Answers to basic questions
The main questions that worry women and to which you need to know the answers so as not to miss a serious illness or complication.
When to call a doctor
You should call an ambulance in case of sharp, sudden, throbbing pain, accompanied by nausea, vomiting, fever, and general weakness. With these symptoms, the patient requires mandatory hospitalization.
If there is throbbing pain on the side of the left or right ovary, this may indicate torsion of the cyst stalk.
An increase in temperature, spotting, pulsation in the lower abdomen after hysteroscopy or ablation (curettage) of the uterine mucosa requires immediate medical intervention.
There is throbbing pain, nausea, vomiting, abdominal tension, bleeding - the main symptoms of a ruptured tube during an ectopic pregnancy, spontaneous miscarriage (abortion), ruptured appendix - you urgently need to call an ambulance.
Important: Such conditions, which doctors call “acute abdomen,” are dangerous to health and life. Therefore, you should not hesitate to see a doctor.
Pulsation radiating into the leg is a consequence of diseases such as complications of a hernia, femoral or inguinal, purulent inflammation of the appendages, acute appendicitis. The best decision is to call an ambulance for immediate hospitalization.
Which doctor should I contact for pain in the ovary?
If you experience mild pain that does not require urgent medical intervention, you need to make an appointment with your local gynecologist and undergo an examination. If there is an assumption that the symptoms are caused by other concomitant pathologies, the doctor will prescribe consultations with the appropriate specialists.
What tests can doctors prescribe for pain in the ovary?
The list of studies depends on the presumptive diagnosis, the possibilities of outpatient or inpatient treatment.
Main research:
- general or detailed blood and urine tests;
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs;
- intravaginal gynecological examination.
If infectious inflammation of the reproductive organs is suspected, vaginal smears or bacterial culture of microflora, sexually transmitted infections (mycoplasma, chlamydia, ureaplasma, gardnerella, gonococcus, candida) are prescribed.
If syphilis or HIV is suspected, an appropriate venous blood test is prescribed.
To identify endocrine disorders of the reproductive glands, blood tests are prescribed for the following hormones:
- LH – luteinizing;
- FSH – follicle stimulating;
- testosterone, estrogen, prolactin, progesterone;
- TSH – thyroid stimulating;
- SHBG – sex hormone binding globulin;
- DEA-S04 – dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate.
If a thyroid disease is suspected, additional tests for hormone levels are prescribed:
- T4-thyroxine;
- T3 – triiodothyronine;
- AT-TPO and AT-TG – antibodies to thyroid peroxidase and thyroglobulin.
Where are the ovaries located in women?
The ovaries are projected onto the anterior surface of the abdominal wall exactly in the lower abdomen above the inguinal folds; it is in this place that pain is felt in the event of pathology on the part of the ovaries.
Age-related changes in the ovaries
But not only the size of the ovary depends on age. The location of the ovaries also correlates with this factor. In nulliparous women, the length of the ovary is located vertically when the woman is standing. In those who have given birth, it is slightly shifted at an angle relative to the vertical axis.
Where do the ovaries hurt?
- the pain is localized in the suprapubic region, radiating to the lower back, buttocks and groin;
- with unilateral damage to the ovary, pain occurs predominantly on the affected side;
- characteristically in the place where the woman has the ovaries, a gradual increase in pain;
- the pain is not constant;
- Unlike other signs of an “acute abdomen”, agitated, restless behavior, and the search for a position that relieves pain are not typical.
Possible causes of pain
Acute pain in the area where the ovaries are located may require urgent surgical intervention, as it can be caused by life-threatening conditions such as ovarian apoplexy with intra-abdominal bleeding, torsion of the cyst stalk or its necrosis.
It's no secret that the cells necessary for conception - eggs - mature in the ovaries, so it is very important to monitor the condition of these glands. Now, knowing where the ovaries are located, you can suspect inflammatory changes in time and seek qualified medical help. And, therefore, thanks to early diagnosis and treatment, you will prevent the inflammatory process from becoming chronic.
Copying information is permitted only with a direct and indexed link to the source
https://womanadvice.ru/gde-nahodyatsya-yaichniki-u-zhenshchin
Primary diagnosis and pain relief
Pain that occurs once, or its mild manifestations, often does not require medical intervention, as it is caused by natural physiological processes in the ovaries.
Recurrent pain syndromes require a thorough examination of the patient:
- external and intravaginal gynecological examination;
- Ultrasound of the reproductive organs, bladder, intestines;
- clinical and biochemical tests of blood and urine;
- diagnostic laparoscopy or puncture of the abdominal cavity followed by histological examination.
Important: In no case should you use a heating pad if you have pain, so as not to aggravate the disease. Pain can be relieved with analgesics, which are usually prescribed by a doctor, based on the individual characteristics of the body.
Why do my ovaries hurt, left or right?
Typically, pain in the ovarian area is cramping and stabbing in nature. However, based on these signs, it is impossible to accurately determine that it is the ovaries that are hurting. After all, inflammation of appendicitis, kidney disease and digestive system have the same expression. Therefore, you should not diagnose yourself; you can see a gynecologist at our medical center in Moscow.
