such symptoms should be a reason to contact a medical facility.
Normal discharge
The nature of secretion changes during the menstrual cycle in girls. Outside the period of critical days, whitish discharge is observed. This is the natural color of mucus and is not cause for concern.
During menstruation, the density of discharge may increase. In the absence of pathologies, such changes are observed in the following cases:
- taking medications affects the process of blood clotting, and thick and dark menstruation is possible;
- abortive activities. In the postoperative period, significant hormonal fluctuations are observed, provoking changes in the nature of the discharge;
- ectopic pregnancy. In this case, menstruation may appear, but its consistency and shade change, and cycle disruptions are also possible;
- use of oral contraception. Under their influence, the appendages cease to function properly, and the concentration of hormones decreases;
- vitamin deficiency, as well as psycho-emotional or physical exhaustion of the body;
- recently installed intrauterine device. Unusual discharge is observed for three months.
In addition, normally the consistency of menstruation on the first day is thicker than it is closer to completion. Similar changes are observed in women over 45 years of age.
What should the discharge be like during menstruation?
A stable menstrual cycle indicates a woman’s health and her readiness to conceive.
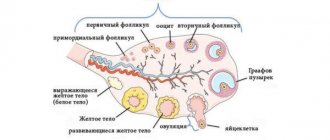
If pregnancy does not occur, the endometrium that has grown in the uterus sloughs off, after which a new one begins to grow, again preparing the uterus for the attachment of a fertilized egg. A woman should pay attention to any changes in menstruation and cycle length, as they may indicate pathology. At the end of the cycle, the overgrown epithelial layer of the uterus is rejected. When it separates, the capillaries are damaged, resulting in bleeding - blood is the basis of the discharge. They usually have a red or dark red tint during menstruation. The color becomes brighter and more saturated on the 2nd–3rd day of bleeding. The ideal indicator is scarlet blood on the 2nd day of menstruation. The discharge should have a slight iron smell.
A smooth discharge is normal, but it may contain small blood clots and clear mucus such as vaginal lubrication, endometrium, and cervical mucus. The presence of other components can change the shade of the discharge and increase its amount.
Heavy menstruation
On average, during menstruation, a woman loses 60 ml of blood per day, which corresponds to approximately two tablespoons - this is the absolute norm. In this case, only blood is taken into account - mucus and other components increase the volume of secretions. A scanty period is considered to be a loss of less than 30 ml of blood per day, and a heavy period is considered to be more than 80 ml. During heavy menstruation, blood comes out with large clots, so a woman needs to monitor her hemoglobin level.
Moderate blood loss does not pose a threat to the body - it quickly makes up for the deficiency. Over the course of a few days, while menstruation occurs, a woman loses up to 250 ml of blood - the duration of bleeding and its duration are purely individual.
Speaking about what menstruation should be like, it is impossible not to recall the normal duration of the cycle - it is ideally 28 days with a bleeding duration of 3-5 days. Normally, the cycle should not go astray, but fluctuations of 2-3 days in one direction or another are not considered a pathology. This condition can occur due to stress, illness, weight gain, etc.
Significant changes in the cycle up to 2 times a year are allowed if the next time your periods come as scheduled and the cycle is restored again. Deviations can be no more than 10 days - a delay or the onset of bleeding earlier than this period requires a health check and examination by a gynecologist.
During menstruation, women often complain of pain in the abdomen or back - this is a normal condition if the discomfort is mild. At the same time, breast engorgement and mood changes may occur.
Sometimes, during monthly bleeding, a woman notices that the discharge has changed in character, but at the same time she feels well and has no suspicions about the presence of any diseases. If this situation occurs once, there is no need to worry. However, it is worth remembering that you cannot engage in self-diagnosis - only a gynecologist can determine how safe the symptoms that appear are.
A woman does not need to worry about changes in the nature of her periods in the following situations:
- The consistency is heterogeneous, with large blood clots. Their formation can be an absolutely normal phenomenon, since during menstruation, blood is released more slowly when sitting or lying down and coagulates, coming out in the form of dark lumps. They are also formed when the structure of the uterus is abnormal - bent, displaced or the presence of septa, which prevents the natural outflow of blood and its accumulation. Clots can also appear when an intrauterine device is installed.
- Pink menstrual discharge may be considered normal in the first days of your period. This shade is explained by a small amount of blood, its mixing with vaginal secretions and the presence of endometrial particles.
- Brown discharge occurs at the beginning of menstruation, which is explained by rapid blood clotting when mixed with vaginal secretions and interacting with oxygen. If they appear at the final stage of menstruation, they can be called a “residual phenomenon” - the body tries to cleanse itself by removing the remaining blood.
