What is a cyst
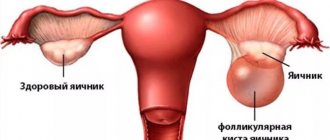
An ovarian cyst is a benign tumor formation, which is a hollow bladder filled with organic content. Women of any age are susceptible to the disease, but more often it manifests itself in reproductive age. The first symptoms are usually mild and may not be noticed. Pronounced symptoms appear when the tumor reaches a large size or during complications (rupture and torsion of the cyst). It is usually diagnosed during an ultrasound procedure. It is treated conservatively (with medications) in the initial stages of development. When neglected, it is removed surgically.
If, during a delay, a pregnancy test shows negative results, this is a reason to consult a doctor and undergo an examination.
The effect of cysts on menstruation
The ovaries are one of the most important female organs in which the formation and fertilization of the egg occurs. They are also directly involved in all processes of the cycle. When a foreign body appears on the ovaries in the form of a cyst, menstruation may change or stop for a while.
Disorders associated with delayed menstruation can be caused by functional cysts. These include:
Follicular. An unruptured follicle, from which an egg should have been released, can develop into a benign tumor.
Why do I have no periods with an ovarian cyst?
When a cyst forms, the release of hormones is provoked, which affect the timing of menstruation, delaying it by 5 days to a month.
Let's consider what changes in menstruation are possible with a follicular cyst:
- The discharge is heavier than usual
- The duration of menstruation increases to 7 days, and sometimes more
- In addition to the usual menstrual pain, additional pain appears on the side, depending on the location of the cyst
The cyst may hurt during menstruation
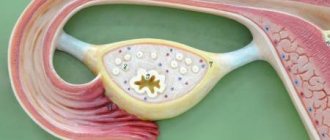
Luteal . The fertilization cycle begins with the release of the egg from the follicle, in its place the corpus luteum is formed - a hormone-rich substance responsible for maintaining the fertilized egg. If fertilization does not occur, the corpus luteum gradually disappears. For various reasons, a cyst may appear in place of the corpus luteum, and hormones will interfere with the onset of menstruation. Symptoms of a luteal cyst:
- There may be a delay of several days
- Nausea in the first days of the cycle
- Heaviness in the lower abdomen
- Pain different from normal these days
- Swelling of the mammary glands, painful sensations in them
The two types of cysts listed are functional and are harmless in the initial stages of development. With proper treatment, they can resolve on their own. There are other types of this tumor that interfere with menstruation.
Endometrioid. A capsule filled with dark brown contents, caused by the spread of endometriosis to the ovaries. The appearance of this type of neoplasm can be manifested by the following symptoms:
- Small spotting appears 2-4 days before the start of menstruation and also after the end
- Heavy discharge during menstruation
- The menstrual period increases by 2-3 days
- Appearance of weakness in the body
- Possible increase in temperature
- Nausea
- The pain is stronger than usual, pulling in the ovarian area. They may get worse during sex and continue for some time after the discharge ends.
A cyst can cause a delay in menstruation; moreover, a delay is the main sign of an ovarian cyst
Types of neoplasms affecting menstruation
A follicular cyst is a neoplasm that arises from a follicle that has not burst in a timely manner. A common cause of delayed menstruation in women of any age. The egg does not come out, is in the membrane, accumulates fluid. As a result of hormonal imbalance, menstruation is delayed. Menstruation may begin after 5-25 days. Symptoms of a cyst are as follows:
- There is heavy bleeding with pain in the ovarian area.
- The duration is broken. Menstruation lasts up to 7 weeks or more.
After some time, the cyst disappears on its own. In most cases, the woman is not at all aware of its existence. If the ovarian cyst continues to grow, hormonal therapy is required. With this diagnosis, pregnancy cannot occur.
Luteal cyst is a formation against the background of a degrading corpus luteum. It begins after the egg leaves the follicle. The neoplasm produces an increase in the hormone gestagen, which prevents menstruation from appearing. In addition to a delay in menstruation, signs of a luteal cyst are:
- soreness of the mammary glands;
- nausea;
- lower abdominal pain;
- all signs of a false pregnancy.
A small cyst of this type disappears on its own after several menstruation. All this time, a woman may be disturbed by:
- bleeding between periods;
- constipation;
- frequent painful urination;
- discomfort in the intestines;
- bloating.
When a cyst ruptures, severe pain in the ovarian area, bleeding, and general malaise are observed. To find out the reason for the delay in menstruation, you should initially conduct a pregnancy test. The test result is negative - you should go to the gynecologist for an appointment.
What happens to a cyst during menstruation?
- Before the discharge begins, the cyst may manifest itself as nagging pain in the lower abdomen, on the right or left, depending on which ovary it is located in
- Physical exercise and active sex life can increase pain and also provoke complications of the cyst.
- During menstruation, the cyst also causes more severe pain. Depending on its size, it can put pressure on the ovary, as well as on the bladder and intestines.
- In addition, patients are often diagnosed with pain radiating to the leg.
A functional cyst in 70-80% of cases can resolve on its own, which cannot be said about other types of neoplasms. In any case, if you notice a delay in menstruation, unusual pain and other listed symptoms, the best solution would be to consult a doctor and undergo an ultrasound examination.
