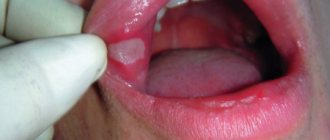
Nausea and increased salivation
Everyone has a feeling of nausea, regardless of age - both adults and children.
This is an unpleasant sensation that causes discomfort in the stomach, dizziness, increased salivation, poor health, and pale skin. Nausea before vomiting can occur even in a healthy person. This is usually associated with disruption of processes in the digestive tract, cardiovascular or central nervous system. If you feel sick for a long time, periodically, this can be a symptom of a number of diseases (cholecystitis, gastritis, meningitis), which occurs during toxicosis during pregnancy.
Types of drooling
Patients who have increased salivation have difficulty pronouncing speech sounds, have bad breath, and are forced to perform more acts of swallowing. Depending on the time of occurrence, hypersalivation is divided into morning, daytime, night and paroxysmal. According to the mechanism of action, salivation is of two types:
False salivation or pseudohypersalivation
Accompanied by a false sensation of increased saliva secretion, in fact, the volume of saliva secretion corresponds to the norm and does not exceed 2.5 liters per day. This condition is associated with weakness of the facial muscles, which leads to the inability to carry out movements, in particular to completely close the mouth. Symptoms of excessive salivation occur in cases where the swallowing process is disrupted due to infectious inflammation of the lymphoid tissue of the pharynx, damage to the nervous system by viruses, nervous diseases that cause involuntary trembling of the lips, increased muscle tone, and lip injuries.
True drooling
It is diagnosed when the volume of saliva secreted in an adult per day exceeds 2.5 liters. In some cases it can reach up to 10-12 liters in 24 hours. More often, this is one of the manifestations of the disease; it occurs against the background of dysfunction of the salivary glands, diseases of the nervous system, reflex effects coming from different organs: the esophagus, oral cavity, intestines, kidneys, pancreas, stomach.
Symptoms of nausea
The main symptom is a feeling of heaviness and pain in the stomach, accompanied by copious saliva in the mouth and possible vomiting. Vomiting alleviates the condition and removes undigested food and toxins from the body. After it, your health improves, your stomach is freed.
- Deterioration in health;
- Severe dizziness;
- Increased salivation (hypersalivation);
- Paleness of the skin;
- Poor appetite;
- Cramps in the abdominal area;
- The mouth is abundantly filled with thick saliva;
- Sweating increases;
- Apathy, want to sleep;
- Decrease or increase in pressure;
- Chills, increased body temperature;
- Diarrhea;
- Vomiting;
- Weight loss;
- Breathing becomes difficult, shortness of breath appears;
- Heart rate increases.
Short-term nausea is not dangerous to humans, but can serve as an alarming symptom of other diseases.
How to understand that everything is normal
The process of salivation is important for the digestion process , maintaining the moist state of the mucous membranes.
Increased secretion of saliva in the mouth occurs in a person when he sees food - this is a normal reaction of the body.
This will be especially noticeable if the person is hungry.
But excessive salivation that occurs during sleep or regardless of the feeling of hunger and other factors may indicate diseases of the thyroid gland and gastrointestinal tract.
If it seems that too much of it is accumulating in the mouth, you need to consult a doctor who will prescribe tests and determine the cause of this phenomenon.
The effect of hyaluronic acid on facial skin is discussed in detail in this article. Find out more!
This publication will tell you about the consequences of using Botox for hair.
The main contraindications to hirudotherapy are presented in this article.
Causes of nausea
There are many reasons that cause nausea. To get rid of an unpleasant feeling, you need to find out and eliminate the source.
Factors that provoke nausea:
- Food poisoning. A feeling of discomfort in the stomach appears several hours after eating, ending with vomiting, undigested food is excreted with vomit. The process is accompanied by high fever and diarrhea.
- Toxicosis during pregnancy. Morning sickness in a woman is the first sign that indicates pregnancy. In the first trimester, hormonal levels change and malaise appears. The symptom goes away by the end of the first trimester. If it is not accompanied by excessive vomiting and deterioration of the body, then it does not harm either the expectant mother or the child.
- Reaction to medications, vitamins. All medications have side effects, nausea is one of them. Individual intolerance to components can provoke it.
- Alcohol in large doses. Causes poisoning of the body, the person becomes sick and ends with vomiting.
- Head injuries. A severe head injury can cause a concussion. Dizziness and vomiting occur. Immediate medical attention is required, possibly hospitalization.
