Genital herpes in women is a widespread viral erosive and ulcerative disease of the genital organs.
The infection occurs everywhere and plays an important role in the impossibility of reproductive function, as well as in the development of serious pathologies of the cervix.
Genital herpes aggravates the course of other genital infections and significantly affects a woman’s quality of life. The issue of reducing relapses of the disease does not lose its relevance.
Causes and routes of infection
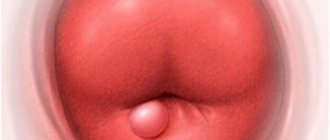
photo genital herpes in women
Genital herpes in women in gynecology occupies a leading position among infectious and inflammatory diseases of the reproductive tract and is the cause of chronicity of various infections, as well as infertility and pathology of the epithelium of the cervical uterus. The cause of the genital form is herpes simplex virus type 2, but type 1 virus (HSV2 and HSV1) is also often diagnosed.
Genital herpes in women often remains unrecognized due to insufficient diagnosis of infectious diseases, as it occurs subclinically.
Asymptomatic virus carriage accounts for up to 70% of cases of transmission of genital herpes, since the absence of significant symptoms does not create restrictions on sexual intercourse.
The virus is transmitted:
- Sexually. Infection occurs during any type of sexual contact with both a patient with genital herpes and a carrier.
- Through autoinoculation. If there are viral blisters on the face, the pathogen can be carried by hands to the genitals.
- Through household contact in the presence of virions on common hygiene items (usually occurring in children).
To introduce a pathogen into the skin, damage is necessary: small cracks, abrasions, and abrasions are enough to become infected.
The pathogen penetrates the mucous membranes freely, which is why women become infected through unprotected sexual contact much more often than men - the area of open and accessible mucous membranes is larger. Herpes in the intimate area in women affects all areas of the skin and mucous membranes.
In clinical practice, it is customary to distinguish between:
- first episode of genital herpes;
- exacerbations.
The largest number of relapses is observed after the primary infection; then, exacerbations are recorded less frequently, but asymptomatic carriage is noted.
Conclusion
When the first symptoms of genital herpes occur, a woman should immediately seek advice from a specialist. The doctor will make a diagnosis and then prescribe treatment. You should not neglect the advice of specialists and hope that the disease will go away on its own. Without treatment, genital herpes can lead to serious health problems for both the woman and her unborn child.
Read
Also:
- White plaque between and on the labia, causes and treatment
- Furuncle or boil on the labia: is it dangerous and how to treat it?
- Sores on the labia: causes, symptoms and treatment of sores on the labia
- Cracks and peeling on the labia, treatment of skin in the intimate area in women
Where does genital herpes occur in women?
The first signs of the disease appear in those places where the virus first took root. The area of primary manifestation of genital herpes coincides with the sites of recurrence of rashes most often.
As a rule, patients suffering from exacerbations of a viral infection already feel and know by a certain set of signs that characteristic symptoms will soon appear.
Herpes type 2 in women is characterized by more massive rashes and a larger area of damage. The first type is easier.
In addition, the severity and consequences of the infection are determined by the extent of involvement of the mucous membranes of the woman’s genital organs.
The more rashes are localized on the mucous membrane, the more severe the disease and the more often complications develop.
Based on the location of the rash, the disease is classified as follows:
- damage to the genital organs and genitourinary tract;
- inflammation of the anus and rectum.
In women, typical locations for rashes are:
- external genitalia;
- vulva and vaginal vestibule;
- skin on the pubic part, in the groin;
- in the perineum;
- on the walls of the vagina and on the surface of the cervix;
- the skin of the anus, buttocks and the mucous membrane of the rectal ampulla.
Herpes of the bladder and urethra is diagnosed less frequently. It is manifested by pain when urinating, blood in the urine, fever, pain in the projection of the bladder.
Herpes as a sexually transmitted infection
Primary genital herpes
The virus usually spreads to the genitals during sexual contact, including oral sex. A visually sick person may not have any signs of illness. Moreover, in people with good immunity, even the first contact with infection can be asymptomatic. But more often, infection still leads to damage to the skin and mucous membranes. Primary infection can only occur when encountering a type with which the body is not yet familiar.
