A change in the nature of menstruation occurs in the first months of taking hormonal contraceptives, in the first years of the appearance of regular menstruation. An examination by a gynecologist is mandatory.
Each woman's menstruation is completely individual. Any changes in the nature of the discharge may be a sign of uterine bleeding and lead to the development of life-threatening complications. Menstruation without clots can occur due to diseases of the ovaries, disruption of pregnancy, and blood diseases.
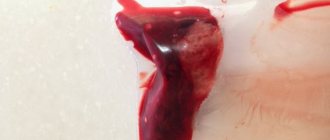
During menstruation, an average of twenty to fifty milliliters of blood is released per day. It is dark in color and flows out in portions. Menstrual discharge is characterized by minor inclusions: lumps of mucus, clots. The number of lumps is constant for the same woman.
It has a specific, mild, individual smell. are also specific to different representatives of the fair sex. The range of shades ranges from pinkish to dark brown or brownish. With each menstruation this shade of color is the same.
Differences between menstruation and uterine bleeding
Discharge of blood without clots may be normal if this type of menstruation is repeated from month to month, the amount of discharge does not exceed normal and its duration is normal. You should be wary of a situation when the characteristics of menstruation change dramatically:
- the volume of discharge increases or decreases;
- blood flows out constantly;
- the discharge becomes liquid;
- their color changes, becomes scarlet, intense red;
- clots disappear in the discharge;
- the specific smell of blood disappears.
Bleeding without clots is characterized by a lengthening or shortening of the period between menstruation, an increase in the number of days of bleeding. It may last longer than usual. Without appropriate treatment, bleeding does not stop for months.
https://youtu.be/W71T7kopdlQ
Normal and abnormal clots
Sometimes heavy menstruation with clots can be considered normal. If the pieces are small—no more than a quarter of a centimeter—and only random, you don't have to worry. Unlike blood clots that form in your veins, they are not dangerous in themselves.
Normal clots:
- less than a quarter;
- found only occasionally;
- appear at the beginning of menstruation;
- bright or dark red.
Abnormal clots are larger than a quarter centimeter in size and occur more frequently. The regular occurrence of large blood clots during menstruation may signal a health condition that requires investigation.
You should seek immediate medical attention if you have a period with large clots and you think you might be pregnant. This could be a sign of a miscarriage.
Causes
The main reasons that provoke this symptom are the following:
- malignant tumors of the cervix and uterine body;
- benign neoplasms;
- hormonal disorders in the ovaries;
- adolescence;
- menopause;
- taking hormonal contraceptives;
- endometriosis;
- pregnancy;
- diseases with increased bleeding;
- taking medications that thin the blood.
In adolescence and menopause, uterine bleeding is caused by hormonal disorders. In girls, they are most often observed in the first few years after the appearance of menstruation. At this time, the cycle is not yet regular. Menstruation occurs at different intervals. They vary in duration and intensity. If periods last a long time, they can lead to the development of anemia.
Taking hormonal contraceptives in the first two or three months, in approximately half of the cases, is accompanied by the release of mucus with brownish streaks. They are insignificant, spotting, and may continue after replacing the drug with another. After normalization of hormonal levels, a few months from the start of using these products, the discharge stops.
With benign tumors, as a rule, there are two types of discharge: massive with the release of liquid blood or long-term (up to several months) with daily rejection of a small amount. These bleedings are dangerous due to the occurrence of complications: shock or anemia.
To treat certain diseases of the heart and blood vessels, the doctor prescribes drugs that make the blood more fluid (for example, aspirin) and prevent the formation of microthrombi. Violation of the regimen for taking such drugs can lead to increased bleeding.
The appearance of mucus with blood or leakage of liquid blood in pregnant women may indicate the onset of placental abruption and become the first sign of an ectopic pregnancy.
What is menstrual flow?
Throughout the menstrual cycle, the uterus prepares for a future pregnancy. The walls thicken for subsequent attachment of the fetus. If pregnancy does not occur, then blood and endometrium come out during menstruation. After your period ends, a new layer of endometrium begins to grow in anticipation of conception.
Blood discharge has certain characteristics, these are:
- bright red color;
- unpleasant odor;
- decreased blood clotting.
On average, the menstrual cycle lasts 4-5 days, and a woman’s body loses about 250 ml of blood during this period. The first days it is intense, and in subsequent days it decreases and acquires a brownish or rich burgundy hue.
Symptoms
A change in the nature of menstruation, an increase in its duration, the volume of blood released, and the disappearance of clots should alert a woman. She should immediately consult a gynecologist.
With massive bleeding, the volume of fluid in the vessels sharply decreases. The woman develops symptoms of shock:
- gaskets get wet at short intervals;
- blood pressure decreases;
- rapid heartbeat occurs;
- dizziness appears;
- the patient becomes pale;
- the skin becomes covered with drops of sweat;
- the condition worsens when standing up suddenly;
- vomiting occurs;
- the woman may lose consciousness.
If the bleeding is spotty and bothers you for a long time, then there is a danger of developing anemia. In this case, the patient is concerned about the following manifestations:
- constant secretion of mucus with brown streaks;
- over time they change color and become lighter;
- increased fatigue;
- drowsiness;
- the skin becomes dry, pale or yellowish;
- brittleness and splitting of nails;
- hair loss;
- dizziness when standing up suddenly;
- rapid heartbeat;
- deterioration in schoolgirls' success;
- loss of consciousness;
- anemia.
If the above symptoms appear, the woman should consult a doctor immediately. Depending on the cause, treatment can be carried out with tablets or surgery.
Treatment process
What to do if your period comes with blood clots? In order to get rid of pathological discharge, you must first determine the cause. You need to see a doctor, take the necessary tests and undergo an ultrasound diagnosis of the pelvic organs. The latter method will confirm or refute the presence of endometriosis. Hormone therapy is used to treat this disease. Although sometimes doctors take drastic measures, solving the problem through surgery. In addition to the above, the attending physician may prescribe a magnetic resonance examination of the urogenital system to exclude the presence of formations.
If the patient is found to have an infectious disease, appropriate medications will be prescribed. Very often, when blood clots appear, Ascorutin and Calcium Gluconate are prescribed.
Causes
Doctors identify several key factors that provoke the appearance of liquid scarlet menstruation. These include:
- Neoplasms in the genital organs of benign and malignant types.
- Improper functioning of the ovaries associated with hormonal imbalance.
- A teenage girl is in transition.
- Taking inappropriate hormonal contraceptives.
- Pregnancy at different stages.
- Pathologies associated with blood clotting.
In most cases, uterine bleeding is somehow related to the balance of hormones in the body. This is especially true for patients in adolescence and menopause. If bright red liquid discharge without clots continues for 6 or more days, the woman may develop a serious illness - anemia.
What are the physiological causes of clots?
