15015
Sweating is a completely normal process. It provides thermoregulation of the body, and also participates in acid-base metabolism, removal of toxins and protection against the penetration of bacteria. However, traces of sweat on clothes and its smell are unlikely to please anyone. We use antiperspirants, creams and other methods to hide all visible manifestations of this physiological process. But, unfortunately, not all people succeed 100%. This is due to severe sweating of the armpits. This situation especially causes women a lot of physical and moral discomfort. And to solve this problem, you need to understand its causes.
Endocrine diseases
Almost always, malfunctions of the endocrine glands are accompanied by hyperhidrosis, because this is one of the basic signs that something is wrong with the regulation of the body. And the body is regulated by those same hormones, and when there are too many or too few of them, the body “goes crazy.”
The most common endocrine diseases include:
- Hyperthyroidism is overproduction of the thyroid gland. With it, severe sweating appears as a symptom, but the problems do not end there. A goiter is palpated on the neck - an enlarged thyroid gland. The eyes are very bulging, the person constantly feels hot, the person becomes emotionally unstable, and loses weight. The whole body usually sweats heavily.
- Diabetes . It is caused either by the death of beta cells of the pancreas that produce insulin (the first type), or by the development of insulin insensitivity in the body tissues (the second). With diabetes, the upper half of the body sweats heavily, while the lower half suffers from dryness. You should think about diabetes if you start drinking a lot, you constantly need to go to the toilet, your mouth is dry, you experience weakness, and an aversion to sweets.
- Obesity . Adipose tissue itself produces hormones, in particular estrogens, which is why obese men often have problems with sweating. Sweating in obesity is associated with a large number of skin folds where air does not enter and where moisture does not evaporate.
- Pheochromocytoma is a tumor of the chromaffin layer of the adrenal glands. It is characterized by attacks of sudden releases of stress hormones into the blood, which is manifested by panic attacks - heavy sweating at night, tachycardia, a lump in the throat, noise in the head, and a feeling of fear.
- Women during menopause also often suffer from excessive sweating.
Women sweat more often than men when sick
Why does sweating worsen at night?
Night sweats are an unpleasant symptom that many women suffer from. It can be permanent or sudden. The physiological factors of sweating are as follows:
- overeating before bedtime (it is recommended to eat 4–6 hours before bedtime);
- low-quality bedding made from synthetic fabrics;
- hormonal changes - this could be premenstrual syndrome or menopause;
- excess weight;
- unventilated room with stale air - regular ventilation of the bedroom improves sleep.
Sweating is also affected by the flow of breast milk during lactation.
The second group that affects excessive sweating includes pathological factors. These are serious pathologies, sweating is only a symptom of disease. These include:
- hypertension or high blood pressure;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- disorders of the endocrine system, including diabetes mellitus;
- tuberculosis;
- oncological diseases.
Sweating in the morning
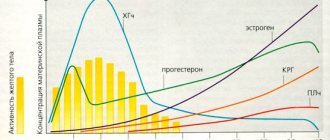
Hyperhidrosis in the morning is associated with various factors. The main reasons are hormonal disorders in the body: pregnancy, menopause, menopause, lactation, premenstrual syndrome.
Other reasons include diseases of the body systems: tuberculosis, diabetes, neurological pathologies, etc.
Infectious diseases
Almost always, with such diseases, a person begins to sweat a lot, especially the legs. This is due to an increase in temperature and then a further drop. Excessive sweating will persist for some time after the illness has passed, this is normal. Sweating not only cools, but also removes from the body the remnants of bacteria and viruses destroyed by the immune system :
- Influenza and other acute respiratory viral infections. At the very beginning of the disease, a person begins to sweat heavily due to a sharp increase in temperature, and chills occur.
- Bronchitis . It can develop as a complication of the point above or as an independent disease. The causes of excessive sweating are similar.
- Tuberculosis . It is characterized by strong and profuse sweating at night, weakness, fever, cough for more than three to four weeks.
