Many people wonder, when they hear the diagnosis “gastropathy,” what it is, and quite often confuse it with gastritis, although these provisions in medicine are completely different.
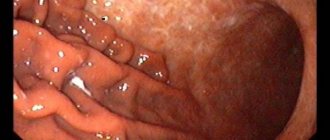
If gastritis is a pathology of the gastric mucosa, accompanied by its inflammation, then gastropathy is the name of various gastric diseases that are characterized by damage to the epithelium and vascular system of the stomach with possible minor inflammation. With this disease, studies will show redness of the surface of the organ.
According to ICD-10, the code for this disease is the same as for gastritis - K29.
Epidemiology
Currently, every second person on the planet has diseases of the digestive system. More than 60% of people are over fifty years of age. The picture takes on enormous proportions if we take into account the fact that the disease does not manifest itself in the initial stages.
Gastropathy occurs in both men and women, and it is also observed in children. In the fairer sex, the disease is diagnosed a little more often, this is due to problems at the hormonal level.
https://youtu.be/_T6TNvi0GTQ
Classification
In medicine, there are several classifications of gastropathy. According to one of them, the disease is divided into acute and chronic, according to another, the disease is distinguished by stages, and still others distinguish the degrees of development of the pathology. According to the degree of development of the disease, gastropathy is:
- 1st degree, which manifests itself in a slight change in the gastric mucosa, as well as a slight decrease in the production of hydrochloric acid,
- 2nd degree, which is caused by more severe pathological processes, cell damage and necrosis of the gastric epithelium passes faster than in the first case. But these changes are convertible if treatment is started in a timely manner.
The stages of the disease depend on its duration, the nature of the course, the effectiveness of treatment, as well as on the condition of the gastric epithelium. The following stages of gastropathy are distinguished:
- The initial stage, characterized by slight inflammation of the mucous membrane without changing its structure,
- Chronic, which is caused by the appearance of erosions and ulcers, damage to the glands of the organ. Typically, this stage occurs if the disease is advanced, diagnosed late or not treated properly,
- The stage of atrophy, manifested in degeneration of the walls of the stomach, replacement of some areas with connective tissue, poor health,
- Hypertrophy, which is the most severe stage, in which thickening and coarsening of the walls of the stomach occurs, the formation of cysts and adenomas.
According to its form, the disease is divided into:
- Acute gastropathy, which occurs when the stomach is exposed to alcohol, acids or alkalis, infections,
- Chronic, characterized by a slow course with a gradual change in the epithelium of the organ, its atrophy, and a decrease in the functions of the stomach. In frequent cases, this form of the disease is asymptomatic,
- Moderate gastropathy, which is caused by the transformation of epithelial cells into connective tissue.
Chemical gastritis
Chemical (reflux gastritis, as well as NSAID gastritis) gastritis is a group of several diseases that have in common the chemical effect of external irritants on the gastric mucosa.
Chemical gastritis is a group of several diseases that have in common the chemical effect of external irritants on the gastric mucosa
It can also develop due to the damaging effects of alcohol or iron and potassium supplements taken orally for a long time.
Reflux gastritis (chemical antral, alkaline gastritis) develops as a result of the reverse reflux of bile and lysolecithin from the duodenum into the stomach, which is possible when the tone of the antral sphincter (sphincter) is weakened. A characteristic feature of severe reflux gastritis is that the pain, which intensifies after eating, is not relieved by antisecretory drugs (antacids, PPIs), which are usually used and help with other types of gastritis. During a painful attack, vomiting mixed with bile is possible.
A well-collected medical history is important to make a correct diagnosis. Gastroscopy, if necessary, can indicate a typical lesion of the antrum of the stomach with minimal inflammation. Treatment depends on the characteristics of the pathological process. If reflux gastritis has developed as a result of gastric surgery, then the question is raised about surgical prevention of reflux by performing a Roux-en-Y operation (connecting the stomach with the jejunum, bypassing the duodenum).
A common place in the treatment of reflux gastritis is the use of ursodeoxycholic acid drugs, which help reduce the aggressive effect of bile on the gastric mucosa. Antacids (phosphalugel, Maalox) in combination with cholestyramine promote the adsorption of bile. To improve gastric motility, as well as improve the coordination of contractions of the antrum and duodenum, prokinetics are used, for example, domperidone (Domrid, Motilium).