- Menses. During menstruation, a hormonal imbalance occurs in the body. The woman feels anxiety, cramps and pain in the abdomen, and dizziness.
- Violation of the vestibular apparatus. When changing body position, darkening of the eyes, noise in the ears, and deterioration of health may occur.
- Diets. An unbalanced diet, an incorrectly selected diet disrupts the functioning of the digestive system, and a person receives insufficient amounts of vitamins and nutrients. There is a malfunction in the stomach.
- Sunstroke.
- Motion sickness in transport, seasickness.
- Psychological disorders, stress. Disruption of the central nervous system causes various reactions in the body, including ailments.
Sudden nausea occurs in diseases: meningitis, appendicitis, gastritis, ulcerative colitis, oncology, inflammation of the gallbladder, cholelithiasis, peritonitis, etc.
Methods of diagnosis and therapy
If you notice increased salivation, go to your doctor .
If necessary, he will refer you to specialists of a narrower profile. First, the doctor will determine the cause of the pathology and, taking it into account, will choose treatment methods.
The following measures will help cope with the problem of hypersalivation :
- Anticholinergic drugs: Scopolamine and Platiphylline. They help stop salivation, but they have many side effects, including heart and eye problems.
- In extreme cases, a procedure may be necessary to remove part of the glands, which will eliminate the problem of increased salivation.
- Radiation therapy, which involves the destruction of the salivary ducts. But it can lead to damage to tooth enamel.
- For neurological diseases, after a stroke, facial massage may be indicated to normalize salivation.
- In order to block part of the salivary ducts, Botox injections can be used, the duration of which does not exceed 6 months.
- Cryotherapy is sometimes used. After a course of procedures at the reflex level, swallowing saliva will become more frequent.
- Homeopathic medicines can be used to reduce the amount of secretion released.
Sometimes such measures are not required , and it will be easier to eliminate the cause of the problem than to force the glands to work normally.
Do you know how often to have your face cleaned by a cosmetologist? Recommendations from experts are in our article.
Reviews of the removal of moles using the radio wave method are presented in this publication.
Whitening facial skin from age spots is discussed in detail here.
First aid for nausea
Painful sensations in the stomach disrupt the usual rhythm of life, you want to be free from discomfort. To help yourself deal with this, try these tips:
- Take a horizontal position - lying down, a person feels better, especially important for dizziness;
- Wash with cool water;
- It is worth limiting physical activity, it is advisable to maintain complete rest;
- Ventilate the room, fresh air will help improve your well-being;
- Rinse your mouth after vomiting;
- Eat healthy foods (fruits, vegetables, dietary meat);
- Eat often, in small portions, plenty of fluid intake is important (salty, spicy, iron-containing foods are not allowed);
- Drink a glass of water with lemon;
- Try to restore your breathing and relax;
- Turn on calm music, your favorite movie. It is important to calm the nervous system;
- Take antiemetics at night;
- If you have problems with stool, take prebiotics.
As soon as the nausea subsides, see your doctor to determine the cause. Pay close attention to changes in how you feel.
Prevention methods
Prevention of pathological hypersalivation not associated with food intake consists of the prevention and timely treatment of diseases of the oral cavity, gastrointestinal tract, and endocrine system organs.
A balanced diet, an active lifestyle and proper personal hygiene will help avoid helminthic infestation and food poisoning, which can provoke increased salivation.
Remember that self-medication of hypersalivation or ignoring this symptom can lead to the development of unpredictable consequences, so if something confuses or worries you, do not put off visiting a doctor.
Saliva production is a normal process. But if salivation is very profuse, it can affect the quality of life and cause discomfort.
But that's not the worst thing. What’s worse is that it can be a symptom of quite serious diseases that cannot be ignored.
Let's take a closer look at the reasons for strong, profuse salivation in women, increased at night or during the day, and learn how to get rid of frequent drooling on your own and with the help of a doctor.
Treatment options
You should consult a doctor immediately if:
- Nausea remains for a long time for no apparent reason;
- There is uncontrollable vomiting, vomit with blood is released;
- A sharp deterioration in health;
- Severe diarrhea, black discharge;
- High body temperature, antipyretics do not help;
- Acute pain in the abdominal area;
- Loss of consciousness occurs;
- Frequent fainting;
- It becomes difficult to breathe;
- There are signs of dehydration.
These symptoms are life-threatening, whether it is an adult or a child. Urgent medical attention, hospitalization, prompt determination of the cause and treatment are needed.
Nausea is not a disease, but a symptom. Therefore, only after diagnosing the cause can treatment begin. Don't self-medicate! If there is an accompanying pathology, there is a risk of aggravating the situation. The doctor prescribes medications according to the diagnosis.