The incubation period is 3-7 days. Symptoms include fever, increased temperature, headaches, weakness, and muscle and joint pain. Local symptoms: pain, itching, difficulty urinating, discharge from the urethra or vagina, enlarged inguinal lymph nodes.
Local symptoms of genital herpes in men:
bubbles appear on the head of the penis, foreskin, frenulum. In some cases, the skin of the scrotum, perineum, buttocks, and thighs is damaged. When the blisters open, ulcers form. 30-40% of men experience symptoms of urethritis, manifested by severe urination problems, cramps, pain, and discharge from the urethra. During anal sexual intercourse, damage to the rectum may occur.
Local symptoms of genital herpes in women:
vesicles containing fluid appear on the labia majora and minora, vestibule of the vagina, and external genitalia. When the blisters open, ulcers form. The vaginal mucosa is inflamed and swollen. In 70-90% of cases, the cervical mucosa is involved in the process, on which blisters and ulcers are also observed. In some patients, inflammation of the cervix may be the only symptom of the disease. Urinary disorders are accompanied by pain and pain during emptying of the bladder and are caused by inflammation of the urethra.
The rash lasts from 4 to 14 days. Antibodies to the herpes virus, which are produced by the immune system, suppress the replication of the virus. The infection is “locked” in the nerve ganglia, and at the slightest decrease in the body’s defenses, it causes a relapse. Full recovery is impossible.
Recurrent genital herpes
After the initial infection, genital herpes remains in the body for life. They provoke an exacerbation of injury, surgery, colds, viral infections, hypothermia, etc. A recurrent course is more typical for the second type of virus. In 90% of patients, the first relapse occurs in the first 12 months after infection. 38% of those infected with herpes simplex virus type 2 experience relapses 6 times a year, 20% - more than 10 times a year.
Local symptoms during relapse are practically no different from those during primary herpes. Before the appearance of rashes, there may be precursors - pain, burning sensation on the skin. The rash can be very painful. However, there are practically no general symptoms in the form of fever and intoxication. The rash continues for several days. Recovery takes 10-15 days.
Diagnosis of herpetic infection is carried out during a visual examination and using laboratory methods. Most often, an enzyme-linked immunosorbent test (ELISA) is used, which detects the presence of specific antibodies to a particular type of virus in the blood serum, and a polymerase chain reaction (PCR), which detects genetic information characteristic of the pathogen.
Symptoms of genital herpes in women
Experts divide the symptoms of genital herpes in women into subjective and objective. In many ways, the set of symptoms depends on where herpes occurs in women - on the skin or mucous membranes of the genital organs, or the anus and rectum.
The incubation period lasts from 2 to 10 days and is determined by the massive contamination of the skin and mucous membranes. In addition, the presence of integrity disorders also accelerates the first appearance of symptoms of genital herpes in women.
Objective clinical signs include typical and atypical manifestations. Typical symptoms include:
- women experience paroxysmal pain along the pudendal nerve, which is burning, shooting, piercing in nature, intensifies at night, as well as during sexual contact;
- redness, swelling and itching occur in the affected area of the skin or mucous membrane. Depending on the area of introduction of the virus, this process appears on the labia majora or minora, on the pubis, clitoris, at the entrance to the vagina, in the anus, on the buttock, and the skin of the perineum;
- single or multiple bubbles in the indicated areas, their contents are transparent, the base is hyperemic. The vesicles continue to itch. Herpes in the vagina and cervix manifests itself as pain during sexual intercourse, since it is impossible to independently visualize swelling, hyperemia and blisters;
- the blisters burst, resulting in the formation of a painful ulcer. The erosions are covered with a gray coating and surrounded by a red rim. If a secondary infection occurs, the ulcers become covered with purulent plaque;
- During a primary infection, the lymph nodes in the groin with herpes on the genitals increase, but not always during relapses.
Atypical forms are described by the following features:
- Local swelling and redness develop on the genitals, but a rash does not form. In this case, pain syndrome is present;
- periodically recurrent cracks in the mucous membrane of the vulva, which heal within a week;
- the hemorrhagic form is described by the accumulation of blood in vesicles;
- the abortive variety is characterized by the formation of an itchy spot on the skin of the external genitalia, buttocks, and perineum, which goes away within 3 days;
- the subclinical form includes the short-term occurrence of a small ulcer or crack in the mucous membrane, accompanied by mild itching.