- Dark menstruation is the norm for teenage girls - they have not yet established the ovulation process, so instead of bleeding there is scanty spotting. Women over 40 who are experiencing premenopause should have the same periods - this indicates the aging of the ovaries and a deterioration in their performance.
Discharge during menstrual bleeding should ideally be red or scarlet - a change in its color, the appearance of uncharacteristic components should alert you. The types of bleeding and possible pathologies that accompany them are presented in the table.
| Nature of the discharge | The pathologies they indicate |
| Orange | Decreased levels of female hormones in the body, high blood pressure |
| Gray | Ectopic pregnancy, infectious disease |
| Blood clots and severe menstrual pain | Anemia, endometriosis |
| Brown | Trauma to the vagina, inflammation of the genital organs, infection (pain in the lower abdomen, itching in the vagina are added), hormonal imbalance, sexually transmitted diseases |
| Pink | Inflammation of the appendages, endometritis, uterine fibroids |
| With mucus | Polyps, ovarian cyst, inflammation of the uterus, green and yellow mucus indicate inflammation of the appendages |
| Spotting | Cervical erosion, tumor, adenomyosis, polyps |
| Green menstruation | Excess of white blood cells, inflammation of the genital organs |
| Dark, almost black discharge | Infectious and inflammatory diseases, metabolic disorders, ectopic pregnancy, endometriosis, benign neoplasm |
| Scarce | Hormonal imbalance, infection, anemia |
| Abundant | Anemia, fibroids, polyps, ectopic pregnancy, cancer, hormonal imbalance |
Pink-red Discharge during menstruation is not only blood, it is also the secretion of the cervical glands, vaginal glands and endometrial tissue. It is thanks to this composition of menstrual fluid that it can be called an indicator of health. Pinkish discharge appears at the beginning of menstruation. After 3 days they change color.
Bright red or scarlet. Absolutely normal color of discharge. The main thing is that they are not too abundant, especially on the third and fourth days after the start of menstruation. This may be a sign of acyclic bleeding, especially if blood clots are present in the discharge. There is no need to worry if you feel normal, but there are blood clots during your period.
Dark red. What is the normal color of blood during menstruation? Of course, dark red. It happens that the color of menstrual blood changes as a result of taking hormonal drugs, as well as due to a sharp loss or gain of weight. A woman’s sensitive body immediately reacts to any changes! It is worth remembering that serious disruptions in the body’s functioning are not manifested by just a change in the nature of the discharge; there must be other symptoms.
Red-orange. If the color of the discharge has a slight orange tint, there is nothing to worry about. Blood can change color when exposed to oxygen to orange. But, if a change in the color of the discharge is accompanied by pain, itching, or an unpleasant odor, this is a sure sign of infection. See a doctor urgently!
Brown-black. Brown discharge is old blood and you shouldn't worry too much about it. Only if menstruation is accompanied by pain should you consult a doctor. Sometimes brown and brownish-black discharge indicates endometriosis - the growth of cells in the inner layer of the uterine wall beyond this layer. The disease is dangerous because it can cause infertility and bleeding.
Grey. What is the most dangerous blood during menstruation? Discharge of a strange faded color may indicate an infection, ectopic pregnancy, or various gynecological diseases. It’s worth checking with a specialist once again to be calm! There is no need to panic: very often, as a result of constant stress, poor nutrition, lack of sleep and physical overload, the discharge changes color.
Remember: the key to women's health is not to worry about anything in vain, not to be nervous! Doctors advise women to remain in a state of mental rest during menstruation. This is really important, because negative emotions change the hormonal levels and the whole body suffers.
Various changes in the color and consistency of menstrual flow should alert a woman.
Signs of the most dangerous conditions are foamy yellow-green, brown spotting, scanty gray discharge, as well as menstruation, which in appearance resembles homemade cheese and has a white tint.
Scarlet blood is normal only during 3 days of menstruation. If this color is observed longer, this indicates bleeding and possible serious consequences.
Almost all pathological changes in the color of menstruation are accompanied by itching, burning in the intimate area, and the presence of an unpleasant odor.
Most often, on the first day, menstruation is dark in color and thick in consistency, which is associated with the release of an egg. In the middle of menstruation, the discharge takes on a red tint, which varies significantly and depends on the amount of blood lost. Therefore, pink color during this period will not be considered a pathology.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ecxbnVAadr0
Scarlet blood during menstruation during the first three days is normal. From about the 3rd day, an active oxidation process occurs in the woman’s body, and the blood darkens. If the color remains the same, then most likely there is a malfunction in the menstrual cycle, as a result of which at the end of menstruation the periods again acquire a dark tone.
