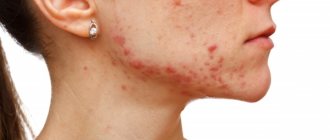
Local causes of mouth ulcers
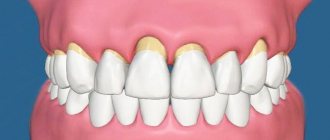
Damage to the mucous and soft tissues of the oral cavity, accompanied by the formation of ulcers of various sizes, depths and shapes, is associated with a number of local diseases and injuries.
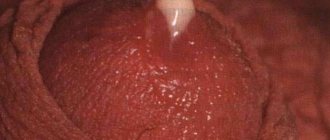
Recurrent aphthous stomatitis is manifested by small ulcerations of the mucous membrane - aphthae, which occur periodically and are painful. (Read about the treatment of stomatitis with folk remedies in this article)
- Appearance: round or oval ulcerations with a diameter of 3-7 mm, without undermined edges, surrounded by a grayish-yellow effusion and a bright red rim.
- Localization: mucous membranes of the lips, cheeks, transitional fold, tongue and its frenulum, hard and soft palate.
- Risk factors: disorders of the gastrointestinal tract, colitis, gastritis; relapse can be triggered by stress, nervous disorder, mechanical microtrauma of the mucous membrane, and in women - menstruation.
- Course of the disease: with a favorable course, aphthae heal in 7-10 days; in more severe forms, a larger area is affected and the healing process of ulcers lasts for half a month or a month. Relapses are more often observed in the winter-spring season, sometimes there are no periods of remission at all. Constant trauma can cause small ulcers to develop into larger, scarring ones.
With herpetiform stomatitis, the ulcers are small but numerous, resembling herpetic lesions of the mucous membrane.
- Appearance – ulcers without clear boundaries with a gray base, covered in the center with a white or grayish film.
- Localization : floor of the mouth and lower surface of the tongue.
- Risk factors - manifests itself mainly in young (under 30 years old), women, with reduced immunity.
- The course of the disease is usually healing without scarring within 7-10 days.
Similar ulcers, covered with a white film, form in children with fungal stomatitis (candidiasis, thrush).
that appear with recurrent necrotizing periadenitis (Setton's aphthae) have a specific shape. This disease is characterized by the formation of compactions under the mucous membrane, which after some time are replaced by deep painful ulcers that prevent a person from eating and speaking.
- Appearance - the ulcers have compacted raised edges, the depression between which is filled with infiltrate, the size of each ulcer is not less than 1 cm.
- Localization – lateral surfaces of the tongue, lips, buccal mucosa.
- Risk factors - Setton's aphthae are more common in women, sometimes formed as a result of complications of the fibrinous form of aphthous stomatitis.
- The course of the disease is long and undulating. The ulcers do not heal for months and form deforming scars. Relapses can continue for years, with at least 1-2 aphthae constantly present in the mouth, and at times of exacerbation their total number can reach 10.
Bednar's aphthae is a traumatic erosion of the mucous membrane.
- Appearance – round ulcerations with clear boundaries covered with a persistent gray-yellow coating, the surrounding tissues are slightly hyperemic.
- Localization - sky, closer to the midline.
- Risk factors appear in infants due to mechanical trauma to the palate and poor oral hygiene, less often in older children. It is observed more often in premature and pathological children.
- Course of the disease: healing is slow, can take several months; if the course is unfavorable, deeper ulcers may form at the site of erosion.
Injuries to the oral cavity often lead to the development of traumatic stomatitis, and their causes are very diverse, in particular:
- mucous bite;
- damage caused by a hard toothbrush;
- injury from dental instruments;
- low-quality fillings, crowns, dentures;
- sharp edges of decaying teeth;
- thermal or chemical burns, exposure to acids, alkalis, and certain medications.
Traumatic ulcers are quite painful and have their own characteristics.
- Appearance: small size, irregular shape, yellowish coating, raised edges, swelling of surrounding tissues.
- Localization: depends on the location of the injury, most often it is the mucous membrane of the lips and cheeks, the tongue.