Subjective signs that may be symptoms of other gynecological pathologies include:
- itching, burning when urinating, pain in the lower abdomen;
- vaginal discharge of a mucopurulent nature with vaginal herpes;
- increased body temperature, headache, nausea, muscle pain, as signs of intoxication, are usually observed during the initial episode of infection.
Important!
With each subsequent exacerbation, the severity of symptoms decreases.
Recurrences of type 2 herpes on the genitals in women occur more often than with type 1 infection.
Since herpes on the cervix manifests itself with minor objective symptoms, this disease often remains undiagnosed.
The moment of exacerbation of genital herpes cannot always be detected during a gynecological examination, since obvious signs - blisters and erosions - are visible during immediate exacerbation.
A woman does not always turn to a gynecologist if she has pain during sexual intercourse, but the appearance of bloody discharge from the area of ulcers most often forces her to consult a gynecologist.
Often, a woman learns about a genital lesion when taking a smear for PCR during the examination.
The infection occurs in varying degrees of severity and is determined by the number of relapses per year. If the genital form of herpes worsens more than 5-6 times a year, then this course is considered severe and a reason for treatment and immunocorrection.
Most often, the infection recurs up to 3 times a year, but in some patients, herpes appears monthly. In reviews, women often note the appearance of relapses on the eve of the next menstruation.
Symptoms
Symptoms of genital herpes in women have their own characteristics. After the first infection with the virus, the disease is usually asymptomatic, and HSV itself is dormant.
You should know that after the first entry into the body, the virus makes a person a carrier.
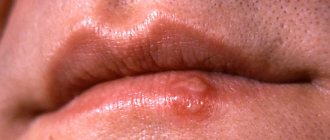
Many women want to know what herpes looks like on the labia. To do this, we can make the following comparison with the manifestation of genial herpes in men:
| Among women | In men |
| On the labia majora | On the scrotum |
| At the entrance to the vagina | On the thighs and groin area |
| On the cervix | In the buttock area |
| In the buttock area | Not far from the anus |
| Not far from the anus | In the area of the glans penis |
Signs of HSV infection:
- Burning or itching in the genital area.
- Small rashes in the form of bubbles. After some time, the blisters burst with the formation of ulcers that become crusted.
- Itching and tingling when urinating.
- Herpes in the groin in women provokes enlarged lymph nodes (as in men).
In men, this disease is called urogenital herpes. The rash may spread throughout the body (in case of immunodeficiency and non-compliance with intimate hygiene rules).
The danger of genital herpes
photo of genital herpes in women
Herpes on the genitals can be dangerous for a woman:
- Viral infections, including herpes, lead to a significant decrease in local vaginal immunity, in particular, they stop the growth and reproduction of lactic acid bacteria. As vaginal dysbiosis progresses, genital herpes leads to easier penetration of pathogenic bacteria into the woman's genital tract. Further, infectious and inflammatory processes become chronic.
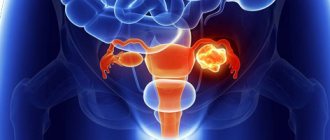
- Herpes and infertility in women are inextricably linked, namely the formation of a tubal-peritoneal form of impossibility of conception. Against the background of frequent activation of herpes infection, pathogenic microorganisms penetrate the endometrium and fallopian tubes, leading to their inflammation. In addition, the virus can independently lead to damage to the higher parts of the reproductive tract, for example, adnexitis, endometritis.
- The likelihood of a child becoming infected during childbirth during an exacerbation of genital herpes is very high, which results in a severe viral infection in the newborn child. If a woman’s primary infection with the genital form of herpes occurs during pregnancy, the virus penetrates to the fetus due to the lack of protective immunoglobulins.
Cervical herpes, along with HPV, accelerates the development of dysplasia and transformation into cancer. Some experts note the role of the herpes simplex virus in the development of ampullary rectal cancer.
