Etiology
Gastric hyperplasia develops due to unfinished treatment of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. As a result, active cell growth begins and polyps appear.
The main causes of hyperplasia:
- changes in hormonal balance, especially when the amount of estrogen is increased;
- genetic predisposition, in particular adenomatous polyposis (characteristic of polyps in the stomach) - if the pathology is diagnosed in a woman, the disease can be inherited by a daughter or granddaughter;
- long-term use of medications that can affect changes in the structure of the gastric mucosa;
- unfavorable environment - a pathological increase in the number of cells may begin.
The cause is the bacterium Helicobacter pylori and other infectious diseases.
Forecast
If a malignant tumor is not actively treated, the subsequent prognosis will be very poor. If there is no action, the patient will not live long, a maximum of 9 months.
When the pathology is revealed at stages 1-2 of development, surgical excision is performed, the patient’s condition returns to normal, and nothing threatens him.
Stage 3-4 of the disease has an uncertain prognosis due to the expansion of metastases. Here, current medicine can slow down the course of metastasis or stop it for a while. The prognosis for stage 3 cancer is quite unfavorable, the survival rate is no more than 15%.
Therefore, it is very important to recognize the disease in time, establish an accurate diagnosis, and determine a suitable treatment regimen in combination with current medications. All this will be the key to a successful recovery.
Classification
In medicine, experts distinguish between many different types of hyperplasia:
- Focal developing hyperplasia of the gastric mucosa. The first stage of development of the anomaly, when certain polyps begin to appear. Focal diagnosed hyperplasia of the stomach covers only some areas (“foci”), which is why it got its name. The lesions look like growths of various shapes and sizes, painted in a different color, so they are clearly visible during examination. Formations arise at the site of previously received damage or erosion.
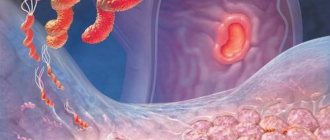
- Follicular identified gastric hyperplasia. This type of pathology is often diagnosed. Lymphatic cells begin to grow. The reasons for the development of the anomaly are different: the influence of carcinogens, hormonal imbalance, the presence of the bacterium Helicobacter pylori, stressful situations and much more. A distinctive feature of this type of disease is the formation of follicles in the stomach.
- Hyperplasia of the integumentary pitted epithelium of the stomach. A dangerous type of pathology that can contribute to the appearance of a malignant tumor in the intestine. The structure of the epithelium changes under the influence of unfavorable factors: cells grow and become larger.
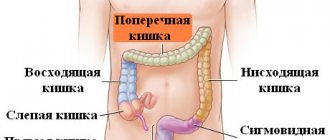
- Hyperplasia involving the antrum of the stomach. The antrum is the last part of the organ before it exits into the intestine. In this place, with the development of hyperplasia, multiple small growths, pits and ridges begin to form.
- Foveal hyperplasia of the gastric mucosa. This type of pathology is characterized by an increase in the length of the folds of the mucous membrane and an increase in their curvature. Pathology occurs due to prolonged inflammation or self-administration of anti-inflammatory drugs.
There are also other types of pathology: glandular, polypoid, lymphoid.
Varieties
Based on the intensity of the manifestation of the pathology, doctors classify and distinguish five types of damage to the gastric mucosa.
Focal hyperplasia
It begins with the formation of a single polyp; as the pathology progresses, multiple lesions appear in each part of the stomach. The “capture” area varies in shape. Diseased tissues have a dark color, which stands out noticeably against the background of healthy areas of the mucosa.
Focal hyperplasia is also called “wart” in another way . The affected area is an area of mucous membrane with clear boundaries.
Lymphoid hyperplasia
Develops as a complication of infection, inflammation of the node or peptic ulcer. Such processes activate human immunity, resulting in an increase in the number of lymphocytes. This gives impetus to the formation of atypical cells in the area of lymphatic vessels located under the epithelium. As a result, changes appear in the submucosal or muscular framework of the stomach. Due to its location, lymphoid hyperplasia is difficult to diagnose.