Coagulated blood leaving the genital tract along with menstruation can be a completely natural physiological phenomenon. The most common probable causes of clots during menstruation are:
- age under 18 years;
- postpartum period for 15-40 days;
- conditions after surgical operations, including abortions;
- spontaneous miscarriage;
- the presence of an intrauterine device, which provokes heavy menstruation;
- abnormal position of the uterus;
- a sudden change in body posture after a long stay in a stationary position, resulting in stagnation of blood in the genitals.
It is believed that if, in the absence of disturbing symptoms, blood clots come out during menstruation, then this does not pose a threat to the woman’s health, while acting as a normal physiological manifestation.
There are about 7 sources of blood clot
Bleeding
If the nature of your critical days has changed without any obvious reason, you need to be wary. Especially if, in combination with an increase in the duration of menstruation, the discharge becomes bright red, without clots. In this case, it is necessary to undergo a diagnostic examination and, if necessary, select appropriate therapy.
If the patient suffers from severe uterine bleeding, the volume of fluid in the vessels decreases, and a state of shock may occur. This dangerous pathology is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Large volume of discharge (even overnight pads last only 30-40 minutes);
- Blood pressure decreases, heart rate increases;
- The patient turns pale and feels very dizzy;
- Beads of sweat may appear on the forehead;
- If you rise suddenly, the condition will only worsen.
Failure to receive prompt medical attention can result in a woman losing consciousness. Bleeding is very dangerous for the health and life of patients.
With anemia, the fair sex often develops brown streaks in normal vaginal discharge. The patient becomes very weak, gets tired quickly, and constantly wants to sleep. Outwardly, anemia manifests itself extremely negatively. This disease leads to hair loss, brittle nails, dry and pale skin. The woman often has attacks of dizziness and rapid heartbeat.
It is very important to promptly distinguish normal menstruation from bleeding, and take advantage of qualified medical help. This way you can normalize the health of the reproductive system and protect yourself from the development of dangerous complications.
Menstruation is an integral part of the intimate life of every woman. Starting from puberty (11-14 years) and ending with menopause (45-50-55 years), representatives of the fair sex experience several unpleasant days every month, which are called critical.
From a physiological point of view, menstruation is the removal of the inner layer of the uterine mucosa (endometrium), which has not accepted a fertilized egg. Due to the detachment of the endometrium, the small blood vessels that supplied it are exposed. The mucus released during menstruation is the rejected uterine lining, and the blood is a small amount of the contents of the uterine vessels.
The color of blood during menstruation depends on the amount of iron in a woman’s body. To be precise, it depends on the number of red blood cells and hemoglobin level. But normally it is considered this way:
- at the beginning of menstruation (1-2 days, depending on the duration), the blood may have a bright red or scarlet color, more liquid and without the admixture of thick inclusions (clots or mucus);
- then the discharge becomes darker, acquires a brownish tint, sometimes turning burgundy-brown - this phenomenon is explained by the fact that iron oxidizes when it comes into contact with oxygen;
- the smell is specific, but without stench;
- the blood does not clot because it mixes with the mucous secretions of the uterus and vagina;
- in recent days, small blood clots, particles of tissue and mucus may be present in the discharge;
- the amount of discharge should not exceed 150 ml for the entire period;
- The duration of menstruation varies from 3 to 7 days.
A woman whose menstrual cycle is established and her menstrual days begin according to schedule will always be able to “calculate” the problem not only by the calendar glitch, but also by the consistency and color of the discharge.
Deviations from this norm can be observed in two cases, which do not cause any particular concern, although a visit to the gynecologist will not hurt:
- in girls whose cycle has not yet established;
- in women during menopause, when such discharge is accompanied by other signs of the onset of menopause.
If, during the reproductive period, a woman is faced with the problem of an unusual color of her periods, their great abundance, started a few days (more than a week) earlier and the continuation of menstrual flow for a long time, this is a reason to consult a doctor immediately. Perhaps you are not having your period, but uterine bleeding. And this condition is life-threatening due to excessive blood loss.
What is heavy bleeding called?
Menstruation has symptoms similar to uterine bleeding. If there are prerequisites for pathological bleeding (for example, the development of diseases of the reproductive organs), the appearance of blood from the vagina will most likely be a sign of bleeding. However, during the postpartum period or during unstable menstruation, difficulties may arise in determining the nature of the discharge.
Very heavy bleeding should be a concern
General signs by which menstruation can be distinguished from uterine bleeding:
- copious discharge that does not reduce intensity;
- scarlet color of blood (during menstruation it has a darker shade);
- absence of mucus and blood clots;
- Duration of heavy discharge for more than 4 days.
Scarlet menstruation without clots can occur in women several years after the onset of menopause. This process can be either natural or pathological.
A special category of women are pregnant women and young mothers. Normally, menstruation does not begin after conception, but in some cases, menstruation can be perceived as a sign of pregnancy if its abundance changes, there are no clots, and its duration is significantly reduced.
Bloody discharge during pregnancy can be dangerous; this is one of the signs of miscarriage.
The danger of menstruation in pregnant women is that the cause of the discharge may be incorrectly determined. During pregnancy, bleeding may begin, indicating the risk of miscarriage or self-abortion, if blood is released from the vagina along with large clots of mucus and endometrial tissue.
After childbirth, also for most women (especially when breastfeeding), menstruation begins only after six months, or even later. However, in the first 40 days, discharge resembling menstruation persists. They are not characterized by the presence of clots and abundance.
If after giving birth a woman begins to have light periods without clots, it is quite possible that early menstruation will begin, but a visit to the gynecologist is required due to the high risk of postpartum bleeding.
Menstruation is a normal part of a woman's monthly cycle. It should not cause severe discomfort. Some women and girls try to stop painful and excessive discharge on their own at home. However, this cannot be done. Self-medication leads to deterioration of the condition and the development of severe complications.
If violations are detected, the doctor will select the appropriate treatment. However, the treatment of menstrual pathologies is strictly individual. In some cases you need to take pills, in others you will need surgery.
When heavy bleeding during menstruation with clots can be called a pathology depends on the amount of blood released. Officially, blood loss of more than 80 ml (or 16 moistened sanitary products) during the menstrual period is considered menorrhagia.
Most women with this kind of heavy bleeding will have low hemoglobin (anemia) or signs of iron deficiency. In practice, only about a third of women are anemic. Therefore, the definition of a heavy period may be adjusted to include 9-12 regular-sized soaked sanitary products per period.
Another very simple way to measure bleeding is to use a menstrual cup, which has markers for 15 and 30 ml of blood loss. To measure blood loss with a menstrual cup, simply add up the estimated amounts from each bowel movement.
Period or bleeding?
Scarlet blood during menstruation, which does not darken and continues to be released for a week, or even more, is no longer menstruation, but uterine bleeding. In this condition, it is necessary to immediately consult a doctor in order to carry out timely treatment measures aimed at eliminating the cause of the pathology.