Can an ovarian cyst burst during menstruation?
Rupture of the membrane can occur at any time, not just during menstruation. Provoking factors are:
- Intense physical activity;
- Sexual contact;
- Constipation and overeating (intra-abdominal pressure increases);
- Increased intestinal peristalsis;
- Sexual infections and inflammation of the reproductive organs.
A woman with an ovarian cyst should avoid sudden movements, heavy lifting, jumping, aerobics and horseback riding. Any awkward movement can lead to tearing of the tumor membrane.
How can you tell if a cyst has burst?
When a tear occurs, sudden pain appears in the abdomen on the right or left. The acute sensation lasts 1-2 minutes, then the woman feels a little better.
The situation when the cyst has completely ruptured is more complicated. First there is severe pain, which after a few minutes turns into a nagging pain. However, the symptoms do not disappear completely and gradually increase.
If the cyst bursts during menstruation, the picture may be blurred due to the pain that accompanies menstruation.
When a large vessel ruptures, signs of blood loss appear:
- Reduced pressure;
- Weakness, dizziness;
- Darkening in the eyes;
- Pale skin;
- Loss of consciousness.
Cycle control when delayed
There are several ways to regulate the cycle with a cyst. The most commonly used drugs are those that regulate hormone levels . Among them are:
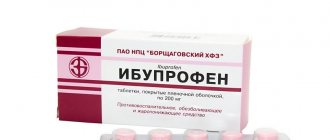
- Duphaston. The drug provides the body with progesterone and promotes the normal development of the egg
- Utrozhestan. The action of the medicine is similar to the previous one. Doctors choose the prescription of a particular drug based on the overall picture of the disease.
- Dysmenorm. Homeopathic remedy based on bee venom. Normalizes the cycle and reduces pain symptoms
- Vitamins C and E. In addition to specialized medications, vitamins affect the production of hormones. Eating foods rich in these vitamins will speed up the onset of menstruation without harm to health.
Do I need to get rid of the cyst or will it disappear on its own?
Medical practice shows that not all types of cysts are amenable to conservative treatment. Without removal, only functional types of formations can be cured:
As long as the tumor of the listed types has not reached a size of 5-7 cm in diameter or more, there is a chance of defeating the disease without surgical intervention. The most important thing in this disease is that only a doctor can confidently say: the tumor needs to be removed or can be treated with medication.
Important! Before prescribing treatment methods for a disease, the patient must undergo a specialized examination to determine the type of disease
There is no clear answer to the question “Can a cyst resolve on its own?” Functional species in the early stages can disappear from the body on their own within 2-3 menstrual cycles. Usually, a woman does not even notice signs of their presence.
Features of menstruation after surgery
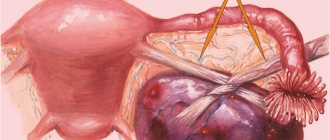
Laparoscopy is an operation to remove benign and malignant neoplasms, cut adhesions, fallopian tubes, restore their patency, and so on. A significant advantage of this type of operation is its low level of trauma to the body. The entire operation is performed through several small holes, which heal quickly and do not leave large, scary stitches.
Menstruation after removal of an ovarian cyst can begin even on the next day (but more often on 5-6) and last up to 2-3 weeks. After laparoscopy, light, clear discharge, possibly with small splashes of blood, is considered normal. This is due to the healing process and should not be a cause for concern.
If intense discharge or blood clots appear, you should inform your doctor (this may be normal in the first days after surgery). This may be evidence of bleeding that began after surgery. A possible infection will be indicated by menstruation that is yellow-green (or brown-green) in color and has an unusual odor. The appearance of Candidiasis fungi is indicated by white discharge, accompanied by burning and itching.
Also after laparoscopy it is possible:
- Changing the duration of the cycle, it can become shorter or longer by several days. After 2-3 cycles it should return to normal.
- The cycle itself is shifting. The gynecologist usually tells the patient that now the beginning of the cycle must be counted from the day of the operation.
- In some cases, there may be a delay for a long time.
Video: Recovery after laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst
An ovarian cyst can appear for various reasons. Most often, its formation is provoked by an unexploded egg before ovulation. Such neoplasms often cause discomfort to patients, interfere with pregnancy and can affect menstruation. Pain and other symptoms increase as a new cycle begins. In some cases, a cyst before menstruation may resolve and come out along with other discharge. However, large lumps require medical treatment or surgical removal.
Menstruation with an ovarian cyst: delay, pain, how it comes out, how many days, removal
In a healthy woman of reproductive age, the menstrual cycle varies between 21-35 days. Menstruation should be regular.
If they are absent in due time, this indicates pregnancy or disruption of the functioning of internal organs and hormonal imbalance. It is not uncommon to experience a delay in menstruation due to an ovarian cyst.
It is important to understand what this symptom means and what actions to take if you are diagnosed with a tumor on the right or left ovary.
The cyst affects menstruation if it is functional (follicular or luteal). With ovarian formations, the menstrual cycle is almost never delayed.
As soon as you notice a delay, you need to take a pregnancy test. Having received a negative result, you should immediately visit a gynecologist and undergo an examination.
