“Mom, my stomach hurts!” – one of the most common complaints of children at any age. Babies who have not yet mastered speech skills express pain by crying, whining, and bending their knees to their chest. Unfortunately, often mothers, without understanding the causes of the disease, simply stuff their children with analgesics and antispasmodics.
Discomfort and pain in the abdomen are a serious signal from a fragile child’s body that it needs help. The pain can be caused by simple indigestion, or it can be one of the manifestations of a serious illness that requires prompt medical attention. Therefore, it is so important to be able to carry out an initial diagnosis in a timely manner and alleviate (and not harm!) the child’s condition before the doctors arrive.
Remember that severe abdominal pain is a reason to consult a doctor immediately!
Causes of abdominal pain and accompanying symptoms
Abdominal pain can be short-term and long-lasting, sharp and weak, in the area near the stomach or throughout the abdomen, but the main rule in this situation is that you cannot wait until the pain becomes unbearable, and unless it is heaviness from eating too much , you need to call a doctor immediately.
The most common causes of abdominal pain in a child:
- Colic
They usually affect infants up to 3-4 months old. The baby draws in his legs, starts screaming, spins and tenses. The pain is relieved by placing a heated diaper on the stomach or drinking dill water. You can try carrying the baby in a column. For particularly excruciating pain, when the child does not sleep at night, the pediatrician prescribes a special medicine. For example, Espumisan, Bobotik, Plantex. (how to help a baby with colic)
- Constipation
In this case, colic is also accompanied by bloating. Usually you can’t do without an enema (how to give an enema to a newborn baby) or a special suppository (glycerin or sea buckthorn). (constipation in a newborn - how to help)
- Crick
It manifests itself in the form of sharp and sharp pain while walking or when trying to sit up straight. It is the result of severe physical strain and sometimes appears after vomiting or severe coughing. Apart from pain, nothing bothers the child, he has a normal appetite and is in normal condition.
- Intestinal obstruction
Characteristic of infants aged 5–9 months. Requires urgent contact with a surgeon. Associated symptoms are nausea, vomiting, blood in the stool.
- Flatulence (bloating) and accumulation of gases
The child becomes capricious and nervous, sleeps poorly. During feeding, the baby may greedily grab the breast or pacifier and then suddenly spit it out. After feeding, regurgitation and belching may be observed. Quite often, flatulence is a sign of other more serious conditions.
- Worms
Usually these are roundworms. The pain is not as acute as with colic or constipation, but it appears regularly. Additional symptoms are headaches, flatulence, itching in the anus. It is a mistake to believe that grinding your teeth in a dream is associated with worms in the body.
- Intolerance to any product
Lactose intolerance (milk and dairy products) is most common in children. Malaise begins 30 - 40 minutes after consuming the product. In addition to pain, the child suffers from bloating, diarrhea, and sometimes vomiting. The pain is of the nature of colic or spasms.
- Jaundice
The disease is quite serious and contagious. Severe pain is localized in the liver area. The sclera of the child's eyes turn yellow, and the urine takes on a dark tint. The disease requires emergency medical attention. (jaundice in newborns)
- Inflammation of the testicles
Usually the child feels pain in the lower abdomen, radiating from the scrotum. Inflammation can be caused by testicular torsion, hernia, or ordinary bruise. It is important to provide qualified medical care.
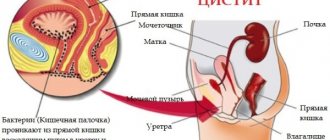
- Pyelonephritis
This disease is typical for girls. Acute and quite severe pain is localized in the lower back, side, and lower abdomen. They are usually accompanied by fever, headache, weakness, increased sweating, chills, nausea and vomiting. The disease is very serious, it is caused by inflammation of the renal pelvis. The cause may be bacteria entering the urinary system or an obstruction in the flow of urine from the kidneys. The disease can be treated with medication, but in particularly severe situations there is no other option other than surgical intervention.
- Gastroenteritis
The disease is characterized by inflammation of the lining of the stomach and small intestine caused by viruses, parasites or bacteria. The pain is paroxysmal, dull. Additional symptoms are rumbling in the stomach, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, fever. At the slightest suspicion of gastroenteritis, you should immediately consult a pediatrician.