Foveal hyperplasia
Uncontrolled proliferation of cells in the area of folds of the mucous membrane leads to an increase in their length and a change in density. A similar phenomenon occurs after long-term use of non-steroidal drugs or against the background of a long course of gastritis.
In the initial stages it does not manifest itself in any way; the disease is discovered accidentally during a routine endoscopic examination. Doctors pay attention to the fact that foveal hyperplasia gives impetus to the development of hyperplastic polit. That’s why it has a second name: “regenerative”.
Symptoms
In the first stages of the development of the disease, it is very difficult to identify the pathology, because there are practically no symptoms: an increase in the number of cells does not cause discomfort to a person, there is no pain even when small polyps appear. When they increase, difficulties begin with the passage of food, which can cause severe bleeding or pain.
As the disease progresses, disruptions in the functioning of the stomach begin, and these are problems with digestion. The following symptoms begin to appear:
- constant or short-term pain that occurs after eating, sometimes during prolonged fasting;
- heartburn;
- flatulence and constipation;
- sour belching;
- nausea and vomiting;
- refusal to eat;
- general weakness, body aches, dizziness;
- anemia.
If such symptoms occur, you should consult your doctor so that the doctor can prescribe an examination.
Symptoms of Barrett's esophagus
As mentioned, Barrett's esophagus is a virtually asymptomatic disease. However, this is accompanied by a characteristic clinical picture of gastroesophageal reflux; the following symptoms and signs attract attention:
- Pain in the chest area, just above the mouth of the stomach, this symptom, in some cases, is confused with a sign of myocardial infarction.
- Cough without sputum due to irritation of the upper respiratory tract when regurgitating acids.
- Hoarseness caused by irritation of the vocal cords from regurgitation of acids.
- Difficulty and pain when swallowing (odynophagia).
- Heartburn.
- Vomiting with traces of blood.
- Black stools indicating bleeding from the digestive tract.
Diagnostics
During the examination, the medical officer collects the patient’s medical history and clarifies the complaints. It is impossible to establish a correct diagnosis using these data alone. Other studies are prescribed:
- gastroscopy - using an endoscope tube inserted into the stomach, the walls of the organ and polyps are examined;
- biopsy - a histological examination will establish an accurate diagnosis; using the procedure, the type of pathology and the main cause of the development of the anomaly are determined.
After an accurate diagnosis is made, effective treatment is prescribed.
Diagnosis of Barrett's esophagus - endoscopic examination
Diagnosis is carried out using a special endoscopic examination of the upper tract of the stomach. The study involves inserting an endoscope through the mouth into the esophagus, which has a light bulb and a miniature video camera on top.
Through a video camera, an image of the epithelium that covers the inner walls of the esophagus is displayed on an external screen. Under normal conditions, the epithelium is pale pink and shiny in color. In case of illness, the epithelium becomes red or scarlet and velvety.
The endoscope also allows you to obtain tissue samples. Its collection is carried out at several points in suspicious areas. The samples are further examined under an electron microscope, which allows the cell mutations to be assessed, as well as the degree of dysplasia, which is a sign of possible cancerous proliferation.
Can be found:
- Intestinal metaplasia without dysplasia. In some areas, the esophageal epithelium has undergone genetic modification, in particular replacement with duodenal cells. All this gives the affected area a red color and a velvety surface.
- Low dysplasia. Less than 50% of the cells adopted the new organization and shape. The rate of cell growth increases. The cells are modified, however, and are contained only in the epithelium.
- High grade dysplasia. Abnormal cells exceed 50% of the total. Their organization is very different from the physiological one, and the growth rate increases significantly. Abnormal cells are still contained in the epithelial layer.
Of course, high-grade dysplasia, as the closest thing to tumor degeneration, requires rapid treatment.
Treatment
Gastric hyperplasia is treated by a gastroenterologist. If necessary, the patient may be scheduled for a consultation with an oncologist or surgeon. Surgery is performed only in extreme cases; usually the treatment regimen is limited to taking medications.