Only a doctor can prescribe competent treatment and determine whether it is possible to do without surgery.
A follicular cyst and a delay in menstruation are interconnected, because this type of neoplasm occurs due to a follicle that does not burst in time. They are absolutely harmless, and with proper treatment they go away quickly.
Such lumps occur in women of any age, and even in girls in adolescence. During follicular formation, the body begins to produce hormones, and a cavity with liquid contents is formed. The capsule can grow and reach 8-10 cm in diameter.
With a follicular cyst, the delay can be from 5 to 20 days. Heavy menstruation or bleeding may then begin. If the lump progresses and grows, your period will be delayed even longer. In addition, the woman will notice:
- weakness;
- increased body temperature;
- discomfort in the lower abdomen;
- pain during intercourse.
A follicular cyst, if not treated in time, can lead to complications - torsion of the pedicle, tissue necrosis, rupture and uterine bleeding. With peritonitis, a woman feels acute pain, nausea, the skin turns pale, cold sweat appears, and she may lose consciousness.
Very often women wonder if a cyst can come out on its own? Yes maybe. Functional formations usually disappear within 1-2 months. How an ovarian cyst comes out during menstruation, and how to make you feel better at this moment, should be told to you by your attending physician who knows the entire clinical picture of the disease.
Delay with a corpus luteum cyst is also normal. The formation occurs when the follicle bursts and the corpus luteum forms. It is designed to produce gestagens and, when pregnancy occurs, to provide the embryo with everything necessary.
A luteal cyst does not always manifest itself as a delay. Sometimes there are scanty periods, but the woman also feels nausea, her mammary glands are enlarged and painful, and there may be aching pain or signs of pregnancy.
However, the test will show a negative result.
If there are several capsules with liquid, the doctor diagnoses polycystic disease. Coping with this problem is not easy, because you need to act on 2-4 or more tumors at once. Menstruation with polycystic ovary syndrome can occur as usual. But more often there is a combination of delays and bleeding, affecting the woman’s well-being and causing anemia.
Refusal of treatment and ignoring the problem can lead to the fact that the affected organ will put pressure on other pelvic organs, and the formation will develop into cancer.
Missing periods with an ovarian cyst is a reason for strict systematic medical monitoring. The doctor will perform an ultrasound and examination of the cervix before your period according to the expected schedule. If the doctor determines that the delay in menstruation is caused by a functional cyst, he will prescribe combined contraceptives, under the influence of which the seal should resolve.
They should be taken according to a special regimen. The question of how to induce menstruation with a cyst should only be answered by an experienced specialist. Do not self-medicate, as this can aggravate the situation and cause complications. The doctor may prescribe taking Duphaston, Utrozhestan, Dysmenorma, vitamins E and C in large quantities.
If within 2-3 months the cycle has not been restored or minor bleeding appears, the gynecologist may recommend surgical removal of the formation.
The operation is performed laparoscopically or laparotomically. The first option is preferable, because it is safe, practically painless, does not leave large scars and allows the body to quickly recover.
The first period after surgery will appear in 2-3 weeks.
The intensity of discharge should be average. Too heavy periods can be a sign of uterine bleeding.
Abdominal pain and clots are normal during the first period after surgery.
The discharge should not change smell or color. The presence of mucus and changes in temperature indicate that an infection has entered the body. Seek medical help immediately! The sooner you pay attention to the symptoms and consult a doctor, the greater the chances of coping with the disease in a conservative way.
The cyst may dissolve and come out along with the discharge.
An ovarian cyst can appear for various reasons. Most often, its formation is provoked by an unexploded egg before ovulation.
Such neoplasms often cause discomfort to patients, interfere with pregnancy and can affect menstruation. Pain and other symptoms increase as a new cycle begins. In some cases, a cyst before menstruation may resolve and come out along with other discharge.
However, large lumps require medical treatment or surgical removal.
During the reproductive period of life, the menstrual cycle lasts 21-36 days, it must be regular - this is an essential sign of a healthy woman.
If menstruation does not come at the right time, this indicates pregnancy or problems in the functioning of internal organs. Often there is a delay in menstruation due to ovarian cysts, which have a different nature.
Depending on the type of cyst, the doctor prescribes a specific treatment.
What to do if there is a delay in menstruation? First you need to check if you are pregnant using a special test sold in a pharmacy. If the test is positive, this indicates pregnancy.
If the test is negative, you need to see a gynecologist to find out the exact reason for the delay.
The most common cause of cycle failure is a follicular cyst, followed by another benign neoplasm, the luteal cyst.
Follicular cyst
This type of neoplasm occurs due to a follicle that did not burst in a timely manner. Follicular formations are harmless and can be quickly cured with proper therapy. Such tumors occur at any age, even in adolescents and virgins.
The formation of a follicle is accompanied by the production of hormones, resulting in a cavity filled with fluid. The tumor grows, sometimes reaching a diameter of 10 centimeters.
If we talk about how many days the delay lasts, then this is a very individual indicator. On average, 5-20 days, after which menstruation begins, sometimes in the form of heavy bleeding. If this does not lead to the resorption of the cyst, menstruation is delayed even more. In addition to the delay, patients note the following symptoms:
- increased body temperature;
- fatigue;
- discomfort in the lower abdomen;
- pain during sexual intercourse.