NSAID gastropathy is damage to the stomach resulting from treatment with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for some time. Most often, the lesion is in the nature of multiple erosions, localized mainly in the antrum of the stomach, less often the body of the stomach or the duodenum are affected. There are no specific symptoms that distinguish NSAID gastritis from other gastritis.
Causes and risk factors
Different types of the disease are currently diagnosed frequently. Doctors divide the causes of the disease into internal and external. These include:
- Poor diet, consumption of alcohol and nicotine, coffee, infections,
- Insufficient secretion of enzymes in the body that are needed for digestion,
- Long-term use of medications, burns and other injuries,
- Reflux of bile into the stomach, stagnation,
- Incomplete blood supply to the stomach due to the formation of internal pathologies,
- Genetic predisposition.
Causes
Congestive gastropathy does not cause structural transformations of the mucous membrane, only minor inflammatory foci are formed. This process is associated with functional deformation of cells or impaired gastric motility simultaneously with a stop in the evacuation of its contents. As a result, erythematous gastroduodenopathy occurs. It is reversible, but provokes many dyspeptic symptoms.
In the appearance of congestive gastropathy, a large role is played by hereditary predisposition. Also, the development of the disease can cause the following factors to affect the human body:
- smoking and alcohol abuse;
- severe head injuries (causing stress ulcers);
- age over 60 years;
- unhealthy diet: eating junk food, overeating (or, conversely, prolonged fasting, dieting);
- increased acidity of gastric juice;
- long-term use of anti-inflammatory non-steroidal drugs;
- presence of Helicobacter pylori in the body;
- prolonged stress;
- pancreatic diseases;
- a pancreatic tumor that causes an increase in gastrin levels in the blood;
- portal hypertension and liver cirrhosis;
- duodenogastric reflux.
Some of these factors cannot be controlled by a person, but for the development of congestive gastropathy, the presence of two or more factors from the list must be present.
Symptoms
At first, the disease shows no signs. In frequent cases, the first symptoms are covered by those that are inherent in other ailments in which gastropathy develops. After some time, gastropathy has symptoms, as with gastritis, it is accompanied by pain and heaviness in the stomach, flatulence, nausea and heartburn.
In addition, appetite is disrupted, vomiting appears, after which the patient’s well-being becomes better. In half of the patients, there is a disturbance in the formation of bile, the tone of the large intestine is disturbed, and constipation occurs.
If there is a pathology of the antrum of the stomach, then bleeding may occur in the organ, the stool becomes reddish in color, and there is an admixture of blood in the vomit.
How to treat congestive gastropathy
Therapy for congestive gastropathy must be comprehensive and include the use of medications, diet, normalization of the daily routine and diet.
Drugs are used that eliminate functional disorders and normalize gastrointestinal motility.
There are many medications to treat this disease:
- proton pump inhibitors;
- histamine H2 receptor blockers;
- antibiotics;
- antacids;
- cytoprotectors;
- drugs that help improve blood circulation.
The main role in the treatment of congestive gastropathy is given to substances that stop the synthesis of hydrochloric acid - proton pump inhibitors (PPIs). It takes at least 18 hours to resume the process. In addition, they have low interactions with other medications and are quite safe when taken over a long period of time. Proton pump inhibitors include the following drugs: Omeprazole, Lansoprazole, Rabeprazole.
"Rabeprazole" is a film-coated tablet, a single dose is 10-20 mg. The treatment regimen is prescribed by the doctor individually. Side effects include: nausea, vomiting, belching, flatulence, constipation, dizziness, insomnia, cough.
"Lansoprazole" are capsules that are taken orally at 30 mg at a time once a day. The duration of the course is 4 weeks. If necessary, the course is extended for another 2-4 weeks. Contraindications include: pregnancy in the first trimester, breastfeeding, allergy to the drug itself. Side effects: constipation or diarrhea, and occasionally there may be rashes on the body.
There are such drugs - blockers of H2-histamine receptors: Kvamatel, Ranitidine.
"Kvamatel" is administered intravenously, a dose of 20-40 mg suppresses the synthesis of hydrochloric acid for half a day. It is recommended to give injections of 20 mg twice a day. Contraindications: lactation period, pregnancy, childhood, presence of malignant neoplasms, hypersensitivity to the drug. Side effects: dry mouth, nausea, abdominal discomfort, increased fatigue, allergies.
Antacid drugs are represented by the following drugs: “Phosphalugel”, “Alka-Seltzer”, “Gasterin”, “Gastal”, “Rennie”.