Menstruation with dark clots
Normally, women may experience heavy, brown periods without a foul odor, in which clots are observed, but only in small quantities. The development of gynecological diseases is indicated by the following clinical manifestations:
- acyclic bleeding;
- pain syndrome localized in the lower abdomen;
- thick abruptly give way to heavy bleeding;
- nausea and vomiting;
- dizziness and deterioration of general condition;
- unpleasant odor from the vagina;
- onset of uterine bleeding.
Features of treatment
If dark, thick discharge appears during the regulative period, you should definitely seek help from a gynecologist. This is due to the fact that such changes often indicate the development of gynecological pathologies that can lead to serious complications (including infertility).
The drug treatment regimen is selected individually, taking into account the characteristics of the clinical picture and the identified disease. For excessive bleeding, hemostatic agents and aminocaproic acid are prescribed. If changes in hormone levels are detected, they resort to the use of hormonal drugs. The duration of therapy with drugs in this group is at least three months.
To restore the vaginal microflora, vaginal suppositories, special irrigation solutions and complex drugs with antifungal, anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties can be used.
Therapy often includes taking antibiotics to stop inflammatory processes. In particularly difficult cases, surgical intervention is resorted to.
Prevention
To avoid the development of gynecological diseases and the appearance of dark-colored and increased density menstruation, you need to follow simple recommendations:
- During menstruation, replace hygiene products at least once every four hours.
- Do not be promiscuous and use barrier contraception. This will prevent infection from entering the vagina.
- Follow the rules of intimate hygiene and wash yourself with special products twice a day. The use of regular soap for this purpose is strongly discouraged. It can wash away not only pathogenic, but also beneficial microflora.
- Systematically undergo examination by a gynecologist and treat all pathologies at an early stage of development.
- Get rid of bad habits.
- Organize your diet correctly. The menu should be complete and balanced.
- Avoid stressful situations and learn to calmly respond to any problems. Nervous shocks are often the cause of strong hormonal fluctuations.
- If there are any changes in the nature of menstruation or the appearance of other symptoms, immediately seek help from a gynecologist.
Thick periods with a dark color most often signal serious problems with a woman’s health. Such symptoms should not be ignored. Only if the cause of uncharacteristic bleeding is identified in a timely manner will it be possible to quickly eliminate it and prevent the development of complications.
Every woman experiences thick periods. In special cases this is the norm and there is no reason to worry. But often an increased density of secretions indicates the presence of pathological processes. Then there are additional symptoms and pain. Every woman knows what menstruation should look like. These are dark discharges of blood of a certain density. They may change from time to time under the influence of various factors. In some cases, the situation does not require drug treatment; it is enough to just improve your lifestyle and diet. In others, unusual periods are a sign of serious diseases, and not only of the reproductive system.
Heavy and scanty periods
Menstruation can be excessively abundant or, on the contrary, it can be unusually scanty.
Abnormal blood loss can occur as a result of:
- disturbances in hormone production;
- use of intrauterine devices;
- carrying heavy objects and physical overload;
- tendency to stress;
- vascular damage or early miscarriage;
- bleeding disorders;
- neoplasm in the uterus, ovaries or endometriosis
If you have excessively heavy periods, do not hesitate to go to the doctor and go to a medical facility as soon as possible.
Scanty periods in the form of spotting (hypomenorrhea) can occur during the first year after the start of menstruation or when using birth control pills. If there are other circumstances, they may indicate serious problems with women's health.
Possible causes of insufficient bleeding:
- menopause and decreased estrogen levels;
- protection against unwanted pregnancy by taking oral contraceptives;
- structural defects of internal female organs;
- exhaustion of the body as a result of physical overload or excessive diet
During childbearing years, insufficient menstruation indicates a deficiency of the hormone estrogen. The use of radical methods of weight loss can lead not only to the scarcity of menstrual flow, but also to its complete disappearance. As a result of such experiments, a full pregnancy may become impossible.
At any age, a woman should visit a gynecologist at least once every six months. Cycle disturbances, changes in the usual pattern of discharge and other sudden changes in the functioning of the body are always a reason for a visit to the doctor.
Cause associated with illness
In addition to changing the nature of menstruation, it is necessary to analyze your well-being, general condition, and the presence of other alarming symptoms.
If alarming symptoms appear and when the situation repeats several cycles in a row, you should urgently seek advice from a specialist.