A cyst, if left untreated, can cause complications. The most common complication is torsion of the cyst stalk. Cyst rupture and bleeding occur somewhat less frequently.
The most dangerous option, threatening the patient’s life, is tissue necrosis. If the operation is not performed in a timely manner, the patient experiences acute pain and cold sweating, the skin turns pale, and the woman loses consciousness.
Without medical care, a patient with necrosis will die.
Such a dangerous scenario for the development of the disease is very rare; it usually happens differently.
A functional neoplasm resolves on its own within 1-4 monthly cycles, without medical intervention. The cyst comes out along with uterine bleeding.
If the tumor is small, the gynecologist usually relies on this option, recommending that the patient return for a re-examination in 1-3 months.
This cystic formation of the corpus luteum is also a normal physiological phenomenon. The task of the corpus luteum in the female body is to produce gestagens so that when pregnancy occurs, the embryo is fully provided with the nutrition it needs.
A luteal cyst does not necessarily lead to a delay in the cycle; menstruation often occurs, but it is quite scanty. The patient's mammary glands swell, nausea occurs, and other signs of pregnancy occur.
But if a woman takes a pregnancy test at this moment, it will be negative.
If several capsules are present, the gynecologist diagnoses polycystic disease. Treating this disease is more difficult than treating one cyst. Sometimes menstruation with polycystic disease occurs on a regular schedule.
Much more often, this diagnosis combines delays and unexpected bleeding, which, if left untreated, gradually cause iron deficiency anemia with all the ensuing symptoms.
What is a cyst
The effect of cysts on menstruation
Ovarian cysts and missed periods are directly related. Changes in the nature of menstruation can occur in two directions. The start of a new cycle is delayed, and after a delay (which sometimes reaches 1 month), the discharge lasts longer. Another option is possible - scanty menstruation. This occurs when the level of female hormones is reduced.
Could there be a delay in menstruation due to a cyst?
Delayed menstruation and ovarian cyst are related, since most often the tumors are of follicular origin. A benign tumor appears if the egg does not leave the follicle on time. In this case, ovulation does not occur, so the period for the start of a new cycle is shifted. The delay period ranges from 5 days to a month.
If the follicular formation does not resolve on its own, but increases in size, the following symptoms are noted during menstruation:
- copious discharge with a cyst of this type;
- duration of menstruation (longer than usual);
- painful sensations increase;
- increased gas formation and feeling of bloating.
In some cases, the discharge, on the contrary, is scanty. This occurs with concomitant hormonal imbalance and a decrease in the level of female hormones. Listen to your feelings, because in some cases the same signs can warn of an ectopic pregnancy. With it, the fertilized egg does not descend into the uterus, but remains in the tube.
Another type of cyst during menstruation is endometrioid. It is formed if mucosal cells enter the fallopian tubes and ovaries. In this case, the woman faces some symptoms:
- dark spotting appears before and after menstruation;
- periods become painful, heavy and prolonged;
- your health worsens, your temperature rises;
- nausea or vomiting appears;
- pain and scanty discharge during sexual intercourse.
A corpus luteum cyst also causes a delay in menstruation. It appears after ovulation and can resolve on its own.
How to induce menstruation with an ovarian cyst?
When the menstrual cycle does not begin due to a benign tumor, the attending physician can select a drug to normalize hormonal levels. There are traditional methods of treatment, but their use must be agreed with a specialist. To induce menstruation, use one of the following:
How does a cyst affect menstruation?
Whatever type of cystic formation is diagnosed in a woman, the menstrual cycle always changes: there is a delay, periods become more abundant or disappear for several cycles.
The tumor interferes with regular healthy ovulation. It may not occur at all due to the fact that the egg remains in an unruptured follicle. In this case, there may be no periods for two or three cycles in a row.
If there is a hormonal imbalance caused by compression of the ovary by a cyst, menstruation occurs with severe pain. In some cases, amenorrhea may occur - the complete absence of menstruation at a young age.
How does an ovarian cyst come out during menstruation?
Follicular-type formations can spontaneously burst and come out during menstruation. Spontaneous resorption is typical in cases where hormonal drugs were used. To determine whether the thickening has dissolved, monitor the nature of the discharge. If you notice large clots, this will be a sign of resorption of the capsule with liquid contents.
Residues may come out during the next menstruation or on another day of the cycle. If this happens during menstruation, the pain will be stronger than always. After this, there is a short-term decrease in discharge and a change in color to a lighter color.
Can a cyst come out during menstruation?
Functional cysts can resolve and leave the body along with menstrual flow. The formation comes out under the influence of hormonal drugs prescribed by a gynecologist, herbal medicine or homeopathic medicines.
In the cycle when the cyst is resolving, the periods are slightly lighter than usual, abundant, with bright clots. The pain is more intense, lasts the entire time the discharge continues, and radiates to the sacrum. The duration of menstruation is longer than usual and can reach up to 7 days.
It is impossible to notice from the discharge whether a cyst has come out - for an accurate diagnosis, after the complete cessation of menstruation, it is worth visiting a gynecologist and having an ultrasound done.