Diagnosis of increased salivation
If there is increased salivation, the patient should consult a doctor to determine the cause of this condition. To determine the diagnosis, the specialist prescribes a detailed examination, including:
- taking an anamnesis - finds out the duration of excessive salivation, the presence of accompanying symptoms, whether there were diseases of the oral cavity and pharynx;
- life history – presence of bad habits, pregnancy, chronic diseases;
- examination - special attention is paid to the condition of the mucous membrane of the oral cavity and tongue (presence of cracks, ulcers, injuries);
- an analysis that determines the functional abilities of the salivary glands and allows you to measure the amount of saliva produced per minute.
Frivolous reasons
Increased salivation and nausea do not always indicate illness. There are other, more harmless causes of hypersalivation.
Sometimes these side effects occur when taking certain medications:
- Nitrazepam is a sleeping pill prescribed for sleep problems. It has many side effects: decreased concentration, dizziness, feeling tired, drooling or dry mouth, nausea, vomiting, low blood pressure.
- Lithium – has an antipsychotic, sedative effect. Side effects include nausea, drooling or dry mouth, vomiting, drowsiness, tremors, and a constant feeling of thirst.
- Pilocarpine is an eye drop for the treatment of glaucoma. After use, you may experience dizziness, headache, increased sweating, salivation, nausea, and itchy eyes.
If you experience these unpleasant symptoms, tell your doctor about them. The doctor will either reduce the dosage or select another drug.
Similar symptoms occur in women during menopause, especially during hot flashes. During menopause, nausea is the first concern, then increased heart rate, sweating, weakness, dizziness, headache, hypersalivation, and anxiety make themselves felt. The state of health worsens due to changes in hormonal levels.
How to prevent unpleasant symptoms associated with hot flashes:
- Physical activity will help cope with stress and depression: playing sports, walking in the fresh air, swimming.
- Dress for the weather. Synthetic fabric does not allow air to pass through, does not absorb sweat, and makes it difficult to transfer heat. It is better to give preference to clothes made from natural materials.
- Take a shower during hot flashes. It has a relaxing effect, helps wash away sweat, and reduce body temperature.
- Rest more, get enough sleep, avoid stressful situations.
- Always carry a water bottle with you and drink at least 2 liters of water per day.
If hot flashes are frequent and prolonged, go to the gynecologist, he will prescribe hormone replacement therapy. You should not take pills without consulting a doctor, because... there are contraindications: oncology, diabetes, hepatic-renal failure, endometriosis, increased blood clotting.
Pregnancy
Most people experience toxicosis at the beginning of pregnancy. It affects cerebral circulation and can provoke increased salivation. Along with hypersalivation, other symptoms of toxicosis appear, the main one being nausea. Toxicosis usually goes away by 16 weeks. To alleviate the condition, follow these recommendations:
- eat more often, but in small portions;
- give up salty, sour, spicy, foods that contain a lot of starch: potatoes, beans, lentils, peas;
- drink water constantly, at least 2 liters per day;
- do not starve, snack on dried fruits and nuts;
- do not smoke, do not chew chewing gum;
- take vitamin complexes, try to eat right.
Help yourself
You need to start fighting the problem by finding out the cause and eliminating it. Therefore, you should not take medications or go for procedures without the knowledge of a specialist.
But if you are prone to this problem, then you can reconsider your diet .
It is recommended to limit foods that are high in sugar , as sweets tend to increase the amount of saliva produced.
Try to limit sugary drinks, sweets and baked goods, and dairy desserts. Avoiding acidic foods helps reduce salivation .
Hypersecretion is provoked by citrus fruits, sauerkraut, yoghurts, and products that contain vinegar.
When the functioning of the salivary glands returns to normal, familiar foods can be returned to the diet.
There are foods that cause dry mouth by helping to fight salivation. These are fiber foods: whole grain bread, whole oats, beans and other legumes.
You can rinse your mouth with shepherd's purse infusion, extract or tincture of water pepper, which are sold in pharmacies.
Poisoning
Another reason for increased salivation and nausea is poisoning. In this case, the patient will be helped by a toxicologist or resuscitator.
Fly agarics
After 1-2 hours, signs of poisoning appear: weakness, nausea, vomiting, headache, dizziness, severe salivation, stomach pain, diarrhea mixed with blood. If the poisoning is severe, hallucinations, delusions appear, and vision deteriorates.