- Drug therapy. Treatment of gastric hyperplasia is aimed at eliminating the underlying cause of the pathology. If the anomaly has developed due to a bacterial infection in the body, the person is prescribed antibacterial drugs. To protect the mucous membrane, the doctor prescribes gastroprotectors. A gastroenterologist may prescribe medications to reduce acidity if the patient's test results show an elevated pH. The doctor prescribes hormonal medications when the disease is associated with hormonal imbalances.
- Carrying out surgery. If too many polyps of a significant size appear, the growths may need to be removed. Usually limited to endoscopic polypectomy. In severe cases, open gastric surgery is performed or part of the stomach is removed.
- Diet. The patient must adhere to dietary nutrition. You can only eat food that does not harm the mucous membrane. The menu will depend on the primary disease that caused the pathology. Fractional nutrition is suitable for any patient with such a deviation, regardless of the cause of the development of the anomaly. There should be up to 5 meals per day, small portions. List of products whose consumption is not recommended: alcohol, strong tea, coffee, carbonated drinks. Lean fish and meat, cereals are useful. It is better to cook if the food is steamed, stewed or boiled. Fried and spicy foods should be excluded from the diet. Hot dishes cannot be eaten. A strict diet will help you recover faster.
- Traditional medicine recipes. Can only be used in combination with traditional medicine after consultation with a doctor.
Causes of the disease
In most cases, hyperplasia appears because the patient has not completed treatment for any disease, such as stomach ulcers, gastritis or other inflammations. This leads to active cell division, which contributes to the formation of polyps. The bacterium Helicobacter pillory can also provoke these changes. Sometimes pathology appears due to various infectious diseases. But these are not the only reasons for the appearance of hyperpasia; there are others:
- disruption of the patient’s hormonal levels, for example, excess estrogen;
- heredity, so if a woman has adenomatous polyposis, her daughter or granddaughter can inherit it; with this disease, polyps also form in the human stomach;
- the patient has been taking certain medications for a long time, which damage the walls of the stomach;
- carcinogens have entered the body, which also contribute to the growth of the gastric epithelium.
Prevention
Basic preventive measures for hyperplasia:
- healthy and balanced diet;
- active lifestyle;
- rejection of bad habits;
- use of medications only as prescribed by a doctor;
- regular preventive examinations;
- urgent treatment of gastric diseases.
Depending on the area of intestinal damage, the gastroenterologist will recommend individual methods of prevention to the person. Self-medication is excluded - you need to consult a doctor at the first symptoms of pathology.
Hyperplastic antral gastritis: how dangerous is pathological proliferation of the mucous membrane?
Hyperplastic gastritis is a lesion of the stomach, in which increased proliferation of the mucosal epithelium occurs, thick folds and polyps are formed. The antrum is most often affected. The pathology is of a secondary type, developing against the background of other processes. Antral gastritis with hyperplasia of the lining membranes accounts for about 5% of the total number of gastrointestinal diseases.
The structure of the stomach and the location of the antrum
Risk factors
Cylindrical cell metaplasia of the esophagus occurs under the influence of the same provoking factors that lead to the appearance of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Experts identify the following risk factors:
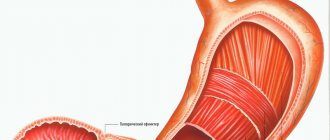
- Decreased tone of the esophageal sphincter in the lower part. This occurs due to insufficient innervation, when the sphincter does not compress tightly and gastric juice is thrown back into the esophagus.
- Changes in the structure of the congenital type. Under the influence of genetic factors, the diameter of the lower part of the esophageal sphincter increases or decreases.
- Previously experienced inflammatory processes. Localized in the lower part of the esophagus, such processes provoke the appearance of scars in the organ and lead to incomplete compression of the sphincter.
- Varicose veins in severe form. In this case, it is the nodes formed during varicose veins that prevent the sphincter from completely closing.
- Disorder of the motor-evacuation function of the stomach and esophagus. Against the background of such a disorder, antiperistalsis is observed, when the walls of the organs begin to move, leading to the movement of food masses into the upper parts of the esophagus.