"Rennie" are tablets, the effect of which is felt after 3-5 minutes. Single dose – 1-2 tablets, no more than 16 tablets per day. You can repeat the use of the medicine periodically every three hours. Contraindications to taking the drug: renal failure, hypercalcemia, hypersensitivity to the drug. Side effects include skin rashes. The drug is not dangerous for pregnant women.
The purpose of cytoprotectors is to ensure the integrity of the mucous membrane of the digestive organ and increase its resistance to an aggressive environment - these are bismuth preparations: Sucralfate, Pentoxifylline, De-nol.
Vitamins
Congestive gastropathy can lead to a decrease in the rate of absorption of vitamin B12, which causes its deficiency in the body. Vitamin deficiency is expressed in chronic fatigue, the presence of tinnitus, dizziness, emotional depression, headaches, decreased vision, and decreased mental abilities.
The vitamin is administered subcutaneously, intramuscularly and intravenously once or twice a day. A single dose is 0.1-0.2 g. For better absorption of the vitamin, it is better to take folic acid at the same time as consuming it, which helps the absorption process.
This vitamin is present in liver, beef, poultry, fish, seaweed, soy, milk, cheese, and eggs. In addition to drug treatment, physiotherapeutic methods are also used.
Physiotherapeutic treatment
This treatment consists of physical exercises and breathing exercises, which aim to strengthen the muscles of the peritoneum and internal digestive organs. Strong physical activity and walks in the fresh air tone the body, increase motor skills and improve blood supply to the stomach.
For pain, electrophoresis with papaverine and novocaine is used.
Among balneological procedures, it is good to drink mineral waters internally and take baths from them. For congestive gastropathy, drink half a glass of mineral water at room temperature an hour and a half before meals. When there is bleeding or ulcers that have degenerated into malignant tumors, hydrotherapy is not recommended.
Surgery
With congestive gastropathy, there may be cases when surgical intervention is necessary, which consists of removing damaged areas of the stomach. In this case, a full-fledged operation can be performed or a laparoscopic method can be used (hybrid operation or manually-assisted). Such operations are very effective, as they significantly reduce the duration and morbidity of surgery.
Diet for gastropathy
For patients with this disease, a gentle diet is recommended. To do this, you should stop eating fried, fatty, spicy foods, and completely quit smoking and alcoholic beverages. When cooking, it is better to give preference to the boiling or steaming method. It is better to eat food 5-6 times a day in small portions.
Traditional methods of treatment
Traditional methods of treatment are used in combination with medication and diet.
The following traditional medicine methods are used:
Unrefined vegetable oil (preferably olive) – 1 spoon, drink before meals.
Take mumiyo dissolved in milk, a third of a glass before meals for 10 days. Then they take a break for three days and repeat the course.
A good means of therapy is honey and products using it:
Mix warm oat decoction (0.5 cups) with 1 tsp. honey and drink this remedy 20 minutes before meals.
You can mix carrot juice with honey and take a quarter glass before meals three times a day.
Potato juice is also mixed with honey (100 ml of juice and 1 tsp of honey) and taken on an empty stomach three times a day.
Used for the treatment of congestive gastropathy and herbs. When using them, it is necessary to take into account the nature of their effect on the mucous membrane of the organ - inhibition or promotion of juice production. For low acidity, it is good to use calamus. Its root is crushed, one teaspoon of the root is infused in a glass of boiling water for half an hour and drunk before meals, a third of a glass at a time.
Aloe has a strong effect on the body during erosion, increased acidity, and heals inflamed areas of the mucous membrane. Drink fresh juice 1 tsp. half an hour before meals, it is allowed to add honey.
Homeopathic remedies
Homeopathy is also used to treat congestive gastropathy. The following drugs are used in treatment:
"Iberogast" - helps to normalize the motility of the gastrointestinal tract, reduces the symptoms of dyspepsia and spasms.
"Gastrokind" - stabilizes the activity of the digestive organs, relieves heaviness in the stomach, reduces the feeling of nausea and flatulence. Approved for use in pediatrics.
“Yazbin” - made from plant and animal ingredients, has an anti-inflammatory effect, helps stimulate the digestion process.
Gastropathy in children
In childhood, this disease ranks second after ARVI. In this case, the disease usually occurs suddenly and progresses rapidly. Gastropathy can be observed in infancy during the transition to artificial feeding or as an allergic reaction to food. The disease is also often provoked by infections, medications, infant formula and expired products.