A healthy woman's periods are characterized by regularity and uniformity, which makes it possible to evaluate the state of the reproductive system. During menstruation, a girl can do this on her own, since the discharge is accessible to inspection. Normally, they resemble venous blood, but in some diseases, instead of the usual picture, various deviations are observed.
Why are periods brown? In some women, from the first menstruation they have a similar color, which is explained by the characteristics of their body. If they do not cause additional unpleasant symptoms, then there is no need to worry. For preventive purposes, you can consult a gynecologist to rule out pathological causes of such discharge.
The situation is different if menstrual blood suddenly or gradually changes its characteristics. More often, instead of normal blood, dark discharge appears, or thicker periods occur. In some gynecological diseases, these symptoms are the only signs of pathology. If a woman is not too attentive to her health, then the disease can be seriously neglected. To avoid unpleasant consequences, you should know the normal properties of menstrual blood and the reasons for their changes.
Causes of heavy or scanty discharge
If you find a significant deviation from the norm in 50 ml of blood and you think that your period has become bleeding, you should urgently be examined by a doctor.
There can be any number of reasons for bleeding - from overload and stress to pathological pregnancy, which is why you shouldn’t delay making a diagnosis. The time of your period also plays a big role - if it lasts more than a week, but previously it was only 3-4 days, then it’s also worth thinking about. This is quite an alarming signal from the body that you need to listen to.
Some girls, especially those with an unstable cycle, do not understand why their periods are always scanty. In fact, in the first year of menstruation, when the cycle is just establishing itself, there is no need to worry at all. The body is just beginning to establish the optimal balance of hormones and their jumps in one direction or another are possible.
If menstruation is scanty already at reproductive age, this most often indicates insufficient production of the hormone estrogen. Often this situation occurs before menopause, otherwise it also requires an immediate visit to the doctor. However, it happens that less blood comes out after overwork or a strict diet for weight loss.
You should not get attached to standards and try to calculate the amount of blood coming out during menstruation - this is very difficult to do. It would be much better to regularly visit a gynecologist, who can determine whether any pathologies are present in the body or whether everything is happening within normal limits. Of course, it’s worth monitoring your health yourself, but don’t get carried away with self-diagnosis and self-medication. The health of the female reproductive system is very important, because it directly affects the ability to have children.
Girls experience their first menstrual blood during puberty. On average, the onset of menstruation occurs at 12-13 years of age, although in recent years this figure has tended to decrease. Not all representatives of the fair sex think about why and why menstruation occurs, how it should proceed correctly and how much blood is lost during the monthly cycle.
Menstruation is normal
With the help of this physiological phenomenon, a woman’s body removes an egg from the uterine cavity every month. At the same time, the inner layer (endometrium) is renewed, which grows monthly under the influence of sex hormones. The menstrual cycle is created by nature to accomplish fertilization - if it does not occur, then the woman’s genitals “get rid” of the changes. Accordingly, with normal hormone levels and no changes in the uterus, the discharge will resemble normal blood.
During menstruation, women usually pay attention to their color, which rarely changes throughout life. But there are other characteristics that fully describe normal properties:
- The main characteristic is the duration, it should not be less than three days or more than a week. Violation of their duration means that not everything is in order with the hormonal background. The correct regulation of the cycle depends on sex hormones.
- Menstruation normally occurs without any unpleasant sensations - but there may be slight malaise or weakness, a feeling of heaviness in the stomach. The appearance of severe pain during this period indicates gynecological pathology.
- Dark red or red-brown periods are a good sign. They must contain fresh blood, so they should not be too dark.
- The largest volume is released at the beginning of menstruation, and the rest of the time the amount of blood released gradually decreases. If too much of it is released during the entire period or the discharge is scanty, then endometrial disease can be suspected.
- The discharge should be uniform in nature - uneven coloring, inclusions in the form of large clots indicate problems with the separation of the inner layer. Black periods directly indicate illness - they occur when blood clots inside the vessels of the uterus.
- The menstrual cycle is constant - discharge begins at a certain period. Black discharge after or before menstruation may not be associated with the cycle, since the source of blood may not depend on sex hormones.
Brown menstruation may be a normal variant, since the discharge contains various impurities - destroyed cells, mucus and blood clots.
Where does blood come from during menstruation?
Where does blood come from during menstruation?
Not all women know why they bleed during menstruation. Blood discharge necessarily accompanies the menstrual cycle. This process is directly related to the function of the egg. Its main goal is to wait for fertilization. If the meeting with the sperm does not take place and fertilization does not occur, there is no need for the egg. It is simply rejected by the body.