- Brucellosis . The main reason to boil milk, especially milk bought at the market, is that a person becomes infected through it. With brucellosis, there is a long increase in temperature and sweating, including night sweating. Also with brucellosis, lymph nodes appear, the liver, musculoskeletal system, and genitals suffer.
- Malaria . Transmitted by malarial mosquitoes, which cause abundant Plasmodium falciparum. Characterized by bouts of fever and heavy sweating every one, three or four days, this is due to the peculiarities of the life activity of plasmodium.
- Septicemia is blood infection with pathogenic bacteria, staphylococci or streptococci. Accompanied by chills, rash, high fever, sweating, and there are also signs of anemia.
- Syphilis . Hyperhidrosis in syphilis is associated with the development of tabes dorsalis (more about it below).
Sweating mechanism
The physiological function of producing and removing sweat from the body performs several important tasks.
- Heat transfer during increased physical activity, which helps maintain normal body temperature.
- Psychogenic sweating occurs during moments of emotional outbursts - this is a reaction of the sweat glands to the release of adrenaline.
- Food sweating is the production of sweat when eating. It is a signal that you are taking food that makes the body work harder. For example, alcohol and hot spices increase sweat production.
- Removal of toxins. This is especially important in case of illness. Recovery from any disease is accelerated if the sweat glands work in an enhanced mode.
- Maintaining water balance involves removing excess moisture.
In general, all these factors indicate that sweating is a condition for the normalization of metabolic processes in the body. Normally, a person produces 650-700 ml of sweat per day. For people living in the tropics, the amount can be 12 liters. With heavy sweating in normal climatic conditions, a person produces a maximum of 3 liters of sweat.
This is interesting! Women sweat twice as much as men. This pattern is an evolutionary feature of the development of sexes. Male and female physical activity varies in almost the same ratio, so the body produces less sweat.
But excessive sweating is more common in women than in the stronger sex. Medical statistics prove this. Doctors say that this fact is associated with the physiological characteristics of the female body.
Nervous system diseases
Among the diseases of the nervous system that lead to excessive sweating are:
- Parkinson's disease . Damage to the central nervous system leads to malfunction of sympathetic fibers, resulting in the development of hyperhidrosis of the face and scalp.
- Tabes dorsalis . It is a sign of advanced syphilis, which has developed into neurosyphilis. Characterized by the death of nerve pathways in the spinal cord. The patient loses vibration and temperature sensitivity, and gait is impaired. The disease may be accompanied by severe sweating throughout the body, as well as anemia.
- Stroke . A stroke is a rupture of blood vessels in the brain and compression of brain tissue by a hematoma. The body's temperature control center or the nucleus of the sympathetic nervous system may also be affected, leading to a feeling of heat and bouts of sweating.
Sweating may occur in diseases of the nervous system
Intimate areas sweat
When increased sweating occurs in women in intimate places, the causes of this unpleasant condition are often triggered by certain diseases in the acute stage.
Cause hyperhidrosis of the intimate areas:
- pathologies of the endocrine system;
- head injuries (craniocerebral pathologies).
An unpleasant odor of sweat may appear in intimate areas before the onset of menstruation. Women who are overweight also often notice increased sweating in their intimate areas.
In addition, increased sweating in girls in intimate places can be caused by wearing synthetic underwear, increased physical activity, general weakness of the body, as well as impaired thermoregulation of the body.
Malignant tumors
Excessive sweating and high temperature cause signs of the so-called paraneoplastic syndrome, poisoning of the body with tumor decay products (in tumors the intensity of cell death is several times higher than in healthy tissues, however, the rate of their reproduction is orders of magnitude higher, so the tumor grows despite that) and the toxins they produce.
- Hodgkin's disease, or lymphogranulomatosis.
- Non-Hodgkin's lymphomas.
Both are tumors of the lymphatic tissue, accompanied by night sweats and enlarged lymph nodes.