Gastropathy is manifested by weakness, anxiety, pain in the abdomen, lack of appetite, diarrhea, nausea and vomiting. The acute form often becomes chronic, characterized by pain and a feeling of discomfort in the stomach.
Prevalence
Doctors around the world record diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, and then compile the information into general statistics so that they know what measures to take to limit the disease.
Congestive gastropathy is a fairly common pathological process, even against the background of other nosologies. It occurs not only against the background of poor nutrition, but also when taking certain medications, after prolonged stress, as well as due to accidents and as a complication of other somatic diseases.
More than a quarter of patients taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs report stomach pain; the percentage of gastropathy after burns, injuries and surgical interventions already reaches eighty. Liver cirrhosis and hypertension also contribute to the general “cauldron”. And given that patients either do not pay attention to the symptoms or hide them from their doctor, the statistics are greatly underestimated.
Varieties
Considering what gastropathy is, it should be noted that this term refers to a large number of stomach diseases. The types of these ailments depend on the description, interpretation of the disease, as well as on the final conclusion.
When describing, they evaluate the gastric mucosa, the size of its walls, and the presence of pathologies. The interpretation is made on the basis of clinical diagnosis, the conclusion is made based on the results of the biopsy. Today there are many types of gastropathy.
Antral gastropathy
This type of gastropathy develops in the atrium of the stomach, which is responsible for grinding food and its further movement into the duodenum. Here, mucus is secreted, which helps neutralize hydrochloric acid, as well as the production of the hormones serotonin, gastrin and endorphin.
This pathology causes a decrease in the rate of food processing, resulting in stagnation and fermentation. The patient begins to feel heaviness and pain. Untimely treatment leads to the development of ulcers that are easy to heal.
Associated and induced gastropathy
These types of diseases include pathologies that appeared as a result of taking NSAIDs in the treatment of various diseases. Such drugs can cause damage to the gastric mucosa, the development of ulcers and erosions, bleeding, and create obstruction of the organ.
Typically, these types of gastropathy do not show symptoms, so they are often diagnosed when complications occur.
Atrophic gastropathy
With this type of disease, the cells of the gastric glands lose the ability to cope with their tasks, they give birth to their own kind as a result of an autoimmune reaction, a mutation occurs that leads to the production of mucus instead of hydrochloric acid. A particular danger in this case is the development of malignant neoplasms.
Hyperemic gastropathy
This pathology is characterized by an increase in the flow of blood to the stomach, which leads to redness of the mucous membrane, its swelling and bruising. Hyperemic gastropathy can spread to various parts of the organ or be located in small areas.
Hypertrophic gastropathy
Pathology appears in the form of deformation of the mucous and muscular membranes of the stomach, resulting in the appearance of benign neoplasms.
Hyperplastic gastropathy
With this disease, there is a strong increase in the cells of the stomach glands, so the tissues grow, folds and growths appear inside the organ. This pathology includes diseases such as Menetrier syndrome, Zollinger-Ellison disease, and hypersecretory gastritis.
Diffuse gastropathy
This pathology extends to the entire body of the stomach, it manifests itself in structural changes in the mucous membrane of the organ and exhibits the same symptoms as gastritis. The disease can have an acute or chronic form.
Gastropathy is congestive
Congestive gastropathy is characterized by impaired gastrointestinal motility. It is manifested by the formation of ulcers and erosions in the antrum of the organ and the upper intestine. At the same time, the blood supply to these organs is disrupted as a result of the harmful effects of nicotine and alcohol, infection with the Helicobacter bacterium.
Granular gastropathy
With this disease, growths in the form of grains form on the walls of the stomach, the size of which can vary from several millimeters to one centimeter. The disease is mainly observed in representatives of the stronger sex who are over forty years old. The initial stage of the disease does not show symptoms, its further development leads to disruption of protein metabolism.
Catarrhal gastropathy
Catarrhal superficial gastropathy is the simplest form of the disease, characterized by the spread of the inflammatory process to the upper layer of the mucous membrane of the organ. This can provoke an increase in the production of hydrochloric acid or, conversely, its deficiency.
The main reason for the development of the disease is food poisoning, injury, etc.
Lymphoid (lymphocytic) gastropathy
This disease is very rare. It is characterized by the formation of lymphocytes on the epithelium of the stomach, which look like follicles. This happens due to the influence of the Helicobacter bacteria, which provokes the growth of folds of lymphoid tissue.