- Appendicitis
Appendicitis is an inflammation of the appendage of the cecum, called the appendix. It usually occurs in 1 in 6 children. And until two years of age, as a rule, it does not worsen. Most often, children aged 8 to 14 years are susceptible to the disease. At first, a dull aching pain in the right or lower abdomen, loss of appetite, weakness, vomiting, and fever are typical. Then sharp cutting pains occur and perforation of the appendix wall quickly develops. All its contents pass into the peritoneum, which poses a serious risk to the child’s life. This cannot be done without urgent surgery. (appendicitis)
Symptoms for urgently calling an ambulance
- For a child under 5 years old, the pain does not go away for more than 3 hours. The baby is capricious and nervous.
- Abdominal pain is accompanied by rashes on the child’s skin or inflammation of the joints.
- Abdominal pain is accompanied by diarrhea, fever, severe nausea or persistent vomiting.
- The pain is localized in the umbilical area.
- The child refuses food and water due to abdominal pain.
- Severe abdominal pain after a fall or blow to the stomach.
- The pain is accompanied by weakness, pallor, and loss of consciousness.
- The pain occurs at night.
- Abdominal pain and lack of stool.
- Regular pain lasting more than 2 weeks.
- Frequent abdominal pain and weight loss (or developmental delays).
- Frequent pain that recurs regularly over several weeks/months (even in the absence of other symptoms).
Dr. Komarovsky tells us when a child urgently needs a doctor for abdominal pain:
Treatment recommendations
The main advice that can be given to parents if a child complains of abdominal pain is not to panic.
Minor problems such as indigestion can be treated at home with remedies from your home medicine cabinet and traditional medicine. Systematic pain is a reason to immediately consult a doctor.
Medicines for children
Self-medication for stomach pain without consulting a specialist is dangerous and can have unpredictable consequences, but it is necessary to have a supply of medicines for stomach pain in the house. If a child’s problems arise due to overeating or abuse of fast food, you can help him with the help of enzymes that improve digestion: Mezim, Festal, Creon. Almagel, Reni, Maalox, popular in pharmacies, will help with heartburn.
If painful sensations suddenly arise in a child, and the mother does not have children’s medicines on hand, No-shpa will help relieve spasms and relieve stomach pain (we recommend reading: dosage of the drug “No-shpa” for children). This remedy relieves pain caused by constipation. Absorbents that remove substances that cause intoxication from the stomach will help against food poisoning: Smecta, Polysorb, Enterosgel. Espumisan, Babynorm, Bobotik and other similar medications will relieve colic.
Before giving your child any medicine, you should carefully study the instructions and clarify the method of use and dosage appropriate to the age and weight of the patient. If possible, try to consult with a specialist.
Folk remedies for stomach pain
Fennel seeds are considered an excellent remedy for relieving abdominal pain, which has no contraindications - it can be given to a child from the first days of life. It eliminates colic and relieves spasms (we recommend reading: an effective remedy for colic and gas in newborns).
Rice water is good for solving stomach problems. To prepare it, boil 0.5 cups of rice in 6 cups of water for 20 minutes, then drain the liquid. You can drink the decoction several times a day before meals; if desired, you can add sugar or honey to it.
Mint infusion relieves spasms and has a calming effect. Mint leaves can be found at any pharmacy. A couple of teaspoons of leaves are brewed in a glass of boiling water, then filtered and drunk warm.
Stomach hurts - first aid
The good news is that quite often pain is caused by indigestion or poor diet, which is harmless and easily goes away after the causes are eliminated. If the pain becomes more and more severe and other signs characteristic of certain diseases are added to it, you should not hesitate to call a doctor.
First aid before the doctor arrives
- Unless you are a medical professional capable of making an initial diagnosis, do not give your child any medications. They can harm or “blur the picture” of the disease, which will complicate the doctor’s diagnosis;
- Do not feed your baby, but make sure your baby drinks plenty of fluids, especially if there is vomiting or diarrhea. You can drink Regidron, a self-prepared water-salt solution or still water (lemonade, juices and milk are prohibited!);
- Control the temperature. If it rises above 38 °C, you need to give the baby an antipyretic;
- It is very important not to place a heating pad or warming compress on your stomach. Heating provokes an inflammatory process and the child’s condition can sharply worsen;
- If you are sure that the cause of the pain is bloating, give the patient a medicine based on simethicone;
- Make sure your child is not constipated. Regardless of the result, an enema cannot be performed by a doctor until a professional diagnosis is performed;
- If your tummy hurts, your temperature rises, and vomiting or watery/smelly diarrhea begins, get ready to treat an intestinal infection (most often this is what is hidden under such symptoms.
Attention!