- Risk factors: malocclusion, premature teething, untreated teeth, bad habits (frequent biting of the mucous membrane);
- Course of the disease: if the traumatic factor is eliminated, traumatic ulcers usually heal in 10-14 days. Possible exacerbation of inflammation and pain due to infection, complications with submandibular lymphadenitis.
Symptoms of aphthous stomatitis
Canker sores usually appear on moving parts of the mouth, such as the tongue or the inside of the lips and cheeks, and at the base of the gums. The ulcers initially appear as small oval or round reddish swellings that usually appear within a day (see photo).
Ruptured ulcers are covered with a thin white or yellow membrane and are surrounded by a red circle around the edge. In general, the ulcers heal within two weeks without leaving scars. Fever is rare and ulcers are rarely associated with other diseases.
Usually a person develops one or more ulcers at a time.
Oral ulcers as local manifestations of general diseases
In addition to local diseases, stomatitis and other pathologies of the mucous membrane, mouth ulcers are characteristic of a number of common infectious diseases, some of them primarily affect adults, others are characteristic mainly of children.
Tuberculosis of the oral mucosa usually develops against the background of pulmonary tuberculosis. The tuberculous tubercles that form in the mouth are soon replaced by ulcers. Their characteristic features:
- shallow, gradually increasing in diameter;
- have a loose bottom and uneven edges;
- often bleed;
- painful.
In this case, other symptoms characteristic of tuberculosis are observed: exhaustion, fatigue, fever, sweating, coating on the tongue.
The formation of ulcers in the mouth is also accompanied by syphilis , they appear immediately after the end of the incubation period.
Mouth ulcers with primary syphilis have the following features:
- practically painless;
- round or oval shape;
- the bottom is bright red, sometimes with a dark gray coating, the edges are smooth and raised;
- specific, cartilaginous infiltrate;
- heal from 3 weeks to 3 months, scarring does not always occur.
With tertiary syphilis , ulcers bleed more often, are slightly painful, the infiltrate is more powerful, dense, bluish-red, and takes longer to heal, with the formation of a star-shaped scar.
Acute necrotizing gingivostomatitis is a disease of a viral nature, usually developing against the background of decreased immunity, vitamin deficiency, overwork or hypothermia, as a result of injuries to the oral mucosa, as a complication of other viral infections or allergic stomatitis. (See how to treat stomatitis in infants here) It is more common in men under 30 years of age. Accompanied by:
- swelling, pain and bleeding of the mucous membrane;
- clouding of the gum epithelium, the appearance of gray-yellow plaque along the edges;
- the formation of ulcers with soft, uneven edges, a loose bleeding bottom, covered with an easily removable greenish coating;
- bad breath;
- increased body temperature, excessive salivation.
Therapy
What to do if an ulcer appears on the roof of your mouth? In any case, treatment should be prescribed by a doctor. The specialist will visually examine the damage to the mucous membrane, take some tests if necessary, and be able to determine the exact cause of the disease. Help from other doctors may also be needed to make a correct diagnosis. When it is accurately determined, you need to directly treat the root cause. For this purpose, complex therapy is usually used. As a rule, it includes sanitation of the oral cavity, elimination of traumatic factors and foci of infection. If the dentition is in satisfactory condition, you can carry out hygienic cleaning using disinfecting compounds.
Causes of ulcers in children
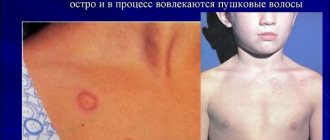
Many infectious diseases characteristic of childhood are accompanied by ulceration of the oral mucosa.
- Herpes usually first affects children aged 1-3 years , and is characterized by the appearance of numerous papules on the mucous membrane, after which, after breaking through, bright red ulcers are formed that heal in a couple of weeks.
- With chickenpox, a rash similar to a rash on the skin may form in a child's mouth: pink dots that turn into fluid-filled swellings.
- A rash on the oral mucosa in the form of small grayish-white dots surrounded by a red border is characteristic of the catarrhal stage of measles .
- With scarlet fever, the rash in the mouth is bright red.