The most common symptoms will be:
- menstruation is scarlet, lasting more than a week;
- liquid in consistency throughout the entire period;
- practically odorless.
Bleeding intensity can vary - from heavy bleeding, in which you need to change the pad more than twice an hour, to almost normal, but with light blood, which does not stop for a long time.
Symptoms of blood loss that threatens health and even life:
- severe weakness and drowsiness;
- unusual and unexplained fatigue;
- dizziness leading to fainting;
- dark spots before the eyes, loss of coordination of movements.
If such manifestations occur, immediately call an ambulance and go to the hospital, where you will receive the necessary assistance and diagnose the causes of this condition.
Treatment
The menstrual cycle is usually called the period between periods, that is, the time from the beginning of one period to the beginning of another. Normally it can last 28-31 days. For all women, the duration of the menstrual cycle is highly individual and may differ with age. At a younger age, the cycle is more regular, as it is controlled by sex hormones produced in the body.
The beginning of the cycle is characterized by the maturation of the follicle and the renewal of the inner mucous layer of the uterus, with pieces of tissue (endomentry) and menstrual blood coming out over the course of three to seven days. The next period of the menstrual cycle is accompanied by thickening of the endometrium and preparation of the follicle for rupture; this is the so-called proliferation phase, which lasts until the middle of the cycle, that is, until the follicle ruptures and the egg is released.
For some time, the reproductive cell remains in the fallopian tube awaiting fertilization, but if there were no favorable conditions and conception did not occur, then the production of sex hormones decreases, and the uterus begins to reject the inner lining. Thus, menstruation begins, and with it a new menstrual cycle. Normally, during menstruation, no more than 200 ml of blood should be released with particles of the endometrium and mucous tissue.
During menstruation, the body increases the production of special enzymes that slow down blood clotting and act as an anticoagulant. If menstruation is too heavy, then an insufficient amount of such enzymes is not able to cope with its task, which is why large clots appear.
If a piece of endometrium up to 0.1 m long comes out with a glandular structure and a dark burgundy tint and with a metallic smell, then in this case there is no need to worry. If fever, pain, or huge clots appear, such discharge is very dangerous and requires immediate attention to a gynecologist.
Normally, large clots should not cause concern to a woman in the following cases:
- age under 18 years;
- if more than a month has passed since the birth of the baby;
- if in the recent past there was an abortion, miscarriage, gynecological surgery or uterine curettage;
- when using intrauterine methods of contraception;
- with congenital abnormal shape of the uterus.
If your period comes with bright scarlet clots, and there is enormous blood loss, you should immediately call emergency help. This may not be menstruation, but uterine bleeding, which is eliminated by completely removing the endometrium.
When using conservative therapy, the goal is to compensate for the lack of iron in the body caused by large blood loss. For this, vitamins and a special diet are prescribed, in which foods with a high iron content predominate in the diet. Bed rest is also indicated and medications may be prescribed to stop bleeding.
In severe situations, in the presence of internal septa, neoplasms or endometrial pathologies, surgical intervention such as curettage or hysteroresectoscopy may be necessary. The most radical treatment method, which is used at the very last moment, is the complete removal of the uterus and appendages.
Thus, if critical days are accompanied by the appearance of clots that do not cause pain or discomfort, then this may well be a variant of the norm. If the discharge is too large and is accompanied by pain, a strong odor and temperature, do not waste time that could be used for treatment, but consult a doctor immediately. Preventive gynecological examinations will allow timely detection of diseases of the reproductive system and prevent its development.
Treatment depends on the cause that caused the increase in blood loss during menstruation, including due to the formation of clots.
Aimed at eliminating factors that provoke bleeding and replenishing iron reserves in the body. Includes:
- Therapeutic and protective regime. Particularly important for juvenile uterine bleeding.
- Cyclic vitamin therapy, especially groups B, A, E and C, folic acid.
- The use of iron supplements with a decrease in hemoglobin.
- Hormonal therapy.
Surgical treatment
Aimed at removing pathological endometrium, uterine fibroids, internal septum, etc. in various ways - from curettage to hysteroresectoscopy. In difficult situations and in case of recurrent pathology, as well as in the case of malignant diseases, removal of the uterus.
A woman's menstruation should not bring excessive discomfort and lead to disruption of her life. In most cases, blood clots, similar to pieces of liver during menstrual periods, are a pathological condition that requires adequate and competent treatment. Otherwise, you may miss serious diseases, including cancer.
The menstrual cycle is one of the most significant processes occurring in a woman’s body. Its mechanism of action is that regularly, every 27-35 days, the egg matures in the reproductive system, ready for subsequent fertilization. In preparation for possible conception, special hormones are produced, resulting in thickening of the endometrium.
The menstrual period lasts on average 30 days
In the absence of fertilization, the amount of hormones decreases significantly, which entails a decrease in the degree of blood saturation of the tissues of the uterine space and detachment of its internal layer through the genitals. This is how menstruation occurs, lasting from 3 to 7 days.
After a visit to the doctor, a woman who produces abundant blood clots during menstruation is prescribed therapeutic measures to get rid of negative symptoms and eliminate the sources of the pathology that provokes its formation. Treatment methods include:
- conservative;
- operational.
Therapeutic actions are carried out in anemic conditions, problems with the endocrine system, menopause, and inflammation. Depending on the diagnosis, certain types of drugs are used in the treatment of pathology. Among them:
- hormonal agents - Duphaston, Utrozhestan;
- iron-containing – Totema, Sobrifer, Aktiferrin, folic acid;
- to stop bleeding and improve hematological parameters - Etamzilat, Dicynon, Eltrombopah, Vikasol;
- vascular strengtheners - Ascorutin, Atorvastatin;
- vitamin complexes.
Treatment takes place in several stages.
Surgical treatment is indicated for fibroids, abnormal deviations in the structure of the uterus, miscarriages, polyps, and also for cancer.
The combination of excess menstruation, blood clots and other negative symptoms requires a thorough medical examination and proper treatment to avoid negative consequences.
For what reasons does scarlet blood appear?
The reasons when red periods indicate pathological processes occurring in the body may be as follows:
- in the early stages of pregnancy, scarlet periods may indicate a miscarriage;
- with an ectopic pregnancy, menstruation will be accompanied by scarlet blood at the moment the egg grows in the tube and a crack appears, which precedes rupture;
- infections of the genitourinary system, which, together with the scarlet color of the discharge, are accompanied by a whole set of unpleasant symptoms: soreness, copious and strong-smelling discharge, discomfort or pain during sexual intercourse;
- ingrowth of the intrauterine device into the cervix. Periods without clots, scarlet or bright red may be the only symptoms of a problem;
- oncological neoplasms in the uterus. This pathology is accompanied by a number of other symptoms: heavy periods, discharge with a watery consistency and an unpleasant odor in the middle of the cycle;
- polyps in the uterine cavity cause heavy periods and pain during sexual intercourse. But this pathology can sometimes be asymptomatic;
- after an abortion, scarlet blood may indicate that particles of the amniotic sac or its membrane remain in the organ cavity;
- endometriosis is characterized by heavy and painful periods with scarlet discharge. Physiological processes such as urination and defecation can cause discomfort and sometimes pain;
- Uterine fibroids provoke abdominal growth only with a certain localization of the tumor and in the later stages of the pathology. In the early stages of the development of the disease, a woman notices heavy light periods, bloody discharge from the vagina outside of menstruation, and some others.