As a result, there is an increase in the endometrium (the mucous membrane inside the uterus). When an egg is rejected, it is injured, mixed with blood particles and removed from the body naturally - from the vagina. Through this, the uterus is cleansed of excess biomaterial. Gradually the wounds heal and the amount of bleeding decreases.
Reasons for changes in the color of menstruation
Lightening of menstrual blood may be observed - this process is normally observed in a woman after childbirth or before menopause. This is due to hormonal changes, which leads to insufficient “maturation” of the endometrium during the cycle. When the period of discharge begins, this immature layer contains insufficient blood vessels. Therefore, menstruation becomes pale - it contains little blood.
More often, instead of normal blood, darker blood appears - this is caused by its coagulation inside the uterine cavity. The reasons that provoke the development of this process affect the vessels of the inner lining. At the same time, the blood in them begins to form many clots, forming black discharge. Normally, women's periods should not be curtailed.
Inflammatory diseases
The development of this process rarely begins on its own - damage to the inner lining of the uterus begins against the background of other diseases. A decrease in immunity means a lot, since the uterine cavity communicates with the environment through the cervix. Therefore, inflammation is usually caused by E. coli - bacteria that live in the digestive tract. When the body's defenses decrease, they penetrate the vagina and can move further to the endometrium:
- Signs of endometritis appear - increased temperature, fever, pain in the lower abdomen.
- When they are recognized in a timely manner, the disease can be cured without consequences. Otherwise, the process becomes lengthy, which leads to permanent changes in the functional layer of the uterus.
- A little later, menstrual irregularities appear - brown periods.
- Instead of normal discharge, a bloody substance appears, which has a spotting character and an unpleasant odor.
- The color change is caused by inflammation - the growth processes of the endometrium are disrupted during the cycle. To the meager amount of blood is added an excess amount of mucus and dead cells.
Instead of the “it will go away on its own” attitude in life, you should choose a different tactic – contact a gynecologist. He will prescribe the right combination of antibiotics and procedures that will eliminate the inflammation. Delaying treatment indefinitely can lead young and “healthy” women to infertility.
It is important to eliminate the cause of endometritis, since the persistence of disturbances in the immune system will cause an exacerbation of the disease in the near future.
Endometriosis
This disease is characterized by a complex development mechanism - its causes are not fully understood. It is based on the spread of cells of the inner lining of the uterus to atypical places - literally to any part of the body. More often they move within the genital organs - into the fallopian tubes, cervix or vagina.
Medical abortions and cesarean sections increase the risk of disease - during these manipulations, endometrial cells can spread to other tissues.
Since they have the properties of the endometrium, they are able to form secretions under the influence of sex hormones. But the blood obtained has different characteristics, unlike the norm:
- Black discharge before menstruation is possible, since these defective cells have excessive activity. In conditions that do not correspond to the uterine cavity, the blood quickly clots. It does not mix with special mucus and cells, so it quickly turns black.
- Black discharge is often combined with other unpleasant symptoms - pain, weakness, fever.
- With this disease, a woman may lose an excess amount of blood, which is lost through areas of abnormal activity of these cells. Repeated repetition of such events causes exhaustion in a woman, making her susceptible to other diseases.
Treatment of the disease is usually surgical - areas of abnormal cells are removed or cauterized. Elimination of such a lesion leads to recovery - the menstrual cycle normalizes, and black periods disappear. But women are monitored for a long time to avoid relapse of the disease.
Tumors
Any neoplasms in the uterine cavity are an obstacle to the normal outflow of menstrual blood. Often they themselves become a source of bleeding. In tumors, a different structure of blood vessels is noted - arteries and veins are tangles with fragile walls. This explains their instability to damage - even an increase in blood pressure can lead to hemorrhages.
Therefore, instead of normal menstruation, black menstruation may occur, containing many clots - blood clots. Tumors can be benign and malignant, which causes differences in their clinical manifestations:
- Bloody discharge, as a symptom, rarely depends on the course of the cycle - they can occur at other times.
- This allows you to confuse the natural onset of menstruation, which is masked by periodic discharge during the cycle.
- Bleeding is typical for twisting of the leg of a polyp or the disintegration of a malignant tumor - cancer.
- At the same time, blood begins to flow from the vessels of the neoplasms into the uterine cavity, which quickly coagulates. This explains why black periods occur - the clots get into the normal discharge, coloring it dark.
Malignant tumors of the uterus have an unpleasant feature - they hardly appear. Late presentation sharply worsens the prognosis, as these tumors quickly spread into the abdominal cavity. Therefore, at the slightest suspicion of a tumor, you should consult a gynecologist.