Armpits sweat
The condition when armpits sweat is familiar to any woman. Increased sweating in this part of the body is constant and does not depend on the time of year or on body temperature conditions. Why does women sweat profusely in the armpits?
The main causes of armpit hyperhidrosis are:
- lack of regular and high-quality body hygiene;
- wearing clothes made of synthetic materials;
- hormonal imbalance (menopause, pregnancy, menstruation);
- thyroid diseases;
- pathologies of a rheumatoid nature;
- tuberculosis;
- oncology;
- nervous disorders;
- intoxication (poisoning) of the body.
Abstinence
In people dependent on drugs or various psychoactive substances, when they are withdrawn, the functioning of the autonomic nervous system is disrupted. There are usually no real threats during withdrawal, but this does not help in any way to reduce suffering. Severe hyperhidrosis during withdrawal is associated with a restructuring of the body’s biochemical background: during use, the substance has managed to become involved in metabolic processes, and it takes time for them to return to normal.
At the first symptoms, we recommend that you immediately go to the hospital
Treatment
When a woman suffers from excessive sweating, treatment and the causes of this condition are always interrelated. When sweat appears as a secondary disease, it is necessary to first cure the underlying pathology.
Each patient is prescribed individual treatment, it depends on her age, concomitant pathologies and the general physiological state of the body.
Treatment of excessive sweating in women has the following scheme:
- medications - sedatives to normalize the functioning of the nervous system;
- physiotherapy - iontophoresis to normalize the functioning of the sweat glands;
- Botox - treatment of hyperhidrosis and control of the functionality of the sweat glands;
- sympathectomy - compresses the nerve and blocks sweating.
Nervous overstrain
Stress that a person cannot cope with leads to depression or anxiety disorders. Sweating with them is associated with temporary psychosomatic factors; this is a kind of protective reaction of the body, which believes that something is threatening it and activates the stress mechanisms of the sympathetic system. In this case, the person needs to consult a psychotherapist.
Cognitive behavioral therapy has shown good effectiveness, based not on digging into the depths of the psyche, like Freudian psychoanalysis, but on teaching a person to manage his reactions here and now.
How to get rid
The problem has a complex treatment algorithm. Some forms, for example, hereditary hyperhidrosis, are not amenable to therapeutic methods, so women have to live with it and try to minimize such manifestations of the disease as constant moisture in the body or certain areas and an unpleasant odor. Therapy for sweating is undesirable during pregnancy, so it has to be eliminated using traditional methods. In any case, you need to get rid of the problem, since it can give rise to other ailments, for example, fungus, skin irritations, external and internal inflammatory processes.
Traditional methods
They include the use of decoctions, compresses, foot and hand baths, and herbal wraps. For example, proven means are actively used that have a positive effect on the normalization of the sweat glands:
- oak bark and other natural raw materials with tanning properties - infusions are made on their basis and used as a means to care for sweaty areas of the body;
- lemon and juice from it, adding slices to water helps in getting rid of sweating in sensitive areas - the solution is used to wipe off problem areas;
- infusions of birch buds, lemon balm and mint, sage and nettle give a good effect - they can be combined or used separately;
- treating problem areas with water and apple or wine vinegar in a concentration of 1 to 5 helps disinfect and reduce odor.
The recipe for herbal infusions is as follows: take 1 tbsp. l. raw materials, brew 1 liter. boiling water, simmer for 15 minutes over low heat, then settle, strain and use for procedures.
What can you buy at the pharmacy?
There are many pharmaceutical remedies against sweating. You need to choose those recommended by your doctor, because not all medications will be useful for you.
- Eltacin, Bellataminal is prescribed for stress sweating.
- Apilak is effective against sweating caused by poisoning and dysfunction of metabolic processes.
- Klimadinon, Remens are necessary for women with hot flashes during menopause.
- Hexamine and salicylic-zinc ointment treat sweating of the armpits.
- Teymurov's paste, Furacilin, is used to solve the problem of sweating feet.
- Universal sprays Formidron, Celandine-deo can be used to eliminate excessive sweating on the hands and feet.