How is genital herpes transmitted?
Viruses penetrate through the mucous membrane of the genital organ, rectum, urethra and minor lesions on the skin. You can become infected both during oral-genital and anal-genital contact. But HSV is also transmitted:
- By airborne droplets.
- Through self-infection (autoinoculation): a person independently transfers pathogens from the lips to the genitals.
- Vertically (from infected mother to child). The virus is transmitted as the baby passes through the birth canal.
- In domestic conditions, when using other people's personal hygiene items: towels, soap, washcloths. It is this way that children and adolescents most often become infected with herpes.
- Upon contact with blood, lymph, sperm of a patient (this risk group includes venereologists and gynecologists).
How to get rid of the virus?
Patients are concerned about how to get rid of genital herpes and is it possible?
It should be noted that the virus circulates in the host’s nerve cells for life, periodically causing relapses of infection. Therefore, treatment of genital herpes in women is aimed at reducing the number of relapses.
Since genital herpes in women is exacerbated by immunodeficiency, treatment is aimed at increasing overall resistance and cellular immune response. And the relapse itself is treated with antiviral drugs.
They are also used for very frequent exacerbations, since severe infection can be treated only by reducing viral replication, and not only with immunomodulators.
Treatment of herpes types 1 and 2 is necessarily accompanied by therapy for concomitant gynecological pathologies. Without normalizing the vaginal head start, it is very difficult to reduce exacerbations.
In addition, normal vaginal biocenosis prevents the negative effect of genital infection by the virus on the epithelium of the cervix, and also prevents ascending infection.
How to cure herpes: prescribed medications, folk remedies and prevention methods
The main goal of therapy for genital herpes is to suppress active replication of the virion during an exacerbation of the disease. In addition, it is necessary to support the human immune system, in this way the period of remission can be significantly extended.
For the treatment of HSV the following is prescribed:
- systemic antiviral drugs;
- human recombinant interferon;
- immunomodulators;
- antiviral drugs for local use, but they are less effective compared to systemic ones.
Currently, several effective ways have been developed to cure herpes. Thus, for rare relapses of HSV (no more than 2 times a year), so-called episodic treatment is possible, when the patient is prescribed an antiviral drug when the first symptoms of an exacerbation appear. Sometimes the stop-dose technique is quite effective, when a large dose of antiviral medication is taken once at the initial signs of HSV (deterioration of health and itching in the absence of rashes). Preventive (suppressive) therapy is indicated for patients with frequent exacerbations, severe symptoms, and in preparation for pregnancy.
The most common and effective treatment regimens
Stop dose:
- Acyclovir 0.8 g once.
For primary infection:
- Acyclovir 0.2 g 5 times a day - 10 days;
- Valacyclovir 0.5 g twice a day - 10 days;
- Famciclovir 0.25 g three times a day for 5–10 days;
- Panavir injections 5 ml intravenously with an interval of 2 days, a total of 5 injections per course;
- Panavir rectal suppositories (200 mcg) at night - 10 days.
Suppressive therapy:
- Acyclovir 0.2 g 4 times a day - 90 days;
- Valacyclovir 0.5 g once a day - three months or more.
To stimulate and normalize the immune system:
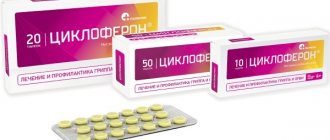
- Cycloferon 12.5%, 2 ml intramuscularly with an interval of 2 days, a total of 10 injections;
- Allokin-alpha, 1 mg subcutaneously at daily intervals (6 injections in total);
- Longidaza 3000 IU, in the form of intramuscular injections (one every 2–3 days), 10 injections per course;
- Intraglobin is administered intravenously at a dose of 25–50 ml once every 1–3 days in a course of 3 to 10 injections.
For local therapy (in combination with oral antivirals):
- Panavir gel;
- Acyclovir cream and ointment;
- Tromantadine ointment;
- Fenistil pencivir gel;
- Viferon gel;
- Epigen spray.