The listed factors can provoke the appearance of gastroesophageal reflux, which in turn can cause erosive type gastritis, which later develops into gastric and intestinal metaplasia of the esophagus.
Etiology
A common cause of mucosal damage is atrophic gastritis of autoimmune origin. The body produces antibodies to parietal cells, which is accompanied by their death and atrophy of the mucous membrane (SM). At the same time, hyperplasia of the lymphoid intramural tissue occurs.
In addition to the above, the following diseases and conditions cause the growth of CO:
- Menetrier's disease (giant hypertrophic gastritis) - an increase in the thickness of the inner layers of the stomach up to 2-3 cm.
- Zollinger-Ellison syndrome - gastrin production due to hormone-producing pancreatic tumors.
- Hypertrophic hypersecretory gastropathy - glandular hyperplasia without gastrinemia. Often accompanied by peptic ulcer.
With hyperplastic processes in the antral zone, inflammatory phenomena are mild or completely absent. Changes in the thickness of CO and its cellular composition come to the fore. Like most hyperplasias, the disease in question is considered a precancerous condition.
Clinical signs and diagnosis
Hyperplastic gastritis of the antrum (HAG) differs somewhat in course depending on what kind of process is taking place.
In the atrophic form, the patient experiences the following symptoms:
- heaviness in the epigastrium after eating;
- feeling of overeating;
- decreased appetite;
- unpleasant taste in the mouth;
- dyspepsia.
Up to a certain point, the disease can be asymptomatic. GAG often develops together with thyroiditis and B12-deficiency anemia.
The hypertrophic variety manifests itself in the form of:
- aching pain in the epigastric area;
- heaviness after eating;
- diarrhea;
- vomiting.
Appetite decreases significantly, up to anorexia. The patient may lose up to 20 kg of weight in a short time. Some patients experience peripheral edema. The reason for this phenomenon is the loss of a large amount of protein with gastric secretions due to insufficient absorption from food. Erosions may form.
The main diagnostic method is FGDS (fibrogastroduodenoscopy). With Ménétrier's disease, gigantic folds are found in the stomach, which outwardly resemble the convolutions of the brain. There are erosions and a large amount of mucus. SO atrophy is characterized by its pallor, smoothness, and visual decrease in volume. Hyperplastic processes at the initial stage occur in the depths of the outer layer. During the study, tissue is taken for biopsy.
Note: The examination of a biopsy specimen is considered reliable only if all layers of the mucous membrane and a plate of muscle tissue are present. Otherwise, it is impossible to speak unequivocally about the absence of hyperplasia, even if there are no visual signs of it.
Therapy methods
Treatment of foveal hyperplasia of the stomach should be comprehensive. Medications are required and can be combined with traditional methods. It is also necessary to adjust your diet. And if there are polyps, they may need to be surgically removed. Features of treatment depend on the severity of deformation of the gastric folds.
How to treat foveal hyperplasia of the stomach is determined by the attending physician. During therapy, the patient should refuse other medications. In particular, hyperplasia is often caused by taking NSAIDs. Therefore, such drugs must be excluded.
If the disease has developed due to Helicobacter pylori, the following medications are prescribed to destroy it:
- Antibiotics. Destroy harmful bacteria. But at the same time, they can negatively affect the microflora of the gastrointestinal tract. Therefore, after a course of antibiotics, it is necessary to take probiotics and prebiotics.
- Medicines to reduce stomach acid production. High acidity can also be one of the causes of stomach problems.
- Products with bismuth. They are antiulcer and have bactericidal properties against Helicobacter pylori.
If growths are detected, the doctor conducts additional tests to determine whether they are malignant. If there is no oncology and the tumors are small in size, surgery is not prescribed. However, the patient will need to undergo regular EGD to monitor the growth. If its size increases over time, surgery may be prescribed.
Surgery may also be required if drug therapy is ineffective. The operation can be open or endoscopic, depending on the characteristics of the disease.