Pathological causes that can cause bright red periods require immediate treatment. Then the pathology of the menstrual cycle will be eliminated.
What diseases can there be
During menstruation, the appearance of huge blood clots may be observed, which, as a rule, indicates the development of pathology. The symptom indicates various diseases and is combined with additional clinical symptoms. This picture indicates the following possible disorders in the body:
- Hormonal imbalance causes a variety of abnormalities in the reproductive system, this may include the appearance of a large number of blood clots during menstruation.
- Iron deficiency anemia is accompanied by other symptoms. This is, first of all, asthenic syndrome - weakness, fatigue, pallor and periodic dizziness.
Sometimes the cause may be low hemoglobin levels - anemia
- Early miscarriage is another cause of clots during menstruation.
- There are a number of pathologies of various organs that increase blood viscosity. This may be liver or kidney damage.
- The penetration of infection into the genitals has a number of effects: it changes the acidity of the environment, blood viscosity and even the structure of uterine tissue.
- Gynecological diseases that affect the properties of the inner layer of the uterus lead to the fact that the endometrium begins to be rejected in larger pieces.
Any spotting during pregnancy is not normal and can be a symptom of various diseases. Differential diagnosis is carried out only by a qualified specialist. If bleeding from the vagina of any intensity occurs, you must visit an obstetrician-gynecologist as soon as possible.
During pregnancy, such symptoms can be dangerous.
Bloody clots during pregnancy may indicate the following pathologies:
- threat of miscarriage - dark, viscous clots with a dark brown tint are observed;
- spontaneous abortion - accompanied by cramping pain, tissue fragments are present in the discharge;
- frozen pregnancy, which may manifest as bleeding interspersed with small dark scarlet clots;
- abruption of the placenta or ovum;
- damage to uterine tissue during implantation of a fertilized egg;
- ectopic pregnancy.
Various fetal pathologies can also cause scanty or heavy periods with clots. In the third trimester of pregnancy, similar symptoms may be accompanied by the passage of the mucus plug, which characterizes the approach of labor.
Pathological causes of blood clots during menstruation cannot be ruled out. Most often they occur with the following diseases:
- endometrial hyperplasia;
- polyps;
- uterine fibroids;
- endometritis;
- displacement of the uterus.
The reason may be various pathologies of the female reproductive system
Endometrial hyperplasia is characterized by thickening of its functional layer. When the disease occurs, blood retention occurs in the tissues with a sharp expansion of capillaries, as a result of which blood circulation is disrupted and blood clots form.
Uterine fibroids are a benign tumor that develops from the myometrium. At an early stage it is asymptomatic, but as the formation grows, the duration and volume of uterine bleeding increases. The menstrual cycle is disrupted, abdominal pain appears, and its volume increases. A large tumor compresses the vessels of the uterus and damages them; many clots form during menstruation.
Endometritis begins after abortion, childbirth or uterine surgery. Characterized by high body temperature, pain in the groin area, bloody discharge with an unpleasant odor. The detachment of the pathologically altered endometrium is disrupted, which during menstruation leads to heavy blood loss and the formation of clots.
Displacement of the uterus. When the position of the uterus changes, the normal outflow of blood from the organ is disrupted, which leads to stagnation.
With endometriosis, the discharge may have an unpleasant odor
What to do with scarlet periods
If you notice a change in the color of menstrual blood that has occurred for the first time and is not typical for your body, you should consult a specialist. If it is bleeding, you need to contact it immediately. If you can’t determine for yourself what happened to you, a specialist will help.
Even if you visited a gynecologist during menstruation, he will be able to collect anamnesis. And based on the results of your conversation, he will conclude that you need to be examined now and urgent measures taken, or he will schedule a visit after the discharge has ended. If necessary, the specialist will advise what medications should be taken during this period.
If, in addition to the color, your periods do not “stray” from the usual schedule, go to an appointment immediately after the end of the discharge. This period will be the most informative in terms of collecting biological material and conducting other instrumental diagnostics.
If your periods come in clots, this may indicate both normality and various diseases. For example, endometriosis, fibroids, polyposis, hormonal disorders.
Regular periods without severe pain and bleeding are a sign of a woman’s health and indicate that the body is ready to bear a child. If the color changes or the intensity of the discharge increases, then the cause may be an inflammatory disease that requires urgent treatment. The most common question that women turn to a gynecologist with is: why do menstruation come with clots and what causes this condition?
During menstruation, the endometrium lining the uterine cavity is detached. The tissue is rejected and, along with the blood, comes out through the vagina. If a girl is in a horizontal or sitting position for a long time, the blood is retained in the uterus and coagulates. After rising, clots that are darker in color than usual may come out. Women who spend their critical days in bed often notice a similar condition.
Another reason why clots accumulate may be uterine retroflexion. This is a congenital or acquired pathology in which the cervix bends. The normal flow of blood is also delayed and leads to clotting.
If your period comes with clots after sitting or lying for a long time, this is not a pathology and does not require any treatment. If bleeding increases, pain appears in the lower abdomen, discharge changes color or has an unpleasant odor, or body temperature rises, you should consult a doctor.
When to see a doctor
Each girl, after the start of her first period, gradually notes the features of the entire menstrual cycle. What is a deviation for some women is the norm for others. A visit to a specialist is necessary when observing deviations in each individual case.
Despite all the peculiarities of menstruation in women, there are certain norms, departure from which should be alarming:
- changing pads more than once in one hour;
- scanty or, conversely, abundant discharge;
- discharge that does not subside throughout the day;
- bright red color of menstrual blood;
- excessively thin blood;
- complete absence of clots;
- no odor from discharge.
It is important to notice the symptoms of the disease in time and begin treatment:
- lowering general blood pressure;
- increased heart rate;
- constant dizziness;
- pale skin;
- the appearance of sweat on the face;
- deterioration of health with sudden movements.
You should immediately consult a doctor if your blood pressure drops
Women are examined by a gynecologist. Already during the first visit it is possible to determine whether bleeding is occurring. If not, the patient is sent for additional examinations to determine the causes of the pathology.
Menstruation without clots is perceived by many women as normal. However, this is not at all true. The presence of clots indicates the healthy process of changing the endometrium in the uterus and the normal functioning of the entire genital system.
Cases where a woman experiences severe blood clots during menstruation require consultation with an experienced gynecologist. This is especially true for a condition that is aggravated by a combination of negative disturbing manifestations. Among them:
- flow is too intense;
- duration over a week;
- foul odor of discharge;
- strong feeling of pain;
- at planned conception.