Gastropathy papular
In medicine, papular gastropathy is an erosion that does not affect the deep layer of the gastric epithelium and is treatable. The pathology is caused by the appearance of papules in various parts of the organ. Papules can be either single or multiple.
Portal gastropathy
Pathology of the gastric mucosa occurs due to vasodilation. So, the pressure in the veins increases, the capillaries expand, filling with blood. With this pathology, mosaic patterns, red fragments or a black-brown pattern are observed on the mucous membrane.
There is no inflammatory process in this disease.
Erosive gastropathy
When exposed to various factors on the gastric mucosa, erosive gastropathy can occur, characterized by the presence of erosions from one to seven centimeters, which are similar to acne with a depression. The pathology may not show any symptoms; in some cases, pain occurs in the hypochondrium on the right side, as well as gastric bleeding.
Ulcerative gastropathy
This type of disease is acute and is caused by the appearance of symptoms similar to those of intoxication. If blood clots are observed in the vomit, you should immediately contact a medical facility to avoid negative consequences.
Diagnostic methods
Fibrogastroduodenoscopy allows you to study the condition of the gastric mucosa.
A gastroenterologist can diagnose congestive gastropathy based on the presence of characteristic symptoms of the disease in the patient. In addition, the patient is prescribed fibrogastroduodenoscopy, ultrasound examination and radiography with contrast. These methods allow you to examine the mucous membrane and detect areas of inflammation, erythema and possible ulceration. A breath test for the presence of Helicobacter pylori is also indicated. A general urine and blood test is mandatory. Magnetic resonance imaging is used to identify possible structural abnormalities in the gastric mucosa.
Treatment
Any gastropathy requires treatment with enzymes, painkillers and gastrocytoprotectors. Medications that reduce the production of hydrochloric acid in the stomach may also be prescribed.
If Helicobacter bacteria are detected, doctors prescribe antibiotics to the patient. Surgery is performed when there is bleeding in the stomach that cannot be stopped. In this case, laparoscopy is used.
Prognosis and prevention
If the disease is treated promptly and effectively, it does not pose a threat to life. A negative prognosis will occur when the disease is advanced and leads to the development of malignant neoplasms, as well as in the presence of pernicious anemia.
Having studied the causes of the development of gastropathy, it is recommended to design prevention methods in such a way as to protect your body from negative external and internal influences. First of all, you need to monitor your diet, give up bad habits, not abuse medications, and avoid stressful situations.
What is erosive gastropathy
The diet is prescribed by the doctor - it depends on the severity of the disease. Here are some recommendations that will be useful to patients who have problems with the gastrointestinal tract.
| 1. | The daily amount of food is divided into small portions; the breaks between meals should not be long. |
| 2. | Food must be steamed or boiled; fried foods are prohibited. If an exacerbation occurs, take only liquid, pureed food. |
| 3. | Extremely hot or cold food should not be consumed. |
| 4. | To restore the tissue of the gastric mucosa, you need to balance the consumption of proteins and fats. Such proportions will speed up recovery. |
| 5 | You should not eat spices, rich broths, canned food, fresh bread and buns, fatty and fried foods. |
| 6. | Legumes, rye bread, radishes - products containing coarse plant fiber should also be excluded. |
| 7. | To avoid irritating the walls of the stomach, you should limit your salt intake. |
Such recommendations will help the patient slow down the disease process and help him recover.
Judging by the fact that you are now reading these lines, victory in the fight against diseases of the gastrointestinal tract is not yet on your side.
Have you already thought about surgery? This is understandable, because the stomach is a very important organ, and its proper functioning is the key to health and well-being. Frequent abdominal pain, heartburn, bloating, belching, nausea, bowel dysfunction. All these symptoms are familiar to you firsthand.
The risk of developing gastropathy increases significantly if:
- The person is 50 years of age or older.
- There are other chronic diseases.
- Hormonal changes occur in the body.
- Medicines are taken uncontrolled.
- All health problems are neglected.
It happens that one of the relatives suffered from gastropathy. There may be a genetic predisposition. Other causes of the disease include:
- The presence of infections in the body.
- Eating incorrectly and irregularly.
- Bad habits: taking drugs, drinking alcohol, smoking.
- The stomach does not produce enough enzymes necessary for digestion.
- The patient took antibiotics or NSAIDs for a long time, suffered an internal burn, etc.
- Poor blood supply to tissues, bile reflux.