Attention! If the cause of exaggerated sweating is tuberculosis, diabetes mellitus or HIV, then medications are needed for the disease, not for sweating, since sweating is a consequence of infectious diseases.
Therapy
Any of the diseases suspected here is a reason to consult a doctor, and quite serious. After examination and medical history, the doctor will find out the cause and prescribe adequate treatment. For tumor diseases, surgery is required; for infectious diseases, treatment with antibiotics or antivirals is required. Neurosyphilis, parkinsonism and some other diseases listed above and of which there are quite a few, are not treated; therapy is reduced to reducing suffering and improving the quality of life, as well as preventing complications.
A significant part of the diseases named in this article can occur in a latent form for almost years. Therefore, it is extremely important to be thoroughly examined if any alarming symptoms appear, as well as undergo medical examinations on time. Yes, we all know how they are carried out in the countries of the former USSR, and what kind of medicine we have, but risking your life to gain a couple of days is not the wisest decision.
When excessive sweating is normal
In some cases, sweating does not pose any threat to human life and health, because it is the norm. This is typical for the following situations:
- Intense physical activity. When the body is forced to expend a large amount of energy, body temperature increases. To prevent overheating, droplets of sweat protrude out through the pores of the skin. Thus, the surface of the body is cooled, the temperature remains at a natural level.
- High temperature outdoors or indoors. Everyone knows that in the summer, when it’s hot or in a bathhouse, a person sweats a lot. This is due to the active work of the sweat glands, with one purpose - to prevent the body from overheating.
- Incorrectly selected bedding. In winter you should sleep under a warm blanket, in summer - under a thin sheet. The materials from which the linen is made must be natural. Otherwise, the body will not be able to breathe during sleep, and there will be a risk of overheating. Therefore, the pillow and sheet will be damp from sweat.
- Stressful situations. With excessive excitement and anxiety, a person begins to sweat heavily. Such moments may not happen often. If emotional overload, accompanied by hyperhidrosis, lasts for quite a long time (for example, several weeks), this is a reason to consult a specialist.
- In young people, men. They are characterized by accelerated metabolism and increased physical activity. The work of the sweat glands is no exception. Dry skin is more common in older people.
- Large body weight. The more a person weighs, the more effort he has to expend to perform any action. The released energy is converted into heat. An important task of the body is to cool the body. So, sweating accompanies any movement of a large person. In addition, subcutaneous fat folds can retain heat energy for a long time, so obese people can sweat even when they are at rest.
- Hereditary predisposition. Often a person does not understand what causes hyperhidrosis in the body. It seems that he does not suffer from obesity, and his emotional state is normal, the environment is also favorable. The answer may lie in heredity. It is enough to remember which of your parents or other close relatives has encountered similar problems - the questions will disappear by themselves.
Important! If the above factors are excluded, you should consider visiting a doctor.
Basic methods for diagnosing hyperhidrosis
When a person’s back gets wet uncontrollably and at least one of the signs appears, it is recommended to immediately seek advice from a specialist. At the appointment, the doctor will conduct an initial examination and prescribe a set of diagnostic procedures, during which the causes of the development of the pathology will be determined. The examination is very comprehensive and includes a set of measures described in the table:
| Type of examination | Description | |
| Laboratory | General blood and urine analysis | |
| Blood chemistry | ||
| Studying the hormonal background of the thyroid gland | ||
| Instrumental | Ultrasound | Examination of the internal glands and organs of the peritoneum |
| CT | Scanning of the brain, lower back and other parts | |
| Other | MRI | |
| X-ray | ||
| Examination by specialists | Neuropathologist | |
| Oncologist | ||
| Endocrinologist | ||
| Therapist | ||
Successful therapy is possible only after all diagnostic complexes have been carried out and the primary sources of pathology development have been determined. It all depends on whether your back has sweated before in the car or at night; targeted treatment of possible development factors is underway. Properly constructed therapy includes complex treatment, sometimes with the possibility of using radical methods.