The presence of unpleasant symptoms when pieces of coagulated blood come out serves as the basis for an urgent visit to a medical facility in order to establish a diagnosis and carry out appropriate therapy.
The periodic appearance of the symptom in question can be considered a variant of the norm. However, there are also situations in which it is necessary to immediately contact a medical facility. A woman should pay attention to 5 main pathological symptoms:
- Prolonged discharge. See a doctor if menstruation lasts more than 8 days. Delayed contact with a gynecologist can be complicated by anemia due to excessive blood loss.
- Large volume of discharge. It is not normal if the pad fills up earlier than after 1.5-2 hours. Increased bleeding can lead to tachycardia and dizziness.
- The presence of an unpleasant odor from the discharge. The sign may indicate infection of the genital organs. The advanced stages of an infectious disease are complemented by an increase in temperature.
- Very severe pain in the lower abdomen. Blood clots after and during menstruation are the first symptom of damage to internal organs by pathological processes.
- Changes in the composition of secretion. It is necessary to contact a gynecologist if white, purulent or bloody streaks appear in the discharge.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EgiskRFgv6M
Self-treatment often leads to dangerous consequences. Endometriosis in an advanced stage complicates the conception of a child. With an ectopic pregnancy, there is a high risk of fallopian tube rupture. This also reduces the chance of successfully conceiving a baby in the future.
Pathological causes
Clots can also appear against the background of gynecological diseases of an inflammatory, infectious or oncological nature. These include:
- endometriosis;
- uterine fibroids;
- polycystic ovary syndrome;
- endometrial polyposis;
- hormonal imbalance.
Provoking factors include menstrual irregularities, prolonged delays in menstruation, previous births and medical abortions, treatment with hormonal drugs and oral contraceptives.
Hormone balance
Sex hormones androgens are responsible for the reproductive function of women. Under their influence, the follicle matures, which contains the egg, and ovulation occurs. The ovaries produce progesterone and estrogens, these hormones prepare the uterus for the attachment of the fertilized egg. If conception occurs, the fetal membrane synthesizes gonadotropin, which is responsible for the growth of the uterus and the cessation of spasms. If fertilization does not occur, hormone levels decrease before the onset of menstruation.
Hormonal imbalance leads to disruption of the menstrual cycle, problems with ovulation, and difficulty for women to become pregnant and carry a child to term. Symptoms of the pathology include:
- weight gain;
- delayed menstruation;
- menstruation with blood clots;
- increased irritability, aggressiveness;
- chronic fatigue;
- insomnia;
- decreased sex drive;
- male pattern hair growth on the face and body;
- alopecia.
The cause of hormonal imbalance may be the onset of menopause, taking oral contraceptives, malignant tumors of the ovaries, uterus, and adrenal glands. An important role is played by lifestyle, proper nutrition and excess body weight.
A special analysis helps determine hormone levels. The pathology is treated by an endocrinologist, gynecologist or oncologist. After a course of therapy, the menstrual cycle normalizes, the discharge acquires normal consistency, volume and color.
Signs of endometriosis
With endometriosis, cells in the inner layer of the uterus grow outside the organ. The new tissue retains the function of the endometrium, which causes bleeding every month that cannot come out. An inflammatory process occurs, acute pain occurs in the lower abdomen, and the uterus increases significantly in size. There may be difficulty urinating and having bowel movements.
Clinical signs may vary depending on the location of the lesions. Endometriosis can be genital and extragenital. In the first case, the growth of the endometrium occurs within the uterus and ovaries. With the extragenital form, the tissues extend into the abdominal cavity. The cause of the disease is hormonal imbalance.
Symptoms of endometriosis:
- sharp pain in the lower abdomen, radiating to the intestines and lower back;
- during menstruation, blood clots, bleeding lasts longer;
- spotting after the end of menstruation;
- painful sexual intercourse;
- premenstrual syndrome;
- pain during urination and bowel movements.
The disease leads to infertility, and it is often with this problem that women turn to the doctor. During the examination, endometriosis is diagnosed. Hormonal drugs are used for treatment; in severe stages, surgical intervention is indicated. The pathology has a favorable prognosis; women can become pregnant and give birth to a healthy child.
Uterine fibroids
This is a benign formation that occurs in the myometrium of the uterus as a result of impaired cell division. The tumor is a cluster of smooth muscle tissue nodes of varying sizes. The disease is most often diagnosed in women of premenopausal age.
The reasons for the formation of fibroids include hormonal disorders, abortions, late onset of menstruation, too much menstruation, previous inflammatory and infectious diseases of the genital area. Provoking factors are: obesity, sedentary lifestyle, frequent stress.
Typical symptoms of uterine fibroids:
- heavy, prolonged menstruation;
- during blood;
- feeling of heaviness, fullness in the lower abdomen;
- anemia due to prolonged menstruation;
- cramping pain;
- in severe stages, urination and defecation are difficult.
At the initial stages, the disease is asymptomatic, but later heaviness and discomfort arise in the groin area. Characteristic symptoms include heavy periods with clots, which can cause anemia. After the end of the critical days, brown spotting persists, and intermenstrual bleeding occurs.
Women feel weakness, apathy, the skin and mucous membranes turn pale, dizziness appears, and fainting may occur. Acute pain occurs when the fibroid stalk located under the peritoneum is torsion. The blood supply to the tumor stops, and the tissue begins to die.
Treatment is carried out conservatively and surgically. Medicines slow down tumor growth and normalize a woman’s hormonal levels. The operation is performed when the formation is large. There are several ways to remove fibroids; which one is most effective depends on the severity of the disease and the age of the patient.
What is endometrial polyposis
Polyps of the uterine body are formed from endometrial tissue. These are benign growths that can have a thin stalk or a wide base and reach several centimeters in diameter. There may be several polyps.
Polyposis develops against the background of hormonal disorders with increased levels of estrogen and progesterone deficiency. The cause of the pathology may also be previous inflammatory, infectious diseases, or medical abortions.
Small growths do not have any special manifestations. With significant growth of the nodes, prolonged bleeding (more than 7 days), cramping pain appears, and spotting dark discharge persists after the end of menstruation. Uterine bleeding may occur between regulae. Polyps obstruct the outflow of blood, it coagulates and can form clots. In young women, the disease causes infertility due to the inability of the fertilized egg to attach to the wall of the uterus.
Treatment is carried out by scraping the walls of the uterus and cervical canal. Hormonal therapy is prescribed at the discretion of the doctor.
What are the causes of abnormal clots
Physical pathologies and hormonal factors can cause heavy periods with clots and disrupt the menstrual cycle. Abundant discharge in itself is a prerequisite for their appearance. And the presence of gynecological diseases increases the chances of developing abnormal blood clots.