- With diphtheria of the pharynx, in addition to the formation of ulcers on the mucous membrane, its redness and swelling, and the appearance of a yellowish-gray coating are observed.
Any rash in the mouth can lead to the formation of quite deep ulcers.
Types of sores in the oral cavity with photos
Ulcers that occur in the oral cavity can be distinguished by 2 main characteristics. This is color and localization. There are two types of sores based on color:
- White. The color can vary from milky to light beige.
- Reds. They can be light or brightly saturated.
Whites, in turn, can be divided into two types:
- leukoplakia;
- candidiasis.
Leukoplakia most often affects the cheeks, gums and tongue. The reason for its formation is excessive cell enlargement. The highest likelihood of this disease occurring is in smokers. There is a risk of developing cancer. Candidiasis, as thrush is scientifically called, is a consequence of the spread of a fungal yeast infection.
Read also: What to do for toothache
In contrast, red ulcers are very painful, causing a lot of trouble and discomfort. At the base they are bright red. They often bleed when touched. Recovery time may take from 7 to 20 days. Among the most common ulcers of this variety are ulcers accompanying herpes, syphilis and canker sores. The place of their localization can be the mucous membrane of the entire oral cavity.
What and how to treat mouth ulcers?
If damage to the oral mucosa is caused by a general infectious disease, this disease needs to be treated first; in parallel, symptomatic local treatment of ulcers can be carried out using medications or traditional medicine recipes.
Folk remedies
First of all, these are rinses with the following compositions:
- for 2 cups of boiling water, 5 tablets of furatsilin, a teaspoon of soda and salt;
- decoctions and infusions of medicinal plants - chamomile, oak bark, calendula, eucalyptus, walnut leaves, coriander seeds;
- an aqueous solution of calendula alcohol tincture (a teaspoon per glass);
- fresh juice of carrots, cabbage, parsley diluted in half with water.
Rinse your mouth with a warm solution as often as possible, spit out the mixture every half a minute and take a new portion.
You can also lubricate the affected areas:
- a paste of soda with water of a creamy consistency;
- sour cream with the addition of chopped garlic or onion;
- grated potatoes (or add small slices);
- a paste of purified glycerin and turmeric powder;
- sea buckthorn oil.
It is also recommended to drink more fresh fruit juices, give up carbonated drinks, and chew basil leaves.
If treatment with traditional methods does not produce a noticeable result, you must consult a doctor to clarify the diagnosis and prescribe specific treatment.
Use of medications
Drug treatment of mouth ulcers can be local and systemic:
- rinsing with antiseptics: sodium bicarbonate solution, chlorhexidine, rivanol 0.1%;
- cauterization with hydrogen peroxide, chlorhexidine, furatsilin solution, with caution - brilliant green;
- lubrication with a solution of dexamethasone (an anti-inflammatory steroid drug), gel with lidocaine (anesthetic), trypsin or chymotrypsin (enzymes with anti-inflammatory and decongestant effects);
- applying tampons soaked in the following composition: dexamethasone - 1 ampoule, vitamin B12 - 2 ampoules, nystatin - 2 tablets;
- orally - take antihistamines, desensitizing drugs, for severe pain - painkillers;
- if the ulcers are caused by the herpes virus - antiviral drugs, for example, acyclovir tablets;
- vitamin therapy , especially vitamins C and P.
Treatment
The therapeutic effect is carried out comprehensively and depends on the type and severity of the disease, as well as the main cause that caused the appearance of ulcers. In the case of a dental nature of the problem, the main bias is towards restoring the health of teeth, gums and mucous membranes.
Then measures are taken to eliminate secondary infection.
If the disorders appear as a result of previous diseases, then first of all you need to eliminate the source, and then the symptoms. Treatment is divided into medicinal and preventive (folk remedies).
All medications and methods of alternative treatment must be agreed with a doctor. The medications are taken according to an individually selected regimen and in a dosage suitable for a particular person.
Medication
To reduce the intensity of symptoms and prevent symptomatic manifestations, doctors prescribe medications.
Medicines used to get rid of mouth ulcers include:
- antiseptic and painkillers - Lidocaine, Anestezin;
The dosage and frequency of administration are calculated individually.