The lion's share of the most dangerous diseases, hidden under severe abdominal pain and, as a rule, requiring the intervention of a surgeon, are not accompanied by low-grade fever! Fever is usually a “companion” of infections.
If you have the slightest doubt, call a doctor - do not delay seeking qualified help. No matter what “cases” await you, no matter how afraid your child is of doctors, call an ambulance without hesitation! It's better to be safe than sorry.
What diagnostic methods can be used to determine the causes of pain?
How to support a child if he has a stomach ache? The first stage is a consultation with a pediatrician. The doctor will conduct a general examination and, if a pathology is suspected, will give a referral to specialists. You may need to consult a urologist, surgeon, or gastroenterologist. In addition to blood, urine and stool tests, they may prescribe:
- colonoscopy - examination of the large intestine; in well-equipped clinics it is possible to carry out the procedure without swallowing the “colon”;
- fibrogastroscopy - examination of internal organs using an endoscope; for young children, such diagnostics are often replaced with an X-ray of the stomach;
- Ultrasound - depending on the symptoms, the pelvic organs, liver, pancreas, bladder, kidneys, spleen are checked;
- irrigoscopy - x-ray examination of the colon;
- Magnetic resonance imaging of the abdominal cavity is prescribed when the diagnosis is unknown.
Functional pain – how to help a child?
Children between the ages of 7 and 15 often have so-called functional pain - it is essentially unclear what caused it, but its symptoms are similar to migraine. They are usually referred to as pain that is completely unrelated to surgery or infection. Even a deep examination does not find the cause of the pain, but despite this, they are not a figment of a child’s imagination, so as not to go to school or not to put away toys. Children really suffer from them.
Functional pain can be caused by:
- Overwork;
- Stress or nervous tension;
- Functional dyspepsia (stomach dysfunction, painful digestion);
- Irritable bowel syndrome (disturbance in the gastrointestinal tract without any organic causes);
- Abdominal migraine (abdominal pain accompanied by headache, pallor, nausea and vomiting) - as the child grows older, the disease develops into migraine headaches.
Functional pain is not dangerous and does not pose any health risks; over time, it stops occurring (it does not require specific treatment). However, proper care is very important for children suffering from such pain. To help ease your child's condition:
- Peace of mind and care from loved ones. Create a pleasant and comfortable atmosphere of kindness and safety for your child. Don't allow yourself to have negative emotions;
- Diet. It has been scientifically proven that introducing grains, vegetables, fresh fruits and dried fruits into the daily menu will help relieve symptoms;
- Medicines. If the pain is severe, there is no need to force the child to endure discomfort. Mild analgesics can be given: ibuprofen or paracetamol;
- Diary of illness. Recording observations will be useful for medical history and understanding “where the legs grow from.” You should record the period of pain (how long it lasts), the means of easing it (what you use to relieve it) and the situations in which the pain occurs.
Children aged 1 to 3 years
If pain occurs in the abdominal area, it is necessary to understand the cause (perhaps something new was eaten or the baby overate) and diagnose the nature of the pain.
And based on this data, give medications.
Among those recommended for children aged 2 and 3 years are Smecta , Riabal , No-shpa .
If the pain is short-term and caused by digestive problems, you can place the child on his back and stroke his stomach in a clockwise direction, thus reducing pain using circular movements that will help relax the intestinal muscles.
The child has a stomach ache – Dr. Komarovsky’s School
Abdominal pain sooner or later, often or rarely, but occurs in any child. And parents are faced with the question: is it dangerous or not, what to do about it; When should you see a doctor immediately, and when can you wait? TV presenter Yanina Sokolova is no exception; she is also very concerned about these questions, and she came to Dr. Komarovsky to understand this topic:
https://youtu.be/X9E_5wkywVE
Do you want to be the first to read our materials? Subscribe to our telegram channel, Facebook page, or VKontakte group.
We are at Yandex.Zen - join us!
Symptoms of stomach pain
The symptoms of many diseases of the stomach and other gastrointestinal tract organs are similar to each other, therefore, a diagnosis cannot be made based only on an oral interview with the child. Mostly children complain about:
- abdominal pain of various types: cutting, aching, cramping, dull, stabbing;
- feeling unwell: chills, fever, weakness;
- diarrhea, constipation, nausea, vomiting;
- headache.
Complaints about one or more of these symptoms should be a signal for parents to pay attention to the child's health. It is important to understand what to do next, how to help him and prevent relapse of the disease.