These drugs are applied to the affected areas of the genital skin 3 to 6 times a day for 1–1.5 weeks. For the treatment of genital herpes in pregnant women, Acyclovir is prescribed in standard doses. For the treatment of newborns: Acyclovir intravenously at a dosage of 10 mg/kg with an interval of 8 hours, the course is continued for up to 2-3 weeks. In children under 2 years of age, Acyclovir is also used to treat HSV, but at half the dose, and after 2 years of age - at the standard dose.
A specialist can also prescribe the modern drug Acyclostad.
Alternative medicine
Traditional healers offer their own recipes for remedies that will quickly get rid of the manifestations of herpes in the intimate area:
- Compresses made from apple cider vinegar, but they can only be applied to the skin of the buttocks and perineum, avoiding contact with mucous membranes.
- Brew a decoction of the herb (a tablespoon of herbs per glass of boiling water), drink half a glass three times a day at the first symptoms of herpes.
- Take 4 parts each of lemon balm herb and raspberry leaves, 3 parts each of thyme herb and 2 parts each of eucalyptus leaves and wormwood herb. Pour 2 tbsp. vegetable mixture with half a liter of boiling water, leave for half an hour and drink throughout the day.
- Apply sunflower petals scalded with boiling water to the herpes lesions.
Doctors emphasize that there is no cure for herpes. However, the main method of prevention is not the constant use of antiviral drugs, but strengthening the immune system. In addition, it is necessary to avoid casual and unprotected sexual contacts, give up alcohol consumption and bad habits, and lead an active lifestyle.
https://youtu.be/H_I7w3G6n2g
How to treat an exacerbation of a viral infection?
To speed up recovery, you should start taking acyclovir medications as early as possible. For treatment use one of the following:
- Acyclovir 200 mg (one tablet) five times a day for five days;
- Valaciclovir 500 mg 2 times a day for 10 days for primary infection and for 5 days for relapse;
- Famciclovir 250 mg 3 times a day for 5 days during primary infection, 125 mg twice a day during exacerbation (5 days).
Severe cases require taking antiviral medications for 4-12 months.
In other situations, the doctor individually selects immunomodulatory therapy. The goal is to reduce the number of exacerbations. They use drugs and interferon inducers, Polyoxidonium, Levamisole, Timalin, Ingavirin, Likopid, Roncoleukin. As part of anti-relapse therapy, some specialists use immunoglobulin against HSV 2.
To normalize the cellular immune response, a herpes vaccine for women is used, for example, Vitagerpavak, Gerpovax. Vaccination is appropriate only during the absence of symptoms.
Antiviral ointments with acyclovir are used locally, and to speed up healing - Solcoseryl, Panthenol, Meliluracil ointment. You can burn the bubbles with any alcohol-containing product.
In case of pronounced plaque, treatment is carried out with hydrogen peroxide. Itching can be stopped with Pox spray, Calamine.
It is prohibited to use douching and vaginal baths in treatment, since irrigation of the vagina with solutions can lead to the spread of the virus.
Maintenance therapy includes taking B vitamins, omega-3 acids and antioxidants.
Treatment methods for herpes on the vagina
Getting rid of the disease at an early stage is much easier. If herpes does not receive quality treatment in due time, it may outgrow the chronic stage. It will subsequently be impossible to eliminate debilitating symptoms that cause not only physiological but also moral discomfort. Treatment of vaginal herpes is carried out on an outpatient basis. The doctor prescribes a set of medications and sends the patient home. In most cases they use:
- antiviral agents - prescribed to destroy the herpes virus;
- drugs to enhance immunity - improve the body’s defenses, allow the immune system to cope with the pathogen on its own;
- local treatment allows you to relieve swelling, redness and dry the blisters that have formed;
- analgesics relieve unpleasant itching, burning and pain in the perineal area.
It should be noted that the effect can be achieved if you approach therapy comprehensively, be sure to use both external medications and internal medications. Genital herpes can progress rapidly and, if the therapy was chosen incorrectly, is characterized by a number of complications, such as: herpetic urethritis, endometritis, salpingitis and herpetic cystitis. These diseases cause severe discomfort and need to be treated in a hospital setting.
The following medications help cure vaginal herpes:
- Interferon;
- Acyclovir;
- Famvir.