- rinses to remove pieces of food;
- creams and ointments to relieve inflammatory processes - Cholisal, Kamistad;
- antiviral and antifungal agents – Acyclovir;
- antiallergenic – Suprastin;
- healing agents – Sea buckthorn oil, Solcoseryl;
- immunomodulators – Remantadine, Ingaverin, Immunal.
It is also very important to observe good oral hygiene when taking medications.
Dietary restrictions will help speed up the healing process - you should avoid hot dishes, spicy or very salty foods. You should avoid solid foods (crackers, smoked meats). It is best to eat food warm, giving preference to pureed dishes.
Home Remedies
Traditional recipes are a mandatory part of the recovery program.
Existing recipes allow you to quickly relieve pain and inflammation, enhance the effectiveness of medications and carry out a preventive effect after completing a course of medication. An infusion made from chamomile (10 g of the plant per 1 glass of boiling water) helps eliminate discomfort. Before use, it should be passed through gauze, cooled, and then rinsed 4 times a day or after each meal.
A decoction made from crushed burdock root works well in relieving inflammation. 20 g of the plant will need to be poured with 2 cups of boiling water, cook for 40 minutes, leave (also 40 minutes), strain. Rinse 2 times a day after meals.
If the inflammatory processes are mild, then rinsing can be done with soda or saline solutions. For 1 glass of warm water you will need to use 1 tablespoon of salt or soda. The selected component must be completely dissolved and rinsed 2 times a day.
Before using herbal components in treatment, you will need to consult a doctor, since herbs can cause an allergic reaction.
Prevention
A diet rich in vitamins and minerals, avoiding vitamin deficiency, strengthening the immune system, timely treatment of gastrointestinal diseases, nervous system disorders, and infectious diseases play a significant role in the prevention of the formation of mouth ulcers. The following factors are especially important:
- maintaining oral hygiene, independent and professional;
- regular and timely dental treatment by a qualified dentist;
- avoiding injuries to the oral mucosa (giving up bad habits, carefully selecting a toothbrush, minimal consumption of spicy, sour, excessively hot foods).
Ulcers on the oral mucosa are caused by various diseases, dental and general, as well as injuries.
Traumatic ulcers can heal without treatment if their cause is eliminated, since the oral mucosa regenerates quite quickly, but this process can be accelerated with the help of folk remedies and medications.
Ulcers caused by an infectious disease must be treated, and in addition to local effects on the affected mucosa, systemic treatment of the infection is required. Treatment of stomatitis, erosions and ulcers in the oral cavity is a protracted process that requires the systematic implementation of all doctor’s instructions.
Video: how to treat mouth ulcers
Causes
Mouth ulcers appear in half of HIV-infected patients, but don’t panic right away; there are a number of other reasons for their formation:
- inappropriate oral hygiene;
- acute lack of vitamins in the body;
- infectious or fungal disease;
- side effect from taking medications;
- failure of normal blood circulation;
- diabetes, heartburn and other chronic diseases;
- regular stressful situations.
Sores can be of various shapes and sizes as shown in the photo.
Although their dimensions do not in any way affect the need for timely treatment. Unfortunately, medicine cannot yet name the first symptoms of mouth ulcers. In most cases, wounds appear unexpectedly. But it is always important to remember that the first signs of damage to the intact mucous membrane are a sign for immediate treatment. You should not wait until the mouth ulcers heal on their own, as it is possible that they will appear again soon.
If the wound does not go away for a long time, you should consult a doctor , as the formation may turn out to be malignant. Although a cancerous mouth ulcer is not particularly life-threatening, it is important to treat it or remove it in the early stages, otherwise the disease can worsen and cause considerable problems.
Wounds on a child
When treating ulcers in a child, dentists resort to more gentle drugs, which is explained by the high susceptibility of the child’s body.
For this reason, the use of alcohol tinctures for rinsing the mouth and treating wounds is unacceptable. It is better to pay attention to soda-salt solutions and carefully strained decoctions of medicinal plants.