Venereal diseases
Some pathogens of sexually transmitted infections infect the inner lining of the uterus. They cause the development of a slow inflammatory process there, which changes the nature of the discharge:
- The pathogens of gonorrhea and chlamydia cause the formation of multiple small ulcers on the surface of the endometrium.
- Their surface bleeds, gradually becoming covered with a layer of dark blood clots.
- Inflammation increases the secretion of mucus, which contains dead epithelial cells (pus).
- Mixing this substance with menstrual blood causes brown periods, which also contain bacterial cells.
Lack of treatment for these diseases leads to infertility, as dense adhesions form inside the uterus. They prevent the fertilization of the egg, as they close the lumens of the fallopian tubes. Therefore, you should protect yourself during sex with condoms, and also consult a venereologist at the first suspicion of these diseases.
Many girls and women at some point have encountered the reasons for the appearance of black or dark periods, but few can explain exactly why the modified discharge occurs and whether this is normal.
Convenient infection what happened leukocytes pain diagrams at the gynecologist stomach hurry heating pad torment pills
Possible reasons
The reasons why menstruation is dark brown or black in color can vary, among the main ones it is customary to highlight the following:
- young age (i.e. onset of puberty, establishment of the menstrual cycle);
- postpartum changes, establishment of the lactation process;
- sexual intercourse during bleeding;
- infections of the genitourinary system or pelvis;
- drug or gynecological treatment (including after duphaston);
- abnormal metabolism.
Also, when trying to conceive, very scanty, sometimes mucous, brown periods may be released on the first day of the cycle, then normalizing.
If the hormonal and endocrine balance is disturbed or there is a long absence of sexual intercourse, dark brown periods may appear.
Unpleasant sensations
Most often, the answer to the question why menstruation began and continues to be dark brown and small is changes in the body’s functioning associated with normalization and debugging of new processes. While rebuilding, the body secretes enzymes that are unusual for itself, which leads to dark-colored periods.
However, there are cases when thick and dark-colored periods are provoked by various infectious diseases, including those caused by sexual intercourse during menstruation. Since the vaginal organs are irritated during menstruation and are also more susceptible to external influences, it is much easier for infections to enter the body.
To protect yourself from the negative consequences that may be associated with black periods or very scanty bleeding, visit a gynecologist to find out what is the reason for such modified menstruation in your particular case, and also, if necessary, receive appropriate treatment or specialist prescriptions.
Differences between black and dark
The shade of menstruation, as a rule, does not affect its symptoms and the reasons for its appearance are similar. The main differences are only that lighter discharges are filled with a lower concentration of blood, and darker ones, respectively, with a greater concentration, which affects their changed shade.
If your periods are brown, to figure out what this means, undergo the necessary examinations in order to find out the exact reasons for the appearance of modified menstruation, and, if necessary, begin appropriate treatment on time.
A real salvation for women
Why is the first menstruation this color?
The body of a young girl, which has launched the puberty program, has significant differences from the female one, since many previously uninvolved processes begin their work and development.
The formation of the body, changes in hormonal composition, the start of the menstrual cycle, as well as many other processes can become factors influencing the shade of the first menstrual flow. When establishing a cycle, it is quite normal to experience dark or black discharge during the first few months, sometimes quite scanty.
Change in color after using Duphaston
Changed color of menstruation or discharge can be caused by the use of gynecological or hormonal medications, such as Duphaston.
Must feel comfortable
Duphaston, in turn, is a synthetic substitute for progesterone, due to the lack of which many women experience problems with menstrual irregularities, as well as problems with pregnancy.
Despite such beneficial effects on the female body, the majority of women using Duphaston, under the intense influence of synthetic hormones entering the body, usually begin to experience scanty discharge, and minor pain and mood changes are also possible.
Depending on the concentration of blood in menstruation, its shade can vary from light brown to dark brown. There is no need to worry or panic excessively because of the discharge that appears, but it is recommended to notify your doctor that you are experiencing unusually discolored bleeding.
When prescribing Duphaston, consult your doctor to see if it can be combined with other medications, and also carefully read the contraindications of the drug so that instead of treatment you do not get the opposite result.
The problem is the color of the discharge
Dark discharge
As a signaling function, informing about the beginning of the menstrual cycle, the female body often produces scanty dark-colored blood spots, which are most often accompanied by the onset of menstruation after a few hours. This is due to the fact that the body needs time to start the processes of the menstrual cycle - by producing a small amount of discharge, it, as it were, tests the system.