If hyperhidrosis is an independent disease, then you need to consult a dermatologist.
Beautician to help
If a woman becomes covered in sweat for no apparent reason, it is possible that this is an individual characteristic of her body. A qualified cosmetologist will help solve the problem. Today, many clinics offer treatment for hyperhidrosis through injections of Botox or Dysport. The principle of the therapy is to block impulses to the sweat glands from the nerve endings.
The choice of drug dosage is individual for each woman. It all depends on the manifestations of hyperhidrosis. In most cases, injections into the armpits, feet and palms are sufficient. Less commonly, injections can be performed in the facial area.
Many cosmetology clinics offer to get rid of excessive sweating with Botox.
The results from using injections are not long in coming. After just 2-3 days, a woman can forget about the problem of increased sweating. But, unfortunately, the procedure will have to be repeated periodically. After 6-10 months, the drug ceases to affect the body.
If injections are performed by a qualified professional, no side effects should be expected. In rare cases, there may be slight numbness in the injection area. But the unpleasant symptom quickly passes. An allergic reaction may also occur in patients who cannot tolerate cow's milk protein. The cosmetologist is obliged to interview the patient and perform a preliminary examination to avoid possible complications.
Treatment of hyperhidrosis with Botox or Dysport cannot be performed on women during pregnancy, or on minor patients. Contraindications also include epilepsy, cancer, and bleeding disorders.
Cosmetological methods for treating excessive sweating can also include the use of antiperspirants. Insoluble compounds, which are part of special deodorants, clog the ducts of the sweat glands. As a result, the release of the secretion becomes more difficult.
Recommended examinations
What to do if your back is constantly wet? Firstly, do not self-medicate. If your back constantly sweats and you do not know the cause of this problem, contact a dermatologist who will refer you to the necessary examinations and help solve this unpleasant problem. As a rule, an ultrasound examination of internal organs, CTG of the head and X-ray of the lungs may be needed. If pathologies are identified, consultation with specialized specialists (neurologist, endocrinologist, gynecologist, etc.) will be required. A general blood test is also required.
Causes
Heavy sweat production is normal if the skin is warm. Sweat should cool the human body. When excessive discharge cannot be explained medically, it should be considered hyperhidrosis.
You can call it sweating sickness. If the nerves responsible for the start of the sweat glands begin to be hyperactive, they are used to stimulate the production of a decent amount of sweat, even in cases where this is not necessary.
There is also the possibility of a hereditary factor. It is worth noting several main reasons that cause profuse sweat:
- hot weather;
- physical exercise;
- spicy food;
- stressful situations.
Excessive sweating also interferes with heart problems, diabetes, kidney and lung diseases. A state of shock in certain cases makes one suffer from similar adversities.
Why doesn't a person sweat during physical activity?
Sweating increases during exercise in healthy people. No wonder they say: “I worked until I sweat.” The absence of sweating in such cases indicates anhidrosis. With this diagnosis, heavy loads are prohibited, especially at high temperatures in the surrounding atmosphere, as thermoregulation is disrupted. A person can work with substances harmful to the body, poisons, various toxic and allergenic substances, in dusty rooms. All this gets on the skin, the pores become clogged, the sweat glands do not secrete sweat well, along with poisonous and toxic substances. If a person does not sweat for a long time, the sweat glands undergo atrophy, and he may develop chronic anhidrosis.
Currently reading: Distal hyperhidrosis, features and treatment
What medications to take
For hyperhidrosis, the doctor prescribes atropine-containing or sedative drugs, which reduce sweat production, but have many side effects. Atropine, for example, can reduce vision, a person experiences a feeling of dry mouth and constipation. Sedatives (calming) - herbal tinctures, decoctions or tranquilizers can cause a feeling of addiction and drowsiness, so the time of their use is limited to seasonal courses.