If there is a bend in the uterus, women suffer from very heavy periods with clots. The obstruction puts additional pressure on the wall of the uterus, reducing the ability of the uterus to contract. When the uterus does not contract properly, blood accumulates and coagulates inside the uterine cavity, forming pieces that are subsequently removed through the cervix along with the blood.
Fibroids are noncancerous, muscle tumors that grow in the wall of the uterus. In addition to heavy bleeding during periods with clots, they can also cause:
- irregular bleeding;
- lower back pain;
- pain during sex;
- protruding belly;
- problems with conception.
After age 50, many women will develop fibroids; the cause is unknown, but genetics and the female hormones estrogen and progesterone likely play a role in their occurrence.
Endometriosis
Endometriosis is a condition in which the lining of the uterus grows outside of the uterus. A clear sign of endometriosis is heavy periods with very large blood clots. During the menstrual cycle, endometriosis also causes:
- painful cramps;
- nausea, vomiting, diarrhea during menstruation;
- discomfort during sex;
- infertility;
- pain in the pelvic area;
- bleeding.
The exact cause of endometriosis is unknown, but heredity, hormones and previous pelvic surgery play a role.
Adenomyosis
Adenomyosis occurs when the lining of the uterus grows into the wall of the uterus for unknown reasons. This causes it to enlarge and thicken. In addition to very heavy periods with clots, this condition can cause the uterus to become two to three times its normal size.
Hormones
Proper growth and thickening of the uterine lining depends on the balance of estrogen and progesterone. If there is too much or too little of one or the other, you may experience heavy menstrual bleeding. What can cause hormonal imbalance:
- menopause;
- stress;
- weight gain or loss.
The main symptom of hormonal imbalance is irregular menstruation. For example, your period may be later or longer than usual, or you may miss it entirely.
Miscarriage
About half of all pregnancies end in miscarriage. Many pregnancy losses occur before a woman even knows she is pregnant. When an early pregnancy is lost, it can result in heavy bleeding, cramping, and clotting of blood clots.
von Willebrand disease
Heavy menstrual flow can also be caused by von Willebrand disease. Between 5 and 24 percent of women with chronic heavy menstrual bleeding have this condition. Von Willebrand disease may be the cause of your heavy periods and period clots. You also bleed easily after a minor cut or your gums bleed after every brushing. Contact your doctor if you suspect this is causing heavy bleeding.
Treatment with boron uterus
Widely used in folk medicine for the treatment of gynecological diseases and female infertility. The plant contains phytohormones that normalize the balance of estrogen and progesterone and have antitumor properties.
The duration of menstruation may increase, blood clots may be released, and breast pain may occur. This is due to intensive renewal of the endometrium, hormonal changes in the body and is considered normal, with the exception of uterine bleeding.
For the treatment of ovarian cysts, endometriosis, erosion, and menstrual irregularities, the uterus and uterus are used. Treatment must be carried out under the supervision of a doctor and after testing for hormone levels. You need to take the herb in courses according to a specific schedule.
To understand why, you should visit a gynecologist and conduct an examination, take tests for the level of sex hormones. Self-medication and delays in visiting a doctor can lead to complications and the development of infertility.
httpss://youtu.be/0OR0n6XsI_0
We recommend similar articles
The nature of menstruation usually changes when you start using hormonal contraceptives or in the first year of regular menstruation. In such cases, it is necessary to visit a gynecologist.
The characteristics of each patient’s cycle are individual. Any unusual phenomena may be symptoms of uterine bleeding and cause life-threatening complications. Menstruation without clots occurs with ovarian pathologies, blood diseases, and abnormal pregnancy.
Climax
Why do my periods come in clots in adulthood? As a rule, women over 50 years of age begin menopause. It is characterized by a decrease in ovarian function, menstrual irregularities, followed by a complete cessation of menstrual periods.
Unfortunately, heavy discharge at this age is extremely dangerous and requires immediate medical attention. Under no circumstances should you self-medicate. Only a qualified specialist can give the right recommendations and draw up a competent treatment plan.
Features of menstruation
What is this phenomenon? Every month, the uterus prepares to receive a fertilized egg. Under the influence of hormones, the endometrium thickens, that is, the layer that serves as a place for the implantation of the embryo and is responsible for its nutrition. In the absence of pregnancy, the level of hormones becomes lower, the mucous membrane of the inner surface of the uterus ceases to be supplied with blood, and the endometrial layer is torn off and comes out. So the discharge during menstruation is a complex mixture of mucus, blood and endometrium.
A cycle is the time from the beginning of the previous menstruation to the appearance of the next. Normally, this period is 20-35 days. It can change under the influence of external factors. Itself from 3 to 7 days. With age, its duration often decreases. You can track your cycle using a special calendar.
They usually appear between the ages of 9 and 16 and indicate that pregnancy may occur.
During menstruation, dark blood is released in portions in a volume of 20-50 ml. Clots and mucus may come out with it. The number of these inclusions in one woman is always constant.
Specific, individual. Its color can also be of different shades: one woman’s is dark brown, another’s is brown. It is saved monthly.
Clots are a natural phenomenon if they form regularly and the amount of discharge and cycle duration do not deviate from the norm. If your period is normal, there is no need to worry about lumps. Since the endometrium is a loose and thick tissue, the discharge is not completely liquid. They include the glandular component and particles of the inner lining of the uterus. The consistency of menstrual fluid changes daily.
But the complete absence of clots may be evidence of pathologies, each of which has its own symptoms and danger.
Typically, they occur immediately after sleep or a long period of sitting. This happens because the fluid is retained in the body and coagulates, and when it begins to move, it is expelled. The process is accelerated by special anticoagulant enzymes. In case of heavy bleeding, they do not have time to thin the blood, and it turns into clots, which is not a pathology.
There are several factors that should alert the patient:
- too abundant or;
- constant leakage of blood;
- the substance is too liquid;
- there are no clots in the discharge;
- there is no specific smell
In the absence of clots, an increase or decrease in its duration is observed. If the pathology is not eliminated by medical methods, the bleeding may not stop for several months, which is unacceptable.
Menstruation with clots reasons
Hormonal disbalance
During adolescence. When a girl’s body is just beginning its menstrual activity and rhythmic ovulation has not yet been established. This is the time to establish the process; this period lasts about 2 years.
Then there may be disruptions in the duration of the cycle, high sensitivity of the body to stressful situations, and any very minor negative factors. Thus, the reproductive system can react with juvenile bleeding, prolonged periods of menstruation (up to 2 weeks) and blood comes out in the form of clots, like the liver.
Disturbances after childbirth or curettage of the uterine cavity. For a month after the birth of a child or in the case of surgery, a woman in labor may discharge huge bloody lumps. It is normal if there is no increase in temperature along with the discharge; otherwise, you need to check whether there are any fragments of the placenta left in the uterus.
During menopause, when female reproductive and menstrual function declines (from the age of 45 years).