Also because of this, in the first day and a half, most girls and women experience spasmodic pain in the lower abdomen associated with the release of blood, as well as the beginning of hemorrhage. It is worth noting that the beginning of the menstrual period is different for everyone and scanty dark or black discharge is not at all a necessary element of the beginning of menstruation. Specific options are quite possible, when menstruation begins abruptly and heavily, and then gradually fades away.
Well absorbed
Examinations for discharge
If you find atypical discharge in the form of dark or black menstruation, the best way to solve this problem is to contact a specialist to determine the causes and prescribe the necessary treatment.
Do not try to cope on your own - self-medication can harm you and lead to irreversible consequences. Do not delay visiting a specialist, since solving health problems in the early stages is much easier and faster.
To identify the causes and consequences of altered discharge, gynecologists most often prescribe:
- smears for flora and infections;
- general blood and urine tests;
- examination on a gynecological chair.
Attention!
The information published on the website is for informational purposes only and is intended for informational purposes only. Site visitors should not use them as medical advice! The site editors do not recommend self-medication. Determining the diagnosis and choosing a treatment method remains the exclusive prerogative of your attending physician! Remember that only complete diagnosis and therapy under the supervision of a doctor will help you completely get rid of the disease!
Thick periods, which can occur in any woman, are always alarming. Not everyone knows whether this is a pathology, or one of the types of normal manifestations of monthly bleeding. After all, they proceed differently even in the same patient. Let's figure out what is considered normal in this case, and what discharge should alert you and serve as a reason to contact a gynecologist.
What a girl should know about menstruation
Every girl needs to know why menstruation occurs every month and where the bleeding comes from. This means that her body is ready to conceive a child, so she must be extremely careful when engaging in sexual intercourse.
On average, during menstruation, 2-4 large spoons of discharge (35 ml) are released, which are taken from the walls of the uterus. Also, 1–6 spoons is considered the norm - it depends on the characteristics of the body.
The arrival of the first menstruation usually occurs at 12–13 years of age, although the limits may be shifted depending on individual characteristics.
Typically, such discharge is slightly darker than regular blood, so if your periods are light, this most likely indicates bleeding that is not associated with menstrual periods.
In the last days of menstruation, the blood becomes even darker - brown. This means there is no oxygen in it and is considered normal.
As soon as your monthly discharge begins, you should use pads or tampons that will absorb it, thereby ensuring proper hygiene.
At first, an irregular cycle may be observed, but after 3–5 months after the start of the critical days, it should normalize. Otherwise, you will need to visit a gynecologist to find out about possible health problems.
Girls experience their first menstrual blood during puberty. On average, the onset of menstruation occurs at 12-13 years of age, although in recent years this figure has tended to decrease. Not all representatives of the fair sex think about why and why menstruation occurs, how it should proceed correctly and how much blood is lost during the monthly cycle.
Features of the menstrual cycle
Every healthy woman experiences monthly vaginal bleeding. They are a physiological norm and indicate the absence of fertilization of the egg. If there are no periods, then a visit to a gynecologist is mandatory. After all, there is a possibility of developing not only a long-awaited pregnancy, but also health problems in the female genital area.
Let's determine how menstruation should proceed in a healthy adult, physiologically mature woman. After all, this is a cyclical, constant phenomenon that meets certain criteria:
- The duration of the menstrual cycle varies, and on average is up to 1 month. However, in some cases it can last about 45 days, which will also be considered the norm.
- Normally, the cycle should be divided into two periods. The first develops in the ovaries and is accompanied by the formation of the corpus luteum and then the follicle. The second one develops in the uterine cavity and ends in monthly bleeding.
- A healthy woman should have regular periods, without delays or failures.
- Their duration on average should not exceed a week, but cannot be less than 2 days.
- The color of bloody vaginal discharge during this period is always much darker than during capillary bleeding.
- The released blood should not normally clot.
- Blood loss during the entire period of menstruation should not be large. On average it cannot exceed 150 ml.
- Throughout this period, the woman should not feel pain or other unpleasant sensations.
- Normally, it indicates the development of pregnancy.
At the same time, against the background of general well-being, dark menstrual discharge appears thicker in consistency than usual. Should this be considered a sign of some disease, or maybe it should be so? What should you do if such symptoms appear? Do I need to go to the doctor?