Epithelial cysts do not disappear on their own. Under the influence of hormones, they can only slightly decrease in size or stop growing.
Do I need to get rid of the cyst or will it resolve on its own?
In most cases, the tumor must be disposed of. The more it increases in size, the more unpleasant symptoms the woman experiences. A tumor of 6–7 cm puts a lot of pressure on the internal organs, causing pain, which intensifies with any movement and even when walking.
Follicular thickening often resolves spontaneously and therefore requires observation. This also applies to the compaction of the corpus luteum. Other varieties require mandatory drug treatment or removal.
The main method of surgical intervention is laparoscopy of ovarian cysts. It involves making a small incision through which the capsule and its contents are removed. The recovery period is short, the patient quickly returns to normal life.
Doctors prescribe hormonal treatment if the lump does not exceed 5–6 cm. The decision to perform an operation is made based on the individual characteristics of a particular patient.
Neoplasms on the internal genital organs cannot be ignored. Delayed menstruation and ovarian cyst are closely related. To restore the cycle, it is necessary to get rid of a benign tumor. Some of its varieties resolve on their own; others are treated with hormonal therapy or surgery to remove the contents.
Author: Nasrullaev Murad
Candidate of Medical Sciences, mammologist-oncologist, surgeon
Delayed menstruation due to ovarian cysts is one of the leading signs of the disease. Due to the absence of menstruation, the doctor may suspect the development of pathology in the female genital area, including benign tumors. This clinical symptom occurs frequently, but has some distinctive features in various forms of the disease.
Characteristic signs of delayed menstruation with some types of ovarian cysts
- With a follicular ovarian cyst, when a tumor arises and grows directly in the body of an immature egg, ovulation does not occur and therefore women do not have periods for a long time. In these cases, the delay can range from a week to a month and occur with moderate pain in the lower abdomen. Once regulation occurs, bleeding without treatment lasts up to 7-8 weeks.
- Delays in menstruation with a functional ovarian cyst occur quite often. However, menstrual irregularities go away along with the tumor, since the tumor is capable of self-healing. As the cyst emerges, it is noticeable by the discharge; they have dense clots consisting of its membranes. Sometimes the disease is latent and women do not even suspect that they had a cyst.
- Neoplasms of the endometrium (uterine mucosa), with their spread to ovarian tissue. These tumors are often the cause of irregular menstruation. With them, a delay in menstruation is caused by a hormonal imbalance, disruption of the normal functioning of the entire reproductive system, it can last a week, a month or more and is accompanied by scanty bloody vaginal discharge, aching pain in the groin and lower back. Upon the onset of menstruation, bleeding can be very heavy and prolonged.
- An ovarian luteal cyst is formed in the corpus luteum; it disrupts the maturation of the egg, which causes irregularity of the menstrual cycle and short-term or long-term delay of critical days. This tumor occurs with false signs of pregnancy (nausea, dizziness, changes in appetite, weight gain, swelling of the mammary glands).
It is impossible to diagnose these pathologies on your own, therefore the slightest suspicion of an ovarian cyst during a delay in menstruation should motivate women to visit a gynecologist and undergo a course of examination.
How to restore the cycle with an ovarian cyst?
Such a problem with a tumor on the appendage as a delay in menstruation overtakes many women. And, naturally, they are looking for different ways to restore the menstrual cycle and get rid of the pathology without surgical intervention. But it is immediately worth noting that drug therapy does not help solve this problem in all cases. Often surgery is the only solution in this situation.
Important! To get rid of problems with discharge and cycle disorders once and for all, use unique medicinal phytotampons. After using phytotampons for 3 weeks, more than 90% of women noted a significant improvement in their health. Almost 60% of them completely got rid of their problems; the rest (usually in the presence of serious stages of the disease) showed significant progress in treatment.
Read more about phytotampons...
Conservative treatment helps only in the initial stages of formation. And it necessarily includes hormonal therapy. Only after this can menstruation begin without any delay. But such treatment must necessarily be accompanied by taking multivitamin complexes and following a diet, which will also help restore hormonal levels.
It is worth understanding that a menstrual cycle that has passed on time does not guarantee a complete cure. To get rid of the pathology, therapy must be carried out over a long period of time. Moreover, all medications must be prescribed by a doctor. If you self-medicate, the situation will only worsen - not only may your period not come on time, but the growth of the cyst will also increase significantly, which will require another treatment - surgical.
Hormonal therapy is selected on an individual basis. To choose the right drug, the doctor prescribes a hormone test, takes into account the patient’s general condition, as well as the presence of contraindications.
How to induce menstruation with an ovarian cyst and regulatory delay
A clinical sign of the development of benign tumors is often a disruption of the menstrual cycle, which is manifested by a delay in menstruation. Its restoration is achieved using a number of pharmacological agents:
- hormone replacement drugs (Duphaston or its analogues), which provide the female body with the necessary amount of estrogens and progesterone (substances responsible for the normal functioning of the ovaries), as a result, these organs “rest”, the ovarian cyst begins to resolve, and menstruation no longer occurs;
- mono- or two-phase oral contraceptives (Marvelon, Logest, Diane-35, Anteovin, Zhanin, etc.), stabilizing the functioning of female organs;
- vitamin therapy (C and E), in order to strengthen the overall tone of the body, improve tissue nutrition, normalize the cycle when menstruation is delayed;
- balneotherapy and diet, which are necessary to stabilize weight and activate the immune system of women.