Hormonal imbalance is visible, if there is a disruption in the functioning of the endocrine glands and a cycle failure , then there is a huge output with lumps of brown blood.
Climax
Often the disorder occurs in women after 45 years of age, during perimenopause. The frequency of ovulation decreases, the amount of blood and endometrium rejected is disrupted, and the discharge comes with a large number of clots.
Endometriosis and adenomyosis
Endometriosis. It is characterized by the growth of the mucous membrane of the uterus outside its boundaries, which is accompanied by painful and prolonged periods, cycle failure and an increased volume of blood that comes out.
Abnormal development of the uterine mucosa (adenomyosis) through damage to its walls is accompanied by constant severe pain and large volumes of discharge with clots.
Adenomyosis no longer affects only the space of the main female organ, but has a chance to spread to the ovaries, intestines and other organs. The appearance of endometriosis is still unclear, although it is generally accepted that endometrial “dropouts” form on inflamed tissues. The reproductive space inside becomes like a honeycomb in painful lesions.
The blood does not clot well, the contractile function of the organ is impaired, and clinical intervention is required for surgical treatment.
Polyposis as a disorder of the endometrium
For women after thirty years of age and even for those who are premenopausal (about 50 years old), discharge in the form of clots is a common occurrence. Endometrial polyposis (polyps) is a disorder of the internal tissues of the uterine cavity. These tissues grow, covering the uterine cavity in the form of polyps, which during menstruation can cause blood clots and pain in the lower abdomen, disruption of the monthly cycle through an abnormal “growth” of the uterine mucosa on the walls and the same unsystematic “removal” of it.
Physiology of menstruation
To understand why large blood clots come out during menstruation, you should know the physiology of this process.
Although the menstrual cycle is regulated by the hypothalamus, the main changes occur in the ovaries and uterus. It goes through several stages:
- Follicle maturation. Under the influence of certain hormones over the course of two weeks, a follicle develops in the ovaries, inside which the egg is located.
- Ovulation. After maturation, the follicle ruptures and the egg is released, and the corpus luteum appears in the vacant space. At this time, intensive release of hormones such as estrogen and progesterone begins. In case of fertilization, they will ensure the attachment of the egg to the wall of the uterus. Under their influence, the epithelium of the uterine mucosa begins to grow, becomes loose and thickens 4-5 times.
- In the absence of fertilization, the corpus luteum dies, and the overgrown layer of the endometrium is rejected. At the same time, the vessels that ensure its vital functions rupture and bleed. This period is called menstruation.
Consequently, during menstruation, accumulated blood, mucus and uterine epithelium are released, which explains the presence of clots in the discharge.
What are the dangers of heavy discharge with clots?
A one-time appearance of clots should not cause concern. Such blood formations are the result of peeling of the epidermis from the walls of the uterus - a normal physiological process.
Menstruation with blood clots may occur when a pathological septum appears. The bend of the cervix can become a kind of “barrier” in which blood discharge cannot come out naturally. Therefore, the blood inside coagulates and turns into clots: in this case, the main thing is that the clots do not accumulate inside. Pathology can be detected during a gynecological examination.
A woman must carefully monitor how much blood is released during her period. You need to start from the figure of 80 g per day. First, you need to weigh a clean pad, and then find out the weight of the sanitary product after use and calculate the difference. This will be real blood loss.
Heavy periods with clots can be caused by a lack of iron. Then the disease takes on the character of iron deficiency anemia. As soon as iron deficiency is eliminated, discharge of this type will no longer bother you.
When determining why clots come out during menstruation, do not forget that with vigorous activity, blood is released from the vagina faster and more abundantly. But in a calm state (lying or sitting), the discharge comes out more slowly. Due to this, blood clots form, which frighten women when they rise sharply from a horizontal position. In this case, such a process is the norm.
There is no need to worry about clots if their release is not accompanied by pain.
Bleeding after menstruation
When a woman smears after her period, it causes great concern and the question of what it could be and whether it is dangerous. Let's look at this question in more detail.
If red smears appear the day after your period, this may be a sign of an ectopic pregnancy. The doctor will confirm or refute this fear only after passing the tests. If the result is negative, the cause may be an infection - herpes, chlamydia, ureaplasma. Such infections occur with an unpleasant odor.
If bleeding appears after a week of menstruation, this may indicate an incipient miscarriage. Scanty discharge requires urgent hospitalization and examination. Depending on what day of the cycle the discharge appeared, you can determine the nature of the disease and begin timely treatment.
If discharge appears 2 weeks after your period, this may be a sign of ovulation. Such smears differ in color from bleeding; during ovulation they are pink and scanty.
If, a few days (2-3 days) after menstruation, spotting secretion from the genitals occurs, without the appearance of additional signs and discomfort, then this may indicate a hormonal imbalance.
Scanty periods: what needs to be examined?
Any deviation from the norm in the body is subject to mandatory examination and treatment. In the case of such a phenomenon as very little blood during menstruation, a woman should seek help from a gynecologist. The doctor will conduct an examination, taking into account all symptoms and complaints. If necessary, he will refer you for additional examination and laboratory tests. What exactly is done to make an accurate diagnosis:
- A thorough examination of the patient on the gynecological chair.
- Examination of the genital organs for the degree of purity and flora by taking a smear from the vagina.
- Diagnosis of the cervix and vaginal walls by colposcopy. A special colposcope device will allow you to see polyps, cysts or endometrial growths.
- Blood test for the concentration of sex hormones. To do this, you will need to collect venous blood on certain days of the menstrual cycle.
- Ultrasound examination of the condition of the pelvic organs - ovaries and uterus.
- It is necessary to exclude or confirm the presence of genitourinary infections by donating PCR smears and blood.
Endometrial polyposis
With this disease, the formation of multiple polyps occurs as a result of the growth of the inner layer of the endometrium, as shown in the photo. Despite the fact that these are benign formations, the monthly cycle is disrupted, large blood clots are released, and severe pain is observed in the lower abdomen. Sometimes polyps, growing to large sizes, are rejected by the body and excreted. After these formations, similar to a piece of connective tissue, have come out, the cycle is restored and all symptoms disappear.
Liquid periods without clots
If a woman’s period does not have clots of scarlet blood and is too runny in consistency, then there may be several reasons. Perhaps this is a normal condition of the female body, perhaps it is a consequence of taking hormonal contraceptives or heart medications with a blood-thinning effect, but pathology should not be ruled out.
- Change of the inner layer of epithelium
- Sexual arousal
- Preparatory stage before ovulation
- Increased blood circulation before menstruation
- Water after swimming
May indicate pathology:
- Fungus
- Chlamydia
- Vaginosis of bacterial etiology
- Vulvitis
The appearance of watery mucus with blood is not a normal condition. Thus, the body signals about possible disturbances in reproductive function. The release of water with the blood is a sign of dysfunction of all systems and metabolic disorders. If the liquid is clear and stretchy, you need to do a pregnancy test, or it is simply a matter of using hormonal contraceptives.