Symptoms not associated with pathology
Of course, for any changes that appear during monthly bleeding, it is necessary to consult with a specialized specialist. However, most often, such symptoms are a variant of the norm. It has been noticed that in women who lead a sedentary lifestyle, such discharge is darker in color and slightly thicker in consistency. Otherwise, she may present the most common complaints for this condition:
- weakness;
- feeling of constant fatigue, even after a long rest;
- heaviness in the lower abdominal region, both during the premenstrual period and in the first days after its onset;
- emotional stress.
As a result, a change in the density of discharge in the absence of adverse complaints or symptomatic manifestations will be considered a variant of the norm. In addition, periods become thicker and darker for various physiological reasons in most women over the age of 30.
What else can affect this indicator:
- Doctors note that taking certain medications also affects the nature of menstrual flow. These include some hormonal medications (especially from the group of contraceptives) or specific medications used to reduce body weight.
- Changes in the position or size of the uterus can affect the quality of discharge during menstrual bleeding. For example, as a result of bending the neck, the discharge becomes quite thick. And a change in the volume and position of the uterus can generally change the structure of the entire cycle.
- A similar phenomenon can often be observed in women during menopause. In this case, the reasons will not be related to the disease. As a rule, it becomes a mechanical rather than a physiological cause of such symptoms.
- Losing or quickly gaining weight can also change not only the nature of your periods, but also the duration of bleeding, as well as the frequency of the entire cycle. Gynecologists warn women about this who are trying to quickly lose weight.
- A similar phenomenon can be observed for some time after.
- Emotional or psychological stress.
- Heavy physical activity.
- Prolonged exposure to the sun.
- Hypothermia.
In addition, this symptom may be a signal of pathology on the part of the endocrine glands, and the genitals will be healthy. True, this condition can be easily corrected with the help of specific medications. To do this, you will need to consult with an endocrinologist.
Or maybe it's time to be wary?
Above, we examined those cases where changes in the consistency and thickness of menstrual flow were not associated with the development of the pathological process. In what case should you consult a doctor? When does this condition signal a disease?
This approach will not be entirely correct. Visits to the gynecologist should be regular, and not only in case of unclear symptoms. Indeed, sometimes serious pathological processes in the pelvic area occur without characteristic manifestations and can only be detected during a routine examination. It is much easier to treat them if, with regular visits, the disease is diagnosed at an early stage.
What symptoms of a change in the density of menstruation should alert you and serve as an impetus for visiting a antenatal clinic:
- Violation of the calendar for the appearance of monthly discharge.
- With constant thick discharge, they are replaced by heavy bleeding.
- Quite large blood clots appeared.
- In the interval between menstruation, bleeding periodically appears.
- Severe pain that accompanies the entire period of menstruation. It can be localized in any area of the pelvis, including the bladder or lower back.
- Change in the characteristic odor of the discharge to fetid or putrefactive. This is a symptom of the development of an infectious process in the genital area.
- Complaints of weakness or fatigue due to weight loss.
In this case, in addition to the examination, the attending physician will recommend a clinical examination. It will include laboratory tests of blood and urine, bacteriological cultures of vaginal discharge, as well as ultrasound of the pelvic organs.
What to do in this case?
Most problems and diseases of the female genital organs can be successfully corrected. However, for this it is necessary to make a diagnosis in time. Indeed, when a pathological process is detected late, most often the only method of help is surgical treatment. How to avoid this:
- Visits to the gynecologist should be regular. As a rule, experts advise undergoing examination at least 2 times a year, and in the presence of suspicious symptoms much more often.
- Unprotected sexual relations with unknown partners are not allowed. Doctors generally advise having one permanent sexual partner.
- Both examinations and diagnostic gynecological examinations should be carried out in a medical institution by a specialized specialist.
There are many reasons that can cause thick and dark-colored periods. They can be caused by both minor physiological abnormalities and serious diseases. Without the necessary knowledge, it is quite difficult to figure this out.
If any complaints, ailments or problems arise, the decision should not be made independently.
This will be done better and more professionally by a medical professional who has the necessary knowledge and skills.
How much blood does a woman lose during menstruation?
If you think about where blood comes from during menstruation, it becomes not entirely clear why there is so much of it. The fact is that during ovulation, the endometrium is completely penetrated by a network of blood vessels, which are destroyed when the endometrium itself is rejected by the uterus. How much blood will be lost during menstruation depends only on the characteristics and physiology of the body itself. Normally, doctors call the figure 50 ml, and we are talking about pure blood. For some reason, women think that much more blood comes out, but this is not so. The basis of menstrual flow is mucus.
The largest amount of pure blood comes out on the 2nd–3rd day of menstruation - at its peak. Most women use pads or tampons with a high degree of protection during this period, as their periods become more profuse.