It is important to help in time, otherwise the situation will worsen. First, motor excitement will develop, and after 6-10 hours it will turn into a drowsy state. Body temperature drops, eyes and skin turn yellow, and paralysis of the respiratory muscles may begin. You should not use unconventional methods of treatment that contain fly agarics, because they can be very dangerous.
To save the patient, you need to call an ambulance and rinse the stomach before arrival, give any adsorbent: Smecta, Polysorb, Enterosgel. Doctors will administer an antidote to the patient - atropine.
Excess iodine is no less dangerous than its deficiency. If iodine enters the stomach in large doses, there is pain and burning in the mouth, stomach, esophagus, thirst, and vomiting. Inhalation of iodine results in runny nose, cough, drooling, lacrimation, metallic taste in the mouth. In severe cases, there may be swelling of the larynx and nose, loss of consciousness, delirium, convulsions, and coma.
You should immediately call an ambulance; with timely medical care, the consequences of poisoning will be insignificant. The antidote is sodium thiosulfate, doctors administer it intravenously, eliminate dehydration, and give painkillers for severe pain.
Acute mercury poisoning is accompanied by weakness, headache, metallic taste in the mouth, pain when swallowing food, increased salivation, bleeding gums, nausea, vomiting, abdominal and chest pain, shortness of breath, cough, and high fever.
If these symptoms appear, the patient must be taken to the hospital immediately. Before the ambulance arrives, you need to take the victim out into the fresh air, rinse the stomach, give a sorbent, make him drink water or weak tea, change clothes before that, and ask him to take a shower. At the hospital, the patient will receive the necessary treatment.
Increased salivation and nausea can be caused by harmless reasons: taking medications, pregnancy, menopause, or they can be symptoms of serious diseases, one of the signs of poisoning. In the first case, they will go away on their own, over time or after stopping the medication. In the second case, urgent medical attention is needed.
What not to do
First of all, you should not diagnose yourself . It is unlikely that you will succeed, and by starting treatment, you risk harming yourself.
If you notice increased salivation, you should give up bad habits and uncontrolled use of medications .
It is important to eliminate the risk of mechanical trauma to the oral cavity.
Hypersalivation, which has no obvious natural cause, should never be ignored, because it can be a symptom of very serious diseases.
Excessive salivation at night
Normally, in a healthy person, salivation decreases sharply at night. A couple of drops of saliva on the pillow in the morning is just evidence that the body woke up earlier than its owner.
Factors that provoke excessive salivation during sleep:
- mouth breathing;
- malocclusion, in which the mouth remains open at night - for example, with an open, mesial and distal bite;
- sleep disturbances - for example, too deep sleep, similar to an unconscious state, during which control over the body is completely lost.
Why do children drool while sleeping?
The causes of hypersalivation, characteristic of adults, can be diagnosed in a child, but children also have their own special causes of salivation.
The first and most common reason is teething . This process is accompanied by profuse salivation, and since a child at this age does not yet know how to control the body’s reflexes, saliva constantly flows out of the mouth. Usually by the age of 4, teeth erupt and hypersalivation stops.
Sometimes, while observing a child, you can find that the luna is leaking due to the fact that the child breathes through his mouth . This may occur due to persistent nasal congestion or other ENT diseases. In this case, you should immediately consult a doctor.
The cause of hypersalivation can be head injuries, progressive diseases of the nervous system and stomatitis.
Inflammation of the gums or gingivitis causes strong salivation, which is a protective function of the child’s body against the disease.
Another unpleasant cause of hypersalivation is infection by parasites . The child is extremely susceptible to any infection, and thus the body signals problems in the gastrointestinal tract.
When a child is poisoned by pesticides or mercury, the first sign is excessive salivation. All other symptoms (fever, diarrhea, vomiting, increased body temperature) appear later. In this case, immediate assistance from specialists is required, and the child must be hospitalized immediately .
In any case, excessive salivation is a signal from the body to the manifestation of any diseases and requires a thorough examination by specialists.
Did you like the article? Share it with your friends on social networks:
Salivation is important for the digestive process, at the very beginning. Every person has 3 salivary glands that are capable of producing about 2 liters of saliva per day.
Saliva helps prevent infection by germs and other organisms and helps food get into the throat.
But in some cases there may be disturbances, which manifest themselves in the form of excessive salivation, after which nausea begins.
How to get rid
The elimination of hypersalivation is carried out by specialized specialists:
- dentists work with local causes,
- gastroenterologists solve problems with the gastrointestinal tract,
- neurologists treat diseases of the nervous system,
- endocrinologists – hormonal imbalances,
- Infectious disease specialists and toxicologists prescribe therapy for poisoning.