During therapy, doctors recommend sexual abstinence and avoidance of stressful situations.
The doctor determines how many days conservative therapy will last. Typically, treatment for ovarian cysts is long-term, requiring complete restoration of the menstrual cycle and reproductive function of women. Often, a follicular tumor or cyst of the corpus luteum, under the influence of drugs, resolves or comes out with menstrual bleeding. Conservative hormone therapy also helps to stop the growth of paraovarian and dermoid tumors, small growths in polycystic disease.
Many patients try to self-medicate and take hormonal medications when their periods are late without a gynecologist’s prescription. However, women need to learn one simple truth - restoration of a regular cycle should be done by a professional. Overuse of medications can cause life-threatening uterine bleeding.
Features of menstruation after removal of a cystic formation in the ovary
Usually a woman feels the cyst hurt before her period. The sensation manifests itself in the part of the abdomen where the tumor is located. The pain is nagging or aching, accompanied by a feeling of heaviness. Active sexual life can make it permanent or intensify, causing torsion of the pedicle of the neoplasm or the ovary itself.
A cyst during menstruation increases pain. The formation puts pressure on the ovary, and if its size is large enough, then on the bladder and intestines. Therefore, a woman has to go to the toilet more often; she feels fermentation and rumbling in her stomach. Constipation or, on the contrary, diarrhea is common.
An ovarian cyst after menstruation may completely disappear and not be visible on an ultrasound if the cause of its appearance was the improper functioning of the organ with retention of the egg in the follicle. The endometrioid formation only moderates its activity, which is expressed by a decrease in the associated discomfort in the abdomen for some time.
After a missed period, a cyst may increase in size due to the feeding of hormones. If the delay is long enough, the pain in the abdomen on the side intensifies and begins to radiate to the leg.
You can guess how a cyst burst during menstruation by the following signs:
- Sharp pain in the lower triangle of the abdomen;
- Sudden attack of nausea, vomiting;
- Chills;
- Irradiation of pain to the area of the coccyx and anus.
If the neoplasm was follicular and small in size, a breakthrough of the capsule with liquid is not so dangerous, although pain cannot be avoided. Endometrioid, luteal, paraovarian or dermoid cysts in this case cause the effusion of contents into the abdominal cavity, which provokes peritonitis and requires immediate medical attention. The woman needs to be operated on to remove the fluid.
It is important to pay attention to the nature of menstrual flow, because it is evidence of normal recovery after the intervention. If they are too heavy, this may mean bleeding, which should be addressed to a doctor immediately. But even normally, during the first menstruation there may be more intense discharge than usual, as well as abdominal pain from the operated organ, and small clots.
Menstruation after laparoscopy of cysts should not have an unpleasant odor or discolored mucus. All this, as well as large clots and an increase in temperature, are signals of an infection that must be eliminated immediately.
Mucous discharge with bloody additions does not fall out of the usual boundaries immediately after the intervention and lasts 3 weeks. It is important to monitor their appearance and smell.
Menstruation after a follicular cyst, if it had to be operated on, returns to normal in the same way as when other types of formations are removed. In all cases, it can linger for a longer period if the ovary is injured during surgery. But this is immediately obvious due to the pain and large clots in the discharge.
A cyst is the cause of a delay in menstruation, and a cycle failure can cause not only poor health, but also infertility. Therefore, it is important not to start its development, so as not to have to remove the entire ovary. After all, this significantly reduces the chances of getting pregnant. Regular visits to the gynecologist, careful attention to menstruation and everything connected with it will help to control the condition of the organs.
- Inflammation of the ovarian cyst: causes, symptoms...
Why inflammation of the ovarian cyst occurred and methods of its treatment. An ovarian cyst is a tumor-like hollow formation... - Hormonal ovarian cyst: treatment with hormonal…
What to do if a hormonal ovarian cyst appears? An imbalance of hormones in the female body can lead to various consequences...
- Multi-chamber ovarian cyst (left and right)…
Multilocular ovarian cyst has its own characteristics of clinical course, treatment tactics and diagnosis.
- Causes and treatment of ovarian cysts during menopause
As the disease progresses, the ovarian cyst begins to behave more actively during menopause, adding to the sensations of an already difficult period.
- Is it possible to cure a paraovarian ovarian cyst without...
Paraovarian ovarian cyst: is treatment possible without surgical intervention?
- Hemorrhagic ovarian cyst (with hemorrhagic…)
A hemorrhagic ovarian cyst has been detected: how is it dangerous, how is it treated, is it possible to get pregnant?
- Before the onset of the critical days, the tumor provokes the appearance of nagging pain in the lower abdomen. They can be localized on both the left and right sides. It all depends on where exactly the cyst is located.
- The pain intensifies during sexual intercourse or exercise. It is best to avoid such stress to prevent complications from developing.