These medications are highly sensitive to herpes of the first and second types, so they can completely stop the manifestations of the disease. Despite the fact that they are sold in pharmacies without a doctor's prescription, you should not use them at your own discretion. The doctor should prescribe them based on your tests. There are a number of cases when the components of the above remedies provoked an allergic reaction in a woman and further worsened her condition. In addition, each of the medications has a list of contraindications for use that should be excluded before taking.
Unfortunately, medicine has not yet figured out how to treat the herpes virus, or rather, how to cure it completely. Modern medications can only reduce the intensity of symptoms and reduce the reproduction of the virus at the cellular level.
Symptoms of herpes zoster during pregnancy and its treatment
To reduce the activity of herpes viruses, suppositories can be prescribed:
- Genferon;
- Lavomax;
- Panavir;
- Hexicon.
Be sure to use immunomodulatory medications, for example:
- Neovir;
- Immunal;
- Arbidol;
- Viferon;
- Imudon.
Treatment of vaginal herpes is a long stage in which every action of the patient can affect the result. It is very important, along with taking these medications, to eat right, consume an increased amount of vitamin-containing foods and adhere to personal hygiene rules. If you have herpes, you need to wash with products that have a low pH. It is prohibited to use products with abrasive particles for hygiene, which will allow the skin with papules to peel off.
Traditional methods of therapy
If for some reason you don’t have the opportunity to visit a doctor, then traditional methods of therapy will come to the rescue; this is in any case better than simply ignoring the pathological process in the body. The following recipes have proven to be the best in treating vaginal herpes:
- They make sitz baths with soda; to prepare them you need half a kilogram of soda per 10 liters of water. Along with soda, you can add chamomile, calendula and lemon balm. These plants have an anti-inflammatory and antiseptic effect, so they will have a good effect on your well-being and eliminate itching in the perineum. You need to sit in the bath for at least half an hour.
- Douching with geranium oil, black tea and clove infusion has a good effect. The ingredients are mixed together, warmed to room temperature and douched 2 times a day.
- Birch buds are brewed in milk, filtered, and after soaking natural tissue in the liquid, they are applied to the site of inflammation.
- An ointment is made from honey and celandine. The ingredients are mixed together and applied in a thin layer to the vaginal area, avoiding the mucous membranes. Honey can prevent the development of bacterial infections and relieve inflammation, and celandine dries out blisters and has a regenerating effect on damaged areas of the skin.
- Aloe leaves have always been famous for their effectiveness in treating skin diseases, and they did not disappoint this time either. You just need to wipe the inflamed area with aloe juice three times a day to reduce redness and relieve inflammation.
https://youtu.be/aN6aY0Ef5OU
As can be seen from the above, there are a lot of options for the treatment of vaginal herpes; it is important not to get carried away with self-medication and, if traditional medicine has not brought results within two weeks, consult a doctor. It is very important not to miss the moment when you can fix everything, because by ignoring the disease, you put your loved ones and relatives at risk who, in contact with you, may also encounter herpes.
Timely therapy and regular visits to the doctor will reduce the intensity of the symptoms of the disease and minimize relapses of herpes. You will be able to return to your normal life and not worry about being a carrier of the infection.
Prevention
Primary prevention of genital herpes is the formation of correct sexual behavior in boys and girls. Early sexual debut and a chaotic sex life will inevitably lead to infection with the virus, which is fraught with more serious consequences than in mature women.
Secondary prevention of genital herpes includes a number of measures aimed at reducing the number of relapses:
- avoiding hypothermia;
- minimizing tanning and overheating procedures;
- proper care of the skin and mucous membranes of the genital organs;
- monogamy sexual life;
- timely treatment of STIs;
- proper and nutritious nutrition that helps normalize the immune response.
On the eve of menstruation, it is not recommended to swim in ponds, pools, or visit baths and saunas - these procedures can provoke an exacerbation.
Before pregnancy, every woman needs to be tested for sexually transmitted infections, including HSV types 1 and 2, and analyze the number of exacerbations of the disease with a doctor. The presence of viruses in the cervical canal requires treatment even in the absence of signs of pathology.
Author: Infectious disease doctor Natalya Aleksandrovna Kulikovskaya