For hyperplasia of the gastric epithelium of the foveolar type, traditional medicine can also be used. But they can only be used after prior consultation with your doctor. The following remedies are useful for the epithelial tissue of the stomach:
- Chamomile and peppermint decoction. You need to take 1 tsp. raw materials, pour 500 ml of boiling water. Boil for 15 minutes over low heat. Then strain. Take after diluting with water 1:3. Adding sugar and other sweeteners is not recommended.
- Ginger tea. To prepare it, you need to boil 0.5 liters of water. Add 4 cm long ginger root. Boil for 1 minute, remove from heat. Add the juice of half a lemon and a cardamom pod. Preferably taken without sugar. To improve the taste of tea, you can add a little honey, but only to a chilled drink.
- Infusion of parsley roots. To prepare it, you need 1 tbsp. crushed raw materials, pour 200 ml of boiling water. Leave until cool, then strain. Take 1 tbsp. three times a day before meals.
A decoction of chamomile and peppermint is a folk remedy for the treatment of foveal hyperplasia of the stomach.
Consultation with your doctor is mandatory. The fact is that some plants can cause allergic reactions and have a number of contraindications. Therefore, their use may not be recommended for some patients.
Treatment
Hyperplasia of the gastric antrum requires diet and pharmacological therapy. Dietary restrictions vary. In case of mucosal hypertrophy, it is recommended to eat fractionally, chemical, thermal and mechanical sparing. With the atrophic type of pathology, food should be mechanically gentle, but stimulate the secretion of gastric juice.
Drug therapy is carried out using drugs from the following groups:
- m-anticholinergics;
- proton pump inhibitors;
- means of replacement treatment for insufficiency of secretory function;
- drugs to suppress immunity in the autoimmune nature of the disease.
Severe hyperplasia with a high risk of malignancy is treated surgically. Depending on the extent of the process, complete or partial resection of the stomach is performed. Subsequently, the patient is prescribed lifelong therapy aimed at compensating for lost digestive functions.
Prognosis and prevention
Nutrition is one of the main methods of preventing gastrointestinal diseases
No specific measures have been developed to prevent membrane hyperplasia.
To reduce the chance of developing pathology, you should adhere to the general rules for the prevention of gastrointestinal diseases:
- eat in small portions;
- avoid overly spicy and rough foods;
- eat liquid hot meals daily;
- do not abuse alcohol;
- stop using toxic substances.
Might be interesting:
The prognosis of the disease is moderately favorable. In most cases, the treatment allows you to lead a full life, not counting some dietary restrictions. In the absence of therapy, the risk of developing cancer and other oncological diseases of the stomach increases significantly, which worsens the prognosis to unfavorable.
Diseases accompanied by hypertrophy of the gastric mucosa indirectly affect the patient's life expectancy. However, against their background, processes may arise that are often not amenable to even surgical treatment. Therefore, the presence of signs of gastrointestinal pathology requires contacting a medical organization for a full examination and prescribing the necessary therapy.
Diet
Treatment of hyperplasia in the stomach can be carried out with medications, diet or surgery, or traditional medicines. The basis of treatment for hyperplasia is nutrition, since poor nutrition is the most common cause of the development of the disease. It is impossible to get rid of pathology without a diet.
The diet should not contain junk food, especially those containing carcinogens or harmful fats. The mode of eating is important. You need to eat small portions (200 g) 5-6 times a day. It is better if the patient’s diet is prepared by a specialist based on blood tests. It is recommended to lead an active lifestyle.
Therapy with pharmaceuticals consists, first of all, in eliminating the causes that provoked the development of hyperplasia. Most often, hormonal therapy is prescribed, with the help of which adequate cell division is restored. If the disease is caused by Helicobacter, antiviral agents are prescribed.
If therapy does not help, another such course may be prescribed. If the patient does not feel better after the second course of treatment, the doctor may recommend surgery. If a patient is diagnosed with hyperplastic polyps (foveal type of disease), the size of which is more than 10 mm, they must be cut out, as there is a danger that they will transform into oncology. After such an operation, the surrounding tissue is taken for histological analysis.