- Menstruation itself is accompanied by severe pain. During this period, the cyst exerts a compressive effect on the organs that are located adjacent to the ovary. This could be the intestines or bladder.
- The pain often radiates to the leg.
If the cyst does not have complications, then in most cases it resolves quietly. However, this does not mean that the unpleasant symptoms that accompany menstruation can be ignored. On the contrary, such a malaise requires increased attention. Therefore, contacting a specialist in such situations is mandatory.
So after surgery, menstruation occurs in a couple of weeks, if the operation did not cause any complications. If laparoscopy was performed on a patient over 30 years of age, then she should wait for her critical days in about a month.
After the operation, menstruation should not change its usual smell and color. If a woman has an elevated body temperature and mucus is released from the vagina, then there is an infection in her body. In this case, you need to visit a doctor so that he can find the cause of the disease and prescribe effective treatment for it.
- With a follicular ovarian cyst, when a tumor arises and grows directly in the body of an immature egg, ovulation does not occur and therefore women do not have periods for a long time. In these cases, the delay can range from a week to a month and occur with moderate pain in the lower abdomen. Once regulation occurs, bleeding without treatment lasts up to 7-8 weeks.
- Delays in menstruation with a functional ovarian cyst occur quite often. However, menstrual irregularities go away along with the tumor, since the tumor is capable of self-healing. As the cyst emerges, it is noticeable by the discharge; they have dense clots consisting of its membranes. Sometimes the disease is latent and women do not even suspect that they had a cyst.
- Neoplasms of the endometrium (uterine mucosa), with their spread to ovarian tissue. These tumors are often the cause of irregular menstruation. With them, a delay in menstruation is caused by a hormonal imbalance, disruption of the normal functioning of the entire reproductive system, it can last a week, a month or more and is accompanied by scanty bloody vaginal discharge, aching pain in the groin and lower back. Upon the onset of menstruation, bleeding can be very heavy and prolonged.
- An ovarian luteal cyst is formed in the corpus luteum; it disrupts the maturation of the egg, which causes irregularity of the menstrual cycle and short-term or long-term delay of critical days. This tumor occurs with false signs of pregnancy (nausea, dizziness, changes in appetite, weight gain, swelling of the mammary glands).
It is impossible to diagnose these pathologies on your own, therefore the slightest suspicion of an ovarian cyst during a delay in menstruation should motivate women to visit a gynecologist and undergo a course of examination.
A clinical sign of the development of benign tumors is often a disruption of the menstrual cycle, which is manifested by a delay in menstruation. Its restoration is achieved using a number of pharmacological agents:
- hormone replacement drugs (Duphaston or its analogues), which provide the female body with the necessary amount of estrogens and progesterone (substances responsible for the normal functioning of the ovaries), as a result, these organs “rest”, the ovarian cyst begins to resolve, and menstruation no longer occurs;
- mono- or two-phase oral contraceptives (Marvelon, Logest, Diane-35, Anteovin, Zhanin, etc.), stabilizing the functioning of female organs;
- vitamin therapy (C and E), in order to strengthen the overall tone of the body, improve tissue nutrition, normalize the cycle when menstruation is delayed;
- balneotherapy and diet, which are necessary to stabilize weight and activate the immune system of women.
The doctor determines how many days conservative therapy will last. Typically, treatment for ovarian cysts is long-term, requiring complete restoration of the menstrual cycle and reproductive function of women. Often, a follicular tumor or corpus luteum cyst, under the influence of medications, resolves or comes out with menstrual bleeding. Conservative hormone therapy also helps to stop the growth of paraovarian and dermoid tumors, small growths in polycystic disease.
Complicated ovarian cysts (progressive or bleeding) are removed surgically using abdominal or laparoscopic surgery. As a rule, the postoperative period goes well. Women recover quickly and are discharged from the hospital a few days after laparotomy.
Ovarian cyst
Can menstruation be delayed after laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst?
Complicated ovarian cysts (progressive or bleeding) are removed surgically using abdominal or laparoscopic surgery.
As a rule, the postoperative period goes well. Women recover quickly and are discharged from the hospital a few days after laparotomy. The appearance of menstruation during the rehabilitation process in patients under 30 years of age usually occurs in the second or third week. In older women, after a longer period (3-4 weeks).
How the cycle changes with different types of cysts
Based on the nature of the cycle disturbances, the doctor can indirectly determine what type of formation a woman has.
Follicular
With a follicular cyst, menstruation becomes irregular - either it comes with a large delay (from 5 to 7 days), or a cycle is missed.
It is characteristic that the pain does not go away during the entire period while menstruation occurs. The bloody discharge is profuse, lasts a long time - up to a week, and is spotty in the last few days.
Follicular cysts periodically resolve on their own, after stabilization of hormonal levels. As soon as the cyst disappears, the menstrual cycle is completely restored.
If fewer hormones are secreted, menstruation becomes very scanty, that is, the entire cycle of secretion occurs literally drop by drop. Without treatment and monitoring by a gynecologist, persistent amenorrhea may occur - the complete absence of menstruation at a young age.