What to do if a constantly wet back causes you serious discomfort. Of course, you need to undergo the necessary examinations as soon as possible and identify the cause of the disease. An identified disease and a well-chosen course of treatment will help you get rid of such a nuisance as profuse back sweating in the shortest possible time.
Which doctor treats
Since there are many reasons for the development of hyperhidrosis, if unpleasant signs appear, you should first consult a pediatrician or therapist. After examination and initial diagnosis, the doctor may give a referral to other specialists.
Who treats sweating:
- endocrinologist – treats diabetes, menopause, and thyroid problems;
- oncologist;
- phthisiatrician – treats tuberculosis;
- infectious disease specialist;
- psychiatrist, psychotherapist;
- toxicologist;
- immunologist;
- cardiologist;
- dermatologist.
To identify the causes of hyperhidrosis and its severity, the doctor prescribes a general urine test, clinical, biochemical and hormonal blood tests, tests for HIV, syphilis, hepatitis, and the Mantoux test. Additionally, you need to do an ultrasound of the thyroid gland, abdominal organs, and ECG. The amount of sweat is measured using special test strips; starch can be poured onto the problem area - if it turns dark blue, sweating is increased.
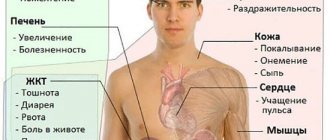
To rule out or suspect serious pathological conditions, the doctor may ask the patient the following:
- Constant or periodic increased sweating, does it increase under stress?
- Is sweating limited to certain areas (forehead, head, palms, feet, armpits) or general?
- Does anyone else in the family suffer from similar discomfort?
- When does sweating occur more often at night or during the day?
- Do you feel hot when those around you do not feel the same or even feel cold?
- Do you experience increased fatigue, weakness, tremors, loss of coordination, or fainting?
- Does excessive sweating affect your work, social, or personal life?
- Has there been a decrease in weight and appetite?
- What medications do you take—for pain, hypertension, glaucoma, etc.?
- Do you have a cough, fever, or swollen lymph nodes?
If a person sweats heavily in certain areas of the body, and this condition is not typical for him, this can be a sign of the development of internal pathology, in which sweating is just a symptom, but it is dangerous to ignore it. But heavy sweating does not always indicate a dangerous disorder; it is often necessary to simply normalize your lifestyle, stop eating heavy foods, get rid of bad habits, and try to pay more attention to your health. Then the sweat glands will begin to function normally and the person will no longer be bothered by anything.
Existing varieties
| Factor | Variety | Description |
| Depending on the root cause of development | Primary | It is congenital and therefore often manifests itself in childhood |
| Secondary | Occurs as a result of internal pathologies or exposure to negative external factors | |
| Compensatory | Develops as a complication after surgery to eliminate hyperhidrosis | |
| Prevalence | Local | Appears in certain areas - face, palms, feet, groin folds, at the base of the hands |
| Generalized | Excess sweating worries the entire body | |
| Periodicity | Seasonal | Signs create discomfort only during certain periods of the year |
| Constant | Worried about constant sweating, the degree of development of which is not affected by external weather factors | |
| Intermittent | It appears periodically, tends to disappear on its own and recur sharply | |
| Degree of manifestation | Lightweight | The production of sweat does not cause any problems or discomfort to a person |
| Average | A sharp release of sweat is sometimes noticeable to others due to an unpleasant odor and wet spots on clothes | |
| Heavy | High sweating is clearly noticeable to others; it happens that it is impossible to approach a person due to an unpleasant body odor |
Hyperhidrosis and depression
For those suffering from hyperhidrosis, it is enough to think about a possible handshake and the palms instantly become wet. Excessive sweating causes uncontrollable fear, which causes sweating. Some people are unable to find an antiperspirant that can completely eliminate sweat because they sweat a lot.