In some cases, the pain may be periodic. In this case, the pain manifests itself either in the lower abdomen, then in the kidney area or in the pubic area. At times you may experience leg cramps. Pain in the left ovary is rare and mainly indicates a harmful external influence. If there is pain in the left ovary, most likely it is due to the medications you are taking.
Pain in this area indicates problems with the reproductive system or hormonal phenomena. Both types of illness can lead to complications, so you should not delay the examination. Only an experienced doctor will be able to accurately determine the disease and say exactly why the ovaries hurt.
Pain whose causes require treatment
If you experience severe, prolonged, sharp pain, you should not self-medicate; you should definitely consult a doctor. The following diseases require competent medical treatment:
- inflammatory diseases of female organs;
- benign or malignant tumors;
- cysts, endometriosis;
- miscarriages, ectopic pregnancy;
- concomitant diseases that cause pain in the gonads.
With an ovarian cyst
The pain, depending on the type of cyst and its progression, is of a different nature and appears at different times. May occur during sexual intercourse or physical activity. When the leg is twisted or an ovarian cyst ruptures, paroxysmal, severe pain occurs.
The patient is concerned about:
- heaviness, feeling of fullness;
- aching pain in the lower abdomen, perineum, radiating to the lower back, sacrum, rectum;
- menstrual irregularities;
- bloody, spotting discharge;
- difficulty urinating, with frequent urge;
- nausea, fever, fainting.
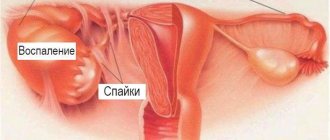
Painful symptoms are caused by gynecological diseases such as adnexitis, salpingoophoritis (simultaneous inflammation of the ovaries and fallopian tubes), apoplexy (rupture of ovarian tissue), polycystic disease, and ovarian endometriosis.
Untreated, neglected cysts lead to serious complications - their ruptures, pedicle torsion, development of tumors, infertility, adhesions. Women undergoing IVF may develop ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome, associated with an excessive amount of medications that increase ovulation.
To avoid these complications, doctors, based on the type of cyst or cystic formation, prescribe medication or surgical treatment. One of the treatment methods that is not often used is puncture, which removes aspirate (contents) from the cystic ovarian cavity.
Related to the menstrual cycle
Ovulatory syndrome - pain in the ovaries before menstruation, after ovulation, is often associated with an insufficiently mature corpus luteum. In this case, partial detachment of the uterine epithelium occurs, which causes discomfort.
The period during which the egg leaves the follicle is characterized by micro-tears of the membrane and micro-hemorrhages. This period occurs during ovulation in the middle of the monthly cycle and is also characterized by a slight pain syndrome. Pain usually occurs on the side on which the egg matures. The occurrence of severe, sudden pain may be a signal of ovarian rupture. And in this case, immediate medical assistance cannot be avoided.
Where are the ovaries located in women?
First, let's define what ovaries are. The ovary is the female reproductive gland, which is a paired organ, which is located in the pelvic cavity. It is in the ovaries that every menstrual cycle the formation and maturation of eggs (female reproductive cells) occurs, and if fertilization does not occur, after menstruation the egg matures again in the ovaries. In addition, the organ produces hormones that are responsible for a woman’s well-being and health, affecting her physique, the beauty of her hair and body. This once again emphasizes their importance in a woman’s body.
Ovaries #8212; where life begins
A woman's ovaries are located in the pelvis, on the sides of the uterus and are connected to the uterus by ligaments.
- pain in the pubic area, lower back, groin;
- pain on one side (in the area of the inflamed ovary);
- gradually increasing pain;
- the pain is not constant.
Severe pain in the ovaries may require surgery and be life-threatening for the woman. That is why it is necessary to immediately seek advice from a specialist.
Also, quite often, pain in the ovaries occurs in women at the time of ovulation. This happens because the ovarian membrane has too dense a structure, and the gland is injured when the egg is released.
Normal ovarian size
The size of the ovaries can be determined using an ultrasound examination. The normal dimensions of the ovaries are: length from 20 to 40 mm, width from 15 to 25 mm and thickness from 15 to 25 mm. Usually the right ovary is slightly larger than the left and this is considered an acceptable norm.
Knowing where the ovaries are located and what their normal size is, as well as regularly visiting the doctor, a woman can be calm about her health and the health of her future children.
Where is the appendix located?
see also
Natural causes of ovarian pain
It is not necessary that a certain pathology be present in the body if there is pain in the lower abdomen. During the week before menstruation, a feeling of discomfort in most women is considered normal. At the same time, the ovary hurts before menstruation. This is a manifestation of natural physiological processes. In addition, the ovary hurts during menstruation for the same reasons.
Another category of natural causes of pain in the lower abdomen is associated with the natural expansion of the uterus and the accumulation of yellow cells due to a woman’s pregnancy. Typically, abdominal pain is felt in the first trimester. But they are not frequent or regular, but appear in isolated cases. However, during pregnancy, the fact that the ovary hurts on the right or left may be the result of some other reasons that will lead to complications and harm the woman’s body and the fetus. These include:
- inflammatory processes;
- infectious diseases;
The most dangerous form of inflammatory processes is inflammation of the ovaries themselves. This disrupts the formation of yellow bodies, which leads to underdevelopment of the fetus at the initial stage of pregnancy. In this case, the left or right ovary colitises, since the inflammation primarily affects it.