Similar signs of pregnancy and regulative delay with ovarian cysts
All neoplasms in the female genital area lead to reproductive dysfunction. Problems with conception (infertility) or pregnancy (spontaneous abortion) are common.
Ovarian cyst, as one of the reasons for delayed menstruation, in most cases becomes the reason for the absence of children. As the tumor grows, normal tissues are replaced by pathological ones, hormonal levels change, and the maturation and vital activity of eggs is disrupted. Symptoms of an ovarian cyst and irregular periods (or their delay) can easily be mistaken for pregnancy and because of this, delay treatment. In the early stages, with hypertonicity of the uterus, pregnant women may experience short-term spotting, reminiscent of scanty periods, and the bleeding that begins with an ovarian cyst may be the same. More often it is abundant and long-lasting, but there are also cases of erased or asymptomatic growth of tumors. An ectopic pregnancy can also occur with similar symptoms; this condition has both a delay in regulation and bleeding from the vagina, it is accompanied by both a severe painful symptom and a painless course.
Carrying out diagnostics for irregular periods or their delay
A missed period due to an ovarian cyst or pregnancy is a symptom of both conditions. Taking a pregnancy test and receiving a negative result indirectly indicates the development of a tumor. The doctor can assume the presence of an ovarian cyst upon examination; palpation reveals pain in the lower abdomen and enlargement of the appendages. Accurate diagnosis is achieved using the ultrasound method. An experienced specialist can always distinguish between a fetus in early pregnancy and a small tumor size. The technique of laparoscopy (examination of a diseased organ using a device with a video camera inserted through a small incision in the abdominal cavity) is considered informative. In some cases, an MRI or computed tomography scan is necessary to determine the location of the tumor.
Cyst and pregnancy
A cyst in women is detected during pregnancy during a routine ultrasound, since the symptoms are not always noticeable. The question arises: can this be dangerous for the expectant mother and fetus? Gynecologists recommend not to worry; in case of small sizes, there is no danger. If growth dynamics are observed and there is a danger of harm, laparoscopy is prescribed. This operation is acceptable during pregnancy.
What should girls planning pregnancy do when diagnosed? Rely on the recommendations of your doctor and control the process. The gynecologist recommends medication and surgical treatment. Don't ignore his advice. The disease is easily treatable if detected early.
Is pregnancy possible if you have a paraovarian cyst?
Previous article
Is it possible to sunbathe with an ovarian cyst: tips and precautions
Next article
Dangerous complications of neoplasms during a woman’s menstruation and their delay
Sometimes an ovarian cyst swells and increases in size during menstruation and can burst when pressure is placed on it or excessive stress on the abdominal muscles.
This is typical for dermoid, endometrioid, and muciotic formations. Their contents spill into the abdominal cavity, causing peritonitis. Such an acute condition requires emergency care and urgent hospitalization in a surgical hospital. In addition, ignoring symptoms and illiterate self-medication can lead to malignancy of cysts. Therefore, any bloody discharge from the vagina is a reason to immediately go to the clinic. Blood outside the normal menstrual cycle should alert a woman; its unexpected appearance in the discharge is a sign of serious diseases of the genital area.
Cystic ovarian formations pose a serious danger to women's health, so it is important to consult a doctor promptly if there are any signs of illness (disturbance in the menstrual cycle, their delay, pain in the lower abdomen, bleeding).
Timely examination helps to identify benign tumors, determine the nature and stage of the disease and begin treatment. Correctly selected conservative therapy often leads to the resorption of ovarian cysts, which reduces the likelihood of delayed menstruation and helps restore the normal functioning of the ovaries, and planned surgical removal of tumors prevents the development of their malignant degeneration.
Functional cysts and menstruation
To understand what pathology is and find out the reasons for its development, it is worth recalling what changes occur in the ovaries during the cycle. The menstrual cycle begins when a woman gets her period. Thus, the mucous layer of the uterus is renewed. At the same time, a dominant follicle is determined in one of the ovaries, which enlarges, and on days 12-16, under the influence of luteinizing hormone, it ruptures, releasing a mature egg (ovulation phase). In place of the follicle, a corpus luteum is formed, producing the hormones progesterone and estrogen. The corpus luteum (luteal) is necessary for the formation of the placenta in the event of fertilization. If conception does not occur, it gradually decreases and then disappears completely until the next ovulation.
A follicular cyst is formed from an unruptured follicle. Its size can vary from 2.5 to 10 cm. The formation consists of a membrane and a single-chamber cavity with follicular fluid saturated with estrogen.
A luteal cyst forms after ovulation. This happens in case of a violation of the reverse development of the corpus luteum. The formation is 6-8 cm in size and consists of a yellow liquid that produces the hormones estrogen and progesterone.
Luteal and follicular cysts are most often found on one side. The main symptoms of their development are delayed menstruation and abnormal periods (heavy lingering or scanty spotting). More noticeable signs in the form of pain in the lower abdomen can be observed if the formation is of significant size (over 6 cm).
Functional cysts are not uncommon; they develop in many women, but due to the mild severity of symptoms and the tendency to self-resorption, they often go unnoticed. As for the causes of the pathology, the provoking factor can be: severe stress, chronic inflammation, infections, scars, adhesions, endocrine disorders, abortion.