A person is uncomfortable with hugs, close contact with people, and only one thought spins in his head: “I sweat a lot and am unpleasant to others.” When your feet sweat, you can forget about going on a visit, because there you will have to take off your shoes. It's the same at the doctor's appointment, at the gym, and at the shoe store. Physiologists believe that hyperhidrosis is a kind of vicious circle that not everyone can break alone. A seemingly trivial problem can over time result in depression, insomnia and neurosis, causing a host of related problems with health and life in society. If your feet are very sweaty, even in cold weather, your feet get wet, and a characteristic smell appears in your boots. Sweaty armpits due to the constant use of various cosmetics make clothes unusable, requiring regular replacement of the wardrobe.
It happens that a person changes two or three shirts per day, which need serious washing. Doctors are trying to treat sweating with sedatives, formalin, hypnosis and surgical methods that cure the disease forever. But due to the high cost, not everyone can afford such an operation.
When should you be wary?
What to do if you are actively sweating in the back? You should immediately observe whether your back is sweating:
- at the slightest physical exertion;
- in the process of an emotional outburst (laughter, sobbing, feeling of fear);
- during sleep and after waking up, even in comfortable environmental conditions;
- from the use of various cosmetics.
Important! If at least one of these symptoms occurs, you must immediately seek medical help.
Strengthen hygiene: what does it mean?
When a woman comes to the doctor with such a delicate problem, the doctor tries to find out the causes of hyperhidrosis. If they are not associated with a serious illness, doctors can advise a simple regimen: enhanced hygiene + proper nutrition + mild sedative therapy. It’s not difficult to figure out proper nutrition, today there is a lot of information on this topic, the doctor himself will recommend sedatives, but what is enhanced hygiene?
Ask yourself a simple question: do you shower every day? And do you do this in the morning and in the evening. If the answer is yes, then you are on the right track, and with proper organization of your soul, sweating should definitely decrease.
Everything is simple here: the sweat itself does not have any sharply negative odor. If you have just left the bathhouse, your body is clean, your condition is vigorous, then the sweat that appears from the heat will not smell. That repulsive smell is caused by pathogens that are activated specifically when the body releases sweat fumes. That is, sweat on an insufficiently clean body is an equally foul odor. But if you take a shower twice (preferably a contrast one), you remove dirt from your skin, prevent bacteria from parasitizing, which means there won’t be that same unpleasant smell.
Try to take a contrast shower. It trains blood vessels and tones muscles. By the way, a local contrast shower can train the sweat glands. For example, you sweat very actively in the armpit area. Give your cavities a quick contrast shower every day, morning and evening. This exercise will help the sweat glands, which are found in large numbers in the armpits, to work adequately.
Folk ways to combat sweating
A woman who is faced with the problem of excessive sweating should first of all restore the functioning of her nervous system. Tinctures of motherwort and valerian will be beneficial. It will be possible to achieve good results with local effects on the areas of greatest manifestation of hyperhidrosis. Several times a day, you should wipe your feet, palms and armpits with decoctions of alder cones, oak or willow bark. Therapeutic baths with the listed components will also be useful.
Baking soda is a popular remedy for hyperhidrosis
You can get rid of excessive sweating with baking soda. The product will help reduce the secretion of skin secretions and also get rid of unpleasant odor. Excellent reviews can be heard about homemade deodorant, which contains corn starch, soda and vegetable oil (you can use any). If you combine the ingredients in equal proportions, you get a thick mass. The product must be placed in the refrigerator. It turns out to be a substitute for antiperspirant.
Excessive sweating can be dealt with using one of the above methods. In this case, prevention is of great importance. It is worth learning to calmly react to stressful situations, eat right, sleep well, and give up bad habits. We must not forget about hygiene.
Non-pathological causes of profuse sweat
A healthy person may experience profuse sweat, but for other reasons. So, if you are not a diabetic and do not know what a dysfunction of the endocrine system is, probably the cause of the pathology lies elsewhere:
- frequent stress, insomnia, depression and everything associated with disorders of the nervous system;
- poisoning with chemical products or food;
- with psoriasis, sweating is observed near the foci of the skin disease;
- infection of the salivary gland or damage to the facial nerve.