Drug therapy
If excess fluid in the oral cavity reduces the quality of life, in addition to general therapy, the doctor prescribes symptomatic treatment - anticholinergics:
Scopolamine has fewer contraindications - only glaucoma. Platiphylline has glaucoma, organic kidney and liver diseases. Riabal is taken during pregnancy, but it is contraindicated for problems with the prostate, gall bladder and kidneys, intestines, cardiovascular system and many other diseases.
A quick but temporary effect is achieved by intramuscular injections of Botox into the area of the salivary glands - in the cheeks and cheekbones. Botox blocks the nerve signals that the salivary glands transmit to the brain, and due to this, a strong response to irritation of the glands does not occur and saliva is not released in large quantities.
Facial massage is useful for hypersalivation of a neurological nature.
The method of selective removal of the salivary glands is used extremely rarely, since the procedure is fraught with damage to the facial nerves.
Hypersalivation in adults
The causes of this disease can be very different, but the result is always the same - severe discomfort . The fact is that men and women in the modern world are forced to communicate a lot with other people. Normal communication is impossible if you do not make a pleasant impression on the interlocutor. Increased salivation does not allow you to look good. A sick person is forced to avoid communication with other people. A psychological complex develops when the patient thinks that everyone around is paying attention to his problem. This is followed by a decrease in self-esteem, and depression sets in.
Increased salivation is explained by increased work of the salivary glands. There are 3 pairs of them in the human oral cavity. The main task of these glands is to secrete saliva in the required volumes. However, if their function is impaired, saliva is produced in excess. It literally floods the oral cavity, which is why the patient is forced to constantly spit it out or swallow it . At the same time, it looks completely unattractive. In addition, the person cannot eat normally: problems with swallowing arise.
Increased salivation in medical practice is called hypersalivation. This problem in adults is caused by various pathological changes in the body. Increased salivation is often caused by various diseases of the digestive system. Also, drooling may begin to flow profusely after taking certain medications. The cause of hypersalivation can be excessively hot or spicy food, etc. In any case, the problem cannot be dealt with unless the source of the disease is accurately determined.
The following signs indicate increased drooling , which are impossible not to notice:
- A person begins to get irritated due to the fact that saliva accumulates in large quantities in the oral cavity.
- The patient constantly fights the urge to swallow or spit out saliva.
- The patient tries to speak less, as excess saliva disrupts normal articulation.
- When sleep comes, a person loses control of himself. In his sleep, he does not swallow, so saliva begins to flow out of his slightly open mouth. After sleep, the patient often finds wet spots on the pillow.
It is worth noting that increased salivation is of two types: true and false . It is quite easy to distinguish them. In the first case, salivation is indeed excessive. In the second, the volume of saliva production is within normal limits, but since the patient’s swallowing mechanism is impaired, there is a feeling of excess fluid in the mouth.
Increased salivation in women
All of the above causes of excessive drooling can occur in both men and women.
But the latter have one condition that is found only among them. We are talking about pregnancy. Read also: What time do baby teeth fall out?
The body of pregnant women changes greatly. These changes mainly affect the endocrine system. A global hormonal change occurs, which causes hypersalivation in the early stages. We are talking about the first 3 months of pregnancy.
Excessive salivation during pregnancy is not normal. It is a sign of early toxicosis. The woman begins to feel severe nausea, sometimes followed by vomiting. In such a situation, there is a high probability of increased salivation.
Sometimes the glands continue to function normally, but the pregnant woman is afraid to swallow saliva , as this may provoke vomiting. In this case, a feeling of hypersalivation is created.
Often, pregnant women begin to drool heavily due to heartburn. The body tries to put out the “fire” in the esophagus by using more saliva. As you know, it contains bicarbonate, which is an alkaline agent.
diseases of the thyroid gland should be noted as a cause of excessive salivation in women . The fact is that thyroid pathologies occur mainly in women.
What does excessive salivation indicate?
- What does excessive salivation indicate?
- What does the color of sputum indicate when you cough?
- What happens in the body during sex
The human salivary glands work constantly, but the amount of fluid they secrete usually does not exceed 12 mg per hour. From time to time, the level of saliva may increase, for example, as a response of the body to tasty, beautiful or aromatic food. Also, the amount of liquid in the mouth increases when the mucous membranes are irritated - an example of this may be the desire to constantly spit out accumulated saliva during dental treatment. However, the constant release of large amounts of saliva indicates health problems.