During surgery, the polyp and tissues in which there is abnormal division at the cellular level are excised. Surgical treatment is not performed often. Most often, conservative therapy helps. Treatment is carried out until the patient fully recovers.
Hyperplasia of the gastric mucosa
Have you been struggling with GASTRITIS and ULCERS for many years without success?
“You will be amazed at how easy it is to cure gastritis and ulcers just by taking it every day.
Hyperplasia is the abnormal growth of tissue caused by accelerated cell division. A similar process can develop in almost any organ, the stomach is no exception. Let's consider gastric hyperplasia - what it is, how it is characterized and whether this pathology can be treated. In the gastric layer, it forms quite often and is considered a very dangerous process, since accelerated cell division and proliferation in many cases leads to neoplasms. In some cases, the disease is not limited to cell growth alone; structural changes occur - however, already at advanced stages.
Clinical manifestations
The insidiousness of the disease lies in the fact that in the early stages there are no expressive signs that are alarming. Most often, it is discovered accidentally during a diagnostic examination using fibrogastroduodenoscopy due to patient complaints of stomach pain.
The most striking symptoms that appear during the progression of the pathological process:
- painful sensations in the upper abdomen, occurring with varying intensity;
- a feeling of sour taste in the mouth;
- disruption of the digestive process;
- decrease in hemoglobin;
- possibility of bleeding.
Pain syndrome typically occurs at night or during a long break between meals. It may occur in the form of minor discomfort.
In the absence of timely treatment, symptoms increase, the following signs appear:
- hiccups, vomiting, nausea;
- bloating;
- loss of appetite;
- pale skin;
- decreased blood pressure;
- diarrhea;
- belching.
Most of the listed symptoms are characteristic of many diseases associated with the gastrointestinal tract. To avoid misdiagnosis, you should undergo a thorough examination and start treatment on time.
The effectiveness of the treatment course depends on this. It is much more difficult to cope with a disease in an advanced stage, when the pathological process becomes chronic.
Factors provoking the disease and symptoms of the pathology
There are many factors under the influence of which hyperplasia of the gastric mucosa can form, but most often the disease is provoked by:
- hormonal changes in the body;
- gastric pathologies that have not been fully cured;
- carcinogens that enter the stomach;
- associated bacteria;
- hereditary factors;
The particular danger of the disease is that the symptoms do not appear immediately, so that the person is not aware of the problem, while a long course transfers the pathology to the chronic stage, after which its main symptoms appear:
- headache develops;
- there is an upset stomach;
- problems arise with digestive processes;
- Signs of anemia may develop.
An examination is necessary if night pain occurs against the background of an empty stomach; they may be the initial symptoms. It is impossible to cure the pathology on your own, since therapy requires the use of complex methods. Gastritis with foci of hyperplasia is characterized by inflammatory processes in certain areas; the focal form can be provoked by stressful situations, an improperly organized diet, and an unwillingness to give up bad habits, including overeating and foods with additives that are dangerous to the body. The following symptoms occur:
- attacks of nausea leading to vomiting;
- belching with a rotten smell and heartburn;
- feeling of heaviness in the stomach after eating;
- pain in the affected area;
- bloating;
- lactose intolerance, which indicates the presence of atrophic damage to the mucous layer.
Complications
A person refuses to eat, a paroxysmal cough occurs, and tracheal perforation and fistulas with subsequent expansion into blood vessels become complications. The state of health noticeably worsens when metastases spread to the liver, pancreas, lungs, and brain.
Replacing esophageal tissue with single-layer columnar epithelium can cause a number of serious complications, including:
- Transformation of foci of metaplasia into malignant neoplasms. The most common form of esophageal cancer is adenocarcinoma.
- Hemorrhagic syndrome localized in foci of metaplasia and damage to the esophagus.
- The appearance of peptic-type strictures. These are adhesions of connective tissue that narrow the lumen of the esophagus at their location and provoke the development of dysphagia, which consists in disrupting the process of swallowing food.
To prevent such complications, it is important to diagnose metaplasia in time and receive appropriate treatment aimed at reducing the size of the lesions and their number.