Natural Causes of Menstrual Clots
Normally, menstrual smears are dark red in color and have a mucus-like structure. Often, lumps of blood or epithelium can be observed in the discharge.
If there are few lumps, your periods are not particularly painful, last no longer than 6 days, and if no more than 100 ml of blood is released, then there is no need to panic.
Let's look at why lumps form in a normal situation:
- Prolonged sitting or lying down. Without movement, the blood begins to accumulate and thicken, and when you change position, it immediately flows out in the form of thick lumps.
- Adhesions or scars of the uterus provoke the appearance of lumps. This occurs due to a violation of the outflow of blood and mucus in the organ cavity.
- Congenital abnormalities in the shape or location of the uterus lead to thick discharge.
- High viscosity due to kidney pathologies, liver diseases, and low fluid intake.
Other causes of clots
- In addition, blood with clots may appear while taking coagulants and hormonal drugs. These drugs increase blood clotting, which leads to the formation of blood clots.
- The contraceptive device can also affect the occurrence of menstrual lumps.
- Accumulations of blood may appear in the first time after an abortion, as particles of the fertilized egg are released from the uterus. During abortion and childbirth, severe hormonal disruption occurs, which causes heavy menstruation.
- Changes in hormonal levels at different age stages in a woman directly affect menstruation. The formation of lumps indicates changes in the mucous membrane.
- The presence of bad habits, irregular nutrition - all this affects changes in menstrual flow. Alcoholic drinks affect blood viscosity, after which large blood clots are visible in the discharge.
Blood clots during menstruation as a sign of pathology
If menstruation occurs with large blood clots that resemble liver, and menstruation itself resembles bleeding and is accompanied by severe pain, this indicates a deviation.
Let's consider the main reasons for this negative phenomenon.
- Poor blood clotting. Blood quickly clots in the uterine cavity, because the necessary enzymes do not act.
- Intrauterine device. The body mistakes a mechanical contraceptive for a foreign body. Unusual conditions affect the nature of the discharge.
- Ectopic pregnancy. In addition to thick bloody discharge, the woman is bothered by pain in the lower abdomen and hyperthermia.
- Childbirth/abortion/curettage. The first menstruation after childbirth or surgery can be pathological. The size of the clots reaches a length of 12 cm. Copious thick discharge can leave the body against the background of elevated body temperature. In this case, you need to consult a doctor and examine the uterus. It is possible that particles of the placenta remained in the cavity. Now you know why large blood clots come out during menstruation.
- Uterine fibroids. The development of a benign tumor in the main reproductive organ disrupts the stable cycle and makes monthly discharge abundant and thick.
- Hormonal disorders. An incorrect balance of hormones makes menstruation irregular, intense, and thick. Sometimes the discharge is brown in color.
- Endometriosis. Hyperplasia, that is, abnormal growth of the uterine mucosa, often leads to the presence of large blood clots in the menstrual flow. The causes of endometriosis and blood clots during menstruation are endocrine disorders, including obesity and diabetes, and hypertension.
- Incorrect structure of the internal genital organs. The development of a girl's genital organs begins in the prenatal period. Improper formation of the structure distorts the body of the uterus, causing it to become unicornuated, bicornuate, curved or saddle-shaped (there may be other anomalies, for example, an intrauterine septum). Such deviations disrupt the contractility of the uterus during menstruation, so bleeding increases and clots come out.
- Oncological diseases. Malignant neoplasms in the organs of the reproductive system provoke bleeding with clots in different phases of the cycle.
- Iron-deficiency anemia. Insufficient iron in the blood leads to decreased hemoglobin levels. Hemoglobin is a protein responsible for supplying cells with oxygen. A deficiency of the substance disrupts the functioning of the body and leads to weakness, nausea, dizziness and painful periods. Clots 2–4 cm in size are visible in the discharge.
- Ovarian cysts. Enlarged ovaries with cyst-like formations cause pain and discomfort. Unpleasant sensations intensify during sexual intercourse. Functional cysts distort the hormonal status and prolong the 2nd phase of MC. Bleeding becomes irregular. When menstrual periods begin, the discharge is abundant with clots.
- Endometrial polyposis. The growth of the inner layer of the uterus occurs according to the formation of polyps. The disease causes pain in the lower abdomen and menstruation with clots.
- The use of drugs that accelerate the onset of menstruation. When menstruation is delayed, some women, without consulting a doctor, take Duphaston, Norkolut and other pills that speed up bleeding. The appearance of clots during menstruation in this case is due to the fact that the delay did not occur due to progesterone deficiency.
Heavy bleeding with clots on menstrual days can worry a woman with infectious diseases of the pelvic organs. Also, the consistency of discharge is affected by excess vitamin B and insufficient fluid intake.
https://youtu.be/ch-5E1Dz1Cc
What is the danger of menstruation that comes with clots?
The presence of small single blood clots is allowed in menstrual discharge. But if dark pieces come out, accompanied by additional symptoms, you need to consult a doctor for clarification.
It is strongly recommended to visit a gynecologist if:
- Worried about dizziness.
- Body temperature fluctuates between 37.5 – 40°C.
- Outside of menstruation, brown discharge appeared.
- Severe pain and other discomfort occurs in the abdomen.
- There is a pre-fainting state.
- Heavy menstruation lasts longer than 7 days.
- My period started on time, but it comes with large brown-black clots and my stomach hurts a lot.
- During all critical days, blood loss exceeded 150–200 ml (in one cycle).
So why are blood clots during menstruation dangerous? They may be a sign of an ectopic pregnancy, a dying polyp, or another life-threatening condition.
If a woman is planning a pregnancy, unusual menstruation should alert her. Pieces in menstruation indicate that the fertilized egg cannot fixate in the uterine cavity.
If the fertilized egg develops in the fallopian tube, the woman will feel a nagging pain in the right or left side. Sometimes the pain symptom does not appear until the fallopian tube is stretched and completely ruptured. Its contents enter the peritoneum and provoke septic shock. In the absence of urgent medical assistance, the woman dies.
If, during menstruation, not only clots come out, but also the above symptoms appear, you should definitely consult a doctor, regardless of your age and desire to have offspring. Problematic discharge may indicate a serious medical condition.
Diagnosis of pathological menstruation begins with a study of blood clotting and determination of hemoglobin levels. Leukocyte counts will help the doctor verify the presence/absence of an inflammatory process. The patient also undergoes blood tests for hormones and antibodies. The second analysis will help identify infectious agents. If there is a suspicion of cancer, the patient is tested for tumor markers.
A biopsy allows you to determine the nature of the tumor. Ultrasound of the pelvic organs reveals neoplasms, anomalies in the location and structure of the internal organs of the reproductive system and endometrial hyperplasia. In addition, the cervix and uterine cavity are examined using a hysteroscope. The optical device makes it easier to examine suspicious areas.