When applying ointments locally, it is necessary to numb the treated area using lidocaine-based gels. To treat ulcers caused by candidiasis, which often occurs in childhood, the use of antifungal drugs such as Nystatin is acceptable.
In addition to local therapy, it is necessary to take measures to increase the child’s immunity.
What are the causes of increased salivation in women and how to eliminate the problem? In this publication we will tell you whether stomatitis is contagious when kissing.
Follow the link https://dentist-pro.ru/lechenie/bolezni-polosti-rta/mukozit-slizistoj-obolochki.html if you are interested in the causes of mucositis and methods of its treatment.
Reviews
Oral ulcers may indicate the presence of many dental or other diseases of the body.
It is worth understanding that, despite the imaginary harmlessness, these formations can lead to serious consequences in the absence of timely treatment.
If you have had to deal with ulcers that have formed on the mucous membrane of your mouth, share your methods of getting rid of them in the comments section.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Recurrent necrotizing peryadenitis
Recurrent necrotizing peryadenitis is also called Setton's aphthae. Its symptoms are:
- Seals appear in the submucosa of the oral cavity;
- Instead of compactions, ulcers with raised edges develop over time;
- The ulcers become inflamed, causing blood and lymphatic discharge.
Places where such afts accumulate are the upper and lower lips, cheeks and sides of the tongue. The pathology is characterized by extremely severe pain. Patients find it so difficult to eat that many give up eating completely. Difficulties also arise during conversation. The healing process of aphthae lasts a long time - sometimes up to several months, and the pathology itself persists for up to several years.
Diet
Since stomatitis provokes severe irritation of the oral mucosa, eating any food can cause quite severe pain. Therefore, patients are prescribed a special diet to speed up recovery. Basic principles of nutrition:
- Limiting sweets in the diet to reduce the severity of symptoms and speed up recovery.
- Refusal of sour, spicy, spicy foods.
- Exclusion of chocolate , cocoa-containing products, coffee.
- Eating warm foods and drinks (too cold or too hot can cause severe pain).
- Temporary exclusion of bread from the diet (especially coarse, dry bread).
If possible, food should be liquid. To strengthen the body's defenses, you can take vitamin complexes. For stomatitis, yoghurt and cottage cheese without additives, non-sour fruits, vegetable juices, milk, kefir, low-fat soups, broths, boiled meat, soft cheeses, herbal teas, currant and blueberry juices (but not very concentrated), jellies, puddings, souffles are indicated. .
Diagnostics
At the first symptoms, you should seek an initial consultation with a dentist. You may also need to consult the following specialists:
- infectious disease specialist;
- oncologist;
- gastroenterologist;
- dermatovenerologist.
First of all, a physical examination of the patient is carried out with the collection of a personal history and a complete clinical picture. To clarify the diagnosis, the following laboratory research methods may be prescribed:
- UAC and BAC;
- tumor marker test;
- STD test;
- scraping the mucous membrane of the affected area for microscopic examination;
- allergen test.
In some cases, instrumental examination methods may be necessary.
How to deal with relapses
Why do mouth ulcers occur? Causes and treatment, photos of the affected areas - all this was presented in this article. However, often the disease, even after a full course of treatment, can manifest itself repeatedly. To minimize the likelihood of exacerbations, it is recommended to regularly monitor the condition of your oral cavity. Try to visit the dentist's office in a timely manner, pay maximum attention to oral hygiene, and choose the right toothpaste and brush. When brushing your teeth, try not to make sudden movements, as this can lead to injury to the mucous membranes.
It is also better to avoid eating foods that irritate your stomach. Try to add as many foods rich in nutrients and vitamins to your diet as possible.
conclusions
- Ulcerative stomatitis is a painful form of the disease, which can be a symptom of other pathologies or an independent problem.
- Diagnostic methods - examination, blood tests, culture. It is important to distinguish ulcerative stomatitis from other diseases with similar symptoms.
- Treatment is medication, folk remedies, physiotherapy. It is possible to combine these techniques.
- Without treatment, serious complications can develop, including inflammation of the middle ear.
This link will tell you how to relieve toothache during pregnancy.